-
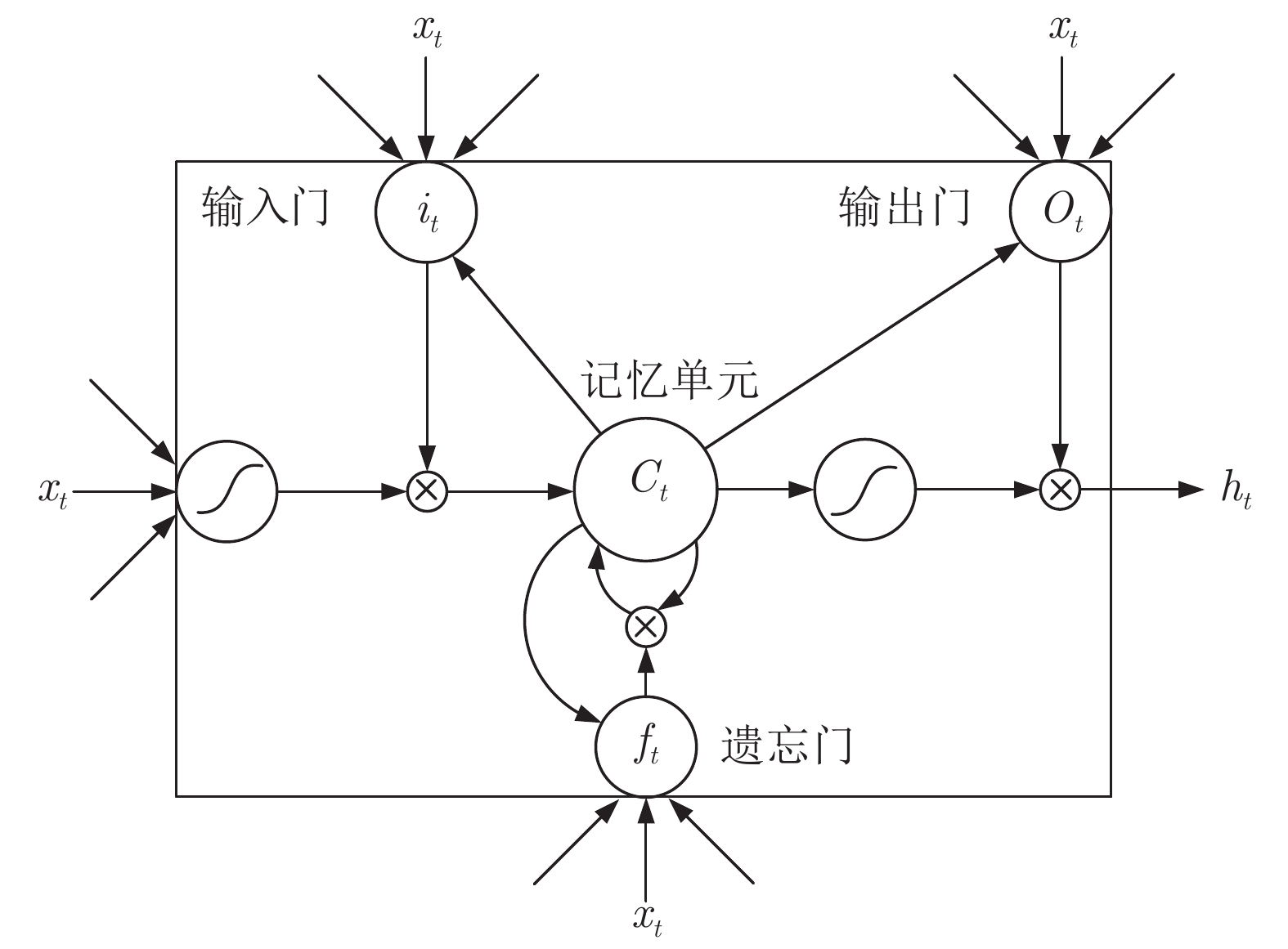
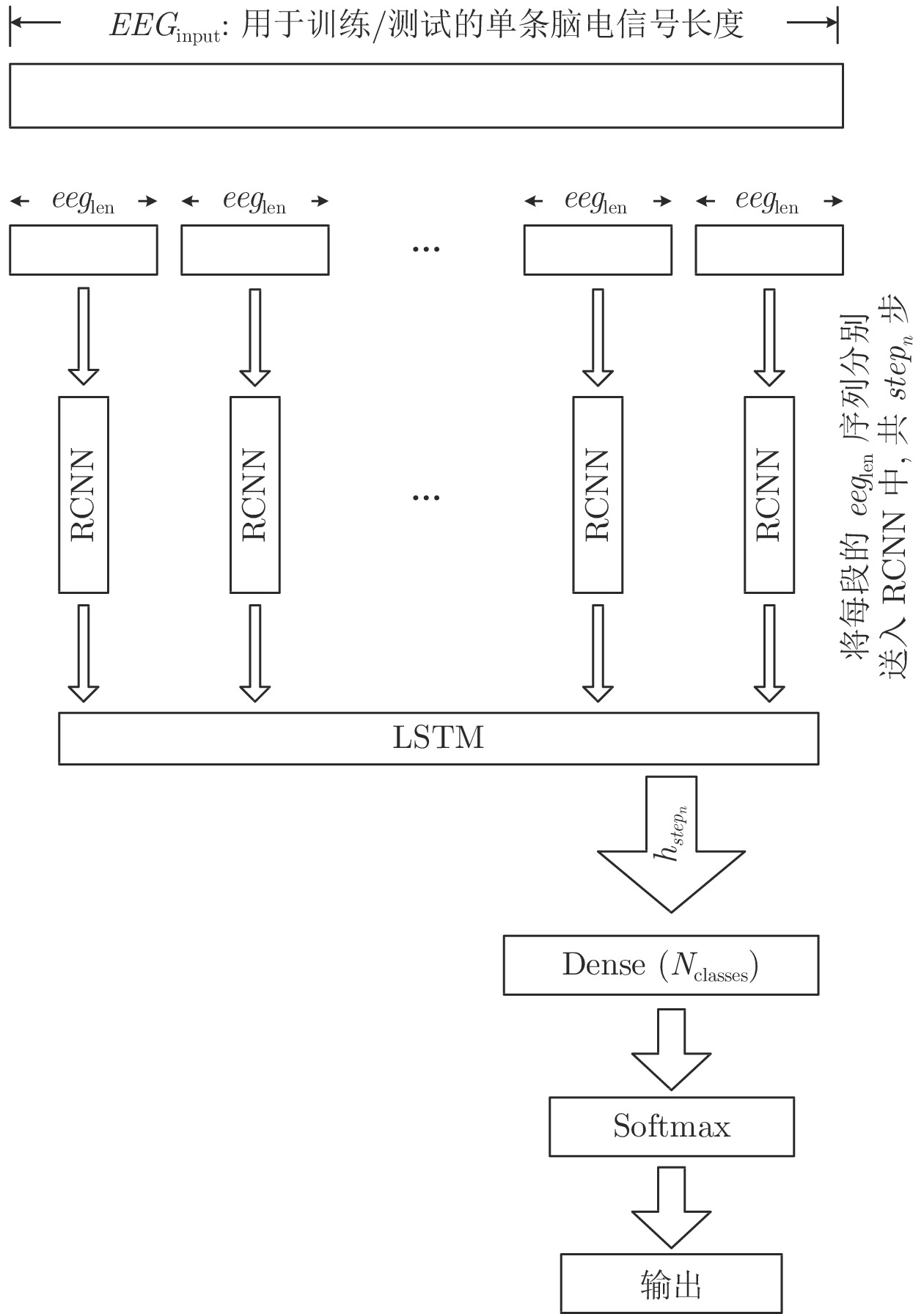
摘要: 情感作为人脑的高级功能, 对人们的个性特征和心理健康有很大的影响, 利用网上公开的脑电情感数据库(DEAP (Database for emotion analysis using physiological signals)数据库), 根据心理效价和激励唤醒度等级进行情感划分, 对压力和平静等5种情感进行研究分析. 针对脑电信号时空特征结合的特点, 把深度学习中的卷积神经网络(Convolutional neural network, CNN)和长短期记忆网络(Long short term memory, LSTM)两者作为基本前提, 并在此基础之上设计了一个RCNN-LSTM的脑电情感信号分类模型. 利用循环卷积神经网络(Recurrent convolutional neural network, RCNN)自动提取脑电信号中的抽象特征, 省去了人工选择与降维的过程, 然后结合LSTM网络对脑电情感信号进行分类识别. 实验结果表明, 利用该方法对5种情感类别的平均分类识别率达到了96.63%, 证明了该方法的有效性.Abstract: As an advanced function of the human brain, emotion has a great influence on people's personality characteristics and mental health. Using the online public EEG (electroencephalogram) database (DEAP (database for emotion analysis using physiological signals) database), emotions are divided according to psychological valence and arousal level. Five emotions, including stress and calm, are studied and analyzed. According to the combination of temporal and spatial features of EEG signals, CNN (convolutional neural network) and LSTM (long short term memory) in deep learning are taken as the basic prerequisites. On the basis of this, a new and more powerful EEG signal classification model is constructed. Use the recurrent convolutional neural network (RCNN) to automatically extract the abstract features of the EEG signal, eliminate the process of manual selection and dimensional reduction, and then send it to the LSTM network to classify and identify EEG signals. The experimental results show that the average accuracy of this method is 96.63%, which demonstrates the effectiveness of this method.
-
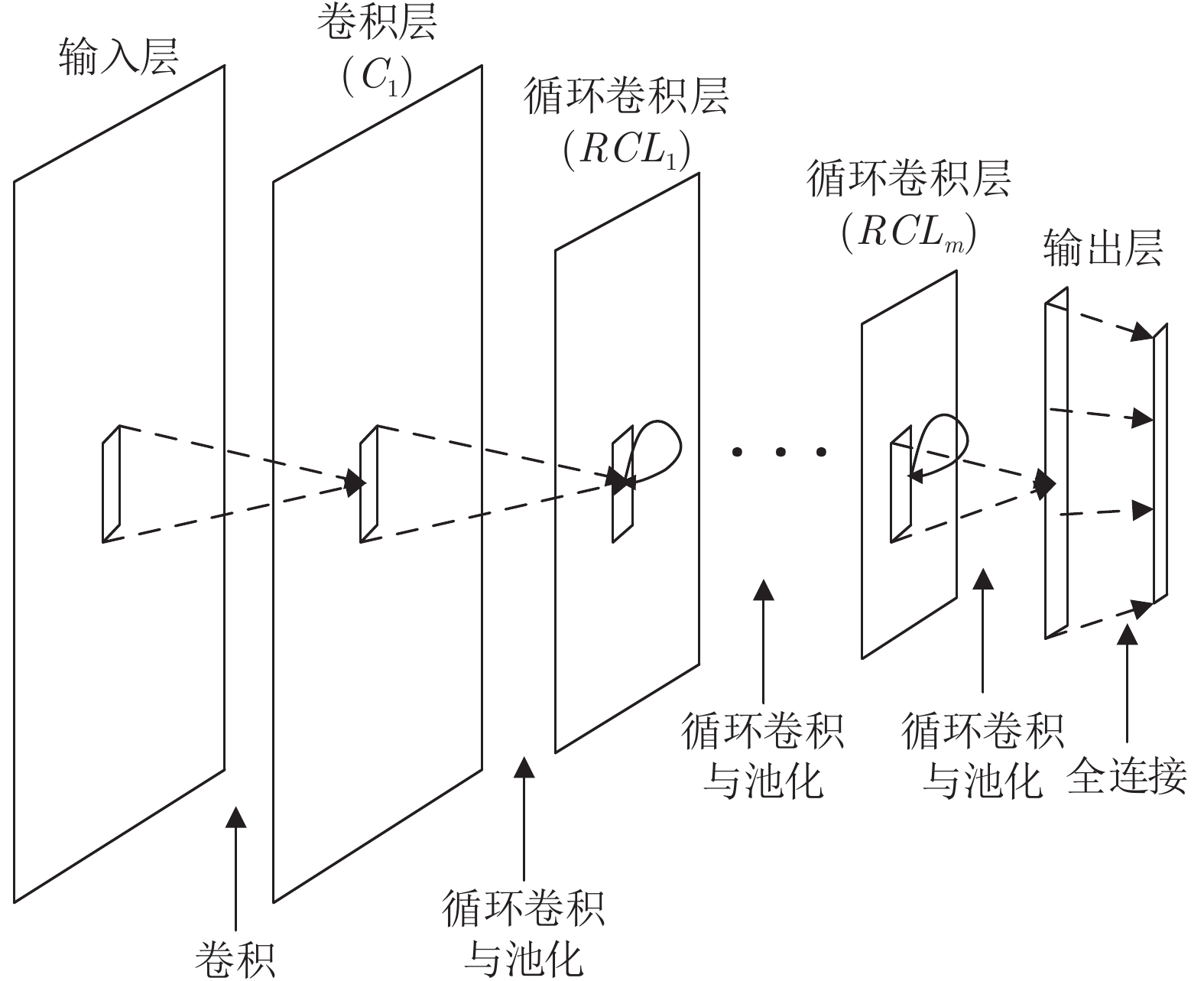
表 1 RCNN网络模型结构
Table 1 RCNN network model structure
网络层 参数设置 输入层 输入结构: (数据长度, 1) 标准卷积层 核数量: 90; 大小: 3; 步长: 1 最大池化层 核大小: 4 步长: 2 RCL层 核数量: 90; 大小: 3; 步长: 1 最大池化层 核大小: 4 步长: 2 RCL层 核数量: 90; 大小: 3; 步长: 1 最大池化层 核大小: 4 步长: 2 RCL层 核数量: 90; 大小: 3; 步长: 1 最大池化层 核大小: 4 步长: 2 RCL层 核数量: 90; 大小: 3; 步长: 1 最大池化层 核大小: 4 步长: 2 表 2 DEAP数据收集统计表
Table 2 DEAP data collection statistics
顺序 内容 1 把电极放在适当的实验位置, 通过铃声来通知开始实验 2 接着调整基线约 2 min, 直到符合要求 (主要目的就是为了使
受试人员能够保持放松)3 显示 2 s 的实验编号来提示具体的进程 4 收集 3 s 的基线数据信息 5 播放 1 min 的音乐, 并且详细地记录这个时间段的数据信息 6 对收集到的数据信息进行统计整理, 并且对各个相应的指标进
行全面评估表 3 不同算法下的召回率和分类识别率(%)
Table 3 Classification recognition rate under differrnt algorithms (%)
轻松 沮丧 快乐 压力 平静 总体识别率 RCNN + LSTM 100 96.6 95.7 96.5 94.3 96.63 CNN + LSTM 79.2 77.1 86.1 92.0 85.4 83.83 CNN 72.8 76.3 82.6 84.9 81.0 79.46 LSTM 73.6 73.7 77.4 81.4 86.2 78.45 SVM 68.0 75.4 83.4 75.2 77.2 75.92 BP 76.0 72.8 75.6 84.1 74.7 76.59 表 4 不同算法下的kappa值和方差
Table 4 Kappa values and variances under different algorithms
kappa 系数 方差 (×10−2) RCNN + LSTM 0.928 0.04 CNN + LSTM 0.763 0.06 CNN 0.70 0.12 LSTM 0.718 0.16 SVM 0.658 0.27 BP 0.675 0.16 表 5 已有研究成果与本文的对比
Table 5 The existing research results are compared with our method
方法 分类类别 识别率 (%) SVM 2 70.1 KNN 2 77.8 CNN + RNN 2 73.09 SAE + RNN 4 79.26 DGCNN 3 90.4 3D-CNN 2 87.965 本文RCNN-LSTM 5 96.63 -
[1] 耿雪青, 佘青山, 韩笑, 孟明. 基于人工蜂群优化高斯过程的运动想象脑电信号分类. 传感技术学报, 2017, 30(03): 378-384 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2017.03.008Geng Xue-Qing, She Qing-Shan, Han Xiao, Meng Ming. Classification of motor imagery EEG based on gaussian process optimized with artificial bee colony. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2017, 30(03): 378-384 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2017.03.008 [2] 王薇蓉, 张雪英, 孙颖, 畅江. 关于脑电信号的情感识别优化仿真. 计算机仿真, 2018, 35(6): 426-431 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2018.06.093Wang Wei-Rong, Zhang Xue-Ying, Sun Ying, Chang Jiang. Emotion optimization identification emulation for EEG signal. Computer Simulation, 2018, 35(6): 426-431 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2018.06.093 [3] Krisnandhika B, Faqih A, Pumamasari P D, Kusumoputro B. Emotion recognition system based on EEG signals using relative wavelet energy features and a modified radial basis function neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Consumer Electronics and Devices (ICCED). London, UK: IEEE, 2017. 50−54 [4] Duan R N, Zhu J Y, Lu B L. Differential entropy feature for EEG-based emotion classification. In: Proceedings of the 6th Internation IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER). San Diego, California, USA: IEEE, 2013. 81−84 [5] Murugappan M, Nagarajan R, Yaacob S. Combining spatial filtering and wavelet transform for classifying human emotions using EEG signals. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 2011, 31(1): 45-51 doi: 10.5405/jmbe.710 [6] 黄柠檬. 基于EEG的情绪识别 [硕士学位论文]. 华南理工大学, 中国, 2016.Huang Ning-Meng. Emotion Recognition Based on EEG [Master thesis]. South China University of Technology, China, 2016. [7] 杨默涵, 陈万忠, 李明阳. 基于总体经验模态分解的多类特征的运动想象脑电识别方法研究. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(05): 743-752Yang Mo-Han, Chen Wan-Zhong, Li Ming-Yang, Multiple feature extraction based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition for motor imagery EEG recognition tasks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(05): 743-752 [8] Zhang T, Chen W Z, Li M Y. AR based quadratic feature extraction in the VMD domain for the automated seizure detection of EEG using random forest classifier. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2017, 100(31): 550-559 [9] 孙颖, 马江河, 张雪英. 结合非线性全局特征和谱特征的脑电情感识别. 计算机工程与应用, 2018, 54(17): 116-121 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1803-0027Sun Ying, Ma Jiang-He, Zhang Xue-Ying. EEG emotion recognition based on nonlinear global features and spectral feature. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2018, 54(17): 116-121 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1803-0027 [10] 吴志勇, 丁香乾, 许晓伟, 鞠传香. 基于深度学习和模糊C均值的心电信号分类方法. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1913-1920Wu Zhi-Yong, Ding Xiang-Qian, Xu Xiao-Wei, Ju Chuan-Xiang. A method for ECG classification using deep learning and fuzzy C-means. Acta Automatic Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1913-1920 [11] Jirayucharoensak S, Setha P N, Pasin I. EEG-based emotion recognition using deep learning network with principal component based covariate shift adaptation [Online], available: https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/627892, March 25 2020 [12] 杨豪, 张俊然, 蒋小梅, 刘飞. 基于深度信念网络脑电信号表征情绪状态的识别研究. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2018, 35(02): 182-190Yang Hao, Zhang Jun-Ran, Jiang Xiao-Mei, Liu Fei. Research of electroencephalography representational emotion recognition based on deep belief networks. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 35(02): 182-190 [13] Cheng C L, Wei X W, Zhou J. Emotion recognition algorithm based on convolution neural network. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering (ISKE). Nanjing, China: IEEE, 2017. 1−5 [14] Wang Y, Huang Z Y, Mccane B, Neo P. EmotioNet: A 3-D convolutional neural network for EEG-based emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: IEEE, 2018. 1−7 [15] 阚威, 李云. 基于LSTM的脑电情绪识别模型[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2019, 55(01): 110-116Kan Wei, Li Yun. Emotion recognition from EEG signals by using LSTM recurrent neural networks. Journal of Nanjing University(Natural Science), 2019, 55(01): 110-116 [16] 李勇, 林小竹, 蒋梦莹. 基于跨连接LeNet-5网络的面部表情识别. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(1): 176-182Li Yong, Lin Xiao-Zhu, Jiang Meng-Ying. Facial expression recognition with cross-connect LeNet-5 network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(1): 176-182 [17] Dutta K K. Multi-class time series classification of EEG signals with recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science and Engineering (Confluence). Noida, India: IEEE, 2019. 337−341 [18] Liang M, Hu X L. Recurrent convolutional neural network for object recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 3367−3375 [19] 汤鹏杰, 王瀚漓, 许恺晟. LSTM逐层多目标优化及多层概率融合的图像描述. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(7): 1237-1249Tang Peng-Jie, Wang Han-Li, Xu Kai-Sheng. Multi-objective layer-wise optimization and multi-level probability fusion for image description generation using LSTM. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(7): 1237-1249. [20] Koelstra S, Muhl C, Soleymani M, Lee J S, Yazdani A, Ebrahimi T, et al. DEAP: a database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2012, 3(1): 18-31. doi: 10.1109/T-AFFC.2011.15 [21] 陈明. 基于脑电信号的情绪识别 [硕士学位论文], 杭州电子科技大学, 中国, 2017.Chen Ming. EEG-based Emotion Recognition [Master thesis], Hangzhou Dianzi University, China, 2017. [22] 谢佳利. 多尺度熵算法在情感脑电识别中的应用 [硕士学位论文], 燕山大学, 中国, 2016.Xie Jia-Li. Multi-Scale Entropy Algorithm and Its Application in Emotion Recognition [Master thesis], Yanshan University, China, 2016. [23] 李霞, 卢官明, 闫静杰, 张正言. 多模态维度情感预测综述. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(12): 2142-2159Li Xia, Lu Guan-Ming, Yan Jing-Jie, Zhang Zheng-Yan. A survey of dimensional emotion prediction by multimodal cues. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(12): 2142-2159 [24] Bastos-Filho T F, Ferreira A, Atencio A C, Argunan S, Kumar D. Evaluation of feature extraction techniques in emotional state recognition. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Intelligent Human Computer Interaction (IHCI). Kharagpur, India: IEEE, 2012. 1−6 [25] 苏建新. 基于脑电信号的情绪识别研究 [硕士学位论文], 南京邮电大学, 中国, 2015.Su Jian-Xin. Emotion Recognition Research Based on EEG Signal [Master thesis]. Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China, 2015. [26] Li X, Song D W, Zhang P, Yu G L, Hou Y X, Hu B. Emotion recognition from multi-channel EEG data through convolutional recurrent neural network. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bio-medicine (BIBM). Shenzhen, China: IEEE, 2016. 352−359 [27] 李幼军, 黄佳进, 王海渊, 钟宁. 基于SAE 和LSTM RNN的多模态生理信号融合和情感识别研究. 通信学报, 2017, 38(12): 109-120 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017294Li You-Jun, Huang Jia-Jin, Wang Hai-Yuan, Zhong Ning. Study of emotion recognition based on fusion multi-modal bio-signal with SAE and LSTM recurrent neural network. Journal on Communications, 2017, 38(12): 109-120 doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017294 [28] Song T F, Zheng W M, Song P, Cui Z. EEG emotion recognition using dynamical graph convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2020, 11(3): 532−541 [29] Shawky E, El-Khoribi R, Shoman M, Wahby Shalaby M. EEG-Based Emotion Recognition using 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 2018, 9(8): 329-337 -




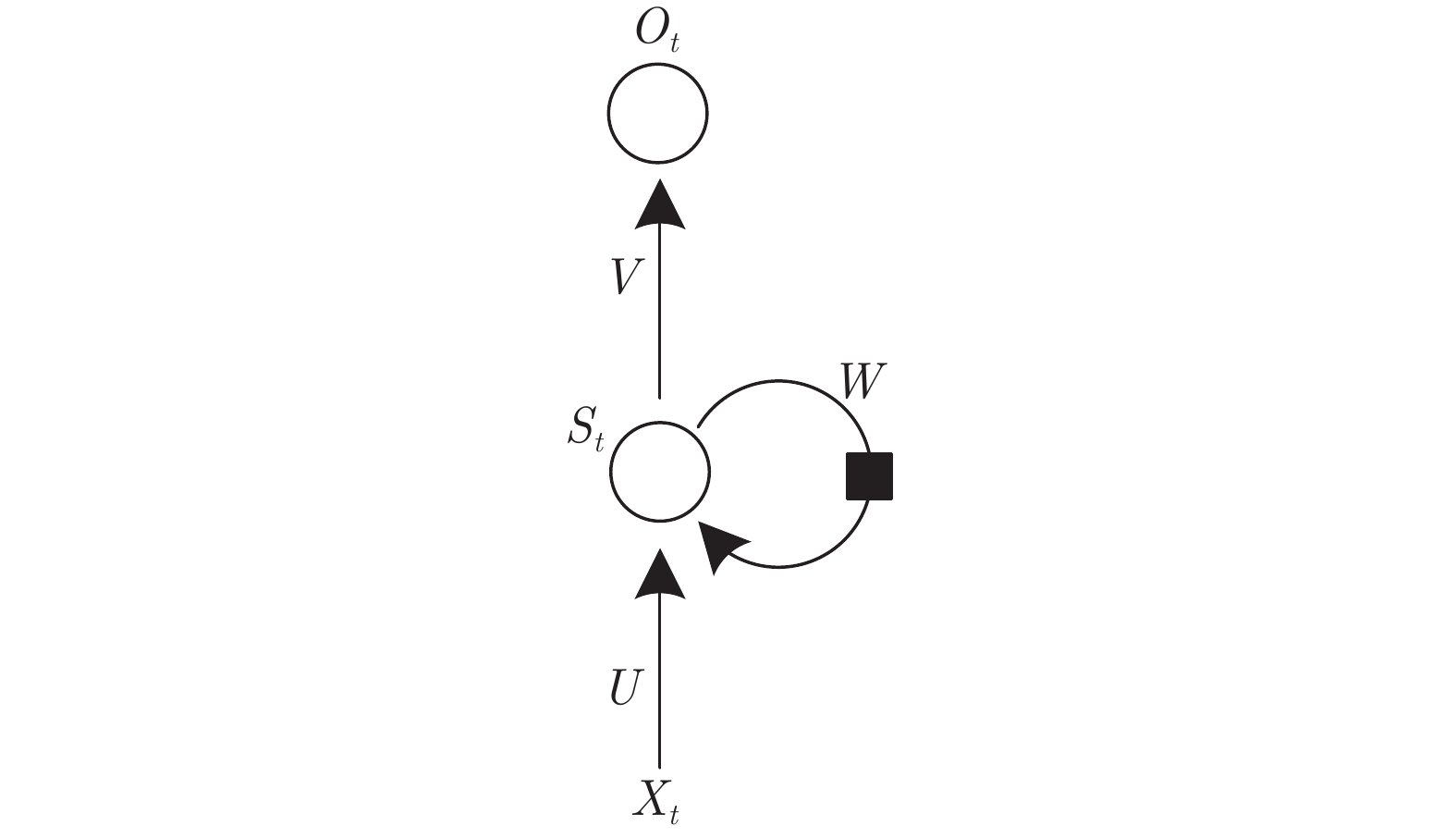
 下载:
下载: