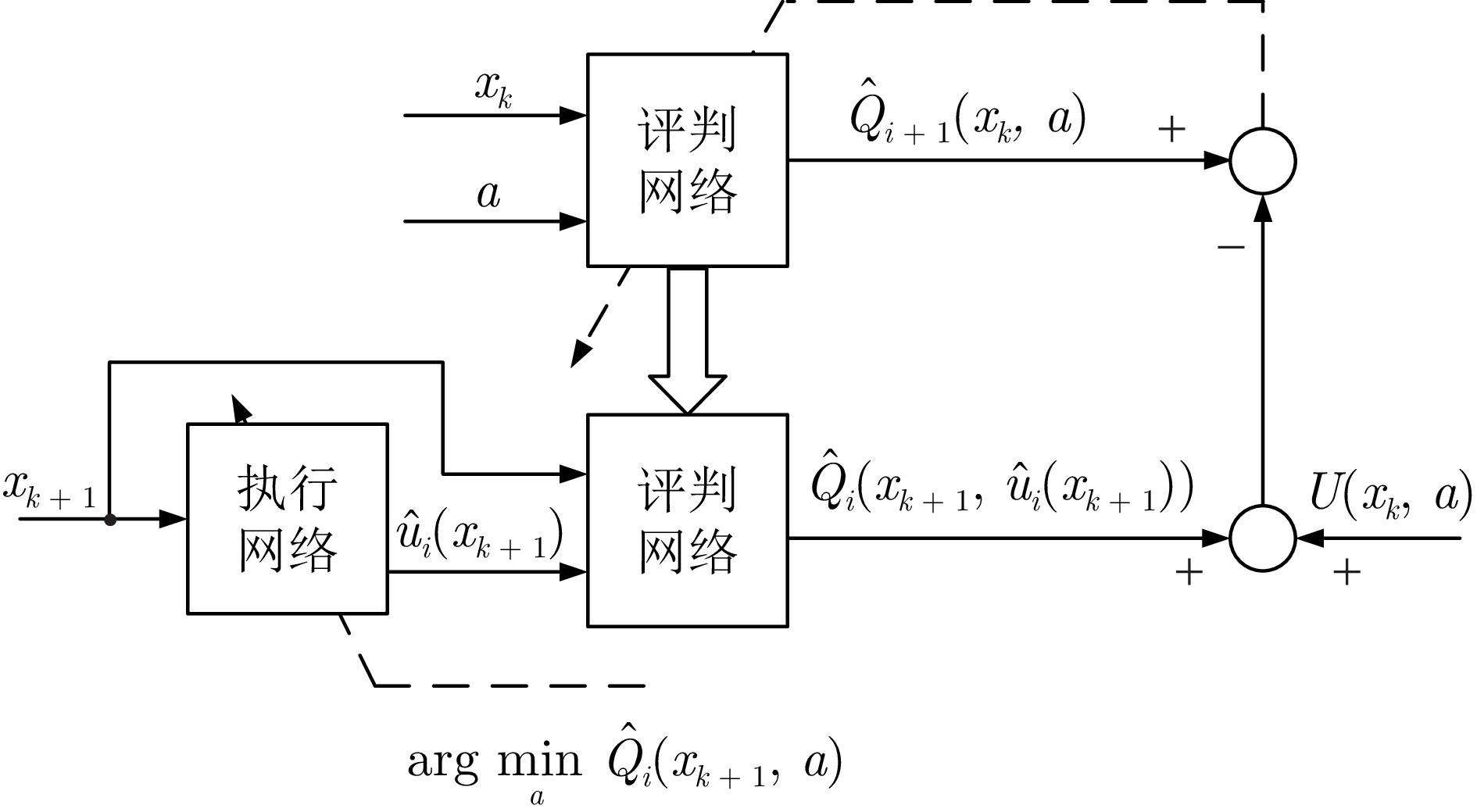
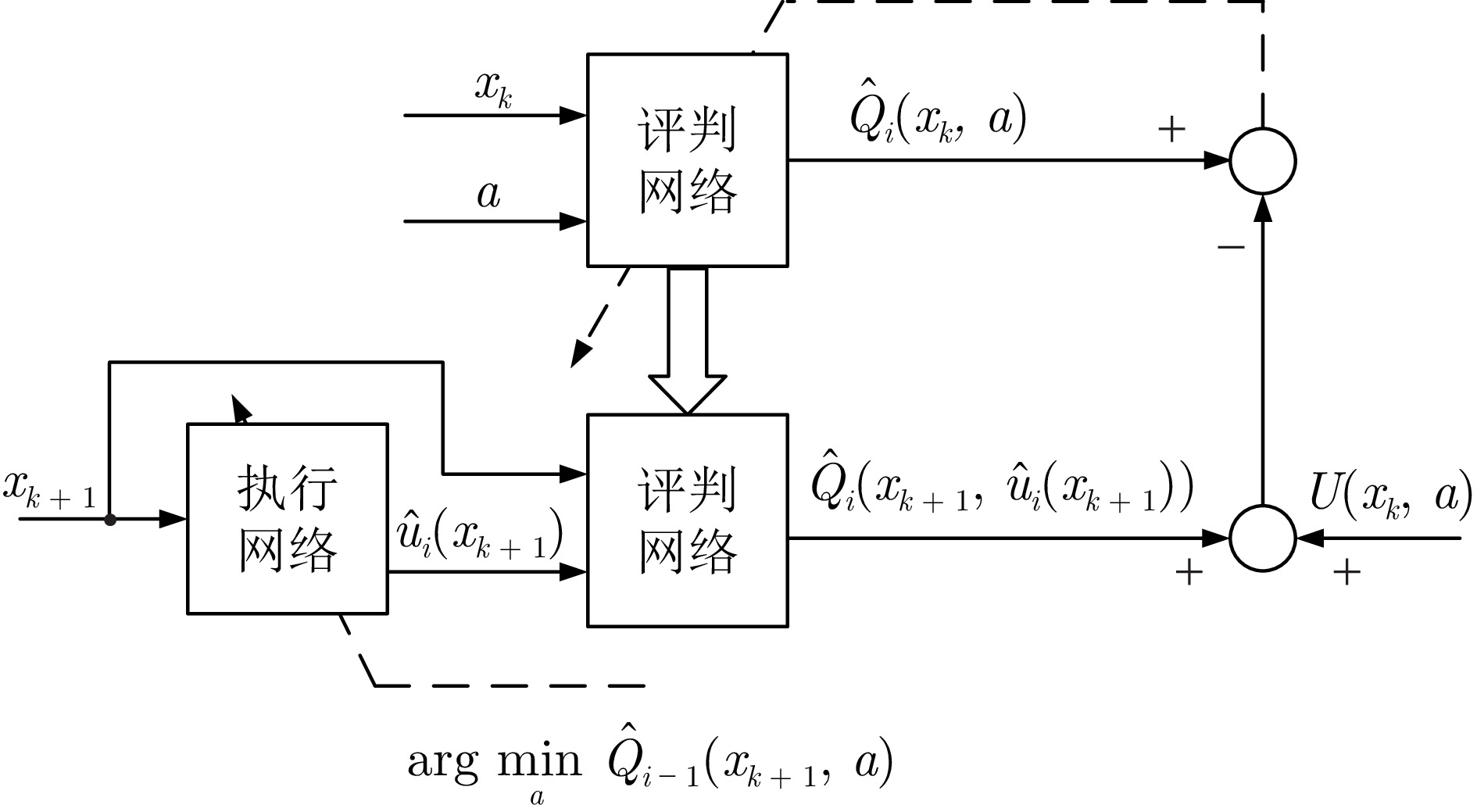
|
[1]
|
张化光, 张欣, 罗艳红, 杨珺. 自适应动态规划综述. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(4): 303−311 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60031-2Zhang Hua-Guang, Zhang Xin, Luo Yan-Hong, Yang Jun. An overview of research on adaptive dynamic programming. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 303−311 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60031-2
|
|
[2]
|
Lewis F L, Vrabie D, Vamvoudakis K G. Reinforcement learning and feedback control: Using natural decision methods to design optimal adaptive controllers. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2012, 32(6): 76−105 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2012.2214134
|
|
[3]
|
Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1998.
|
|
[4]
|
Werbos P J. Approximate Dynamic Programming for Real-time Control and Neural Modeling. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1992.
|
|
[5]
|
刘德荣, 李宏亮, 王鼎. 基于数据的自学习优化控制: 研究进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(11): 1858−1870 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01858Liu De-Rong, Li Hong-Liang, Wang Ding. Data-based self-learning optimal control: Research progress and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1858−1870 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01858
|
|
[6]
|
Mao R Q, Cui R X, Chen C L P. Broad learning with reinforcement learning signal feedback: Theory and applications. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(7): 2952−2964 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3047941
|
|
[7]
|
Shi Y X, Hu Q L, Li D Y, Lv M L. Adaptive optimal tracking control for spacecraft formation flying with event-triggered input. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(5): 6418−6428 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3181067
|
|
[8]
|
孙长银, 穆朝絮. 多智能体深度强化学习的若干关键科学问题. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(7): 1301−1312Sun Chang-Yin, Mu Chao-Xu. Important scientific problems of multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(7): 1301−1312
|
|
[9]
|
Wei Q L, Liao Z H, Shi G. Generalized actor-critic learning optimal control in smart home energy management. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(10): 6614−6623 doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3042631
|
|
[10]
|
王鼎, 赵明明, 哈明鸣, 乔俊飞. 基于折扣广义值迭代的智能最优跟踪及应用验证. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 182−193Wang Ding, Zhao Ming-Ming, Ha Ming-Ming, Qiao Jun-Fei. Intelligent optimal tracking with application verifications via discounted generalized value iteration. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 182−193
|
|
[11]
|
Sun J Y, Dai J, Zhang H G, Yu S H, Xu S, Wang J J. Neural-network-based immune optimization regulation using adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(3): 1944−1953 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3179302
|
|
[12]
|
Liu D R, Ha M M, Xue S. State of the art of adaptive dynamic programming and reinforcement learning. CAAI Artificial Intelligence Research, 2022, 1(2): 93−110 doi: 10.26599/AIR.2022.9150007
|
|
[13]
|
Wang D, Gao N, Liu D R, Li J N, Lewis F L. Recent progress in reinforcement learning and adaptive dynamic programming for advanced control applications. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(1): 18−36 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123843
|
|
[14]
|
王鼎, 赵明明, 哈明鸣, 任进. 智能控制与强化学习: 先进值迭代评判设计. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2024.Wang Ding, Zhao Ming-Ming, Ha Ming-Ming, Ren Jin. Intelligent Control and Reinforcement Learning: Advanced Value Iteration Critic Design. Beijing: Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2024.
|
|
[15]
|
孙景亮, 刘春生. 基于自适应动态规划的导弹制导律研究综述. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(7): 1101−1113Sun Jing-Liang, Liu Chun-Sheng. An overview on the adaptive dynamic programming based missile guidance law. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(7): 1101−1113
|
|
[16]
|
Zhao M M, Wang D, Qiao J F, Ha M M, Ren J. Advanced value iteration for discrete-time intelligent critic control: A survey. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2023, 56: 12315−12346 doi: 10.1007/s10462-023-10497-1
|
|
[17]
|
Wang D, Ha M M, Zhao M M. The intelligent critic framework for advanced optimal control. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2022, 55(1): 1−22 doi: 10.1007/s10462-021-10118-9
|
|
[18]
|
Al-Tamimi A, Lewis F L, Abu-Khalaf M. Discrete-time nonlinear HJB solution using approximate dynamic programming: Convergence proof. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part B: Cybernetics, 2008, 38(4): 943−949 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2008.926614
|
|
[19]
|
Li H L, Liu D R. Optimal control for discrete-time affine non-linear systems using general value iteration. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2012, 6(18): 2725−2736 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2011.0783
|
|
[20]
|
Wei Q L, Liu D R, Lin H Q. Value iteration adaptive dynamic programming for optimal control of discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(3): 840−853 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2492242
|
|
[21]
|
Wang D, Zhao M M, Ha M M, Qiao J F. Stability and admissibility analysis for zero-sum games under general value iteration formulation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(11): 8707−8718 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3152268
|
|
[22]
|
Wang D, Ren J, Ha M M, Qiao J F. System stability of learning-based linear optimal control with general discounted value iteration. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(9): 6504−6514 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3137524
|
|
[23]
|
Heydari A. Stability analysis of optimal adaptive control under value iteration using a stabilizing initial policy. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Syetems, 2018, 29(9): 4522−4527 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2755501
|
|
[24]
|
Wei Q L, Lewis F L, Liu D R, Song R Z, Lin H Q. Discrete-time local value iteration adaptive dynamic programming: Convergence analysis. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 48(6): 875−891 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2623766
|
|
[25]
|
Zhao M M, Wang D, Ha M M, Qiao J F. Evolving and incremental value iteration schemes for nonlinear discrete-time zero-sum games. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(7): 4487−4499 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3198078
|
|
[26]
|
Ha M M, Wang D, Liu D R. Neural-network-based discounted optimal control via an integrated value iteration with accuracy guarantee. Neural Networks, 2021, 144: 176−186 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2021.08.025
|
|
[27]
|
Luo B, Liu D R, Huang T W, Yang X, Ma H W. Multi-step heuristic dynamic programming for optimal control of nonlinear discrete-time systems. Information Sciences, 2017, 411: 66−83 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2017.05.005
|
|
[28]
|
Wang D, Wang J Y, Zhao M M, Xin P, Qiao J F. Adaptive multi-step evaluation design with stability guarantee for discrete-time optimal learning control. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(9): 1797−1809 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123684
|
|
[29]
|
Rao J, Wang J C, Xu J H, Zhao S W. Optimal control of nonlinear system based on deterministic policy gradient with eligibility traces. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2023, 111: 20041−20053 doi: 10.1007/s11071-023-08909-6
|
|
[30]
|
Yu L Y, Liu W B, Liu Y R, Alsaadi F E. Learning-based T-sHDP (λ) for optimal control of a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2022, 32(5): 2624−2643 doi: 10.1002/rnc.5847
|
|
[31]
|
Al-Dabooni S, Wunsch D. An improved n-step value gradient learning adaptive dynamic programming algorithm for online learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(4): 1155−1169 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2919338
|
|
[32]
|
Wang J Y, Wang D, Li X, Qiao J F. Dichotomy value iteration with parallel learning design towards discrete-time zero-sum games. Neural Networks, 2023, 167: 751−762 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2023.09.009
|
|
[33]
|
Wei Q L, Wang L X, Lu J W, Wang F Y. Discrete-time self-learning parallel control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(1): 192−204 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.2995646
|
|
[34]
|
Ha M M, Wang D, Liu D R. A novel value iteration scheme with adjustable convergence rate. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(10): 7430−7442 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3143527
|
|
[35]
|
Ha M M, Wang D, Liu D R. Novel discounted adaptive critic control designs with accelerated learning formulation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(5): 3003−3016 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3233593
|
|
[36]
|
Wang D, Huang H M, Liu D R, Zhao M M, Qiao J F. Evolution-guided adaptive dynamic programming for nonlinear optimal control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(10): 6043−6054 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3417230
|
|
[37]
|
Liu D R, Wei Q L. Policy iteration adaptive dynamic programming algorithm for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(3): 621−634 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2281663
|
|
[38]
|
Liu D R, Wei Q L. Generalized policy iteration adaptive dynamic programming for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2015, 45(12): 1577−1591 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2015.2417510
|
|
[39]
|
Liang M M, Wang D, Liu D R. Neuro-optimal control for discrete stochastic processes via a novel policy iteration algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(11): 3972−3985 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2907991
|
|
[40]
|
Luo B, Yang Y, Wu H N, Huang T W. Balancing value iteration and policy iteration for discrete-time control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(11): 3948−3958 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2898389
|
|
[41]
|
Li T, Wei Q L, Wang F Y. Multistep look-ahead policy iteration for optimal control of discrete-time nonlinear systems with isoperimetric constraints. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(3): 1414−1426 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3327492
|
|
[42]
|
Yang Y L, Kiumarsi B, Modares H, Xu C Z. Model-free λ-policy iteration for discrete-time linear quadratic regulation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(2): 635−649 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3098985
|
|
[43]
|
Huang H M, Wang D, Wang H, Wu J L, Zhao M M. Novel generalized policy iteration for efficient evolving control of nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing, 2024, 608: Article No. 128418 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.128418
|
|
[44]
|
Dierks T, Jagannathan S. Online optimal control of affine nonlinear discrete-time systems with unknown internal dynamics by using time-based policy update. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(7): 1118−1129 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2196708
|
|
[45]
|
Wang D, Xin P, Zhao M M, Qiao J F. Intelligent optimal control of constrained nonlinear systems via receding-horizon heuristic dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(1): 287−299 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3306338
|
|
[46]
|
Moghadam R, Natarajan P, Jagannathan S. Online optimal adaptive control of partially uncertain nonlinear discrete-time systems using multilayer neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(9): 4840−4850 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3061414
|
|
[47]
|
Zhang H G, Qin C B, Jiang B, Luo Y H. Online adaptive policy learning algorithm for H∞ state feedback control of unknown affine nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(12): 2706−2718 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2313915
|
|
[48]
|
Ming Z Y, Zhang H G, Yan Y Q, Zhang J. Tracking control of discrete-time system with dynamic event-based adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(8): 3570−3574
|
|
[49]
|
罗彪, 欧阳志华, 易昕宁, 刘德荣. 基于自适应动态规划的移动机器人视觉伺服跟踪控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(11): 2286−2296Luo Biao, Ouyang Zhi-Hua, Yi Xin-Ning, Liu De-Rong. Adaptive dynamic programming based visual servoing tracking control for mobile robots. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(11): 2286−2296
|
|
[50]
|
Ha M M, Wang D, Liu D R. Discounted iterative adaptive critic designs with novel stability analysis for tracking control. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2022, 9(7): 1262−1272 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2022.105692
|
|
[51]
|
Dong L, Zhong X N, Sun C Y, He H B. Adaptive event-triggered control based on heuristic dynamic programming for nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(7): 1594−1605 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2541020
|
|
[52]
|
Wang D, Hu L Z, Zhao M M, Qiao J F. Dual event-triggered constrained control through adaptive critic for discrete-time zero-sum games. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(3): 1584−1595 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3201671
|
|
[53]
|
Yang X, Wang D. Reinforcement learning for robust dynamic event-driven constrained control. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, DOI: 10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3394251
|
|
[54]
|
王鼎. 基于学习的鲁棒自适应评判控制研究进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1031−1043Wang Ding. Research progress on learning-based robust adaptive critic control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(6): 1031−1043
|
|
[55]
|
Ren H, Jiang B, Ma Y J. Zero-sum differential game-based fault-tolerant control for a class of affine nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(2): 1272−1282 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3215716
|
|
[56]
|
Zhang S C, Zhao B, Liu D R, Zhang Y W. Event-triggered decentralized integral sliding mode control for input-constrained nonlinear large-scale systems with actuator failures. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(3): 1914−1925 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3331150
|
|
[57]
|
Wei Q L, Zhu L, Song R Z, Zhang P J, Liu D R, Xiao J. Model-free adaptive optimal control for unknown nonlinear multiplayer nonzero-sum game. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(2): 879−892 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3030127
|
|
[58]
|
Ye J, Bian Y G, Luo B, Hu M J, Xu B, Ding R. Costate-supplement ADP for model-free optimal control of discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(1): 45−59 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3172126
|
|
[59]
|
Li Y Q, Yang C Z, Hou Z S, Feng Y J, Yin C K. Data-driven approximate Q-learning stabilization with optimality error bound analysis. Automatica, 2019, 103: 435−442
|
|
[60]
|
Al-Dabooni S, Wunsch D C. Online model-free n-step HDP with stability analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(4): 1255−1269 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2919614
|
|
[61]
|
Ni Z, He H B, Zhong X N, Prokhorov D V. Model-free dual heuristic dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(8): 1834−1839 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2424971
|
|
[62]
|
Wang D, Ha M M, Qiao J F. Self-learning optimal regulation for discrete-time nonlinear systems under event-driven formulation. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 65(3): 1272−1279 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2926167
|
|
[63]
|
Wang D, Ha M M, Qiao J F. Data-driven iterative adaptive critic control toward an urban wastewater treatment plant. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(8): 7362−7369 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3001840
|
|
[64]
|
Wang D, Hu L Z, Zhao M M, Qiao J F. Adaptive critic for event-triggered unknown nonlinear optimal tracking design with wastewater treatment applications. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(9): 6276−6288 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3135405
|
|
[65]
|
Zhu L, Wei Q L, Guo P. Synergetic learning neuro-control for unknown affine nonlinear systems with asymptotic stability guarantees. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2025, 36(2): 3479−3489 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3347663
|
|
[66]
|
Pang B, Jiang Z P. Adaptive optimal control of linear periodic systems: An off-policy value iteration approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(2): 888−894 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.2987313
|
|
[67]
|
Xu Y S, Zhao Z G, Yin S. Performance optimization and fault-tolerance of highly dynamic systems via Q-learning with an incrementally attached controller gain system. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(11): 9128−9138 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3155876
|
|
[68]
|
Yang X, Xu M M, Wei Q L. Adaptive dynamic programming for nonlinear-constrained H∞ control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(7): 4393−4403 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3247888
|
|
[69]
|
Werbos P J. Neural networks for control and system identification. In: Proceedings of the 28th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Tampa, FL, USA: IEEE, 1989. 260−265
|
|
[70]
|
Prokhorov D V, Wunsch D C. Adaptive critic designs. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1997, 8(5): 997−1007 doi: 10.1109/72.623201
|
|
[71]
|
Watkins C. Learning From Delayed Rewards [Ph.D. dissertation], King's College of Cambridge, UK, 1989.
|
|
[72]
|
Al-Tamimi A, Lewis F L, Abu-Khalaf M. Model-free Q-learning designs for linear discrete-time zero-sum games with application to H-infinity control. Automatica, 2007, 43(3): 473−481 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.09.019
|
|
[73]
|
Kiumarsi B, Lewis F L, Modares H, Karimpour A, Naghibi-Sistani M. Reinforcement Q-learning for optimal tracking control of linear discrete-time systems with unknown dynamics. Automatica, 2014, 50(4): 1167−1175 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.02.015
|
|
[74]
|
Jiang Y, Jiang Z P. Computational adaptive optimal control for continuous-time linear systems with completely unknown dynamics. Automatica, 2012, 48(10): 2699−2704 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.06.096
|
|
[75]
|
Kiumarsi B, Lewis F L, Jiang Z P. H∞ control of linear discrete-time systems: Off-policy reinforcement learning. Automatica, 2017, 78: 144−152 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.12.009
|
|
[76]
|
Farjadnasab M, Babazadeh M. Model-free LQR design by Q-function learning. Automatica, 2022, 137: Article No. 110060 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.110060
|
|
[77]
|
Lopez V G, Alsalti M, Müller M A. Efficient off-policy Q-learning for data-based discrete-time LQR problems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(5): 2922−2933 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3235967
|
|
[78]
|
Nguyen H, Dang H B, Dao P N. On-policy and off-policy Q-learning strategies for spacecraft systems: An approach for time-varying discrete-time without controllability assumption of augmented system. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2024, 146: Article No. 108972 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2024.108972
|
|
[79]
|
Skach J, Kiumarsi B, Lewis F L, Straka O. Actor-critic off-policy learning for optimal control of multiple-model discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(1): 29−40 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2618926
|
|
[80]
|
Wen Y L, Zhang H G, Ren H, Zhang K. Off-policy based adaptive dynamic programming method for nonzero-sum games on discrete-time system. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2020, 357(12): 8059−8081 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.05.038
|
|
[81]
|
Xu Y, Wu Z G. Data-efficient off-policy learning for distributed optimal tracking control of HMAS with unidentified exosystem dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(3): 3181−3190 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3172130
|
|
[82]
|
Cui L L, Pang B, Jiang Z P. Learning-based adaptive optimal control of linear time-delay systems: A policy iteration approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(1): 629−636 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3273786
|
|
[83]
|
Amirparast A, Sani S K H. Off-policy reinforcement learning algorithm for robust optimal control of uncertain nonlinear systems. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2024, 34(8): 5419−5437 doi: 10.1002/rnc.7278
|
|
[84]
|
Qasem O, Gao W N, Vamvoudakis K G. Adaptive optimal control of continuous-time nonlinear affine systems via hybrid iteration. Automatica, 2023, 157: Article No. 111261 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.111261
|
|
[85]
|
Jiang H Y, Zhou B, Duan G R. Modified λ-policy iteration based adaptive dynamic programming for unknown discrete-time linear systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(3): 3291−3301 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3244934
|
|
[86]
|
Zhao J G, Yang C Y, Gao W N, Park J H. Novel single-loop policy iteration for linear zero-sum games. Automatica, 2024, 163: Article No. 111551 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2024.111551
|
|
[87]
|
肖振飞, 李金娜. 基于非策略Q学习方法的两个个体优化控制. 控制工程, 2022, 29(10): 1874−1880Xiao Zhen-Fei, Li Jin-Na. Two-player optimization control based on off-policy Q-learning algorithm. Control Engineering of China, 2022, 29(10): 1874−1880
|
|
[88]
|
Liu Y, Zhang H G, Yu R, Xing Z X. H∞ tracking control of discrete-time system with delays via data-based adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(11): 4078−4085 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2946397
|
|
[89]
|
Zhang H G, Liu Y, Xiao G Y, Jiang H. Data-based adaptive dynamic programming for a class of discrete-time systems with multiple delays. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(2): 432−441 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2758849
|
|
[90]
|
Tan X F, Li Y, Liu Y. Stochastic linear quadratic optimal tracking control for discrete-time systems with delays based on Q-learning algorithm. AIMS Mathematics, 2023, 8(5): 10249−10265 doi: 10.3934/math.2023519
|
|
[91]
|
Zhang L L, Zhang H G, Sun J Y, Yue X. ADP-based fault-tolerant control for multiagent systems with semi-markovian jump parameters. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(10): 5952−5962 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2024.3411310
|
|
[92]
|
Li Y, Zhang H, Wang Z P, Huang C, Yan H C. Data-driven decentralized control for large-scale systems with sparsity and communication delays. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(9): 5614−5624 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3274292
|
|
[93]
|
Shen X Y, Li X J. Data-driven output-feedback LQ secure control for unknown cyber-physical systems against sparse actuator attacks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(9): 5708−5720 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2957146
|
|
[94]
|
Qasem O, Davari M, Gao W N, Kirk D R, Chai T Y. Hybrid iteration ADP algorithm to solve cooperative, optimal output regulation problem for continuous-time, linear, multiagent systems: Theory and application in islanded modern microgrids with IBRs. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(1): 834−845 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3247734
|
|
[95]
|
Zhang H G, Liang H J, Wang Z S, Feng T. Optimal output regulation for heterogeneous multiagent systems via adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(1): 18−29 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2499757
|
|
[96]
|
Wang W, Chen X. Model-free optimal containment control of multi-agent systems based on actor-critic framework. Neurocomputing, 2018, 314(7): 242−250
|
|
[97]
|
Cui L L, Wang S, Zhang J F, Zhang D S, Lai J, Zheng Y, et al. Learning-based balance control of wheel-legged robots. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(4): 7667−7674 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3100269
|
|
[98]
|
Liu T, Cui L L, Pang B, Jiang Z P. A unified framework for data-driven optimal control of connected vehicles in mixed traffic. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023, 8(8): 4131−4145 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3287131
|
|
[99]
|
Davari M, Gao W N, Aghazadeh A, Blaabjerg F, Lewis F L. An optimal synchronization control method of PLL utilizing adaptive dynamic programming to synchronize inverter-based resources with unbalanced, low-inertia, and very weak grids. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22: 24−42 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2023.3329479
|
|
[100]
|
Wang Z Y, Wang Y Q, Davari M, Blaabjerg F. An effective PQ-decoupling control scheme using adaptive dynamic programming approach to reducing oscillations of virtual synchronous generators for grid connection with different impedance types. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(4): 3763−3775 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3279564
|
|
[101]
|
Si J, Wang Y T. Online learning control by association and reinforcement. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2001, 12(2): 264−276 doi: 10.1109/72.914523
|
|
[102]
|
Liu F, Sun J, Si J, Guo W T, Mei S W. A boundedness result for the direct heuristic dynamic programming. Neural Networks, 2012, 32: 229−235 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2012.02.005
|
|
[103]
|
Sokolov Y, Kozma R, Werbos L D, Werbos P J. Complete stability analysis of a heuristic approximate dynamic programming control design. Automatica, 2015, 59: 9−18 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2015.06.001
|
|
[104]
|
Malla N, Ni Z. A new history experience replay design for model-free adaptive dynamic programming. Neurocomputing, 2017, 266(29): 141−149
|
|
[105]
|
Luo B, Wu H N, Huang T W, Liu D R. Data-based approximate policy iteration for affine nonlinear continuous-time optimal control design. Automatica, 2014, 50(12): 3281−3290 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.056
|
|
[106]
|
Zhao D B, Xia Z P, Wang D. Model-free optimal control for affine nonlinear systems with convergence analysis. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2015, 12(4): 1461−1468 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2014.2348991
|
|
[107]
|
Xu J H, Wang J C, Rao J, Zhong Y J, Wu S Y, Sun Q F. Parallel cross entropy policy gradient adaptive dynamic programming for optimal tracking control of discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(6): 3809−3821 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3373456
|
|
[108]
|
Wei Q L, Lewis F L, Sun Q Y, Yan P F, Song R Z. Discrete-time deterministic Q-learning: A novel convergence analysis. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(5): 1224−1237 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2542923
|
|
[109]
|
王鼎, 王将宇, 乔俊飞. 融合自适应评判的随机系统数据驱动策略优化. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(5): 980−990Wang Ding, Wang Jiang-Yu, Qiao Jun-Fei. Data-driven policy optimization for stochastic systems involving adaptive critic. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(5): 980−990
|
|
[110]
|
Qiao J F, Zhao M M, Wang D, Ha M M. Adjustable iterative Q-learning schemes for model-free optimal tracking control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(2): 1202−1213 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3324215
|
|
[111]
|
Ni Z, Malla N, Zhong X N. Prioritizing useful experience replay for heuristic dynamic programming-based learning systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(11): 3911−3922 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2853582
|
|
[112]
|
Al-Dabooni S, Wunsch D. The boundedness conditions for model-free HDP (λ). IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(7): 1928−1942 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2875870
|
|
[113]
|
Zhao Q T, Si J, Sun J. Online reinforcement learning control by direct heuristic dynamic programming: From time-driven to event-driven. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(8): 4139−4144 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3053037
|
|
[114]
|
Wei Q L, Liao Z H, Song R Z, Zhang P J, Wang Z, Xiao J. Self-learning optimal control for ice-storage air conditioning systems via data-based adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(4): 3599−3608 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2978699
|
|
[115]
|
Zhao J, Wang T Y, Pedrycz W, Wang W. Granular prediction and dynamic scheduling based on adaptive dynamic programming for the blast furnace gas system. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(4): 2201−2214 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2901268
|
|
[116]
|
Wang D, Li X, Zhao M M, Qiao J F. Adaptive critic control design with knowledge transfer for wastewater treatment applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(2): 1488−1497 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3278875
|
|
[117]
|
Qiao J F, Zhao M M, Wang D, Li M H. Action-dependent heuristic dynamic programming with experience replay for wastewater treatment processes. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(4): 6257−6265 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3344130
|
|
[118]
|
Luo B, Liu D R, Wu H N. Adaptive constrained optimal control design for data-based nonlinear discrete-time systems with critic-only structure. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(6): 2099−2111 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2751018
|
|
[119]
|
Zhao M M, Wang D, Qiao J F. Stabilizing value iteration Q-learning for online evolving control of discrete-time nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2024, 112: 9137−9153 doi: 10.1007/s11071-024-09524-9
|
|
[120]
|
Xiang Z R, Li P C, Zou W C, Ahn C K. Data-based optimal switching and control with admissibility guaranteed Q-learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, DOI: 10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3405739
|
|
[121]
|
Li X F, Dong L, Xue L, Sun C Y. Hybrid reinforcement learning for optimal control of non-linear switching system. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(11): 9161−9170 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3156287
|
|
[122]
|
Li J N, Chai T Y, Lewis F L, Ding Z T, Jiang Y. Off-policy interleaved Q-learning: Optimal control for affine nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(5): 1308−1320 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2861945
|
|
[123]
|
Song S J, Zhao M M, Gong D W, Zhu M L. Convergence and stability analysis of value iteration Q-learning under non-discounted cost for discrete-time optimal control. Neurocomputing, 2024, 606: Article No. 128370 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.128370
|
|
[124]
|
Song S J, Zhu M L, Dai X L, Gong D W. Model-free optimal tracking control of nonlinear input-affine discrete-time systems via an iterative deterministic Q-learning algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(1): 999−1012 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3178746
|
|
[125]
|
Wei Q L, Liu D R. A novel policy iteration based deterministic Q-learning for discrete-time nonlinear systems. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(12): 1−15
|
|
[126]
|
Yan P F, Wang D, Li H L, Liu D R. Error bound analysis of Q-function for discounted optimal control problems with policy iteration. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2017, 47(7): 1207−1216 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2563982
|
|
[127]
|
Wang W, Chen X, Fu H, Wu M. Model-free distributed consensus control based on actor-critic framework for discrete-time nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(11): 4123−4134 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2883801
|
|
[128]
|
Luo B, Liu D R, Wu H N, Wang D, Lewis F L. Policy gradient adaptive dynamic programming for data-based optimal control. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(10): 3341−3354 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2623859
|
|
[129]
|
Zhang Y W, Zhao B, Liu D R. Deterministic policy gradient adaptive dynamic programming for model-free optimal control. Neurocomputing, 2020, 387: 40−50 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.11.032
|
|
[130]
|
Xu J H, Wang J C, Rao J, Zhong Y J, Zhao S W. Twin deterministic policy gradient adaptive dynamic programming for optimal control of affine nonlinear discrete-time systems. International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, 2022, 20(9): 3098−3109 doi: 10.1007/s12555-021-0473-6
|
|
[131]
|
Xu J H, Wang J C, Rao J, Wu S Y, Zhong Y J. Adaptive dynamic programming for optimal control of discrete-time nonlinear systems with trajectory-based initial control policy. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(3): 1489−1501 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3327450
|
|
[132]
|
Lin M D, Zhao B. Policy optimization adaptive dynamic programming for optimal control of input-affine discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(7): 4339−4350 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3247466
|
|
[133]
|
Lin M D, Zhao B, Liu D R. Policy gradient adaptive critic designs for model-free optimal tracking control with experience replay. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(6): 3692−3703 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3071968
|
|
[134]
|
Luo B, Yang Y, Liu D R. Adaptive Q-learning for data-based optimal output regulation with experience replay. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(12): 3337−3348 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2821369
|
|
[135]
|
Qasem O, Gutierrez H, Gao W N. Experimental validation of data-driven adaptive optimal control for continuous-time systems via hybrid iteration: An application to rotary inverted pendulum. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(6): 6210−6220 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3292873
|
|
[136]
|
李满园, 罗飞, 顾春华, 罗勇军, 丁炜超. 基于自适应动量更新策略的Adams算法. 上海理工大学学报, 2023, 45(2): 112−119Li Man-Yuan, Luo Fei, Gu Chun-Hua, Luo Yong-Jun, Ding Wei-Chao. Adams algorithm based on adaptive momentum update strategy. Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, 2023, 45(2): 112−119
|
|
[137]
|
姜志侠, 宋佳帅, 刘宇宁. 一种改进的自适应动量梯度下降算法. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(5): 137−143Jiang Zhi-Xia, Song Jia-Shuai, Liu Yu-Ning. An improved adaptive momentum gradient descent algorithm. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(5): 137−143
|
|
[138]
|
姜文翰, 姜志侠, 孙雪莲. 一种修正学习率的梯度下降算法. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 46(6): 112−120Jiang Wen-Han, Jiang Zhi-Xia, Sun Xue-Lian. A gradient descent algorithm with modified learning rate. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 46(6): 112−120
|
|
[139]
|
Zhao B, Shi G, Liu D R. Event-triggered local control for nonlinear interconnected systems through particle swarm optimization-based adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(12): 7342−7353 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3298065
|
|
[140]
|
Zhang L J, Zhang K, Xie X P, Chadli M. Adaptive critic control with knowledge transfer for uncertain nonlinear dynamical dystems: A reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, DOI: 10.1109/TASE.2024.3453926
|
|
[141]
|
Gao X, Si J, Huang H. Reinforcement learning control with knowledge shaping. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(3): 3156−3167 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3243631
|
|
[142]
|
Gao X, Si J, Wen Y, Li M H, Huang H. Reinforcement learning control of robotic knee with human-in-the-loop by flexible policy iteration. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(10): 5873−5887 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3071727
|
|
[143]
|
Guo W T, Liu F, Si J, He D W, Harley R, Mei S W. Online supplementary ADP learning controller design and application to power system frequency control with large-scale wind energy integration. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(8): 1748−1761 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2431734
|
|
[144]
|
Zhao M M, Wang D, Ren J, Qiao J. Integrated online Q-learning design for wastewater treatment processes. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2025, 21(2): 1833−1842 doi: 10.1109/TII.2024.3488790
|
|
[145]
|
Zhang H G, Wei Q L, Luo Y H. A novel infinite-time optimal tracking control scheme for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems via the greedy HDP iteration algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2008, 38(4): 937−942 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2008.920269
|
|
[146]
|
Song S J, Gong D W, Zhu M L, Zhao Y Y, Huang C. Data-driven optimal tracking control for discrete-time nonlinear systems with unknown dynamics using deterministic ADP. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2025, 36(1): 1184−1198 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3323142
|
|
[147]
|
Luo B, Liu D R, Huang T W, Wang D. Model-free optimal tracking control via critic-only Q-learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(10): 2134−2144 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2585520
|
|
[148]
|
Li C, Ding J L, Lewis F L, Chai T Y. A novel adaptive dynamic programming based on tracking error for nonlinear discrete-time systems. Automatica, 2021, 129: Article No. 109687 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.109687
|
|
[149]
|
Wang D, Gao N, Ha M M, Zhao M M, Wu J L, Qiao J F. Intelligent-critic-based tracking control of discrete-time input-affine systems and approximation error analysis with application verification. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(8): 4690−4701 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2023.3312320
|
|
[150]
|
Liang Z T, Ha M M, Liu D R, Wang Y H. Stable approximate Q-learning under discounted cost for data-based adaptive tracking control. Neurocomputing, 2024, 568: Article No. 127048 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.127048
|
|
[151]
|
Wang Y, Wang D, Zhao M M, Liu A, Qiao J F. Adjustable iterative Q-learning for advanced neural tracking control with stability guarantee. Neurocomputing, 2024, 584: Article No. 127592 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.127592
|
|
[152]
|
Zhao M M, Wang D, Li M H, Gao N, Qiao J F. A new Q-function structure for model-free adaptive optimal tracking control with asymmetric constrained inputs. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2024, 38(5): 1561−1578 doi: 10.1002/acs.3761
|
|
[153]
|
Wang T, Wang Y J, Yang X B, Yang J. Further results on optimal tracking control for nonlinear systems with nonzero equilibrium via adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(4): 1900−1910 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3105646
|
|
[154]
|
Li D D, Dong J X. Approximate optimal robust tracking control based on state error and derivative without initial admissible input. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(2): 1059−1069 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3320653
|
|
[155]
|
Zhang H G, Luo Y H, Liu D R. Neural-network-based near-optimal control for a class of discrete-time affine nonlinear systems with control constraints. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(9): 1490−1503 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2009.2027233
|
|
[156]
|
Marvi Z, Kiumarsi B. Reinforcement learning with safety and stability guarantees during exploration for linear systems. IEEE Open Journal of Control Systems, 2022, 1: 322−334 doi: 10.1109/OJCSYS.2022.3209945
|
|
[157]
|
Zanon M, Gros S. Safe reinforcement learning using robust MPC. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(8): 3638−3652 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3024161
|
|
[158]
|
Yang Y L, Vamvoudakis K G, Modares H, Yin Y X, Wunsch D C. Safe intermittent reinforcement learning with static and dynamic event generators. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(12): 5441−5455 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2967871
|
|
[159]
|
Yazdani N M, Moghaddam R K, Kiumarsi B, Modares H. A safety-certified policy iteration algorithm for control of constrained nonlinear systems. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2020, 4(3): 686−691 doi: 10.1109/LCSYS.2020.2990632
|
|
[160]
|
Yang Y L, Vamvoudakis K G, Modares H. Safe reinforcement learning for dynamical games. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2020, 30(9): 3521−3800 doi: 10.1002/rnc.4942
|
|
[161]
|
Song R Z, Liu L, Xia L N, Lewis F L. Online optimal event-triggered H∞ control for nonlinear systems with constrained state and input. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(1): 131−141 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3173275
|
|
[162]
|
Fan B, Yang Q M, Tang X Y, Sun Y X. Robust ADP design for continuous-time nonlinear systems with output constraints. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(6): 2127−2138 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2806347
|
|
[163]
|
Liu S H, Liu L J, Yu Z. Safe reinforcement learning for affine nonlinear systems with state constraints and input saturation using control barrier functions. Neurocomputing, 2023, 518: 562−576 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.11.006
|
|
[164]
|
Farzanegan B, Jagannathan S. Continual reinforcement learning formulation for zero-sum game-based constrained optimal tracking. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(12): 7744−7757 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3299556
|
|
[165]
|
Marvi Z, Kiumarsi B. Safe reinforcement learning: A control barrier function optimization approach. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2021, 31(6): 1923−1940 doi: 10.1002/rnc.5132
|
|
[166]
|
Qin C B, Qiao X P, Wang J G, Zhang D H, Hou Y D, Hu S L. Barrier-critic adaptive robust control of nonzero-sum differential games for uncertain nonlinear systems with state constraints. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(1): 50−63 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3302656
|
|
[167]
|
Xu J H, Wang J C, Rao J, Zhong Y J, Wang H Y. Adaptive dynamic programming for optimal control of discrete-time nonlinear system with state constraints based on control barrier function. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2021, 32(6): 3408−3424
|
|
[168]
|
Jha M S, Kiumarsi B. Off-policy safe reinforcement learning for nonlinear discrete-time systems. Neurocomputing, 2024, 611: Article No. 128677
|
|
[169]
|
Zhang L Z, Xie L, Jiang Y, Li Z S, Liu X Q, Su H Y. Optimal control for constrained discrete-time nonlinear systems based on safe reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2025, 36(1): 854−865 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3326397
|
|
[170]
|
Cohen M H, Belta C. Safe exploration in model-based reinforcement learning using control barrier functions. Automatica, 2023, 147: Article No. 110684 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110684
|
|
[171]
|
Liu S H, Liu L J, Yu Z. Fully cooperative games with state and input constraints using reinforcement learning based on control barrier functions. Asian Journal of Control, 2024, 26(2): 888−905 doi: 10.1002/asjc.3226
|
|
[172]
|
Zhao M M, Wang D, Song S J, Qiao J F. Safe Q-learning for data-driven nonlinear optimal control with asymmetric state constraints. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(12): 2408−2422 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2024.124509
|
|
[173]
|
Liu D R, Li H L, Wang D. Neural-network-based zero-sum game for discrete-time nonlinear systems via iterative adaptive dynamic programming algorithm. Neurocomputing, 2013, 110: 92−100 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2012.11.021
|
|
[174]
|
Luo B, Yang Y, Liu D R. Policy iteration Q-learning for data-based two-player zero-sum game of linear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(7): 3630−3640 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2970969
|
|
[175]
|
Zhong X N, He H B, Wang D, Ni Z. Model-free adaptive control for unknown nonlinear zero-sum differential game. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(5): 1633−1646 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2712617
|
|
[176]
|
Wang Y, Wang D, Zhao M M, Liu N, Qiao J F. Neural Q-learning for discrete-time nonlinear zero-sum games with adjustable convergence rate. Neural Networks, 2024, 175: Article No. 106274 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2024.106274
|
|
[177]
|
Zhang Y W, Zhao B, Liu D R, Zhang S C. Event-triggered control of discrete-time zero-sum games via deterministic policy gradient adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(8): 4823−4835 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3105663
|
|
[178]
|
Lin M D, Zhao B, Liu D R. Policy gradient adaptive dynamic programming for nonlinear discrete-time zero-sum games with unknown dynamics. Soft Computing, 2023, 27: 5781−5795 doi: 10.1007/s00500-023-07817-6
|
|
[179]
|
王鼎, 赵慧玲, 李鑫. 基于多目标粒子群优化的污水处理系统自适应评判控制. 工程科学学报, 2024, 46(5): 908−917Wang Ding, Zhao Hui-Ling, Li Xin. Adaptive critic control for wastewater treatment systems based on multiobjective particle swarm optimization. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2024, 46(5): 908−917
|
|
[180]
|
Yang Q M, Cao W W, Meng W C, Si J. Reinforcement-learning-based tracking control of waste water treatment process under realistic system conditions and control performance requirements. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(8): 5284−5294 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3122802
|
|
[181]
|
Yang R Y, Wang D, Qiao J F. Policy gradient adaptive critic design with dynamic prioritized experience replay for wastewater treatment process control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(5): 3150−3158 doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3106402
|
|
[182]
|
Qiao J F, Yang R Y, Wang D. Offline data-driven adaptive critic design with variational inference for wastewater treatment process control. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2024, 21(4): 4987−4998 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2023.3305615
|
|
[183]
|
Sun B, Kampen E J V. Incremental model-based global dual heuristic programming with explicit analytical calculations applied to flight control. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 89: Article No. 103425 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2019.103425
|
|
[184]
|
Zhou Y, Kampen E J V, Chu Q P. Incremental model based online heuristic dynamic programming for nonlinear adaptive tracking control with partial observability. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 105: Article No. 106013 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.106013
|
|
[185]
|
赵振根, 程磊. 基于增量式Q学习的固定翼无人机跟踪控制性能优化. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(2): 391−400Zhao Zhen-Gen, Cheng Lei. Performance optimization for tracking control of fixed-wing UAV with incremental Q-learning. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(2): 391−400
|
|
[186]
|
Cao W W, Yang Q M, Meng W C, Xie S Z. Data-based robust adaptive dynamic programming for balancing control performance and energy consumption in wastewater treatment process. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(4): 6622−6630 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3346468
|
|
[187]
|
Fu Y, Hong C W, Fu J, Chai T Y. Approximate optimal tracking control of nondifferentiable signals for a class of continuous-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(6): 4441−4450 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3027344
|




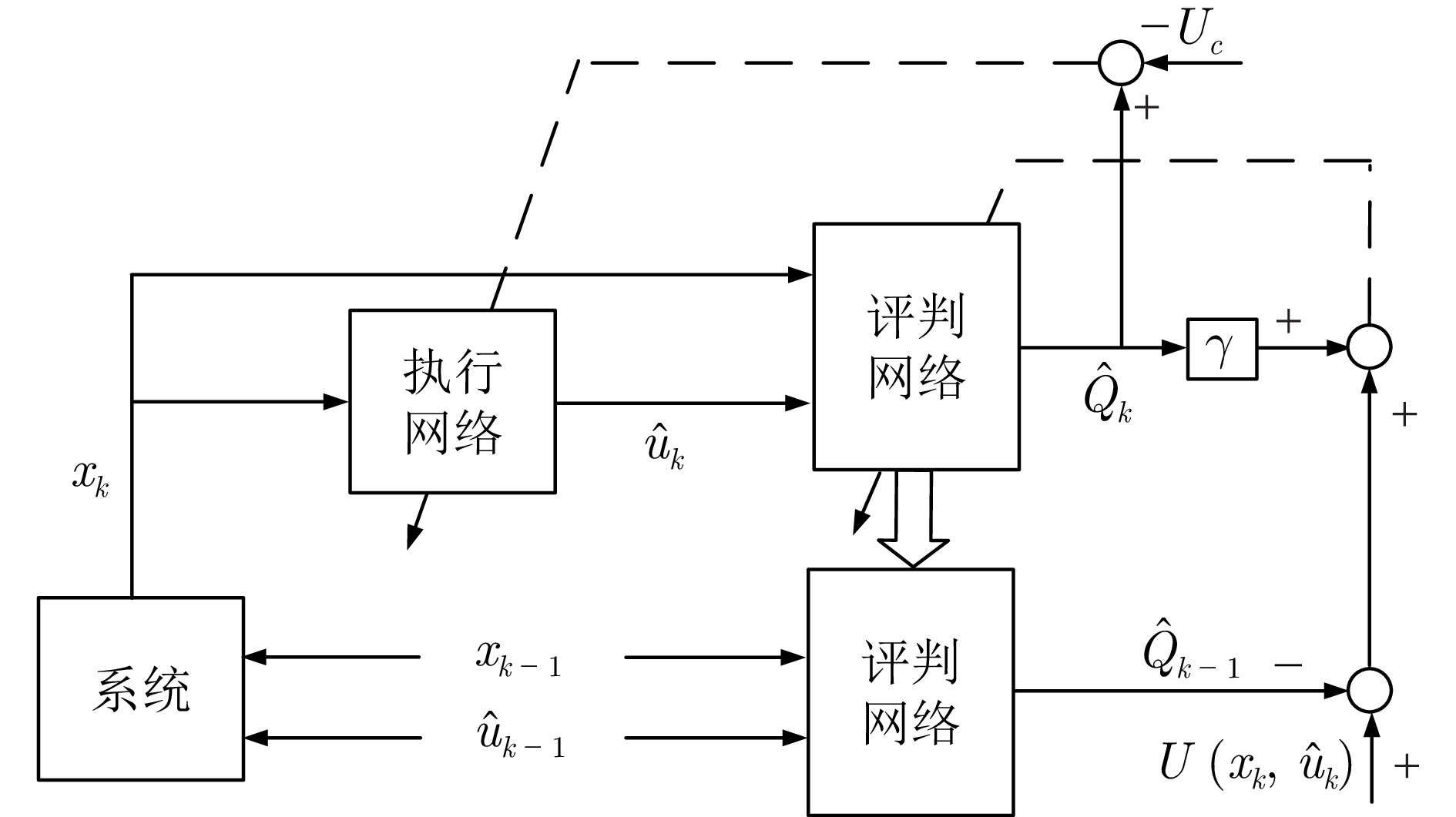
 下载:
下载: