Autonomous Perception-Planning-Control Strategy Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
-
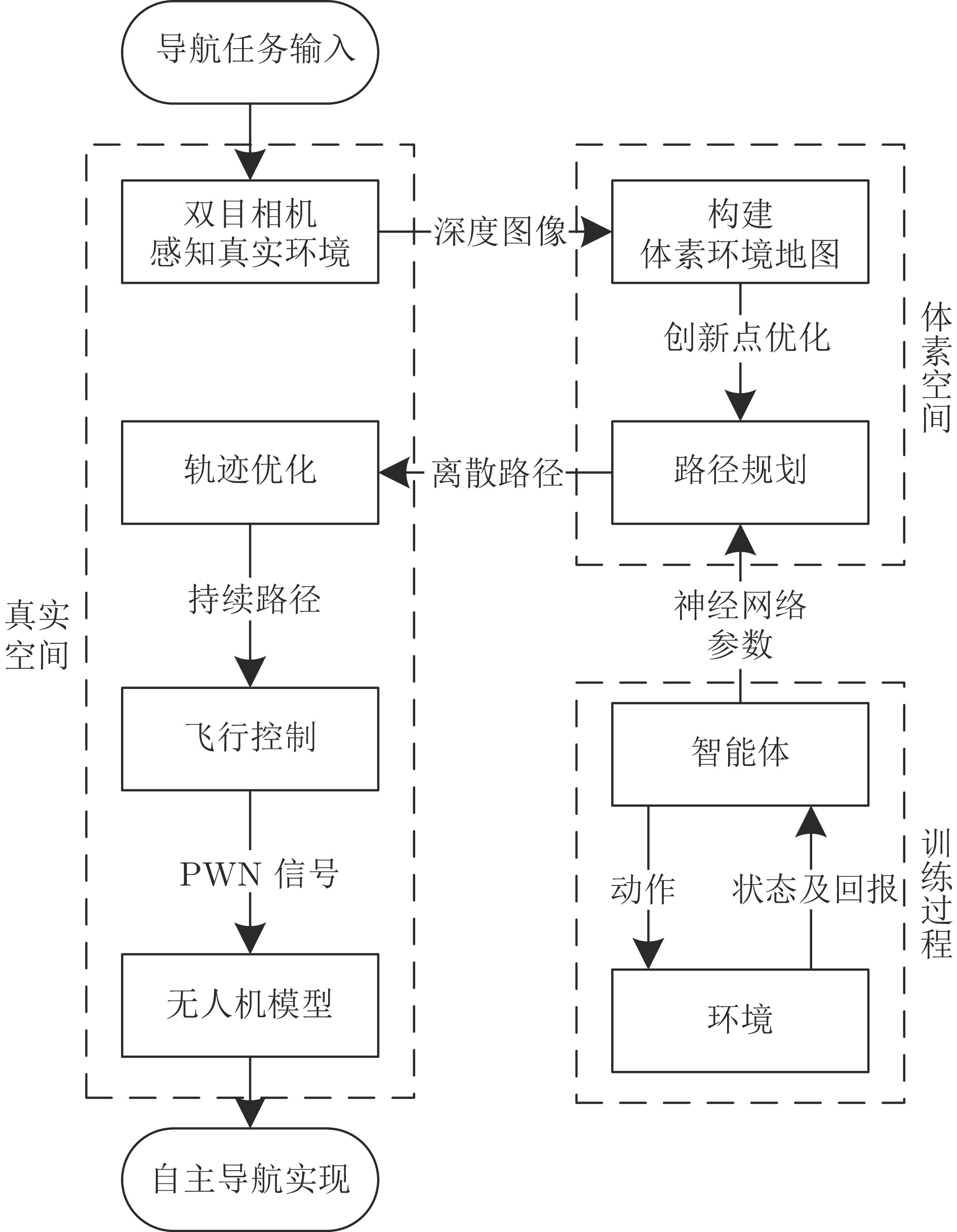
摘要: 近年来, 随着深度强化学习(DRL)方法快速发展, 其在无人机(UAV)自主导航上的应用也受到越来越广泛的关注. 然而, 面对复杂未知的环境, 现存的基于DRL的UAV自主导航算法常受限于对全局信息的依赖和特定训练环境的约束, 极大地限制了其在各种场景中的应用潜力. 为解决上述问题, 提出多尺度输入用于平衡感受野与状态维度, 以及截断操作来使智能体能够在扩张后的环境中运行. 此外, 构建自主感知−规划−控制架构, 赋予UAV在多样复杂环境中自主导航的能力.Abstract: In recent years, with the rapid development of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) methods, their application in the field of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) autonomous navigation has attracted increasing attention. However, when facing complex and unknown environments, existing DRL-based UAV autonomous navigation algorithms are often limited by their dependence on global information and the constraints of specific training environments, greatly limiting their potential for application in various scenarios. To address these issues, multi-scale input is proposed to balance the receptive field and the state dimension, and truncation operation is proposed to enable the agent to operate in the expanded environment. In addition, the autonomous perception-planning-control architecture is constructed to give the UAV the ability to navigate autonomously in diverse and complex environments.
-
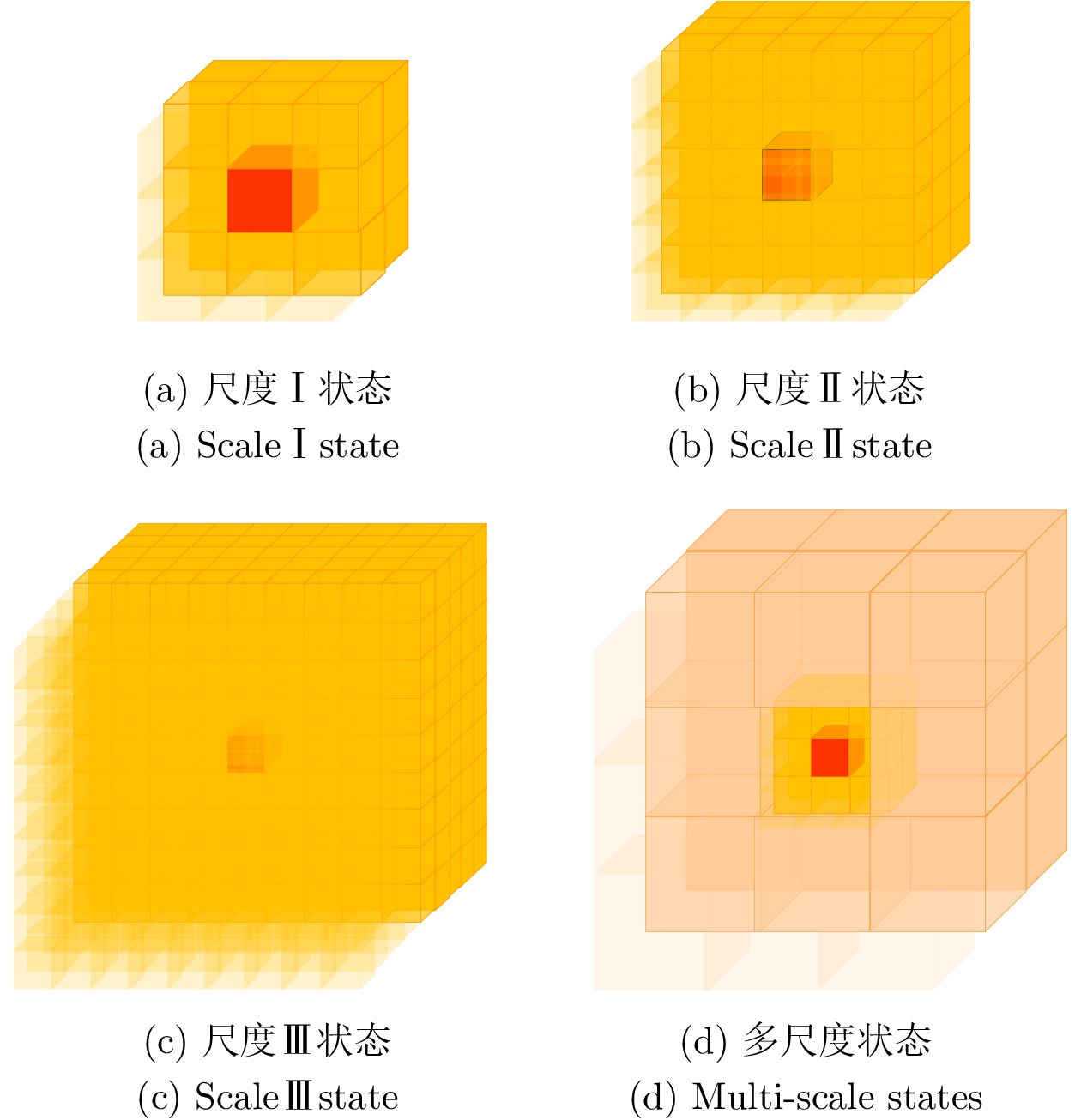
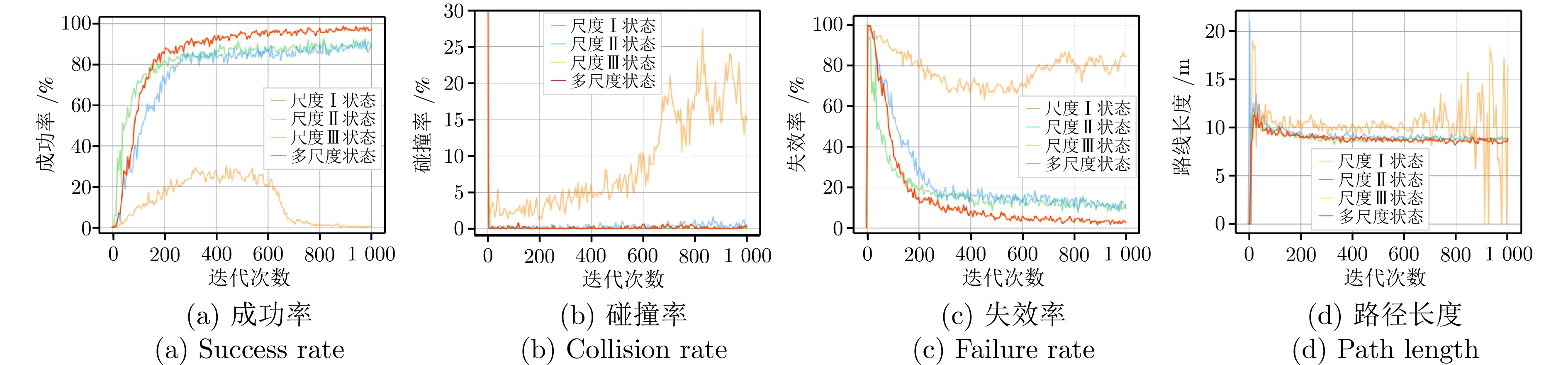
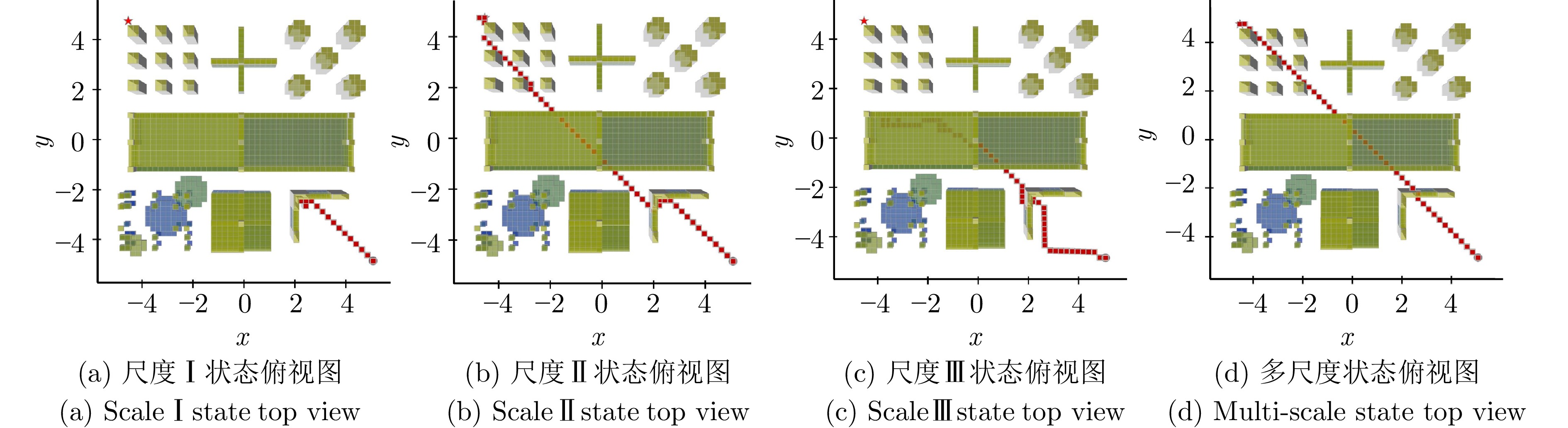
表 1 迭代训练后不同尺度输入下智能体导航性能
Table 1 Navigation performance of agents under different scale inputs after iterative training
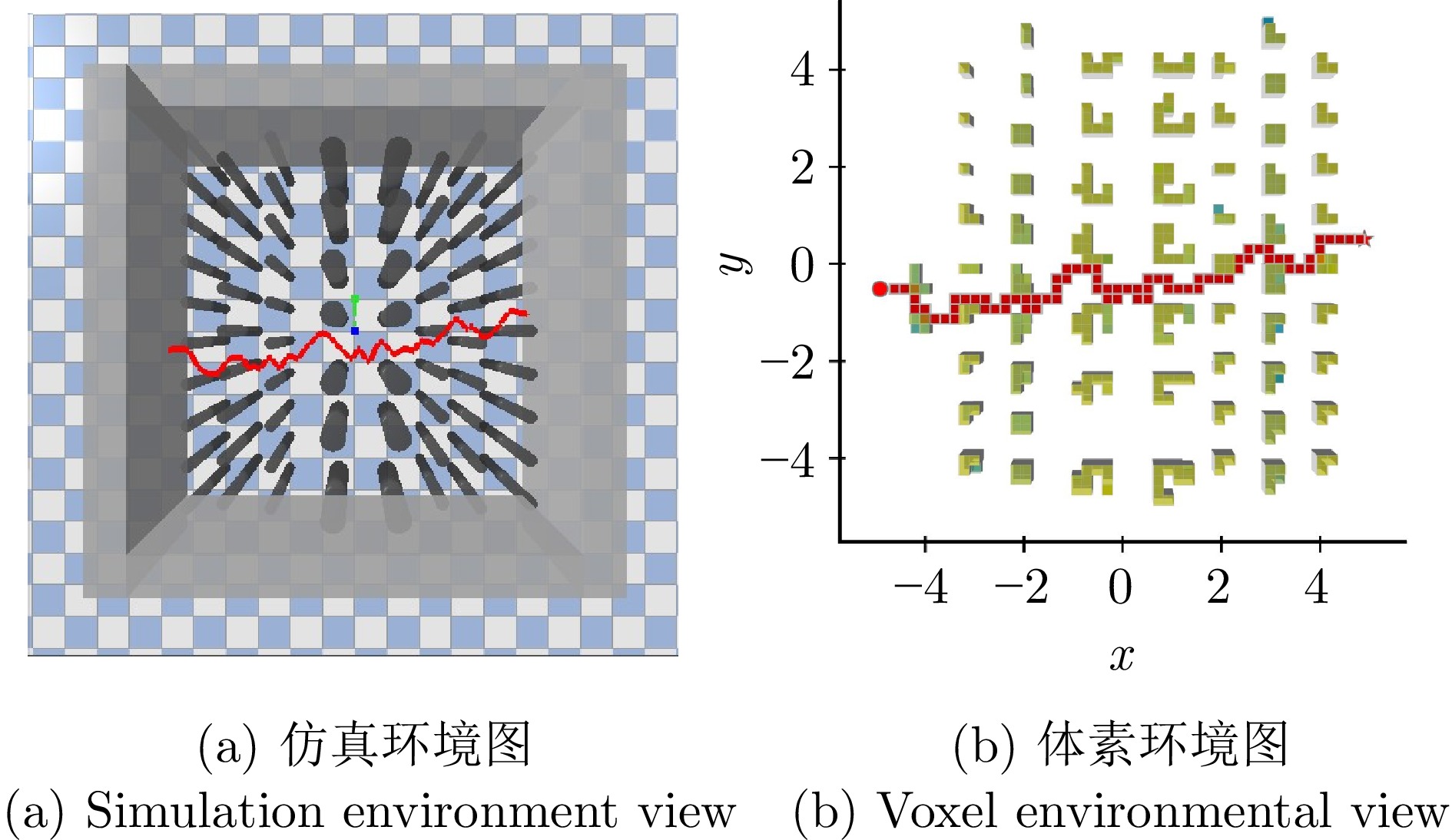
成功率(%) 碰撞率(%) 失效率(%) 路径长度(m) 尺度I状态 89.61 0.02 10.37 8.73 尺度II状态 88.25 0.72 11.03 8.79 尺度III状态 0.51 17.66 81.83 11.56 多尺度状态 97.19 0.08 2.74 8.62 表 2 不同体素环境下的导航性能
Table 2 Navigation performance in different voxel environments
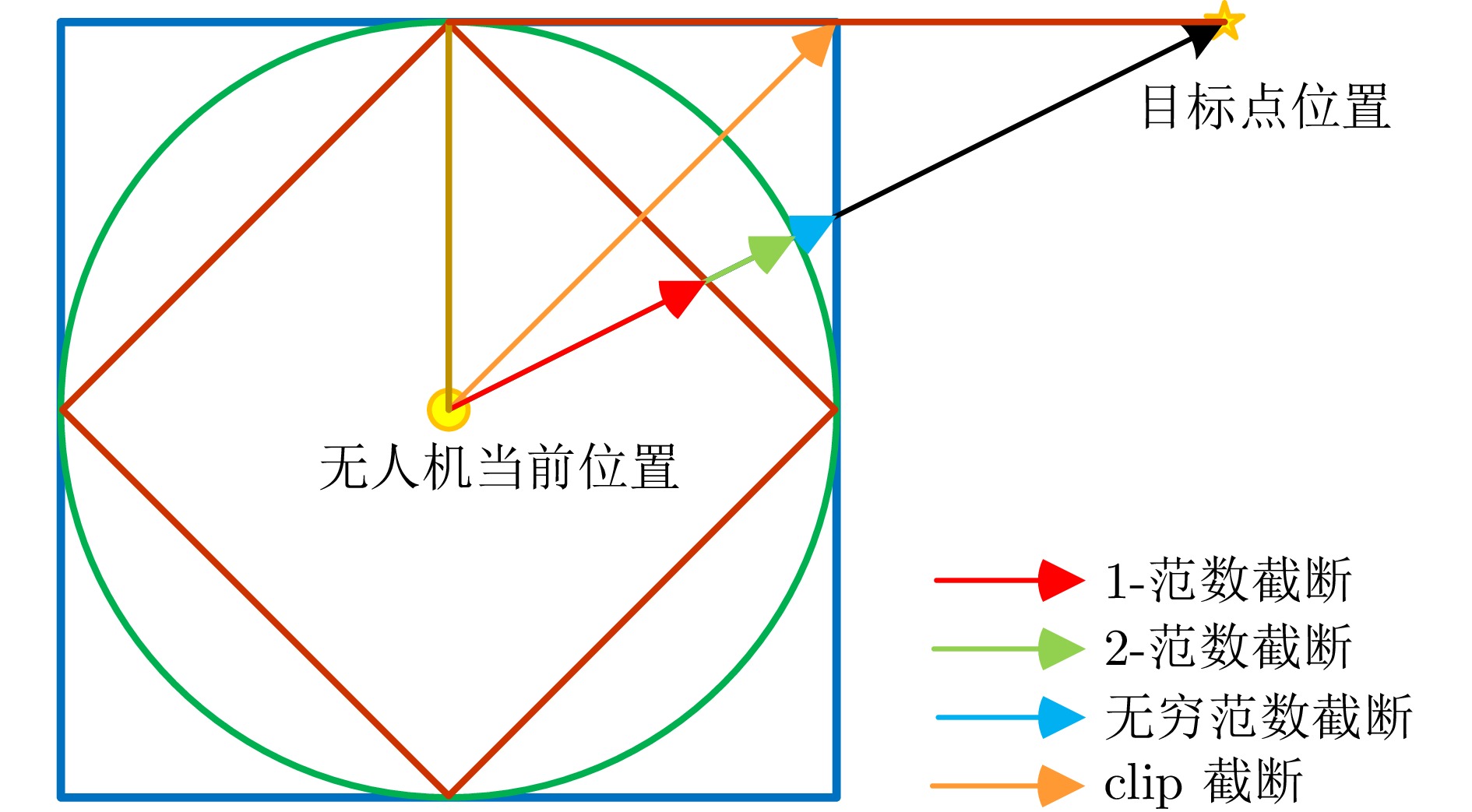
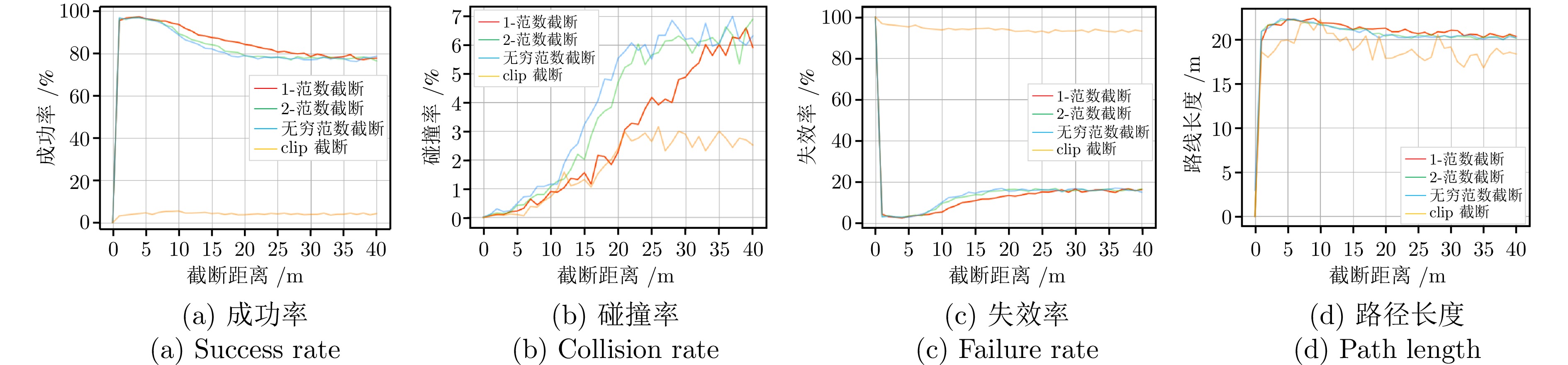
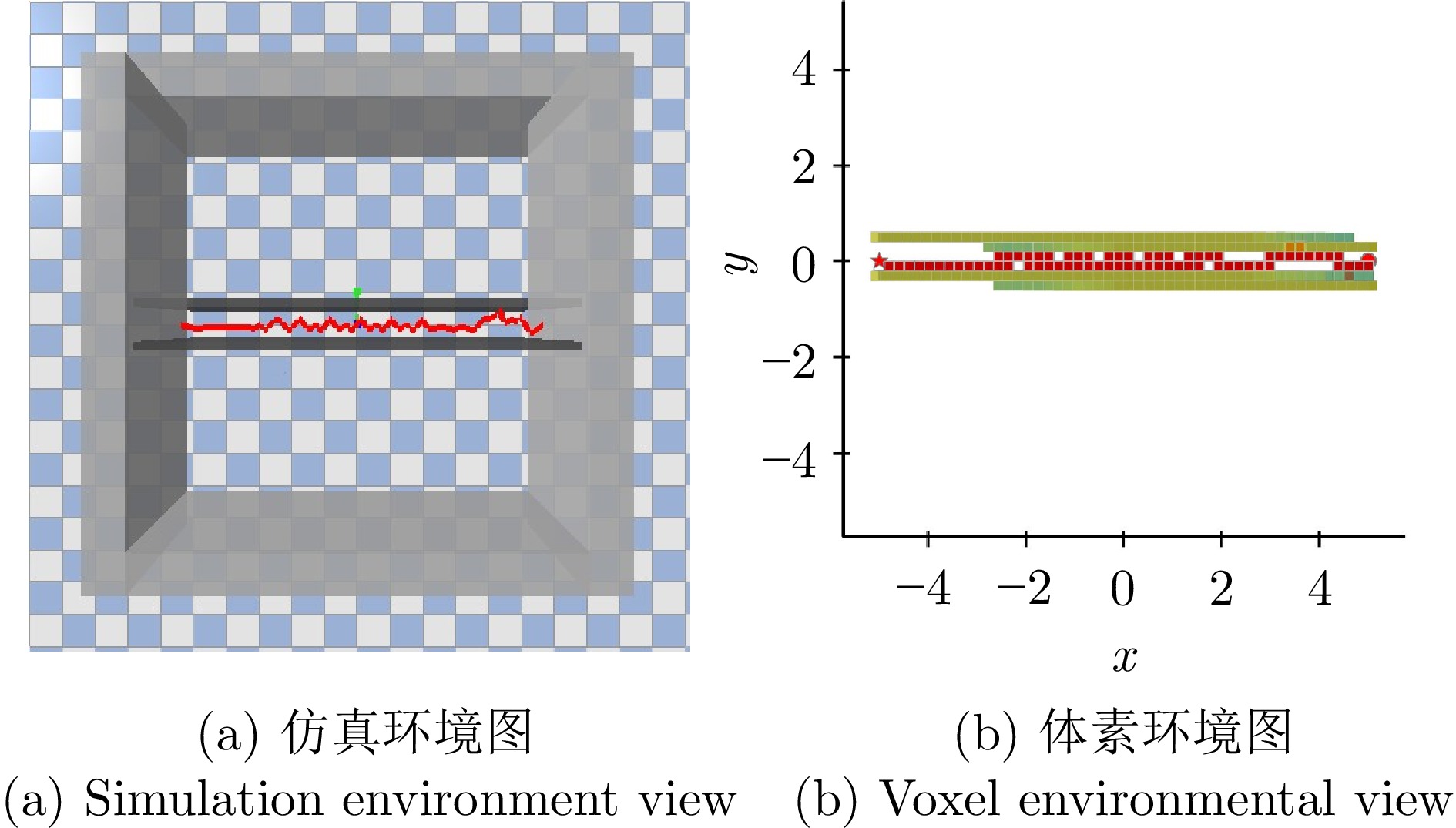
成功率(%) 碰撞率(%) 失效率(%) 路径长度(m) 训练环境 97.19 0.08 2.74 8.62 测试环境(未采取截断操作) 77.20 6.52 16.29 20.30 测试环境(采取截断操作) 96.93 0.17 2.89 21.90 表 3 A* 算法与DRL路径规划器导航情况对比 (m)
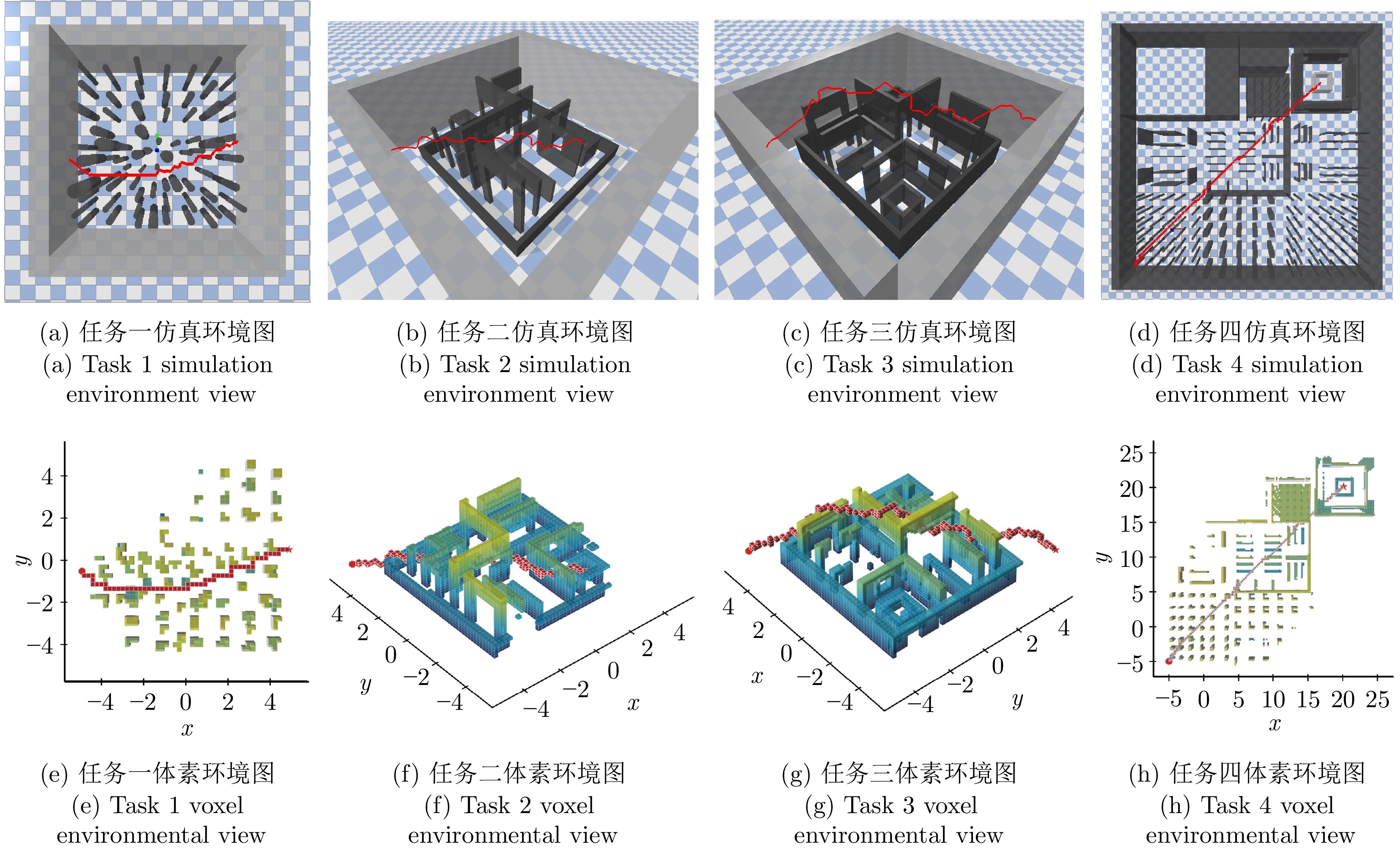
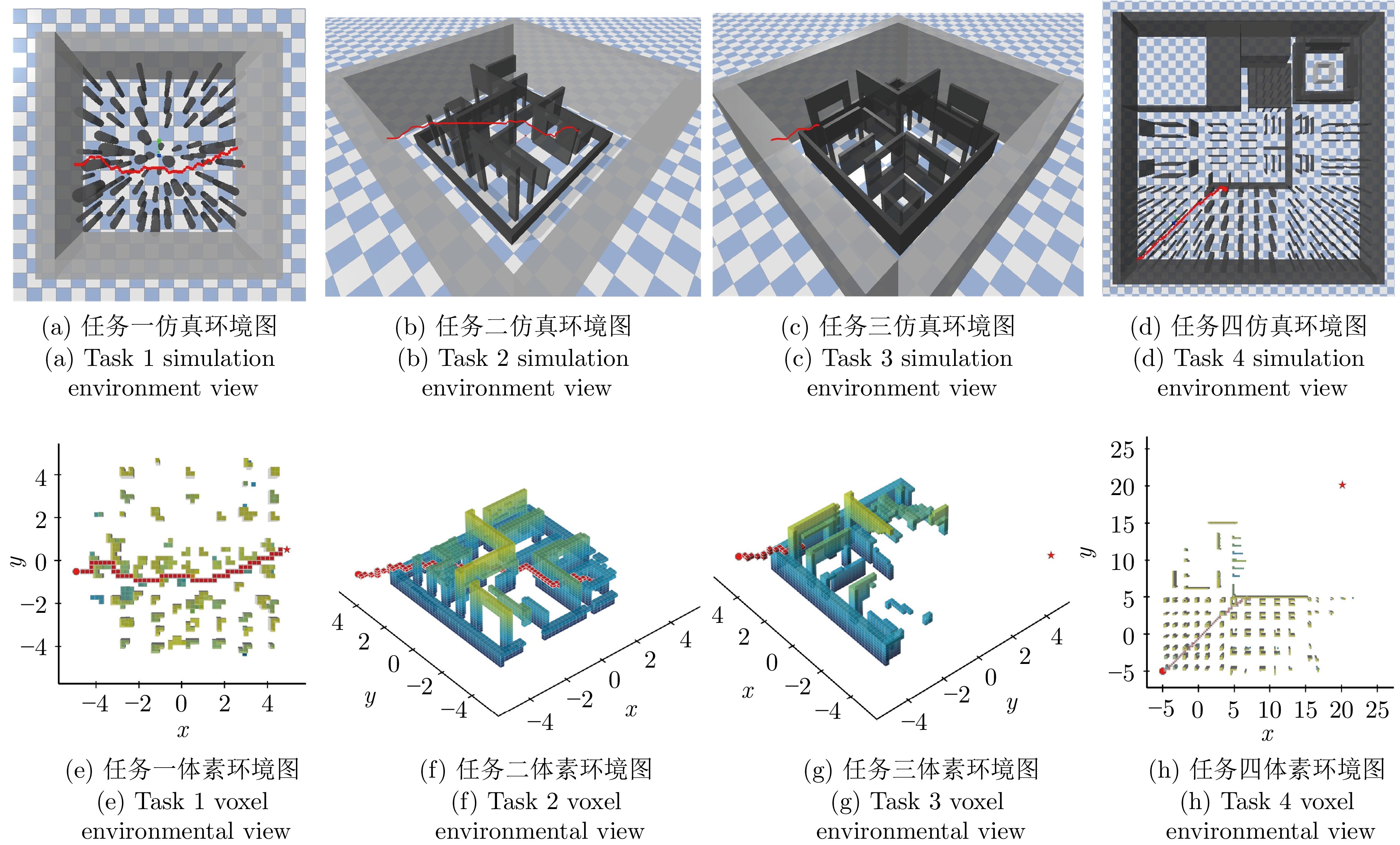
Table 3 Comparison of A* algorithm with DRL path planner navigation (m)
任务一 任务二 任务三 任务四 任务直线距离 9.65 10.84 13.85 35.07 A* 算法 11.68 11.97 导航碰撞 导航碰撞 DRL路径规划器 11.59 13.39 18.80 40.26 -
[1] 陈锦涛, 李鸿一, 任鸿儒, 鲁仁全. 基于RRT森林算法的高层消防多无人机室内协同路径规划. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(12): 2615−2626Chen Jin-Tao, Li Hong-Yi, Ren Hong-Ru, Lu Ren-Quan. Indoor collaborative path planning of high-rise fire multi-UAV based on RRT forest algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(12): 2615−2626 [2] 郭复胜, 高伟. 基于辅助信息的无人机图像批处理三维重建方法. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(6): 834−845 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60056-7Guo Fu-Sheng, Gao Wei. A 3D reconstruction method for UAV image batch processing based on auxiliary information. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(6): 834−845 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60056-7 [3] 张广驰, 何梓楠, 崔苗. 基于深度强化学习的无人机辅助移动边缘计算系统能耗优化. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(5): 1635−1643Zhang Guang-Chi, He Zi-Nan, Cui Miao. Energy consumption optimization of UAV-assisted mobile edge computing system based on deep reinforcement learning. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2023, 45(5): 1635−1643 [4] 林韩熙, 向丹, 欧阳剑, 兰晓东. 移动机器人路径规划算法的研究综述. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(18): 38−48Lin Han-Xi, Xiang Dan, Ouyang Jian, Lan Xiao-Dong. Research review of path planning algorithms for mobile robots. Journal of Computer Engineering & Applications, 2021, 57(18): 38−48 [5] Tong G, Jiang N, Li B Y, Zhu X, Wang Y, Du W B. UAV navigation in high dynamic environments: A deep reinforcement learning approach. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021, 34(2): 479−489 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.05.011 [6] 孙辉辉, 胡春鹤, 张军国. 移动机器人运动规划中的深度强化学习方法. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(6): 1281−1292Sun Hui-Hui, Hu Chun-He, Zhang Jun-Guo. Deep reinforcement learning in mobile robot motion planning. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(6): 1281−1292 [7] 高阳, 陈世福, 陆鑫. 强化学习研究综述. 自动化学报, 2004, 30(1): 86−100Gao Yang, Chen Shi-Fu, Lu Xin. Review of reinforcement learning research. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2004, 30(1): 86−100 [8] Yang Y, Li J T, Peng L L. Multi-robot path planning based on a deep reinforcement learning DQN algorithm. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, 2020, 5(3): 177−183 doi: 10.1049/trit.2020.0024 [9] 赵静, 裴子楠, 姜斌, 陆宁云, 赵斐, 陈树峰. 基于深度强化学习的无人机虚拟管道视觉避障. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(11): 2245−2258Zhao Jing, Pei Zi-Nan, Jiang Bin, Lu Ning-Yun, Zhao Fei, Chen Shu-Feng. Virtual tube visual obstacle avoidance for UAV based on deep reinforcement learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(11): 2245−2258 [10] 赵栓峰, 黄涛, 许倩, 耿龙龙. 面向无人机自主飞行的无监督单目视觉深度估计. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(2): 145−154Zhao Shuan-Feng, Huang Tao, Xu Qian, Geng Long-Long. Unsupervised monocular visual depth estimation for autonomous flight of unmanned aerial vehicles. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(2): 145−154 [11] 刘佳铭. 基于深度卷积神经网络的无人机识别方法研究. 舰船电子工程, 2019, 39(2): 22−26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2019.02.007Liu Jia-Ming. UAV recognition method based on deep convolutional neural network. Naval Electronic Engineering, 2019, 39(2): 22−26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2019.02.007 [12] Bouhamed O, Ghazzai H, Besbes H, Massoud Y. Autonomous UAV navigation: A DDPG-based deep reinforcement learning approach. In: Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems. Seville, Spain: IEEE, 2020. 1−5 [13] Luo X Q, Wang Q Y, Gong H F, Tang C. UAV path planning based on the average TD3 algorithm with prioritized experience replay. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 38017-38029 [14] Lei H, Nabil A, Song B. Explainable deep reinforcement learning for UAV autonomous path planning. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 118: Article No. 107052 [15] Xi Z L, Han H R, Zhang Y R, Cheng J. Autonomous navigation of QUAVs under 3D environments based on hierarchical reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of 42nd Chinese Control Conference. Tianjin, China: IEEE, 2023. 4101−4106 [16] Ugurlu H I, Pham X H, Kayacan E. Sim-to-real deep reinforcement learning for safe end-to-end planning of aerial robots. Robotics, 2022, 11(5): Article No. 109 doi: 10.3390/robotics11050109 [17] 郭子恒, 蔡晨晓. 基于改进深度强化学习的无人机自主导航方法. 信息与控制, 2023, 52(6): 736−746Guo Zi-Heng, Cai Chen-Xiao. UAV autonomous navigation method based on improved deep reinforcement learning. Information Control, 2023, 52(6): 736−746 [18] 满恂钰, 刘元盛, 齐含, 严超, 杨茹锦. 未知环境下无人车自主导航探索与地图构建. 汽车技术, 2023(11): 34−40Man Xun-Yu, Liu Yuan-Sheng, Qi Han, Yan Chao, Yang Ru-Jin. Autonomous navigation exploration and map construction of unmanned vehicles in unknown environment. Automobile Technology, 2023(11): 34−40 [19] 杨永祥, 王念杰, 胡涵川. 分层强化学习在无人机领域应用综述. 人工智能与机器人研究, 2024, 13(1): 66−71Yang Yong-Xiang, Wang Nian-Jie, Hu Han-Chuan. A review of the application of hierarchical reinforcement learning in the field of drones. Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Research, 2024, 13(1): 66−71 [20] 董校成, 于浩淼, 郭晨. 能耗与时间约束下的UUV三维路径规划. 大连海事大学学报, 2022, 48(2): 11−20Dong Xiao-Cheng, Yu Hao-Miao, Guo Chen. UUV 3D path planning under energy consumption and time constraints. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2022, 48(2): 11−20 [21] van Hasselt H, Guez A, Silver D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Phoenix, Arizona, USA: AAAI Press, 2016. 2084−2090 [22] 朱少凯, 孟庆浩, 金晟, 戴旭阳. 基于深度强化学习的室内视觉局部路径规划. 智能系统学报, 2022, 17(5): 908−918 doi: 10.11992/tis.202107059Zhu Shao-Kai, Meng Qing-Hao, Jin Sheng, Dai Xu-Yang. Indoor visual local path planning based on deep reinforcement learning. Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2022, 17(5): 908−918 doi: 10.11992/tis.202107059 [23] Frantisek D, Andrej B, Martin K, Peter B, Martin F, Tomas F, et al. Path planning with modified a star algorithm for a mobile robot. Procedia Engineering, 2014, 96: 59−69 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.098 [24] Shiri F M, Perumal T, Mustapha N, Raihani M. A comprehensive overview and comparative analysis on deep learning models: CNN, RNN, LSTM, GRU. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2305.17473, 2023. [25] Hutsebaut-Buysse M, Mets K, Latré S. Hierarchical reinforcement learning: A survey and open research challenges. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 2022, 4(1): 172−221 doi: 10.3390/make4010009 [26] 王雪松, 王荣荣, 程玉虎. 安全强化学习综述. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(9): 1813−1835Wang Xue-Song, Wang Rong-Rong, Cheng Yu-Hu. Review on security reinforcement learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(9): 1813−1835 -




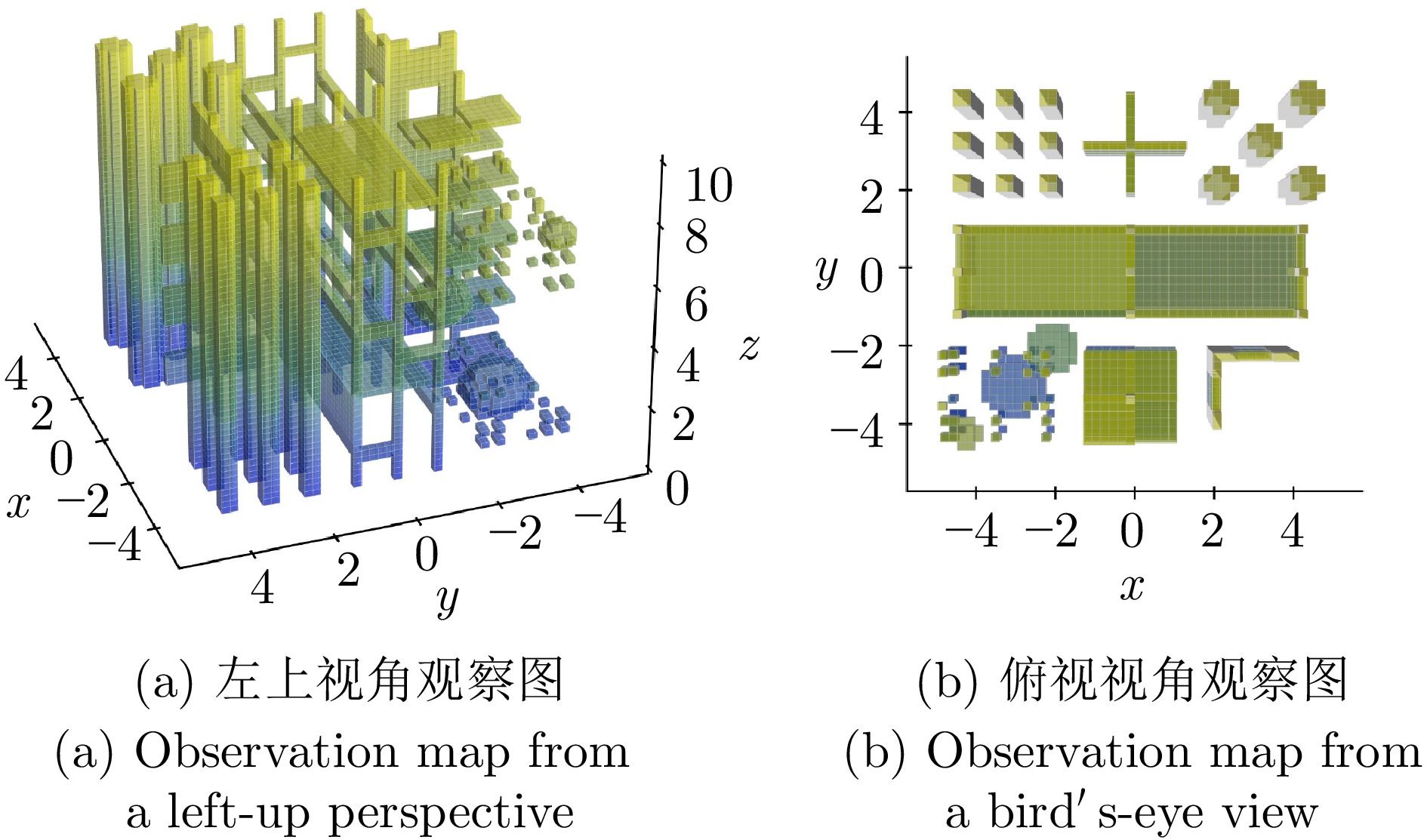
 下载:
下载: