A New Deep Transfer Learning-based Online Detection Method of Rolling Bearing Early Fault
-
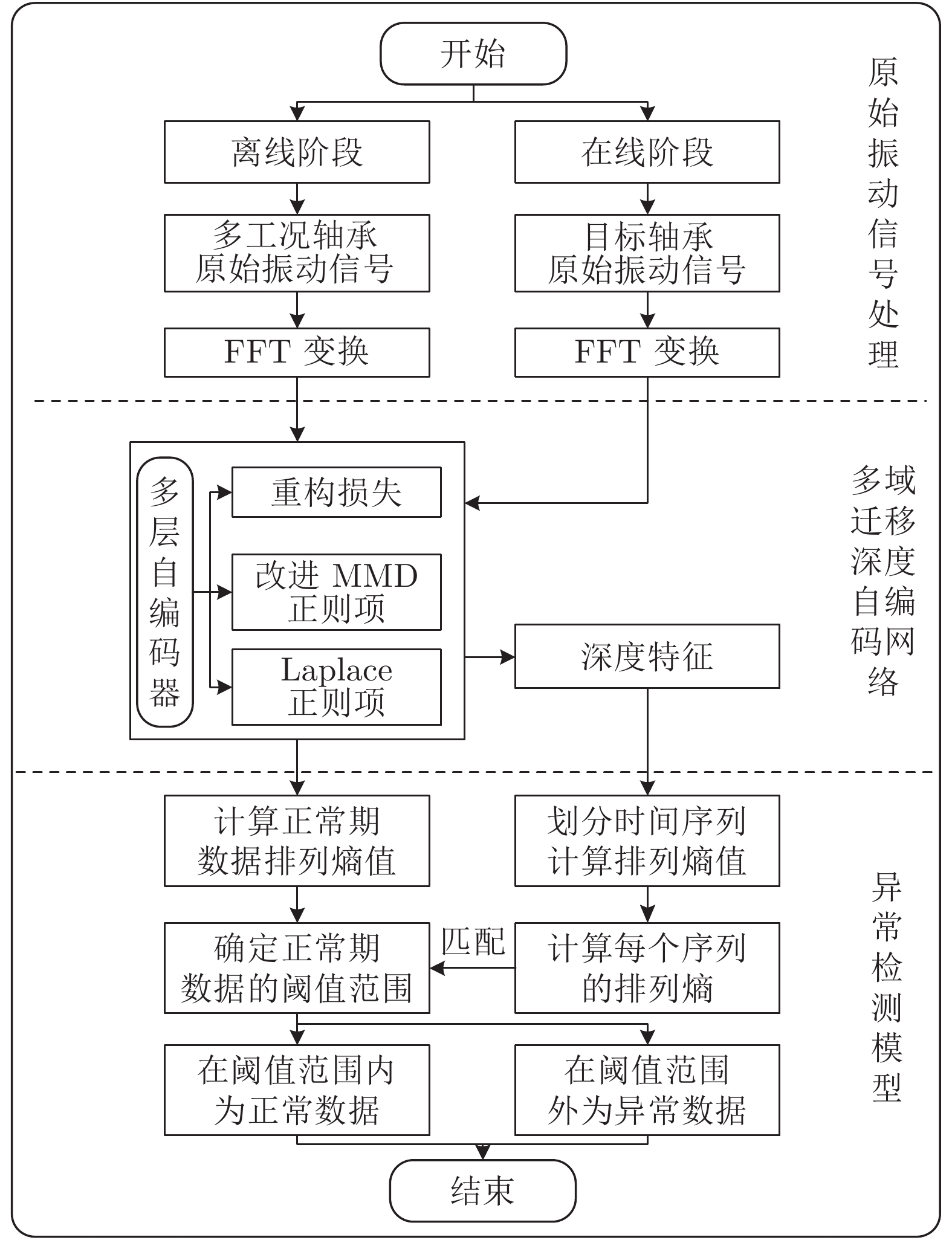
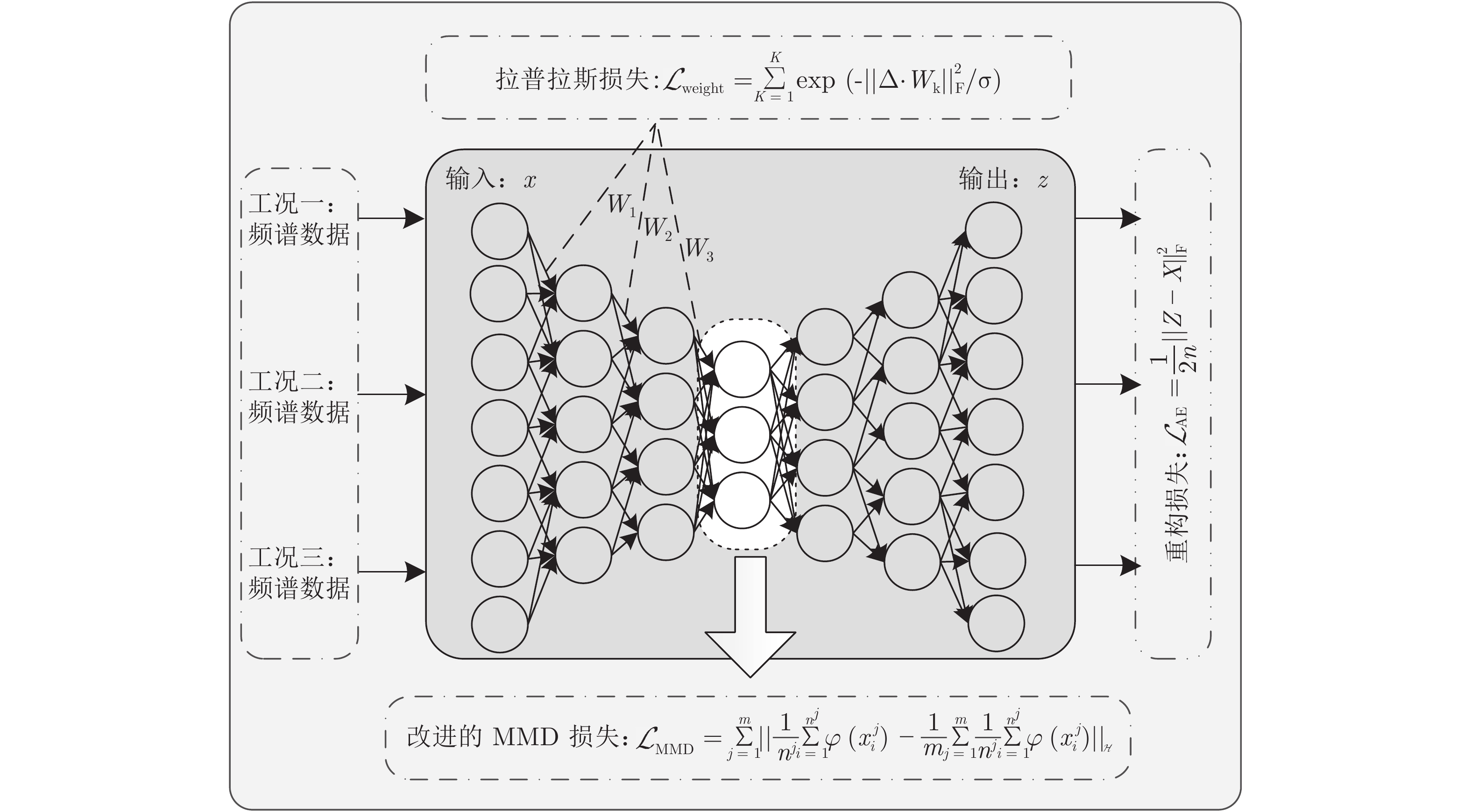
摘要: 近年来, 深度学习技术已在滚动轴承故障检测和诊断领域取得了成功应用, 但面对不停机情况下的早期故障在线检测问题, 仍存在着早期故障特征表示不充分、误报警率高等不足. 为解决上述问题, 本文从时序异常检测的角度出发, 提出了一种基于深度迁移学习的早期故障在线检测方法. 首先, 提出一种面向多域迁移的深度自编码网络, 通过构建具有改进的最大均值差异正则项和Laplace正则项的损失函数, 在自适应提取不同域数据的公共特征表示同时, 提高正常状态和早期故障状态之间特征的差异性; 基于该特征表示, 提出一种基于时序异常模式的在线检测模型, 利用离线轴承正常状态的排列熵值构建报警阈值, 实现在线数据中异常序列的快速匹配, 同时提高在线检测结果的可靠性. 在XJTU-SY数据集上的实验结果表明, 与现有代表性早期故障检测方法相比, 本文方法具有更好的检测实时性和更低的误报警数.Abstract: In recent years, deep learning techniques have been successfully applied to fault detection and diagnosis for rolling bearings. However, for online detection of incipient fault without system halt, these techniques still have some shortcomings such as insufficient feature representation of incipient fault and high false alarm rate. To solve such problems, this paper presents a new deep transfer learning-based online detection approach on the perspective of temporal anomaly detection. First, a new deep auto-encoder network with multi-domain transferring is proposed by constructing a new loss function with the maximum mean discrepancy regularizer and Laplace regularizer. This model can adaptively extract the common feature representation among the data of different domains, and effectively improve the feature difference between normal state and early fault state as well. Second, with the obtained feature representation, a new online detection model based on temporal anomaly pattern is proposed. By utilizing the permutation entropy of normal state of offline bearings to build an alarm threshold, this model can match quickly anomaly sequence of the online monitoring data, and then improve the detection reliability. The experimental results on the XJTU-SY bearings dataset demonstrates that the proposed approach obtains better real-time detection performance and lower false alarm rate compared to some state-of-the-art methods of incipient fault detection.
-
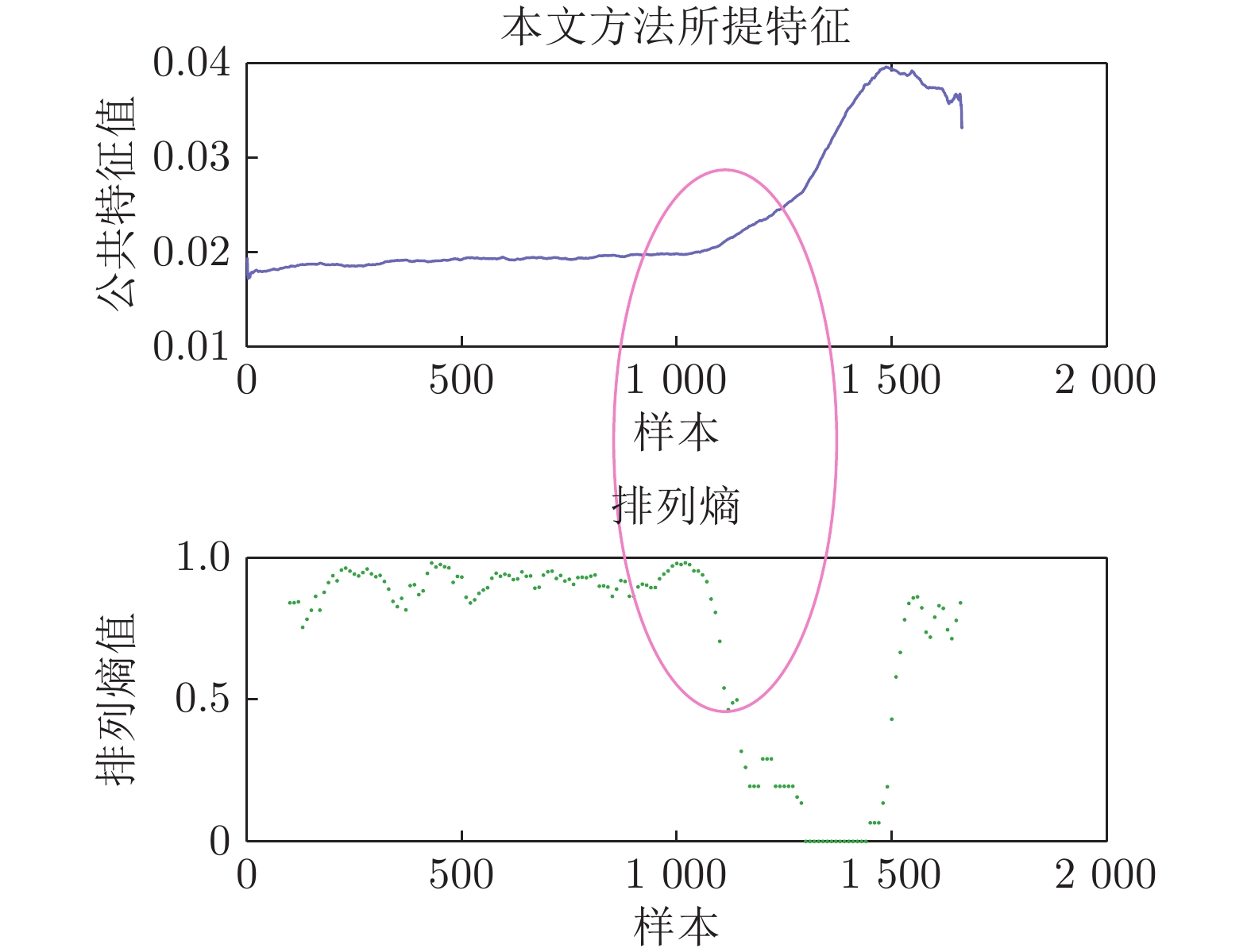
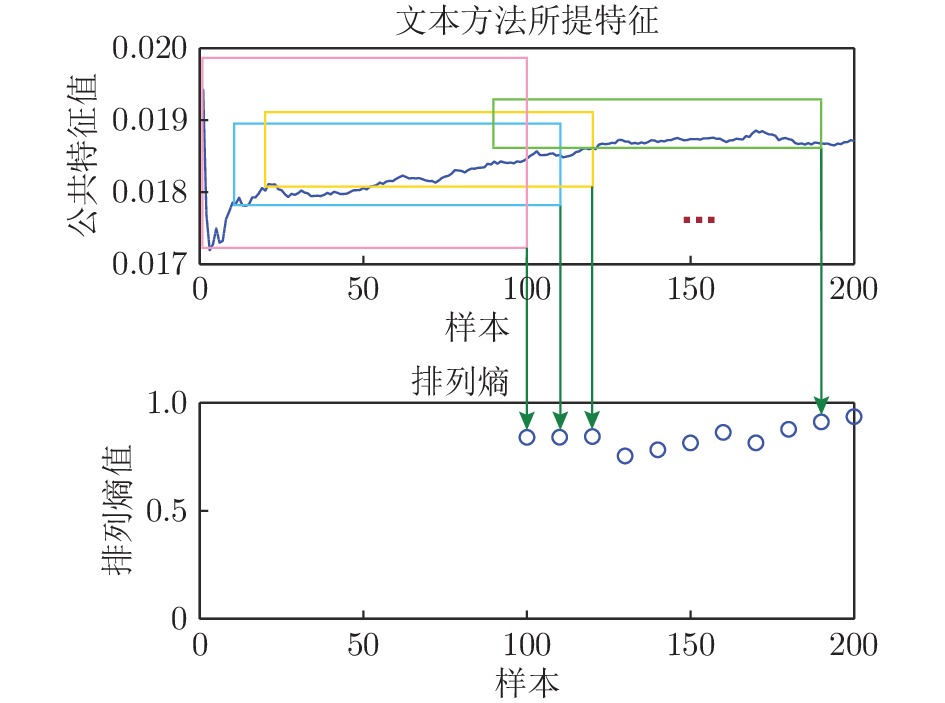
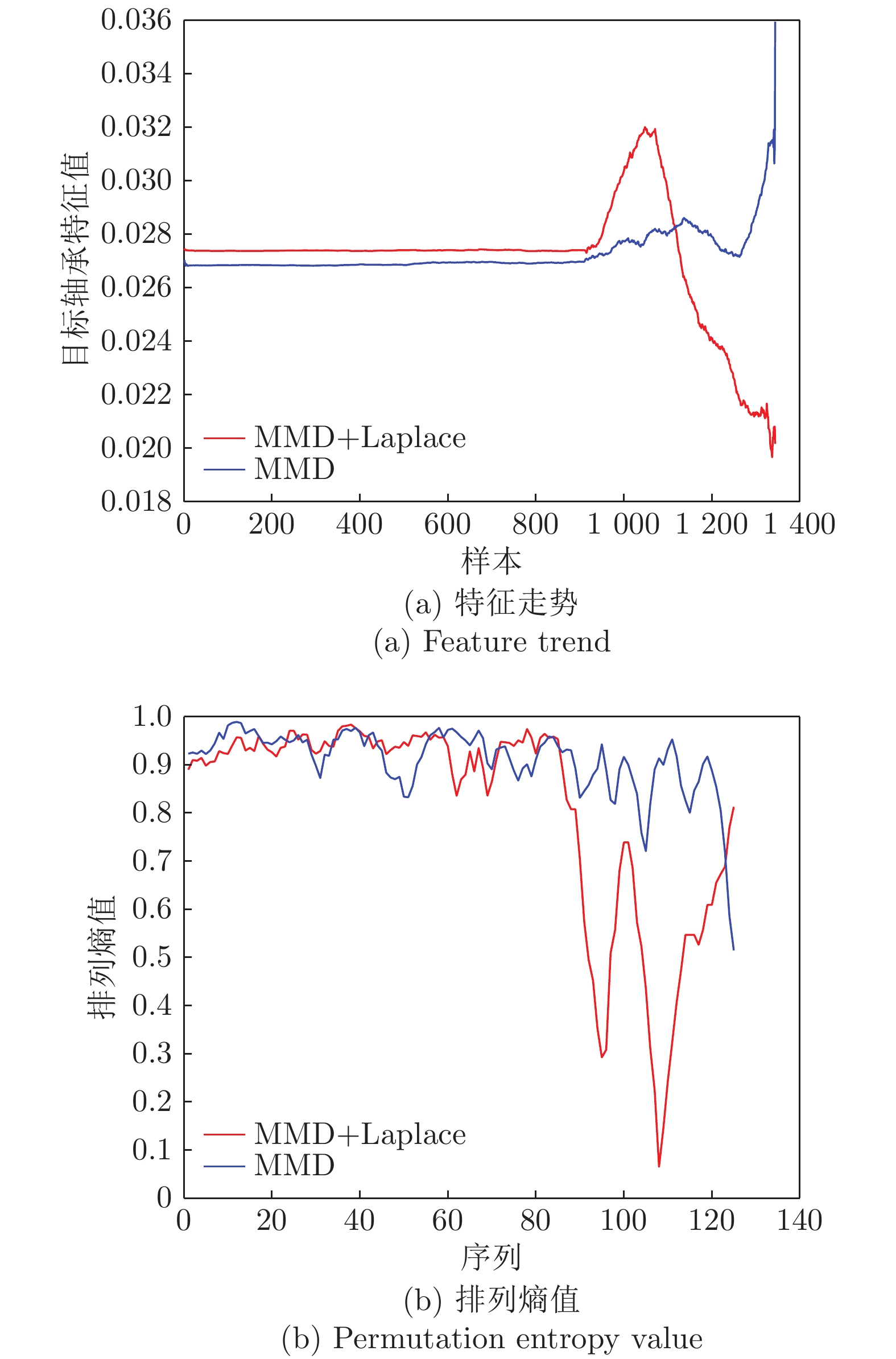
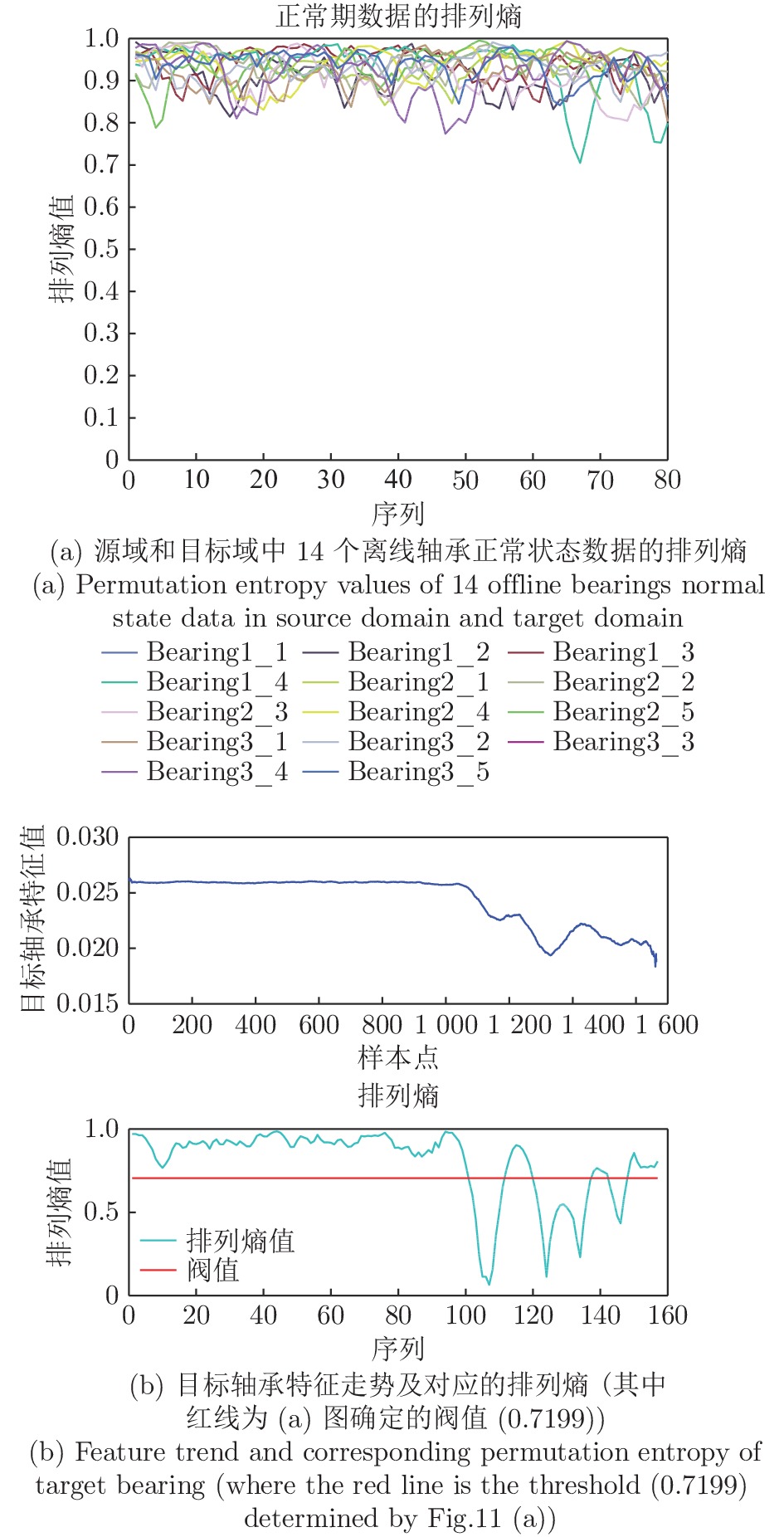
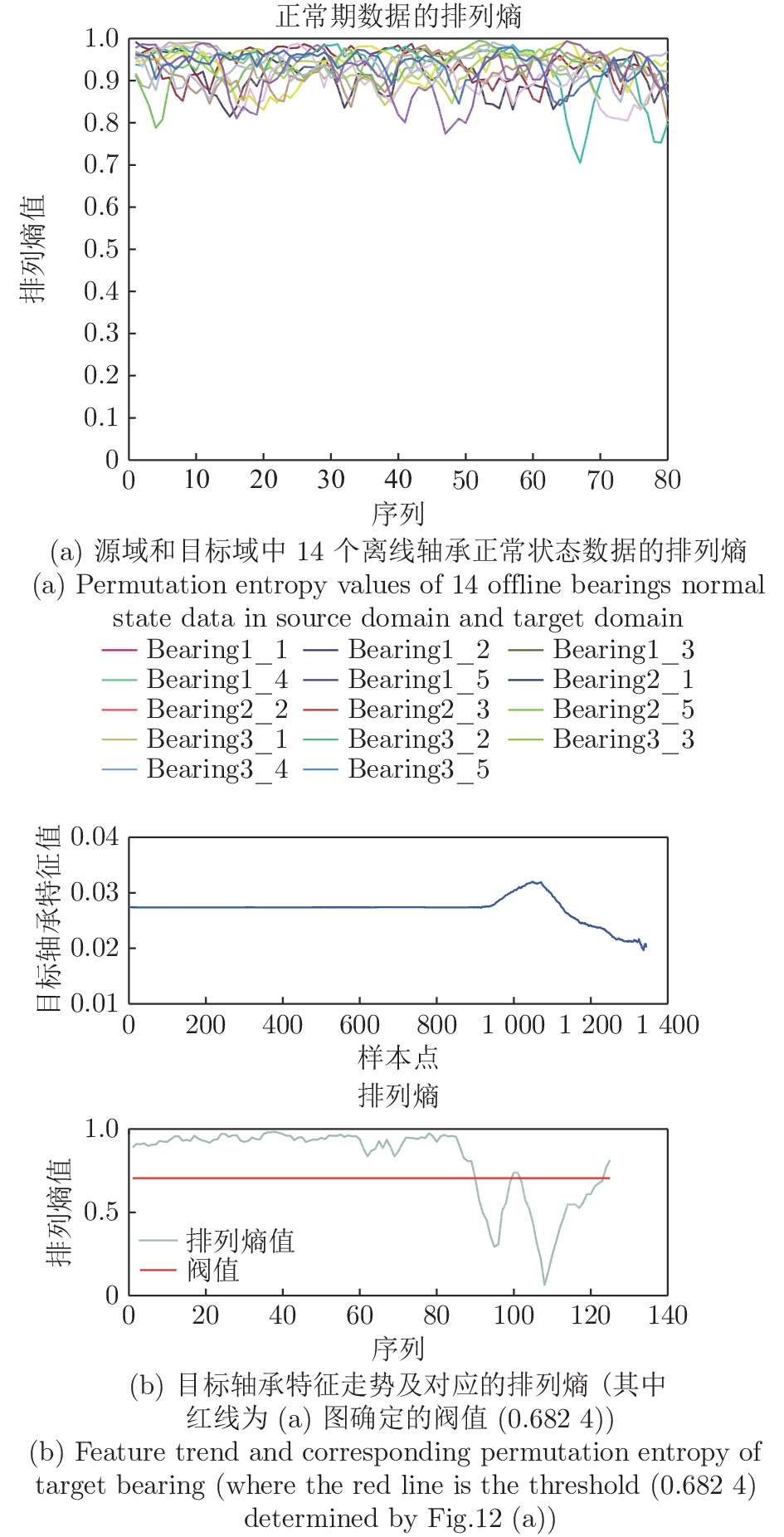
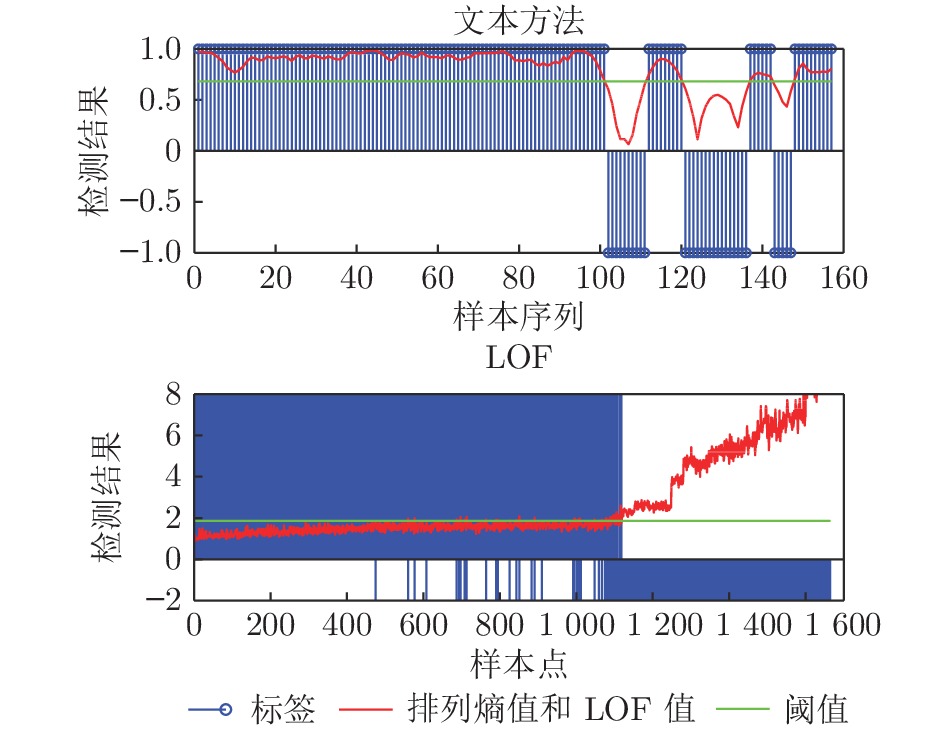
图 14 本文方法与LOF算法的检测结果对比图 (其中, 本文方法横坐标为序列编号(即样本号除以100), 标签值大于0表示样本识别为正常样本, 小于0表示识别为异常样本)
Fig. 14 Comparative detection results between the proposed method and LOF algorithm (while x-coordinate of the proposed method denotes sequence number (equal to the sample number divided by 100), the label value greater than 0 means the corresponding sample is recognized as normal sample, else as anomaly)
表 1 本文所用符号与对应描述
Table 1 Symbols and corresponding descriptions used in this paper
符号 描述 符号 描述 ${\cal D}{^{ s}}$ 源域 ${\cal D}{^{ t}}$ 目标域 $W,b$ 自编码器的权重矩阵和偏置 $f,g$ 激活函数 ${s_c}$ 工况数量 $m$ 监测数据的组数 $X$ 数据矩阵 $Y$ 标签矩阵 ${\boldsymbol{x}}$ 单个样本 $y$ 单个样本的标签 $n$ 样本数量 $H$ 特征矩阵 $p$ 数据分布 $W'$ $W$的转置 表 2 XJTU-SY数据集中三种工况描述
Table 2 Description of three working conditions in XJTU-SY dataset
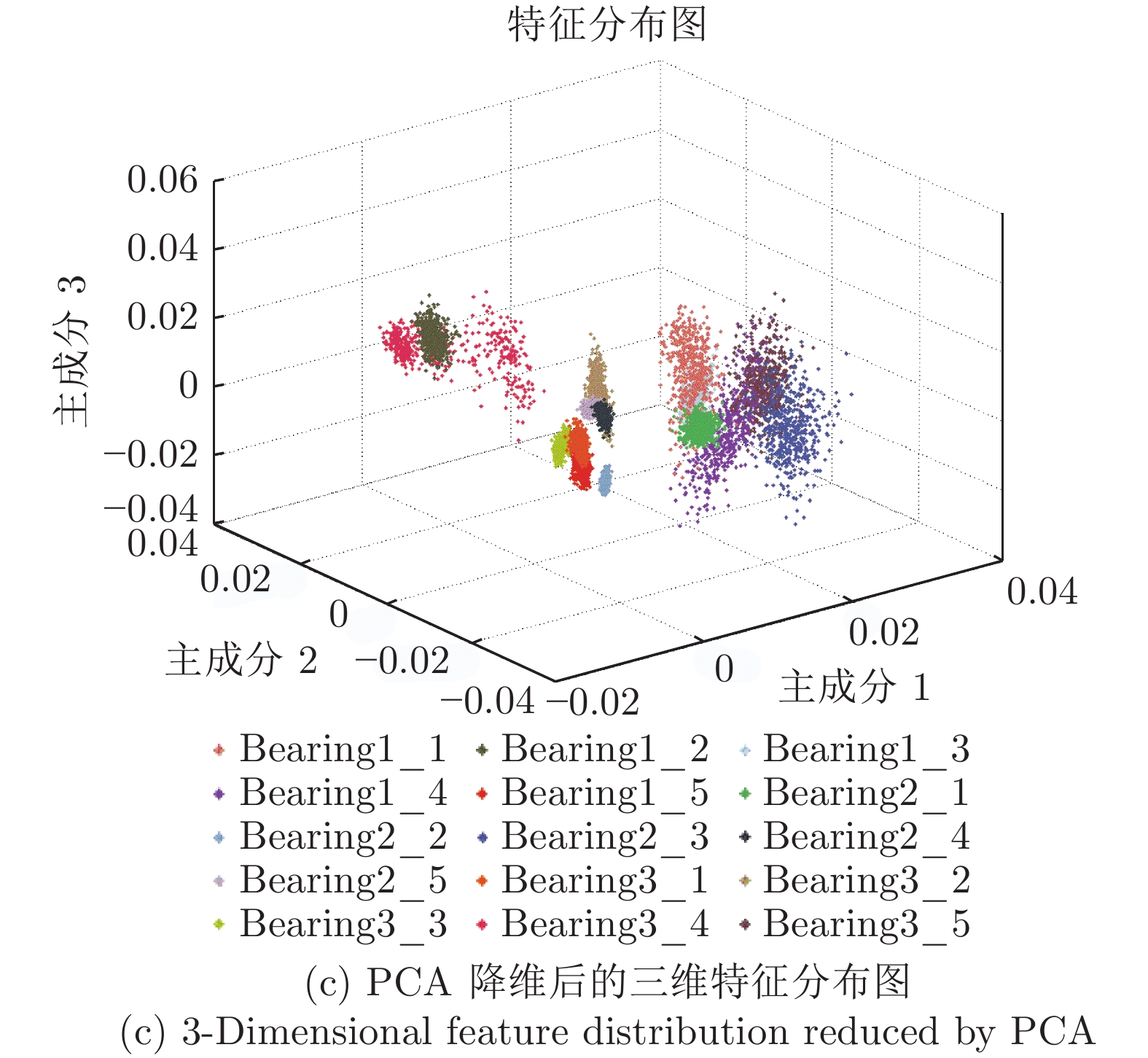
运行条件 径向力 (kN) 转速 (r/min) 轴承数据集 工况1 12 2100 Bearing 1_1 Bearing 1_2 Bearing 1_3 Bearing 1_4 Bearing 1_5 工况2 11 2250 Bearing 2_1 Bearing 2_2 Bearing 2_3 Bearing 2_4 Bearing 2_5 工况3 10 2400 Bearing 3_1 Bearing 3_2 Bearing 3_3 Bearing 3_4 Bearing 3_5 -
[1] Lei Y G, Li N P, Guo L,Li N B,Yan T,Lin J. Machinery health prognostics: A systematic review from data acquisition to RUL prediction. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 104: 799-843. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.11.016 [2] Liu R N, Yang B Y, Zhang X L,Wang S B, Chen X F. Time-frequency atoms-driven support vector machine method for bearings incipient fault diagnosis. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 75: 345-370. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.12.020 [3] 杨蕊, 李宏坤, 贺长波. 利用最优小波尺度循环谱的滚动轴承早期故障特征提取. 机械工程学报, 2017, 54(17): 209-217.Yang Rui, Li Hong-Kun, He Chang-Bo. Early fault feature extraction of rolling bearing by using optimal wavelet scale cyclic spectrum. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 54(17): 209-217.(in Chinese) [4] 孙鲜明, 刘欢, 赵新光. 基于瞬时包络尺度谱熵的滚动轴承早期故障奇异点识别及特征提取. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(3): 73-80. doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.03.073Sun Xian-Ming, Liu Huan, Zhao Xin-Guang. Identification and feature extraction of early fault singularity of rolling bearing based on instantaneous envelope scale spectrum entropy. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(3): 73-80.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.03.073 [5] Dhamande L S, Chaudhari M B. Compound gear-bearing fault feature extraction using statistical features based on time-frequency method. Measurement, 2018, 125: 63-77. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.04.059 [6] Li F, Wang J X, Chyu M K, Tang B P. Weak fault diagnosis of rotating machinery based on feature reduction with Supervised Orthogonal Local Fisher Discriminant Analysis. Neurocomputing, 2015, 168: 505-519. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.05.076 [7] Amar M, Gondal I, Wilson C. Vibration spectrum imaging: A novel bearing fault classification approach. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 62(1): 494-502. [8] Fernández-Francos D, Martínez-Rego D, Fontenla-Romero O, Alonso-Betanzos A. Automatic bearing fault diagnosis based on one-class v-SVM. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2013, 64(1): 357-365. [9] 张柯, 姜斌. 基于故障诊断观测器的输出反馈容错控制设计. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(2): 274-281. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00274Zhang Ke, Jiang Bin. Fault diagnosis observer-based output feedback fault tolerant control design. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(2): 274-281.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00274 [10] Jia F, Lei Y G, Guo L. A neural network constructed by deep learning technique and its application to intelligent fault diagnosis of machines. Neurocomputing, 2018, 272: 619-628. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.07.032 [11] Shao H D, Jiang H K, Zhang X. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis using an optimization deep belief network. Measurement Science and Technology, 2015, 26(11): 115002. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/26/11/115002 [12] 庄福振, 罗平, 何清, 史忠植. 迁移学习研究进展. 软件学报, 2015, 26(1): 26-39.Zhuang Fu-Zhen, Luo Ping, He Qing, Shi Zhong-Zhi. Research progress in transfer learning.Research progress in transfer learning. Journal of Software, 2015, 26(1): 26-39.(in Chinese) [13] 贺敏, 汤健, 郭旭琦,阎高伟. 基于流形正则化域适应随机权神经网络的湿式球磨机负荷参数软测量. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(2): 398-406. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170289He Min, Tang Jian, Guo Xu-Qi,Yan Gao-Wei. Soft sensor for ball mill load using DAMRRWNN model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(2): 398-406.(in Chinese) doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170289 [14] 张雪松, 庄严, 闫飞, 王伟. 基于迁移学习的类别级物体识别与检测研究与进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1224-1243. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180093Zhang Xue-Song, Zhuang Yan, Yan Fei, Wang Wei. Status and development of transfer learning based category-level object recognition and detection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1224-1243.(in Chinese) doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180093 [15] Shen S, Sadoughi M, Li M. Deep convolutional neural networks with ensemble learning and transfer learning for capacity estimation of lithium-ion batteries. Applied Energy, 2020, 260: 114296. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.114296 [16] Din I U, Islam N, Rodrigues J. A novel deep learning based framework for the detection and classification of breast cancer using transfer learning. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2019, 125(1): 1-6. [17] 雷亚国, 杨彬, 杜兆钧, 吕娜. 大数据下机械装备故障的深度迁移诊断方法. 机械工程学报, 2018, 55(7): 1-8.Lei Ya-Guo, Yang Bin, Du Zhao-Jun, Lv Na. Deep transfer diagnostic method for mechanical equipment failure under big data. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 55(7): 1-8.(in Chinese) [18] Lu W N, Liang B, Cheng Y, Meng D S,Yang J,Zhang T. Deep model based domain adaptation for fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(3): 2296-2305. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2627020 [19] Wen L, Gao L, Li X. A new deep transfer learning based on sparse auto-encoder for fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(1): 136-144. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2754287 [20] Yang B, Lei Y, Jia F, Xing S. An intelligent fault diagnosis approach based on transfer learning from laboratory bearings to locomotive bearings. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 122: 692-706. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.12.051 [21] Cai D, He X F, Hu Y X, Han J W. Learning a spatially smooth subspace for face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE Computer Society, Minneapolis, USA, June 2007, pp. 1−7. [22] 冯辅周, 饶国强, 司爱威. 基于排列熵和神经网络的滚动轴承异常检测与诊断. 噪声与振动控制, 2013, 33(3): 212-217.Feng Fu-Zhou, Rao Guo-Qiang, Si Ai-Wei. Abnormality detection and diagnosis of rolling bearing based on permutation entropy and neural network. Noise and Vibration Control, 2013, 33(3): 212-217.(in Chinese) [23] Wang B, Lei Y G, Li N P, Li N B. A hybrid prognostics approach for estimating remaining useful life of rolling element bearings. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 69(1): 401-412. doi: 10.1109/TR.2018.2882682 [24] Cho K, Courville A, Bengio Y. Describing multimedia content using attention-based encoder-decoder networks. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2015, 17(11): 1875-1886. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2015.2477044 [25] Li Y B, Xu M Q , Liang X H, Huang W H. Application of bandwidth EMD and adaptive multi-scale morphology analysis for incipient fault diagnosis of rolling bearings. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(8): 6506-6517. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2650873 [26] Ma H H, Hu Y, Shi H B. Fault detection and identification based on the neighborhood standardized local outlier factor method. Industrial Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(6): 2389-2402. doi: 10.1021/ie302042c [27] Domingues R, Filippone M, Michiardi P. A comparative evaluation of outlier detection algorithms: Experiments and analyses. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 74: 406-421. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.09.037 [28] Mao W, Chen J, Liang X. A New Online Detection Approach for Rolling Bearing Incipient Fault via Self-Adaptive Deep Feature Matching. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(2): 443-456. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2903699 [29] 郭小萍, 刘诗洋, 李元. 基于稀疏残差距离的多工况过程故障检测方法研究. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(3): 617-625.Guo Xiao-Ping, Liu Shi-Yang, Li Yuan. Fault detection of multi-mode processes employing sparse residual distance. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 617-625.(in Chinese) -




 下载:
下载: