Cyber-physical Security Analysis of Smart Grids With Bayesian Sequential Game Models
-
摘要: 智能电网是利用信息技术优化从供应者到消费者的电力传输和配电网络.作为一种信息物理系统(Cyber-physical system,CPS),智能电网由物理设备和负责数据计算与通信的网络组成.智能电网的诸多安全问题会出现在通信网络和物理设备这两个层面,例如注入坏数据和收集客户隐私信息的网络攻击,攻击电网物理设备的物理攻击等.本文主要研究了智能电网的系统管理员(防护者)如何确定攻击者类型,从而选择最优防护策略的问题.提出了一种贝叶斯序贯博弈模型以确定攻击者的类型,根据序贯博弈树得到博弈双方的均衡策略.首先,对类型不确定的攻击者和防护者构建静态贝叶斯博弈模型,通过海萨尼转换将不完全信息博弈转换成完全信息博弈,得到贝叶斯纳什均衡解,进而确定攻击者的类型.其次,考虑攻击者和防护者之间的序贯博弈模型,它能够有效地帮助防护者进行决策分析.通过逆向归纳法分别对两种类型的攻击者和防护者之间的博弈树进行分析,得到博弈树的均衡路径,进而得到攻击者的最优攻击策略和防护者的最优防护策略.分析表明,贝叶斯序贯博弈模型能够使防护者确定攻击者的类型,并且选择最优防护策略,从而为涉及智能电网信息安全的相关研究提供参考.Abstract: A smart grid is a network which uses communication and information technologies to optimize the transmission and distribution of power from suppliers to consumers. As a kind of cyber-physical system (CPS), a smart grid consists of the network part of data computing and communication and the physical part of all devices. Many security issues arise in both components of the grid, such as injecting bad data, collecting customer privacy information (cyber attacks) and attacking the grid physical devices (physical attacks). In this paper, we study how the system administrator (defender) can determine the type of attack and make optimal protection strategy. We propose a Bayesian sequential game model to defermine the type of attack, and analyze the equilibrium strategy of both game sides according to the sequential game tree. Firstly, we construct a static Bayesian game model between the attacker of an indeterminate type and the defender. We transform the incomplete information game into a complete information game through Harsanyi transformation, and analyze the Bayesian Nash equilibrium to determine the type of attacker. Secondly, we consider the sequential game model between attackers and defenders, which can effectively help defender to make decision in dynamic networks. Through the backward induction, the game tree is analyzed between two types of attackers and defenders, respectively. Then we obtain the equilibrium path of the game tree and make the optimal strategies for both players. It is shown that the defender can determine the type of attacker and make the optimal strategy by the Bayesian sequential game model, which provides a reference for the security research on smart grids.1) 本文责任编委 孙秋野
-
表 1 攻击者类型为网络攻击
Table 1 The type of attacker is a cyber attack
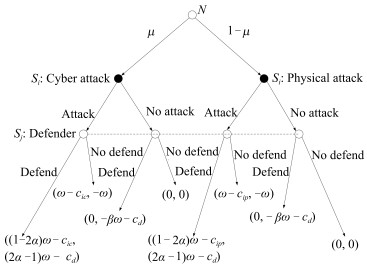
防护 不防护 攻击 (1-2α)ω-cic, (2α-1)ω-cd ω-cic; -ω 不攻击 0, -βω-cd 0, 0 表 2 攻击者类型为物理攻击
Table 2 The type of attacker is a physical attack
防护 不防护 攻击 (1-2α)ω-cip, (2α-1)ω-cd ω-cip; -ω 不攻击 0, -βω-cd 0, 0 表 3 行为函数收益
Table 3 The payoff of the behavioral function
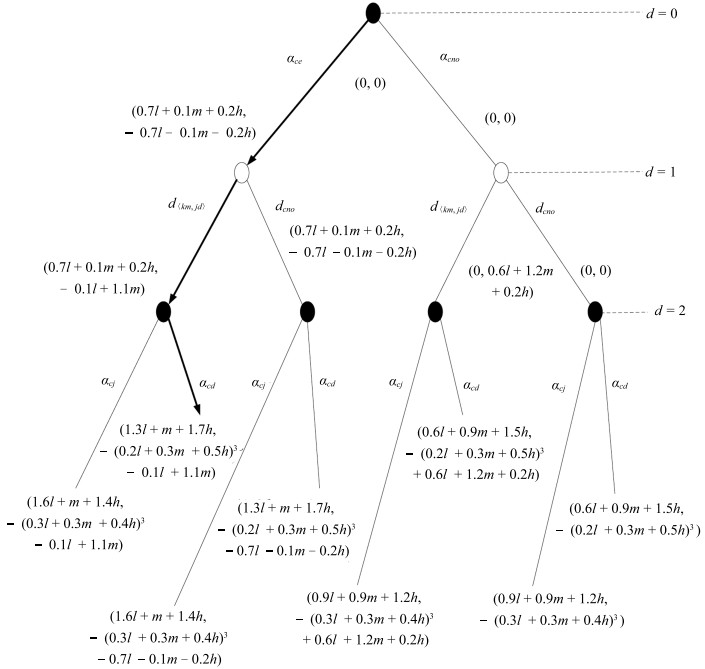
$A(S, a, d)$ $a$为攻击者策略 $a$为防护者策略 $S$为攻击者 d×Impact(a) 0 $S$为防护者 $ - Impact(a)^{d}$ d×Impact(a) 表 4 行为策略$a$的影响函数(网络攻击)
Table 4 The payoff of the behavioral function
行为策略$(a)$ $C(a)$ $I(a)$ $A(a)$ $SF(a)$ $Impact(a)$ $d_{\langle km, jd\rangle}$ $m$ $m$ $l$ $h$ $0.3l + 0.6m + 0.1h$ $a_{ce}$ $h$ $l$ $l$ $m$ $0.7l + 0.1m + 0.2h$ $a_{cj}$ $l$ $h$ $m$ $l$ $0.3l + 0.3m + 0.4h$ $a_{cd}$ $l$ $h$ $m$ $h$ $0.2l + 0.3m + 0.5h$ 表 5 行为策略$a$的影响函数(物理攻击)
Table 5 The payoff of the behavioral function (physical attack)
行为策略$(a)$ $C(a)$ $I(a)$ $A(a)$ $SF(a)$ $Impact(a)$ $d_{\langle ca, mp\rangle}$ $l$ $m$ $m$ $m$ $0.1l + 0.9m$ $a_{ps}$ $m$ $l$ $l$ $m$ $0.8l + 0.2m$ $a_{pn}$ $l$ $m$ $m$ $m$ $0.1l + 0.9m$ $a_{pt}$ $l$ $h$ $h$ $h$ $0.1l + 0.9h$ -
[1] Derler P, Lee E A, Vincentelli A S.Modeling cyber-physical systems.Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(1):13-28 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2011.2160929 [2] Mitchell R, Chen I R.Effect of intrusion detection and response on reliability of cyber physical systems.IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2013, 62(1):199-210 doi: 10.1109/TR.2013.2240891 [3] Cao X H, Cheng P, Chen J M, Sam Ge S, Cheng Y, Sun Y X.Cognitive radio based state estimation in cyber-physical systems.IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2014, 32(3):489-502 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2014.1403002 [4] Baheti R, Gill H.Cyber-physical systems.The Impact of Control Technology.Washington D.C., USA:IEEE, 2011.161-166 [5] Cintuglu M H, Mohammed O A, Akkaya K, Uluagac A S.A survey on smart grid cyber-physical system testbeds.IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2017, 19(1):446464 doi: 10.1109/COMST.2016.2627399 [6] Liu Y, Peng Y, Wang B L, Yao S R, Liu Z H.Review on cyber-physical systems.IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 4(1):27-40 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510349 [7] 温景容, 武穆清, 宿景芳.信息物理融合系统.自动化学报, 2012, 38(4):507-517 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17704.shtmlWen Jing-Rong, Wu Mu-Qing, Su Jing-Fang.Cyber-physical system.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(4):507-517 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17704.shtml [8] Liu E D, Cheng P.Achieving privacy protection using distributed load scheduling:a randomized approach.IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017, 8(5):2460-2473 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2017.2703400 [9] Dai W B, Dubinin V N, Christensen J H, Vyatkin V, Guan X P.Toward self-manageable and adaptive industrial cyber-physical systems with knowledge-driven autonomic service management.IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13(2):725-736 doi: 10.1109/TII.2016.2595401 [10] Deng R L, Zhuang P, Liang H.CCPA:coordinated cyber-physical attacks and countermeasures in smart grid.IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017, 8(5):2420-2430 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2017.2702125 [11] Humayed A, Lin J Q, Li F J, Luo B.Cyber-physical systems security-a survey.IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(6):1802-1831 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2703172 [12] Tian J, Tan R, Guan X H, Liu T.Enhanced hidden moving target defense in smart grids.IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, DOI: 10.1109/TSG.2018.2791512, 2018. [13] Yang Q Y, Li D H, Yu W, Liu Y K, An D, Yang X Y, et al.Toward data integrity attacks against optimal power flow in smart grid.IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(5):1726-1738 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2709252 [14] 孙秋野, 滕菲, 张化光.能源互联网及其关键控制问题.自动化学报, 2017, 43(2):176-194 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18999.shtmlSun Qiu-Ye, Teng Fei, Zhang Hua-Guang.Energy internet and its key control issues.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(2):176-194 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18999.shtml [15] Luo X Y, Yao Q, Wang X Y, Guan X P.Observer-based cyber attack detection and isolation in smart grids.International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems, 2018, 101:127-138 doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2018.02.039 [16] Yan Y, Qian Y, Sharif H, Tipper D.A survey on cyber security for smart grid communications.IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2012, 14(4):998-1010 doi: 10.1109/SURV.2012.010912.00035 [17] Hasan M M, Mouftah H T.A study of resource-constrained cyber security planning for smart grid networks.In:Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference.Ottawa, Canada:IEEE, 2016.1-6 [18] Mo Y L, Kim T H J, Brancik K, Dickinson D, Lee H, Perrig A, et al.Cyber-physical security of a smart grid infrastructure.Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(1):195-209 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2011.2161428 [19] Osborne M J, Rubinstein A.A Course in Game Theory.Cambridge:MIT Press, 1994. [20] Hewett R, Rudrapattana S, Kijsanayothin P.Cyber-security analysis of smart grid SCADA systems with game models.In:Proceedings of the 9th Annual Cyber and Information Security Research Conference.Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA:ACM, 2014.109-112 [21] Maharjan S, Zhu Q Y, Zhang Y, Gjessing S, Basar T.Dependable demand response management in the smart grid:a Stackelberg game approach.IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2013, 4(1):120-132 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2012.2223766 [22] Ma J H, Liu Y T, Song L Y, Han Z.Multiact dynamic game strategy for jamming attack in electricity market.IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2015, 6(5):2273-2282 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2015.2400215 [23] Sanjab A, Saad W.Data injection attacks on smart grids with multiple adversaries:a game-theoretic perspective.IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(4):2038-2049 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2016.2550218 [24] Roy S, Ellis C, Shiva S, Dasgupta D, Shandilya V, Wu Q S.A survey of game theory as applied to network security.In:Proceedings of the 43rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences.Honolulu, HI, USA:IEEE, 2010.1-10 [25] 袁勇, 王飞跃.不完全信息议价博弈的序贯均衡分析与计算实验.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5):724-734 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18862.shtmlYuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue.Sequential equilibrium analysis and computational experiments of a bargaining game with incomplete information.Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5):724-734 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18862.shtml [26] Wang K, Du M, Maharjan S, Sun Y F.Strategic honeypot game model for distributed denial of service attacks in the smart grid.IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017, 8(5):2474-2482 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2017.2670144 [27] 张维迎.博弈论与信息经济学.上海:格致出版社, 上海三联书店, 上海人民出版社, 2012.Zhang Wei-Ying.Game Theory Information Economics.Shanghai:Truth and Wisdom Press, Shanghai Joint Publishing, Shanghai People's Publishing House, 2012. [28] Lakshmanan K, de Niz D, Rajkumar R, Moreno G.Resource allocation in distributed mixed-criticality cyber-physical systems.In:Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems.Genova, Italy:IEEE, 2010.169-178 [29] 约翰·纳什[著], 张良桥, 王晓刚[译].纳什博弈论论文集.北京: 首都经济贸易大学出版社, 2015.Nash J[Author], Zhang Liang-Qiao, Wang Xiao-Gang[Translator].Essays on Game Theory.Beijing: Capital University of Economics and Business Press, 2015. [30] 罗斯[著], 龚光鲁[译].随机过程.第2版.北京:机械工业出版社, 2013.Ross S M[Author], Gong Guang-Lu[Translator].Stochastic Processes (2nd edition).Beijing:China Machine Press, 2013. [31] Li Y Z, Shi L, Cheng P, Chen J M, Quevedo D E.Jamming attacks on remote state estimation in cyber-physical systems:a game-theoretic approach.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(10):2831-2836 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2461851 [32] Xie L, Mo Y L, Sinopoli B.False data injection attacks in electricity markets.In:Proceedings of the 1st IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications.Gaithersburg, MD, USA:IEEE, 2010.226-231 [33] Smith R.Assault on California power station raises alarm on potential for terrorism.Wall Street Journal, 2014, 1-7 [34] Tsang R.Cyberthreats, vulnerabilities and attacks on SCADA networks.University of California, Berkeley, USA, 2010. [35] Lee A.Guidelines for Smart Grid Cyber Security, NIST Interagency/Internal Report (NISTIR)-7628, 2010. -




 下载:
下载: