Distributed Sliding Mode Control Strategy for High-speed EMU Strong Coupling Model
-
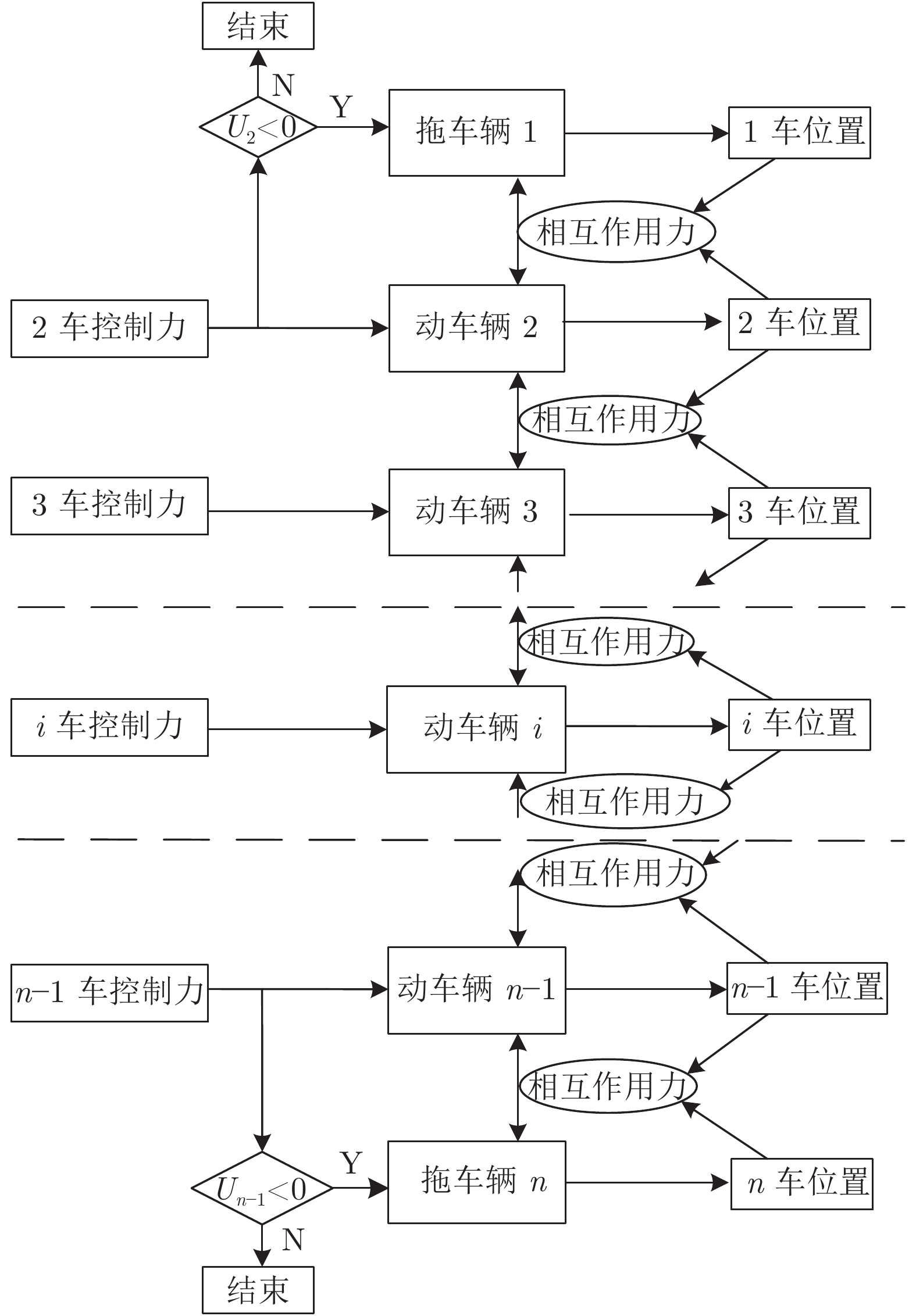
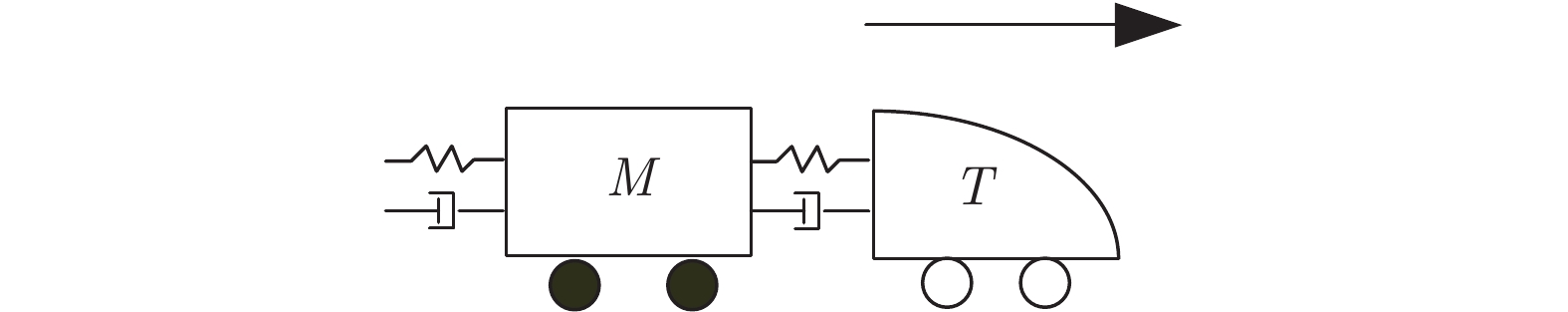
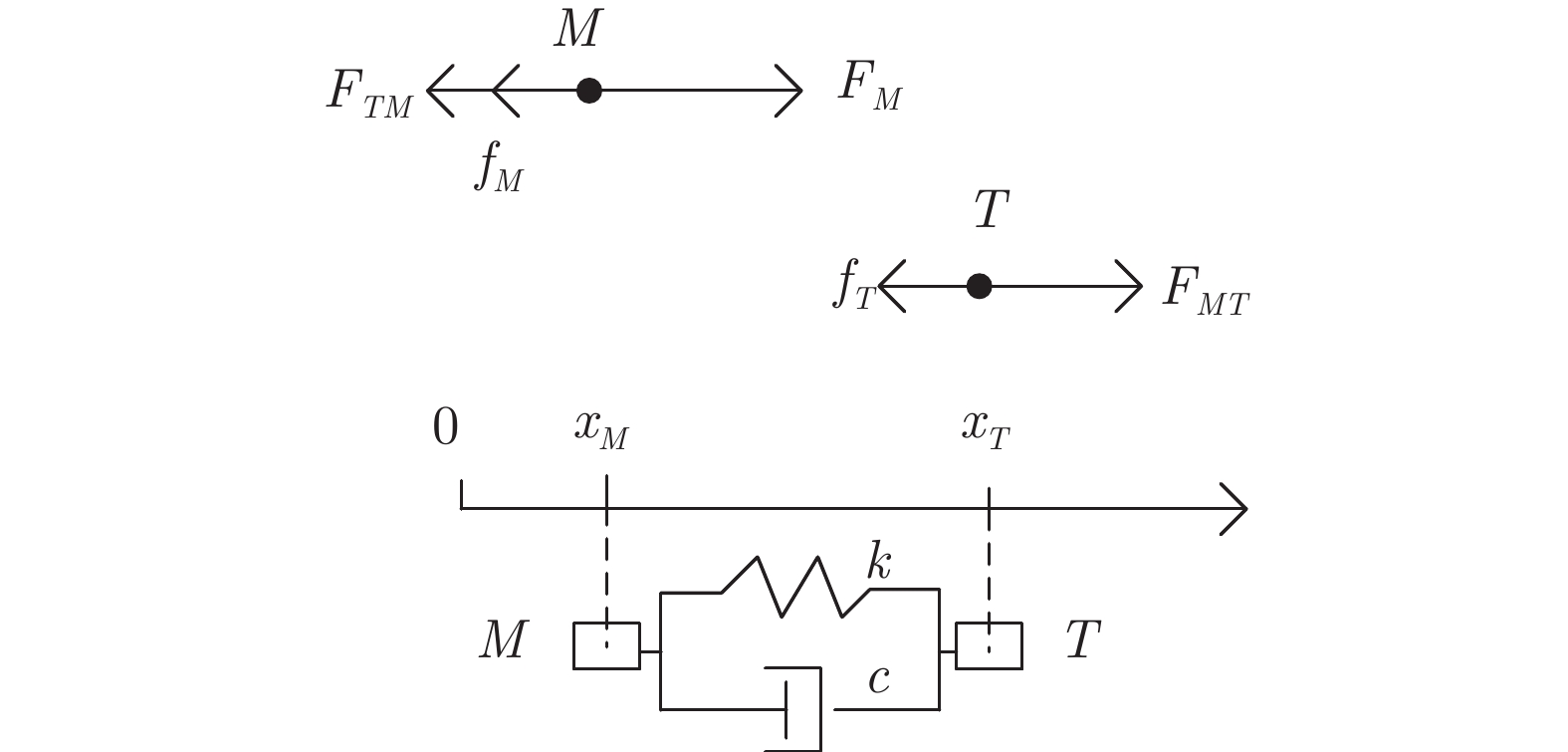
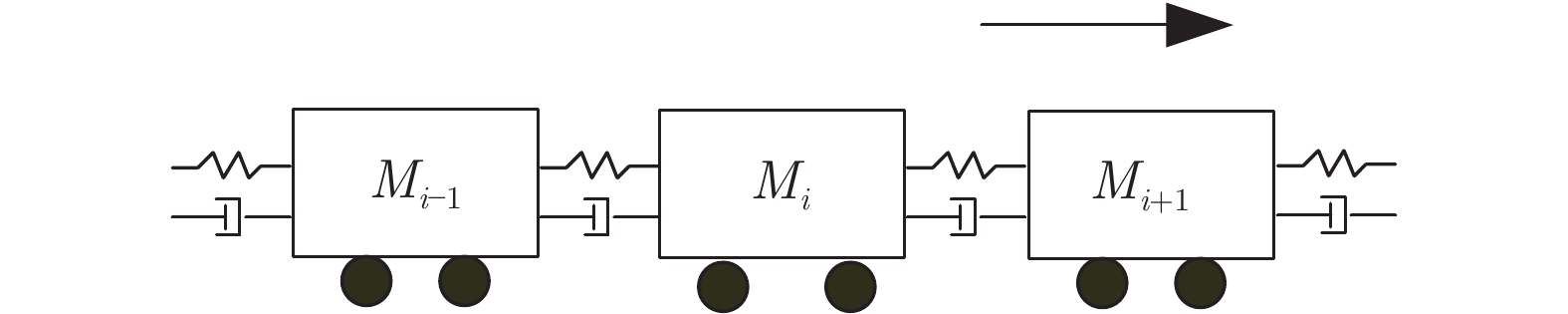
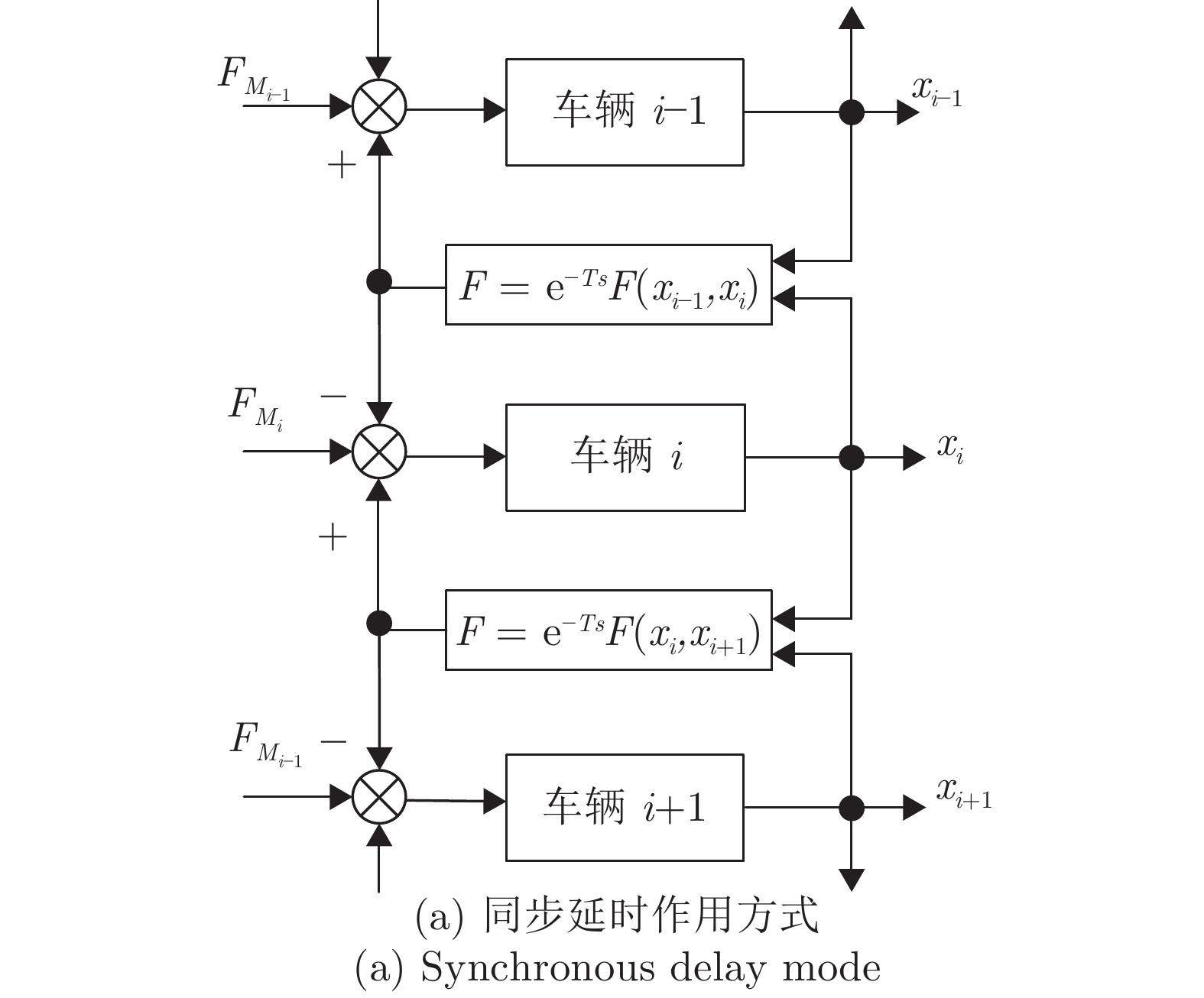
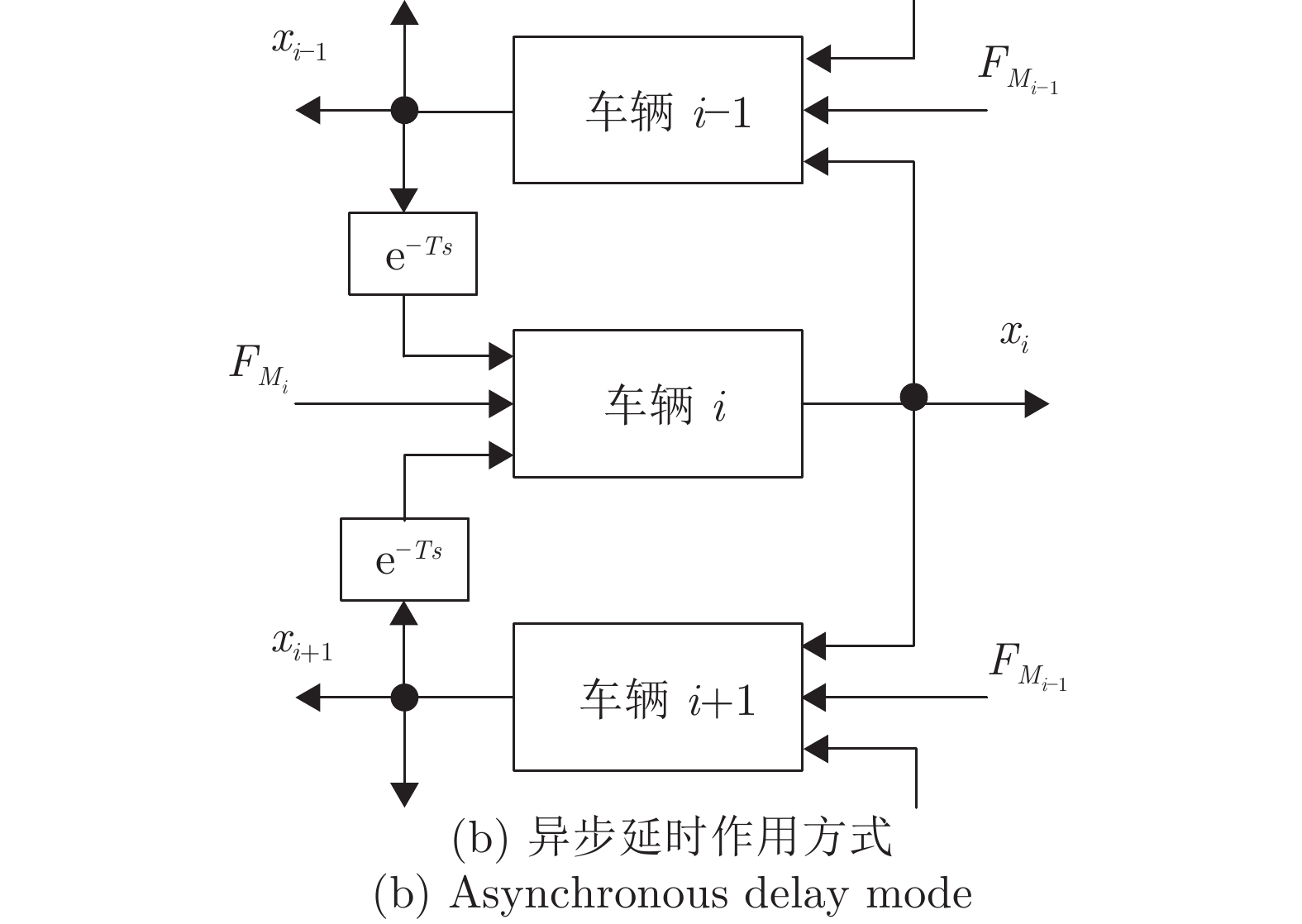
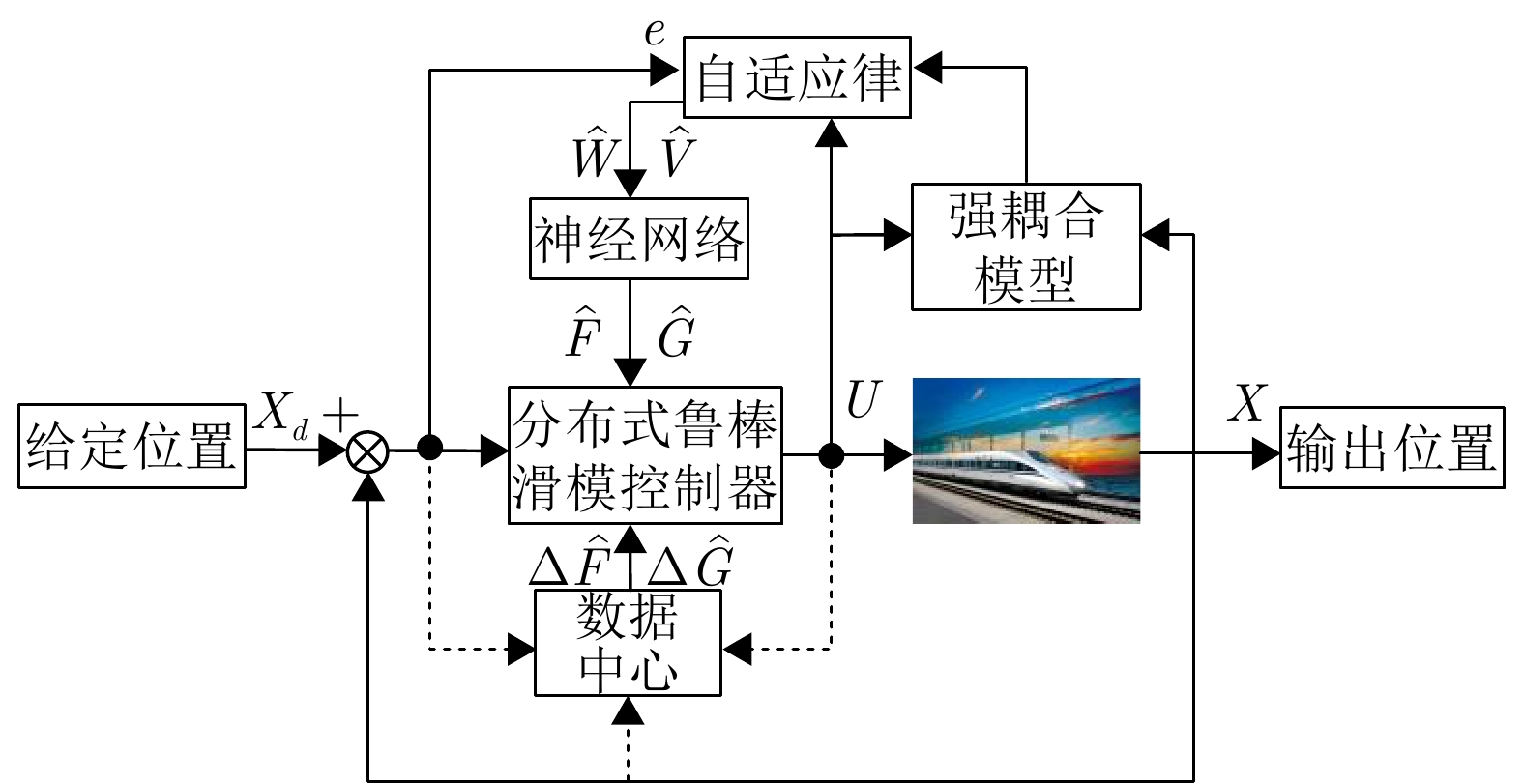
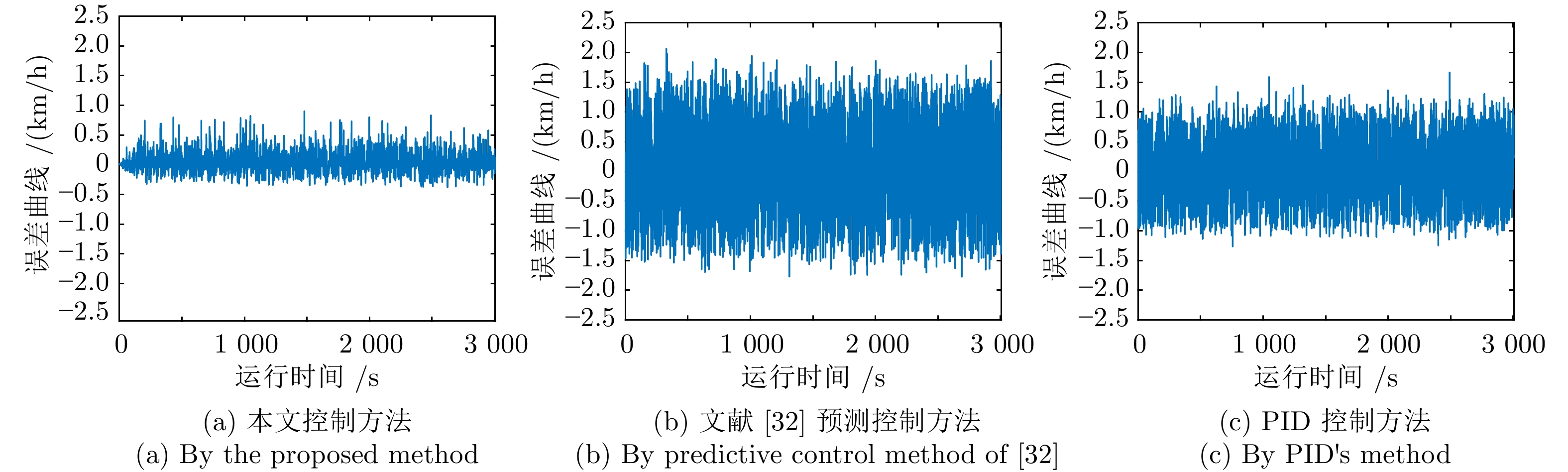
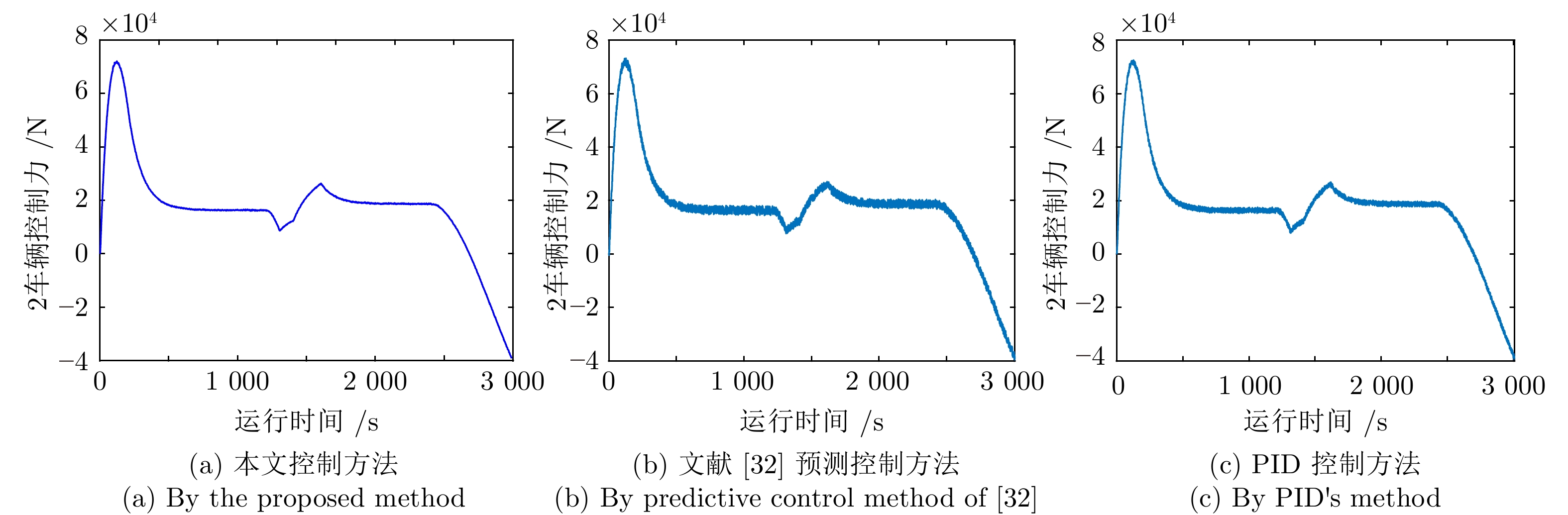
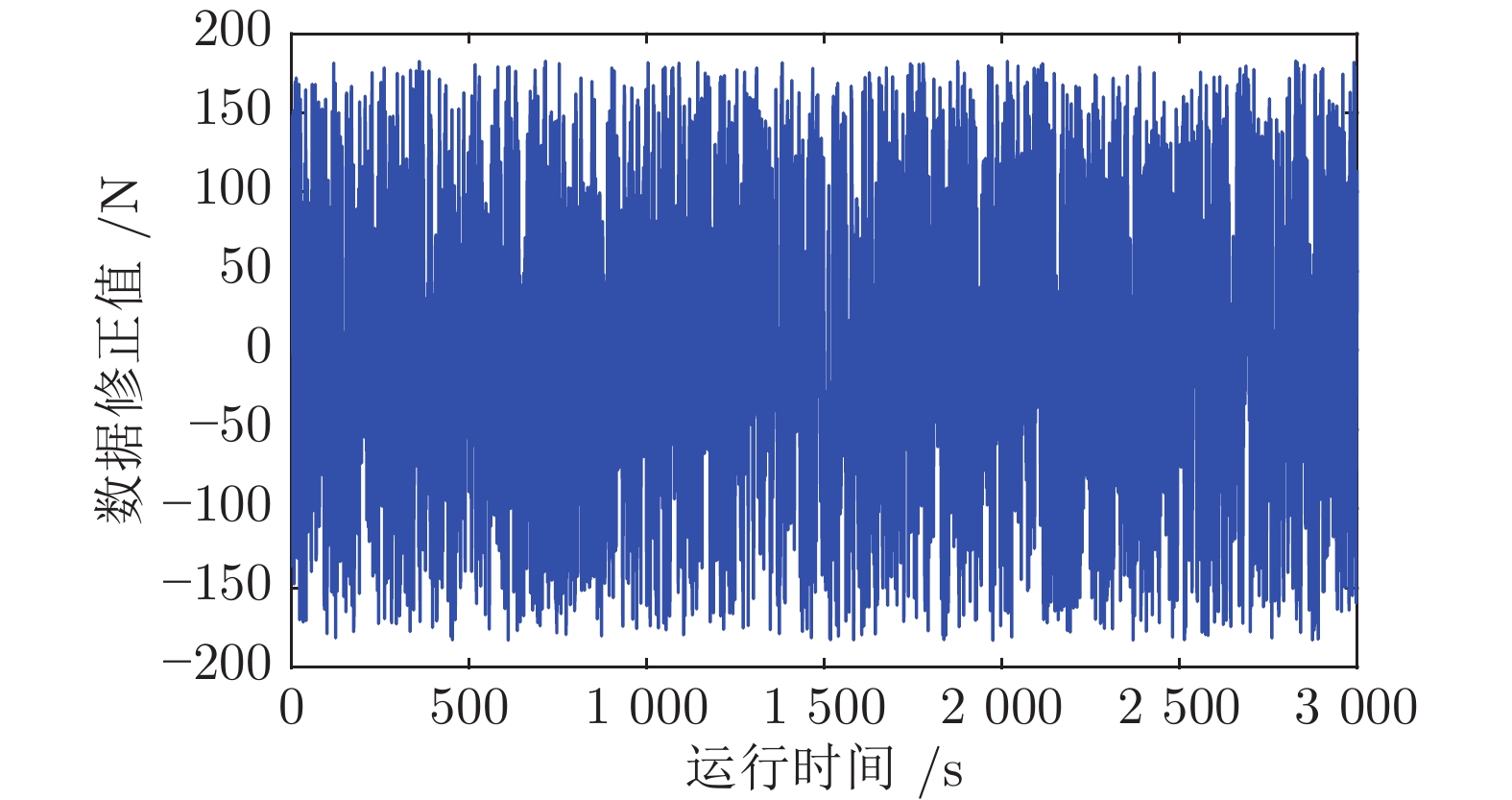
摘要: 高速动车组是由多节车辆与钩缓装置链接而成的复杂系统. 将钩缓装置等效成弹簧 − 阻尼器系统, 分析动车组运行过程中钩缓装置对相邻车辆作用的动力学机理, 明确作用方式, 建立高速动车组的强耦合模型. 根据列车模型动力或制动力输入的分散特征, 设计分布式神经网络滑模控制策略, 对高速动车组进行速度跟踪控制. 为减小速度跟踪过程中未知因素对高速动车组控制精度的影响, 利用列车历史运行数据, 采用历史工况数据中心对当前控制律输出进行补偿以提高控制精度与实用稳定性. 采用高速动车组运行仿真平台的仿真实验结果表明, 该建模方法较以往多质点模型更能体现高速动车组运行特性, 且采用补偿规则的控制策略优于传统控制效果.
-
关键词:
- 高速动车组 /
- 强耦合模型 /
- 分布式神经网络滑模控制 /
- 跟踪控制 /
- 数据补偿
Abstract: The high-speed EMU (electric multiple units) is a complex system composed of multi-section vehicles and hooking devices. This paper compares the hooking device into a spring-damper system, and analyzes the dynamic mechanism and mode of the action of coupler and buffer device on adjacent vehicles during the operation of high-speed EMU, and then, establishes the strong coupling model of high-speed EMU. According to the decentralized characteristics of the input of train model power or braking force, a distributed neural network sliding mode control strategy is designed to track the speed of high-speed EMU. In order to reduce the influence of unknown factors on the control accuracy of high-speed EMU during speed tracking, using the historical train operating data, the historical operating data center is used to compensate the current control law to improve control accuracy and practical stability. The simulation results of the high-speed EMU Operation Simulation Platform show that the modeling method can better reflect the operation characteristics of the high-speed EMU than the previous multi-point model, and the control strategy with compensation rules is better than the traditional control effect. -
表 1 CRH380A型动车组各节车辆质量
Table 1 The CRH380A EMU vehicle quality
车辆 类型 质量 (kg) 1 拖车 60 800 2 动车 62 000 3 动车 60 800 4 动车 56 560 5 动车 55 800 6 动车 60 800 7 动车 62 000 8 拖车 60 800 -
[1] 1 Dong H R, Ning B, Cai B, Hou Z S. Automatic train control system development and simulation for high-speed railways. IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine, 2010, 10(2): 6−18 doi: 10.1109/MCAS.2010.936782 [2] 2 Chen C L. Reshaping Chinese space-economy through high-speed trains: opportunities and challenges. Journal of Transport Geography, 2012, 22(2): 312−316 [3] 吴萌岭, 程光华, 王孝延, 金碧筠. 列车制动减速度控制问题的探讨. 铁道学报, 2009, 31(1): 94−973 Wu Meng-Ling, Cheng Guang-Hua, Wang Xiao-Yan, Jin Bi-Yun. Discussion on the problem of train brake deceleration control. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2009, 31(1): 94−97 [4] 李德仓, 孟建军, 胥如迅, 银铭. 强风下高速列车滑膜自适应鲁棒H∞ 控制方法. 铁道学报, 2018, 40(7): 67−73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2018.07.0104 Li De-Cang, Meng Jian-Jun, Xu Ru-Xun, Yin Ming. Adaptive robust H∞ control method for high speed trains under high winds. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(7): 67−73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2018.07.010 [5] 张守帅, 田长海. 高速铁路长大下坡地段列车运行速度相关问题研究. 中国铁道科学, 2017, 38(3): 124−129 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2017.03.185 Zhang Shou-Shuai, Tian Chang-Hai. Study on the related problems of train running speed in long and downhill sections of high speed railway. China Railway Science, 2017, 38(3): 124−129 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2017.03.18 [6] 卢毓江, 肖守讷, 朱涛, 杨光武, 杨超. 列车纵向−垂向碰撞动力学耦合模型建模与研究. 铁道学报, 2014, 36(12): 6−13 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.12.0026 Lu Yu-Jiang, Xiao Shou-Na, Zhu Tao, Yang Guang-Wu, Yang Chao. Modeling and research on coupled longitudinal-vertical collision dynamics model. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2014, 36(12): 6−13 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.12.002 [7] 丁莉芬, 谢基龙, Ahmed A. Shabana. 非惯性坐标在列车纵向力分析中的运用. 铁道学报, 2012, 34(1): 13−18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.01.0037 Ding Li-Fen, Xie Ji-Long, Ahmed A, Shabana. Application of non-inertial coordinates in longitudinal force analysis of trains. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2012, 34(1): 13−18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.01.003 [8] 李中奇, 杨辉, 刘明杰, 刘杰民. 高速动车组制动过程的建模及跟踪控制. 中国铁道科学, 2016, 37(5): 80−86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2016.05.118 Li Zhong-Qi, Yang Hui, Liu Ming-Jie, Liu Jie-Min. Modeling and tracking control of high speed EMU braking process. China Railway Science, 2016, 37(5): 80−86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2016.05.11 [9] 杨辉, 张坤鹏, 王昕, 衷路生. 高速列车多模型广义预测控制方法. 铁道学报, 2011, 33(8): 80−87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.08.0149 Yang Hui, Zhang Kun-Peng, Wang Xin, Zhong Lu-Sheng. Multi-model generalized predictive control method for high-speed trains. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2011, 33(8): 80−87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.08.014 [10] 余进, 何正友, 钱清泉. 基于混合微粒群优化的多目标列车控制研究. 铁道学报, 2010, 32(1): 38−42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.01.00710 Yu Jin, He Zheng-You, Qian Qing-Quan. Research on multi-objective train control based on hybrid particle swarm optimization. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2010, 32(1): 38−42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.01.007 [11] 郭红戈, 孙志毅, 张春美. 动车组列车制动系统Hammerstein模型的广义预测控制研究. 铁道学报, 2014, 36(6): 47−54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.06.00811 Guo Hong-Ge, Sun Zhi-Yi, Zhang Chun-Mei. Research on generalized predictive control of Hammerstein model for EMU train braking system. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2014, 36(6): 47−54 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.06.008 [12] 郜春海, 陈德旺. 基于模型选择和优化技术的自动驾驶制动模型辨识研究. 铁道学报, 2011, 33(10): 57−60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.10.01112 Gao Chun-Hai, Chen De-Wang. Research on automatic driving braking model identification based on model selection and optimization technology. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2011, 33(10): 57−60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.10.011 [13] 冷勇林, 陈德旺, 阴佳腾. 基于专家系统及在线调整的列车智能驾驶算法. 铁道学报, 2014, 36(02): 62−68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.02.01013 Leng Yong-Lin, Chen De-Wang, Yin Jia-Teng. Train intelligent driving algorithm based on expert system and online adjustment. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2014, 36(02): 62−68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.02.010 [14] 于振宇, 陈德旺. 城轨列车制动模型及参数辨识. 铁道学报, 2011, 33(10): 37−40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.10.00714 Yu Zhen-Yu, Chen De-Wang. Braking model and parameter identification of urban rail trains. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2011, 33(10): 37−40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2011.10.007 [15] 衷路生, 李兵, 龚锦红, 张永贤, 祝振敏. 高速列车非线性模型的极大似然辨识. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(12): 2950−299415 Zhong Lu-Sheng, Li Bing, Gong Jin-Hong, Zhang Yong-Xian, Zhu Zhen-Min. Maximum likelihood identification of nonlinear models for high speed trains. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(12): 2950−2994 [16] 杨辉, 严瑾, 张坤鹏. 动车组制动过程多模型自适应PID控制. 铁道学报, 2014, 36(3): 42−48 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.03.00816 Yang Hui, Yan Jin, Zhang Kun-Peng. Multi-model adaptive PID control for EMU braking process. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2014, 36(3): 42−48 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.03.008 [17] 衷路生, 颜争, 杨辉, 齐叶鹏, 张坤鹏, 樊晓平. 数据驱动的高速列车子空间预测控制. 铁道学报, 2013, 35(4): 77−83 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2013.04.01217 Zhong Lu-Sheng, Yan Zheng, Yang Hui, Qi Ye-Peng, Zhang Kun-Peng, Fan Xiao-Ping. Data-driven subspace prediction control for high-speed trains. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2013, 35(4): 77−83 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2013.04.012 [18] 衷路生, 颜争, 龚锦红, 张永贤, 祝振敏, 樊晓平. 时变遗忘因子的高速列车自适应子空间预测控制. 铁道学报, 2013, 35(5): 54−61 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2013.05.00918 Zhong Lu-Sheng, Yan Zheng, Gong Jin-Hong, Zhang Yong-Xian, Zhu Zhen-Min, Fan Xiao-Ping. Adaptive subspace predictive control for high-speed trains with time-varying forgetting factor. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2013, 35(5): 54−61 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2013.05.009 [19] 王青元, 吴鹏, 冯晓云, 张彦栋. 基于自适应终端滑模控制的城轨列车精确停车算法. 铁道学报, 2016, 38(2): 56−63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2016.02.00819 Wang Qing-Yuan, Wu Peng, Feng Xiao-Yun, Zhang Yan-Dong. Accurate parking algorithm for urban rail trains based on adaptive terminal sliding mode control. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2016, 38(2): 56−63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2016.02.008 [20] 王龙生, 徐洪泽, 张梦楠, 段宏伟. 基于混合系统模型预测控制的列车自动驾驶策略. 铁道学报, 2015, 37(12): 53−60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2015.12.00920 Wang Long-Sheng, Xu Hong-Ze, Zhang Meng-Nan, Duan Hong-Wei. Train automatic driving strategy based on hybrid system model predictive control. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2015, 37(12): 53−60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2015.12.009 [21] 杨艳飞, 崔科, 吕新军. 列车自动驾驶系统的滑模PID组合控制. 铁道学报, 2014, 36(6): 61−67 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.06.01021 Yang Yan-Fei, Cui Ke, Lv Xin-Jun. Sliding mode PID combination control for train autopilot system. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2014, 36(6): 61−67 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.06.010 [22] 杨辉, 张芳, 张坤鹏, 李中奇, 付雅婷. 基于分布式模型的动车组预测控制方法. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(9): 1912−192122 Yang Hui, Zhang Fang, Zhang Kun-Peng, Li Zhong-Qi, Fu Ya-Ting. The EMU predictive control method based on distributed model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(9): 1912−1921 [23] 李中奇, 杨辉, 张坤鹏, 付雅婷. 基于多智能体模型的动车组分布式预测控制. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(11): 2625−263123 Li Zhong-Qi, Yang Hui, Zhang Kun-Peng, Fu Ya-Ting. Distributed predictive control of EMU based on multi-agent model(In English). Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(11): 2625−2631 [24] 罗恒钰, 徐洪泽. 基于参考模型的ATO自适应控制算法研究. 铁道学报, 2013, 35(7): 68−73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2013.07.01124 Luo Heng-Yu, Xu Hong-Ze. Research on ATO adaptive control algorithm based on reference model. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2013, 35(7): 68−73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2013.07.011 [25] Adang Suwandi Ahmad. Brain inspired cognitive artificial intelligence for knowledge extraction and intelligent instrumentation system. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Electronics and Smart Devices (ISESD), Yogyakarta, Indonesia: IEEE, 2017. 352−356 [26] 刘金琨. 滑模变结构控制MATLAB仿真(第3版). 清华大学出版社, 2015. 349−355Liu Jin-Kun. Sliding Mode Variable Structure Control MATLAB Simulation (3 Edition). Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2015. 349−355 [27] 27 Yang Y C, Zhou H T, Su H S, Zeng W. Semi-global consensus with position limited and rate disturbances via low gain feedback and integral sliding mode control. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2017, 11(8): 1173−1183 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2016.0754 [28] 刘京, 李洪文, 邓永停. 基于扰动观测器的永磁同步电机电流环自适应滑模控制. 光学精密工程, 2017, 25(5): 1229−1241 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172505.122928 Liu Jing, Li Hong-Wen, Deng Yong-Ting. Current adaptive sliding mode control based on disturbance observer for permanent magnet synchronous motor. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(5): 1229−1241 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172505.1229 [29] 苏皓, 杨先海. 阀控液压缸系统低通滤波滑模变结构控制抖振问题的研究. 煤矿机械, 2018, 39(11): 77−7929 Su Hao, Yang Xian-Hai. Research on low-pass filter sliding mode variable structure control chattering problem of valve-controlled hydraulic cylinder system. Coal mining machinery, 2018, 39(11): 77−79 [30] 30 Cui R X, Chen L P, Yang C G, Chen M. Extended state observer-based integral sliding mode control for an underwater robot with unknown disturbances and uncertain nonlinearities. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(8): 6785−6795 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2694410 [31] 田猛, 张波文, 周腊吾, 杨宏智, 龙燕. 基于RBF神经网络滑模变结构独立变桨控制研究. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(4): 107−11431 Tian Meng, Zhang Bo-Wen, Zhou La-Wu, Yang Hong-Zhi, Long Yan. Research on sliding mode variable structure independent pitch control based on RBF neural network. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(4): 107−114 [32] 32 Yang H, Fu Y, Wang D. Multi-ANFIS model based synchronous tracking control of high-speed electric multiple unit. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(3): 1472−1484 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2725819 [33] 33 Huang W C, Shuai B. A methodology for calculating the passenger comfort benefits of railway travel. Journal of Modern Transportation, 2018, 26(2): 107−118 doi: 10.1007/s40534-018-0157-y [34] 姜斌, 吴云凯, 陆宁云, 冒泽慧. 高速列车牵引系统故障诊断与预测技术综述. 控制与决策, 2018, 33(5): 841−85534 Jiang Bin, Wu Yun-Kai, Lu Ning-Yun, Mao Ze-Hui. Overview of Fault Diagnosis and Prediction Technology for High Speed Train Traction System. Control and Decision, 2018, 33(5): 841−855 -





 下载:
下载: