Model Free Adaptive Control of Molten Iron Quality Based on Multi-parameter Sensitivity Analysis and GA Optimization
-
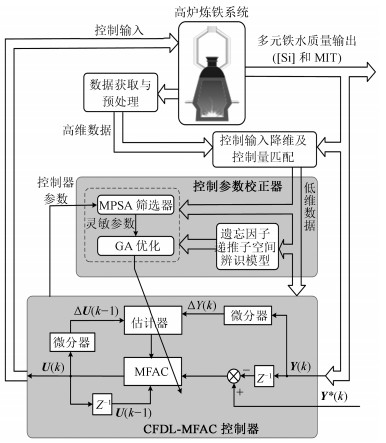
摘要: 铁水硅含量(化学热)和铁水温度(物理热)是高炉炼铁过程最重要的铁水质量指标, 其建模与控制对于整个高炉炼铁过程的运行优化意义重大. 针对高炉炼铁过程极复杂动态特性以及铁水质量难以进行常规机理建模与控制的难题, 基于直接数据驱动控制思想, 提出一种基于多参数灵敏度分析与大规模变异遗传参数优化的高炉铁水质量无模型自适应控制方法. 首先, 基于紧格式动态线性化(Compact form dynamic linearization, CFDL)无模型自适应控制(Model free adaptive control, MFAC)技术确定铁水质量的多变量数据驱动控制器结构; 然后, 针对CFDL-MFAC众多可调参数对控制器性能影响大, 同时对众多参数整体优化非常耗时且效果不理想的问题, 基于多参数灵敏度分析(Multi-parameter sensitivity analysis, MPSA)技术, 提出基于大规模变异与精英局部搜索遗传优化的CFDL-MFAC控制器参数整定方法; 最后, 将参数整定后的CFDL-MFAC控制器应用到高炉炼铁过程多元铁水质量控制, 并与基于递推子空间辨识的数据驱动预测控制进行比较研究, 验证所提控制方法的有效性和先进性.Abstract: The silicon content (Chemical heat) and the molten iron temperature (Physical heat) are two important molten iron quality indices of blast furnace ironmaking process, whose modeling and control is of great importance to the operation and optimization of the whole blast furnace ironmaking process. Considering the extremely complicated dynamic characteristics and the puzzle of conventional mechanism modeling and control of the blast furnace ironmaking process, a multi-parameter sensitivity analysis (MPSA) and large-scale mutation genetic parameter optimization based blast furnace molten iron quality model free adaptive control method is proposed based on direct data-driven control theory. First, a multivariable data-driven controller structure for molten iron quality is determined based on compact form dynamic linearization (CFDL) based model free adaptive control (MFAC) technique. Then, considering that it is very time-consuming and less effective to adjust all the CFDL-MFAC adjustable parameters, which have a high influence on the controller performance, a CFDL-MFAC controller parameter tuning method based on large-scale mutation and elite local search genetic optimization is proposed. Finally, applied the parameter-tuned CFDL-MFAC controller into the control of multivariate molten iron quality in the blast furnace ironmaking process and compare it to data-driven predictive control based on recursive subspace identification to verify the effectiveness and advancement of the proposed control method.
-
Key words:
- Data-driven control /
- model free adaptive control /
- multi-parameter sensitivity analysis /
- blast furnace ironmaking /
- molten iron quality /
- genetic algorithm /
- large-scale mutation
1) 本文责任编委 伍洲 -
表 1 输入输出灰色关联系数
Table 1 Grey correlation coefficients between input and output
[Si] MIT 压差 0.9978 0.9976 设定喷煤量 0.9998 0.9974 表 2 CFDL-MFAC参数表
Table 2 Parameters of CFDL-MFAC
参数 含义 取值下限 取值上限 DS 取值 累计频率分布曲线 $ \lambda $ 惩罚控制输入量过大变化的权重因子 0 20 0.9987 0.5 
$ \mu $ 惩罚PJM估计值过大变化的权重因子 0 20 0.9899 0.5 
$ \eta $ 伪雅可比矩阵步长因子 0 2 0.9981 0.5 
$ \rho $ 控制输入步长因子 0 1 0.6172 0.9999 
$ \alpha $ 伪雅可比矩阵取值限定参数 1 20 0.9993 1.5 
$ b_1 $ 伪雅可比矩阵取值限定参数 0 20 0.9994 0.52 
$ b_2 $ 伪雅可比矩阵取值限定参数 0 1 000 0.9990 0.8 
$ \varphi _{11} $ 伪雅可比矩阵初值 $ - $20 20 0.4975 0.5143 
$ \varphi _{12} $ 伪雅可比矩阵初值 $ - $20 20 0.4840 $ - $1.1435 
$ \varphi _{21} $ 伪雅可比矩阵初值 $ - $20 20 0.0795 1.1436 
$ \varphi _{22} $ 伪雅可比矩阵初值 $ - $20 20 0.7548 0.5144 
表 3 GA参数设定
Table 3 Set value of GA parameters
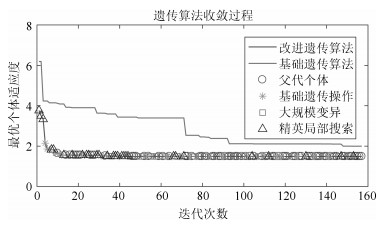
参数 参数含义 取值 $ g_e $ 最大遗传代数 300 $ r $ 种群规模 50 $ g_b $ 染色体变异概率 0.0125 $ g_s $ 大规模变异概率 0.25 $ g_j $ 染色体交叉概率 0.7 $ m_b $ 变异算子精度 20 $ T $ Metropolis准则温度参数 1 $ \alpha _T $ Metropolis准则温度衰减系数 0.5 表 4 控制器性能对比
Table 4 Control performance comparision
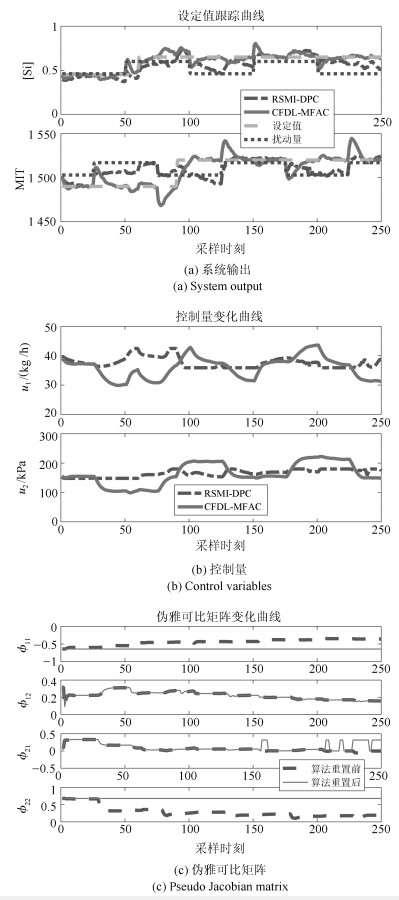
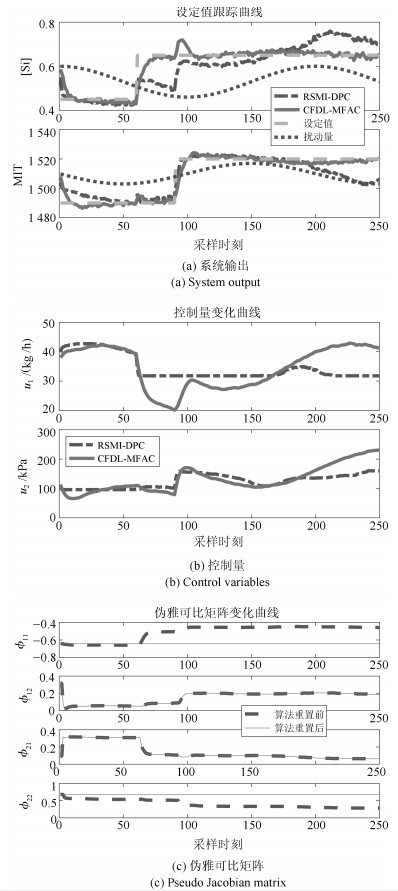
模型 CFDL-MFAC RSMI-DPC 测试样本数 250 250 平均控制量更新时间(s) 0.000019 0.0513 方波扰动下[Si]含量RMSE (%) 0.0364 0.0792 方波扰动下MIT RMSE (℃) 6.3768 9.6553 正弦扰动下[Si]含量RMSE (%) 0.0229 0.0524 正弦扰动下MIT RMSE (℃) 3.0290 5.3546 -
[1] 宋贺达, 周平, 王宏, 柴天佑. 高炉炼铁过程多元铁水质量非线性子空间建模及应用. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(21): 1664-1679 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150819Song He-Da, Zhou Ping, Wang Hong, Chai Tian-You. Nonlinear subspace modeling of multivariate molten iron quality in blast furnace ironmaking and its application. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(21): 1664-1679 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150819 [2] Zhou P, Lv Y B, Wang H, Chai T Y. Data-driven robust RVFLNs modeling of a blast furnace iron-making process using Cauchy distribution weighted M-estimation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(9): 7141-7151 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2686369 [3] 范广权. 高炉炼铁操作. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2008, 61-65Fan Guang-Quan. Blast Furnace Ironmaking Operation. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2008, 61-65 [4] 储满生, 王宏涛, 柳政根, 唐珏. 高炉炼铁过程数学模拟的研究进展. 钢铁, 2014, 49(11): 1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6764.2014.11.001Chu Man-Sheng, Wang Hong-Tao, Liu Zheng-Gen, Tang Jue. Research progress on mathematical modeling of blast furnace ironmaking process. Iron and Steel, 2014, 49(11): 1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6764.2014.11.001 [5] 蒋朝辉, 董梦林, 桂卫华, 阳春华, 谢永芳. 基于Bootstrap的高炉铁水硅含量二维预报. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(5): 715-723 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150574Jiang Zhao-Hui, Dong Meng-Lin, Gui Wei-Hua, Yang Chun-Hua, Xie Yong-Fang. Two-dimensional prediction for silicon content of hot metal of blast furnace based on bootstrap. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5): 715-723 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150574 [6] Cui G M, Jiang Z G, Liu P L, Chen Z H, Shi L. Prediction of blast furnace temperature based on multi-information fusion of image and data. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Chinese Automation Congress, Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2018. 2317-2322 [7] 周平, 张丽, 李温鹏, 戴鹏, 柴天佑. 集成自编码与PCA的高炉多元铁水质量随机权神经网络建模. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1799-1811 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170299Zhou Ping, Zhang Li, Li Wen-Peng, Dai Peng, Chai Tian-You. Autoencoder and PCA based RVFLNs modeling for multivariate molten iron quality in blast furnace ironmaking. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018. 44(10): 1799-1811 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170299 [8] Zhang L, Zhou P, Song H D, Yuan M, Chai T Y. Multivariable dynamic modeling for molten iron quality using incremental random vector functional-link networks. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2016, 23(11): 1151-1159 doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30170-4 [9] Zhou P, Guo D W, Wang H, Chai T Y. Data-driven robust M-LS-SVR-based NARX modeling for estimation and control of molten iron quality indices in blast furnace ironmaking. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018. 29(9): 4007-4021 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2749412 [10] Liu Y, Gao Z. Enhanced just-in-time modelling for online quality prediction in BF ironmaking. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2015, 42(5): 321-330 http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000038813372010_076b.html [11] Zeng J S, Gao C H, Su H Y. Data-driven predictive control for blast furnace ironmaking process. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2010, 34(11): 1854-1862 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959152410001691 [12] Hou Z S, Huang W H. The model-free learning adaptive control of a class of SISO nonlinear systems. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference. Albuquerque, USA: IEEE, 1997. 343-344 [13] Hou Z S, Wang Z. From model-based control to data-driven control: Survey, classification and perspective. Information Sciences, 2013, 235(235): 3-35 http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Zhong_Sheng_Hou/publication/245568640_On_Data-driven_Control_Theory_the_State_of_the_Art_and_Perspective/links/56d2e5c308aeb52500d1706c.pdf [14] Sala A. Integrating virtual reference feedback tuning into a unified closed-loop identification framework. Automatica, 2007, 43(1): 178-183 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.08.005 [15] Hjalmarsson H. From experiment design to closed-loop control. Automatica, 2005, 41(3): 393-438 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2004.11.021 [16] Safonov M G, Tsao T C. The unfalsified control concept: a direct path from experiment to controller. Feedback Control, Nonlinear Systems, and Complexity. Birlin: Springer-Verlag, 1995. 196-214 [17] Karimi A, Miškovi L, Bonvin D. Iterative correlation-based controller tuning with application to a magnetic suspension system. Control Engineering Practice. , 2003, 11(9): 1069-1078 doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(02)00191-0 [18] Hou Z S, Liu S D, Tian T T. Lazy-learning-based data-driven model-free adaptive predictive control for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks Learning System, 2017, 28(8): 1914-1928 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2561702 [19] 侯忠生. 非线性系统参数辨识自适应控制及无模型学习自适应控制[博士学位论文], 东北大学, 中国, 1994Hou Zhong-Sheng. The Parameter Identiflcation, Adaptive Control and Model Free Learning Adaptive Control for Nonlinear Systems [Ph. D. Dissertation], Northeastern University, China, 1994 [20] Hou Z S, Jin S T. Data-driven model-free adaptive control for a class of MIMO nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(12): 2173-2188 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2176141 [21] 侯忠生, 金尚泰. 无模型自适应控制: 理论与应用. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013. 34-135Hou Zhong-Sheng, Jin Shang-Tai. Model Free Adaptive Control: Theory and Application. Beijing: Science Press, 2013. 34-135 [22] Fox R L, Kapoor M P. Rates of change of eigenvalues and eigenvectors. AIAA Journal, 1968, 6(12): 2426-2429 doi: 10.2514/3.5008 [23] Van B H. Theory of adjoint structures. AIAA Journal, 1976, 14(7): 977-979 doi: 10.2514/3.7174 [24] McCuen R H. Modeling Hydrologic Change: Statistical Methods. Boca Raton: CRC press, 2003. 333-365 [25] Choi J, Harvey J W, Conklin M H. Use of multi-parameter sensitivity analysis to determine relative importance of factors influencing natural attenuation of mining contaminants. In: Proceedings of the Toxic Substances Hydrology Program Meeting. Charleston, USA, 1999. 185-192 [26] 曲双石, 王会娟. Monte Carlo方法及其应用. 统计教育, 2009, (1): 45-55 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJJY200901013.htmQu Shuang-Shi, Wang Hui-Juan. Monte Carlo method and its application. Statistical Thinktank, 2009, (1): 45-55 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJJY200901013.htm [27] 王纲胜, 夏军, 陈军锋. 模型多参数灵敏度与不确定性分析. 地理研究, 2010, 29(2): 263-270 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ201002009.htmWang Gang-Sheng, Xia Jun, Chen Jun-Feng. A multi-parameter sensitivity and uncertainty analysis method to evaluate relative importance of parameters and model performance. Geographical Research, 2010, 29(2): 263-270 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLYJ201002009.htm [28] Zhou P, Dai P, Song H D, Chai T Y. Data-driven recursive subspace identification based online modelling for prediction and control of molten iron quality in blast furnace ironmaking. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2017, 11(14): 2343-2351 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8025896/ [29] Baskar S, Subbaraj P, Rao M V C, Tamilselvi S. Genetic algorithms solution to generator maintenance scheduling with modified genetic operators. IEE Proceedings of Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 2003, 150(1): 56-60 doi: 10.1049/ip-gtd:20030073 [30] Goldberg D E. Real-coded genetic algorithms, virtual alphabets and Blocking. Complex Systems, 1990, 5(2): 139-167 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download;jsessionid=078DE40DE2031131376BBE4F605F2292?doi=10.1.1.52.9880&rep=rep1&type=pdf [31] 王小平, 曹立明. 遗传算法—理论、应用与软件实现. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 1998. 48Wang Xiao-Ping, Chao Li-Ming. Genetic Algorithms——Theory, Application and Software Implementation. Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press, 1998. 48 [32] 王宏刚, 曾建潮. 基于Metropolis判别准则的遗传算法. 控制与决策, 1998, (2): 181-184 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.1998.02.021Wang Hong-Gang, Zeng Jian-Chao. Metropolis Discriminant Criterion based Genetic Algorithm. Control and Decision, 1998, (2): 181-184 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.1998.02.021 [33] Liu S F, Cai H, Cao Y, Yang Y J. Advance in grey incidence analysis modeling. IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 2011, 33(8): 1886-1890 http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sifeng_Liu/publication/225139235_The_Model_of_New_Grey_Incidence_and_Its_Application/links/0a85e53a8b7ad47cfb000000 -





 下载:
下载: