A Semi-supervised Encoder Generative Adversarial Networks Model for Image Classification
-
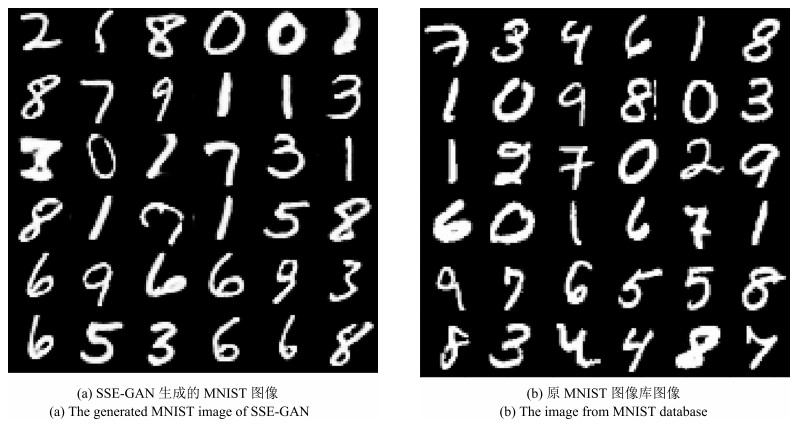
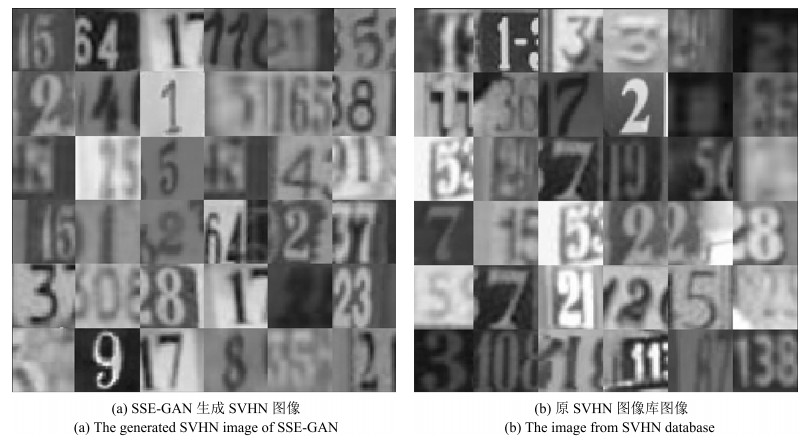
摘要: 在实际应用中, 为分类模型提供大量的人工标签越来越困难, 因此, 近几年基于半监督的图像分类问题获得了越来越多的关注.而大量实验表明, 在生成对抗网络(Generative adversarial network, GANs)的训练过程中, 引入少量的标签数据能获得更好的分类效果, 但在该类模型的框架中并没有考虑用于提取图像特征的结构, 为了进一步利用其模型的学习能力, 本文提出一种新的半监督分类模型.该模型在原生成对抗网络模型中添加了一个编码器结构, 用于直接提取图像特征, 并构造了一种新的半监督训练方式, 获得了突出的分类效果.本模型分别在标准的手写体识别数据库MNIST、街牌号数据库SVHN和自然图像数据库CIFAR-10上完成了数值实验, 并与其他半监督模型进行了对比, 结果表明本文所提模型在使用少量带标数据情况下得到了更高的分类精度.Abstract: The semi-supervised image classification task has attracted more and more attention recently owing to the problem that adequate labeled data is hard to acquire from industrial applications. Meanwhile, considerable works demonstrate that the improved generative adversarial networks (GANs) can achieve great classification performance with only few labeled images. Intuitively, GAN is a generative model, there is no semantic feature extractor in the main framework. In order to further utilize the ability of GANs, we propose to add an encoder in the framework to extract features of images directly, and simultaneously to use a new semi-supervised training method to train this new image classification model. The classification results of experiments have shown the state-of-the-art accuracy performance in semi-supervised MNIST, SVHN and CIFAR-10.
-
Key words:
- Deep learning /
- generative adversarial network (GAN) /
- image classification /
- semi-supervised learning
1) 本文责任编委 金连文 -
表 1 MNIST数据库上不同数量带标数据的半监督训练分类准确率
Table 1 Using different number of labeled data when semi-supervised training on MNIST
表 2 SVHN数据库上不同数量带标数据的半监督训练分类准确率
Table 2 Using different number of labeled data when semi-supervised training on SVHN
表 3 CIFAR-10数据库上不同数量带标数据的半监督训练分类准确率
Table 3 Using different number of labeled data when semi-supervised training on CIFAR-10
-
[1] 张号逵, 李映, 姜晔楠.深度学习在高光谱图像分类领域的研究现状与展望.自动化学报, 2018, 44(6): 961-977 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170190Zhang Hao-Kui, Li Ying, Jiang Ye-Nan. Deep learning for hyperspectral imagery classification: the state of the art and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(6): 961-977 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170190 [2] Suddarth S C, Kergosien Y L. Rule-injection hints as a means of improving network performance and learning time. Neural Networks. EURASIP 1990, 1990. 120-129 [3] 李敏, 禹龙, 田生伟, 吐尔根·依布拉音, 赵建国.基于深度学习的维吾尔语名词短语指代消解.自动化学报, 2017, 43(11): 1984- 1992 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160330Li Min, Yu Long, Tian Sheng-Wei, Ibrahim T, Zhao Jian-Guo. Coreference resolution of uyghur noun phrases based on deep learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(11): 1984-1992 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160330 [4] 王坤峰, 左旺孟, 谭营, 秦涛, 李力, 王飞跃.生成式对抗网络:从生成数据到创造智能.自动化学报, 2018, 44(5): 769-774 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.y000001Wang Kun-Feng, Zuo Wang-Meng, Tan Ying, Qin Tao, Li Li, Wang Fei-Yue. Generative adversarial networks: from generating data to creating intelligence. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(5): 769-774 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.y000001 [5] Dosovitskiy A, Fischer P, Springenberg J T, Riedmiller M, Brox T. Discriminative unsupervised feature learning with exemplar convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(9): 1734-1747 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2496141 [6] Rasmus A, Valpola H, Honkala M, Berglund M, Raiko T. Semi-supervised learning with ladder networks. arXiv: 1507. 02672, 2015. [7] Miyato T, Maeda S, Ishii S, Koyama M. Virtual adversarial training: a regularization method for supervised and semi-supervised learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018. 2858821 [8] Kingma D P, Rezende D J, Mohamed S, Welling M. Semi-supervised learning with deep generative models. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Neural Information Processing Systems. Massachusetts, USA: MIT Press, 2014. 3581-3589 [9] Springenberg J T. Unsupervised and semi-supervised learning with categorical generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1511.06390, 2015. [10] Salimans T, Goodfellow I, Zaremba W, Cheung V, Radford A, Chen X. Improved techniques for training GANs. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Neural Information Processing Systems. Massachusetts, USA: MIT Press, 2016. 1-10 [11] Saatchi Y, Wilson A G. Bayesian GAN. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Neural Information Processing Systems. Massachusetts, USA: MIT Press, 2017. 1-16 [12] Radford A, Metz L, Chintala S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Learning Representations. Piscataway, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1-16 [13] Donahue J, Krähenbühl P, Darrell T. Adversarial feature learning. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Learning Representations. Piscataway, USA: IEEE, 2017. 111-128 [14] Tenenbaum J B, de Silva V, Langford J C. A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2319-2323 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2319 [15] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Machine Learning. Piscataway, USA: IEEE, 2015. 11-21 [16] Zheng L, Wang S J, Tian L, He F, Liu Z Q, Tian Q. Query-adaptive late fusion for image search and person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1741-1750 [17] LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324 doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [18] Netzer Y, Wang T, Coates A, Bissacco A, Wu B, Na A Y. Reading digits in natural images with unsupervised feature learning. In: Proceedings of the 2011 Neural Information Processing Systems. Massachusetts, USA: MIT Press, 2011. 5-16 [19] Krizhevsky A. Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada, 2009. [20] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Neural Information Processing Systems. Massachusetts, USA: MIT Press, 2012. 1106-1114 [21] Dumoulin V, Belghazi I, Poole B, Mastropietro O, Lamb A, Arjovsky M, et al. Adversarially Learned Inference. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Learning Representations. Piscataway, USA: IEEE, 2017. 111-128 [22] Kilinc O, Uysal I. GAR: an efficient and scalable graph-based activity regularization for semi-supervised learning. Neurocomputing, 2018, 296: 46-54 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.03.028 [23] Miyato T, Maeda S, Koyama M, Nakae K, Ishii S. Distributional smoothing with virtual adversarial training. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Learning Representations. Piscataway, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1-12 -





 下载:
下载: