A Model and Data Hybrid Parallel Learning Method for Stochastic Configuration Networks
-
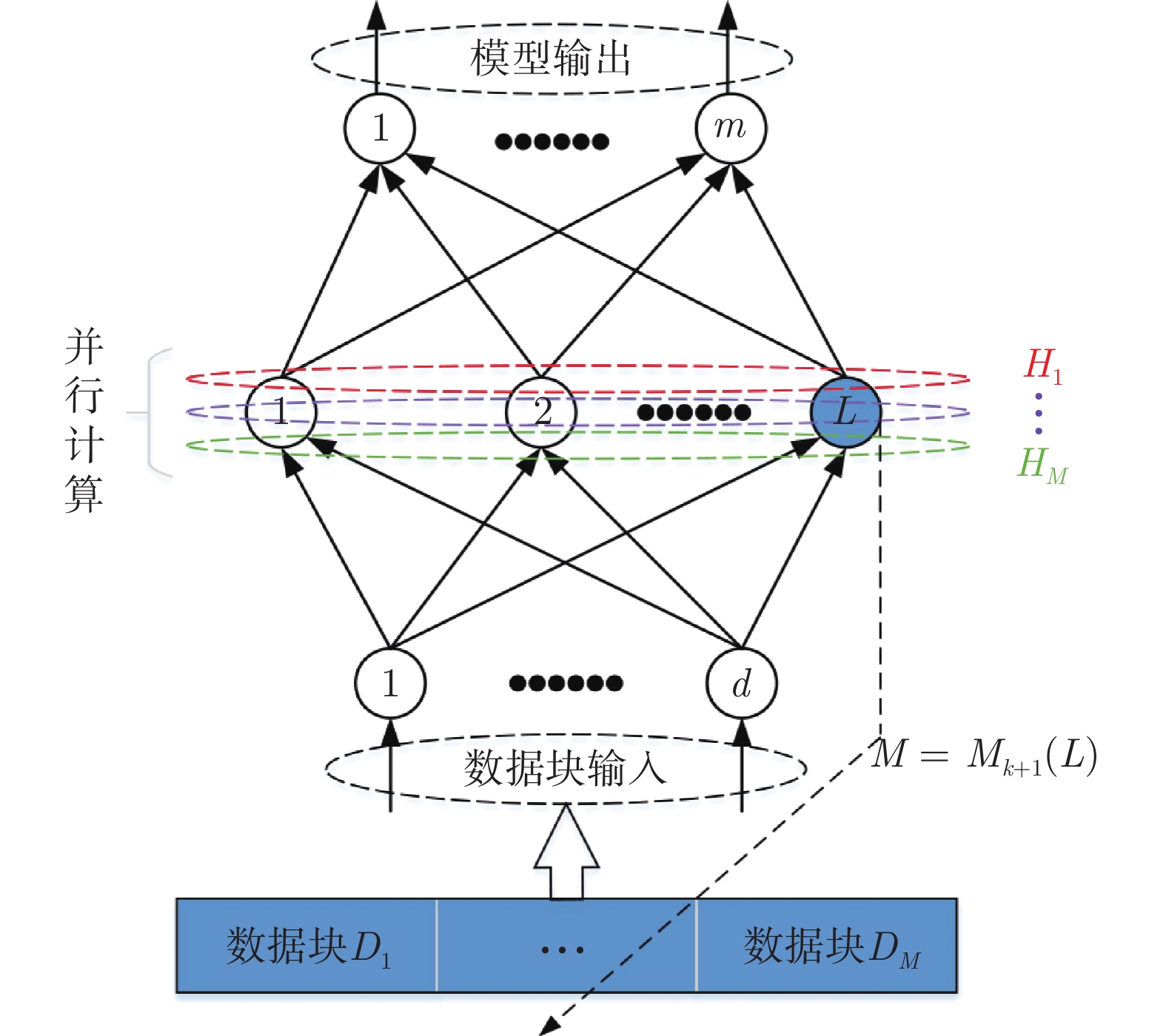
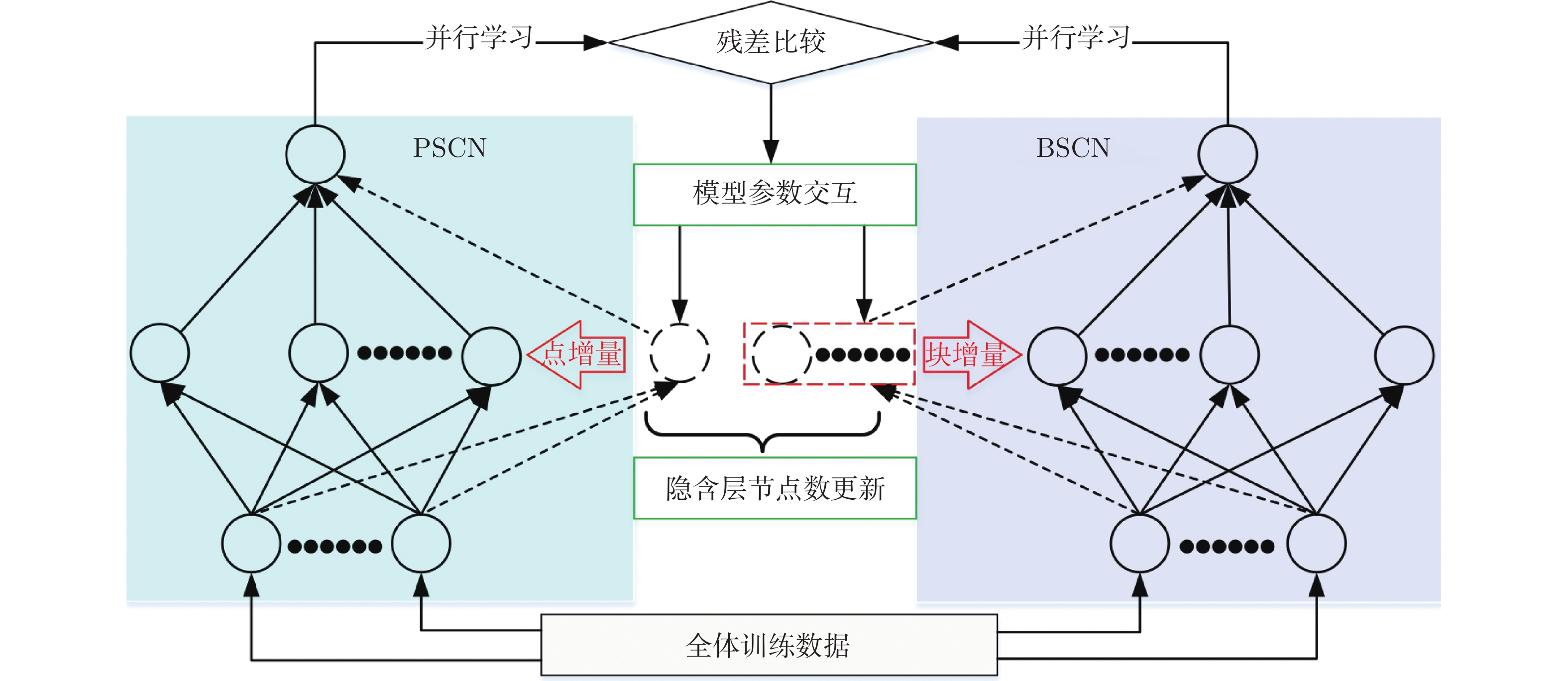
摘要: 随机配置网络(Stochastic configuration networks, SCNs)在增量构建过程引入监督机制来分配隐含层参数以确保其无限逼近特性, 具有易于实现、收敛速度快、泛化性能好等优点. 然而, 随着数据量的不断扩大, SCNs的建模任务面临一定的挑战性. 为了提高神经网络算法在大数据建模中的综合性能, 本文提出了一种混合并行随机配置网络(Hybrid parallel stochastic configuration networks, HPSCNs)架构, 即: 模型与数据混合并行的增量学习方法. 所提方法由不同构建方式的左右两个SCNs模型组成, 以快速准确地确定最佳隐含层节点, 其中左侧采用点增量网络(PSCN), 右侧采用块增量网络(BSCN); 同时每个模型建立样本数据的动态分块方法, 从而加快候选“节点池”的建立、降低计算量. 所提方法首先通过大规模基准数据集进行了对比实验, 然后应用在一个实际工业案例上, 表明其有效性.Abstract: Stochastic configuration networks (SCNs) that employ a supervisory mechanism to assign hidden-node parameters in the incremental construction process can work successfully in building a universal approximator, which indicates remarkable merits in simplicity of implementation, fast convergence and sound generalization. However, an increasing amount of data makes the modeling task with SCNs a challenge. In order to improve the comprehensive performance of neural network algorithms in large-scale data modeling, this paper proposes a hybrid parallel stochastic configuration networks (HPSCNs) architecture by incorporating dual parallelism of model and data. The proposed architecture consists of two SCN models with different construction methods to fast determine the required hidden nodes. The first one is point-incremental SCN (PSCN) which uses point incremental algorithm, and another one is block-incremental SCN (BSCN) which adopts block incremental algorithm. Besides, a dynamic block method of sample data is established and applied for each model, which accelerates the establishment of candidate node pool and reduces the computational load. Comparative experiments were first conducted through large-scale benchmark data sets and then a real-world industrial application case, indicating the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 基准数据集说明
Table 1 Specification of benchmark data sets
数据集 属性 样本数 输入变量 输出变量 DB1 14 4 241 600 DB2 12 1 10 000 DB3 10 1 40 768 DB4 26 1 14 998 表 2 分块数递增区间长度及其上下界
Table 2 Incremental interval length of block number and its upper and lower bounds
$L_{en}^k$ $L_{\max }^k$ $L_{\min }^k$ 50 50 0 100 150 50 150 300 150 ··· ··· ··· 表 3 不同算法性能比较
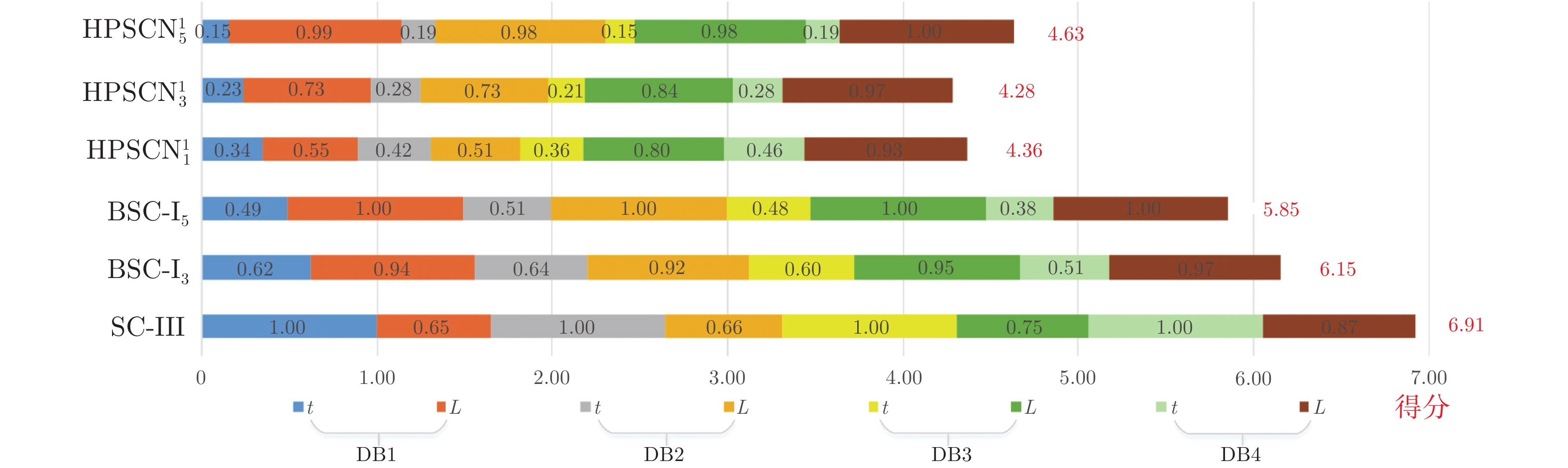
Table 3 Performance comparison of different algorithms
数据集 算法 t(s) k L DB1 SC-III 24.35$\pm $1.69 164.40$\pm $7.76 164.40$\pm $7.76 ${\rm{BSC - }}{{\rm{I}}_3}$ 12.60$\pm $1.21 69.20$\pm $3.03 207.60$\pm $9.09 ${\rm{BSC - }}{{\rm{I}}_5}$ 9.41$\pm $1.33 44.00$\pm $3.24 220.00$\pm $16.20 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_1^1$ 3.48$\pm $0.38 122.40$\pm $8.02 122.40$\pm $8.02 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_3^1$ 3.03$\pm $0.28 63.40$\pm $4.16 162.80$\pm $7.90 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_5^1$ 2.96$\pm $0.19 45.00$\pm $2.83 215.00$\pm $9.71 DB2 SC-III 26.97$\pm $2.54 300.00$\pm $14.18 300.00$\pm $14.18 ${\rm{BSC - }}{{\rm{I}}_3}$ 14.66$\pm $1.33 120.40$\pm $3.98 361.20$\pm $11.93 ${\rm{BSC - }}{{\rm{I}}_5}$ 11.01$\pm $1.07 78.80$\pm $2.91 394.00$\pm $14.87 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_1^1$ 7.22$\pm $0.95 239.30$\pm $14.55 239.3$\pm $14.55 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_3^1$ 5.47$\pm $0.33 123.50$\pm $3.34 301.90$\pm $10.99 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_5^1$ 4.39$\pm $0.42 81.80$\pm $3.74 378.60$\pm $16.54 DB3 SC-III 18.04$\pm $2.15 106.60$\pm $3.36 106.60$\pm $3.36 ${\rm{BSC - }}{{\rm{I}}_3}$ 8.96$\pm $1.21 39.80$\pm $2.28 119.40$\pm $6.84 ${\rm{BSC - }}{{\rm{I}}_5}$ 6.81$\pm $0.55 25.20$\pm $1.10 126.00$\pm $5.48 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_1^1$ 3.45$\pm $0.24 97.00$\pm $2.65 97.00$\pm $2.65 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_3^1$ 2.05$\pm $0.13 41.20$\pm $2.17 106.40$\pm $4.39 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_5^1$ 1.88$\pm $0.12 25.00$\pm $1.22 121.00$\pm $6.44 DB4 SC-III 9.16$\pm $0.34 161.20$\pm $2.56 161.20$\pm $2.56 ${\rm{BSC - }}{{\rm{I}}_3}$ 3.79$\pm $0.68 54.20$\pm $0.84 162.60$\pm $2.51 ${\rm{BSC - }}{{\rm{I}}_5}$ 2.59$\pm $0.13 33.40$\pm $0.89 167.00$\pm $4.47 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_1^1$ 4.23$\pm $0.13 154.80$\pm $2.59 154.80$\pm $2.59 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_3^1$ 2.01$\pm $0.13 59.00$\pm $2.00 162.60$\pm $2.41 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_5^1$ 1.36$\pm $0.11 34.20$\pm $1.09 166.20$\pm $3.03 表 4 不同块宽的算法性能比较
Table 4 Performance comparison of algorithms with different block sizes
数据集 算法 nR nL Eff (%) DB1 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_1^1$ 61.3 61.1 49.9 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_2^1$ 63.8 22.4 26.0 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_3^1$ 52.8 12.6 19.3 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_5^1$ 42.5 2.5 5.6 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_{10}^1$ 24.2 0.6 2.4 DB2 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_1^1$ 119.2 120.1 50.2 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_2^1$ 115.0 56.4 32.9 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_3^1$ 99.2 24.3 19.7 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_5^1$ 74.2 7.6 9.3 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_{10}^1$ 44.6 0.4 0.9 DB3 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_1^1$ 48.4 48.6 50.1 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_2^1$ 40.8 23.4 36.4 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_3^1$ 33.6 7.6 18.4 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_5^1$ 24.0 1.0 4.0 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_{10}^1$ 13.6 0.2 1.4 DB4 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_1^1$ 77.3 77.5 50.0 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_2^1$ 64.2 29.4 31.4 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_3^1$ 51.8 7.2 12.2 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_5^1$ 33.0 1.2 3.5 ${\rm{HPSCN}}_{10}^1$ 17.0 0.2 1.1 -
[1] Chen Xing, Niu Ya-Wei, Wang Guang-Hui, Yan Gui-Ying. MKRMDA: Multiple Kernel Learning-based Kronecker Regularized Least Squares for MiRNA-disease Association Prediction. Journal of Translational Medicine, 2013, 15(1): 251-264 [2] 周平, 刘记平. 基于数据驱动多输出ARMAX建模的高炉十字测温中心温度在线估计. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 552-561Zhou Ping, Liu Ji-ping. Data-driven Multi-output ARMAX Modeling for Online Estimation of Central Temperatures for Cross Temperature Measuring in Blast Furnace Ironmaking. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(9): 1569-1589 [3] 汤健, 乔俊飞, 柴天佑, 刘卓, 吴志伟. 基于虚拟样本生成技术的多组分机械信号建模. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(9): 1569-1589Tang Jian, Qiao Jun-Fei, Chai Tian-You, Liu Zhuo, Wu ZhiWei. Modeling Multiple Components Mechanical Signals by Means of Virtual Sample Generation Technique. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(9): 1569-1589 [4] Witten Ian H, Frank E, Hall M A. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Technique, 3rd Edition. Amsterdam: Morgan Kaufmann, 2011 [5] Pao Y H, Takefji Y, Functional-link Net Computing: Theory, System Architecture, and Functionalities. Computer, 1992, 25(5): 76-79 doi: 10.1109/2.144401 [6] Schmidt W F, Kraaijveld M A, Duin R P W. Feedforward neural networks with random weights. International Conference on Pattern Recognition IEEE Computer Society, 1992 [7] Cao Wei-Peng, Wang Xi-Zhao, Ming Zhong, Gao Jin-Zhu. A Review on Neural Networks with Random Weights. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275: 278-287 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.08.040 [8] Scardapane S, Wang Dian-Hui. Randomness in Neural Networks: An Overview. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2017, 7(2): e1200 doi: 10.1002/widm.1200 [9] Lu Jing, Zhao Jian-Wei, Cao Fei-Long. Extended Feed Forward Neural Networks with Random Weights for Face Recognition. Neurocomputing, 2014, 136: 96-102 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.01.022 [10] Dai Wei, Liu Qiang, Chai Tian-You. Particle Size Estimate of Grinding Processes Using Random Vector Functional Link Networks with Improved Robustness. Neurocomputing, 2015, 169: 361-372 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.08.098 [11] Dai Weo, Chen Qi-Xin, Chu Fei, Chai Tian-You. Robust Regularized Random Vector Functional Link Network and Its Industrial Application. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 16162-16172 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2737459 [12] Li Ming, Wang Dian-Hui. Insights into Randomized Algorithms for Neural Networks: Practical Issues and Common Pitfalls. Information Sciences, 2017, 382: 170-178 [13] Gorban A N, Tyukin I Y, Prokhorov D V, Sofeikov K I. Approximation with Random Bases: Pro et contra. Information Sciences, 2016, 364: 129-145 [14] Wang Dian-Hui, Li Ming. Stochastic Configuration Networks: Fundamentals and Algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(10): 3466-3479 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2734043 [15] Zhu Xiao-Long, Feng Xiang-Chu, Wang Wei-Wei, Jia XiXi, He Rui-Qiang. A Further Study on the Inequality Constraints in Stochastic Configuration Networks. Information Sciences, 2019, 487: 77-83 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.02.066 [16] Wang Dian-Hui, Cui Cai-Hao. Stochastic Configuration Networks Ensemble for Large-Scale Data Analytics. biochemical treatment process. Information Sciences, 2017, 417: 55-71 [17] Sheng Zhui-Yong, Zeng Zhi-Qiang, Qu Hong-Quan, Zhang Yuan. Optical fiber intrusion signal recognition method based on TSVD-SCN. Optical Fiber Technology, 2019, 48: 270-277 doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2019.01.023 [18] 王前进, 杨春雨, 马小平, 张春富, 彭思敏. 基于随机配置网络的井下供给风量建模. 自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c190602Wang Qian-Jin, Yang Chun-Yu, Ma Xiao-Ping, Zhang Chun-Fu, Peng Si-Min. Underground Airflow Quantity Modeling Based on SCN. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c190602 [19] Wang Dian-Hui, Li Ming. Deep stochastic configuration networks with universal approximation property. In: Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2018. [20] Wang Dian-Hui, Li Ming. Robust Stochastic Configuration Networks with Kernel Density Estimation for Uncertain Data Regression. Information Sciences, 2017, 412-413: 210-222 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2017.05.047 [21] Li Ming, Huang Chang-Qin, Wang Dian-Hui. Robust Stochastic Configuration Networks with Maximum Correntropy Criterion for Uncertain Data Regression. Information Sciences, 2019, 473: 73-86 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.09.026 [22] He Qing, Shang Tang-Feng, Zhuang Fu-Zhen, Shi Zhon-Zhi. Parallel Extreme Learning Machine for Regression Based on MapReduce. Neurocomputing, 2013, 102: 52-58 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2012.01.040 [23] Duan Ming-Xing, Li Ken-Li, Liao Xiang-Ke, Li Ke-Qin. A Parallel Multiclassification Algorithm for Big Data Using an Extreme Learning Machine. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(6): 2337-2351 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2654357 [24] Wang Yue-Qing, Dou Yong, Liu Xin-Wang, Lei Yuan-Wu. PR-ELM: Parallel Regularized Extreme Learning Machine Based on Cluster. Neurocomputing, 2016, 173: 1073-1081 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.08.066 [25] Lancaster P, Tismenetsky M. The Theory of Matrices: With Applications. Elsevier, 1985 [26] Dai Wei, Li De-Peng, Zhou Ping, Chai Tian-You. Stochastic Configuration Networks with Block Increments for Data Modeling in Process Industries. Information Sciences, 2019, 484: 367-386 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.01.062 [27] UCI Machine Learning Repository. [Online], available: https://archive.ics.uci.edu, 2013 [28] KEEL data-mining software tool: Data set repository, integration of algorithms and experimental analysis framework. [Online], available: http://www.keel.es/, 2011 [29] Dai Wei, Zhou Ping, Zhao Da-Yong, Lu Shao-Wen, Chai Tian-You. Hardware-in-the-loop Simulation Platform for Supervisory Control of Mineral Grinding Process. Powder technology, 2016, 288: 422-434 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2015.11.032 -




 下载:
下载: