Furnace Temperature Control Using IT2FBLS-based Reinforcement Learning PID for MSWI Process
-
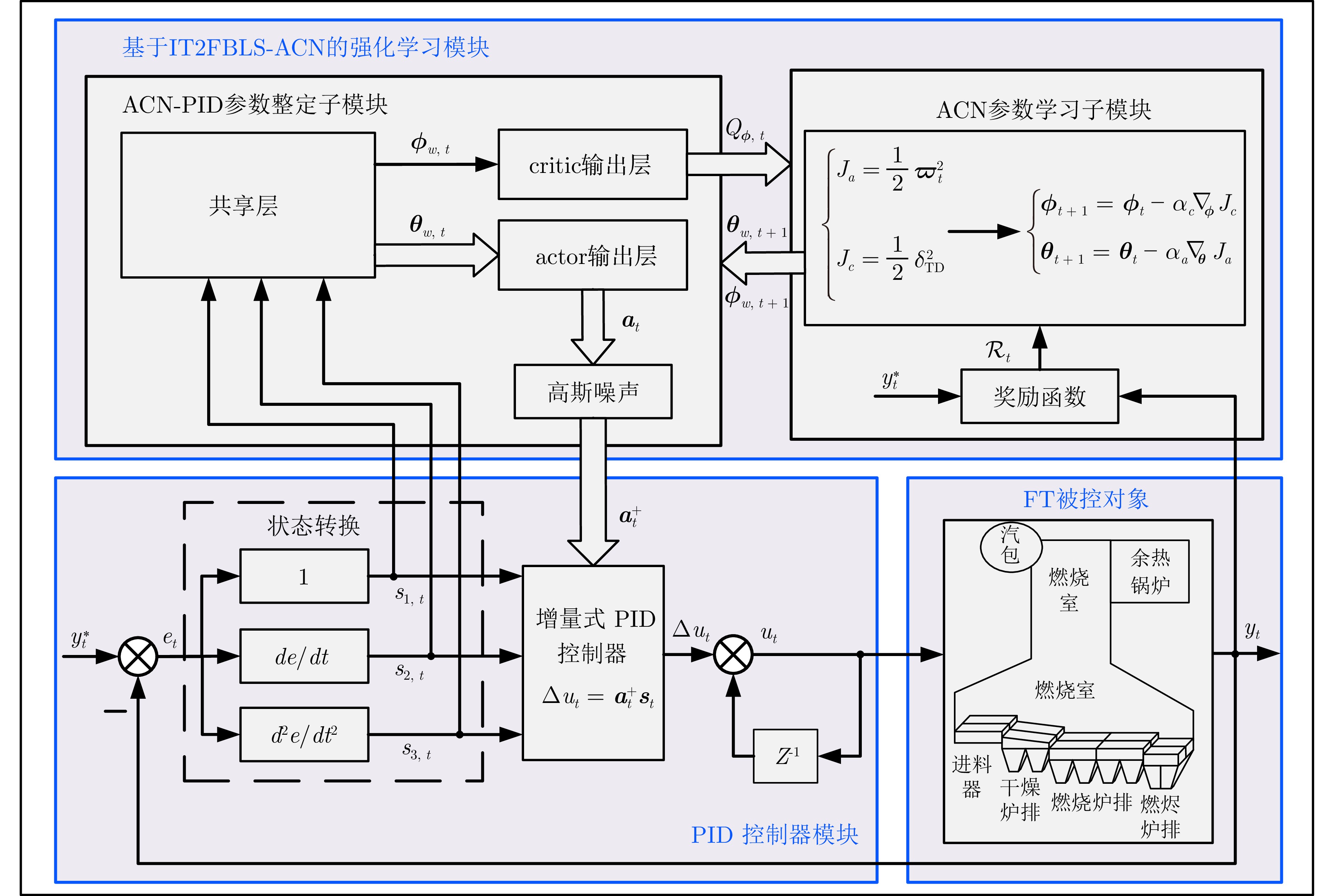
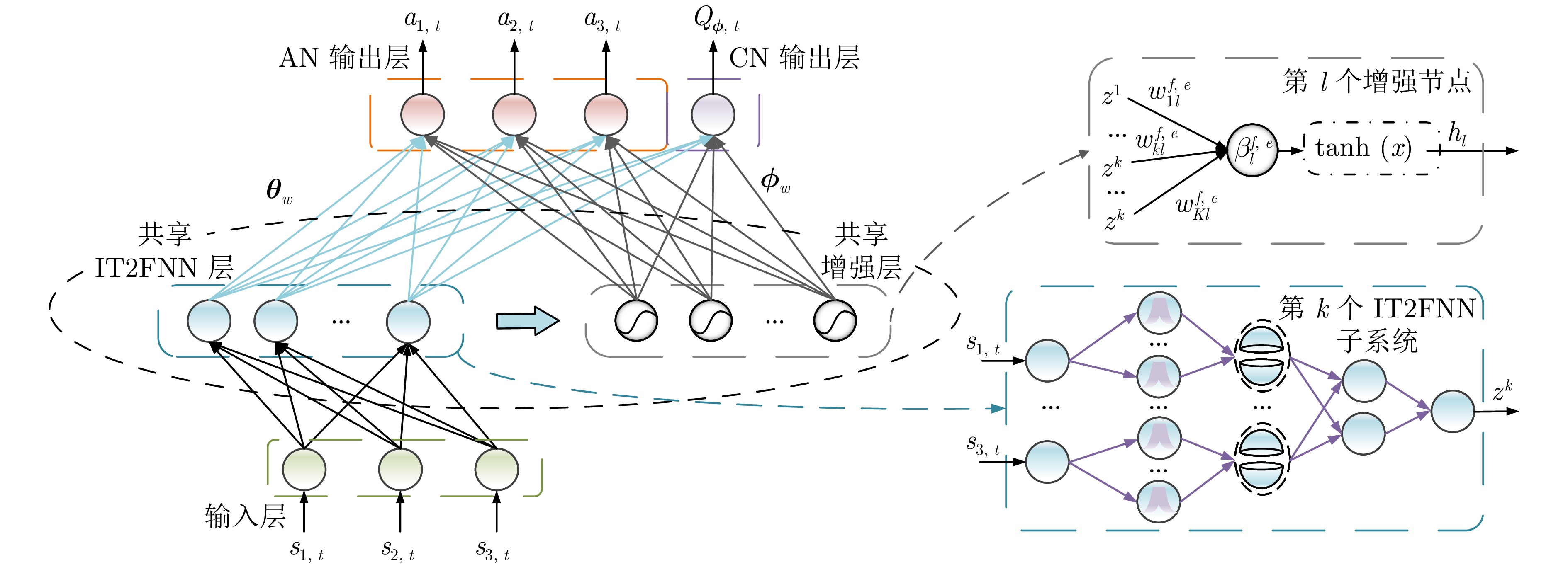
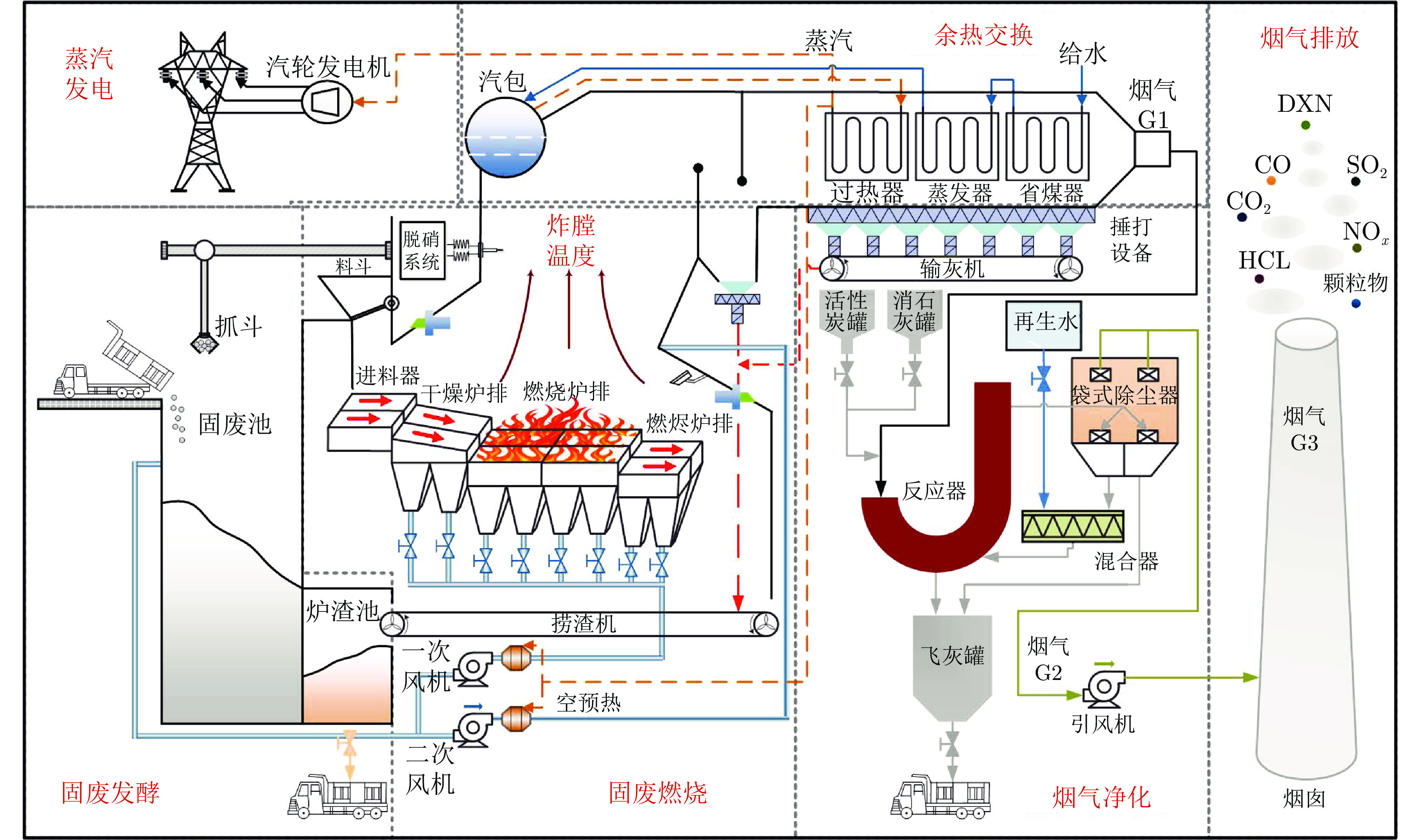
摘要: 城市固废焚烧(MSWI)过程中固有的非线性、时变性和不确定性导致领域专家需要凭借经验通过高频率手动干预进行炉膛温度控制. 针对上述问题, 为模拟专家的自适应机制, 提出了基于强化学习的比例−积分−微分(PID)自整定控制策略, 即采用共享机制区间二型模糊宽度学习系统(IT2FBLS)拟合Actor-critic网络(ACN)进行PID参数优化. 首先, 采用共享机制IT2FBLS拟合ACN以克服焚烧过程的不确定性、减少计算消耗和确保紧凑的网络结构; 然后, 利用基于时间差分误差的梯度下降法更新ACN参数以实现快速学习; 最后, 利用李雅普诺夫第二法, 证明Actor-critic算法的收敛性和控制过程的稳定性. 通过MSWI过程的实际运行数据仿真验证了该方法的有效性.
-
关键词:
- 城市固废焚烧 /
- 炉膛温度控制 /
- 强化学习 /
- 区间二型模糊宽度学习系统 /
- Actor-critic网络 /
- 共享机制 /
- PID参数优化
Abstract: The inherent nonlinearity, time-variability, and uncertainty in the municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) process require domain experts to frequently intervene manually for furnace temperature control. To address this issue, an reinforcement-learning-based proportional-integral-derivative (PID) self-tuning control strategy is proposed to simulate the adaptive mechanisms of experts, using a shared mechanism for interval type-2 fuzzy broad learning system (IT2FBLS) to fit the actor-critic network (ACN) for PID parameter optimization. First, the shared mechanism IT2FBLS is used to fit the ACN to overcome the uncertainties of the incineration process, reduce computational load, and ensure a compact network structure. Then, a gradient descent method based on temporal difference error is used to update the ACN parameters for fast learning. Finally, Lyapunov's second method is used to prove the convergence of the actor-critic algorithm and the stability of the control process. The effectiveness of the proposed method is validated through simulations based on actual operational data from the MSWI process. -
表 1 某天关键 MV 与被控变量的波动范围
Table 1 The fluctuation range of the key MV and the controlled variable on a certain day
过程变量 单位 波动范围 一次风量 km3N/h [53, 76] 二次风量 km3N/h [0, 20] 进料器均速 % [20, 53] 干燥炉排均速 % [20, 60] 氨水注入量 L/h [16, 84] 炉膛温度 ℃ [880, 988] 表 2 控制器超参数设置
Table 2 Controller hyperparameter setting
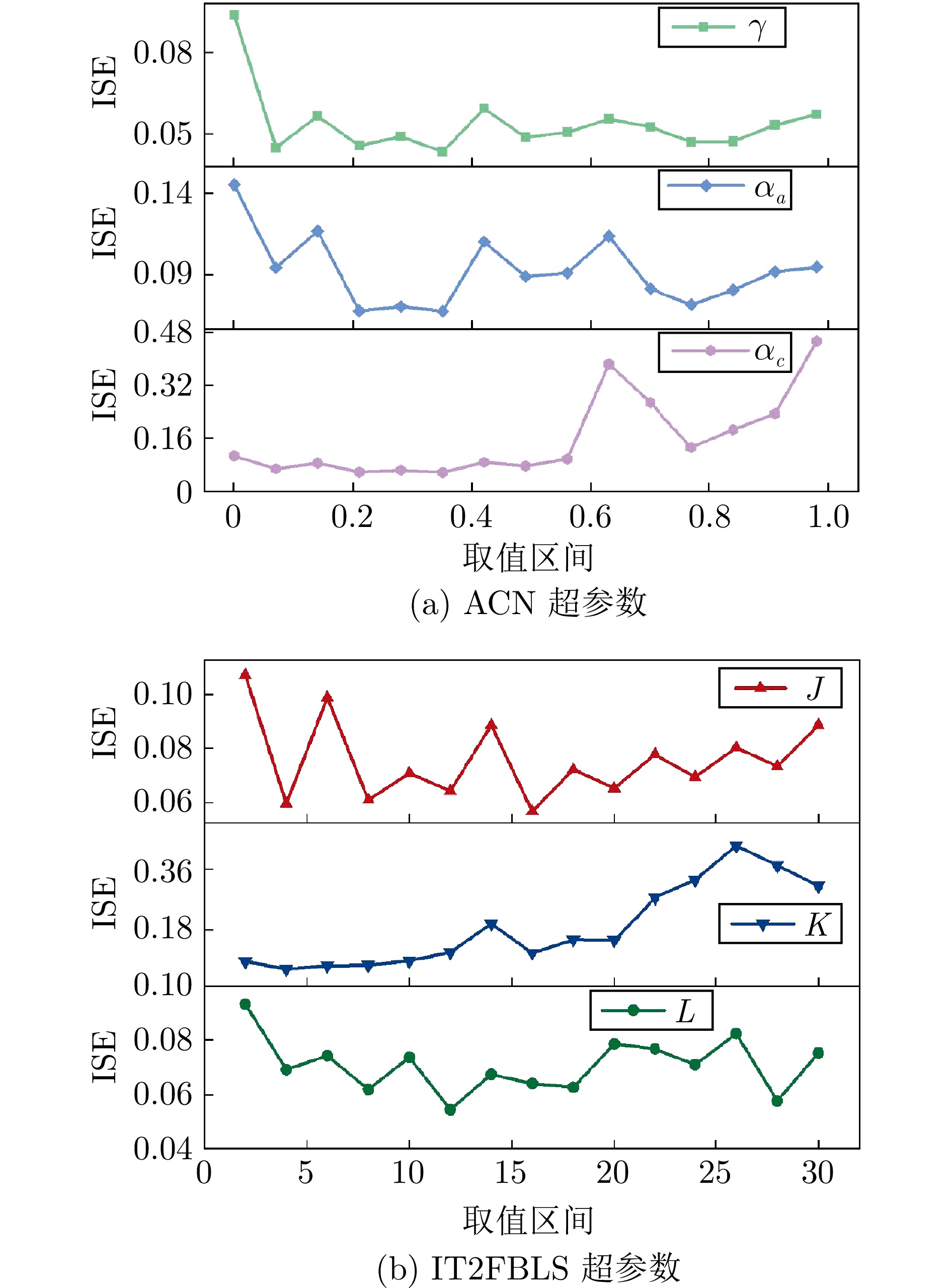
控制器 控制器超参数 BPNN-ACN-PID $ \gamma = 0.9 \quad \eta_1 = 0.1 \quad \eta_2 = 0.1 \quad H_{\text{BPNN}} = 6 $ RBF-ACN-PID $ \gamma = 0.9 \quad \eta_1 = 0.09 \quad \eta_2 = 0.09 \quad H_{\text{RBFNN}} = 10 $ FNN-ACN-PID $ \gamma = 0.9 \quad \eta_1 = 0.5 \quad \eta_2 = 0.5 \quad J_{\text{FNN}} = 10 $ IT2FNN-ACN-PID $ \gamma = 0.9 \quad \eta_1 = 0.5 \quad \eta_2 = 0.1 \quad J_{\text{IT2FNN}} = 10 \quad q_{\text{IT2FNN}} = 0.3 $ IT2FBLS-ACN-PID $ \gamma = 0.9 \quad \eta_1 = 0.8 \quad \eta_2 = 0.001 \quad K = 6 \quad J = 2 \quad L = 9 $ IT2FBLS-ACN-PID-2 $ \gamma = 0.9 \quad \eta_1 = 0.8 \quad \eta_2 = 0.001 \quad K = 6 \quad J = 2 \quad L = 9 $ SA-PID $ \eta_{k_{\mathrm{p}}} =\eta_{k_{\mathrm{i}}}=\eta_{k_{\mathrm{d}}}=\eta_{k}= 0.5 $ PID $ k_{\mathrm{p}}=0.5\quad k\mathrm{_i}=0.3\quad k_{\mathrm{d}}=0.3 $ 表 3 可变设定值的性能指标比较结果
Table 3 Comparison results of performance indicators for variable setpoints
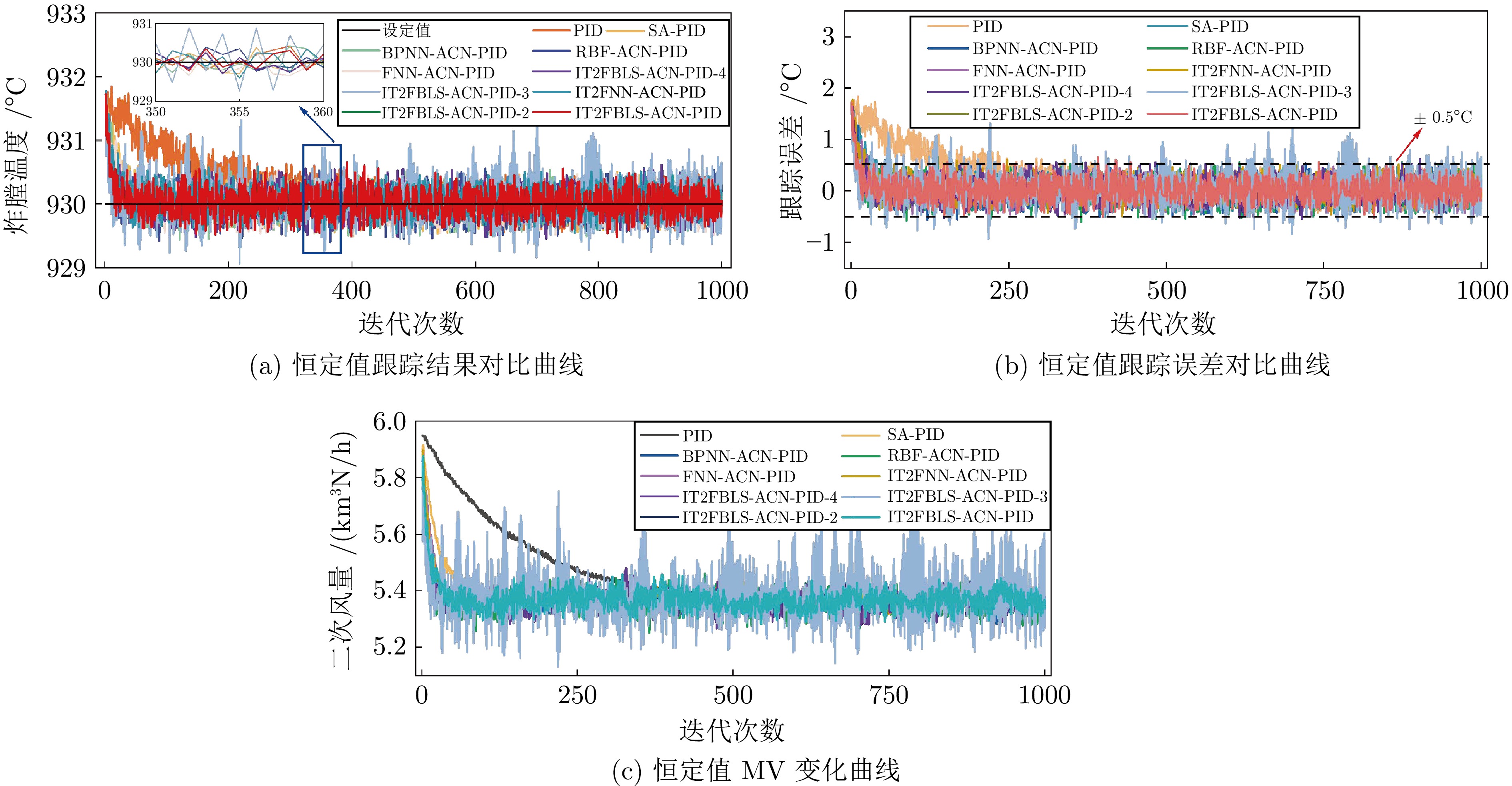
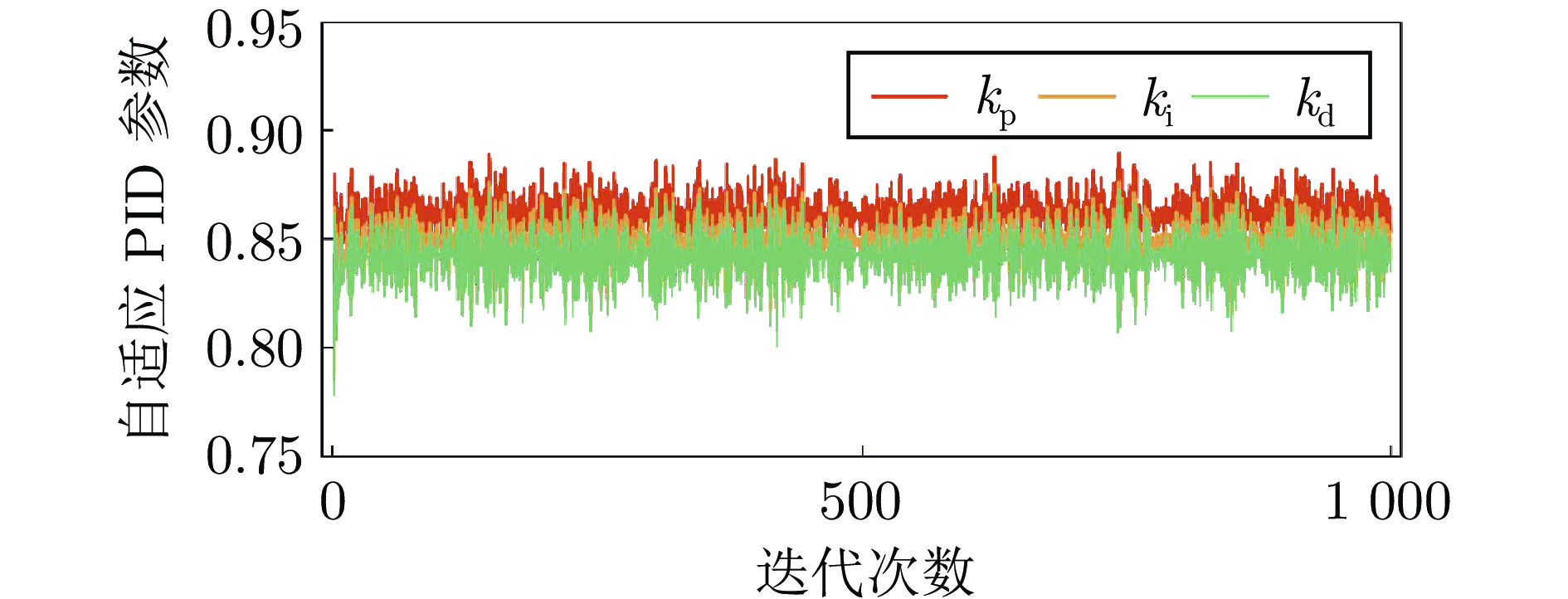
性能指标 $ \mathrm{ISE} $ $ \mathrm{IAE} $ $ \mathrm{Dev^{max}} $ $ \mathrm{RTE} $ $ \mathrm{Times} $ $ \mathrm{BP NN - ACN - PID} $ $ 6.8237e - 02 $ $ 2.0042e - 01 $ $ 1.7204e + 00 $ $ 2.1551e - 01 $ $ 3.0979e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{RBF-ACN-PID} $ $ 6.5013e - 02 $ $ 2.0105e - 01 $ $ 1.7204e + 00 $ $ 2.1619e - 01 $ $ 3.2829e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{FNN-ACN-PID} $ $ 6.6985e - 02 $ $ 2.0108e - 01 $ $ 1.7204e + 00 $ $ 2.1073e - 01 $ $ 3.5140e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{IT2FNN-ACN-PID} $ $ 6.9213e - 02 $ $ 2.0414e - 01 $ $ 1.7715e + 00 $ $ 2.1950e - 01 $ $ 3.5546e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{IT2FBLS-ACN-PID} $ $ 6.3198e - 02 $ $ 1.9915e - 01 $ $ 1.7204e + 00 $ $ 2.1413e - 01 $ $ 3.4852e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{IT2FBLS-ACN-PID}-2 $ $ 6.3195e - 02 $ $ 1.9914e - 01 $ $ 1.7204e + 00 $ $ 2.1413e - 01 $ $ 4.0619e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{IT2FBLS-ACN-PID-3} $ $ 1.4851e - 01 $ $ 3.0492e - 01 $ $ 1.7205e + 00 $ $ 3.2787e - 01 $ $ 3.6160e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{IT2FBLS-ACN-PID-4} $ $ 6.4439e - 02 $ $ 2.0016e - 01 $ $ 1.7209e + 00 $ $ 2.2286e - 01 $ $ 3.6369e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{SA-PID} $ $ 7.6684e - 02 $ $ 2.0435e - 01 $ $ 1.7204e + 00 $ $ 2.1973e - 01 $ $ 3.0443e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{PID} $ $ 2.4123e - 01 $ $ 3.4265e - 01 $ $ 1.8397e + 00 $ $ 3.6844e - 01 $ $ 3.0745e + 00 $ 表 4 可变设定值的性能指标比较结果
Table 4 Comparison results of performance indicators for variable setpoints
性能指标 $ \mathrm{ISE} $ $ \mathrm{IAE} $ $ \mathrm{Dev^{max}} $ $ \mathrm{RTE} $ $ \mathrm{Times} $ $ \mathrm{BP NN - ACN - PID} $ $ 8.4128e - 01 $ $ 3.7392e - 01 $ $ 1.0262e + 01 $ $ 1.2036e + 00 $ $ 9.2577e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{RBF-ACN-PID} $ $ 7.2286e - 01 $ $ 3.4509e - 01 $ $ 1.0279e + 01 $ $ 1.1107e + 00 $ $ 9.4656e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{FNN-ACN-PID} $ $ 9.0199e - 01 $ $ 3.8692e - 01 $ $ 1.0097e + 01 $ $ 1.1716e + 00 $ $ 9.1770e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{IT2FNN-ACN-PID} $ $ 1.1288e + 00 $ $ 1.1288e + 00 $ $ 1.0946e + 01 $ $ 1.2590e + 00 $ $ 1.1038e + 01 $ $ \mathrm{IT2FBLS-ACN-PID} $ $ 6.5344e - 01 $ $ 3.1451e - 01 $ $ 1.0111e + 01 $ $ 1.0127e + 00 $ $ 1.0187e + 01 $ $ \mathrm{IT2FBLS-ACN-PID-2} $ $ 6.7844e - 01 $ $ 3.2273e - 01 $ $ 1.0150e + 01 $ $ 1.0398e + 00 $ $ 1.1434e + 01 $ $ \mathrm{IT2FBLS-ACN-PID-3} $ $ 6.9442e - 01 $ $ 3.2448e - 01 $ $ 1.0152e + 01 $ $ 1.0447e + 00 $ $ 1.0703e + 01 $ $ \mathrm{IT2FBLS-ACN-PID-4} $ $ 6.9264e - 01 $ $ 3.2414e - 01 $ $ 1.0450e + 01 $ $ 1.0437e + 00 $ $ 1.0451e + 01 $ $ \mathrm{SA-PID} $ $ 1.1892e + 00 $ $ 4.6032e - 01 $ $ 1.0249e + 01 $ $ 6.1289e + 02 $ $ 8.9879e + 00 $ $ \mathrm{PID} $ $ 1.4143e + 00 $ $ 5.1122e - 01 $ $ 5.1122e - 01 $ $ 1.6455e + 00 $ $ 9.0585e + 00 $ 表 5 附录 1 英文缩略语
Table 5 Appendix 1 abbreviations in english
Abbreviation Describe FT Furnace Temperature MSW Municipal Solid Waste MSWI Municipal Solid Waste Incineration FNN Fuzzy Neural Network IT2FNN Interval Type - 2 Fuzzy Neural Network PID Proportion, Integration and Differentiation RBFNN Radial Basis Function Neural Network RL Reinforcement Learning ACN Actor - Critic Network BPNN Back - Propagation Neural Network AN Actor Network CN Critic Network BLS Broad Learning System IT2BLS Interval Type - 2 Fuzzy Broad Learning System SOFNN Self - Organizing Fuzzy Neural Network FBLS Fuzzy Broad Learning System T2BLS Type - 2 Fuzzy Broad Learning System MV Manipulated Variable PCC Pearson Correlation Coefficient MDP Markov Decision Process TD Time Difference BIBO Bounded Input - Bounded Output ISE Integrated Square Error IAE Integrated Absolute Error Dev$ \mathrm{_{max}} $ Setpoint Maximum Deviation RTE Relative Tracking Error SA Self - Adaptation -
[1] Sun B, Jiang M, Han G, Zhang L, Zhou J, Bian C, et al. Experimental warming reduces ecosystem resistance and resilience to severe flooding in a wetland. Science Advances, 2022, 8(4): Article No. eabl9526 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl9526 [2] Shahar D. Harm, responsibility, and the far-off impacts of climate change. Environmental Ethics, 2021, 43(1): 3−20 doi: 10.5840/enviroethics202142717 [3] 乔俊飞, 郭子豪, 汤健. 面向城市固废焚烧过程的二噁英排放浓度检测方法综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(6): 1063−1089Qiao Jun-Fei, Guo Zi-Hao, Tang Jian. Dioxin emission concentration measurement approaches for municipal solid wastes incineration process: a survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(6): 1063−1089 [4] Fu L, Wang Q. Spatial and temporal distribution and the driving factors of carbon emissions from urban production energy consumption. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(19): Article No. 12441 doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912441 [5] Pivato A, Girotto F, Megido L, Raga R. Estimation of global warming emissions in waste incineration and landfilling: An environmental forensic case study. Environmental Forensics, 2018, 19(4): 253−264 doi: 10.1080/15275922.2018.1519741 [6] Roy S K, Krishna G, Dubey S R, Chaudhuri B B. HybridSN: Exploring 3-D-2-D CNN feature hierarchy for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(2): 277−281 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2918719 [7] Chu X, Jin Y, Wang X, Wang X, Song X. The evolution of the spatial-temporal differences of municipal solid waste carbon emission efficiency in China. Energies, 2022, 15(11): Article No. 3987 doi: 10.3390/en15113987 [8] Stocker T, Qin D, Plattner GK, Tignor M, Allen S, Boschung J, et al. Summary for policymakers. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC), Cambridge University Press, 2018, 3−24. [9] Zeng C, Yan L, Wang D. Application of fly ash and slag generated by incineration of municipal solid waste in concreteJ. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2020(2020): 1−7 [10] Martínez J, Romero S, Ramasco J, Estrada E. The world-wide waste web. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): Article No. 1615 doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28810-x [11] Kammen D M, Sunter D A. City integrated renewable energy for urban sustainability. Science, 2016, 352(6288): 922−928 doi: 10.1126/science.aad9302 [12] Hunsinger H, Jay K, Vehlow J. Formation and destruction of PCDD/F inside a grate furnace. Chemosphere, 2002, 46(9−10): 1263−1272 doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00256-9 [13] 汤健, 夏恒, 余文, 乔俊飞. 城市固废焚烧过程智能优化控制研究现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(10): 2019−2059Tang Jian, Xia Heng, Yu Wen, Qiao Jun-Fei. Research status and prospects of intelligent optimization control for municipal solid waste incineration process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(10): 2019−2059 [14] Tian H, Tang J, Xia H, Wang T, Cui C, Pan X. Furnace temperature control based on adaptive TS-FNN for municipal solid waste incineration process. In: Proceedings of 2023 35th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). Yichang, China: IEEE, 2023. 360−365 [15] 丁海旭, 汤健, 乔俊飞. 城市固废焚烧过程数据驱动建模与自组织控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 550−566Ding Hai-Xu, Tang Jian, Qiao Jun-Fei. Data-driven Modeling and Self-organizing Control of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 550−566 [16] Ding H, Qiao J, Huang W, Yu T. Cooperative event-triggered fuzzy-neural multivariable control with multi-task learning for municipal solid waste incineration process. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(1): 765−774 [17] Ding H, Qiao J, Huang W, Yu T. Event-triggered fuzzy neural multivariable control for a municipal solid waste incineration process. Science China Technological Sciences, 2023, 66: 3115−3128 [18] Ding H, Qiao J, Huang W, Yu T. Event-triggered online learning fuzzy-neural robust control for furnace temperature in municipal solid waste incineration process. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2024, 21(2): 1201−1213 [19] He H, Meng X, Tang J, Qiao J. Event-triggered-based self-organizing fuzzy neural network control for the municipal solid waste incineration process. Science China Technological Sciences, 2023, 66(4): 1096−1109 doi: 10.1007/s11431-022-2078-3 [20] 汤健, 田昊, 夏恒, 等. 基于区间II型FNN的MSWI过程炉膛温度控制. 北京工业大学学报, 2025, 51(2): 157−172Tang Jian, Tian Hao, Xia Heng, Qiao Jun-Fei. Interval Type-II FNN-based furnace temperature control for municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) process. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2025, 51(2): 157−172 [21] Borase R, Maghade D K, Sondkar S Y, Pawar S N. A review of PID control, tuning methods and applications. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2021, 9(2): 818−827 doi: 10.1007/s40435-020-00665-4 [22] 刘宁, 柴天佑. PID控制器参数的优化整定方法. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(11): 2272−2285Liu Ning, Chai Tian-You. An optimal tuning method of PID controller parameters. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(11): 2272−2285 [23] 柴天佑, 周正, 郑锐, 刘宁, 贾瑶. 端边云协同的PID整定智能系统. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 514−527Chai Tian-You, Zhou Zheng, Zheng Rui, Liu Ning, Jia Yao. PID tuning intelligent system based on end-edge-cloud collaboration. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 514−527 [24] 王天峥, 汤健, 夏恒, 乔俊飞. 城市固废焚烧过程的回路控制半实物仿真平台. 系统仿真学报, 2023, 35(2): 241−253Wang Tian-Zheng, Tang Jian, Xia Heng, Qiao Jun-Fei. Hardware-in-the-loop simulation platform of loop control for municipal solid waste incineration process. Journal of System Simulation, 2023, 35(2): 241−253 [25] Somefun O, Akingbade K, Dahunsi F. The dilemma of PID tuning. Annual Reviews in Control, 2021, 52: 65−74 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2021.05.002 [26] 何海军, 蒙西, 汤健, 等. 城市固废焚烧过程炉膛温度建模与控制研究. 控制工程, 2023, 30(10): 1852−1862He Hai-Jun, Meng Xi, Tang Jian. Modeling and control of furnace temperature in urban solid waste incineration process. Control Engineering, 2023, 30(10): 1852−1862 [27] 何海军, 蒙西, 汤健. 基于ET-RBF-PID的城市固废焚烧过程炉膛温度控制方. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(12): 2262−2273He Hai-Jun, Meng Xi, Tang Jian. A furnace temperature control method for urban solid waste incineration process based on ET-RBF-PID. Control Theory and Applications, 2022, 39(12): 2262−2273 [28] Ding H, Tang J, Qiao J. MIMO modeling and multi-loop control based on neural network for municipal solid waste incineration. Control Engineering Practice, 2022, 127: Article No. 105280 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2022.105280 [29] Guan Z, Yamamoto T. Design of a reinforcement learning PID controller. IEEE Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2021, 16: 1354−60 [30] Liu K, Tang P, Yang W. Application of fuzzy-PID control system in full-mechanized coal face. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology (English Edition), 2005, 15(1): 48−51 [31] Ghith E, Tolba F. Tuning PID controllers based on hybrid arithmetic optimization algorithm and artificial gorilla troop optimization for Micro-Robotics systems. IEEE access, 2023, 11: 27138−27154 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3258187 [32] He Y, Zhou Y, Wei Y, Luo Q, Deng W. Wind driven butterfly optimization algorithm with hybrid mechanism avoiding natural enemies for global optimization and PID controller design. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2023, 20(6): 2935−2972 doi: 10.1007/s42235-023-00416-z [33] Du S, Yan Q, Qiao J. Event-triggered PID control for wastewater treatment plants. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2020, 38: Article No. 101659 doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101659 [34] Wang X, Cheng Y, Sun W. A proposal of adaptive PID controller based on reinforcement learning. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2007, 17(1): 40−44 doi: 10.1016/S1006-1266(07)60009-1 [35] Grondman I. A survey of actor-critic reinforcement learning: Standard and natural policy gradients. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2012, 42(6): 1291−1307 doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2012.2218595 [36] Konda V, John T. Actor-critic algorithms. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 1999, 12: 1−11 [37] Konda V, John N. On actor-critic algorithms. SIAM journal on Control and Optimization, 2003, 42(4): 1143−1166 doi: 10.1137/S0363012901385691 [38] 杜胜利, 陈培锡, 乔俊飞. 一种基于深度强化学习的溶解氧浓度自适应PID控制方法, 国家知识产权局, 202310427799.1, 2023-04- 20Du Sheng-Li, Chen Pei-Xi, Qiao Jun-Fei. A deep reinforcement learning based adaptive PID control method for dissolved oxygen concentration, China, Patent 202310427799.1, April 2023 [39] Li, Q. Diffusion welding furnace temperature controller based on actor-critic. In: Proceedings of 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Guangzhou, China: IEEE, 2019 [40] Sedighizadeh M, Rezazadeh A. A modified adaptive wavelet PID control based on reinforcement learning for wind energy conversion system control. Advances in Electrical And Computer Engineering, 2010, 10(2): 153−159 doi: 10.4316/aece.2010.02027 [41] Han H, Liu H, Li J. Cooperative fuzzy-neural control for wastewater treatment process. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 17(9): 5971−5981 [42] Han H, Liu Z, Li J. Design of syncretic fuzzy-neural control for WWTP. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2022, 30(8): 2837−2849 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2021.3075842 [43] Liu L, Fei J. Extended state observer based interval type-2 fuzzy neural network sliding mode control with its application in active power filter. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 37(5): 5138−5154 [44] Feng S, Chen CLP. Fuzzy broad learning system: A novel neuro-fuzzy model for regression and classification. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(2): 414−424 [45] Han H, Liu Z, Liu H, Qiao J, Chen CLP. Type-2 Fuzzy Broad Learning System. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(10): 10352−10363 [46] Han H, Yang F, Yang H. Type-2 fuzzy broad learning controller for wastewater treatment process. Neurocomputing, 2021, 459(4): 188−200 [47] Wang D. Data-driven tracking control design with reinforcement learning involving a wastewater treatment application. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 123: Article No. 106242 [48] Wang X, Cheng Y, Wei S. A proposal of adaptive PID controller based on reinforcement learning. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2007, 17(1): 40−44 [49] Sedighizadeh M, Rezazadeh A. Adaptive PID controller based on reinforcement learning for wind turbine control. Proceedings of World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 2008, 27: 257−262 [50] Shalaby R, El-Hossainy M, Abo-Zalam B. Optimal fractional-order PID controller based on fractional-order actor-critic algorithm. Neural Computing and Applications. 2023, 35: 2347–2380 [51] Yang Y, Goh Y, Zakaria R, Nasserzadeh V, Swithenbank J. Mathematical modelling of MSW incineration on a travelling bed. Waste Management, 2002, 22(4): 369−380 doi: 10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00019-3 [52] Duan J, Guan Y, Li S, Ren Y, Sun Q, Cheng B. Distributional soft actor-critic: Off-policy reinforcement learning for addressing value estimation errors. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(11): 6584−6598 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3082568 [53] Tsitsiklis J, Van B. An analysis of temporal-difference learning with function approximation. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1997, 42(5): 674−690 doi: 10.1109/9.580874 [54] Tsitsiklis J, Van B. Average cost temporal-difference learning. Automatica, 1999, 35(11): 1799−1808 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(99)00099-0 [55] Chen C, Liu. Z. Broad learning system: An effective and efficient incremental learning system without the need for deep architecture. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(1): 10−24 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2716952 [56] Begian M, Melek W, Mendel J. Stability analysis of type-2 fuzzy systems. In: Proceedings of 2008 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence). Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2008. 947−953 [57] Lakhani A, Chowdhury M, Lu Q. Stability-preserving automatic tuning of PID control with reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2112.15187, 2021. [58] Wang D. Data-driven tracking control design with reinforcement learning involving a wastewater treatment application. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 123: Article No. 106242 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106242 [59] Khater A, El-Nagar A, El-Bardini M, El-Rabaie N. A novel structure of actor-critic learning based on an interval type-2 TSK fuzzy neural network. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 28(11): 3047−3061 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2949554 [60] Liu P, Bai C, Zhao Y, Bai C, Zhao W, Tang X. Generating attentive goals for prioritized hindsight reinforcement learning. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 203: Article No. 106140 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106140 [61] Guan Z, Yamamoto T. Design of a reinforcement learning PID controller. IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2021, 16(10): 1354−1360 doi: 10.1002/tee.23430 [62] Qiu Z, Li C, Zhang X. Experimental study on active vibration control for a kind of two-link flexible manipulator. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 118: 623−644 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.09.001 [63] Ramirez J, Yu W. Reinforcement learning from expert demonstrations with application to redundant robot control. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 119: 105753−105763 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105753 [64] Han H, Wu X, Zhang L, Tian Y, Qiao J. Self-organizing RBF neural network using an adaptive gradient multiobjective particle swarm optimization. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 2017, 49(1): 69−82 [65] Yu W, Li X. Some new results on system identification with dynamic neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2001, 12(2): 412−417 doi: 10.1109/72.914535 [66] Ba D, Li Y, Tong S. Fixed-time adaptive neural tracking control for a class of uncertain nonstrict nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing, 2019, 363: 273−280 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.06.063 [67] Xia H, Tang J, Wang T Z. Interpretable controlled object model offurnace temperature for MSWI process based on a novellinear regressiondecision tree. In: Proceedings of 2023 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). Yichang, China: IEEE, 2023. 325−330 -




 下载:
下载: