-
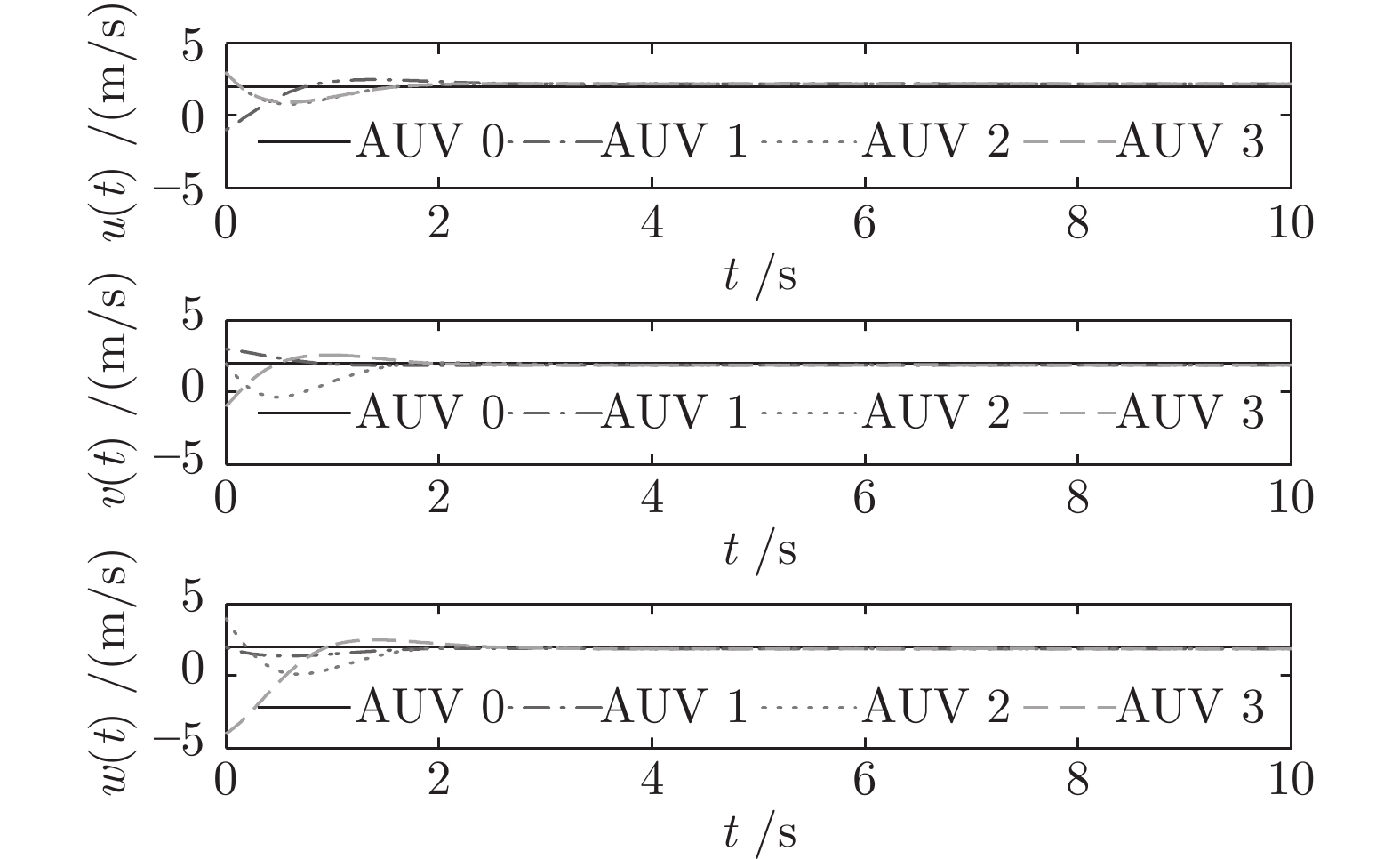
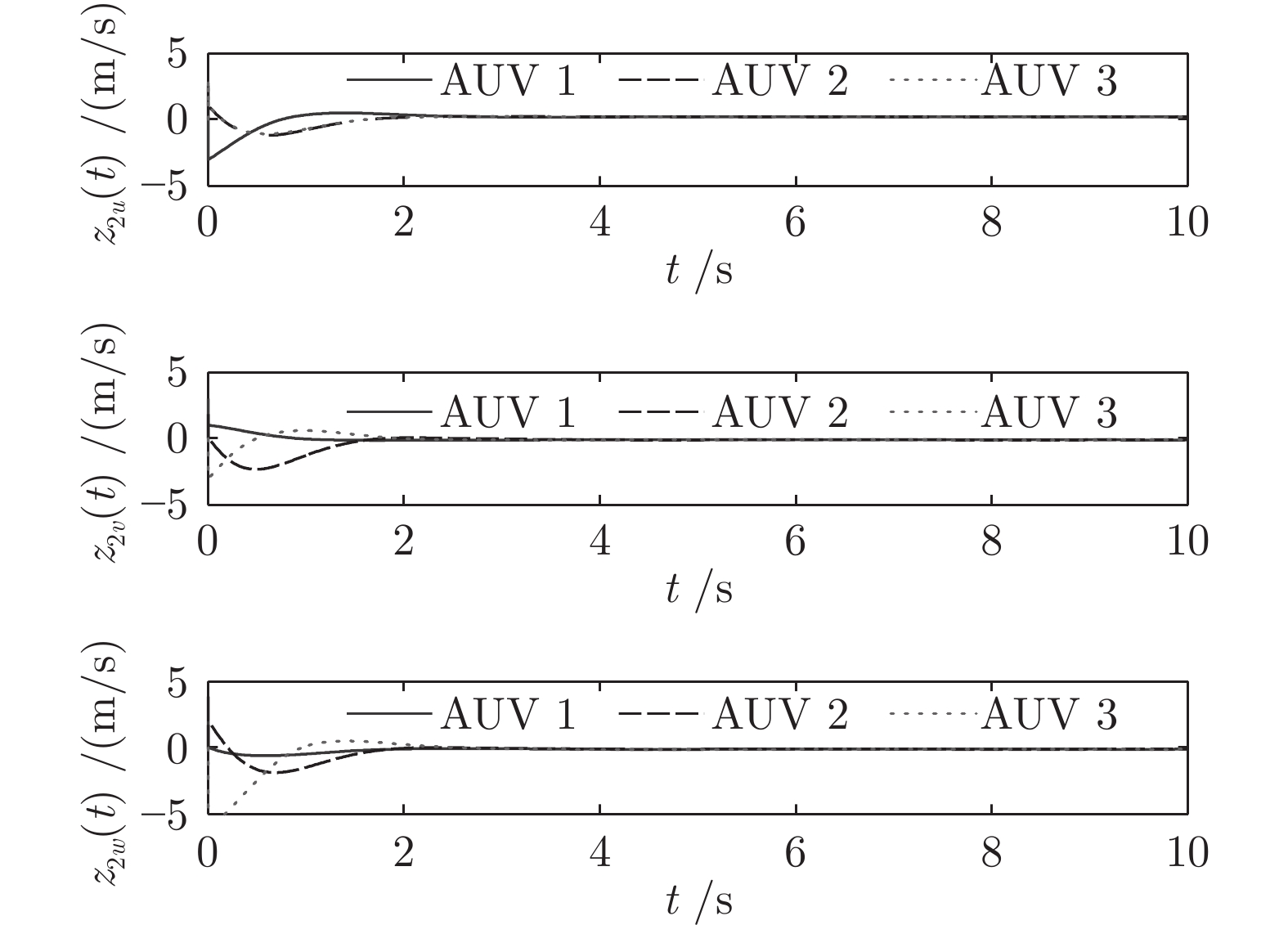
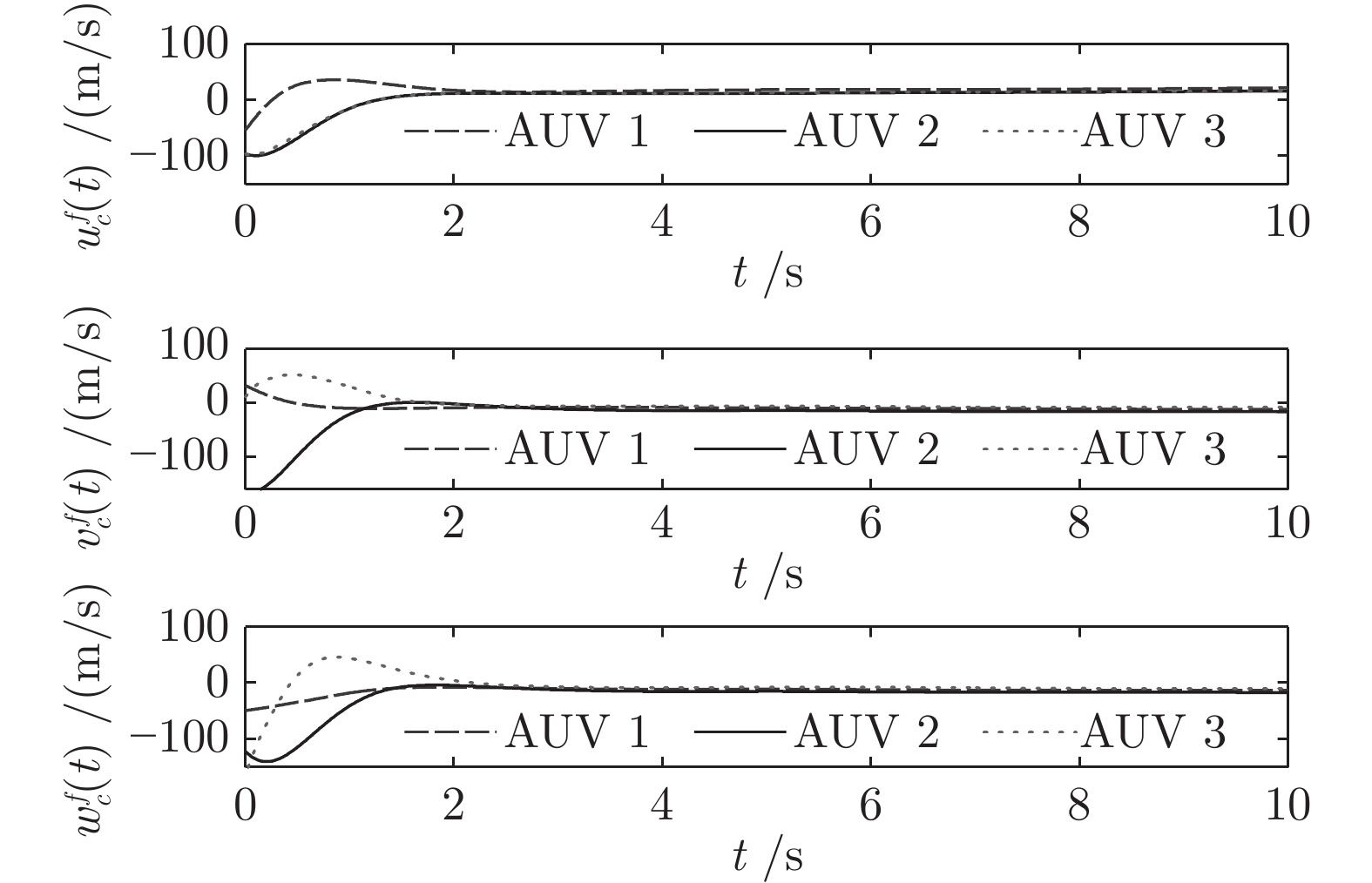
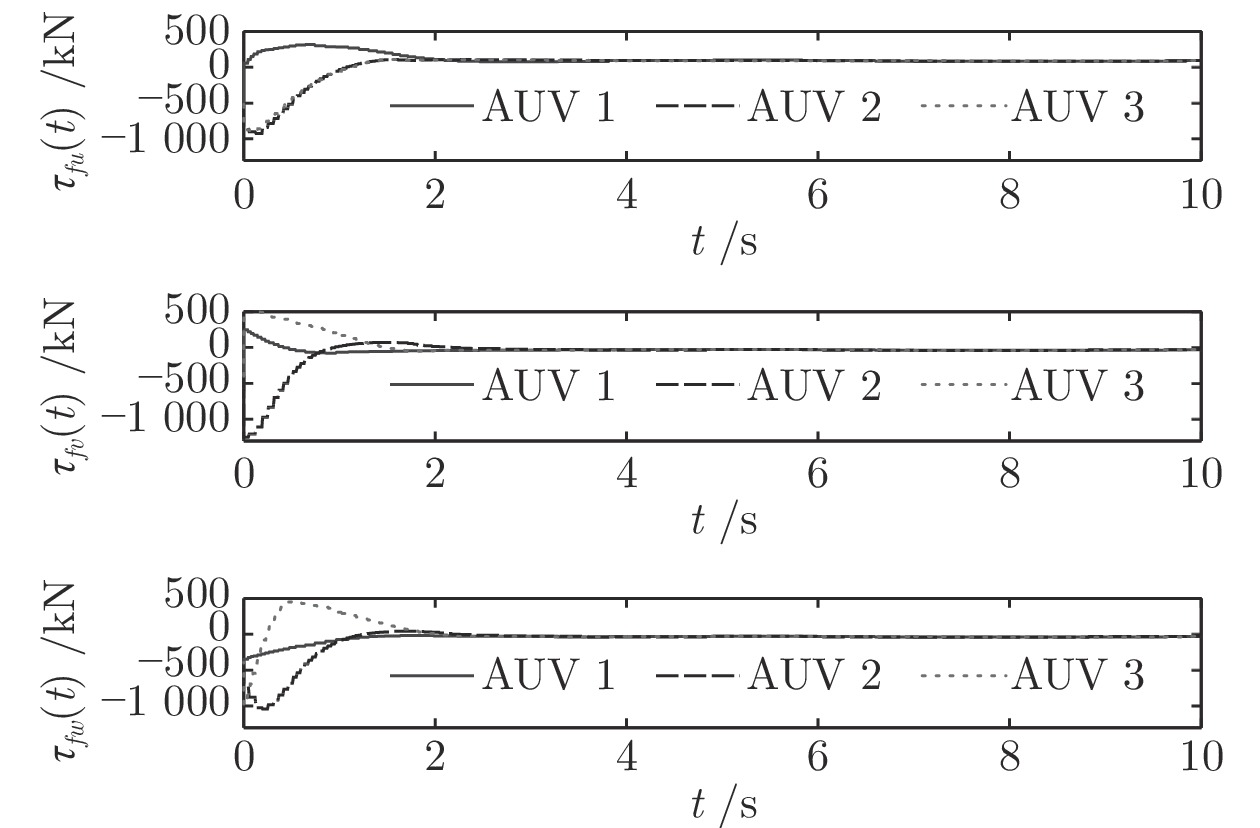
摘要: 针对多自主水下航行器编队系统受限于有限的通信资源及收敛速度慢等问题, 提出一种基于事件触发的自主水下航行器固定时间领航−跟随编队控制方法. 首先, 将动态面控制算法与反步法结合, 消除“计算膨胀”问题; 其次, 为节约有限通信资源, 将事件触发通讯机制和固定时间理论引入多自主水下航行器编队控制中, 设计编队控制器, 实现编队系统的固定时间稳定, 且系统收敛时间与初始状态无关, 并通过理论证明无Zeno行为; 最后, 对4艘自主水下航行器的编队进行仿真实验, 验证算法的有效性.Abstract: In this paper, the limited communication resources and slow convergence speed of multi-autonomous underwater vehicles formation system are considered, a fixed-time leader-follower formation control method of autonomous underwater vehicles with event-triggered mechanism is proposed. Firstly, by combining dynamic surface control with backstepping technique, the algorithm can overcome the “explosion of complexity” problem. Secondly, in order to save communication resources, the formation controller is designed by combining the event-triggered control strategy and the fixed-time theory. Thus, the target of formation is stable in fixed-time and the convergence time of system is independent of the initial state, and the theory is used to prove that there is no Zeno behavior. Finally, in order to verify the validity of algorithm, the formation experiment of four autonomous underwater vehicles is studied by simulation.
-
表 1 跟随 AUVs 的任意初始状态
Table 1 The arbitrary initial state of AUVs
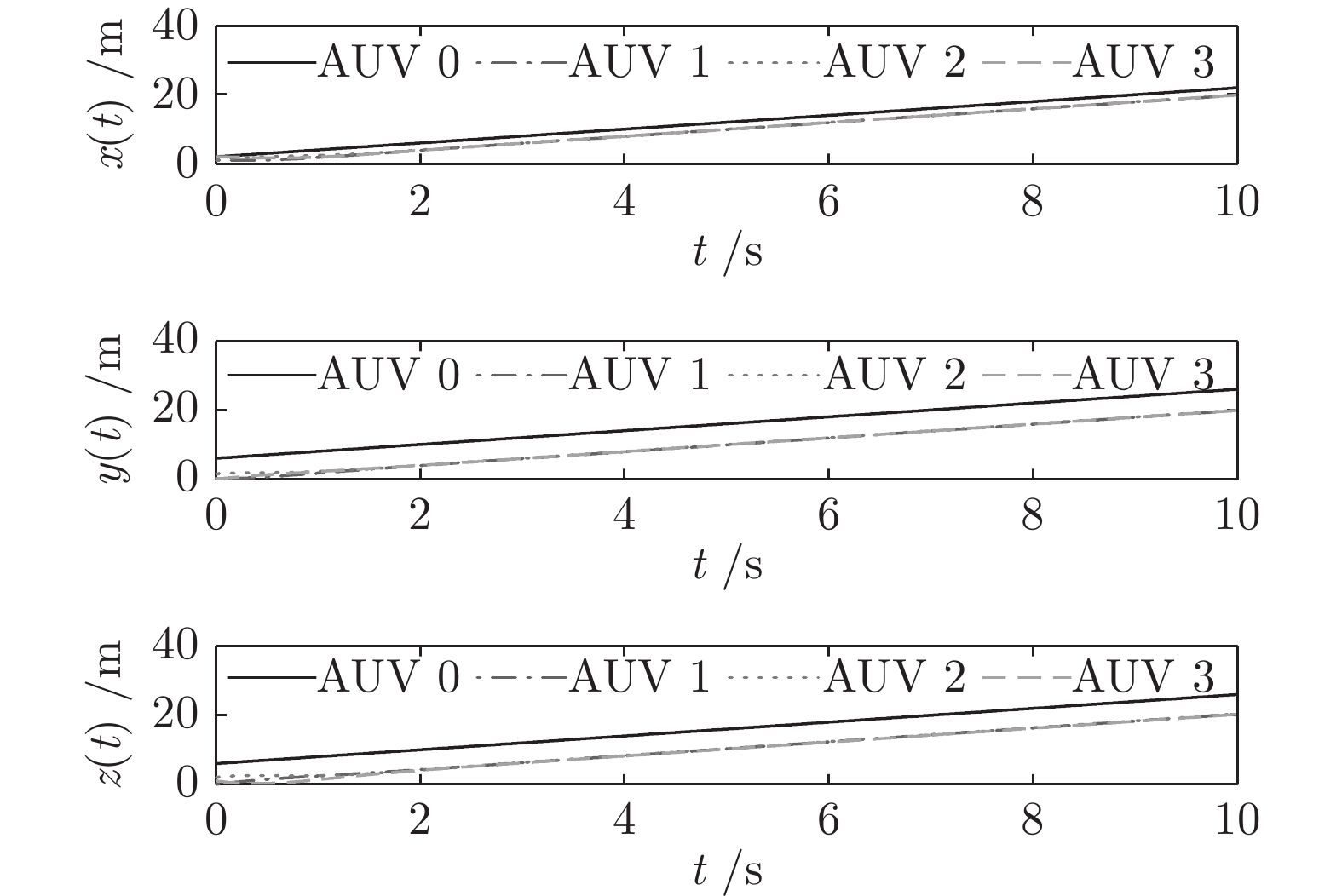
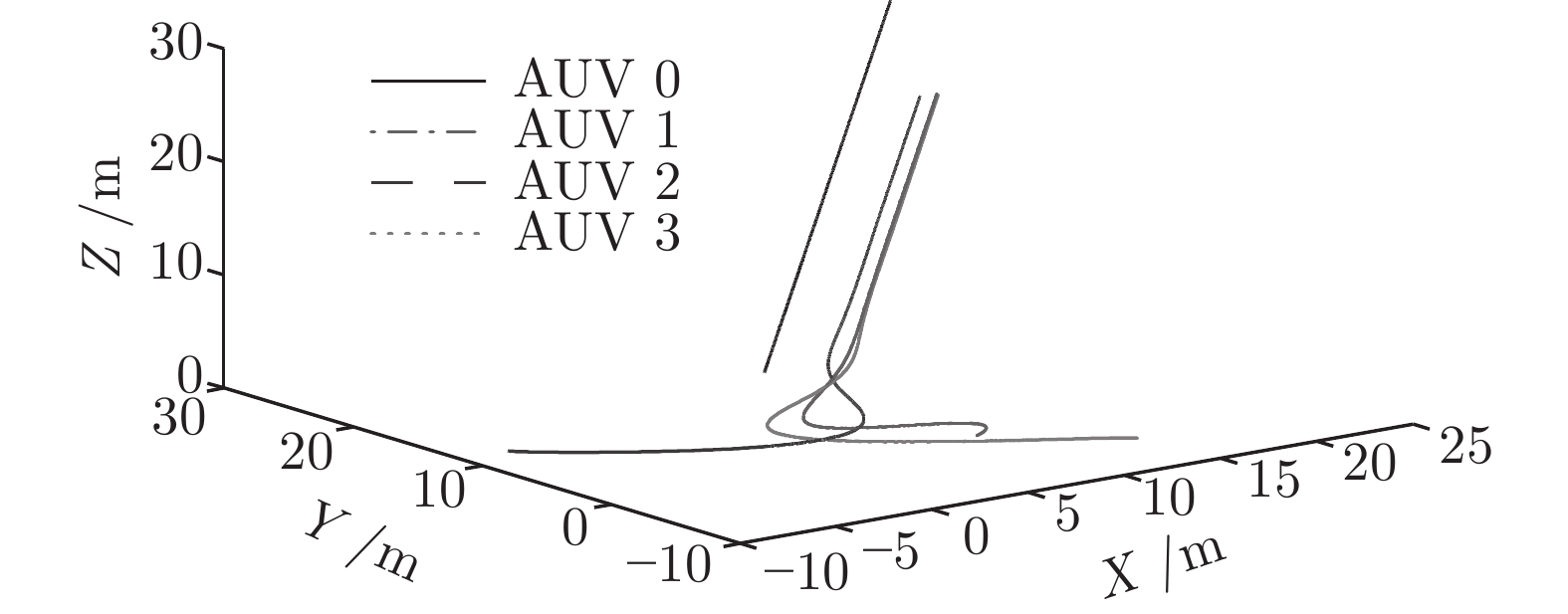
工况 状态 AUV 1 AUV 2 AUV 3 1 ${p_f}\left( 0 \right)$ ${\left[ {1,0,0} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ ${\left[ {1,1.5,2} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ ${\left[ {2,0,1} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ ${\upsilon _f}\left( 0 \right)$ ${\left[ { - 1,3,2} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ ${\left[ {3,2,4} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ ${\left[ {3, - 1, - 4} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ 2 ${p_f}\left( 0 \right)$ ${\left[ {7, - 3,2} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ ${\left[ { - 10,8,2} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ ${\left[ {12, - 8,2} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ ${\upsilon _f}\left( 0 \right)$ ${\left[ {6,0,8} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ ${\left[ {4, - 3,1} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ ${\left[ { - 1,4, - 3} \right]^{\rm{T}}}$ 表 2 跟随者AUVs的事件触发次数和触发率
Table 2 Event-triggered and triggered ratios for follower AUVs
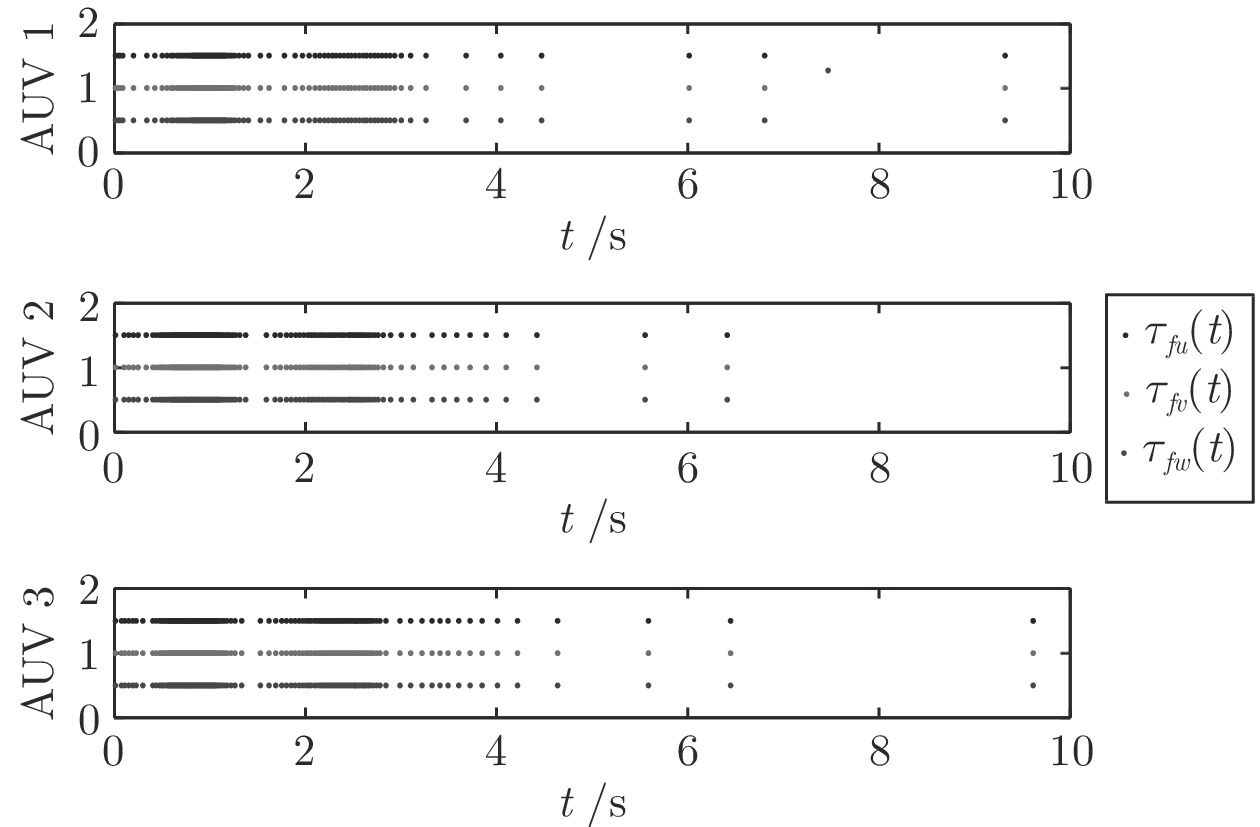
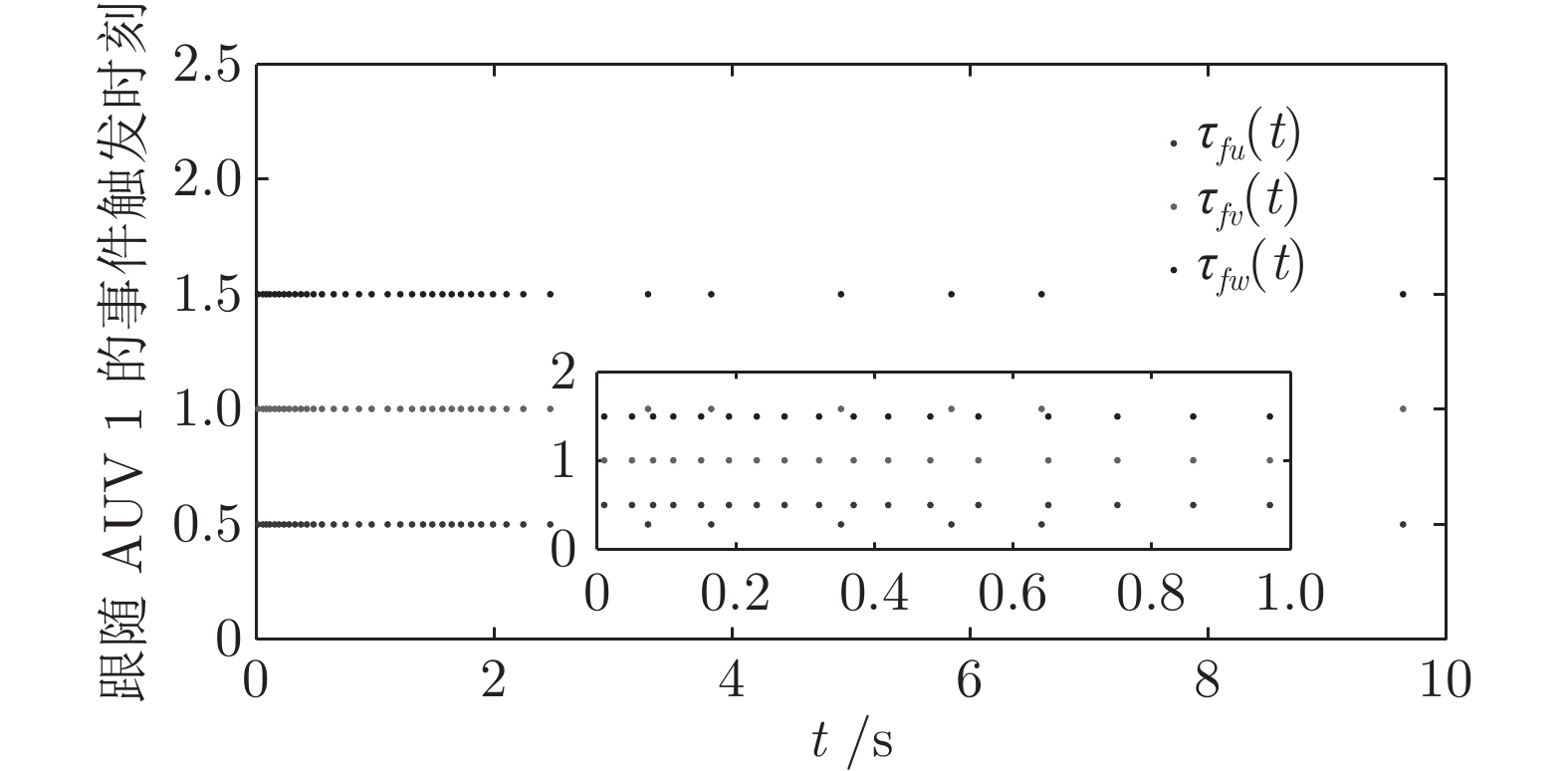
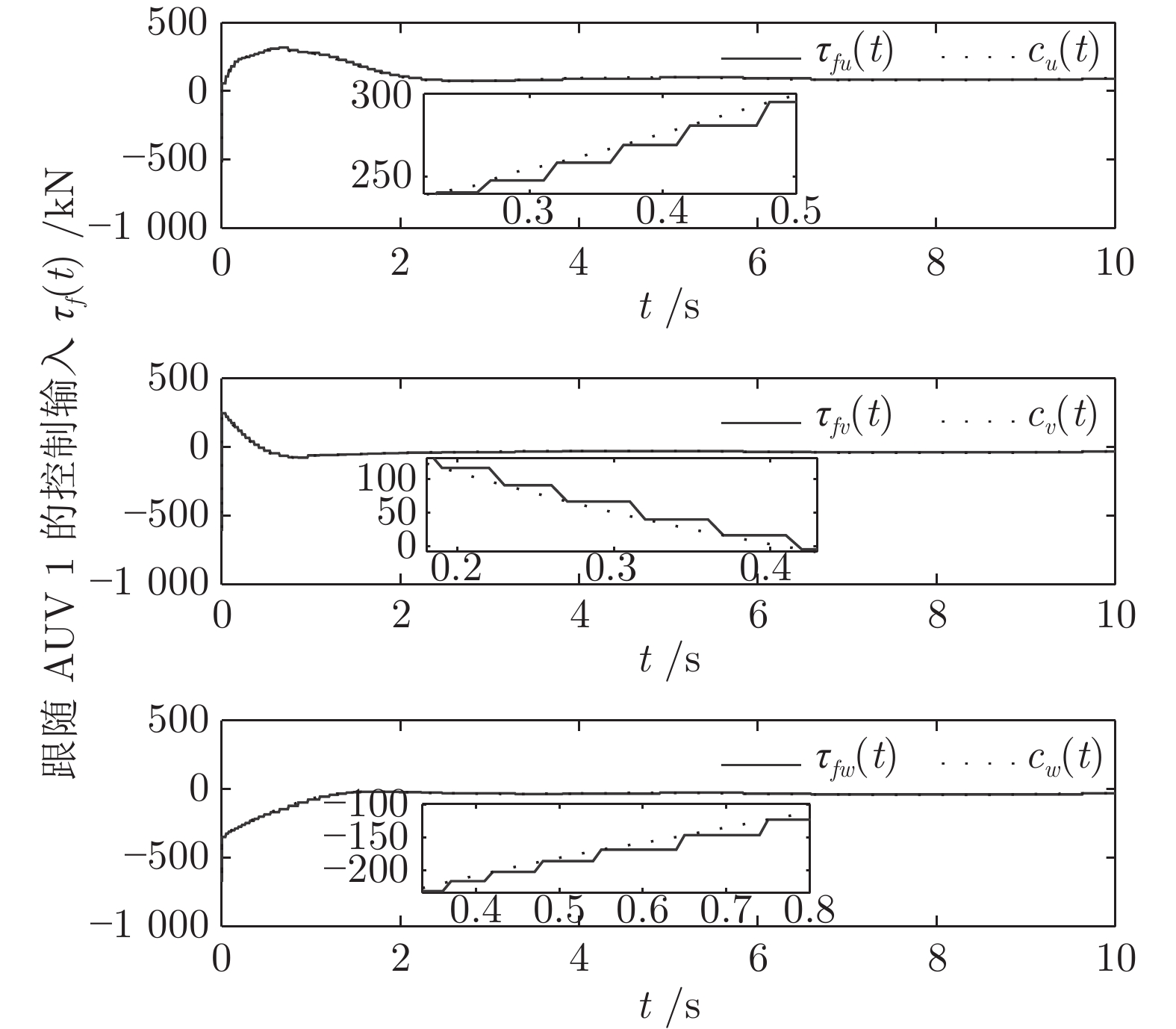
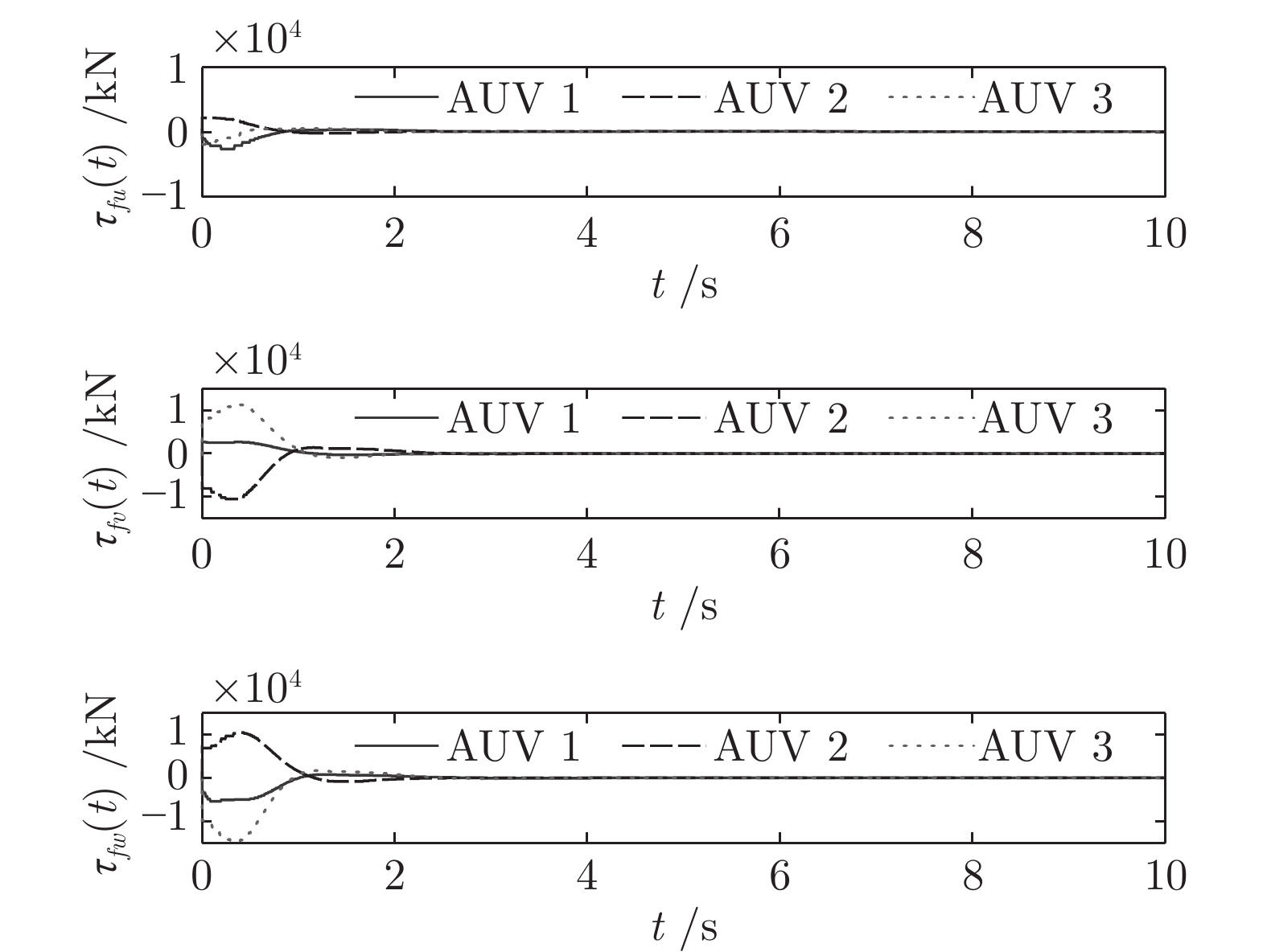
工况 采样次数 触发次数 触发率 (%) 1 2 1 2 1 2 AUV 1 — — 37 99 3.7 9.9 AUV 2 1000 1000 56 125 5.6 12.5 AUV 3 — — 58 135 5.8 13.5 表 3 本文算法和PID算法的比较结果
Table 3 Comparison results in the algorithm of proposed in paper and PID
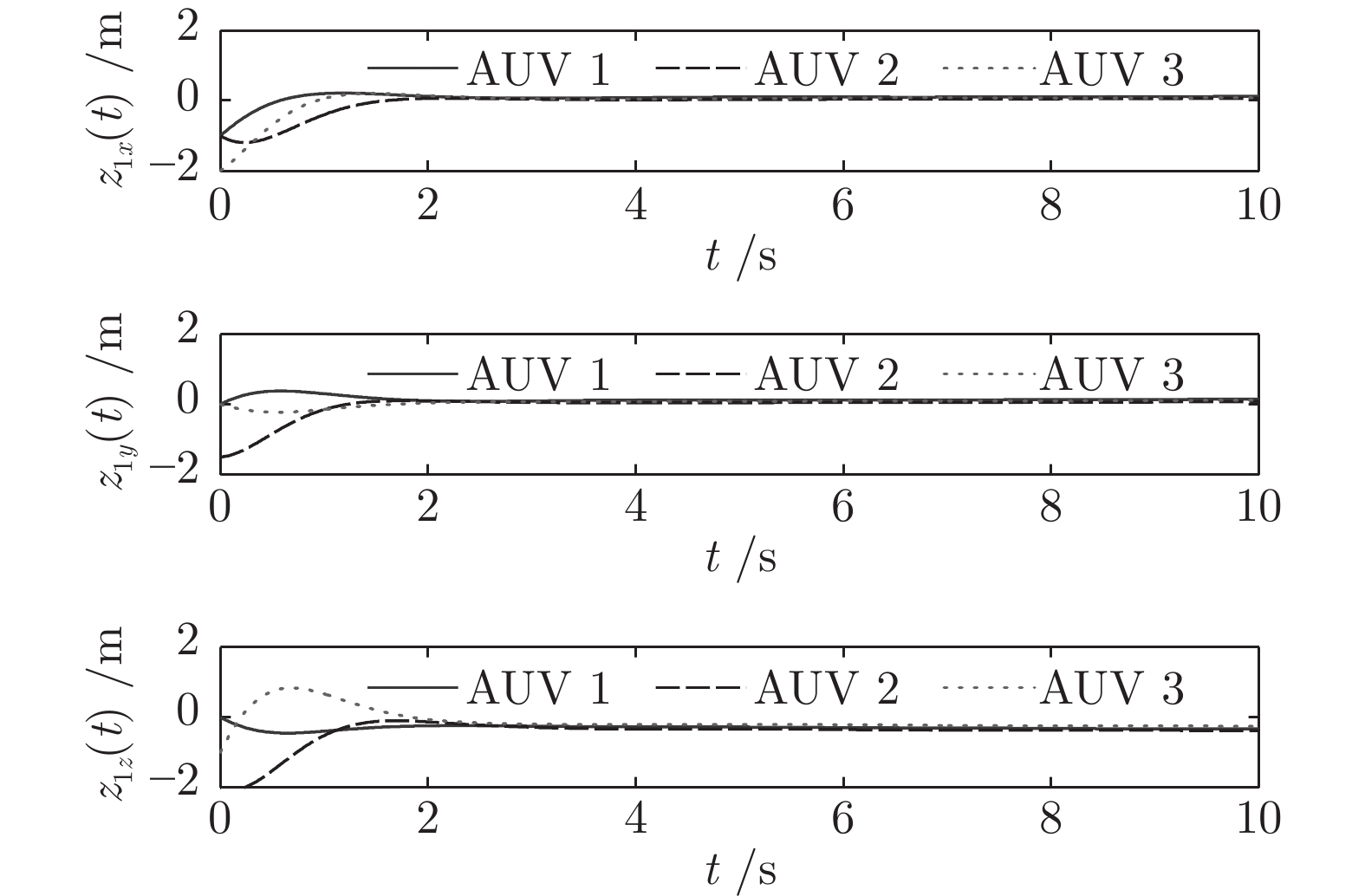
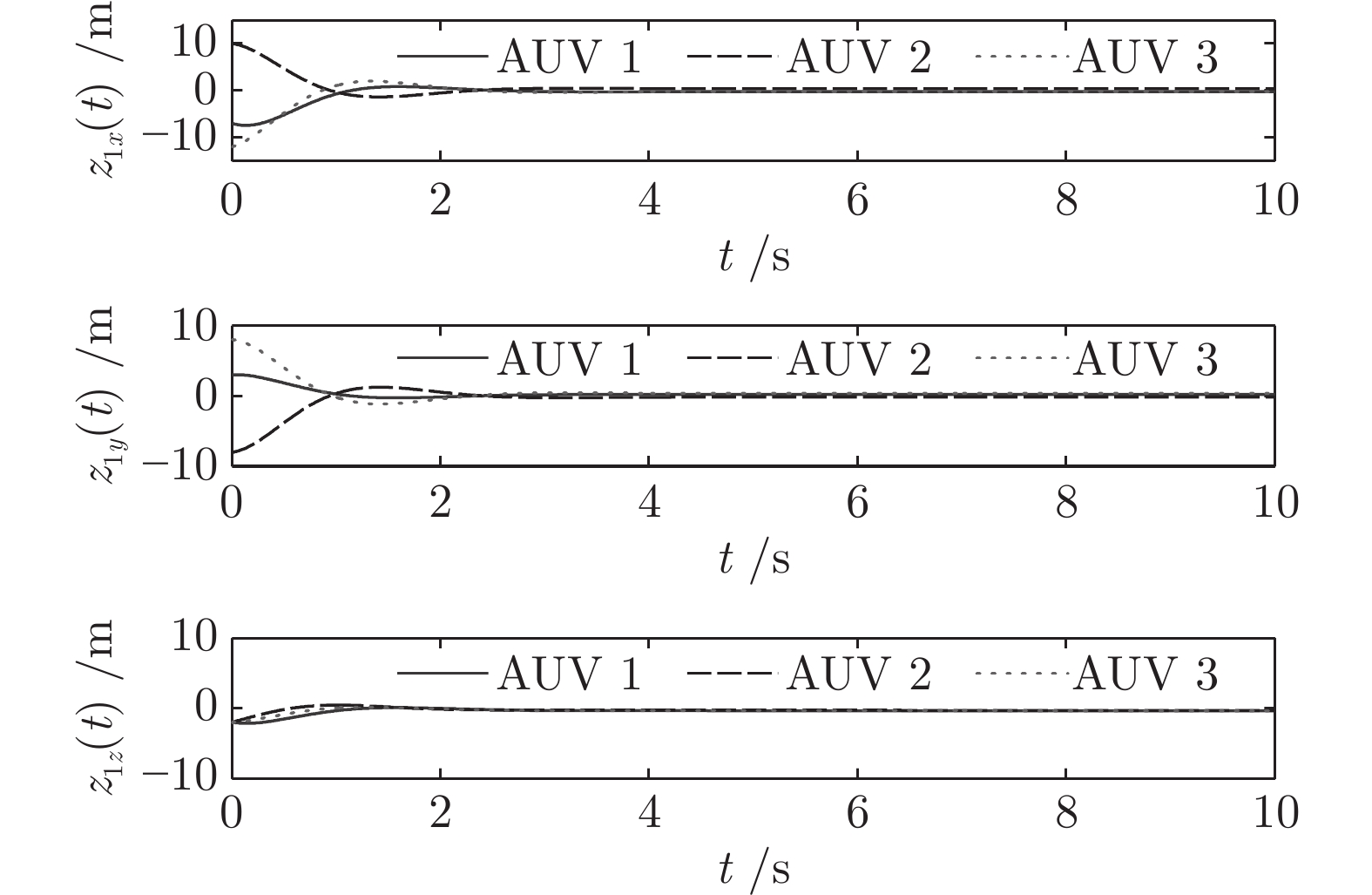
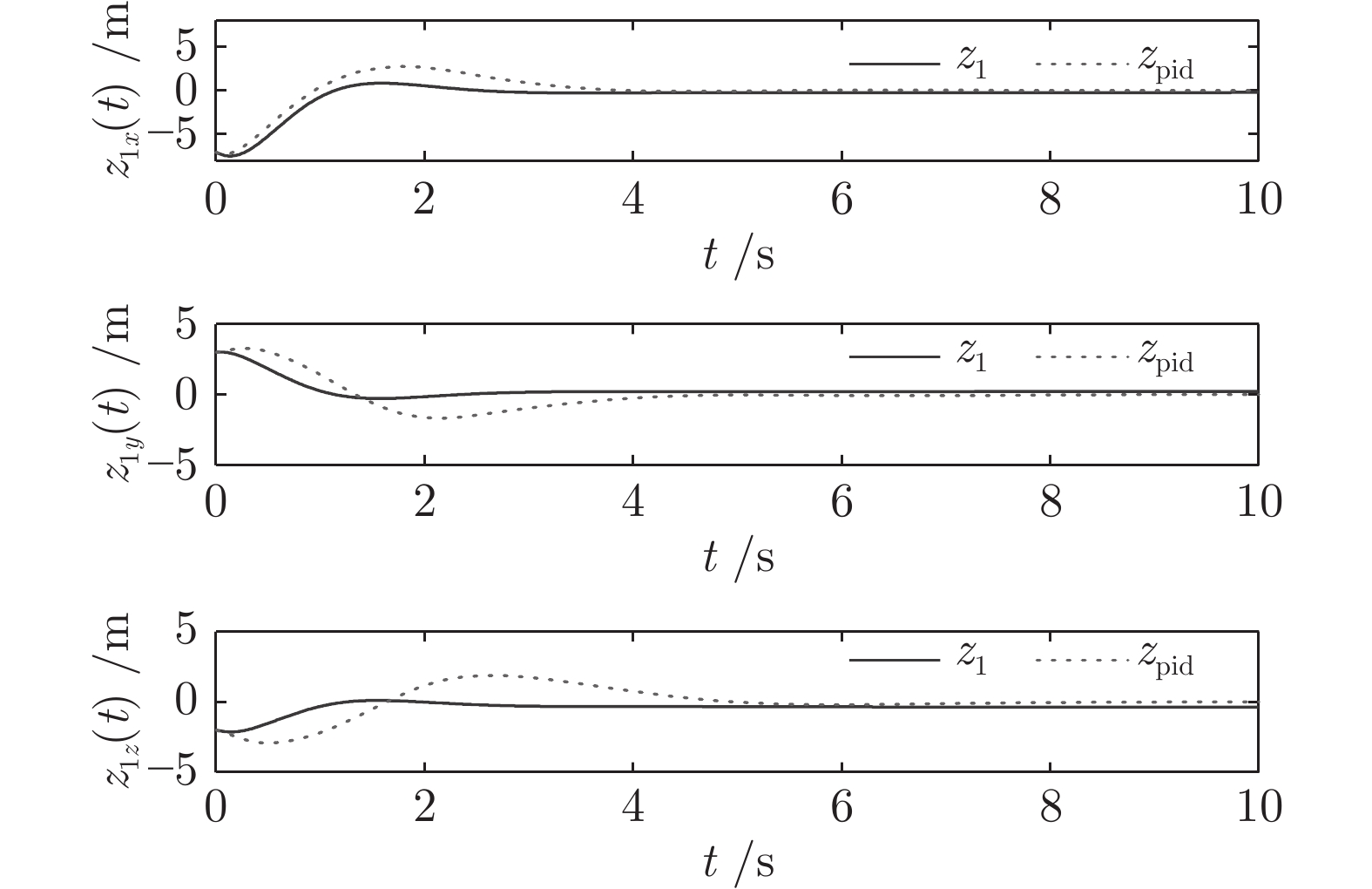
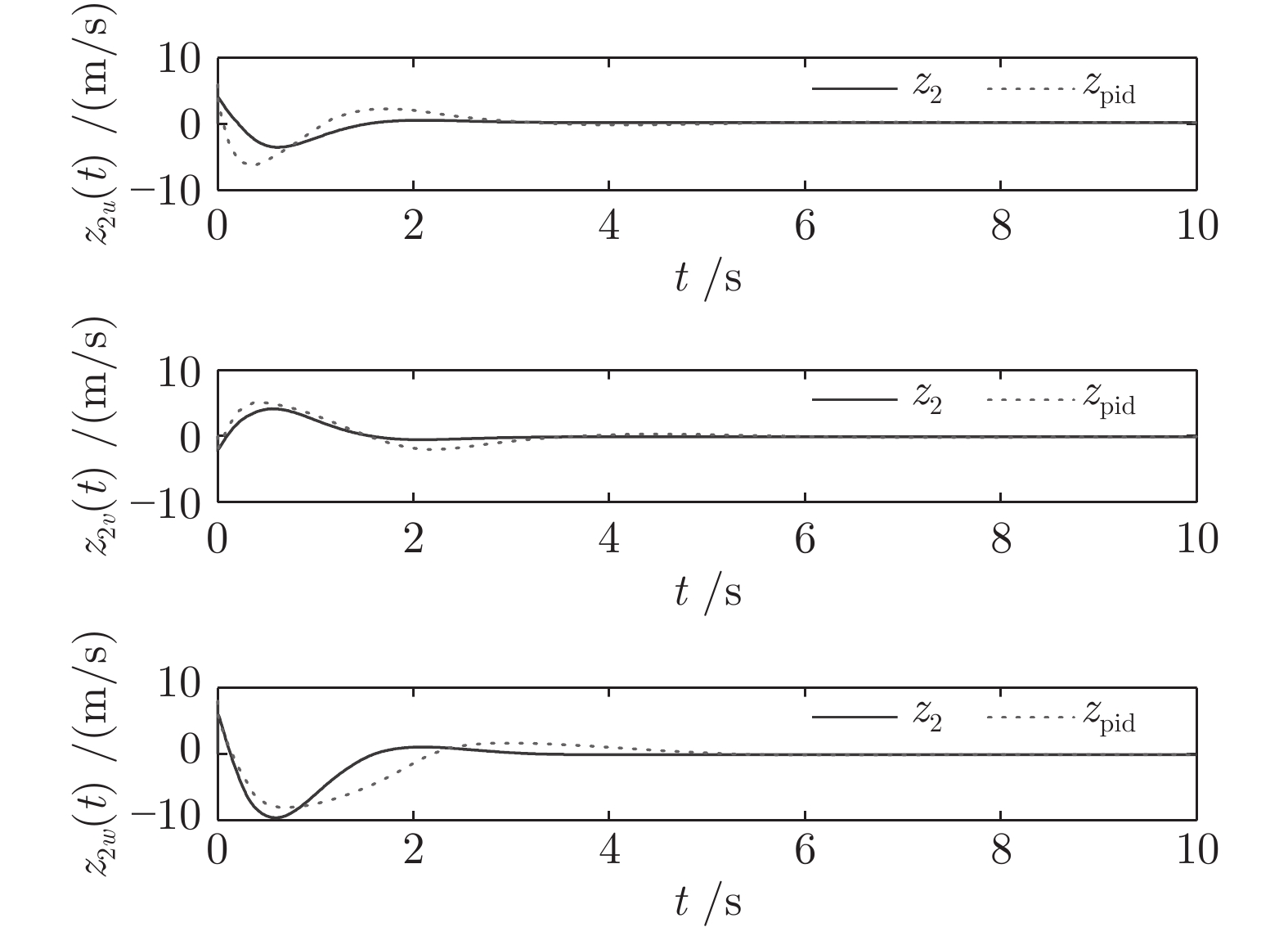
均方差 PID算法 本文算法 平均值 PID算法 本文算法 ${D_{{z_{1x}}}}$ 2.9667 1.6717 ${E_{{z_{1x}}}}$ −1.0323 −0.6265 ${D_{{z_{1y}}}}$ 1.4782 0.6209 ${E_{{z_{1y}}}}$ 0.4794 0.3294 ${D_{{z_{1z}}}}$ 1.3127 0.4251 ${E_{{z_{2z}}}}$ −0.3611 −0.4203 ${D_{{z_{2u}}}}$ 2.1902 0.9823 ${E_{{z_{2u}}}}$ 0.3229 0.0098 ${D_{{z_{2v}}}}$ 1.6632 1.0471 ${E_{{z_{2v}}}}$ 0.0898 0.0871 ${D_{{z_{2w}}}}$ 3.4603 2.3432 ${E_{{z_{2w}}}}$ −0.0569 −0.7105 -
[1] Liu M, Li W, Pei X. Convex optimization algorithms for cooperative localization in autonomous underwater vehicles. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(5): 704-710 [2] Wu D, Yan Z, Chen T. Cooperative current estimation based multi-AUVs localization for deep ocean applications. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 188: 106-148 [3] Braginsky B, Baruch A, Guterman H, Development of an autonomous surface vehicle capable of tracking autonomous underwater vehicles. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 197: 106-868 [4] Meyer H, Roberts E, Rapp H, Davies A. Spatial patterns of arctic sponge ground fauna and demersal fish are detectable in autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) imagery. Deep-Sea Research Part I, 2019, 153: 103-137 [5] 张国庆, 黄晨峰, 吴晓雪, 张显库. 考虑伺服系统增益不确定的船舶动力定位自适应有限时间控制. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1907−1912Zhang Guo-Qing, Huang Chen-Feng, Wu Xiao-Xue, Zhang Xian-Ku. Adaptive finite time dynamic position control of fully actuated ship with servo system uncertainties. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1907-1912 [6] Gao Z, Guo G. Velocity free leader-follower formation control for autonomous underwater vehicles with line-of-sight range and angle constraints. Information Sciences, 2019, 486: 359-378 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.02.050 [7] Yan Z, Yang Z, Yue L, Wang L, Jia H, Zhou J. Discrete time coordinated control of leader-following multiple AUVs under switching topologies and communication delays. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 172: 361-372 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.12.018 [8] Wang J, Wang C, Wei Y, Zhang C. Sliding mode based neural adaptive formation control of underactuated AUVs with leader-follower strategy. Applied Ocean Research, 2020, 94: 10-19 [9] Yan Z, Wang M, Xu J. Robust adaptive sliding mode control of underactuated autonomous underwater vehicles with uncertain dynamics. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 173: 802-809 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.01.008 [10] Sorbi L, De Capua G P, Fontaine J G. A behavior based mission planner for cooperative autonomous underwater vehicles. Marine Technology Society Journal, 2012, 46(2): 32-44 doi: 10.4031/MTSJ.46.2.5 [11] Xing L, Wen C, Guo F, Liu Z. Event-based consensus for linear multi-agent systems without continuous communication. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(8): 2132-2142 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2610419 [12] Wang J, Xu Y, Xu Y, Yang D. Time-varying formation for high-order multi-agent systems with external disturbances by event-triggered integral sliding mode control. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2019, 369: 333-343 [13] 杨彬, 周琪, 曹亮, 鲁仁全. 具有指定性能和全状态约束的多智能体系统事件触发控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1527-1535Yang Bin, Zhou Qi, Cao Liang, Lu Ren-Quan. Event-triggered control for multi-agent systems with prescribed performance and full state constraints. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1527-1535 [14] Fu M, Yu L. Finite-time extended state observer based distributed formation control for marine surface vehicles with input saturation and disturbances. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 159: 219-227 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.04.016 [15] Jin X. Fault tolerant finite-time leader-follower formation control for autonomous surface vessels with LOS range and angle constraints. Automatica, 2016, 68: 228-236 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.01.064 [16] Huang C, Zhang X, Zhang G. Improved decentralized finite-time formation control of underactuated USVs via a novel disturbance observer. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 174: 117-124 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.01.043 [17] Tian B, Lu H, Zuo Z, Yang W. Fixed-time leader-follower output feedback consensus for second-order multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(4): 1545-1550 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2794759 [18] Liu J, Zhang Y, Sun C, Yu Y. Fixed-time consensus of multi-agent systems with input delay and uncertain disturbances via event-triggered control, Information Sciences, 2019, 480: 261-272 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.12.037 [19] Liu Y, Yang G, Fixed-time fault-tolerant consensus control for multi-agent systems with mismatched disturbances. Neurocomputing, 2019, 366: 154-160 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.07.093 [20] Guo Z, Chen C. Event-triggered fixed-time cooperative tracking control for uncertain nonlinear second-order multi-agent systems under directed network topology. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019: 1-20 [21] Gao Z, Guo G. Fixed-time Sliding Mode Formation Control of AUVs Based on a Disturbance Observer. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(02): 539-545 [22] Polyakov A. Nonlinear feedback design for fixed-time stabilization of linear control systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(8): 2016-2110 -




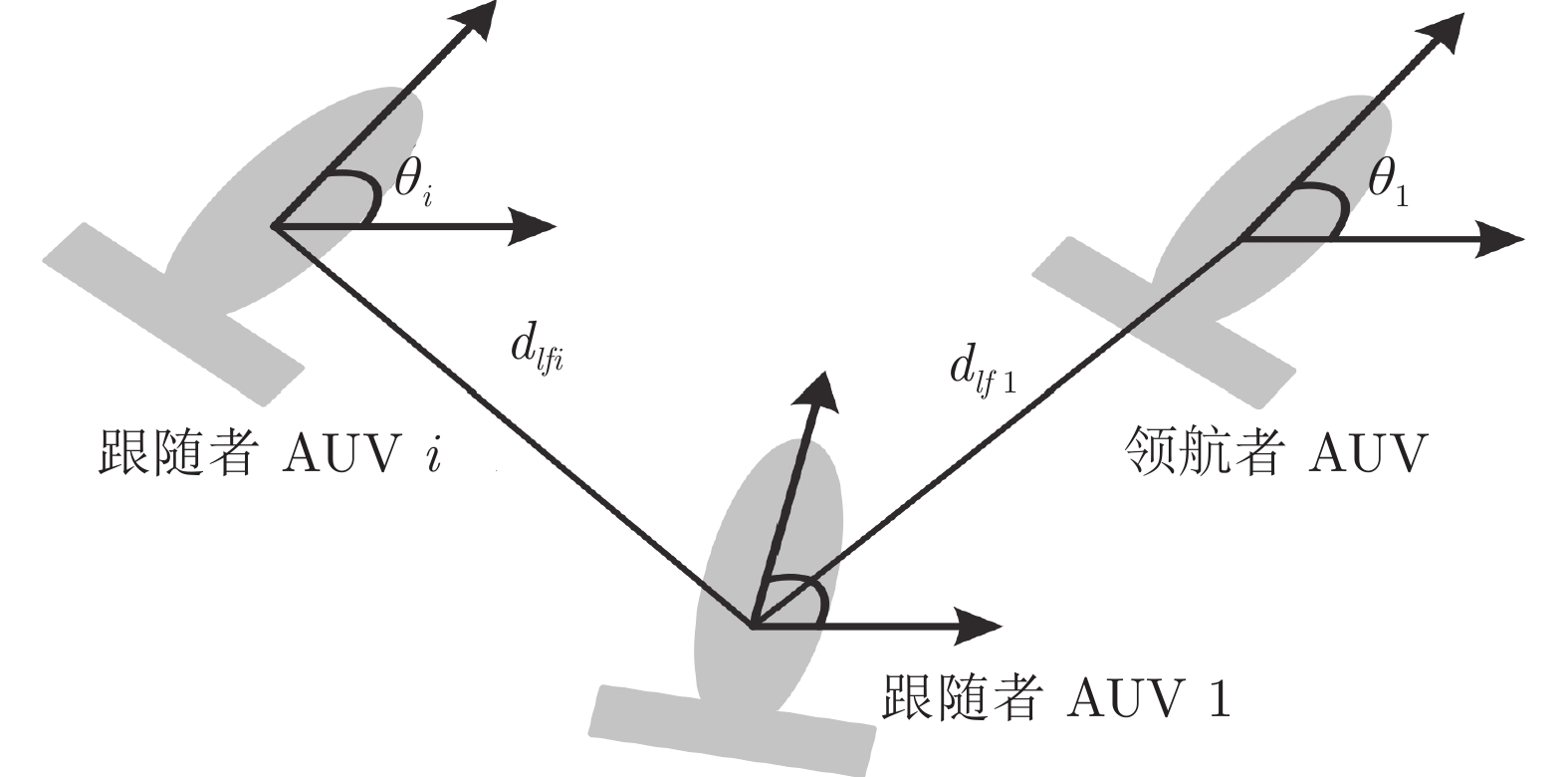
 下载:
下载: