Dynamic Modeling and Reconstruction Based Fault Detection and Location of Train Bearings
-
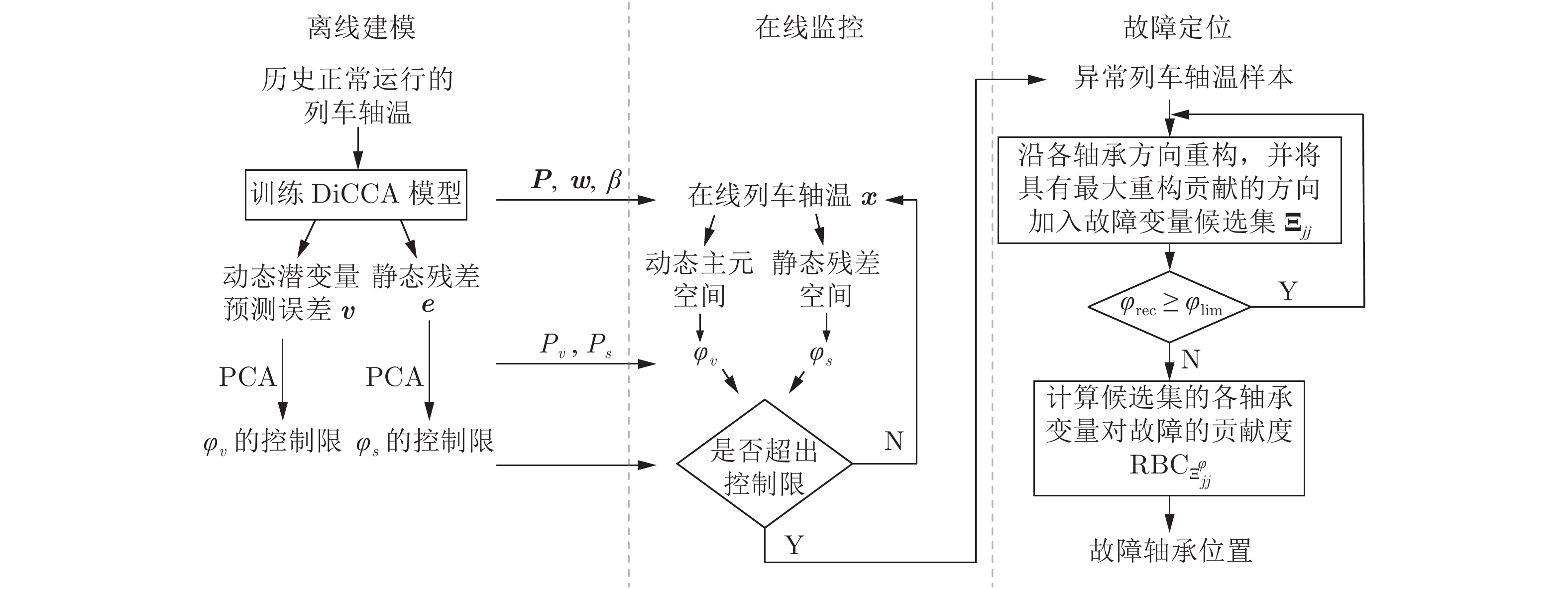
摘要: 列车运行时轴承故障的检测与定位对于列车运行安全与健康维护至关重要. 现有的轴承故障报警系统主要是基于单一轴温变量的规则诊断, 报警不及时. 针对上述问题, 本文结合运行于相似环境和速度的同车多轴轴温的相关性及轴温动态性, 提出了一种数据驱动的基于多轴轴温动态潜结构的列车轴承故障检测与定位方法. 首先, 提出基于动态内在典型相关分析(Dynamic-inner canonical correlation analysis, DiCCA)的列车多轴轴温动态潜结构建模方法; 其次, 利用所建立的模型, 提出基于DiCCA综合指标的列车轴承故障检测方法; 在此基础上, 提出基于DiCCA多向重构的列车轴承故障定位方法. 利用某列车实际运行时的轴温数据进行验证, 结果表明了所提方法的有效性.Abstract: The effective fault detection and diagnosis is necessary for operation safety and maintenance of the trains. The existing bearing alarm system normally applies rule-based method that cannot detect the fault into account before the bearing is heavily damaged. In this paper, taking the correlation and dynamic relation of multi-bearing temperatures, a data-driven dynamic latent structure based train bearing fault detection and diagnosis method is proposed. Firstly, a dynamic-inner canonical correlation analysis (DiCCA) based dynamic latent structure method is applied to extract the cross and auto dynamic relations within multi-dimensional bearing temperatures of the train. Secondly, a DiCCA based combined index is defined for fault detection of dynamic system and applied to detect the operational abnormality of the bearings. Thirdly, a DiCCA based multi-directional reconstruction method is proposed to locate the faulty bearing. Finally, application results using bearing temperature data collected from the practical operation of a train demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 基于规则的列车轴温预警及报警限
Table 1 Rule-based warning and alarm limits oftrain bearings
传感器位置 预警限($^{\circ} {\rm C}$) 报警限($^{\circ} {\rm C}$) 轴箱 100 120 齿轮箱 110 130 电机定子 160 180 电机传动端 110 130 电机非传动端 90 110 表 2 各方法的轴承故障检测结果对比
Table 2 Result comparison among faultdetection methods
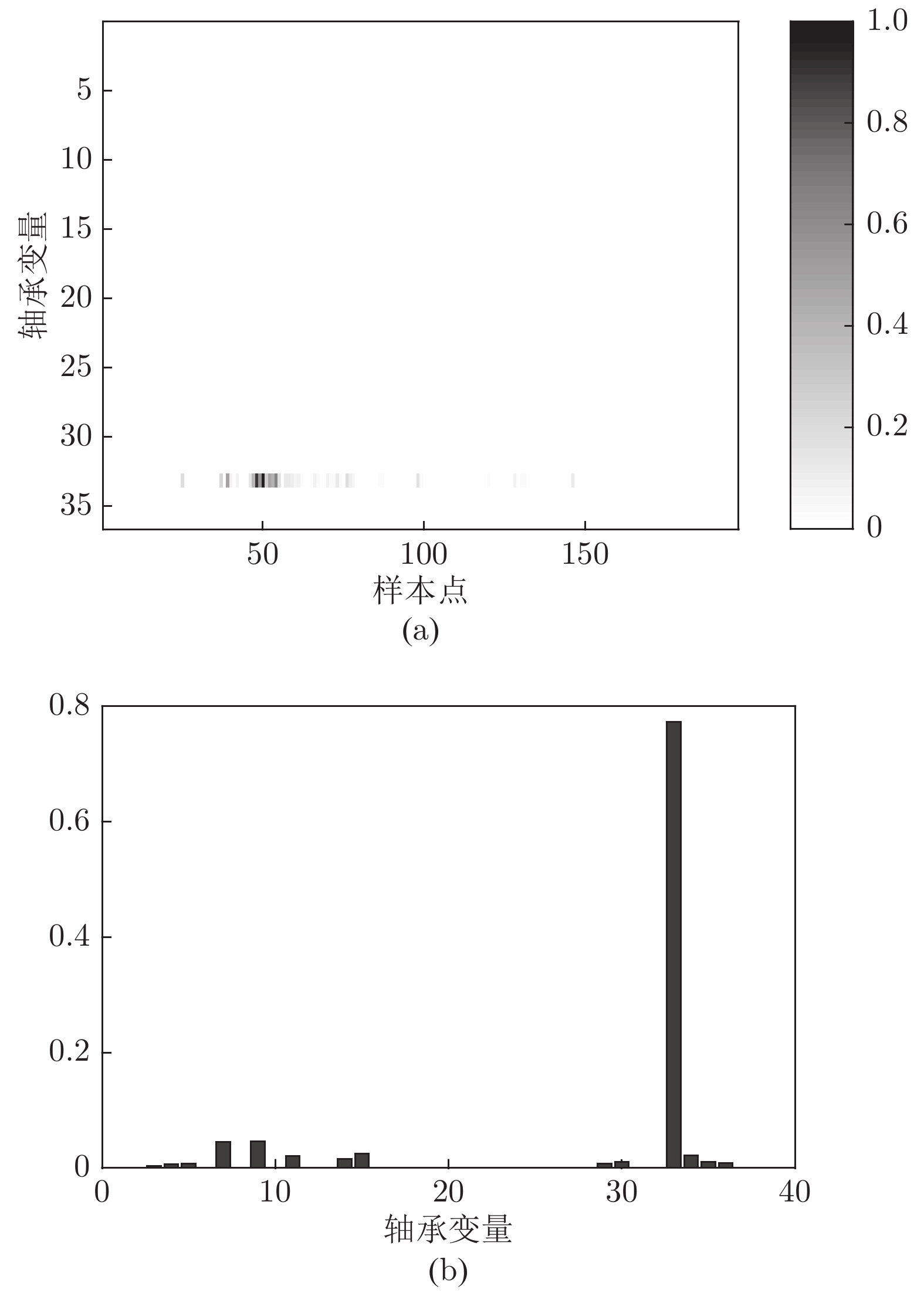
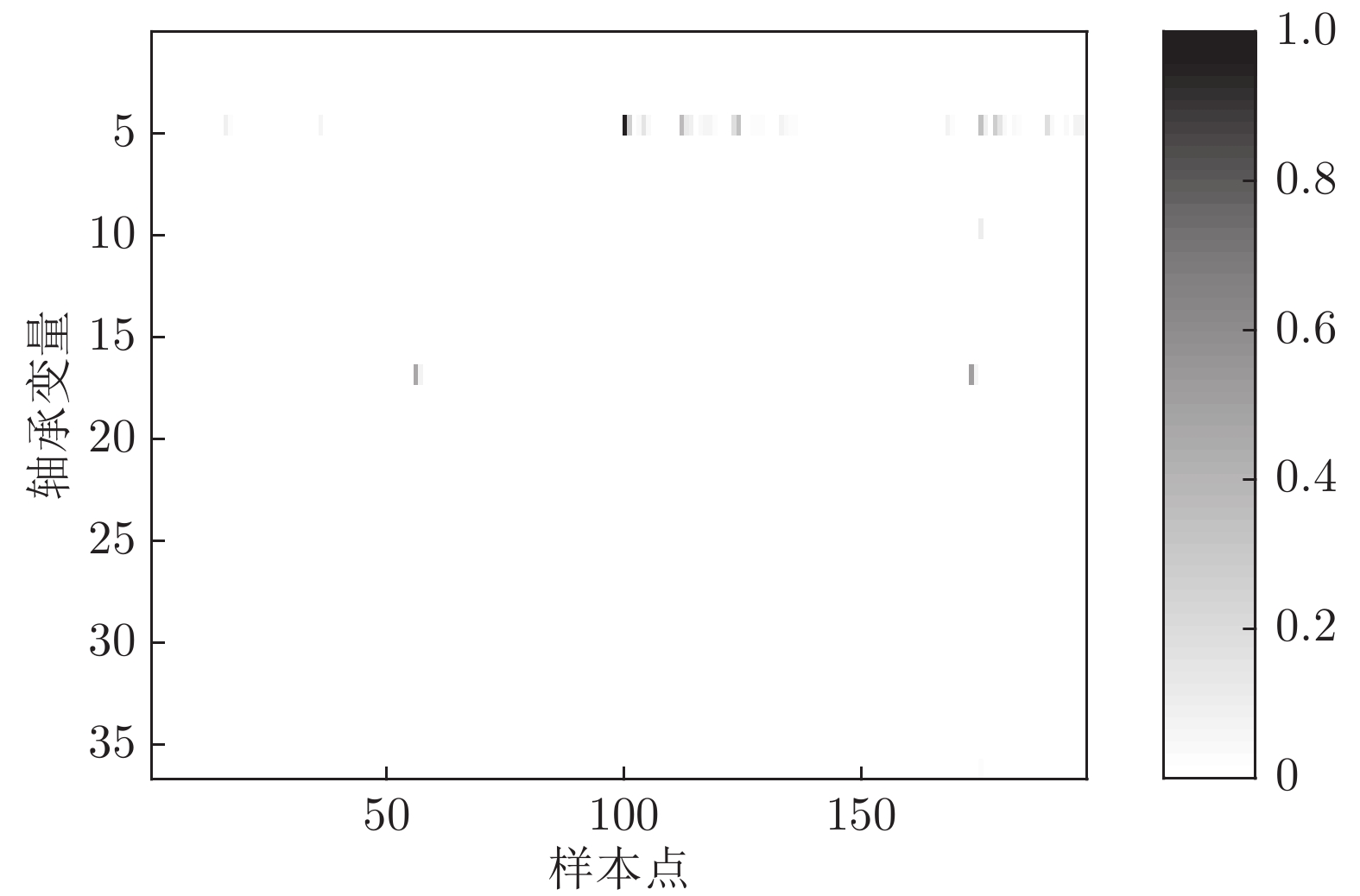
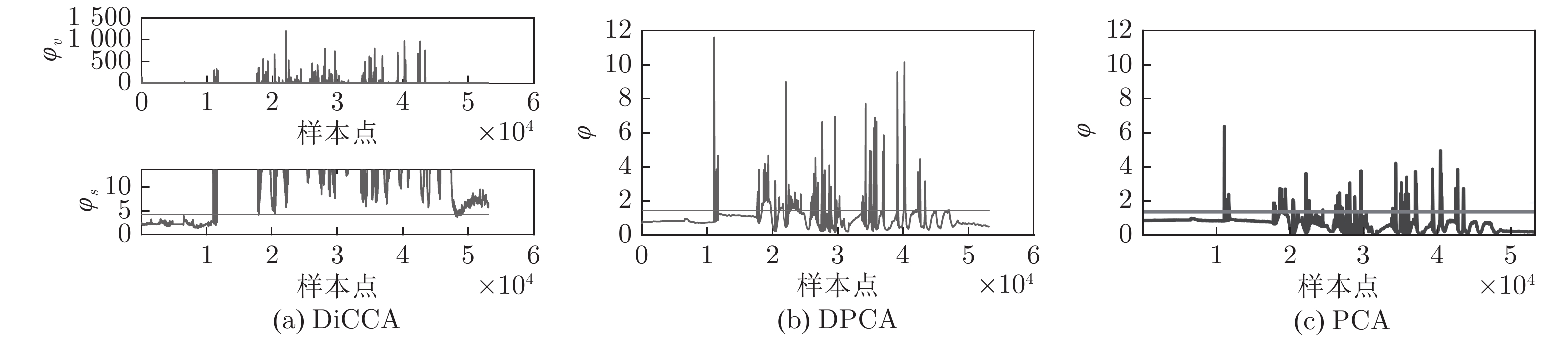
故障案例 开始检测到异常的样本点 规则方法 PCA DPCA DiCCA 电机定子 9 000 8 982 8 235 7 324 电机非传动端 35 930 35 010 35 008 35 007 齿轮箱 19 340 11 042 11 039 11 027 轴箱 7 406 6 821 6 820 6 770 电机传动端 14 200 8 340 8 321 8 292 -
[1] 贾华强, 李利军. 提高我国高铁动车组装备制造水平和运行品质的思考. 中国铁路, 2014, (1): 30−33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-683X.2014.01.0071 Jia Hua-Qiang, Li Li-Jun. Thinking on improving the manufacturing level and operation quality of high speed train EMU in China. Chinese Railways, 2014, (1): 30−33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-683X.2014.01.007 [2] 2 Borghesani P, Pennacchi P, Randall R B, Sawalhi N, Ricci R. Application of cepstrum pre-whitening for the diagnosis of bearing faults under variable speed conditions. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 36(2): 370−384 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.11.001 [3] 3 Nikolaou N G, Antoniadis I A. Rolling element bearing fault diagnosis using wavelet packets. NDT & E International, 2002, 35(3): 197−205 [4] 4 Elbouchikhi E, Choqueuse V, Amirat Y, Benbouzid M E H, Turri S. An efficient Hilbert-Huang transform-based bearing faults detection in induction machines. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2017, 32(2): 401−413 doi: 10.1109/TEC.2017.2661541 [5] 5 Rai V K, Mohanty A R. Bearing fault diagnosis using FFT of intrinsic mode functions in Hilbert-Huang transform. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2007, 21(6): 2607−2615 [6] 6 Van M, Kang H, Shin K. Rolling element bearing fault diagnosis based on non-local means de-noising and empirical mode decomposition. IET Science, Measurement and Technology, 2014, 8(6): 571−578 [7] 7 Lu S L, He Q B, Hu F, Kong F R. Sequential multiscale noise tuning stochastic resonance for train bearing fault diagnosis in an embedded system. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2014, 63(1): 106−116 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2013.2275241 [8] 8 Soualhi A, Medjaher K, Zerhouni N. K A. Bearing health monitoring based on Hilbert-Huang transform, support vector machine, and regression. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2015, 64(1): 52−62 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2014.2330494 [9] 9 Wang Z W, Zhang Q H, Xiong J B, Xiao M, Sun G X, He J. Fault diagnosis of a rolling bearing using wavelet packet denoising and random forests. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(17): 5581−5588 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2726011 [10] 10 Lou X S, Loparo K A. Bearing fault diagnosis based on wavelet transform and fuzzy inference. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2004, 18(5): 1077−1795 doi: 10.1016/S0888-3270(03)00077-3 [11] 11 Henao H, Kia S, and Capolino G. Torsional vibration assessment and gear-fault diagnosis in railway traction system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2011, 58(5): 1707−1717 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2011.2106094 [12] 12 Qin S J. Survey on data-driven industrial process monitoring and diagnosis. Annual Reviews in Control, 2012, 36(2): 220−234 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2012.09.004 [13] 13 Jia R X, W J, Zhou J L. Fault diagnosis of industrial process based on the optimal parametric t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding. Science China Information Sciences, 2019. doi: 10.1007/s11432-018-9807-7 [14] 陈晓露, 王瑞璇, 王晶, 周靖林. 基于混合型判别分析的工业过程监控及故障诊断. 自动化学报, 2019, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c180089Chen Xiao-Lu, Wang Rui-Xuan, Wang Jing, Zhou Jing-Lin. Industrial process monitoring and fault diagnosis based on hybrid discriminant analysis. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c180089 [15] 贾宝柱, 贾志涛, 余培文. 数据驱动的船舶智能故障诊断方法. 控制工程, 2019, 26(10): 1892−189815 Jia Bao-Zhu, Jia Zhi-Tao, Yu Pei-Wen. Data-driven vessel smart fault diagnosis method. Control Engineering of China, 2019, 26(10): 1892−1898 [16] 16 Guo H Y, Cao D P, Chen H, Lv C, Wang H J, Yang S Q. Vehicle dynamic state estimation: state of the art schemes and perspectives. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2018, 5(2): 418−431 [17] 17 Dai C X, Liu Z G, Hu K T, Huang K. Fault diagnosis approach of traction transformers in high-speed railway combining kernel principal component analysis with random forest. IET Electrical Systems in Transportation, 2016, 6(3): 202−206 doi: 10.1049/iet-est.2015.0018 [18] 18 Ji H Q, He X, Shang J, Zhou D H. Incipient fault detection with smoothing techniques in statistical process monitoring. Control Engineering Practice, 2017, 62: 11−21 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2017.03.001 [19] 19 Ku W, Storer R H, Georgakis C. Disturbance detection and isolation by dynamic principal component analysis. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 1995, 30(1): 179−196 doi: 10.1016/0169-7439(95)00076-3 [20] 20 Dong Y N, Qin S J. Dynamic latent variable analytics for process operations and control. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 2018, 114: 69−80 [21] 21 Dong Y N, Qin S J. Dynamic-Inner canonical correlation and causality analysis for high dimensional time series data. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(18): 476−481 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.09.379 [22] 22 Dong Y N, Qin S J. A novel dynamic PCA algorithm for dynamic data modeling and process monitoring. Journal of Process Control, 2018, 67: 1−11 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2017.05.002 [23] 23 Johan A W, Stephen P G, Age K S. Generalized contribution plots in multivariate statistical process monitoring. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2000, 51(1): 95−114 doi: 10.1016/S0169-7439(00)00062-9 [24] Li G, Qin S J, Chai T Y. Multi-directional reconstruction based contributions for root-cause diagnosis of dynamic processes. In: Proceedings of the 2014 American Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA: IEEE, 2014. 3500−3505 [25] 周东华, 纪洪泉, 何潇. 高速列车信息控制系统的故障诊断技术. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(7): 1153−116425 Zhou Dong-Hua, Ji Hong-Quan, He Xiao. Fault diagnosis technology for high speed train information control system. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(7): 1153−1164 [26] 26 Yue H H, Qin S J. Reconstruction-based fault identification using a combined index. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2001, 40(20): 4403−4414 doi: 10.1021/ie000141+ [27] 27 Box, G. Some theorems on quadratic forms applied in the study of analysis of variance problems, I. Effect of inequality of variance in the one-way classification. Ann. Math. Stat, 1954, 25: 290−302 doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177728786 -




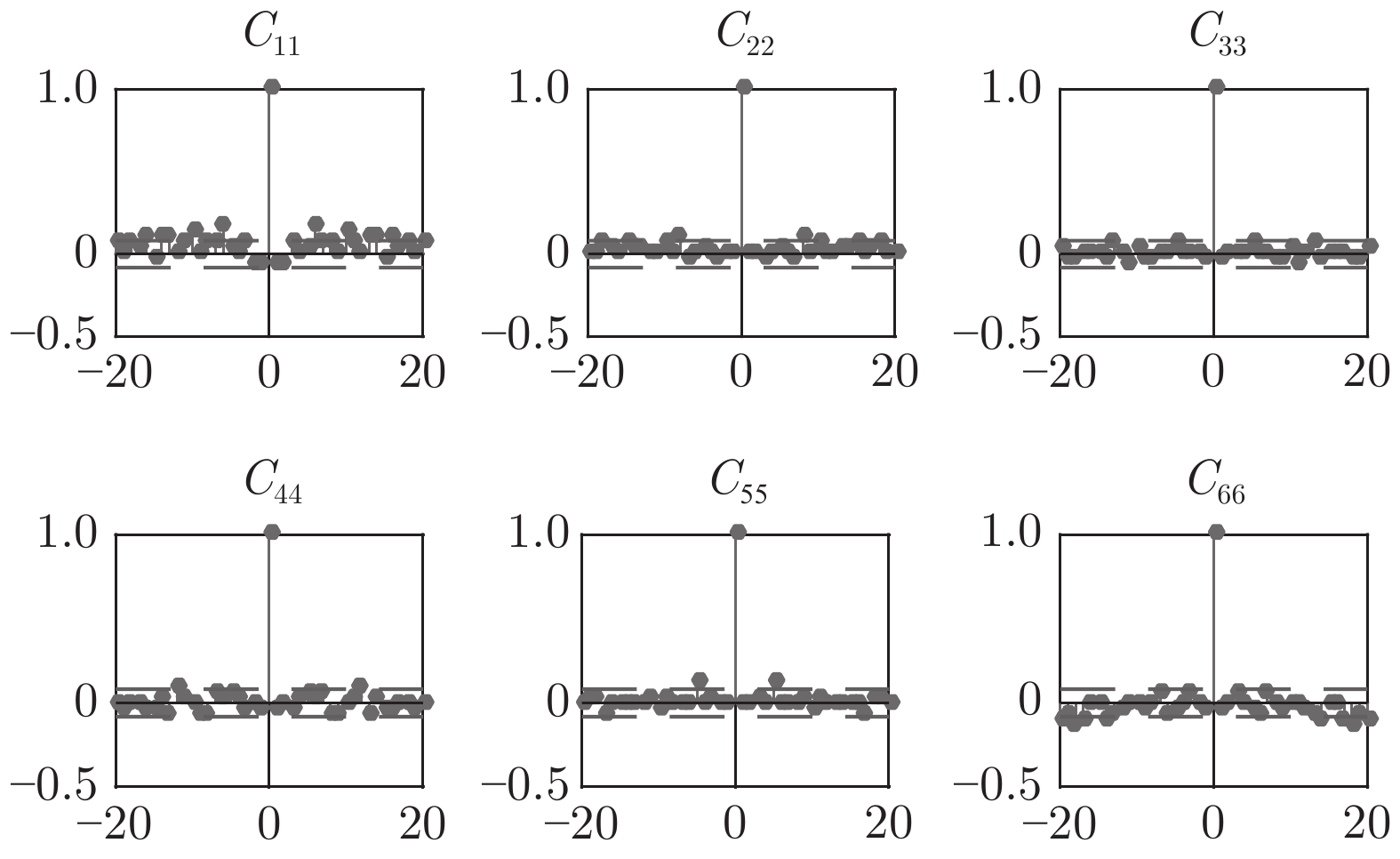


 下载:
下载: