Fully Overlapped Handwritten Number Recognition and Separation Based on Deep EM Capsule Network
-
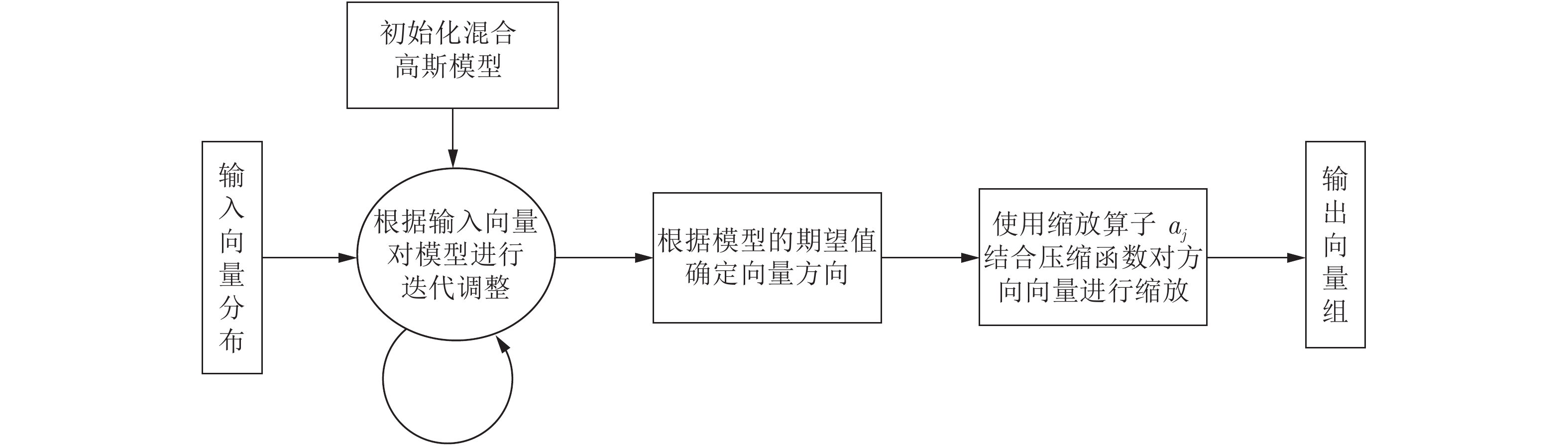
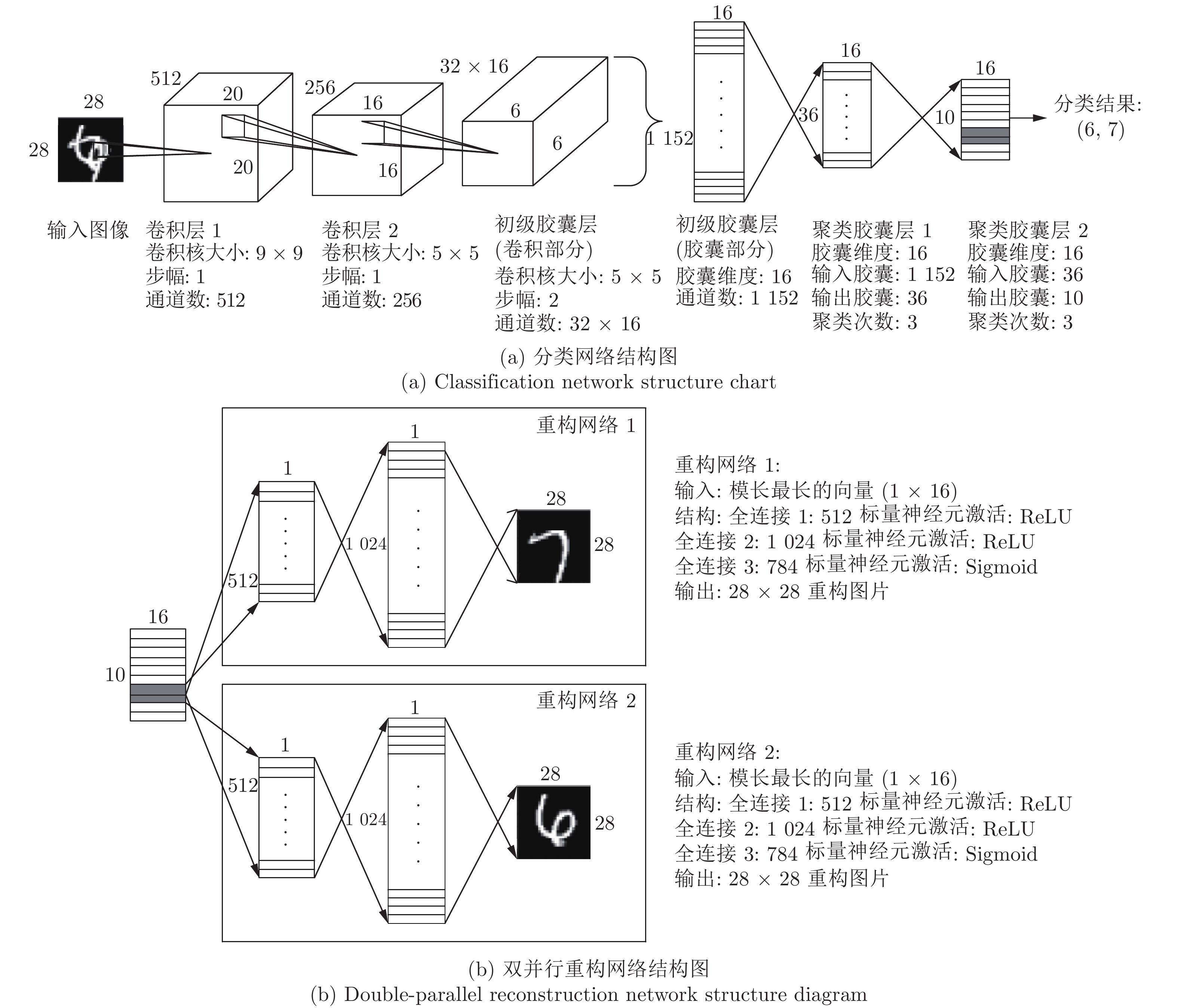
摘要: 基于胶囊网络的向量神经元思想和期望最大算法(Expectation-maximization, EM), 设计了一种以EM为向量聚类算法的深度胶囊网络(Deep capsule network, DCN), 实现了重叠手写数字的识别与分离. 该网络由两部分组成, 第 1 部分是“识别网络”, 将 EM 算法改为 EM 向量聚类算法, 以替换原胶囊网络CapsNet 中的迭代路由部分, 这一改动优化了网络的运算过程, 实现了重叠数字识别. 第 2 部分是“重构网络”, 由结构完全相同的两个并行网络组成, 对双向量进行并行重构, 实现了重叠数字的分离. 实验结果显示, 对于 100% 全重叠手写数字图片本网络识别率达到了 96%, 对比CapsNet 在 80% 的重叠率下 95% 的识别率, 本文网络在难度提升的情况下, 识别率有明显提高, 能够将完全重叠的两张手写数字进行图片进行准确地分离.Abstract: Based on the idea of vector neuron of capsule network and expectation maximization algorithm (EM), a deep capsule network (DCN) with EM as the vector clustering algorithm is designed to recognize and separate overlapping handwritten digits The network consists of two parts. The first part is “identification network”. The EM algorithm is changed to EM vector clustering algorithm to replace the iterative routing part of the original capsule network CapsNet. This change optimizes the network operation process and realizes overlapping number recognition. The second part is the “reconstruction network”, which is composed of two parallel networks with identical structure. The bi-vector are reconstructed in parallel to realize the separation of overlapping digits. The experimental results show that for 100% full overlap handwritten digit, the recognition rate of the network reaches 96%. Compared with the 95% recognition rate of CapsNet at 80% overlap rate, the recognition rate of the network in this paper is significantly improved in the case of increased difficulty, and can accurately separate two completely overlapping handwritten digits.
-
表 1 数据集标签
Table 1 Dataset label
输入图像 标签 说明 
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0) 无叠加 
(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2) 两个相同数字叠加 
(0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0) 两个不同数字叠加 表 2 在不同聚类次数下的激活向量模长
Table 2 Active vector module length under different clustering times
网络结构及聚类形式 所用训练集 R = 1 R = 2 R = 3 DCN EM 聚类/CapsNet 路由聚类 MNIST数据集 0.0413/0.0536 0.5241/0.4122 0.9800/0.8792 全重叠数据集 0.0332/0.0423 0.4342/0.5865 0.9943/0.8653 混合数据集 0.0323/0.0354 0.4543/0.3252 0.9923/0.9173 表 3 参数量与不同聚类次数下的单Epoch消耗时间(s)
Table 3 Parameter quantity and single epoch consumption time under different clustering times (s)
网络结构 参数量 聚类算法 R = 1 R = 2 R = 3 CapsNet 8 215568 迭代路由 150±2 210±2 240±2 DCN 20128032 EM 240±2 300±2 340±2 表 4 DCN不同聚类算法单Epoch消耗时间(s)
Table 4 Single epoch consumption time of different DCN clustering algorithms (s)
聚类算法 R = 1 R = 2 R = 3 迭代路由 350±2 410±2 440±2 EM 240±2 300±2 340±2 表 5 DCN识别手写数字效果对比 (%)
Table 5 Effect comparison of handwritten digits recognized by DCN (%)
所用训练集 无重叠手写
数字识别率全重叠手写
数字识别率MNIST 数据集 99.6 55.2 全重叠手写数字数据集 80.7 96.75 混合数据集 95.7 96.55 表 6 重叠手写数字识别率对比(R = 3) (%)
Table 6 Comparison of recognition rate of overlapping handwritten digits (R = 3) (%)
网络模型 训练集 重叠率 正确率 CapsNet MutiMNIST 80 95 全重叠数据集 100 88 DCN 全重叠数据集 100 96.75 表 7 全重叠手写数字分类与重构的部分结果
Table 7 Partial results of classification and reconstruction of fully overlapped handwritten digits
分类标签 (3, 7) (9, 1) (0, 8) (0, 4) (9, 7)* (7, 9)* (7, 9)* (5, 9)• 分类结果 (3, 7) (9, 1) (8, 0) (0, 4) (7, 9)* (7, 9)* (7, 9)* (8, 9)• 输入图片 







重构图片 1 







重构图片 2 







表 8 部分识别和分离结果
Table 8 Partial identification and separation results
分类标签 (不, 专) (下, 不) (丑, 下) (不, 丑) (下, 世) (下, 专) (王, 丑) (也, 卫) 分类结果 (不, 专) (下, 不) (丑, 下) (不, 丑) (下, 世) (下, 专) (丑, 不能确定) (不能确定, 不能确定) 输入图片 







重构图片 1 







重构图片 2 







-
[1] Hinton G E, Ghahramani Z, Teh Y W. Learning to parse images. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Denver, USA: MIT Press, 1999. 463−469 [2] Goodfellow I J, Bulatov Y, Ibarz J, Arnoud S, Shet V B. Multi-digit number recognition from street view imagery using deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations. Banff, Canada: ICLR, 2014. [3] Ba J, Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K. Multiple object recognition with visual attention. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA: ICLR, 2015. [4] Greff K, Rasmus A, Berglund M, Hao T H, Schmidhuber J, Valpola H. Tagger: Deep unsupervised perceptual grouping. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: Curran Associates Inc., 2016. 4491−4499 [5] Sabour S, Frosst N, Hinton G E. Dynamic routing between capsules. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 3859−3869 [6] Gupta M R, Chen Y H. Theory and use of the EM algorithm. Foundations and Trends in Signal Processing, 2011, 4(3): 223−296 [7] Xuan G R, Zhang W, Chai P Q. EM algorithms of Gaussian mixture model and hidden Markov model. In: Proceedings of the 2001 International Conference on Image Processing (Cat. No.01CH37205). Thessaloniki, Greece: IEEE, 2001. 145−148 [8] Jain A K, Dubes R C. Algorithms for Clustering Data. Prentice-Hall Inc., 1988. [9] Wang D L, Liu Q. An optimization view on dynamic routing between capsules. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada: ICLR, 2018. [10] Jaiswal A, AbdAlmageed W, Wu Y, Natarajan P. CapsuleGAN: Generative adversarial capsule network. In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 526−535 [11] LaLonde R, Bagci U. Capsules for object segmentation. arXiv Preprint arXiv:1804.04241, 2018. [12] Rajasegaran J, Jayasundara V, Jayasekara S, Jayasekara H, Seneviratne S, Rodrigo R. DeepCaps: Going deeper with capsule networks. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 10717−10725 [13] Hinton G E, Sabour S, Frosst N. Matrix capsules with EM routing. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada: ICLR, 2018. [14] Zhang H Y, Cissé M, Dauphin Y N, Lopez-Paz D. mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada: ICLR, 2018. [15] Tokozume Y, Ushiku Y, Harada T. Between-class learning for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018. 5486−5494 [16] 朱周华. 期望最大(EM)算法及其在混合高斯模型中的应用. 现代电子技术, 2003, 26(24): 88−90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-373X.2003.24.032Zhu Zhou-Hua. EM algorithm and its application in mixture of Gaussian. Modern Electronics Technique, 2003, 26(24): 88−90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-373X.2003.24.032 -




 下载:
下载: