Principle of Least Potential Energy in the Cellular Automaton Model for Collective Motion of Fish Schools
-
摘要:
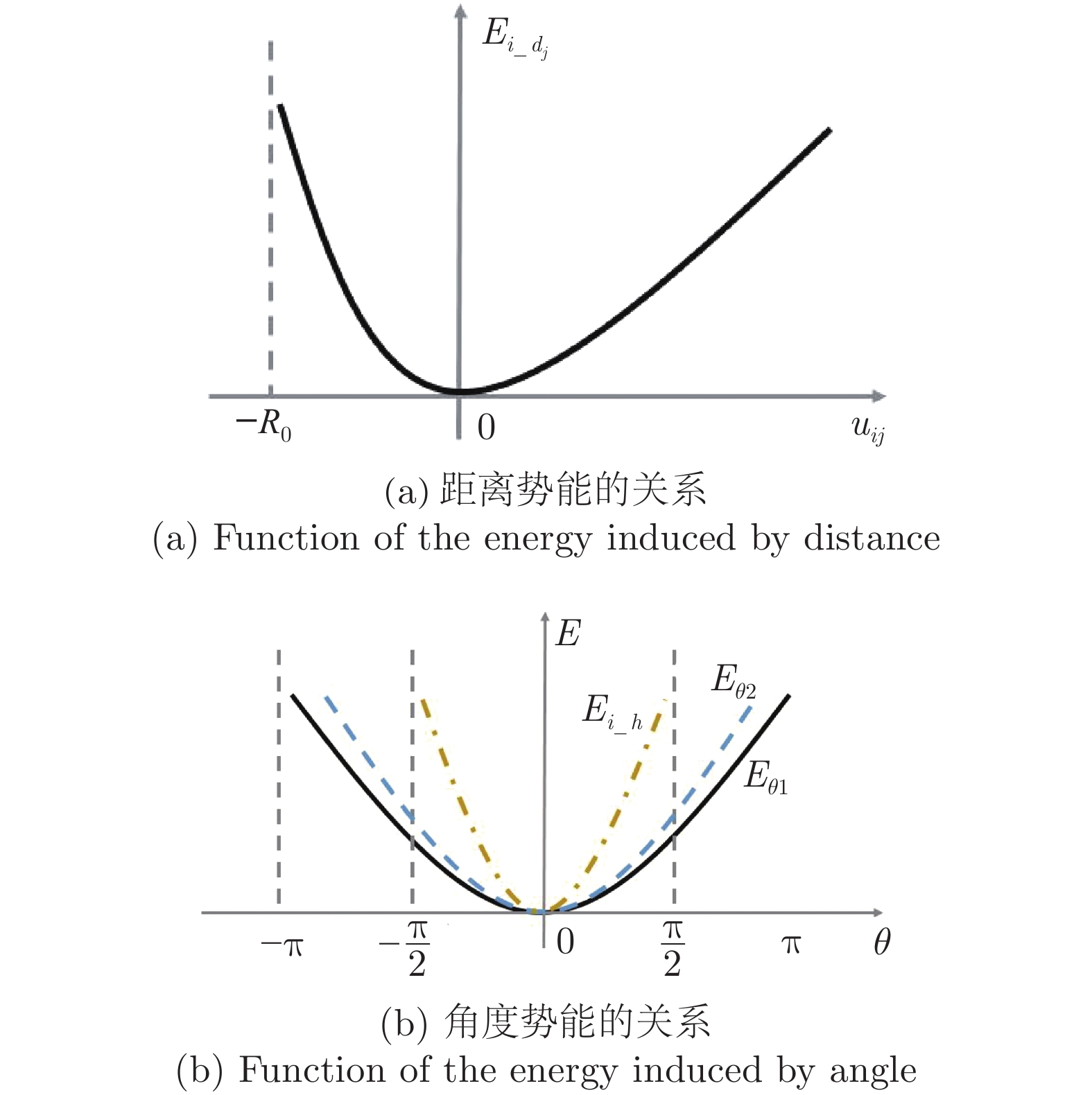
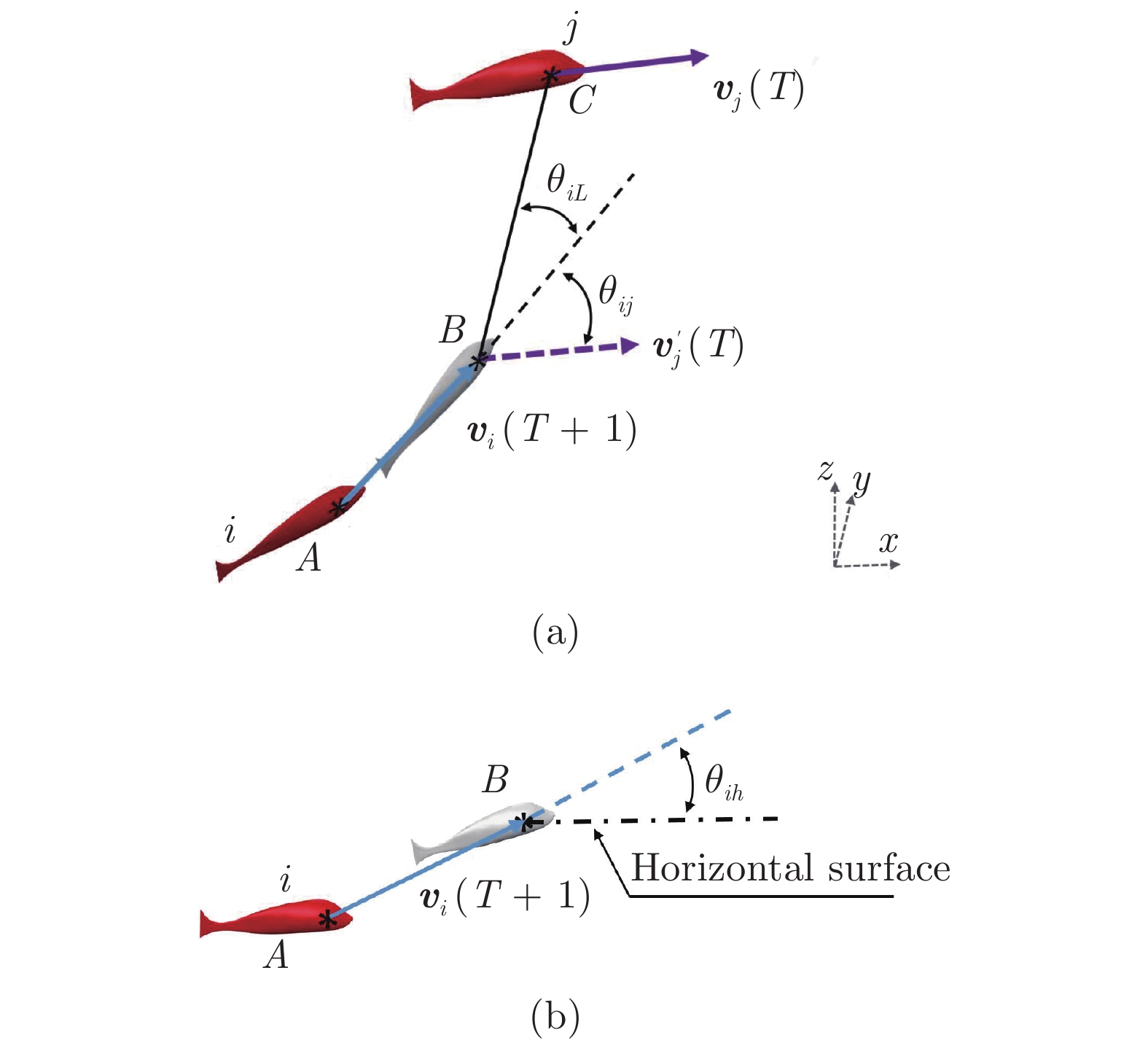
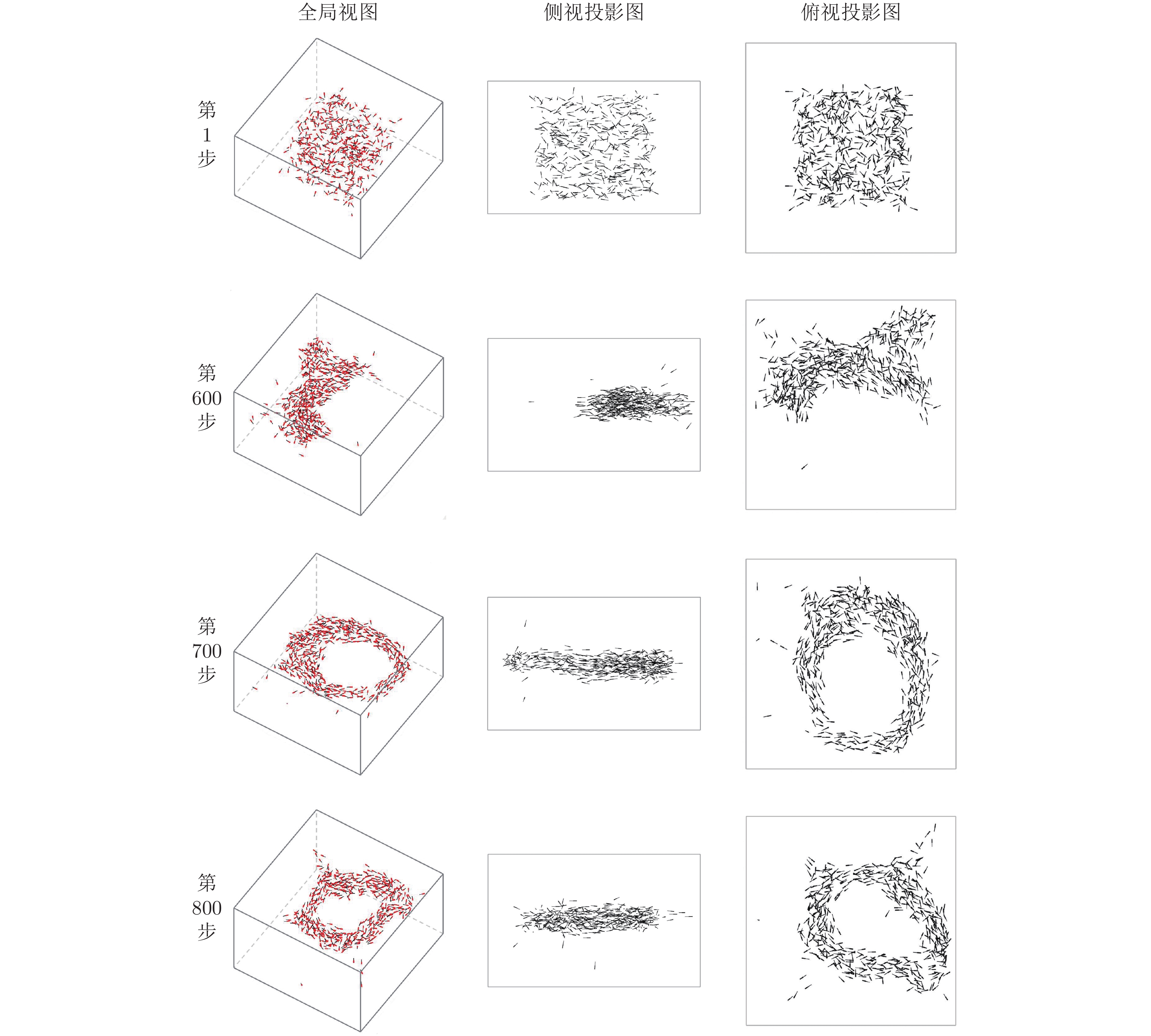
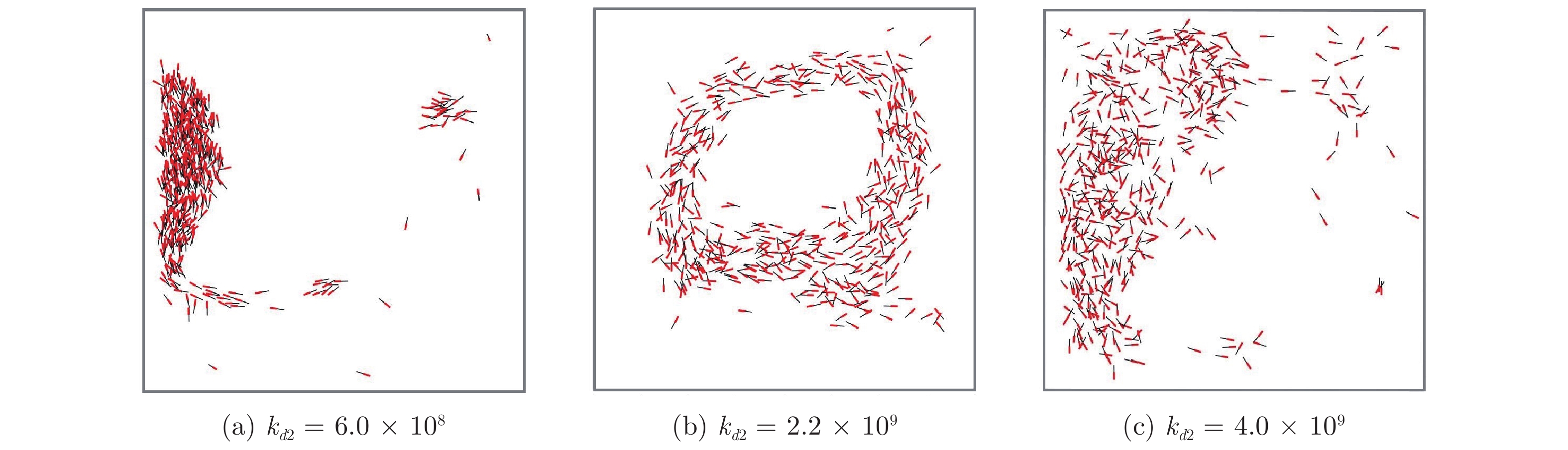
群体运动是自然界中一种常见的生物行为. 在一定的环境条件下, 社会有机体会表现出不同的集体运动形态. 其中, 旋转是鱼群中常见的群体运动. 但是, 虽然研究人员对鱼群的运动进行过一系列的研究, 这种旋转行为的机理尚不清楚. 本研究假定鱼群的运动模式受势能的支配, 相应提出了鱼类个体运动的势函数并将之融合到元胞自动机中以模拟鱼群的运动. 数值模拟表明, 有限空间内鱼群运动时会形成多种形状, 但当此生物系统按照能量最小原则发展时, 其运动形态最终可能演化成为一个漩涡. 数值模拟与针对红斑马鱼的观察之间的比较验证了本模型的合理性. 能量最小原理是自然界的基本定律之一, 而势能函数的建立定义了鱼类个体与环境之间的关系. 因此, 本研究为深入理解群体运动规律提供了新视角, 表明从流体力学上进一步探究鱼群运动的物理机理是一个具有潜力的研究方向.
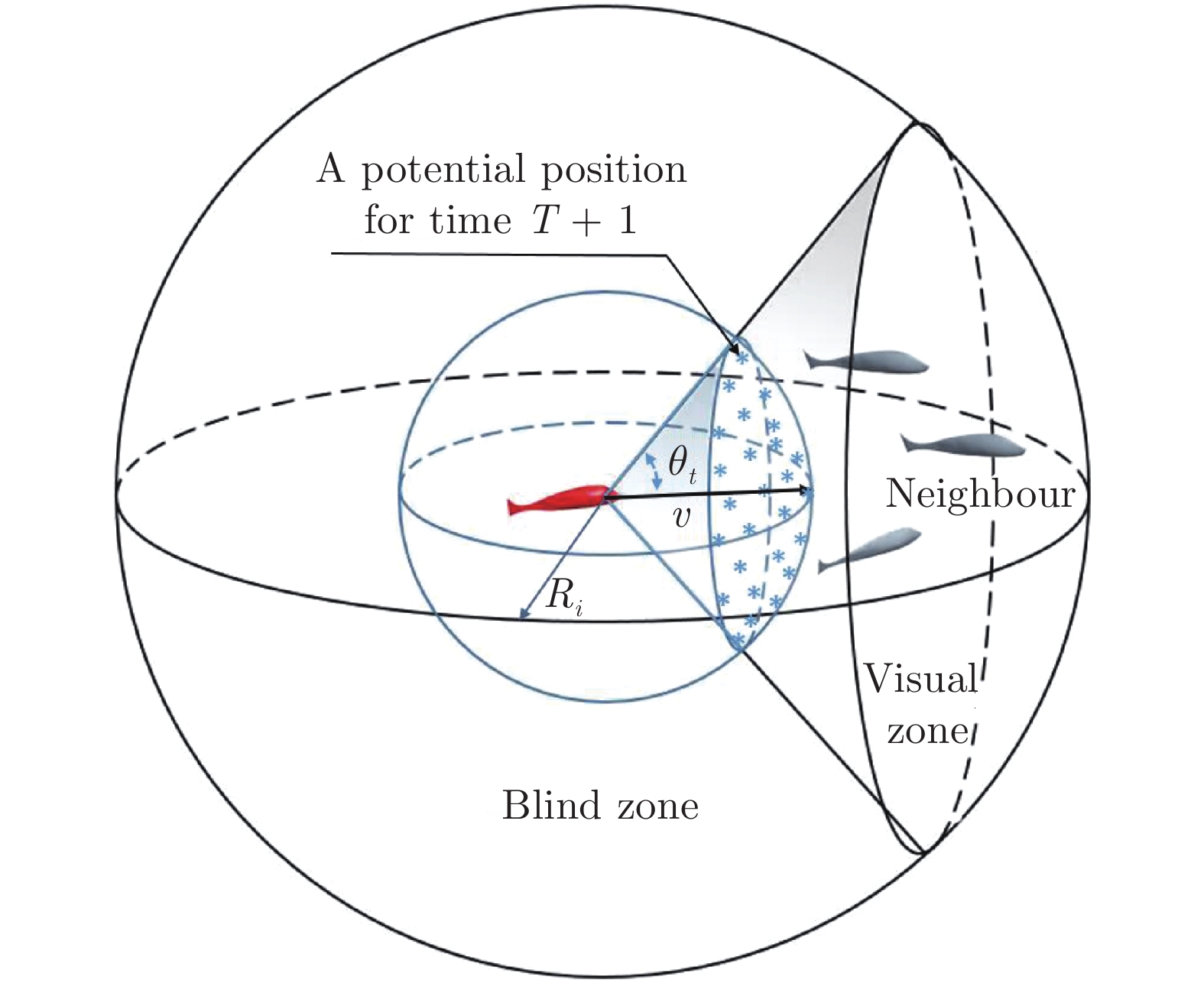
Abstract:Collective motion is a common biological behavior in nature. Social organisms will exhibit different group motions under certain environmental conditions. Among them, whirling is a common collective motion in fish schools, however, the mechanism about this behaviour is still unclear although researchers have conducted a series of investigation on the motion of fish schools. In this work, it is assumed that the motion modes of fish schools are governed by potential energy. Accordingly, a potential function for an individual fish is proposed and incorporated into a cellular automaton to simulate the collective behaviour of fish schools. Numerical modellings show that a group of fish will form various shapes in limited spaces but evolve to a whirl when the biological system develops under the rule of least potential energy. The rationality of the proposed model is verified by the comparison between the numerical simulation and the observation on red zebrafish. The principle of least potential energy is one of the fundamental laws about the nature essence, and the proposed potential function defines the relationship between individuals and the environment. Therefore, the present study provides a new perspective for understanding the behaviour of collective motion, showing that it is promising to further explore the physical mechanism of the movement of fish schools by means of fluid mechanics.
-
Key words:
- Fish /
- collective motion /
- least potential energy /
- cellular automaton
-
-
[1] Suzuki T N, Kutsukake N. Foraging intention affects whether willow tits call to attract members of mixed-species flocks. Royal Society Open Science, 2017, 4(6): 170222 doi: 10.1098/rsos.170222 [2] Fischhoff I R, Sundaresan S R, Cordingley J, Larkin H M, Sellier M J, Rubenstein D I. Social relationships and reproductive state influence leadership roles in movements of plains zebra, equus burchellii. Animal Behaviour, 2007, 73(5): 825−831 doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2006.10.012 [3] 柳玲飞, 周应祺, 钱卫国, 赵媛, 王明. 红鼻鱼群体结构的数学建模与仿真可视化. 水产学报, 2010, 34(12): 1869−1876Liu Ling-Fei, Zhou Ying-Qi, Qian Wei-Guo, Zhao Yuan, Wang Ming. Modeling and simulation on schooling structure of hemigrammus bleheri. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2010, 34(12): 1869−1876 [4] 班晓娟, 宁淑荣, 涂序彦. 人工鱼群高级自组织行为研究. 自动化学报, 2008, 34(10): 1327−1332Ban Xiao-Juan, Ning Shu-Rong, Tu Xu-Yan. Research on advanced self-organization behavior for artificial fish school. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2008, 34(10): 1327−1332 [5] Koch A L, White D. The social lifestyle of myxobacteria. Bioessays, 2015, 20(12): 1030−1038 [6] Reynolds C W. Flocks, herds, and schools: A distributed behavioral model. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics, 1987, 21(4): 25−34 doi: 10.1145/37402.37406 [7] Zienkiewicz A K, Ladu F, Barton D A W, Porfiri M, Bernardo M D. Data-driven modelling of social forces and collective behaviour in zebrafish. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2018, 443: 39−51 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2018.01.011 [8] 杨永娟. 用java实现鱼群游动模拟系统. 安徽理工大学学报(自科版), 2006, 26(4): 67−71Yang Yong-Juan. Realization of fish-swimming simulation system with java. Journal of Anhui University of science and Technology (Natural Science), 2006, 26(4): 67−71 [9] Dai L, He G, Zhang X, Zhang X. Stable formations of self-propelled fish-like swimmers induced by hydrodynamic interactions. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2018, 15(147): 13 [10] Nagy M, Ákos Z, Biro D, Vicsek T. Hierarchical group dynamics in pigeon flocks. Nature, 2010, 464(7290): 890−893 doi: 10.1038/nature08891 [11] Gueron S, Levin S A, Rubenstein D I. The dynamics of herds: From individuals to aggregations. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1996, 182(1): 85−98 doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1996.0144 [12] Couzin I D, Krause J. Self-organization and collective behavior in vertebrates. Advances in the Study of Behavior, 2003, 32: 1−75 doi: 10.1016/S0065-3454(03)01001-5 [13] Li S, Batra R, Brown D, Chang H D, Ranganathan N, Hoberman C, Rus D, Lipson H. Particle robotics based on statistical mechanics of loosely coupled components. Nature, 2019, 567(7748): 361−365 [14] 雷斌. 群体机器人系统合作控制问题研究 [硕士学位论文]. 武汉理工大学, 中国, 2009.Lei Bin. Research on cooperative control problem of swarm robots system [Master thesis]. Wuhan University of Technology, China, 2009. [15] Neumann J V, Burks A W. Theory of Self-Reproduction Automata. University of Illinois press, Urbana, 1966. [16] Bertin E, Droz M, Grégoire G. Hydrodynamic equations for self-propelled particles: microscopic derivation and stability analysis. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical, 2009, 42(44): 445001 doi: 10.1088/1751-8113/42/44/445001 [17] Yuan W F, Tan K H. A model for simulation of crowd behaviour in the evacuation from a smoke-filled compartment. Physica A Statistical Mechanics & Its Applications, 2011, 390(23-24): 4210−4218 [18] Pattanayak S, Mishra S. Collection of polar self-propelled particles with a modified alignment interaction. Journal of Physics Communications, 2018, 2(4): 045007 doi: 10.1088/2399-6528/aab8cc [19] Bertrand L, Colby T, Christa W, Tammy T, Shea Q, David S. Motion cues tune social influence in shoaling fish. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 9785 doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27807-1 [20] Ballerini M, Cabibbo N, Candelier R, Cavagna A, Cisbani E, Giardina I, Lecomte V, Orlandi A, Parisi G, Procaccini A, Viale M, Zdravkovic V. Interaction ruling animal collective behavior depends on topological rather than metric distance: Evidence from a field study. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2008, 105(4): 1232−1237 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711437105 [21] Maria D M D, Miranda M, Alvarez S J, Gurarie E, Fagan W F, Penteriani V, Virgilio A D, Morales J M. The importance of individual variation in the dynamics of animal collective movements. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2018, 373(1746): 20170008 doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0008 -




 下载:
下载: