Deep RBM Algorithm with Adaptive Adjustment Parameters and De-noising in Hidden Layer
-
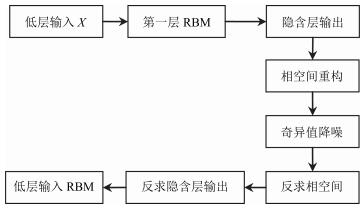
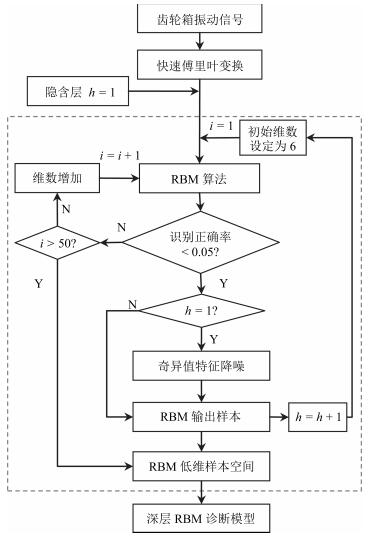
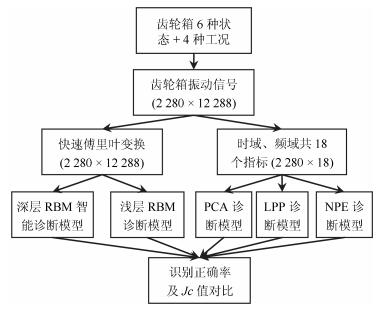
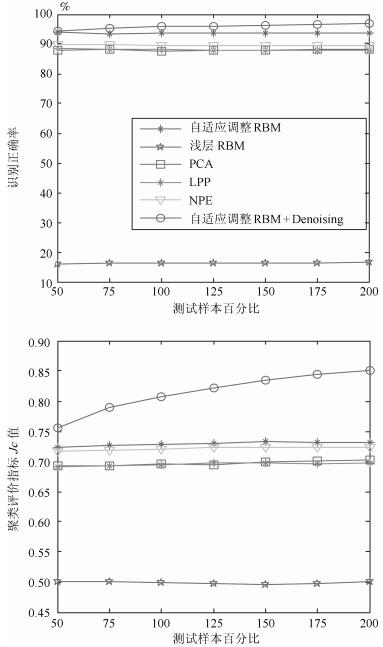
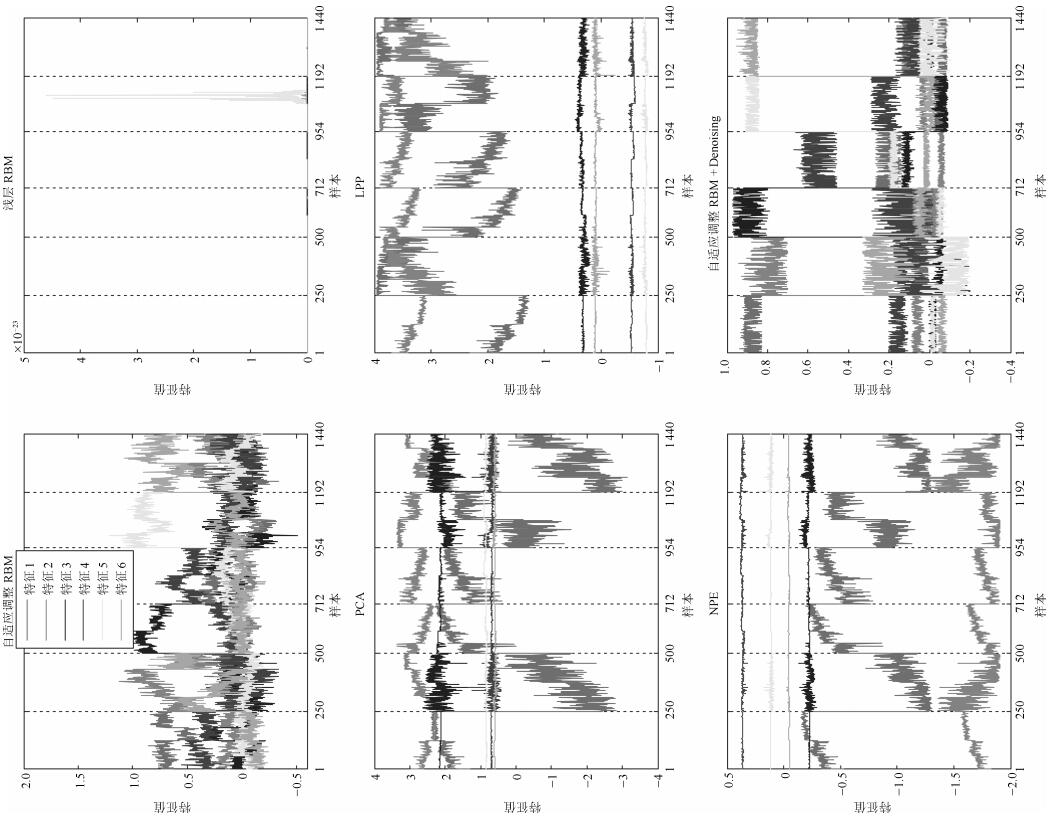
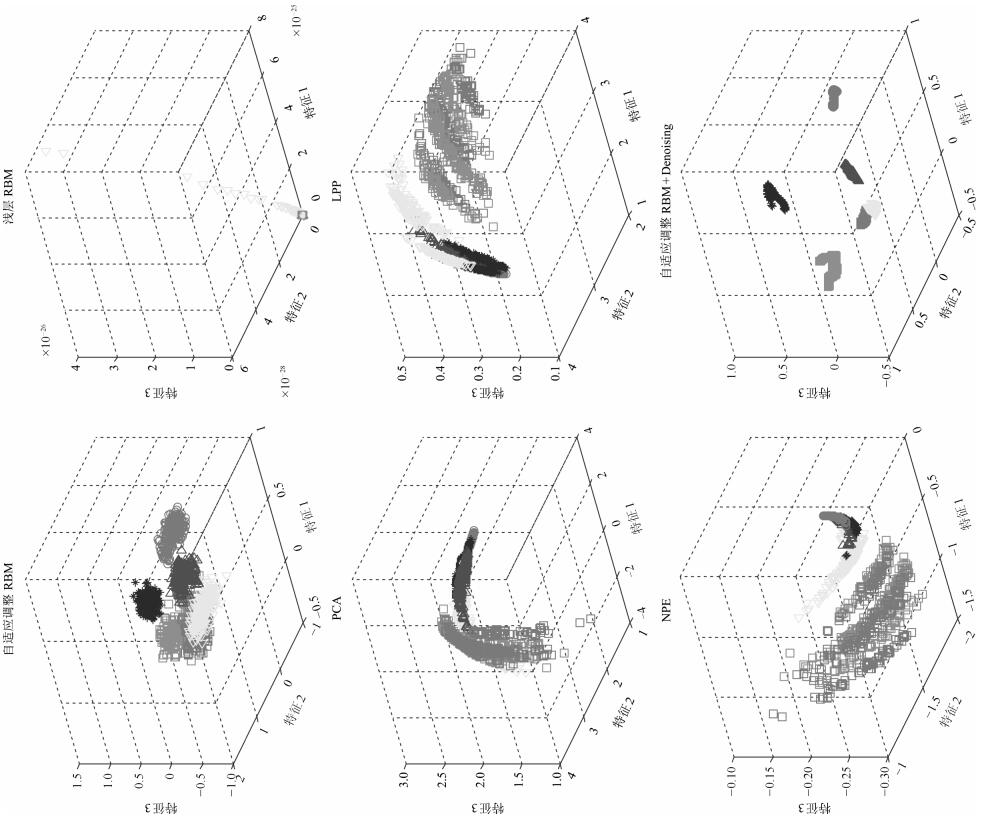
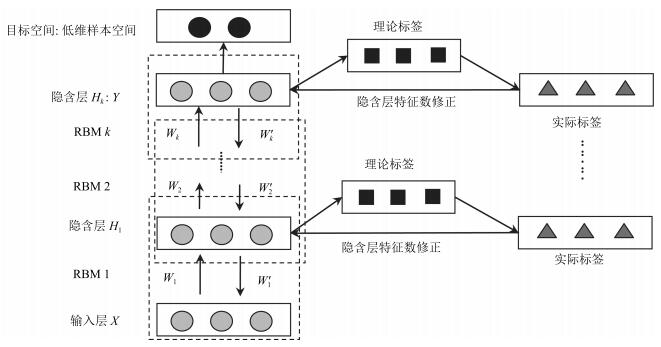
摘要: 深度置信网络是由若干层无监督的限制玻尔兹曼机(Restricted Boltzmann machines,RBM)和一层有监督的反馈神经网络组成的深层结构,该结构通过对低层输入的逐层抽象转化提取复杂输入及复杂分类数据的有效信息.然而,深度置信网络模型存在隐含层数及特征维数难以确定,后向有监督过程存在“导数消亡”问题,使得低层结构参数得不到有效的训练,而且噪声干扰直接影响识别结果的问题.针对以上问题,提出以下解决方法:每个隐含层位置构建当前层输出与样本标签之间的映射转换矩阵,根据理论标签与实际标签之间的差异,实现隐含层特征维数的自适应调整,缓解“导数消亡”问题,同时在第一隐含层位置进行特征空间降噪,保证计算效率及提高诊断模型的识别效果.复杂工况的齿轮箱故障模拟实验,验证所提方法的有效性.Abstract: Deep belief nets consist of several-layered unsupervised restricted Boltzmann machines and one-layered supervised feedback neural network. It digs the inner structure and pattern of the complex input data through effective information abstraction layer by layer, which can well reflect the input mode. However, the hidden layer numbers and the feature dimension are difficult to determine. The feedback process exhibits the vanishing gradient problem, which results in ineffective structural parameters training for lower layers. Moreover, noise affects the recognition results directly. To aim at the problem, a transformation matrix between samples and labels is made for each layer to realize adaptive adjustment of the parameter of hidden layer, and the feature of the hidden layer is de-noised for improving recognition accuracy and calculation efficiency. Simulation experiments on fault diagnosis of a gearbox in complex working conditions have proved the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- Restricted Boltzmann machines (RBM) /
- feature extraction /
- de-noising /
- gearbox
-
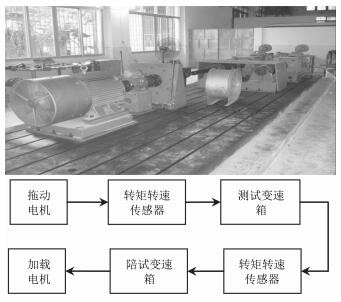
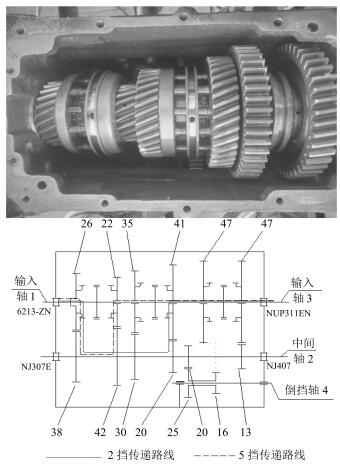
表 1 6种齿轮箱状态在4种工况下的时域波形
Table 1 The time waveform of 6 states of gear box under four conditions

1 000 rmp/0 N·m 1 000 rmp/50 N·m 1 250 rmp/0 N·m 1 250 rmp/50 N·m 正常 



二挡剥落 



五档断齿 



内圈故障0.2 mm 



内圈故障+五挡断齿 



内圈故障+二挡剥落 



-
[1] Kung S Y, Diamantaras K I. A neural network learning algorithm for adaptive principal component extraction (APEX). In: Proceedings of the 1990 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA: IEEE, 1990. 861-864 [2] Yu J B. A nonlinear probabilistic method and contribution analysis for machine condition monitoring. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 37(1-2): 293-314 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2013.01.010 [3] Gui J, Sun Z N, Jia W, Hu R X, Lei Y K, Ji S W. Discriminant sparse neighborhood preserving embedding for face recognition. Pattern Recognition, 2012, 45(8): 2884-2893 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2012.02.005 [4] Hinton G E. Training products of experts by minimizing contrastive divergence. Neural Computation, 2002, 14(8): 1771-1800 doi: 10.1162/089976602760128018 [5] 周风余, 尹建芹, 杨阳, 张海婷, 袁宪锋.基于时序深度置信网络的在线人体动作识别.自动化学报, 2016, 42(7): 1030-1039 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18894.shtmlZhou Feng-Yu, Yin Jian-Qin, Yang Yang, Zhang Hai-Ting, Yuan Xian-Feng. Online recognition of human actions based on temporal deep belief neural network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(7): 1030-1039 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18894.shtml [6] Li F, Tran L, Thung K H, Ji S William, Shen D G, Li J. Robust deep learning for improved classification of AD/MCI patients. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Boston, MA, USA: Springer International Publishing, 2014, 8679: 240-247 [7] 唐朝辉, 朱清新, 洪朝群, 祝峰.基于自编码器及超图学习的多标签特征提取.自动化学报, 2016, 42(7): 1014-1021 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18892.shtmlTang Chao-Hui, Zhu Qing-Xin, Hong Chao-Qun, Zhu William. Multi-label feature selection with autoencoders and hypergraph learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(7): 1014-1021 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18892.shtml [8] Tamilselvan P, Wang P F. Failure diagnosis using deep belief learning based health state classification. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2013, 115: 124-135 doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2013.02.022 [9] Fu Y, Zhang Y, Qiao H Y, Li D Q, Zhou H M, Leopold J. Analysis of feature extracting ability for cutting state monitoring using deep belief networks. In: Proceedings of the 15th Conference on Modelling of Machining Operations. Karlsruhe, Germany: Elsevier, 2015. 29-34 [10] Tran V T, AThobiani F, Ball A. An approach to fault diagnosis of reciprocating compressor valves using Teager-Kaiser energy operator and deep belief networks. Expert Systems with Applications, 2014, 41(9): 4113-4122 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2013.12.026 [11] Gan M, Wang C, Zhu C A. Construction of hierarchical diagnosis network based on deep learning and its application in the fault pattern recognition of rolling element bearings. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 72-73: 92-104 [12] 王宪保, 李洁, 姚明海, 何文秀, 钱沄涛.基于深度学习的太阳能电池片表面缺陷检测方法.模式识别与人工智能, 2014, 27(6): 517-523 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MSSB201406006.htmWang Xian-Bao, Li Jie, Yao Ming-Hai, He Wen-Xiu, Qian Yun-Tao. Solar cells surface defects detection based on deep learning. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2014, 27(6): 517-523 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MSSB201406006.htm [13] 黄海波, 李人宪, 杨琪, 丁渭平, 杨明亮.基于DBNs的车辆悬架减振器异响鉴别方法.西南交通大学学报, 2015, 50(5): 776-782 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201505002.htmHuang Hai-Bo, Li Ren-Xian, Yang Qi, Ding Wei-Ping, Yang Ming-Liang. Identifying abnormal noise of vehicle suspension shock absorber based on deep belief networks. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(5): 776-782 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201505002.htm [14] Li C, Sanchez R V, Zurita G, Cerrada M, Cabrera D, Vásquez R E. Gearbox fault diagnosis based on deep random forest fusion of acoustic and vibratory signals. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 76-77: 283-293 [15] 谢吉朋. 云平台下基于深度学习的高速列车走行部故障诊断技术研究[硕士学位论文], 西南交通大学, 中国, 2015Xie Ji-Peng. Research on Fault Diagnosis of High Speed Running Gear based on Deep Learning under Cloud Platform [Master dissertation], Southwest Jiaotong University, China, 2015 [16] Hinton G E. A practical guide to training restricted Boltzmann machines. Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade (Second edition). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2012. 599-619 [17] 张绍辉, 李巍华. 可变近邻参数的局部线性嵌入算法及其在轴承状态识别中的应用. 机械工程学报, 2013, 49(1): 81−87 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB201301013.htmZhang Shao-Hui, Li Wei-Hua. Variable nearest neighbor locally linear embedding and applications in bearing condition recognition. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(1): 81-87 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB201301013.htm -




 下载:
下载: