Autoencoder and PCA Based RVFLNs Modeling for Multivariate Molten Iron Quality in Blast Furnace Ironmaking
-
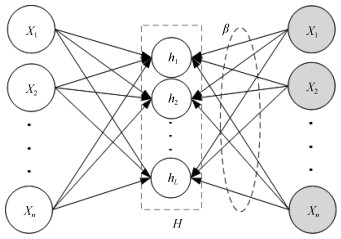
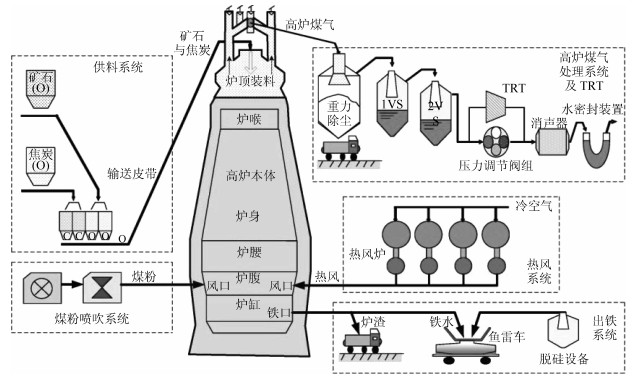
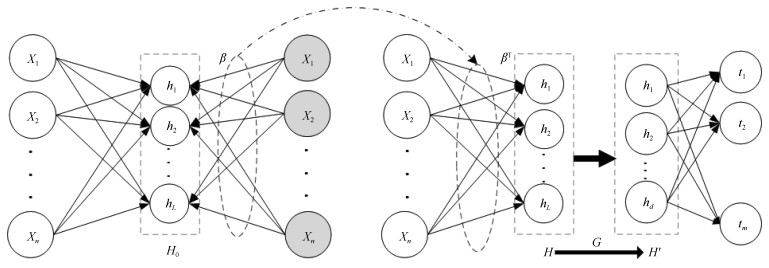
摘要: 针对随机权神经网络(Random vector functional-link networks,RVFLNs)建模存在的过拟合和泛化能力差的问题,集成自编码(Autoencoder)和主成分分析(Principal component analysis,PCA)技术,提出一种新型的改进RVFLNs算法,即AE-P-RVFLNs算法,用于建立高炉多元铁水质量在线估计的NARX(Nonlinear autoregressive exogenous)模型.首先,为了尽可能挖掘实际复杂工业数据中的有用信息和充分揭示输入数据之间的内在关系,采用Autoencoder前馈随机网络技术训练建模输入数据,并将训练得到的输出权值作为后续RVFLNs的输入权值;然后,引入PCA技术对RVFLNs的高维隐层输出矩阵进行降维,避免隐层输出矩阵多重共线性问题,从而解决由于隐层节点过多导致模型过拟合的问题;最后,基于所提AE-P-RVFLNs算法建立某大型高炉多元铁水质量在线估计的NARX模型.工业实验和比较分析表明:采用本文算法建立的多元铁水质量在线估计模型可有效提高运算效率和估计精度,尤其是避免常规RVFLNs建模存在的过拟合问题.Abstract: Aiming at the problems of overfitting and poor generalization capability of the conventional random vector functional-link networks (RVFLNs), this paper proposes a novel improved RVFLNs algorithm, named AE-P-RVFLNs, by combining hybrid techniques of autoencoder and principal component analysis (PCA), and applies it to nonlinear autoregressive exogenous (NARX) modeling of blast furnace ironmaking process for online estimation of multivariable molten iron quality indices. First, in order to find the useful information from the complex real industrial data and reveal the underlying relationship of input variables, autoencoder is introduced to train the input data and then calculate the output weights, which are treated as the input weights of the RVFLNs model. Then, PCA is used to reduce the dimension of hidden layer output matrix so as to avoid the multicollinearity problem in calculation and reduce the number of hidden nodes, which simplifies the network structure and gets rid of the overfitting problem caused by too many hidden nodes. Finally, the proposed AE-P-RVFLNs algorithm is used to establish the NARX model for online estimation of multivariable molten iron quality indices in blast furnace ironmaking. Industrial test and comparative analysis show that the developed model can not only effectively improve the operation efficiency and estimation accuracy, but also effectively solve the overfitting problem in conventional RVFLNs modeling.
-
Key words:
- RVFLNs /
- AE-P-RVFLNs /
- autoencoder /
- principal component analysis (PCA) /
- NARX modeling /
- blast furnance /
- overfitting
1) 本文责任编委 贺威 -
表 1 PCA求取的各主成分特征值、方差贡献率以及累积方差贡献率
Table 1 PCA to obtain the principal component eigenvalues, variance contribution rate and cumulative variance contribution rate
主成分 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累计方差贡献率(%) 1 7.467 46.666 46.666 2 4.205 26.279 72.945 3 1.951 12.196 85.141 4 1.130 7.063 92.204 5 0.683 4.268 96.472 6 0.360 2.251 98.723 7 0.140 0.874 99.597 8 0.034 0.211 99.809 9 0.020 0.126 99.935 10 0.004 0.024 99.959 11 0.003 0.021 99.980 12 0.001 0.009 99.989 13 0.001 0.006 99.995 14 0.001 0.004 99.999 15 0.000 0.001 100.000 16 0.000 0.000 100.000 表 2 因子载荷矩阵(由PCA提取的6个主成分)
Table 2 Factor load matrix (Six principal components extracted by PCA)
物理变量 主成分 1 2 3 4 5 6 冷风流量 0.816 -0.449 0.310 -0.180 0.004 0.032 送风比 0.813 -0.445 0.320 -0.179 0.007 0.041 热风压力(kPa) 0.186 0.250 0.897 0.133 0.159 -0.045 透气性 0.625 -0.318 -0.549 -0.347 -0.110 0.000 阻力系数 -0.786 0.226 0.526 0.071 0.133 -0.081 热风温度(℃) 0.161 0.958 -0.021 -0.177 0.141 -0.045 富氧流量 0.797 0.221 -0.175 0.525 -0.090 -0.036 富氧率 0.781 0.242 -0.188 0.534 -0.093 -0.037 设定喷煤量(m3/h) -0.049 0.868 0.040 0.067 -0.064 0.480 鼓风湿度(RH) 0.105 -0.512 -0.362 0.200 0.737 0.111 理论燃烧温度(℃) 0.747 0.580 -0.080 0.094 0.080 -0.286 炉顶压力(kPa) 0.813 -0.452 0.312 -0.181 0.003 0.033 实际风速 0.526 0.763 -0.119 -0.321 0.139 -0.028 鼓风动能 0.681 0.623 -0.049 -0.346 0.132 -0.018 炉腹煤气量(kg/t) 0.967 -0.138 0.158 0.105 -0.024 0.082 炉腹煤气指数 0.958 -0.129 0.162 0.100 -0.026 0.102 表 3 不同算法相关统计指标比较
Table 3 Comparison of statistical indicators for difierent algorithms
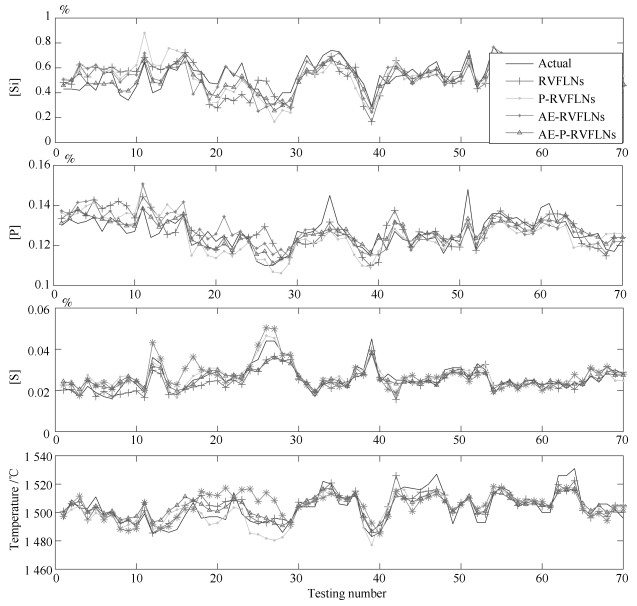
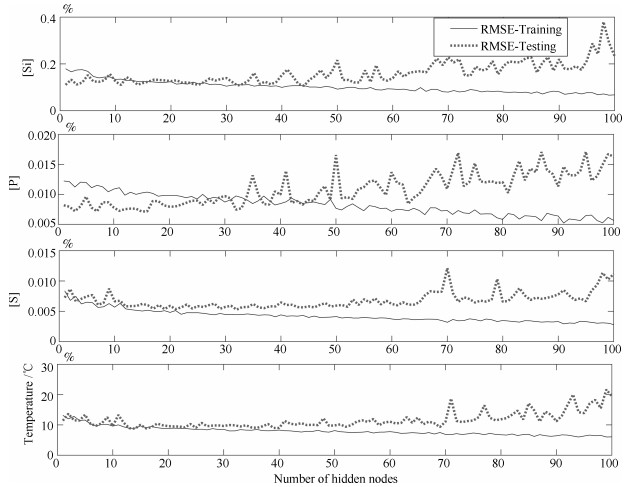
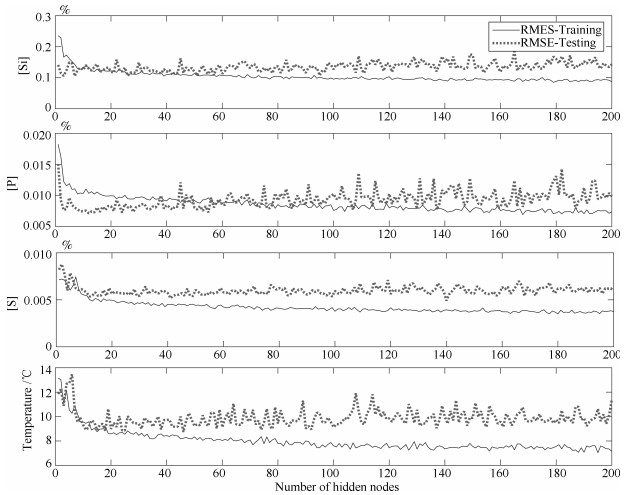
算法 运算 RMSE MAPE (%) 时间 [Si] [P] [Si] MIT [Si] [P] [S] MIT RVFLNs 0.002269 0.1172 0.0080 0.0056 9.8078 5.1192 5.4152 4.5631 5.4759 P-RVFLNs 0.001457 0.1464 0.0087 0.0065 10.0500 4.8998 4.4591 5.9490 5.1976 AE-RVFLNs 0.002027 0.1307 0.0135 0.0064 11.4555 6.8174 6.0327 6.6126 7.4414 AE-P-RVFLNs 0.001358 0.1124 0.0071 0.0054 9.0443 4.5551 2.9175 3.0825 4.6068 -
[1] 宋贺达, 周平, 王宏, 柴天佑.高炉炼铁过程多元铁水质量非线性子空间建模及应用.自动化学报, 2016, 42(21):1664-1679 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18956.shtmlSong He-Da, Zhou Ping, Wang Hong, Chai Tian-You. Nonlinear subspace modeling of multivariate molten iron quality in blast furnace ironmaking and its application. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(21):1664-1679 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18956.shtml [2] Jian L, Gao C H, Xia Z H. Constructing multiple kernel learning framework for blast furnace automation. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2012, 9(4):763-777 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2012.2211100 [3] Zhou P, Lv Y B, Wang H, Chai T Y. Data-driven robust RVFLNs modeling of a blast furnace iron-making process using Cauchy distribution weighted M-estimation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(9):7141-7151 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2686369 [4] 蒋朝辉, 董梦林, 桂卫华, 阳春华, 谢永芳.基于Bootstrap的高炉铁水硅含量二维预报.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5):715-723 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18861.shtmlJiang Zhao-Hui, Dong Meng-Lin, Gui Wei-Hua, Yang Chun-Hua, Xie Yong-Fang. Two-dimensional prediction for silicon content of hot metal of blast furnace based on bootstrap. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5):715-723 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18861.shtml [5] de Castro J A, Nogami H, Yagi J I. Three-dimensional multiphase mathematical modeling of the blast furnace based on the multifluid model. ISIJ International, 2002, 42(1):44-52 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.42.44 [6] 崔桂梅, 孙彤, 张勇.支持向量机在高炉铁水温度预测中的应用.控制工程, 2013, 20(5):809-812, 817 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7848.2013.05.005Cui Gui-Mei, Sun Tong, Zhang Yong. Application of support vector machine (SVM) in prediction of molten iron temperature in blast furnace. Control Engineering of China, 2013, 20(5):809-812, 817 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7848.2013.05.005 [7] 储满生, 王宏涛, 柳政根, 唐珏.高炉炼铁过程数学模拟的研究进展.钢铁, 2014, 49(11):1-8 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gt201411001Chu Man-Sheng, Wang Hong-Tao, Liu Zheng-Gen, Tang Jue. Research progress on mathematical modeling of blast furnace ironmaking process. Iron and Steel, 2014, 49(11):1-8 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gt201411001 [8] Lvanov E B, Klimovitskii M D, Anisimov E F. Expert system for blast-furnace operators. Metallurgist, 2011, 54(11-12):730-736 doi: 10.1007/s11015-011-9366-x [9] Liu J K, Wang S Q. Construction of the inference engine of blast furnace expert system. Journal of Iron & Steel Research (International), 1998, 5(2):22-27 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YING199802004.htm [10] Zarandi M H F, Ahmadpour P. Fuzzy agent-based expert system for steel making process. Expert Systems with Applications, 2009, 36(5):9539-9547 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2008.10.084 [11] Cai J H, Zeng J S, Luo S H. A state space model for monitoring of the dynamic blast furnace system. ISIJ International, 2012, 52(12):2194-2199 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.52.2194 [12] Bhattacharya T. Prediction of silicon content in blast furnace hot metal using partial least squares (PLS). ISIJ International, 2005, 45(12):1943-1945 doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.45.1943 [13] Gao C H, Ge Q H, Jian L. Rule extraction from fuzzy-based blast furnace SVM multiclassifier for decision-making. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2014, 22(3):586-596 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2013.2269145 [14] Yuan M, Zhou P, Li M L, Li R F, Wang H, Chai T Y. Intelligent multivariable modeling of blast furnace molten iron quality based on dynamic AGA-ANN and PCA. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2015, 22(6):487-495 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtyjxb-e201506005 [15] Chen J. A predictive system for blast furnaces by integrating a neural network with qualitative analysis. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2001, 14(1):77-85 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ027275069 [16] Zhou P, Yuan M, Wang H, Chai T Y. Data-driven dynamic modeling for prediction of molten iron silicon content using ELM with self-feedback. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015, 2015:Article No.326160, http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ba88b75f470cc7ce64a55473cf2142cc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [17] Zhou P, Yuan M, Wang H, Wang Z, Chai T Y. Multivariable dynamic modeling for molten iron quality using online sequential random vector functional-link networks with self-feedback connections. Information Sciences, 2015, 325:237-255 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.07.002 [18] Zhang L, Zhou P, Song H D, Yuan M, Chai T Y. Multivariable dynamic modeling for molten iron quality using incremental random vector functional-link networks. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2016, 23(11):1151-1159 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gtyjxb-e201611004 [19] Zhao J, Wang W, Liu Y, Pedrycz W. A two-stage online prediction method for a blast furnace gas system and its application. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2011, 19(3):507-520 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=9fff45396394326ad8576e6605843d3a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [20] 王炜, 陈畏林, 叶勇, 徐智慧, 贾斌.神经网络在高炉铁水硫含量预报中的应用.钢铁, 2016, 41(10):19-22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5115.2016.10.008Wang Wei, Chen Wei-Lin, Ye Yong, Xu Zhi-Hui, Jia Bin. Application of neural network to predict sulphur content in hot metal. Iron and Steel, 2016, 41(10):19-22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5115.2016.10.008 [21] Rumelhart D E, Hinton G E, Williams R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 1986, 323(6088):533-536 doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [22] Vincent P, Larochelle H, Lajoie I, Bengio Y, Manzagol PA. Stacked denoising Autoencoders:learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11(12):3371-3408 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1b5321cd3b5fdc0bc4d9b0d4fa8975ef&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [23] Kasun L L C, Zhou H M, Huang G B, Vong C. Representational learning with extreme learning machine for big data. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2013, 28(6):31-34 [24] Zhang H G, Yin Y X, Zhang S. An improved ELM algorithm for the measurement of hot metal temperature in blast furnace. Neurocomputing, 2016, 174:232-237 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.04.106 [25] Good R P, Kost D, Cherry G A. Introducing a unified PCA algorithm for model size reduction. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 2010, 23(2):201-209 doi: 10.1109/TSM.2010.2041263 -




 下载:
下载: