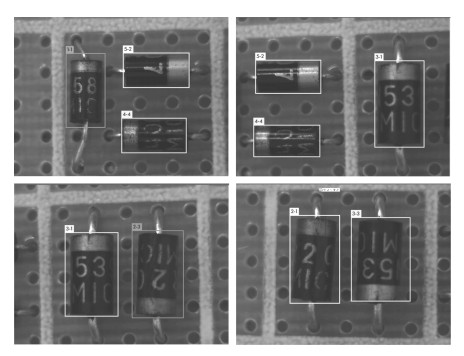
-
摘要:
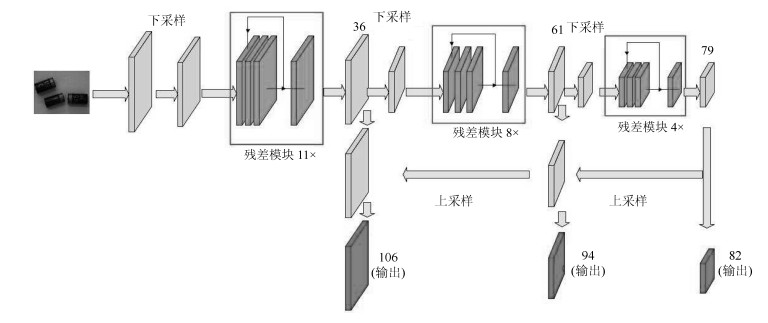
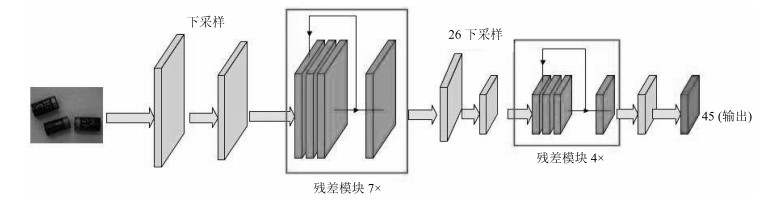
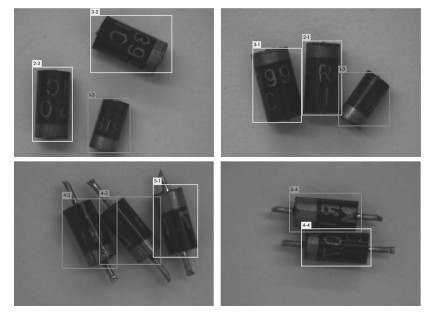
极性电子元器件的类别、方向识别、定位在工业生产、焊接和检测等领域发挥着至关重要的作用. 本文首先将极性电子元器件的方向识别问题转化为一个分类问题, 然后, 采用Faster RCNN (Region convolutional neural network) 与YOLOv3方法实现了极性电子元器件的准确分类、方向识别和精准定位. 实验取得良好的效果, 两种算法的平均准确率(Mean average precision, mAP) 分别达到97.05 %、99.22 %. 此外, 我们通过数据集目标框的长宽分布, 利用K-means算法对Faster RCNN和YOLOv3的Anchor boxes进行了改进设计, 使准确率分别提高了1.16 %、0.1 %, 并提出针对大目标检测的网络结构: YOLOv3-BigObject, 在提高准确率的同时, 将检测单张图片的时间大幅缩减为原来检测时间的一半, 并最终用焊接有元器件的电路板进行检测, 得到了很好的实验结果.
-
关键词:
- 电子制造 /
- 深度学习 /
- 方向识别 /
- 目标检测 /
- Faster RCNN
Abstract:The category, direction identification and positioning of polar electronic components play an important role in the industrial production, welding and inspection. In this paper, we first successfully transform the original problem of directional identification of polar electronic components into a classification problem. Then, the Faster RCNN (region convolutional neural network) and YOLOv3 methods are used to realize the correct classification, direction identification and accurate positioning of the polar electronic components. The experiments validate the effectiveness of our proposed method and the mAP (mean average precision) of the two proposed algorithms can reach 97.05 %, 99.22 %. In addition, we improve the anchor boxes of the Faster RCNN and YOLOv3 by K-means algorithm through the length and width distributions of the target frames of the datasets, the accuracy can be improved by 1.16 %, 0.1 %. We also propose the YOLOv3-BigObject network structure for the large target detection, while improving the accuracy, the cost time for detecting a single picture is also greatly reduced. Finally, the board with the electronic components is chosen to test and good experimental results are obtained.
-
Key words:
- Electronic manufacturing /
- deep learning /
- direction recognition /
- object detection /
- Faster RCNN
-
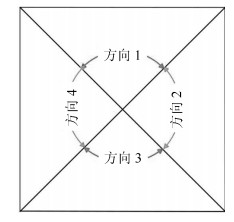
表 1 数据集1包含各类的图片数量和目标数量
Table 1 The dataset 1 contains the number of images and targets of targets in each category
二极管型号 方向1 (上) 方向2 (右) 方向3 (下) 方向4 (左) 总计 型号1 2 775 (2 934) 3 129 (3 300) 2 739 (2 899) 3 264 (3 460) 9 793 (12 593) 型号2 2 833 (2 970) 3 123 (3 315) 2 813 (2 946) 3 180 (3 369) 9 800 (12 600) 型号3 2 840 (2 993) 3 090 (3 309) 2 827 (2 977) 3 108 (3 321) 9 800 (12 600) 总计 7 032 (8 897) 7 570 (9 924) 6 975 (8 822) 7 676 (10 150) 14 000 (37 793) 表 2 数据集2包含各类的图片数量和目标数量
Table 2 The dataset 2 contains the number of images and targets of targets in each category
二极管型号 方向1 (上) 方向2 (右) 方向3 (下) 方向4 (左) 总计 型号1 1 278 (1 365) 1 349 (1 448) 1 322 (1 461) 1 329 (1 441) 4 949 (5 714) 型号2 1 282 (1 380) 1 380 (1 467) 1 307 (1 400) 1 344 (1 430) 4 970 (5 677) 总计 2 155 (2 745) 2 289 (2 915) 2 214 (2 861) 2 673 (2 871) 5 691 (11 391) 表 3 数据集1的实验结果
Table 3 Experimental result of dataset 1
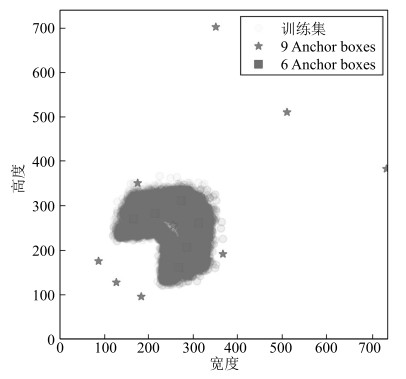
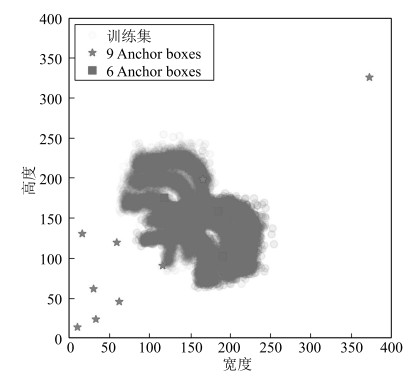
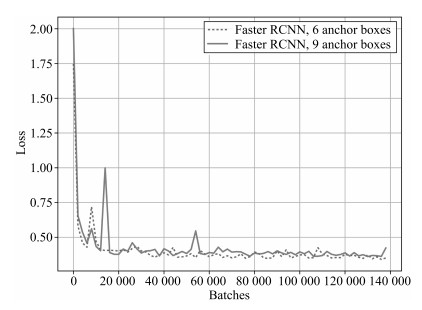
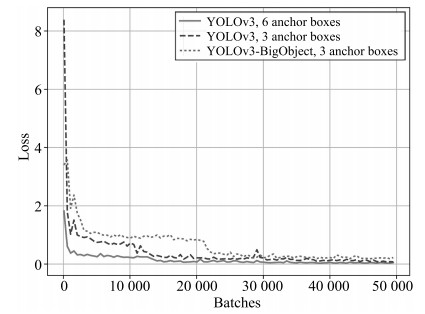
Backbone Anchor boxes Anchor boxes与训练集的平均IoU mAP (%) 测试速度(s) Faster RCNN VGG-16 9 0.7037 93.77 - Faster RCNN VGG-16 6 0.8577 94.95 - Faster RCNN ResNet101 9 0.7037 97.05 - Faster RCNN ResNet101 6 0.8577 97.36 - YOLOv3 Darknet-53 9 0.5728 99.22 - YOLOv3 Darknet-53 3 0.7362 99.31 0.0217 YOLOv3-BigObject - 3 0.7362 99.44 0.0118 表 4 数据集1和数据集2的实验结果
Table 4 Experimental result of datasets 1 and 2
Backbone Anchor boxes Anchor boxes与训练集的平均IoU mAP (%) 测试速度(s) Faster RCNN ResNet101 9 0.6294 97.28 - Faster RCNN ResNet101 6 0.8000 97.53 - FPN ResNet101 9+ - 98.70 - SSD ResNet101 9+ - 76.25 - YOLOv3 Darknet-53 9 0.4476 99.26 - YOLOv3-BigObject - 3 0.6645 99.20 0.0118 -
[1] 杜思思, 李卓球, 张雪峰. 电子元器件图像外形特征的精确定位技术研究. 武汉理工大学学报, 2008, 30(3): 359-362 doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1007-144X.2008.03.007Du Si-Si, Li Zhuo-Qiu, Zhang Xue-Feng. Research on accurate positioning technology of image features of electronic components. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2008, 30(3): 359-362 doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1007-144X.2008.03.007 [2] 李文英, 曹斌, 曹春水, 黄永祯. 一种基于深度学习的青铜器铭文识别方法. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(11): 2023-2030 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c180152Li Wen-Ying, Cao Bin, Cao Chun-Shui, Huang Yong-Zhen. A deep learning based method for bronze inscription recognition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(11): 2023-2030. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c180152 [3] 罗建豪, 吴建鑫. 基于深度卷积特征的细粒度图像分类研究综述. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1306-1318 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160425Luo Jian-Hao, Wu Jian-Xin. A survey on fine-grained image categorization using deep convolutional features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1306-1318 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160425 [4] 田娟秀, 刘国才, 谷珊珊, 鞠忠建, 刘劲光, 顾冬冬. 医学图像分析深度学习方法研究与挑战. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 401-424 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170153Tian Juan-Xiu, Liu Guo-Cai, Gu Shan-Shan, Ju Zhong-Jian, Liu Jin-Guang, Gu Dong-Dong. Deep learning in medical image analysis and its challenges. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 401-424 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170153 [5] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Spain, 2012. 1097-1105 [6] 郑文博, 王坤峰, 王飞跃. 基于贝叶斯生成对抗网络的背景消减算法. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(5): 878-890 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170562Zheng Wen-Bo, Wang Kun-Feng, Wang Fei-Yue. Background subtraction algorithm with bayesian generative adversarial networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(5): 878-890 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170562 [7] 张慧, 王坤峰, 王飞跃. 深度学习在目标视觉检测中的应用进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1289-1305 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160822Zhang Hui, Wang Kun-Feng, Wang Fei-Yue. Advances and perspectives on applications of deep learning in visual object detection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1289-1305 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160822 [8] 于进勇, 丁鹏程, 王超. 卷积神经网络在目标检测中的应用综述. 计算机科学, 2018, 45(Z11): 17-26 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJA2018S2003.htmYu Jin-Yong, Ding Peng-Cheng, Wang Chao. Overview: Application of convolution neural network in object detection. Computer Science, 2018, 45(Z11): 17-26 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJA2018S2003.htm [9] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Jitendra M. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 580-587 [10] Uijlings J R R, Van De Sande K E A, Gevers T, Smeulders A W M. Selective search for object recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 104(2): 154-171 doi: 10.1007/s11263-013-0620-5 [11] Zitnick C L, Dollár P. Edge boxes: Locating object proposals from edges. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 391-405 [12] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognitions[Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2952, April 10, 2015 [13] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770-778 [14] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 91-99 [15] Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 3431-3440 [16] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1440-1448 [17] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C Y, Berg A C. SSD: Single shot multibox detector. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag, 2016. 21-37 [18] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779-788 [19] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 7263-7271 [20] Redmon J, Farhadi A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement[Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767, April 8, 2018 [21] 杜思思, 单忠德, 黄樟灿, 刘红旗, 刘世立. 电子元器件自动分类的算法研究与系统开发. 机电产品开发与创新, 2008, 21(6): 133- 135 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDCP200806059.htmDu Si-Si, San Zhong-De, Huang Zhang-Can, Liu Hong-Qi, Liu Shi-Li. Algorithm research and system development for automatic classification of electronic components. Mechanical and Electrical Product Development and Innovation, 2008, 21(6): 133-135 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDCP200806059.htm [22] 陈翔, 俞建定, 陈晓爱, 翟影. 基于卷积神经网络的电子元器件分类研究. 无线通信技术, 2018, 27(2): 7-12 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WYWT201802002.htmChen Xiang, Yu Jian-Ding, Chen Xiao-Ai, Zhai Ying. Classification of electronic components based on convolutional neural networks. Wireless Communication Technology, 2018, 27(2): 7-12 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WYWT201802002.htm [23] Rumelhart D E, Hinton G E, Williams R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 1986, 323(6088): 533-536 doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [24] Hinton G E, Srivastava N, Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Salakhutdinov R R. Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1207.0580, July 3, 2012 [25] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, He K M, Hariharan B, Belongie S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2117-2125 -




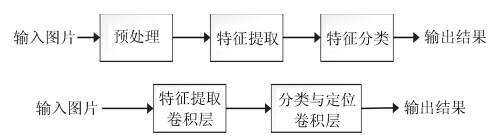
 下载:
下载: