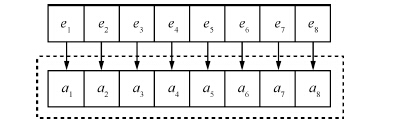
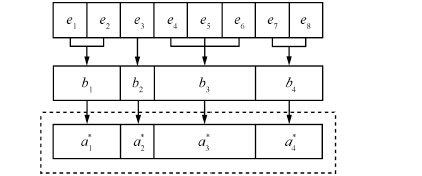
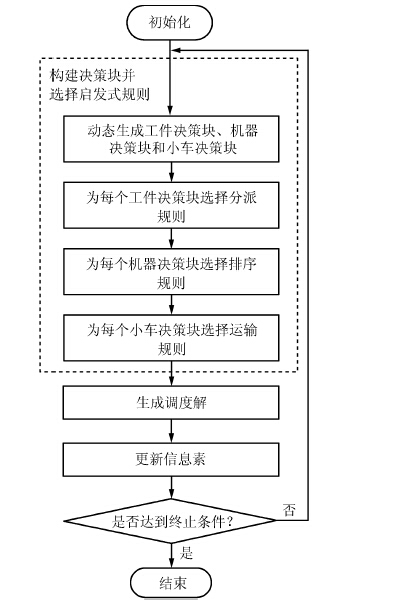
-
摘要: 对运输能力受限条件下的跨单元调度问题进行分析, 提出一种基于动态决策块和蚁群优化 (Ant colony optimization, ACO) 的超启发式方法, 同时解决跨单元生产调度和运输调度问题. 在传统超启发式方法的基础上, 采用动态决策块策略, 通过蚁群算法合理划分决策块, 并为决策块选择合适的规则. 实验表明, 采用动态决策块策略的超启发式方法比传统的超启发式方法具有更好的性能, 本文所提的方法在最小化加权延迟总和目标方面有较好的优化能力 并且具有较高的计算效率.Abstract: In this paper, the inter-cell scheduling problem with a transportation capacity constraint is analyzed. An ant colony optimization (ACO)-based hyper-heuristic with dynamic decision blocks is proposed, which selects appropriate heuristic rules for production and transportation simultaneously. On the basis of traditional hyper-heuristics, a dynamic decision block strategy is proposed, in which several entities are grouped into a decision block under the guidance of pheromones, and appropriate heuristic rules are selected for each decision block. Comparisons between the proposed method and other hyper-heuristics with different decision block strategies are conducted. Computational results show a satisfying performance of the proposed method in minimizing total weighted tardiness with less computational costs.
-
表 1 生成算例属性值
Table 1 Attributes for generating test problems
算例产生参数 取值范围 工件数 U[5, 450] 机器数 U[6, 120] 单元数(小车数) U(3, 15] 每个单元内机器数 U[2, 6] 小车容量 U[2, 10] 工件权重 U(0, 1] 工序加工时间 U[1, 30] 单元间转移时间 U[6, 50] 表 2 DABH参数
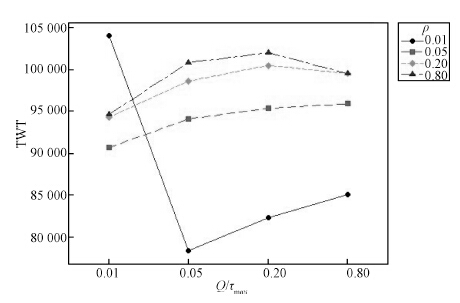
Table 2 Parameters in DABH
参数 范围 ρ (0.01, 0.05, 0.2, 0.8) Q/τmax (0.01, 0.05, 0.2, 0.8) 表 3 DABH 与静态决策块划分策略的性能比较
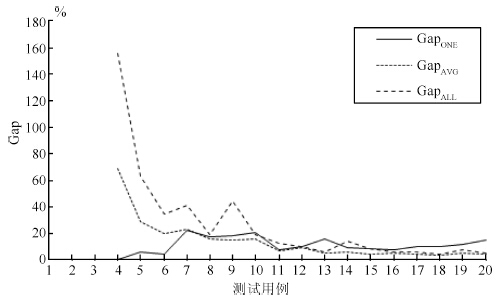
Table 3 Comparison between DABH and static decision block strategies
测试用例 TWT 运行时间(s) GapONE(%) GapALL(%) GapAVG(%) DABH DABH-ONE DABH-ALL DABH-AVG p5m6c3 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.8 - - - p15m8c3 0 0.0 10.5 0.0 4.5 - - - p20m11c3 0 0.0 15.5 0.0 5.6 - - - p40m13c5 1317.5 1320.3 3363.7 2224.9 28.2 0.2 155.3 68.9 p50m15c5 4463.4 4717.4 7292.8 5750.6 38.6 5.7 63.4 28.8 p60m16c5 7853.8 8183.2 10594.3 9416.9 48.9 4.2 34.9 19.9 p70m20c7 7966.6 9736.6 11216.2 9798.4 74.5 22.2 40.8 23.0 p80m21c7 16504.9 19385.3 19653.919 137.8 84.1 17.5 19.1 16.0 p90m21c7 8312.6 9853.9 11981.9 9554.0 98.9 18.5 44.1 14.9 p100m25c9 21774.826 339.4 25924.7 25197.7 93.3 21.0 19.1 15.7 p120m30c9 41868.645 104.2 47292.2 44605.0 145.2 7.7 13.0 6.5 p140m35c11 43255.4 47646.4 47523 47284.2 199 10.2 9.9 9.3 p160m40c11 53375.9 61828.7 56588.8 56262.8 232 15.8 6.0 5.4 p180m45c13 78761 86352.7 89622.8 83336.1 299.5 9.6 13.8 5.8 p200m50c15 110299.3 119319.6 119545.3 115330.3 323.3 8.2 8.4 4.6 p250m65c15 155422.9 167271.9 164193.1 164003.1 447.5 7.6 5.6 5.5 p300m75c15 232254.5 255936 247079.6 243052.9 514.5 10.2 6.4 4.6 p350m90c15 303144.1 334527.3 316700.5 314547.5 692.0 10.4 4.5 3.8 p400m100c15 378489.1 421689.9 406151.6 397148 798.5 11.4 7.3 4.9 p450m120c15 466779.7 535080.7 489769.7 486647.2 1187.9 14.6 4.9 4.3 平均值 11.5 26.8 14.2 表 4 DABH 与DGBH 的性能比较
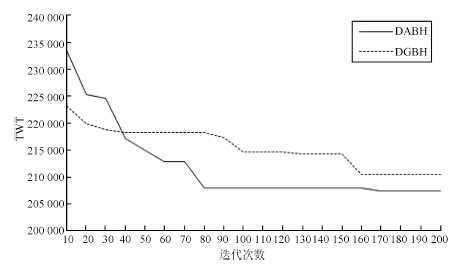
Table 4 Comparison between DABH and DGBH
测试用例 TWT 运行时间(s) GapDGBH(%) DABH DGBH p10m10 6865 7048.0 1.9 2.7 p20m10 26176 26686.8 4.0 2.0 p20m15 37625 39070.2 6.4 3.8 p20m20 23791.8 25214.8 9.3 6.0 p25m20 41136.7 44152.3 14.3 7.3 p25m24 62536.8 67871.5 18.9 8.5 p28m25 118555.2 123994.3 18.9 4.6 p32m25 147814.5 155273.5 25.8 5 p30m30 100600.2 105500 29.4 4.9 p40m25 207853.8 219031.5 32.2 5.4 平均值 5.0 -
[1] Wemmerlov U, Johnson D J. Cellular manufacturing at 46 user plants: implementation experiences and performance improvements. International Journal of Production Research, 1997, 35(1): 29-49 doi: 10.1080/002075497195966 [2] Garza O, Smunt T L. Countering the negative impact of intercell flow in cellular manufacturing. Journal of Operations Management, 1991, 10(1): 92-118 doi: 10.1016/0272-6963(91)90037-X [3] Solimanpur M, Elmi A. A tabu search approach for cell scheduling problem with makespan criterion. International Journal of Production Economics, 2013, 141(2): 639-645 doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2012.10.001 [4] Tang J, Wang X, Kaku I, Yung K L. Optimization of parts scheduling in multiple cells considering intercell move using scatter search approach. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2009, 21(4): 525-537 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2006533609&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Javadian N, Khorrami A, Gholipour-Kanani Y. Design of a scatter search method for a novel multi-criteria group scheduling problem in a cellular manufacturing system. Expert Systems with Applications, 2010, 37(3): 2661-2669 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2009.08.012 [6] Zeng C K, Tang J F, Yan C J. Job-shop cell-scheduling problem with inter-cell moves and automated guided vehicles. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2015, 26(5): 845-859 doi: 10.1007/s10845-014-0875-x [7] Elmi A, Solimanpur M, Topaloglu S, Elmi A. A simulated annealing algorithm for the job shop cell scheduling problem with intercellular moves and reentrant parts. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2011, 61(1): 171-178 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1997058568&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [8] Li D N, Wang Y, Xiao G X, Tang J F. Dynamic parts scheduling in multiple job shop cells considering intercell moves and flexible routes. Computers & Operations Research, 2013, 40(5): 1207-1223 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1971316543&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [9] Vepsalainen A P J, Morton T E. Priority rules for job shops with weighted tardiness costs. Management Science, 1987, 33(8): 1035-1047 doi: 10.1287/mnsc.33.8.1035 [10] Ruiz R, Vázquez-Rodríguez J A. The hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 2010, 205(1): 1-18 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2009.09.024 [11] Park S C, Raman N, Shaw M J. Adaptive scheduling in dynamic flexible manufacturing systems: a dynamic rule selection approach. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1997, 13(4): 486-502 doi: 10.1109/70.611301 [12] Burke E K, Gendreau M, Hyde M, Kendall G, Ochoa G, Özcan E, Qu R. Hyper-heuristics: a survey of the state of the art. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 2013, 64(12): 1695-1724 doi: 10.1057/jors.2013.71 [13] Huang J, Süer G A. A dispatching rule-based genetic algorithm for multi-objective job shop scheduling using fuzzy satisfaction levels. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2015, 86: 29-42 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2063972265&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [14] Zhang R, Song S J, Wu C. A dispatching rule-based hybrid genetic algorithm focusing on non-delay schedules for the job shop scheduling problem. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 67(1-4): 5-17 doi: 10.1007/s00170-013-4751-1 [15] Vázquez-Rodríguez J A, Petrovic S, Salhi A. An investigation of hyper-heuristic search spaces. In: Proceeding of the 2007 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. Singapore: IEEE, 2007. 3776-3783 [16] Vázquez-Rodríguez J A, Petrovic S. A new dispatching rule based genetic algorithm for the multi-objective job shop problem. Journal of Heuristics, 2010, 16(6): 771-793 doi: 10.1007/s10732-009-9120-8 [17] Li D N, Li M, Meng X W, Tian Y N. A hyperheuristic approach for intercell scheduling with single processing machines and batch processing machines. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2015, 45(2): 315-325 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2014.2332443 [18] 贾凌云, 李冬妮, 田云娜. 基于混合蛙跳和遗传规划的跨单元调度方法. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(5): 936-948 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18668.shtmlJia Ling-Yun, Li Dong-Ni, Tian Yun-Na. An Intercell scheduling approach using shuffled frog leaping algorithm and genetic programming. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(5): 936-948 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18668.shtml [19] 刘兆赫, 李冬妮, 王乐衡, 田云娜. 考虑运输能力限制的跨单元调度方法. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(5): 885-898 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18663.shtmlLiu Zhao-He, Li Dong-Ni, Wang Le-Heng, Tian Yun-Na. An inter-cell scheduling approach considering transportation capacity constraints. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(5): 885-898 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18663.shtml [20] Yang T, Kuo Y, Cho C. A genetic algorithms simulation approach for the multi-attribute combinatorial dispatching decision problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, 176(3): 1859-1873 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2005.10.048 [21] Huang K L, Liao C J. Ant colony optimization combined with taboo search for the job shop scheduling problem. Computers & Operations Research, 2008, 35(4): 1030-1046 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2011649121&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [22] Montgomery D C. Design and Analysis of Experiments (6th Edition). New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2005. -




 下载:
下载: