-
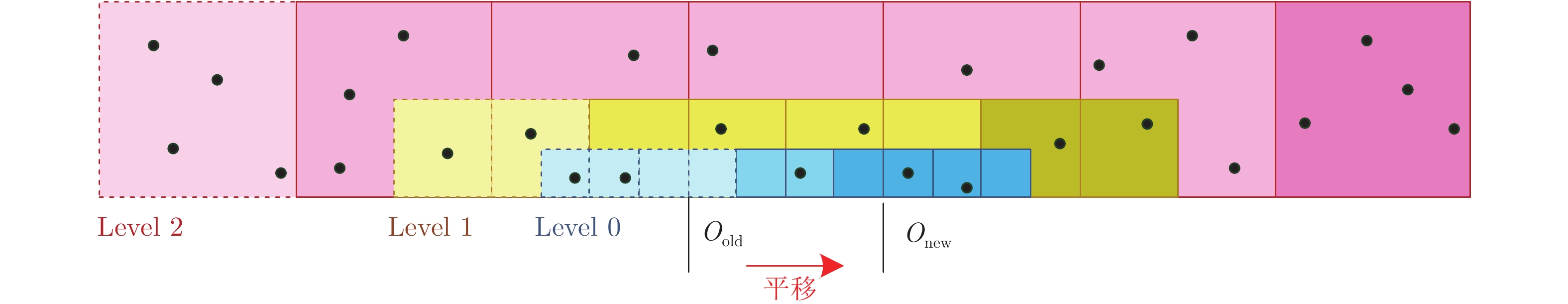
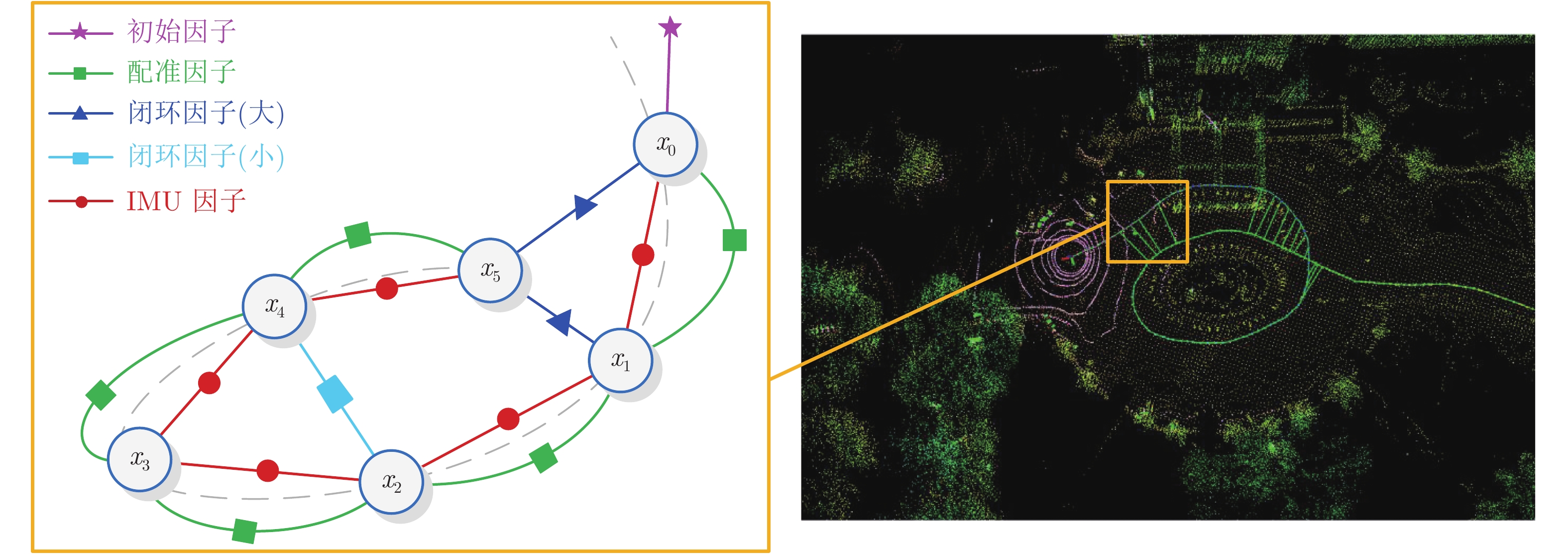
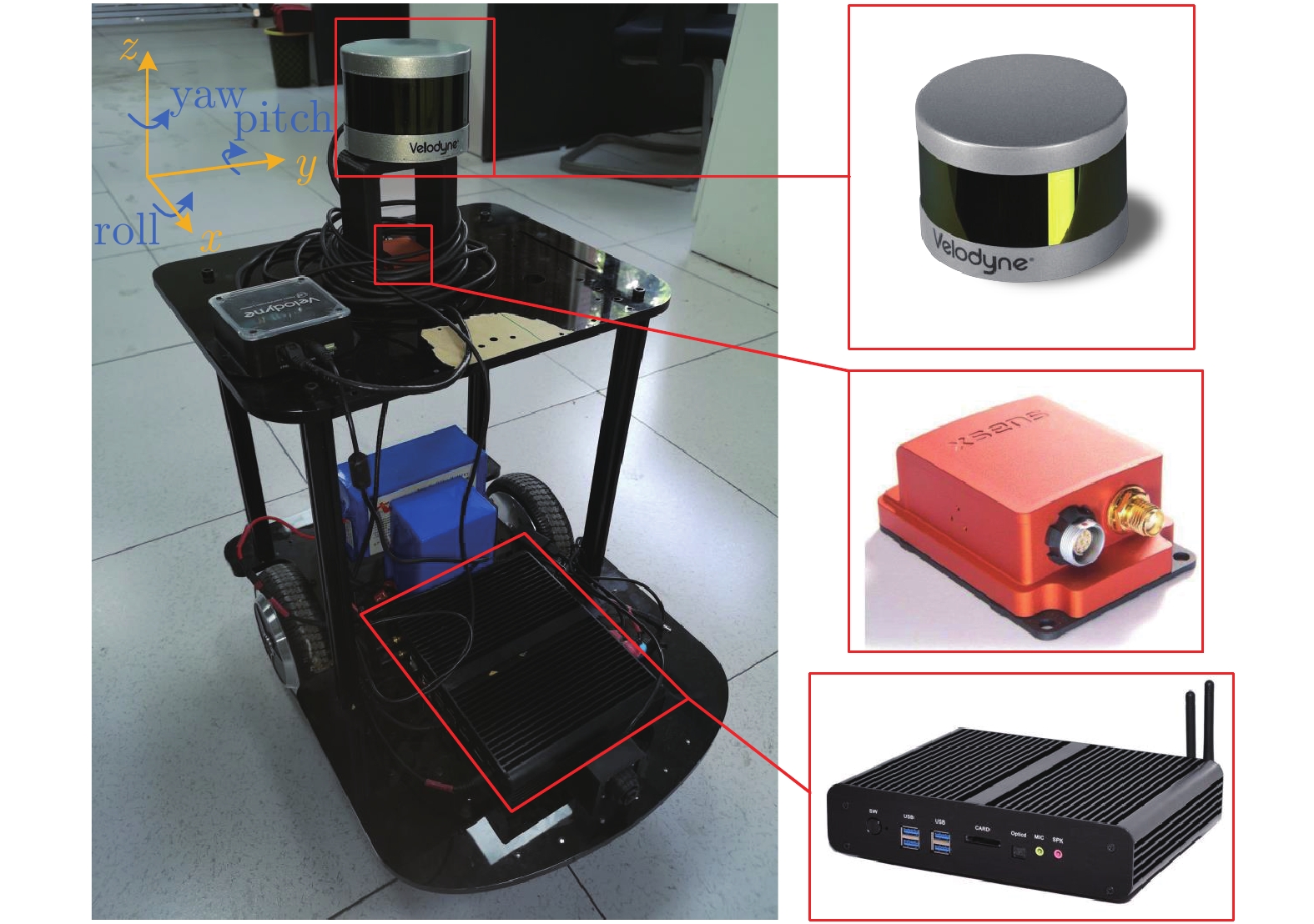
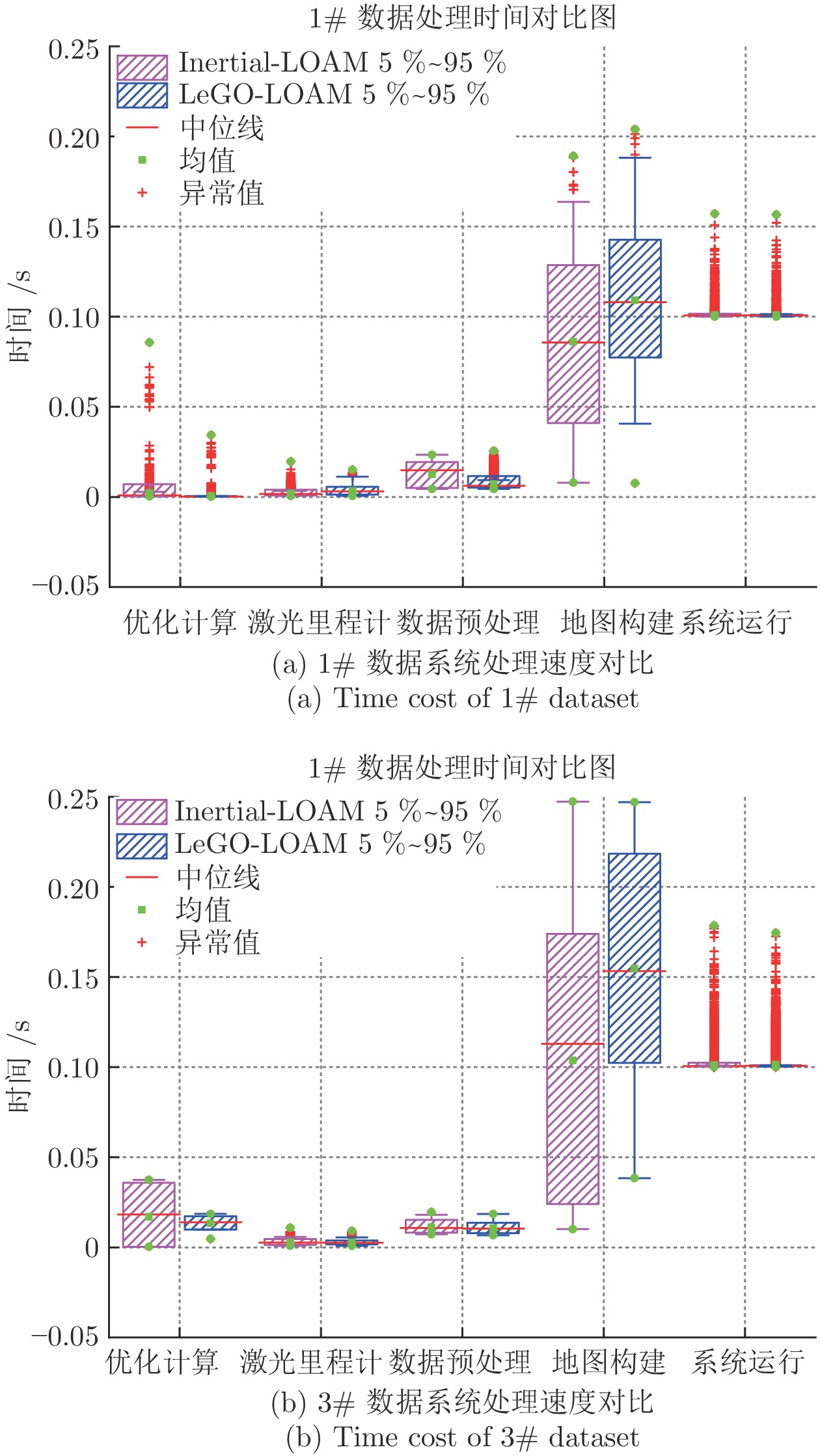
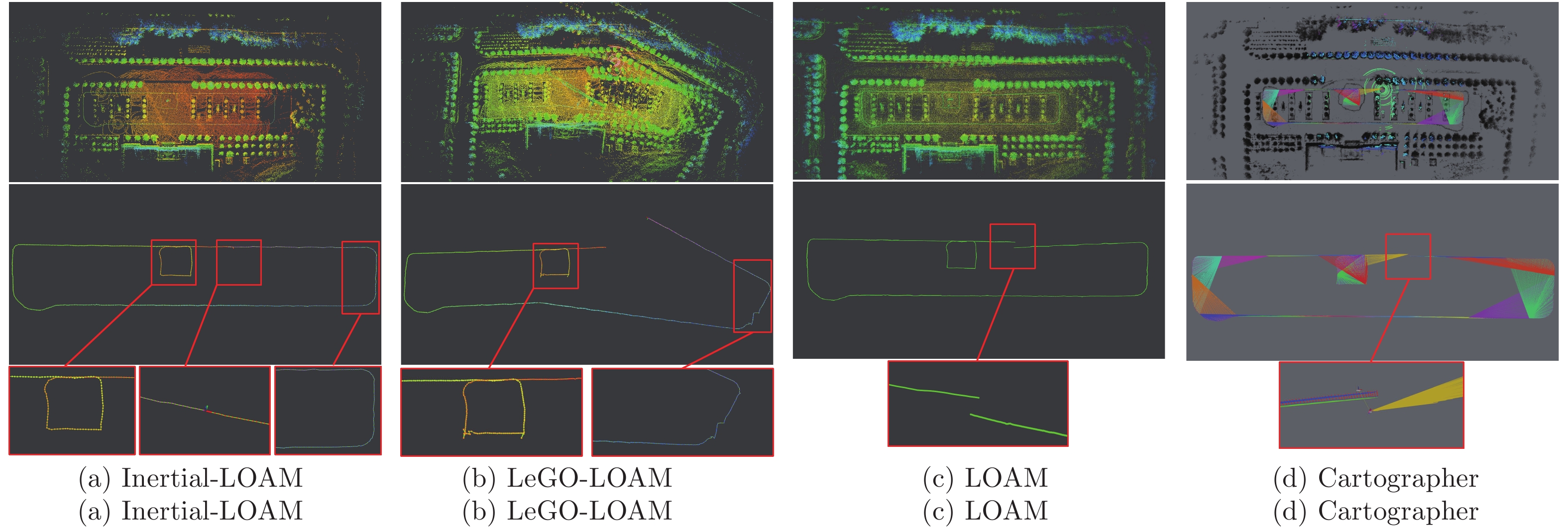
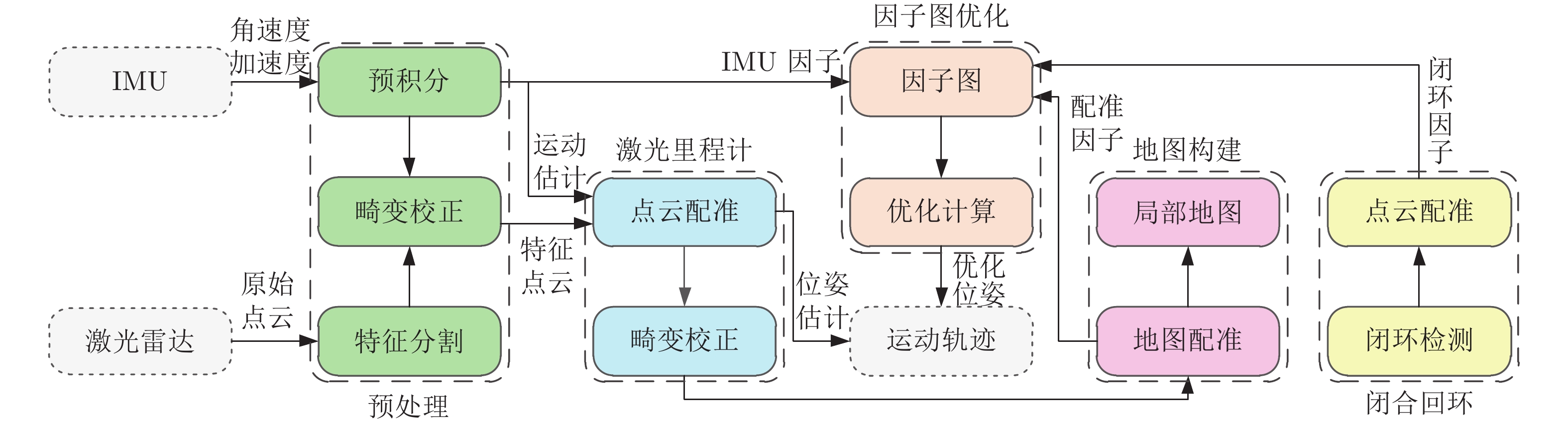
摘要: 本文以实现移动小型智能化系统的实时自主定位为目标, 针对激光里程计误差累计大, 旋转估计不稳定, 以及观测信息利用不充分等问题, 提出一种LiDAR/IMU紧耦合的实时定位方法 — Inertial-LOAM. 数据预处理部分, 对IMU数据预积分, 降低优化变量维度, 并为点云畸变校正提供参考. 提出一种基于角度图像的快速点云分割方法, 筛选结构性显著的点作为特征点, 降低点云规模, 保证激光里程计的效率; 针对地图构建部分存在的地图匹配点搜索效率低和离散点云地图的不完整性问题, 提出传感器中心的多尺度地图模型, 利用环形容器保持地图点恒定, 并结合多尺度格网保证地图模型中点的均匀分布. 数据融合部分, 提出LiDAR/IMU紧耦合的优化方法, 将IMU和LiDAR构成的预积分因子、配准因子、闭环因子插入全局因子图中, 采用基于贝叶斯树的因子图优化算法对变量节点进行增量式优化估计, 实现数据融合. 最后, 采用实测数据评估Inertial-LOAM的性能并与LeGO-LOAM, LOAM和Cartographer对比. 结果表明, Inertial-LOAM在不明显增加运算负担的前提下大幅降低连续配准误差造成的误差累计, 具有良好的实时性; 在结构性特征明显的室内环境, 定位精度达厘米级, 与对比方法持平; 在开阔的室外环境, 定位精度达分米级, 而对比方法均存在不同程度的漂移.Abstract: Aiming at the problem of the high-drift of LiDAR odometry, the unstability of purely rotation estimation, and the underutilization of sensor observation, a LiDAR/IMU tightly coupled real-time localization method, Inertial-LOAM, is presented in the paper, to achieve real-time and autonomous localization for small intelligence system, such as mobile robot. In data preprocessing section, we conduct IMU pre-integration to address the rapid growth of the number of variables in the optimizer and provide reference for point cloud deskewing. A fast point cloud segmentation approach based on angle image is proposed to screen out featured points and downsize the magnitude of point cloud, which increase the accuracy and efficiency of LiDAR odometry. In mapping section, a sensor-centered multi-resolution map model is proposed to solve the problem of the costly searching for correspondences among local map, and the incomplete representation of accumulated point cloud map. We keep the number of points in local map constant by restoring them in a circular vector, and use multi-resolution grids to keep map points uniform, which promote the increasing of efficiency and accuracy of scan-to-map registration. In data fusion section, we present a LiDAR/IMU tightly coupled optimization method by adding pre-integration factors, registration factors and loop closure factors into the global factor graph, and applying optimization algorithm based on Bayesian tree to estimate all variable nodes, which achieves deeply integration of multi-source information. Finally, we evaluate and compare the performance of Inertial-LOAM with that of LeGO-LOAM, LOAM, and Cartographer using test data gathered by mobile robot. It shows that Inertial-LOAM, with the help of optimization back-end, could dramatically reduce the impact from wrong registrations of point cloud without increasing calculation burden, and has good real time performance. It can achieve centimeter-level positioning accuracy in structured indoor environments, which is similar to other counterparts. And decimeter-level positioning accuracy could be achieved in open and structureless outdoor environments, while all other solutions have different extent of drift.
-
Key words:
- SLAM /
- LiDAR odometry /
- pre-integration /
- data fusion /
- factor graph optimization
-
表 1 累计误差结果
Table 1 Error accumulation result
场景 方法 横滚 (°) 俯仰 (°) 航向 (°) 角度偏差 (°) X方向 (m) Y方向 (m) Z方向 (m) 位置偏差 (m) 2# 数据[11] IMU 0.748 1.018 0.598 1.398 35.095 84.652 −665.782 672.059 Cartographer 0.113 −0.709 0.989 1.222 0.405 1.317 0.670 1.532 LOAM 0.016 0.141 0.925 0.936 0.316 0.349 0.025 0.471 LeGO-LOAM 0.061 0.081 0.916 0.921 0.068 0.338 0.115 0.364 Inertial-LOAM 0.013 0.026 0.917 0.918 0.061 0.258 0.023 0.266 室内环境 Cartographer 0.003 −0.001 0.017 0.017 0.023 0.037 0.028 0.052 LOAM 0.001 0.004 0.068 0.068 0.032 0.083 0.032 0.095 LeGO-LOAM −0.006 −0.002 −0.021 0.022 0.016 0.047 −0.032 0.059 Inertial-LOAM −0.008 0.001 −0.020 0.021 0.021 0.043 0.027 0.055 室外环境 Cartographer 0.075 −0.024 0.081 0.113 1.747 2.592 −0.449 3.158 LOAM −0.031 0.006 0.096 0.101 0.0467 2.368 −0.065 2.353 LeGO-LOAM −0.024 −0.543 0.041 0.545 −19.857 −14.914 −0.355 24.836 Inertial-LOAM 0.006 −0.080 0.003 0.080 −0.310 −0.100 −0.030 0.328 -
[1] 李帅鑫. 激光雷达/相机组合的3D SLAM技术研究 [硕士学位论文], 战略支援部队信息工程大学, 中国, 2018Li Shuai-Xin. Research on 3D SLAM Based on Lidar/Camera Coupled System [Master thesis], PLA Strategic Support Force Information Engineering University, China, 2018 [2] Besl P J, McKay N D. Method for registration of 3-D shapes. In: Proceedings Volume 1611, Sensor Fusion IV: Control Paradigms and Data Structures. Boston, MA, USA: SPIE, 1992. 586−606 [3] Pomerleau F, Colas F, Siegwart R, Magnenat S. Comparing ICP variants on real-world data sets. Autonomous Robots, 2013, 34(3): 133−148 doi: 10.1007/s10514-013-9327-2 [4] Surmann H, Nűchter A, Lingemann K, Hertzberg J. 6D SLAM-preliminary report on closing the loop in six dimensions. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2004, 37(8): 197−202 doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)31975-4 [5] Moosmann F, Stiller C. Velodyne SLAM. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV). Baden-Baden, Germany: IEEE, 2011. 393−398 [6] Droeschel D, Schwarz M, Behnke S. Continuous mapping and localization for autonomous navigation in rough terrain using a 3D laser scanner. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2017, 88: 104−115 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2016.10.017 [7] Droeschel D, Behnke S. Efficient continuous-time SLAM for 3D lidar-based online mapping. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, QLD, Australia: IEEE, 2018. 5000−5007 [8] Zhang J, Singh S. LOAM: Lidar odometry and mapping in real-time. In: Proceedings of Robotics: Science and Systems. Berkeley, CA, USA: 2014. [9] Zhang J, Singh S. Low-drift and real-time lidar odometry and mapping. Autonomous Robots, 2017, 41(2): 401−416 doi: 10.1007/s10514-016-9548-2 [10] Geiger A, Lenz P, Urtasun R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, RI, USA: IEEE, 2012. 3354−3361 [11] Shan T X, Englot B. LeGO-LOAM: Lightweight and ground-optimized lidar odometry and mapping on variable terrain. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Madrid, Spain: IEEE, 2018. 4758−4765 [12] Hess W, Kohler D, Rapp H, Andor D. Real-time loop closure in 2D LIDAR SLAM. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Stockholm, Sweden: IEEE, 2016. 1271−1278 [13] Forster C, Carlone L, Dellaert F, Scaramuzza D. On-manifold preintegration for real-time visual-inertial odometry. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017, 33(1): 1−21 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2016.2597321 [14] Sarvrood Y B, Hosseinyalamdary S, Gao Y. Visual-LiDAR odometry aided by reduced IMU. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2016, 5(1): 3 doi: 10.3390/ijgi5010003 [15] Thrun S, Burgard W, Fox D. Probabilistic Robotics. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2005. [16] Hening S, Ippolito C A, Krishnakumar K S, Stepanyan V, Teodorescu M. 3D LIDAR SLAM integration with GPS/INS for UAVs in urban GPS-degraded environments. In: AIAA Information Systems-AIAA Infotech@Aerospace. Grapevine, Texas: AIAA, 2017. [17] Dellaert F, Kaess M. Factor graphs for robot perception. Foundations and Trends® in Robotics, 2017, 6(1-2): 1−139 [18] Leutenegger S, Lynen S, Bosse M, Siegwart R, Furgale P. Keyframe-based visual-inertial odometry using nonlinear optimization. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2015, 34(3): 314−334 doi: 10.1177/0278364914554813 [19] Konolige K, Grisetti G, Kűmmerle R, Burgard W, Limketkai B, Vincent R. Efficient sparse pose adjustment for 2D mapping. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Taipei, China: IEEE, 2010. 22−29 [20] Kaess M, Ranganathan A, Dellaert F. ISAM: Incremental smoothing and mapping. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(6): 1365−1378 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2008.2006706 [21] Indelman V, Williams S, Kaess M, Dellaert F. Factor graph based incremental smoothing in inertial navigation systems. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Information Fusion. Singapore: IEEE, 2012. 2154-2161 [22] Kaess M, Johannsson H, Roberts R, Ila V, Leonard J J, Dellaert F. iSAM2: Incremental smoothing and mapping using the Bayes tree. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2012, 31(2): 216−235 doi: 10.1177/0278364911430419 [23] Qin T, Li P L, Shen S J. VINS-mono: A robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(4): 1004−1020 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2853729 [24] Qin T, Shen S J. Online temporal calibration for monocular visual-inertial systems. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Madrid, Spain: IEEE, 2018. 3662−3669 [25] Li S X, Li G Y, Zhou Y L, Wang L, Fu J Y. Real-time dead reckoning and mapping approach based on three-dimensional point cloud. In: proceedings of the 2018 China Satellite Navigation Conference. Harbin, China: Springer, 2018. 643−662 [26] Barfoot T D. State Estimation for Robotics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017. [27] Zhang J, Singh S. Laser-visual-inertial odometry and mapping with high robustness and low drift. Journal of Field Robotics, 2018, 35(8): 1242−1264 doi: 10.1002/rob.21809 [28] Behley J, Stachniss C. Efficient surfel-based SLAM using 3D laser range data in urban environments. In: Proceedings of Robotics: Science and Systems. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, 2018. -




 下载:
下载: