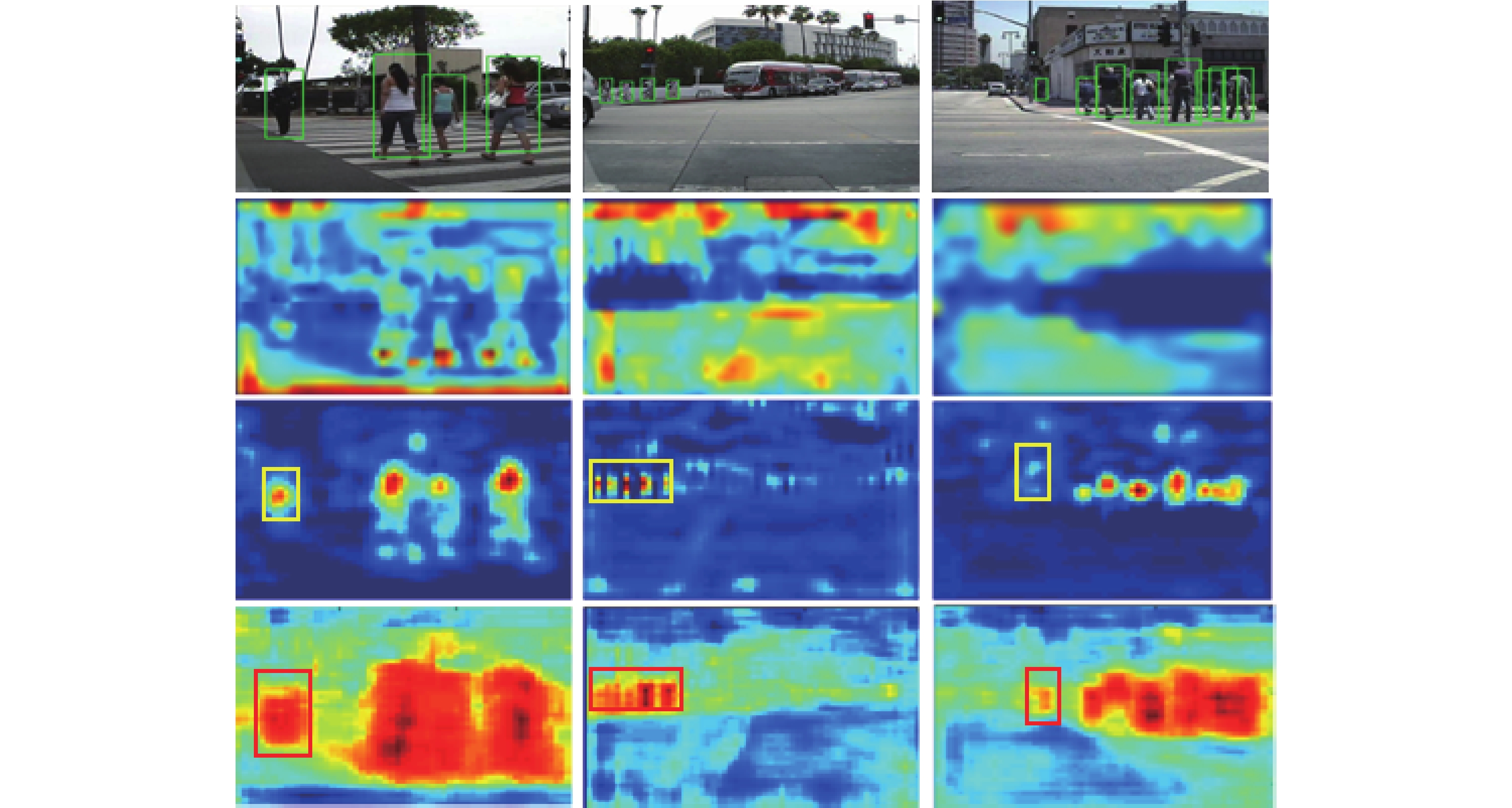
-
摘要: 遮挡及背景中相似物干扰是行人检测准确率较低的主要原因. 针对该问题, 提出一种结合语义和多层特征融合(Combining semantics with multi-level feature fusion, CSMFF)的行人检测算法. 首先, 融合多个卷积层特征, 并在融合层上添加语义分割, 得到的语义特征与相应的卷积层连接作为行人位置的先验信息, 增强行人和背景的辨别性. 然后, 在初步回归的基础上构建行人二次检测模块(Pedestrian secondary detection module, PSDM), 进一步排除误检物体. 实验结果表明, 所提算法在数据集Caltech和CityPersons上漏检率(Miss rate, MR)为7.06 %和11.2 %. 该算法对被遮挡的行人具有强鲁棒性, 同时可方便地嵌入到其他检测框架.Abstract: Occlusion and similar objects in the background typically degrade the accuracy of pedestrian detection. To solve the above problems, this paper proposes a pedestrian detection algorithm that combines semantics with multi-level feature fusion (CSMFF). Firstly, multi-convolutional-layer features are fused, and semantic segmentation is added to the fusion layer. The obtained semantic features are connected to the corresponding convolutional layers as the prior information of the pedestrian target location, which enhances the discrimination between pedestrian and background. Based on the preliminary regression, a pedestrian secondary detection module (PSDM) is constructed to further eliminate false positives. The experimental results show that the miss rates (MR) of the proposed algorithm on the datasets Caltech and CityPersons are 7.06 % and 11.2 %, respectively. The algorithm has strong robustness to occluded pedestrians, and can be easily embedded into other detection frameworks.
-
Key words:
- Pedestrian detection /
- semantic segmentation /
- feature fusion /
- occlusion /
- secondary detection
-
表 1 Caltech数据集中部分子集的划分标准
Table 1 Evaluation settings for partial subsets of the Caltech dataset
子集 行人高度 (Height) 行人被遮挡程度 (Occlusion) Reasonable $ > $50 PXs occ$ < $0.35 Partial $ > $50 PXs 0.10$ < $occ$ \le $0.35 Heavy $ > $50 PXs 0.35$ < $occ$ \le $0.80 表 2 CityPersons数据集中部分子集的划分标准
Table 2 Evaluation settings for partial subsets of the CityPersons dataset
子集 行人高度 (Height) 行人被遮挡程度 (Occlusion) Bare $ > $50 PXs occ$ \le $0.10 Reasonable $ > $50 PXs occ$ < $0.35 Partial $ > $50 PXs 0.10$ < $occ$ \le $0.35 Heavy $ > $50 PXs 0.35$ < $occ$ \le $0.80 表 3 在Caltech测试数据集上对比算法性能以及运行速度比较
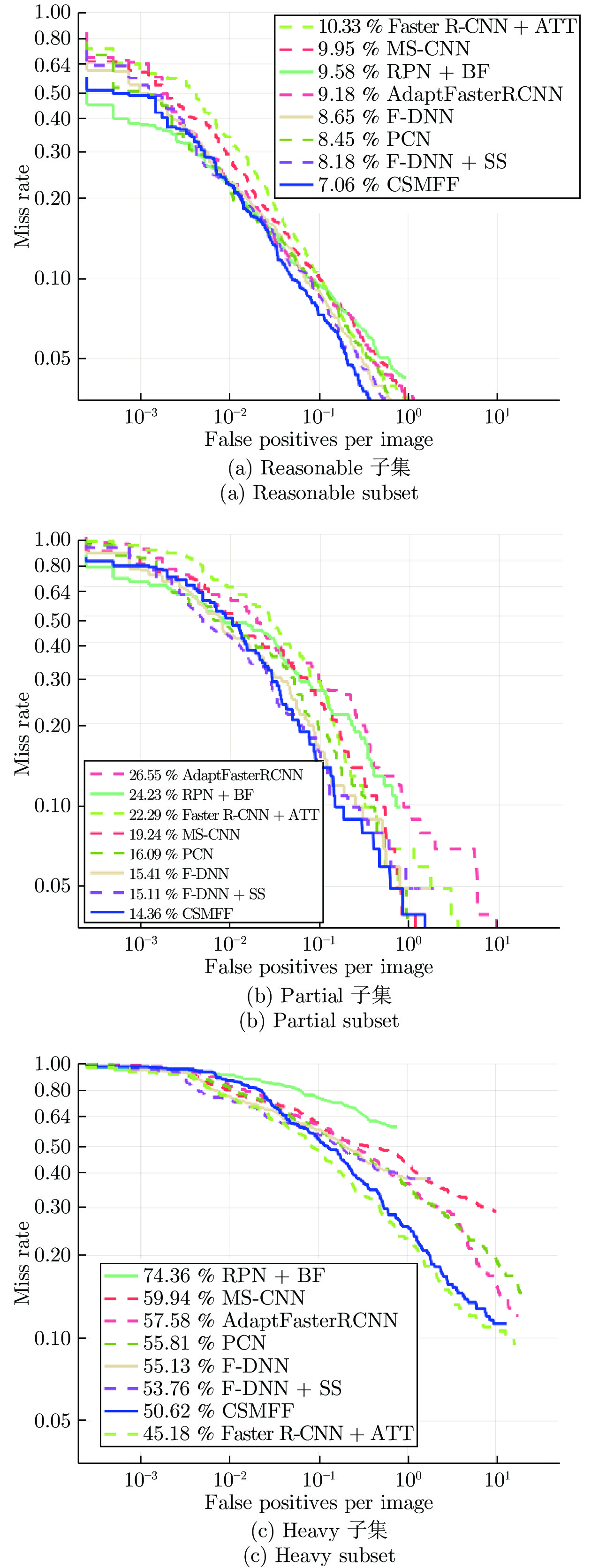
Table 3 Performance and runtime comparisons of our proposed CSMFF with state-of-the-art approaches on the Caltech test dataset
方法 Reasonable MR (%) Partial MR (%) Heavy MR (%) 速度 (s/帧) PL-CNN[16] 12.40 16.68 — — Faster R-CNN$ + $ATT[32] 10.33 22.29 45.18 — MS-CNN[10] 9.95 19.24 59.94 0.40 RPN$ + $BF[13] 9.58 24.23 74.36 0.60 AdaptFasterRCNN[14] 9.18 26.55 57.58 — F-DNN[21] 8.65 15.41 55.13 0.30 PCN[20] 8.45 16.09 55.81 — F-DNN$ + $SS[21] 8.18 15.11 53.76 2.48 CSMFF 7.06 14.36 50.62 0.12 表 4 在CityPersons测试数据集上不同算法性能比较
Table 4 Performance comparison of our proposed CSMFF with state-of-the-art approaches on the CityPersons test dataset
表 5 在Caltech测试数据集上融合不同卷积层的性能
Table 5 Performance of fusing different convolutional layers on the Caltech test dataset
卷积层 MR (%) Conv2_2 Conv3_3 Conv4_3 Conv5_3 PFEM CSMFF √ √ √ 12.22 7.06 √ √ √ 32.42 18.15 √ √ √ √ 18.72 11.79 表 6 在Caltech数据集上测试每个组件的消融实验
Table 6 Ablation experiments for testing each component on the Caltech dataset
组件 选择 Faster R-CNN √ 多层特征融合 √ √ √ 语义分割分支 √ √ PSDM √ PFEM MR (%) 14.93 13.27 12.58 12.22 CSMFF MR (%) 12.11 9.53 8.68 7.06 -
[1] Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan F S, Felsberg M. Atom: Accurate tracking by overlap maximization. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, California, USA: IEEE, 2019. 4660−4669 [2] 李幼蛟, 卓力, 张菁, 李嘉锋, 张辉. 行人再识别技术综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(9): 1554-1568Li You-Jiao, Zhuo Li, Zhang jing, Li Jia-Feng, Zhang Hui. Overview of Pedestrian Re-identification Technology. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(9): 1554-1568 [3] Geiger A, Lenz P, Urtasun R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, Rhode Island, USA: IEEE, 2012. 3354−3361 [4] 王梦来, 李想, 陈奇, 李澜博, 赵衍运. 基于CNN的监控视频事件检测[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(6): 892-903Wang Meng-Lai, Li Xiang, Chen Qi, Li Yuan-Bo, Zhao Yan-Yun. CNN-based surveillance video event detection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6): 892-903 [5] Kanazawa A, Black M J, Jacobs D W, Malik J. End-to-end recovery of human shape and pose. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA: IEEE, 2018. 7122−7131 [6] Zhang S, Benenson R, Omran M, Hosang J, Schiele B. How far are we from solving pedestrian detection? In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1259−1267 [7] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1440−1448 [8] Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Montreal, Quebec, Canada: MIT Press, 2015. 91−99 [9] Yang F, Choi W, Lin Y. Exploit all the layers: Fast and accurate CNN object detector with scale dependent pooling and cascaded rejection classifiers. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2129−2137 [10] Cai Z, Fan Q, Feris R S, Vasconcelos N. A unified multi-scale deep convolutional neural network for fast object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Scottsdale, AZ, USA: Springer, 2016. 354−370 [11] Gidaris S, Komodakis N. Object detection via a multi-region and semantic segmentation-aware CNN model. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1134−1142 [12] Li J, Liang X, Shen S M, Xu T F, Feng J S, Yan S C. Scale-aware Fast R-CNN for pedestrian detection. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017, 20(4): 985-996 [13] Zhang L L, Lin L, Liang X D, He K M. Is Faster R-CNN doing well for pedestrian detection? In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, Noord-Holland, The Netherlands: IEEE, 2016. 443−457 [14] Zhang S, Benenson R, Schiele B. CityPersons: A diverse dataset for pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3213−3221 [15] Dollár P, Wojek C, Schiele B, Perona P. Pedestrian detection: A benchmark. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, Florida, USA: IEEE, 2009. 304−311 [16] Yun I, Jung C, Wang X R, Hero A O, Kim J K. Part-level convolutional neural networks for pedestrian detection using saliency and boundary box alignment. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 23027-23037 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2899105 [17] Fidler S, Mottaghi R, Yuille A, Urtasun R. Bottom-up segmentation for top-down detection. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, Oregon, USA: IEEE, 2013. 3294−3301 [18] Hariharan B, Arbeláez P, Girshick R, Malik J. Simultaneous detection and segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 297−312 [19] Arbeláez P, Pont-Tuset J, Barron J T, Marques F, Malik J. Multiscale combinatorial grouping. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, Ohio, USA: IEEE, 2014. 328−335 [20] Wang S G, Cheng J, Liu H J, Tang M. PCN: Part and context information for pedestrian detection with CNNs. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1804.04483, 2018. [21] Du X, El-Khamy M, Lee J, Davis L. Fused DNN: A deep neural network fusion approach to fast and robust pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Santa Rosa, California, USA: IEEE, 2017. 953−961 [22] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1409. 1556, 2014. [23] Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Espoo, Finland, German: Springer, 2011. 315−323 [24] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [25] Hochreiter S, Younger A S, Conwell P R. Learning to learn using gradient descent. In: Proceedings of the 2001 International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Vienna, Austria, German: Springer, 2001. 87−94 [26] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1502.03167, 2015. [27] Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L J, Li K, Li F F. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, Florida, USA: IEEE, 2009. 248−255 [28] Jia Y Q, Shelhamer E, Donahue J, Karayev S, Long J, Girshick R. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1408.5093, 2014. [29] Zhang S, Benenson R, Schiele B. Filtered channel features for pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, Massachusetts, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1751−1760 [30] Cordts M, Omran M, Ramos S, Rehfeld T, Enzweiler M, Benenson R. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3213−3223 [31] Dollar P, Wojek C, Schiele B, Perona P. Pedestrian Detection: An evaluation of the state of the art. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 34(4): 743-761 [32] Zhang S, Yang J, Schiele B. Occluded pedestrian detection through guided attention in CNNs. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA: IEEE, 2018. 6995−7003 [33] Song T, Sun L Y, Xie D, Sun H M, Pu S L. Small-scale pedestrian detection based on topological line localization and temporal feature aggregation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 536−551 [34] Wang X, Xiao T, Jiang Y, Shao S, Sun J, Shen C H. Repulsion loss: Detecting pedestrians in a crowd. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA: IEEE, 2018. 7774−7783 [35] Cao J L, Pang Y W, Han J G, Gao B L, Li X L. Taking a look at small-scale pedestrians and occluded pedestrians. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 3143-3152. [36] Zhao Y, Yuan Z J, Chen B D. Training cascade compact cnn with region-iou for accurate pedestrian detection. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019: 1-11. [37] Zhang S F, Wen L Y, Bian X, Lei Z, Li S Z. Occlusion-aware R-CNN: Detecting pedestrians in a crowd. In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 637−653 -




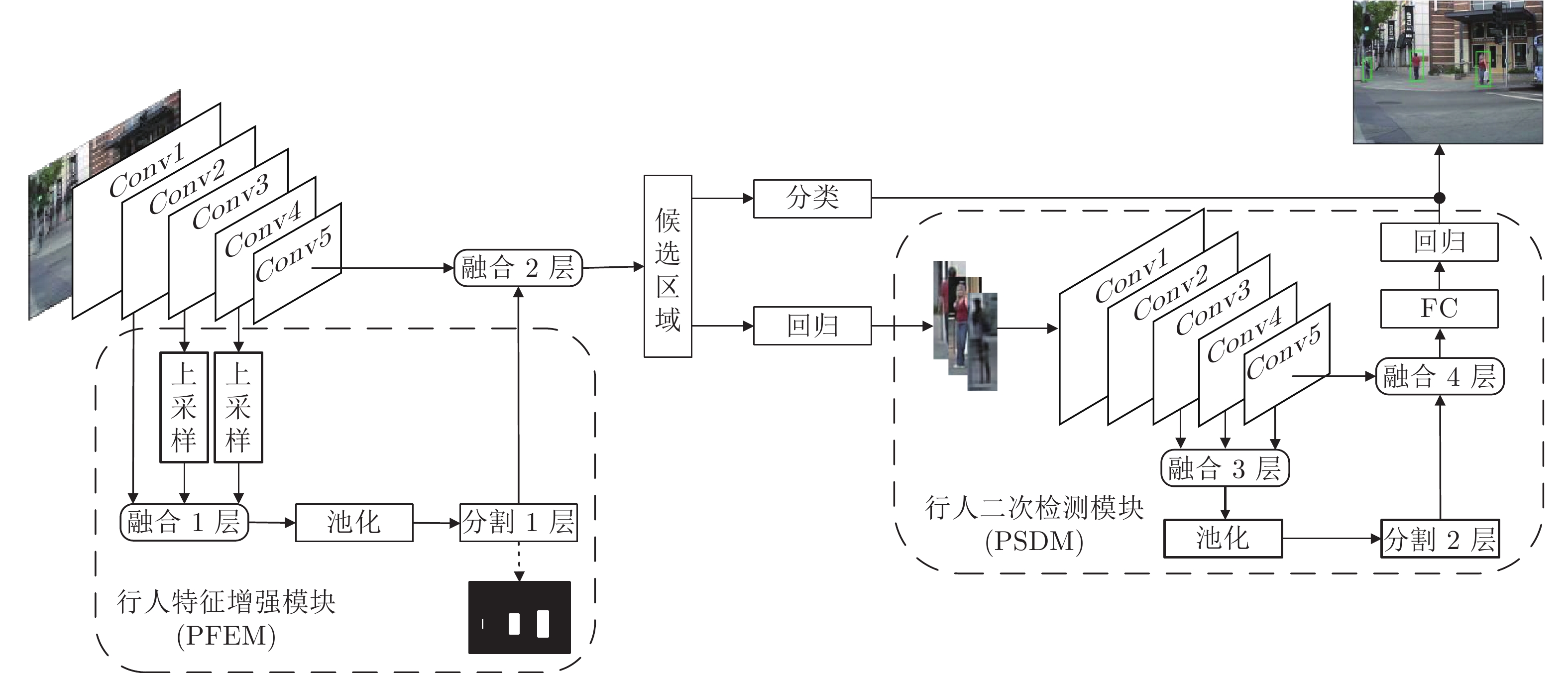
 下载:
下载: