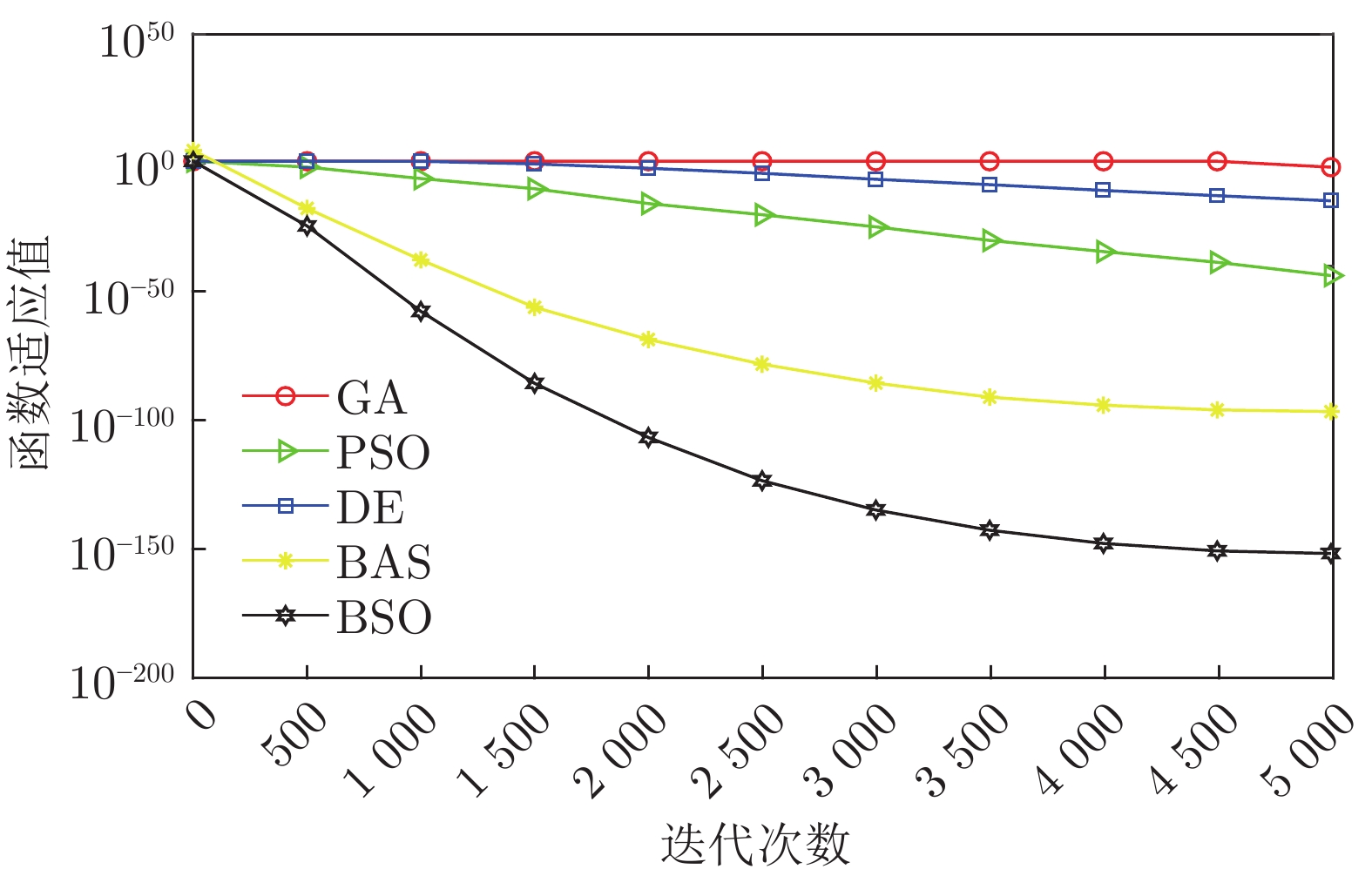
-
摘要: 正则化极限学习机(Regularized extreme learning machine, RELM)因其极易于实现、训练速度快等优点在诸多领域均取得了成功应用. 对此, 本文将RELM引入到入侵检测中, 设计了天牛群优化算法(Beetle swarm optimization, BSO), 并针对RELM由于随机初始化参数带来的潜在缺陷, 提出基于天牛群优化与改进正则化极限学习机(BSO-IRELM)的网络入侵检测算法. 使用LU分解求解RELM的输出权值矩阵, 进一步缩短了RELM的训练时间, 同时利用BSO对RELM的权值和阈值进行联合优化. 为避免BSO算法陷入局部最优, 引入Tent映射反向学习、莱维飞行的群体学习与动态变异策略提升优化性能. 实验结果表明, 在机器学习UCI数据集上, 相比于RELM、IRELM、GA-IRELM、PSO-IRELM等算法, BSO-IRELM的数据分类性能提升明显. 最后, 将BSO-IRELM应用于网络入侵检测数据集NSL-KDD, 并与BP (Back propagation)、LR (Logistics regression)、RBF (Radial basis function)、AB (AdaBoost)、SVM (Support vector machine)、RELM、IRELM等算法进行了对比, 结果证明BSO-IRELM算法在准确率、精确率、真正率和假正率等指标上均具有明显优势.Abstract: Regularized extreme learning machine (RELM) has been successfully applied in many fields due to its advantages of easy realization and fast training speed. In this regard, RELM is introduced into intrusion detection. Potential flaws caused by random initialization parameters, and a network intrusion detection algorithm based on the beetle swarm optimization (BSO) and improved RELM (BSO-IRELM) was proposed. LU decomposition was used to solve the output of weighting matrix of RELM, which further shortened the training of RELM. At the same time, BSO algorithm was designed to jointly optimize the weights and thresholds of RELM. To prevent the BSO algorithm from falling into a local optimum, Tent mapping inverse learning, Levy flight group learning and dynamic mutation strategies were introduced to improve optimization performance. Experimental results show that compared to algorithms such as RELM, IRELM, GA-IRELM, and PSO-IRELM on machine learning UCI datasets, BSO-IRELM's data classification performance improves significantly. Finally, the BSO-IRELM was applied to the network intrusion detection dataset NSL-KDD, and compared with BP (back propagation), LR (logistics regression), RBF (radial basis function), AB (AdaBoost), SVM (support vector machine), RELM, IRELM and other algorithms. It is clear that the BSO-IRELM algorithm has obvious advantages in terms of accuracy, precision, true positive rate, and false positive rate.
-
表 1 群智能算法参数
Table 1 Swarm intelligence algorithm parameters
参数 值 参数 值 自学习因子 2.4 群体学习因子 1.6 交叉概率 0.7 遗传概率 0.5 惯性权重 0.8 种群数量 50 比例系数 0.4, 0.6 惩罚因子 0.5 表 2 UCI数据集
Table 2 UCI dataset
数据集 维度 类别数 样本总数 测试样本数 Iris 4 3 150 30 Wine 13 3 178 30 表 3 各算法在UCI数据集上的准确率(%)
Table 3 Accuracy of each algorithm on UCI dataset (%)
数据集 RELM IRELM GA-IRELM PSO-IRELM BSO-RELM BSO-IRELM Iris 76.6667 (23/30) 90 (27/30) 96.6667 (29/30) 100 (30/30) 100 (30/30) 100 (30/30) Wine 80 (24/30) 90 (27/30) 93.3333 (28/30) 93.3333 (28/30) 93.3333 (28/30) 96.6666 (29/30) 表 4 各算法在Iris数据集上的性能评价指标
Table 4 Performance evaluation index of each algorithm on Iris dataset
算法 类别 精确率 (%) TPR (%) FPR (%) F值 (%) AUC RELM 1 100 (9/9) 81.8182 (9/1) 0 (0/14) 90 0.9091 2 50 (5/10) 83.3333 (5/6) 21.7391 (5/23) 62.5 0.8125 3 81.8182 (9/11) 69.2308 (9/13) 12.5 (2/16) 75 0.7873 IRELM 1 100 (8/8) 100 (8/8) 0 (0/19) 100 1 2 75 (9/12) 100 (9/9) 14.2857 (3/21) 85.7143 0.9286 3 100 (10/10) 76.9231 (10/13) 0 (0/17) 86.9565 0.8846 GA-IRELM 1 100 (13/13) 100 (13/13) 0 (0/16) 100 1 2 100 (7/7) 87.5 (7/8) 0 (0/22) 93.3333 0.9375 3 90 (9/10) 100 (9/9) 4.7619 (1/21) 94.7368 0.9762 PSO-IRELM 1 100 (8/8) 100 (8/8) 0 (0/22) 100 1 2 100 (12/12) 100 (12/12) 0 (0/28) 100 1 3 100 (10/10) 100 (10/10) 0 (0/20) 100 1 BSO-RELM 1 100 (13/13) 100 (13/13) 0 (0/17) 100 1 2 100 (10/10) 100 (10/10) 0 (0/20) 100 1 3 100 (7/7) 100 (7/7) 0 (0/23) 100 1 BSO-IRELM 1 100 (12/12) 100 (12/12) 0 (0/18) 100 1 2 100 (5/5) 100 (5/5) 0 (0/25) 100 1 3 100 (13/13) 100 (13/13) 0 (0/17) 100 1 表 5 各算法在Wine数据集上的性能评价指标
Table 5 Performance evaluation index of each algorithm on Wine dataset
算法 类别 精确率 (%) TPR (%) FPR (%) F值 (%) AUC RELM 1 81.8182 (9/11) 100 (9/9) 11. 7647 (2/17) 90 0.9524 2 66.6667 (8/12) 80 (8/10) 20 (4/20) 72.7273 0.8000 3 100 (7/7) 63.6364 (7/11) 0 (0/17) 77.7778 0.8182 IRELM 1 88.8889 (8/9) 88.8889 (8/9) 5 (1/20) 88.8889 0.9206 2 90.9091 (10/11) 83.3333 (10/12) 5.5556 (1/18) 86.9565 0.8889 3 90 (9/10) 100 (9/9) 5.2632 (1/19) 94.7368 0.9762 GA-IRELM 1 87.5 (7/8) 100 (7/7) 4. 5455 (1/22) 93. 3333 0.9783 2 100 (16/16) 88. 8889 (16/18) 0 (0/12) 94.1176 0.9444 3 83.3333 (5/6) 100 (5/5) 4.1667 (1/24) 90.9091 0.9800 PSO-IRELM 1 90 (9/10) 100 (9/9) 5 (1/20) 94.7368 0.9762 2 90. 9091 (10/11) 90.9091 (10/11) 5.2632 (1/19) 90.9091 0.9282 3 100 (9/9) 90 (9/10) 0 (0/19) 94.7368 0.9500 BSO-RELM 1 90.9091 (10/11) 100 (10/10) 5.2632 (1/19) 95.2381 0.9750 2 87.5 (7/8) 87.5 (7/8) 4.5455 (1/22) 87.5 0.9148 3 100 (11/11) 91.6667 (11/12) 0 (0/17) 95.6522 0.9583 BSO-IRELM 1 100 (12/12) 92.3077 (12/13) 0 (0/17) 96 0.9615 2 92.3077 (12/13) 100 (12/12) 5.5556 (1/18) 96 0.9722 3 100 (5/5) 100 (5/5) 0 (0/24) 100 1 表 6 各算法的准确率(%)
Table 6 Accuracy of each algorithm (%)
算法 准确率 BP 78.1 (1562/2000) LR 81.3 (1626/2000) RBF 88.9 (1778/2000) AB 86.15 (1723/2000) SVM 91.15 (1823/2000) RELM 81.45 (1629/2000) IRELM 83.9 (1678/2000) GA-IRELM 89.5 (1790/2000) PSO-IRELM 90.45 (1809/2000) BSO-IRELM 91.25 (1825/2000) 表 7 各算法的性能评价指标
Table 7 Performance evaluation index of each algorithm
算法 类别 精确率 (%) TPR (%) FPR (%) F值 (%) AUC BP 1 45.2915 (303/669) 80.8 (303/375) 22.5231 (366/1625) 58.046 0.7914 2 94.5905 (1259/1331) 77.4769 (1259/1625) 19.2 (72/375) 85.1827 0.7914 LR 1 85.7143 (6/7) 1.5831 (6/379) 0.06169 (1/1621) 3.1088 0.5076 2 81.2845 (1620/1993) 99.9383 (1620/1621) 98.4169 (373/379) 89.6514 0.5076 RBF 1 67.8663 (264/389) 73.1302 (264/361) 7.6266 (125/1639) 70.4 0.8275 2 93.9789 (1514/1611) 92.3734 (1514/1639) 26.8698 (97/361) 93.1692 0.8275 AB 1 67.9825 (155/228) 43.1755 (155/359) 4.4485 (73/1641) 52.8109 0.6936 2 88.4876 (1568/1772) 95.5515 (1568/1641) 56.8245 (204/359) 91.884 0.6936 SVM 1 89.7674 (193/215) 55.4598 (193/348) 1.3317 (22/1652) 68.5613 0.7706 2 91.3165 (1630/1785) 98.6683 (1630/1652) 44.5402 (155/348) 94.8502 0.7706 RELM 1 53.6339 (140/261) 35.8974 (140/390) 7.5155 (121/1610) 43.0088 0.6711 2 85.6239 (1489/1739) 92.4844 (1489/1610) 64.1025 (250/390) 88.9220 0.7076 IRELM 1 55.5556 (145/261) 41.3105 (145/351) 7.0346 (116/1649) 47.3856 0.6714 2 88.1541 (1533/1739) 92.9654 (1533/1649) 58.6894 (206/351) 90.4958 0.7280 GA-IRELM 1 88.8412 (207/233) 52.9412 (20/391) 1.6159 (26/1609) 66.3462 0.7566 2 89.5868 (1583/1767) 98.3840 (1583/1609) 47.0588 (184/391) 93.7792 0.7955 PSO-IRELM 1 84.5588 (230/272) 60.686 (230/379) 2.5910 (42/1621) 70.6605 0.7905 2 91.3773 (1579/1728) 97.4090 (1579/1621) 39.3139 (149/379) 94.2967 0.8066 BSO-IRELM 1 86.747 (216/249) 60.3352 (216/358) 2.0097 (33/1642) 71.1697 0.7916 2 91.9428 (1609/1751) 97.9902 (1609/1642) 39.6648 (142/358) 94.8702 0.8416 表 8 不同算法检测准确率(%)
Table 8 Accuracy of different algorithms (%)
算法 准确率 BP 73.1 (1462/2000) LR 47.2 (944/2000) RBF 81.95 (1639/2000) AB 76.05 (1521/2000) SVM 83.15 (1663/2000) RELM 62.7 (1254/2000) IRELM 71.9 (1438/2000) GA-IRELM 86.35 (1727/2000) PSO-IRELM 86.15 (1723/2000) BSO-IRELM 88.7 (1774/2000) 表 9 各算法在Normal上的性能评价指标
Table 9 Performance evaluation index of each algorithm on Normal
算法 精准率 (%) TPR (%) FPR (%) F值 (%) AUC BP 77.7778 (14/18) 3.8674 (14/362) 0.27548 (4/1452) 7.3684 0.5181 LR 76.4706 (13/17) 3.6723 (13/354) 0.42781 (4/935) 7.0081 0.5172 RBF 66.9377 (247/369) 73.5119 (247/336) 8.0581 (122/1514) 70.0709 0.8301 AB 52.3517 (256/489) 66.8407 (256/383) 15.5541 (233/1498) 58.7156 0.7622 SVM 91.2863 (220/241) 63.0372 (220/349) 1.4344 (21/1464) 74.5763 0.8088 RELM 89.5238 (188/210) 53.4091 (188/352) 2.0221 (22/1088) 66.9039 0.7604 IRELM 49.7619 (209/420) 58.3799 (209/358) 14.6528 (211/1440) 53.7275 0.7277 GA-IRELM 88.9706 (242/272) 64.191 (242/377) 1.9802 (30/1515) 74.5763 0.8117 PSO-IRELM 80.3571 (225/280) 61.3079 (225/367) 3.5415 (55/1553) 69.5518 0.7897 BSO-IRELM 83.9552 (225/268) 66.1765 (225/340) 2.701 (43/1592) 74.0132 0.8179 表 10 各算法在Probe上的性能评价指标
Table 10 Performance evaluation index of each algorithm on Probe
算法 精准率 (%) TPR (%) FPR (%) F值 (%) AUC BP 82.9787 (390/470) 97.5 (390/400) 6.9444 (80/1152) 89.6552 0.9625 LR 62.6039 (226/361) 56.7839 (226/398) 15.8265 (135/853) 59.552 0.7418 RBF 99.5902 (243/244) 59.7052 (243/407) 0.071582 (1/1397) 74.6544 0.7982 AB 89.6359 (320/357) 82.4742 (320/388) 2.9887 (37/1238) 85.906 0.9009 SVM 73.3728 (372/507) 88.7828 (372/419) 9.467 (135/1426) 80.3456 0.9012 RELM 51.7661 (425/821) 97.7011 (425/435) 32.3265 (396/1225) 67.6752 0.8620 IRELM 79.9065 (342/428) 91.4439 (342/374) 7.2758 (86/1182) 85.2868 0.9308 GA-IRELM 89.8851 (391/435) 92.435 (391/423) 3.1884 (44/1380) 91.1422 0.9482 PSO-IRELM 89.7638 (3422/381) 94.4751 (342/362) 2.7465 (39/1420) 92.0592 0.9605 BSO-IRELM 89.6629 (399/445) 93.8824 (399/425) 3.2372 (396/1225) 91.7241 0.9548 表 11 各算法在DoS上的性能评价指标
Table 11 Performance evaluation index of each algorithm on DoS
算法 精准率 (%) TPR (%) FPR (%) F值 (%) AUC BP 93.0233 (600/645) 81.5217 (600/736) 4.9614 (45/907) 86.8936 0.8898 LR 42.1687 (665/1577) 87.5 (665/760) 76.5743 (912/1191) 56.9106 0.5698 RBF 99.4074 (671/675) 90.9214 (671/738) 0.41152 (4/972) 94.9752 0.9530 AB 90.3509 (515/570) 70.6447 (515/729) 5.1838 (55/1061) 79.2918 0.8316 SVM 84.7118 (676/798) 90.1333 (676/750) 11.0009 (122/1109) 87.3385 0.9019 RELM 96.7391 (178/184) 25.0704 (178/710) 0.55453 (6/1082) 39.821 0.6230 IRELM 96.7059 (411/425) 54.0079 (411/761) 1.3449 (14/1041) 69.3086 0.7644 GA-IRELM 90.7539 (638/703) 89.4811 (638/713) 5.6326 (65/1154) 90.113 0.9222 PSO-IRELM 93.5302 (665/711) 89.502 (665/742) 4.1667 (16/1104) 91.4718 0.9292 BSO-IRELM 96.3636 (689/715) 93.6141 (689/736) 2.3402 (26/1111) 94.969 0.9578 表 12 各算法在R2L上的性能评价指标
Table 12 Performance evaluation index of each algorithm on R2L
算法 精准率 (%) TPR (%) FPR (%) F值 (%) AUC BP 87.5 (14/16) 31.1111 (14/45) 0.13793 (2/1450) 45.9016 0.5150 LR NaN (0/0) 0 (0/32) 0 (0/944) NaN 0 RBF 68 (17/25) 56.6667 (17/30) 0.4908 (8/1630) 61.8182 0.7813 AB NaN (0/0) 0 (0/36) 0 (0/1521) NaN 0 SVM NaN (0/0) 0 (0/36) 0 (0/1663) NaN 0 RELM 50 (1/2) 3.4483 (1/29) 0.079745 (1/1254) 6.4516 0.5147 IRELM 81.8182 (9/11) 39.1304 (9/23) 0.13976 (2/1431) 52.9412 0.6951 GA-IRELM 90.9091 (20/22) 57.1429 (20/35) 0.11703 (2/1709) 70.1754 0.7852 PSO-IRELM 90.9091 (20/22) 54.0541 (20/37) 0.1173 (2/1705) 67.7966 0.7698 BSO-IRELM 92.3077 (24/26) 82.7586 (24/29) 0.39728 (7/1762) 69.0909 0.8258 表 13 各算法在U2R上的性能评价指标
Table 13 Performance evaluation index of each algorithm on U2R
算法 精准率 (%) TPR (%) FPR (%) F值 (%) AUC BP 52.1739 (44/851) 97.1554 (444/457) 28.5614 (407/1425) 67.8899 0.8539 LR 88.8889 (40/45) 8.7719 (40/456) 0.55006 (5/909) 15.9681 0.5422 RBF 67.1033 (461/687) 94.274 (461/489) 16.0969 (226/1404) 78.4014 0.8966 AB 73.6301 (430/584) 92.6724 (430/464) 12.3695 (154/1245) 82.0611 0.9132 SVM 87.0044 (395/454) 88.565 (395/446) 4.4461 (59/1327) 87.7778 0.9238 RELM 59.0038 (462/783) 97.4684 (462/474) 28.841 (321/1113) 73.5084 0.8822 IRELM 65.2235 (467/716) 96.4876 (467/484) 20.4098 (249/1220) 77.8333 0.9003 GA-IRELM 76.7606 (436/568) 96.4602 (436/452) 9.2762 (132/1423) 85.4902 0.9397 PSO-IRELM 77.7228 (471/606) 95.9267 (471/491) 9.7332 (135/1387) 85.8706 0.9349 BSO-IRELM 80.9524 (442/546) 94.0426 (442/470) 7.2423 (104/1436) 87.0079 0.9362 -
[1] Tsai C F, Hsu Y F, Lin C Y, Lin W Y. Intrusion detection by machine learning: A review. Expert Systems With Applications, 2009, 36(10): 11994-12000 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2009.05.029 [2] 任家东, 刘新倩, 王倩, 何海涛, 赵小林. 基于KNN离群点检测和随机森林的多层入侵检测方法. 计算机研究与发展, 2019, 56(3): 566-575Ren Jia-Dong, Liu Xin-Qian, Wang Qian, He Hai-Tao, Zhao Xiao-Lin. An multi-level intrusion detection method based on KNN outlier detection and random forests. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(3): 566-575 [3] 高妮, 高岭, 贺毅岳, 王海. 基于自编码网络特征降维的轻量级入侵检测模型. 电子学报, 2017, 45(3): 730-739Gao Ni, Gao Ling, HE Yi-Yue, Wang Hai. A lightweight intrusion detection model based on autoencoder network with feature reduction. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(3): 730-739 [4] Ahmad I, Basheri M, Iqbal M J, Rahim A. Performance comparison of support vector machine, random forest, and extreme learning machine for intrusion detection. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 33789-33795 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2841987 [5] Mabu S, Gotoh S, Obayashi M, Kuremoto T. A random-forests-based classifier using class association rules and its application to an intrusion detection system. Artificial Life and Robotics, 2016, 21(3): 371-377 doi: 10.1007/s10015-016-0281-x [6] Shenfield A, Day D, Ayesh A. Intelligent intrusion detection systems using artificial neural networks. ICT Express, 2018, 4(2): 95-99 doi: 10.1016/j.icte.2018.04.003 [7] Ding H W, Wan L. Research on intrusion detection based on KPCA-BP neural network. In: Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT). Chongqing, China: IEEE, 2018. 911−915 [8] Wang T, Wei L H, Ai J Q. Improved BP Neural Network for Intrusion Detection Based on AFSA. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Computers and Informatics (ISCI). Beijing, China: Atlantis Press, 2015. 373−380 [9] Huang G, Song S J, Gupta J N D, Wu C. Semi-supervised and unsupervised extreme learning machines. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(12): 2405-2417 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2307349 [10] 陆慧娟, 安春霖, 马小平, 郑恩辉, 杨小兵. 基于输出不一致测度的极限学习机集成的基因表达数据分类. 计算机学报, 2013, 36(2): 341-348Lu Hui-Juan, An Chun-Lin, Ma Xiao-Ping, Zheng En-Hui, Yang Xiao-Bing. Disagreement measure based ensemble of extreme learning machine for gene expression data classification. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2013, 36(2): 341-348 [11] 陈晓云, 廖梦真. 基于稀疏和近邻保持的极限学习机降维. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(2): 325-333Chen Xiao-Yun, Liao Meng-Zhen. Dimensionality reduction with extreme learning machine based on sparsity and neighborhood preserving. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(2): 325-333 [12] Yang Z X, Wang X B, Wong P K, Zhong J H. ELM based representational learning for fault diagnosis of wind turbine equipment. Proceedings of ELM-2015 Volume 2: Theory, Algorithms and Applications (II). Cham: Springer, 2016. 169−178 [13] 邹伟东, 夏元清. 基于压缩动量项的增量型ELM虚拟机能耗预测. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1290-1297Zou Wei-Dong, Xia Yuan-Qing. Virtual machine power prediction using incremental extreme learning machine based on compression driving amount. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1290-1297 [14] Ku J H, Zheng B. Intrusion detection based on self-adaptive differential evolution extreme learning machine with gaussian kernel. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Parallel Architecture, Algorithm and Programming. Haikou, China: Springer, 2017. 13−24 [15] Deng W Y, Zheng Q H, Chen L. Regularized extreme learning machine. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Data Mining. Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2009. 389−395 [16] Huang G B, Wang D H, Lan Y. Extreme learning machines: A survey. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2011, 2(2): 107-122 doi: 10.1007/s13042-011-0019-y [17] Jiang X Y, Li S. BAS: Beetle antennae search algorithm for optimization problems [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.10724.pdf, March 27, 2019 [18] Jiang X Y. Li S. Beetle antennae search without parameter tuning (BAS-WPT) for multi-objective optimization. Filomat, 2020, 34(15): 5113−5119 [19] 刘影, 钱志鸿, 贾迪. 室内环境中基于天牛须寻优的普适定位方法. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1565-1571 doi: 10.11999/JEIT181021Liu Ying, Qian Zhi-Hong, Jia Di. Universal localization algorithm based on beetle antennae search in indoor environment. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1565-1571 doi: 10.11999/JEIT181021 [20] Wu Q, Ma Z P, Xu G, Li S, Chen D C. A novel neural network classifier using beetle antennae search algorithm for pattern classification. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 64686-64696 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2917526 [21] Kaur G, Arora S. Chaotic whale optimization algorithm. Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 2018, 5(3): 275-284 doi: 10.1016/j.jcde.2017.12.006 [22] Ling Y, Zhou Y Q, Luo Q F. Lévy flight trajectory-based whale optimization algorithm for global optimization. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 6168-6186 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2695498 [23] Sarangi A, Samal S, Sarangi S K. Analysis of Gaussian and Cauchy mutations in modified particle swarm optimization algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS). Coimbatore, India: IEEE, 2019. 463−467 [24] Rudolph G. Local convergence rates of simple evolutionary algorithms with Cauchy mutations. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 1997, 1(4): 249-258 doi: 10.1109/4235.687885 [25] Gauthama Raman M R, Somu N, Kirthivasan K, Liscano R, Shankar Sriram V S. An efficient intrusion detection system based on hypergraph-Genetic algorithm for parameter optimization and feature selection in support vector machine. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 134: 1-12 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2017.07.005 [26] Mazini M, Shirazi B, Mahdavi I. Anomaly network-based intrusion detection system using a reliable hybrid artificial bee colony and AdaBoost algorithms. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 2019, 31(4): 541-553 doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2018.03.011 [27] 王东风, 孟丽. 粒子群优化算法的性能分析和参数选择. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(10): 1552-1561 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150774Wang Dong-Feng, Meng Li. Performance analysis and parameter selection of PSO algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1552-1561 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150774 [28] UCI. UCI dataset [Online], available: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/index.php, June 27, 2019 [29] NSL-KDD dataset [Online], available: https://www.unb.ca/cic/datasets/nsl.html, June 27, 2019 [30] Vinayakumar R, Alazab M, Soman K P, Poornachandran P, Al-Nemrat A, Venkatraman S. Deep learning approach for intelligent intrusion detection system. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 41525-41550 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2895334 -




 下载:
下载: