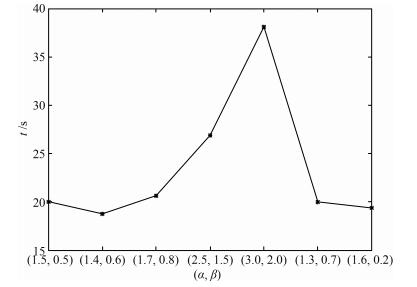
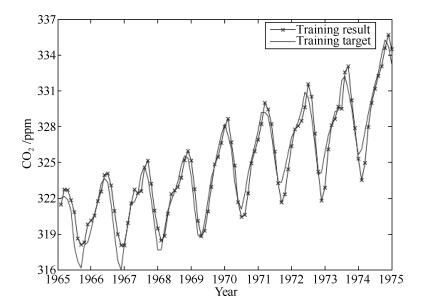
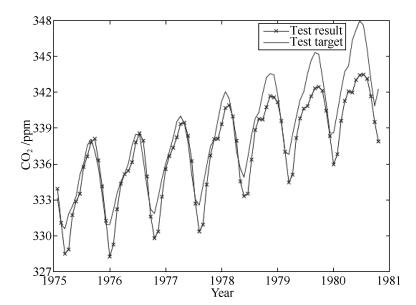
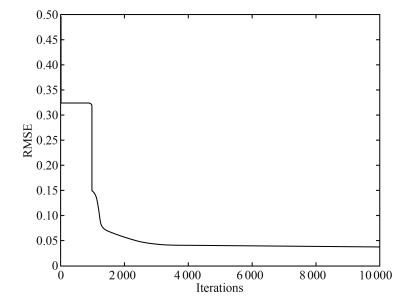
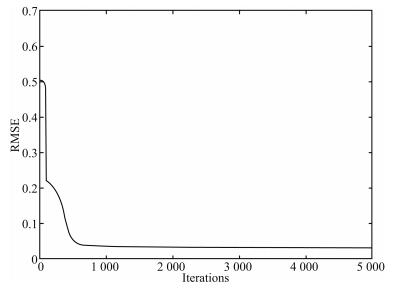
-
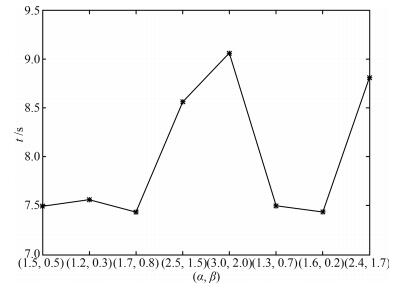
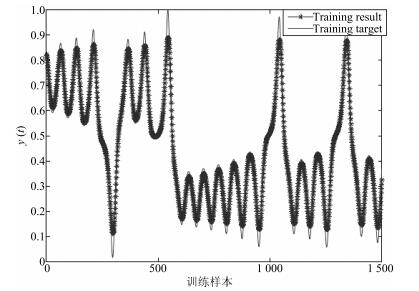
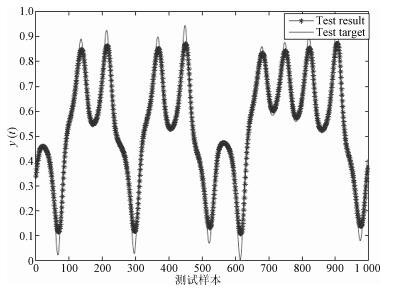
摘要: 针对深度信念网(Deep belief network,DBN)预训练耗时长的问题,提出了一种基于自适应学习率的DBN(Adaptive learning rate DBN,ALRDBN).ALRDBN将自适应学习率引入到对比差度(Contrastive divergence,CD)算法中,通过自动调整学习步长来提高CD算法的收敛速度.然后设计基于自适应学习率的权值训练方法,通过网络性能分析给出学习率变化系数的范围.最后,通过一系列的实验对所设计的ALRDBN进行测试,仿真实验结果表明,ALRDBN的收敛速度得到了提高且预测精度也有所改善.Abstract: A deep belief network with adaptive learning rate (ALRDBN) is proposed to solve the time-consuming problem in the pre-training period of DBN. The ALRDBN introduces the idea of adaptive learning rate into contrastive divergence (CD) algorithm and accelerates its convergence by a self-adjusting learning rate. The training method of weights in this case is designed, in which the adjusting scope of the coefficient in learning rate is determined by performance analysis. Finally, a series of experiments are carried out to test the performance of ALRDBN, and the corresponding results show that the convergence rate is accelerated significantly and the accuracy of prediction is improved as well.1) 本文责任编委 王占山
-
表 1 MNIST手写数字实验结果对比
Table 1 Result comparison of MNIST experiment
方法 隐含层数 每层节点数 正确识别率 运算时间(s) ALRDBN 2 100 93.1 % 20.0 CDBN 2 100 93.0 % 34.3 DBN[21] 2 100 92.6 % 32.9 表 2 CO2浓度变化实验结果对比
Table 2 Result comparison of CO2 forecasting
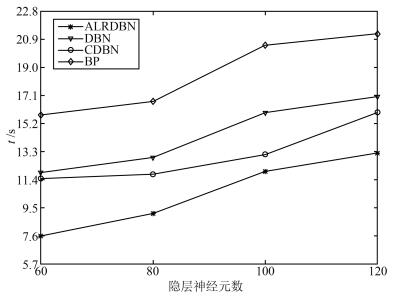
方法 网络结构 RMSE (训练) RMSE (测试) 运算时间(s) ALRDBN 3-20-40-1 0.9164 1.1671 7.6 DBN 3-20-40-1 0.9487 1.2830 11.9 CDBN[22] 3-20-40-1 0.9133 1.1507 11.5 BP 3-60-1 >0.1 1.3 ~ 6.6 15.8 -
[1] Bengio Y H, Delalleau O. On the expressive power of deep Architectures. In:Proceeding of the 22nd International Conference. Berlin Heidelberg, Germany:Springer-Verlag, 2011. 18-36 [2] Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 2006, 313(5786):504-507 doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 [3] 郭潇逍, 李程, 梅俏竹.深度学习在游戏中的应用.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5):676-684 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18857.shtmlGuo Xiao-Xiao, Li Cheng, Mei Qiao-Zhu. Deep learning applied to games. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5):676-684 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18857.shtml [4] LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature, 2015, 521(7553):436-444 doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [5] 贺昱曜, 李宝奇.一种组合型的深度学习模型学习率策略.自动化学报, 2016, 42(6):953-958 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18886.shtmlHe Yu-Yao, Li Bao-Qi. A combinatory form learning rate scheduling for deep learning model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6):953-958 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18886.shtml [6] 马帅, 沈韬, 王瑞琦, 赖华, 余正涛.基于深层信念网络的太赫兹光谱识别.光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(12):3325-3329 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10674-1015636153.htmMa Shuai, Shen Tao, Wang Rui-Qi, Lai Hua, Yu Zheng-Tao. Terahertz spectroscopic identification with deep belief network. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(12):3325-3329 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10674-1015636153.htm [7] 耿志强, 张怡康.一种基于胶质细胞链的改进深度信念网络模型.自动化学报, 2016, 42(6):943-952 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18885.shtmlGeng Zhi-Qiang, Zhang Yi-Kang. An improved deep belief network inspired by glia chains. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6):943-952 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18885.shtml [8] Abdel-Zaher A M, Eldeib A M. Breast cancer classification using deep belief networks. Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 46:139-144 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.10.015 [9] Rumelhart D E, Hinton G E, Williams R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 1986, 323(6088):533-536 doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [10] Mohamed A R, Dahl G E, Hinton G. Acoustic modeling using deep belief networks. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2012, 20(1):14-22 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2011.2109382 [11] Bengio Y. Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2009, 2(1):1-127 doi: 10.1561/2200000006 [12] Lopes N, Ribeiro B. Improving convergence of restricted Boltzmann machines via a learning adaptive step size. Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer Vision, and Applications, Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Berlin Heidelberg:Springer, 2012. 511-518 [13] Raina R, Madhavan A, Ng A Y. Large-scale deep unsupervised learning using graphics processors. In:Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, NY, USA:ACM, 2009. 873-880 [14] Ly D L, Paprotski V, Danny Y. Neural Networks on GPUs:Restricted Boltzmann Machines, Technical Report, University of Toronto, Canada, 2009. [15] Lopes N, Ribeiro B. Towards adaptive learning with improved convergence of deep belief networks on graphics processing units. Pattern Recognition, 2014, 47(1):114-127 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2013.06.029 [16] Le Roux N, Bengio Y. Representational power of restricted boltzmann machines and deep belief networks. Neural Computation, 2008, 20(6):1631-1649 doi: 10.1162/neco.2008.04-07-510 [17] Hinton G E. Training products of experts by minimizing contrastive divergence. Neural Computation, 2002, 14(8):1771-1800 doi: 10.1162/089976602760128018 [18] Yu X H, Chen G A, Cheng S X. Dynamic learning rate optimization of the backpropagation algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1995, 6(3):669-677 doi: 10.1109/72.377972 [19] Magoulas G D, Vrahatis M N, Androulakis G S. Improving the convergence of the backpropagation algorithm using learning rate adaptation methods. Neural Computation, 1999, 11(7):1769-1796 doi: 10.1162/089976699300016223 [20] Lee H, Ekanadham C, Ng A. Sparse deep belief net model for visual area V2. In:Proceedings of the 2008 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA:MIT Press, 2008. 873-880 [21] Ji N N, Zhang J S, Zhang C X. A sparse-response deep belief network based on rate distortion theory. Pattern Recognition, 2014, 47(9):3179-3191 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2014.03.025 [22] 乔俊飞, 潘广源, 韩红桂.一种连续型深度信念网的设计与应用.自动化学报, 2015, 41(12):2138-2146 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18786.shtmlQiao Jun-Fei, Pan Guang-Yuan, Han Hong-Gui. Design and application of continuous deep belief network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12):2138-2146 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18786.shtml [23] Chang L C, Chen P A, Chang F J. Reinforced two-step-ahead weight adjustment technique for online training of recurrent neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(8):1269-1278 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2200695 [24] Chen Q L, Chai W, Qiao J F. A stable online self-constructing recurrent neural network. Advances in Neural Networks-ISNN 2011. Berlin Heidelberg:Springer, 2011, 6677:122-131 -




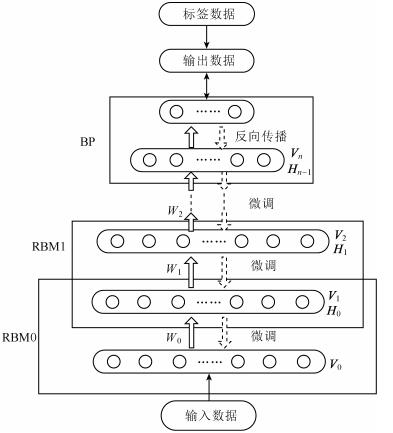
 下载:
下载: