-
摘要: 针对车联网环境下路侧边缘计算节点部署不均衡、服务密度小、实时调度计算压力大等问题, 提出一种基于智能车移动边缘计算(Mobile edge computing, MEC)的任务排队建模与调度算法, 提供弹性计算服务, 将具备感知、计算、控制功能的智能车作为移动边缘计算服务器, 设计了车联网环境下的MEC体系架构. 首先基于虚拟化技术对智能车进行虚拟化抽象, 利用排队论对虚拟车任务构建了GI/GI/1排队模型. 然后基于云平台Voronoi分配算法对虚拟车任务进行分配绑定, 进而实现了智能车的优化调度与分布式弹性服务, 解决了边缘计算任务分配不均衡等问题. 最后通过城市交通路网中的车辆污染排放的实时计算实验, 验证了该方法的有效性.Abstract: The edge computing of internet of vehicles is confronted with some challenges, such as the unbalanced arrangement, the service inflexible and the time delay for the real-time computing of roadside nodes. In this paper, a new queuing model and scheduling algorithm of mobile edge computing (MEC) is proposed based on intelligent vehicles integrating the sensing, computing and control together. The GI/GI/1 task queuing model is firstly set up for the distributed services of vehicular networks, in which intelligent vehicles are virtualized into virtual vehicles. Moreover, according to the Voronoi allocation algorithm, the tasks generated by virtual vehicles are allocated and bound to intelligent vehicles. The optimal scheduling and distributed elastic service of intelligent vehicles are presented to solve the problem of unbalanced distribution of tasks in edge computing. The simulation experiment of the vehicle pollutant emission illustrates the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- Internet of vehicles /
- mobile edge computing (MEC) /
- queue model /
- scheduling /
- allocation algorithm
-
表 1 VSP排放等级与平均排放清单
Table 1 VSP modes and the average modal emission rates of each
VSP 等级 VSP mode ${\rm{C} }{ {\rm{O} }_2}\left( {\rm{g/s}} \right)$ ${\rm{CO} }\left( {\rm{g/s}} \right)$ ${\rm{N} }{ {\rm{O} }_X}\left( {\rm{g/s}} \right)$ ${\rm{HC} }\left( {\rm{g/s}} \right)$ ${\rm{VSP}} < -2$ 1 1.54369 0.01103 0.00101 0.00090 $-2\le {\rm{VSP}} < 0$ 2 1.60441 0.00872 0.00104 0.00090 $0\le {\rm{VSP}} < 1$ 3 1.13083 0.00468 0.00042 0.00084 $ \cdot \cdot \cdot $ $ \cdot \cdot \cdot $ $ \cdot \cdot \cdot $ $ \cdot \cdot \cdot $ $ \cdot \cdot \cdot $ $ \cdot \cdot \cdot $ $28\le {\rm{VSP} } < 33$ 12 7.61770 0.24781 0.01438 0.00457 $33\le {\rm{VSP}} < 39$ 13 8.32244 0.41307 0.01597 0.00570 $39\le {\rm{VSP}}$ 14 8.47503 0.62466 0.01672 0.00716 表 2 VVs的任务计算参数
Table 2 VVs calculation parameters
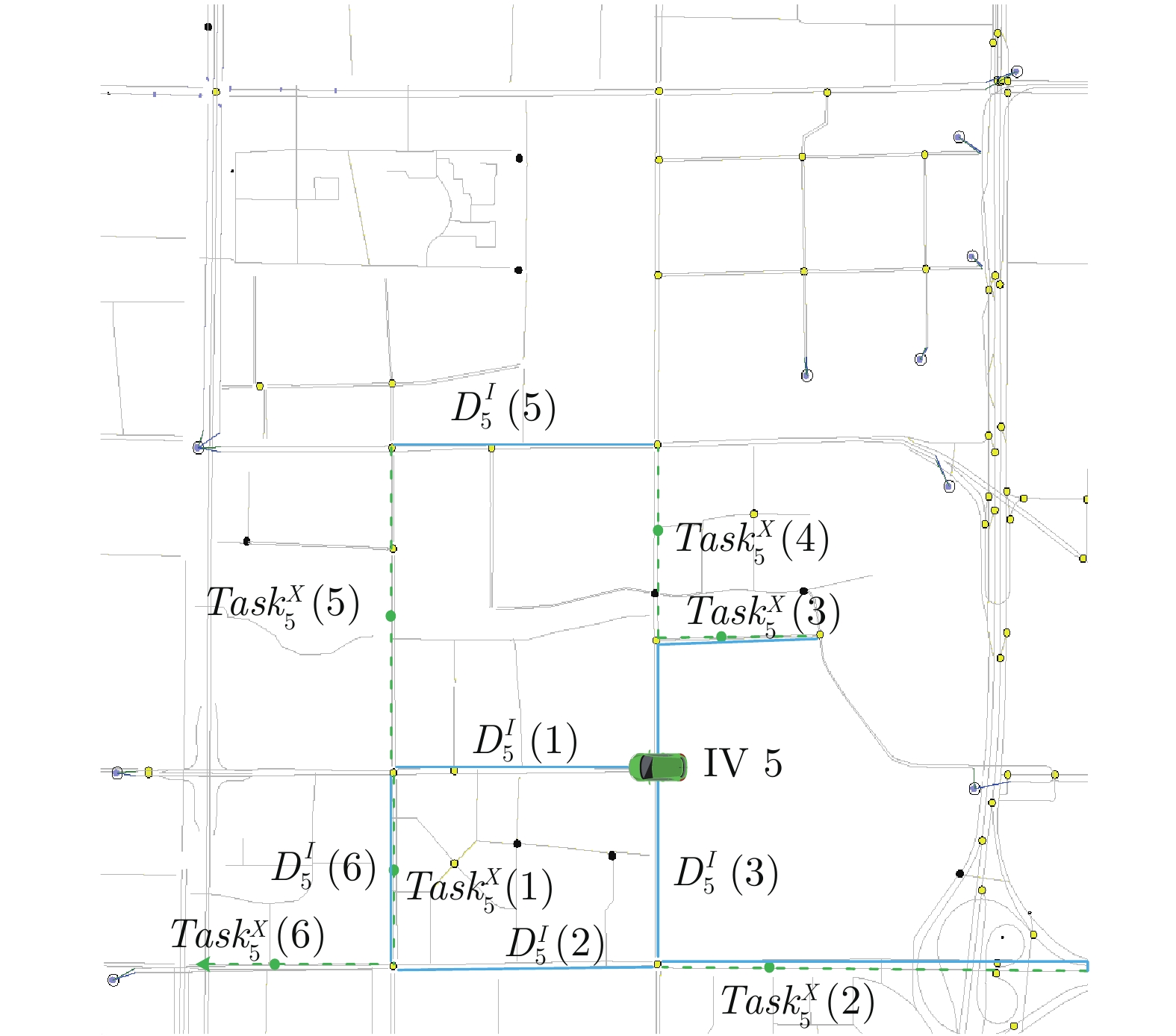
$Tas{{k}_{i}}\left( j \right)$ $T_{i}^{\rm{arr}}\left( j \right)$ $task_{i}^{X }\left( j \right)$ $T_{i}^{V{\rm{tra}}}\left( j \right)$ $T_{i}^{s}\left( j \right)$ $T_{i}^{V{\rm{ser}}}\left( j \right)$ $T_{i}^{Vd}\left( j \right)$ $i=2,\;j=2$ 9:09:02 (39.8726, 116.466) 89 169 258 9:13:20 $i=3,\;j=3$ 9:13:37 (39.8702, 116.476) 110 80 190 9:16:47 $i=7,\;j=1$ 9:16:52 (39.875, 116.475) 200 60 260 9:21:12 $i=9,\;j=6$ 9:21:14 (39.8787, 116.471) 0 52 52 9:22:06 $i=12,\;j=3$ 9:22:06 (39.8767, 116.466) 78 60 138 9:24:24 $i=15,\;j=4$ 9:24:34 (39.8705, 116.466) 40 43 83 9:25:57 表 3 IV的实际运行参数
Table 3 Actual operating parameters of IV
$Tas{{k}_{m}}\left( n \right)$ $T_{m}^{I{\rm{tra}}}\left( n \right)$ $T_{m}^{Is}\left( n \right)$ $T_{m}^{I{\rm{ser}}}\left( n \right)$ $T_{m}^{\rm{finish}}\left( n \right)$ ${\rm{C O}}_{2} \left({\rm{g} } \right)$ ${\rm{CO}}\left({\rm{g} } \right)$ ${\rm{NO}}_{X} \left({\rm{g} }\right)$ ${\rm{HC}}\left({\rm{g} }\right)$ $m=5,\;n=1$ 95 178 273 9:13:35 992.78 6.76 0.81 0.51 $m=5,\;n=2$ 117 76 193 9:16:50 1144.42 7.76 0.79 0.63 $m=5,\;n=3$ 202 58 260 9:21:12 426.80 2.96 0.29 0.24 $m=5,\;n=4$ 0 50 50 9:22:04 590.63 4.11 0.41 0.33 $m=5,\;n=5$ 83 63 146 9:24:32 1658.42 11.41 1.14 0.92 $m=5,\;n=6$ 37 39 46 9:25:20 868.51 5.92 0.61 0.48 -
[1] 王晓, 要婷婷, 韩双双, 曹东璞, 王飞跃. 平行车联网: 基于ACP的智能车辆网联管理与控制. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(8): 1391−1404Wang Xiao, Yao Ting-Ting, Han Shuang-Shuang, Cao Dong-Pu, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel internet of vehicles: the ACP-based networked management and control for intelligent vehicles. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(8): 1391−1404 [2] 周悦芝, 张迪. 近端云计算: 后云计算时代的机遇与挑战. 计算机学报, 2019, 42(04): 677−700Zhou Yue-Zhi, Zhang Di. Near-end cloud computing: opportunities and challenges in the post-cloud computing era. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(04): 677−700 [3] 夏元清. 云控制系统及其面临的挑战. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(1): 1−12Xia Yuan-Qing. Cloud control systems and their challenges. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(1): 1−12 [4] Xu Wen-Bo, Wang Shu, Yan Shu, He Jian-Hua. An efficient wideband spectrum sensing algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle communication networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 1768−1780 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2882532 [5] Yang Bo-Ran, Wu Da-Peng, Wang Ru-Yan. CUE: an intelligent edge computing framework. IEEE Network, 2019, 33(3): 18−25 doi: 10.1109/MNET.2019.1800316 [6] Zhou Fu-Hui, Wu Yong-Peng, Hu Qing-Yang, Qian Yi. Computation rate maximization in UAV-enabled wireless powered mobile-edge computing systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(9): 1927−1941 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2864426 [7] Ahmed A, Ahmed E. A survey on mobile edge computing. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Control. Coimbatore, India: IEEE, 2016. 1−8 [8] 王飞跃, 张军, 张俊, 王晓. 工业智联网: 基本概念、关键技术与核心应用. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(9): 1606−1617Wang Fei-Yue, Zhang Jun, Zhang Jun, Wang Xiao. Industrial internet of minds: concept, technology and application. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(9): 1606−1617 [9] 王飞跃, 张俊. 智联网: 概念、问题和平台. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(12): 2061−2070Wang Fei-Yue, Zhang Jun. Industrial internet of minds: the concept, issues and platforms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(12): 2061−2070 [10] Zhang Ke, Mao Yu-Ming, Leng Su-Peng, He Ye-Jun, Zhang Yan. Mobile-edge computing for vehicular networks: a promising network paradigm with predictive off-loading. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2017, 12(2): 36−44 doi: 10.1109/MVT.2017.2668838 [11] Shao Cai-Xing, Leng Su-Peng, Zhang Yan, Vinel A. Performance analysis of connectivity probability and connectivity-aware MAC protocol design for platoon-based VANETs. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 64(12): 5596−5609 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2479942 [12] Sukhpal S G, Rajkumar B. Secure: self-protection approach in cloud resource management. IEEE Cloud Computing, 2018, 5(1): 60−72 doi: 10.1109/MCC.2018.011791715 [13] Dai Yue-Yue, Xu Du, Maharjan S, Zhang Yan. Joint load balancing and offloading in vehicular edge computing and networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 4377−4387 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2876298 [14] Chen Xu, Jiao Lei, Li Wen-Zhong, Fu Xiao-Ming. Efficient multi-user computation offloading for mobile-edge cloud computing. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2016, 24(5): 2795−2808 doi: 10.1109/TNET.2015.2487344 [15] Nunna S, Kousaridas A, Ibrahim M, Dillinger M. Enabling real-time context-aware collaboration through 5G and mobile edge computing. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Information Technology — New Generations. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2015. 601−605 [16] Yu Rong, Huang Xu-Min, Kang Jia-Wen, Ding Jie-Fei. Cooperative resource management in cloud-enabled vehicular networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(12): 7938−7951 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2481792 [17] 刘业, 刘林峰, 郑隆, 王华锋. 车联网RSU单元下行流量的性能研究. 软件学报, 2015, 26(7): 1700−1710Liu Ye, Liu Lin-Feng, Zheng Long, Wang Hua-Feng. Study on the downlink performance of roadside unit in vehicular ad-hoc networks. Journal of Software, 2015, 26(7): 1700−1710 [18] 姜岩, 王琦, 龚建伟, 陈慧岩. 无人驾驶车辆局部路径规划的时间一致性与鲁棒性研究. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(3): 518−527Jiang Yan, Wang Qi, Gong Jian-Wei, Chen Hui-Yan. Research on temporal consistency and robustness in local planning of intelligent vehicles. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(3): 518−527 [19] 郭春钊, 山部尚孝, 三田诚一, 基于立体视觉平面单应性的智能车辆可行驶道路边界检测. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(4): 371−380 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60036-1Guo Chun-Zhao, Takayuki Y, Seiichi M. Drivable road boundary detection for intelligent vehicles based on stereovision with plane-induced homography. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 371−380 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60036-1 [20] Zhu Hao, Yuen Ka-Veng, Mihaylova L, Leung H. Overview of environment perception for intelligent vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(10): 2584−2601 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2658662 [21] Love J, Jariyasunant J, Pereira E T, Zennaro M, Hedrick K, Kirsch C, et al. CSL: A language to specify and re-specify mobile sensor network behaviors. In: Proceedings of the 15th IEEE Real-time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2009. 67−76 [22] Sasaki K, Suzuki N, Makido S, Nakao A. Vehicle control system coordinated between cloud and mobile edge computing. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Conference of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers of Japan (SICE). Tsukuba, Japan: IEEE, 2016. 1122−1127 [23] 李力, 王飞跃. 地面交通控制的百年回顾和未来展望. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(4): 577−583Li Li, Wang Fei-Yue. Ground traffic control in the past century and its future perspective. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(4): 577−583 [24] 李力, 王飞跃, 郑南宁, 张毅. 驾驶行为智能分析的研究与发展. 自动化学报, 2007, 33(10): 1014−1022Li Li, Wang Fei-Yue, Zheng Nan-Ning, Zhang Yi. Research and developments of intelligent driving behavior analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2007, 33(10): 1014−1022 [25] Liang D. Connected vehicle technology: beyond smart driving—a discussion with scott McCormick, president of connected vehicle trade association. IEEE Engineering Management Review, 2018, 46(1):34−36 doi: 10.1109/EMR.2018.2809908 [26] Boeing G. OSMnx: new methods for acquiring, constructing, analyzing, and visualizing complex street networks. Computers Environment and Urban Systems, 2017, 65: 126−139 doi: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2017.05.004 [27] Krainer C, Kirsch C M. Cyber-physical cloud computing implemented as PaaS. In: Proceedings of the 4th ACM SIGBED International Workshop on Design, Modeling, and Evaluation of Cyber-physical Systems. New York, USA: ACM, 2014. 15−18 [28] Craciunas S S, Haas A, Kirsch C M, Payer H, Ock H, Rottmann A, et al. Information-acquisition-as-a-service for cyber-physical cloud computing. In: Proceedings of the 2th Usenix Conference on Hot Topics in Cloud Computing. Boston, USA: USENIX Association Berkeley, 2010. 14−19 [29] Huang J C. From the Real Vehicle to the Virtual Vehicle [Ph. D. dissertation], University of California, America, 2013 [30] Kirsch C M, Pereira E, Sengupta R, Chen H, Hansen R, Huang J C, et al. Cyber-physical cloud computing: The binding and migration problem. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Design, Automation and Test in Europe Conference and Exhibition (DATE). Dresden, Germany: IEEE, 2012. 1425−1428 [31] Du Bo-Wen, Huang Run-He, Xie Zhi-Pu, Ma Jian-Hua, Lv Wei-Fang. KID model-driven things-edge-cloud computing paradigm for traffic data as a service. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(1): 34−41. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1700169 [32] Plotkin G. A structural approach to operational semantics. Journal of Logic and Algebraic Programming, 2004, 60(1): 17−139 -





 下载:
下载: