A Model Predictive Control Based Distributed Coordination of Multi-microgrids in Energy Internet
-
摘要: 研究了预测不确定性条件下含多个微电网的能源互联网分布式协同调度策略.各微电网都拥有多种智能负荷,如功率可调负荷、可调度负荷和关键负荷;部分微电网含有分布式电源,如微型燃气轮机、风电机组、光伏发电系统等;且部分微电网还拥有储能设备,如电池储能系统.每个微电网都可当做一个独立的实体,拥有自己的运行目标,这些运行目标可表示成混合整数规划模型.提出了基于并行分布式优化的博弈模型以较小的信息通信量协调各微电网带有竞争性的运行目标.在此基础上,引入模型预测控制(MPC)机制以降低能源互联网中风、光等可再生能源输出、负荷需求及电价波动的不确定性产生的不利影响.算例证明了本文所提方法的可行性和有效性.Abstract: This paper focuses on the development of optimization-based distributed scheduling strategies for the coordination of an energy internet (EI) with multi-microgrids with consideration of forecast uncertainties. All microgrids have flexible loads, schedulable loads and critical loads; some microgrids have distributed generators, such as micro-turbines, wind turbines, photovoltaic panels; besides, a few microgrids have energy storage devices, such as battery storage. Each microgrid is considered as an individual entity and has its individual objective, these objective functions of microgrids are formulated by mixed integer programming (MIP) models. A game theory based parallel distributed optimization algorithm is proposed to coordinate the competitive objectives of the microgrids with only a little information interaction. A model predictive control (MPC) framework which integrates the distributed optimization algorithm is developed to reduce the negative impacts introduced by the uncertainties of the EI. Simulation results show that our method is flexible and efficient.
-
Key words:
- Energy internet (EI) /
- game theory /
- model predictive control (MPC) /
- multi-microgrids /
- parallel optimization
-
A. Index $t$ time index $i$ microgrid index $k$ iteration step index $a$ index of schedulable appliances in microgrid $i$ B. Constants $M$ set of microgrids in the EI system ( $i\in M$ ) $T$ number of periods for the control horizon ( $t\in T$ ) $N$ a preset iteration coefficient used for accelerating the convergence speed $A_{i, s}$ set of schedulable appliances in microgrid $i$ ( $a\in A$ ) $\Delta t$ time interval of each period (h) $P_{i, l}^{\rm max}, P_{i, O}^{\rm max}$ the rated power that can be purchased/sold from/to the utility for microgrid $i$ (kW) $E_{i, E}^{\rm max}, E_{i, E}^{\rm min}$ the maximum, minimum available energy level of the ESD unit in microgrid $i$ (kWh) $E_{i, E}^{\rm init}$ the initial energy level of ESD unit in microgrid $i$ (kWh) $P_{i, Ec}^{\rm max}, P_{i, Ec}^{\rm min}$ the maximum, minimum charging power of the ESD unit in microgrid $i$ (kW) $P_{i, Ed}^{\rm max}, P_{i, Ed}^{\rm min}$ the maximum, minimum discharging power of the ESD unit in microgrid $i$ (kW) $\eta_{i, Ed}, \eta_{i, Ec}$ discharging, charging efficiency of the ESD unit in microgrid $i$ (%) $\varepsilon_{i, E}$ self-discharging rate of the ESD unit in microgrid $i$ (kWh/h) $c_{i, E}^{\rm O \ M}$ operation and maintenance cost of the ESD unit in microgrid $i$ ($) $c_{i, E}^{\rm switch}$ status switch cost of the ESD unit in microgrid $ i $ ($) $P_{i, \rm DDG}^{\rm max}, P_{i, \rm DDG}^{\rm min}$ the maximum, minimum allowed power output of the DDG unit in microgrid $i$ (kW) $T_{i, \rm DDG}^{\rm down}, T_{i, \rm DDG}^{\rm up}$ the minimum down, operation time of the DDG unit in microgrid $i$ (h) $c_{i, \rm DDG}^{\rm down}, c_{i, \rm DDG}^{\rm up}$ shut-down, start-up cost of the DDG unit in microgrid $i$ ($) $R_{i, \rm DDG}$ the maximum ramp down/up power rate of the DDG unit in microgrid $i$ (kW) $c_{i, \rm DDG}^{1}, c_{i, \rm DDG}^{2}$ cost coefficients of the DDG unit in microgrid $i$ ( $$/\rm{kW^2}, $/\rm{kW}$ ) $\alpha 1, \alpha 2$ cost coefficients of the utility generator ( $$/\rm{kW^2}, $/\rm{kW)}$ $l_{i, a}^{\rm min}, l_{i, a}^{\rm max}$ the minimum, maximum load demand of appliance a for microgrid $i$ (kW) $l_{i, B}^{\rm max}$ rated capacity of the critical loads in microgrid $i$ (kW) $P_{i, PV}^{\rm max}$ rated power capacity of the PV plant in microgrid $i$ (kW) $P_{i, \rm wind}^{\rm max}$ rated power capacity of the wind farm in microgrid $i$ (kW) $T_{i, a}^{\rm start}, T_{i, a}^{\rm end}$ start time, deadline of appliance a for microgrid $i$ (h) $E_{i, a}$ total energy demand of the appliance a for microgrid $i$ (kWh) $D_{i}$ spinning reserve ratio for microgrid $i$ (%) $\xi_{1}, \xi_{2}, \xi_{3}, \xi_{4}$ preset stopping criteria for the distribution optimization algorithm $\theta_{i, F}^{\rm max}$ the maximum curtailment ratio of flexible loads in microgrid $i$ (%) $c_{i, F}^{\rm curt}$ penalty cost coefficient for curtailing flexible loads in microgrid $i$ $P_{u}^{\rm max}, P_{u}^{\rm min}$ the maximum, minimum power limit of the utility generator (kW) C. Parameters $P_{i, \rm wind}(t)$ power output of the wind turbines in microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (kW) $P_{i, PV}(t)$ power output of the PV plant in microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (kW) $l_{i, B}(t)$ demand of the critical loads in microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (kW) $l_{i, F}(t)$ demand of the flexible loads in microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (kW) $p_u(t)$ base electricity price for the utility company ($/kWh) $p_{i, b}(t), p_{i, s}(t)$ buying, selling electricity price for microgrid $i$ at time $t$ ($) $p_{i, b}(t), p_{i, s}(t)$ buying, selling price coefficient D. Variables $P_{i, l}(t), P_{i, O}(t)$ power imported/exported from/to the utility for microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (kW) $\delta_{i, l}(t), \delta_{i, O}(t)$ purchasing, selling power status for microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (0/1) $P_{i, Ec}(t), P_{i, Ed}(t)$ charging, discharging power rate of the ESD unit for microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (kW) $\delta_{i, Ec}(t), \delta_{i, Ed}(t)$ charging, discharging status of the ESD unit for microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (0/1) $E_{i, E}(t)$ energy level of the ESD unit for microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (kWh) $P_{i, \rm DDG}(t)$ power output of the DDG unit for microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (kWh) $\delta_{i, \rm DDG}(t)$ operation status of the DDG unit for microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (0/1) $\theta_{i, F}(t)$ curtailment ratio of the flexible loads for microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (%) $l_{i, a}(t)$ load demand of appliance a for microgrid $i$ at time $t$ (kW) Table Ⅰ ALGORITHM FOR PARALLEL DISTRIBUTED OPTIMIZATION METHOD FOR EI SYSTEM
$\textbf{Algorithm 1:}$ for utility at time $t$
$\textbf{begin}$
$k$ = 0; ${\%}$ iteration counter
Obtain the initial $P_{i, I}^k(\tau)$ , $P_{i, O}^k(\tau)$ of each microgrid according to the random generation technique; $\tau\in[t, t+1, \ldots, t+T-1]$
Calculate utility cost $\Psi_u^k$ according to (29), the retail buying electricity price $p_{i, b}^k(\tau)$ and selling price $p_{i, s}^k(\tau)$ according to (26) and (27), respectively;
do
Broadcast updated retail prices to all microgrids;
Receive the newly updated $P_{i, I}^{k+1}(\tau)$ , $P_{i, O}^{k+1}(\tau)$ simultaneously from all the microgrids according to Algorithm 2 shown in the following; $i\in[1, M]$
Calculate utility cost $\Psi_u^{k+1}$ , retail electricity price $p_{i, s}^{k+1}(\tau)$ , $p_{i, b}^{k+1}(\tau)$
$k:=k+1$ ;
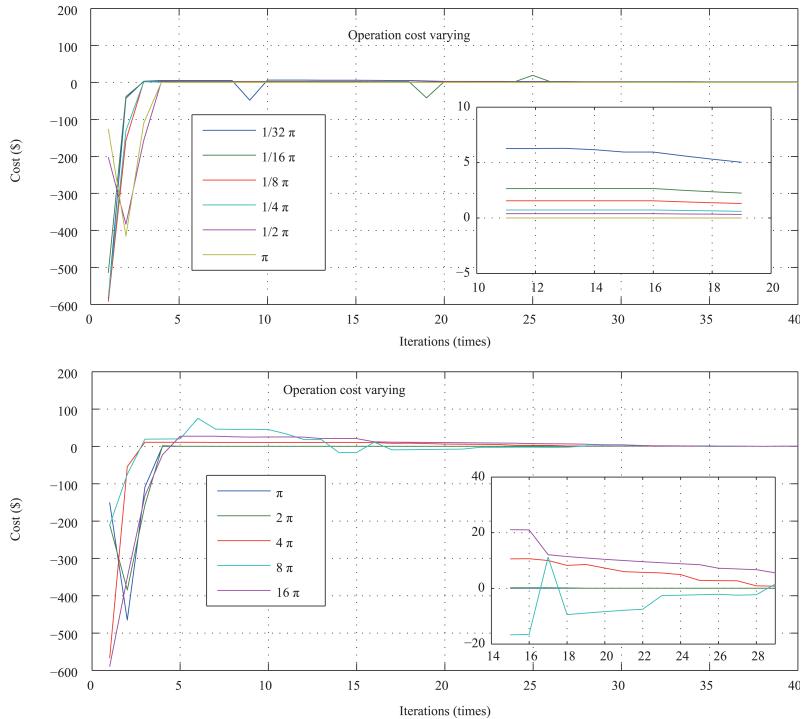
$\textbf{until}$ $||\Psi_u^k\!-\!\Psi_u^{k-1}||\leq \xi_1, ||l^k(\tau)\!-\!l^{k-1}(\tau)||\!\leq\!\xi_2, $
$|||P_{Ed}^k(\tau)\!-\!P_{Ec}^k(\tau)||- ||P_{Ed}^{k-1}(\tau)-P_{Ec}^{k-1}(\tau)|||\leq\xi_3, $
$||P_{\rm DDG}^k(\tau)-P_{\rm DDG}^{k-1}(\tau)||\leq\xi_4$
$\textbf{end}$
$\textbf{Algorithm 2:}$ for microgrid $i$ at time $t$
$\textbf{begin}$
$k$ = 0; ${\%}$ iteration counter
Initialize $P_{i, I}^k(\tau), P_{i, O}^k(\tau)$ according to the random generation technique;
Report $P_{i, I}^k(\tau)$ , $P_{i, O}^k(\tau)$ to the EI operator; $\tau\in[t, t+1, \ldots, t+T-1]$
While
Update the received retail electricity price $p_{i, s}^k (\tau)$ , $p_{i, b}^k (\tau)$ from the EI operator
Solve the optimization problem (31) and obtain the newly updated $P_{i, I}^{k+1}(\tau)$ , $P_{i, O}^{k+1}(\tau)$ ;
Report $P_{i, I}^{k+1}(\tau)$ , $P_{i, O}^{k+1}(\tau)$ to the EI operator;
$ k:=k+1$ ;
end
endTable Ⅱ POWER LIMITS OF MICROGRIDS AND INDEPENDENT USER
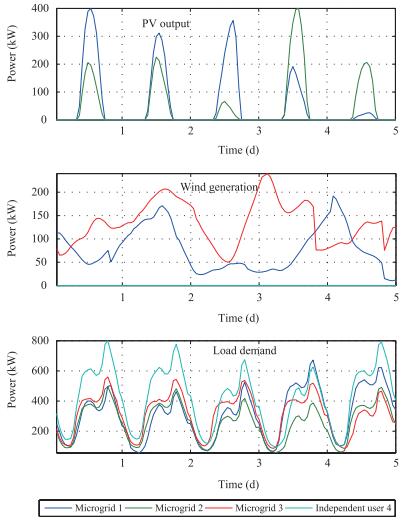
PV plant Wind farm PCC node Critical load Microgrid 1 400 192 1200 672 Microgrid 2 400 0 800 496 Microgrid 3 0 240 800 560 Independent user 0 0 1500 800 Table Ⅲ PARAMETER OF SCHEDULABLE LOADS
Power demand
(kW)Operation interval
(h)Time window
(h)Duration
(h)Task 1 22 15-21 6 2 Task 2 28 14-23 9 4 Task 3 45 8-18 10 6 Task 4 37.5 6-24 18 8 Task 5 12 2-22 20 12 Task 6 60 8-22 14 7 Task 7 75 6-24 18 9 Table Ⅳ PARAMETER OF ESDS
Max charge/ discharge power Min charge/ discharge power O & M cost Switch cost Max energy level Charge / discharge efficiency Microgrid 1 160 5 0.05 0.06 320 0.95 Microgrid 2 140 8 0.05 0.05 300 0.95 Microgrid 3 120 6 0.05 0.07 260 0.95 Table Ⅴ PARAMETER OF CONTROLLABLE GENERATORS
Max power Min power Ramp rate Min up/down time Startup/shut down cost Cost coefficients Microgrid 2 150 5 100 2/2 1.2/1.2 0.0042/0.32 Utility 4500 50 - - - 0.00048/0.28 Table Ⅵ SCHEDULING COSTS AND THE TOTAL COSTS FOR BOTH DMPC APPROACH AND DDA APPROACH
Cost (×105$) Microgrid
1Microgrid
2Microgrid
3Microgrid
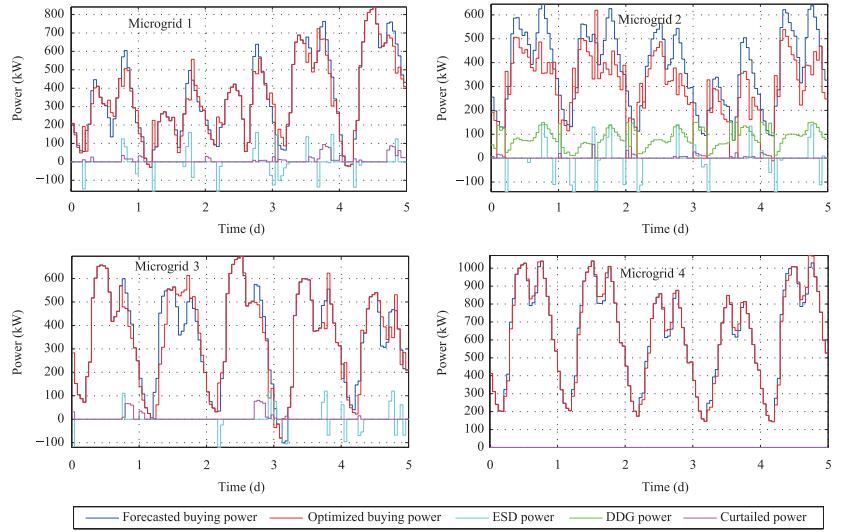
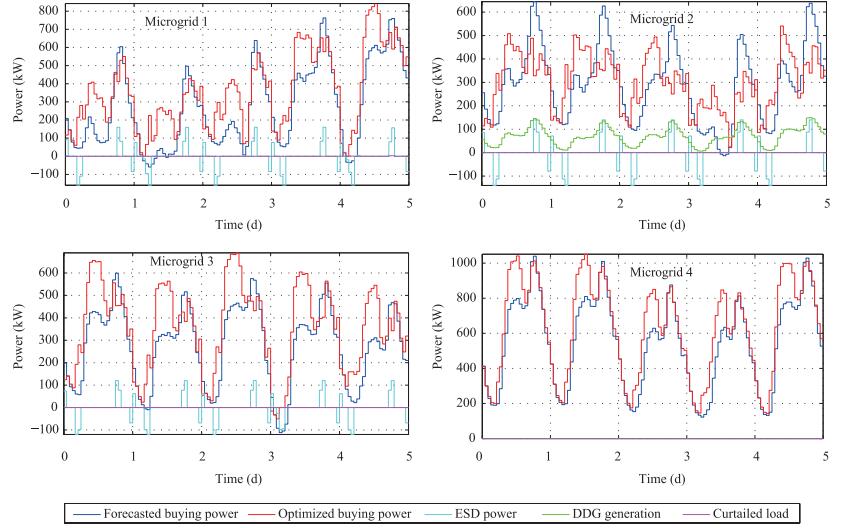
4Scheduling cost with no optimization 0.6661 0.6721 0.6716 1.1479 Scheduling cost with DDA 0.6316 0.5741 0.6376 1.0982 Scheduling cost with DMPC 0.6484 0.5867 0.6537 1.0993 Total cost with no optimization 0.6764 0.6831 0.6856 1.1619 Total cost with DDA 0.6574 0.6016 0.6717 1.1338 Total cost with DMPC 0.6502 0.5878 0.6555 1.1005 Table Ⅶ SCHEDULING COSTS AND TOTAL COSTS FOR DMPC APPROACH WITHOUT SOME DISPATCHABLE ELEMENTS
Cost (×105$) Microgrid
1Microgrid
2Microgrid
3Microgrid
4Scheduling cost without ESDs 0.6522 0.5920 0.6617 1.1186 Total cost without ESDs 0.6536 0.5929 0.6631 1.1201 Scheduling cost without ESDs and DDG 0.6800 0.6961 0.6846 1.1617 Total cost without ESDs and DDG 0.6788 0.6951 0.6831 1.1605 -
[1] H. Farhangi, "The path of the smart grid, " IEEE Power Energy Mag. , vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 18-28, Jan-Feb. 2010. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=5357331 [2] A. Q. Huang, M. L. Crow, G. T. Heydt, J. P. Zheng, and S. J. Dale, "Energy future renewable electric delivery and management (FREEDM) system: the energy internet, " Proc. IEEE, vol. 99, no. 1, pp. 133-148, Jan. 2011. [3] Y. B. Zha, T. Zhang, Z. Huang, Y. Zhang, B. L. Liu, and S. J. Huang, "Analysis of energy internet key technologies, " Sci. Sin. Inf. , vol. 44, no. 6, pp. 702-713, Jan. 2014. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-PZKX201406004.htm [4] D. Zhang, N. Shah, and L. G. Papageorgiou, "Efficient energy consumption and operation management in a smart building with microgrid, " Energy Convers. Manage. , vol. 74, pp. 209-222, Oct. 2013. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196890413002355 [5] J. Wu and X. H. Guan, "Coordinated multi-Microgrids optimal control algorithm for smart distribution management system, " IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 2174-2181, Dec. 2013. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6654349/ [6] Z. Y. Dong, J. H. Zhao, F. S. Wen, and Y. S. Xue, "From smart grid to energy internet: basic concept and research framework, " Automat. Electric Power Syst. , vol. 38, no. 15, pp. 1-11, Aug. 2014. [7] T. Zhang, F. X. Zhang, and Y. Zhang, "Study on energy management system of energy internet, " Power Syst. Technol. , vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 146-155, Jan. 2016. [8] R. H. Lasseter, "Smart distribution: coupled microgrids, " Proc. IEEE, vol. 99, no. 6, pp. 1074-1082, Jun. 2011. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5768104/ [9] N. Hatziargyriou, H. Asano, R. Iravani, and C. Marnay, "Microgrids, " IEEE Power Energy Mag. , vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 78-94, Jul-Aug. 2007. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=4263070 [10] J. Lee, J. Guo, J. K. Choi, and M. Zukerman, "Distributed energy trading in microgrids: a game-theoretic model and its equilibrium analysis, " IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. , vol. 62, no. 6, pp. 3524-3533, Jun. 2015. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7001088/ [11] J. M. Guerrero, M. Chandorkar, T. L. Lee, and P. C. Loh, "Advanced control architectures for intelligent microgrids-Part Ⅰ: decentralized and hierarchical control, " IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. , vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 1254-1262, Apr. 2013. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6184305/ [12] J. Silvente, G. M. Kopanos, E. N. Pistikopoulos, and A. Espuña, "A rolling horizon optimization framework for the simultaneous energy supply and demand planning in microgrids, " Appl. Energy, vol. 155, pp. 485-501, Oct. 2015. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261915007230 [13] M. H. Albadi and E. F. EL-Saadany, "A summary of demand response in electricity markets, " Electric Power Syst. Res. , vol. 78, no. 11, pp. 1989-1996, Nov. 2008. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378779608001272 [14] B. Chai, J. M. Chen, Z. Y. Yang, and Y. Zhang, "Demand response management with multiple utility companies: a two-level game approach, " IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 722-731, Mar. 2014. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6740887/ [15] W. C. Su and J. H. Wang, "Energy management systems in microgrid operations, " Electricity J. , vol. 25, vol. 8, pp. 45-60, Oct. 2012. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S104061901200214X [16] C. Chen, J. H. Wang, and Y. Heo, and S. Kishore, "MPC-based appliance scheduling for residential building energy management controller, " IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 1401-1410, Sep. 2013. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6575202/ [17] A. Parisio, E. Rikos, and L. Glielmo, "A model predictive control approach to microgrid operation optimization, " IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. , vol. 22, no. 5, pp. 1813-1827, Sep. 2014. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6705582/ [18] D. H. Zhu and G. Hug, "Decomposed stochastic model predictive control for optimal dispatch of storage and generation, " IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 2044-2053, Jul. 2014. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6839132/ [19] W. C. Su, J. H. Wang, K. L. Zhang, and A. Q. Huang, "Model predictive control-based power dispatch for smart distribution system considering plug-in electric vehicle uncertainty, " Electric Power Syst. Resour. , vol. 106, pp. 29-35, Jan. 2014. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378779613002113 [20] J. W. Cao and M. B. Yang, "Energy internet-Towards Smart Grid 2. 0, " in Proc. 4th Int. Conf. Networking and Distributed Computing (ICNDC), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2013, pp. 105-110. [21] Y. F. Tang, J. Yang, J. Yan, and H. B. He, "Intelligent load frequency controller using GrADP for island smart grid with electric vehicles and renewable resources, " Neurocomputing, vol. 170, pp. 406-416, Dec. 2015. [22] Y. F. Tang, H. B. He, Z. Ni, J. Y. Wen, and T. W. Huang, "Adaptive modulation for DFIG and STATCOM with high-voltage direct current transmission, " IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. , vol. 27, no. 8, pp. 1762-1772, Aug. 2016. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26701900 [23] Y. F. Tang, H. B. He, Z. Ni, X. N. Zong, D. B. Zhao, and X. Xu, "Fuzzy-based goal representation adaptive dynamic programming, " IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. , to be published. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7346472/ [24] M. H. Amini, R. Jaddivada, S. Mishra, and O. Karabasoglu, "Distributed security constrained economic dispatch, " in Proc. IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologiesâ€"â€"Asia (ISGT ASIA), Bangkok, Thailand, 2015. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7387167/ [25] K. Deng, Y. Sun, S. S. Li, Y. Lu, J. Brouwer, P. G. Mehta, M. C. Zhou, and A. Chakraborty, "Model predictive control of central chiller plant with thermal energy storage via dynamic programming and mixed-integer linear programming, " IEEE Trans. Automat. Sci. Eng. , vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 565-579, Apr. 2015. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6899700/ [26] M. Huber, F. Sanger, and T. Hamacher, "Coordinating smart homes in microgrids: a quantification of benefits, " in Proc. 20134th IEEE/PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT Europe), Copenhagen, 2013, pp. 1-5. [27] D. E. Olivares, C. A. Cañizares, and M. Kazerani, "A centralized energy management system for isolated microgrids, " IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1864-1875, Jul. 2014. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6805674/ [28] Y. Z. Zhou, H. Wu, Y. N. Li, H. H. Xin, and Y. H. Song, "Dynamic dispatch of multi-microgrid for neighboring islands based on MCS-PSO algorithm, " Automat. Electric Power Syst. , vol. 38, no. 9, pp. 204-210, May 2014. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DLXT201409030.htm [29] X. Ai and J. J. Xu, "Study on the microgrid and distribution network co-operation model based on interactive scheduling, " Power Syst. Prot. Control, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 143-149, Jan. 2013. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-JDQW201301026.htm [30] M. Fathi and H. Bevrani, "Adaptive energy consumption scheduling for connected microgrids under demand uncertainty, " IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. , vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 1576-1583, Jul. 2013. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6510487/ [31] Z. Y. Wang, B. K. Chen, J. H. Wang, M. M. Begovic, and C. Chen, "Coordinated energy management of networked microgrids in distribution systems, " IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 45-53, Jan. 2015. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6872821/ [32] F. Kamyab, M. Amini, S. Sheykhha, M. Hasanpour, and M. M. Jalali, "Demand response program in smart grid using supply function bidding mechanism, " IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 1277-1284, May 2016. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7112524/ [33] G. E. Asimakopoulou, A. L. Dimeas, and N. D. Hatziargyriou, "Leader-follower strategies for energy management of multi-microgrids, " IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 1909-1916, Dec. 2013. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6519333/ [34] P. Yang, P. Chavali, E. Gilboa, and A. Nehorai, "Parallel load schedule optimization with renewable distributed generators in smart grids, " IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 1431-1441, Sep. 2013. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6576918/ [35] Y. Zhang, T. Zhang, R. Wang, Y. J. Liu, and B. Guo, "Optimal operation of a smart residential microgrid based on model predictive control by considering uncertainties and storage impacts, " Solar Energy, vol. 122, pp. 1052-1065, Dec. 2015. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0038092X15005782 [36] E. Camponogara, D. Jia, B. H. Krogh, and S. Talukdar, "Distributed model predictive control, " IEEE Control Syst. , vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 44-52, Feb. 2002. [37] D. P. Bertsekas and J. N. Tsitsiklis, Parallel and Distributed Computation:Numerical Methods. Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA:Prentice-Hall, 1989. [38] I. Prodan and E. Zio, "A model predictive control framework for reliable microgrid energy management, " Int. J. Electric. Power Energy Syst. , vol. 61, pp. 399-409, Oct. 2014. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142061514001197 [39] J. S. Netz, "Price regulation: A (non-technical) overview, " in Encyclopedia of Law and Economics, B. Bouckaert and G. De Geest, Eds, Cheltenham, Edward Elgar, 2000, pp. 1396-1465. [40] Y. X. Xu and C. Singh, "Power system reliability impact of energy storage integration with intelligent operation strategy, " IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 1129-1137, Mar. 2014. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6583282/ [41] L. Y. Jia, Z. Yu, M. C. Murphy-Hoye, A. Pratt, E. G. Piccioli, and L. Tong, "Multi-scale stochastic optimization for home energy management, " in Proc. IEEE Int. Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2011. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6135900/ [42] ELIA, Belgium's electricity transmission system operator. Grid data, [EB/OL]. [Online]. Available: http://www.elia.be/en/grid-data. [43] C. Yang and L. Xie, "A novel ARX-based multi-scale spatio-temporal solar power forecast model, " North American Power Symp. (NAPS), Champaign, IL, USA, 2012, pp. 1-6. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6336383/ [44] R. Hanna, J. Kleissl, A. Nottrott, and M. Ferry, "Energy dispatch schedule optimization for demand charge reduction using a photovoltaic-battery storage system with solar forecasting, " Solar Energy, no. 103, pp. 269-287, May 2014. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0038092X1400098X [45] R. Blonbou, "Very short-term wind power forecasting with neural networks and adaptive Bayesian learning, " Renewable Energy, vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 1118-1124, Mar. 2011. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960148110003976 [46] J. Löfberg, "YALMIP: a toolbox for modeling and optimization in MATLAB, " in 2004 IEEE Int. Symp. Computer Aided Control Systems Design, New Orleans, LA, 2004, pp. 284-289. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1393890 -





 下载:
下载: