Super-twisting Sliding Mode Control for Asynchronous Motor Based on Flux Online Identification
-
摘要: 研究基于磁链在线辨识的异步电机超螺旋滑模控制问题. 针对异步电机, 设计一种改进的超螺旋滑模速度控制器, 提升系统的动态响应性能. 为抑制算法中符号函数高频切换所引起的系统抖振问题, 构造一种可变指数切换函数. 进一步地, 考虑到转子磁链受惯性延迟的影响, 设计磁链在线观测器, 可辨识转子磁链幅值, 提升系统的控制精度和参数鲁棒性. 数值仿真和实验结果验证了所提算法的可行性和有效性.Abstract: The problem of super-twisting sliding mode control for asynchronous motor based on flux online identification is studied. In order to enhance the dynamic response performance of the system, an improved super-twisting sliding mode speed controller is designed for the asynchronous motor. To suppress the system chattering problem caused by the high-frequency switching of the sign function in the algorithm, a variable exponent switching function is constructed. Furthermore, considering the influence of the inertia delay on the rotor flux, a flux online observer is designed to identify the rotor flux amplitude, which boosts the control accuracy and parameter robustness of the system. Numerical simulations and experimental results verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 异步电机基本参数
Table 1 Basic parameters of asynchronous motor
参数 数值 额度功率$ \rm (kW) $ 5.5000 额度转速$ \rm (r/min) $ 1455 定子电阻$ (\Omega) $ 0.6930 转子电阻$ (\Omega) $ 0.5850 定子漏感$ \rm (H) $ 0.0018 转子漏感$ \rm (H) $ 0.0018 转动惯量$ \rm (kg{\cdot }m^{2}) $ 0.0233 极对数 2 表 2 IMSTSMC-FOO参数
Table 2 Parameters of IMSTSMC-FOO
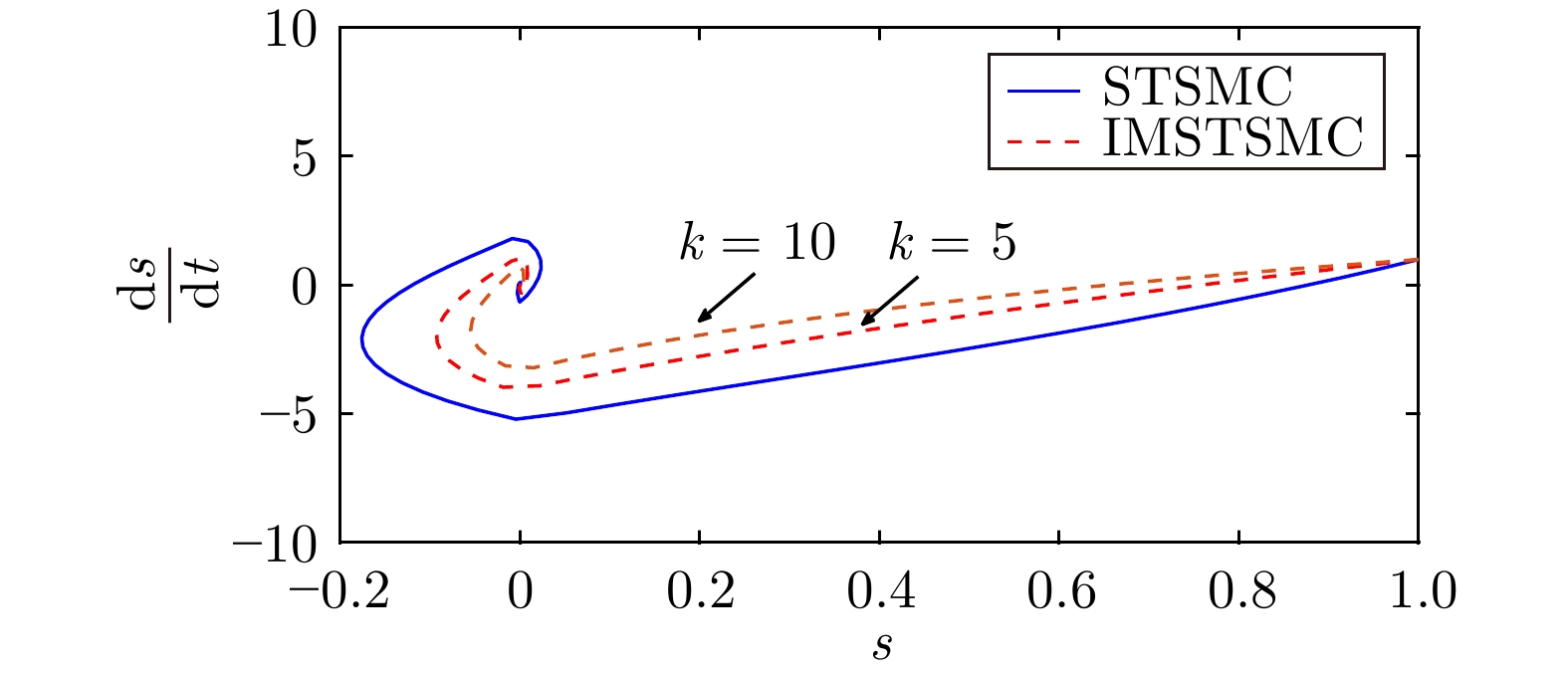
参数 数值 调节系数$ \lambda $ 35 调节比例系数$ k $ 5 调节系数$ \alpha $ 2 可调节指数$ m $ 0.2 调节系数$ K $ 1 阻尼系数$ \xi $ 100 中心频率$ \omega_{c1} $ 1 截止频率$ \omega_{c2} $ 100 表 3 三种控制方案下的阶跃转速控制性能表
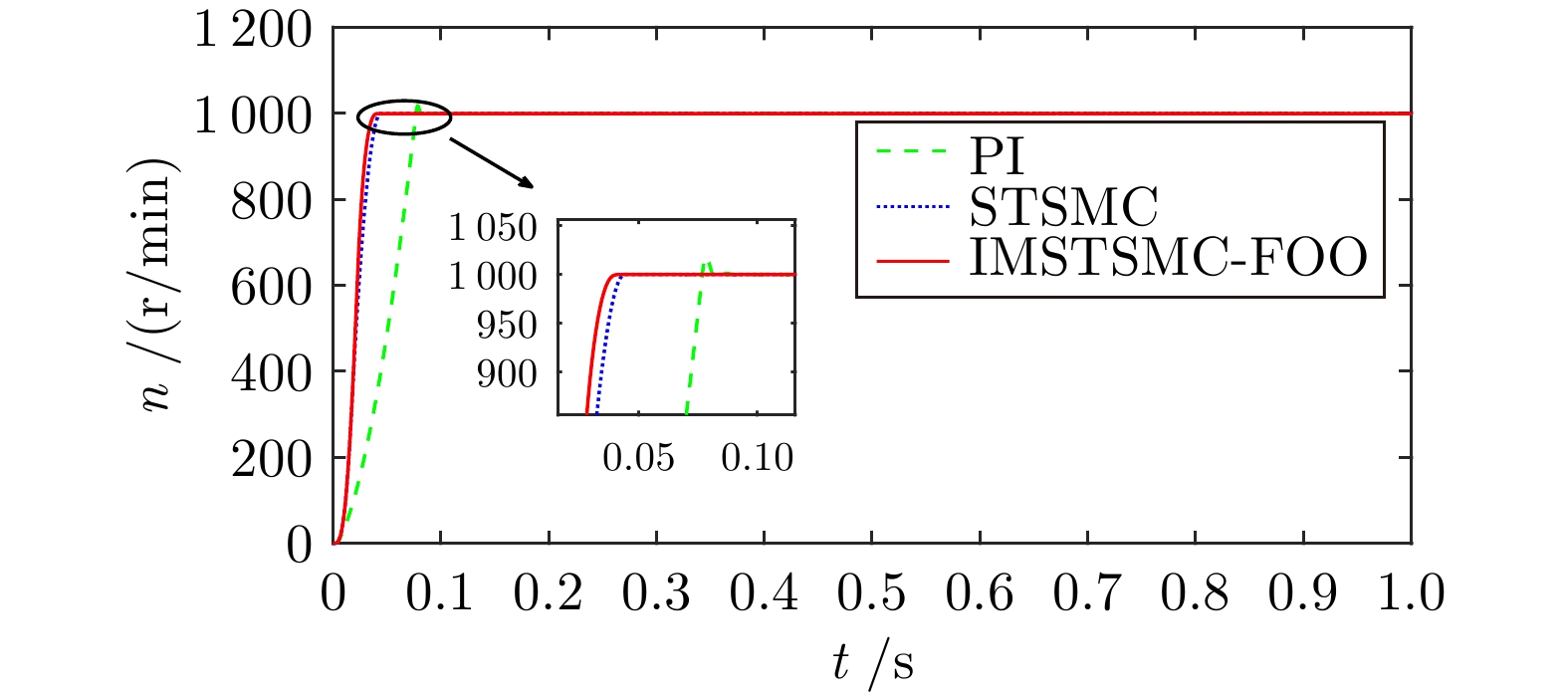
Table 3 The performance table of step speed control under three control schemes
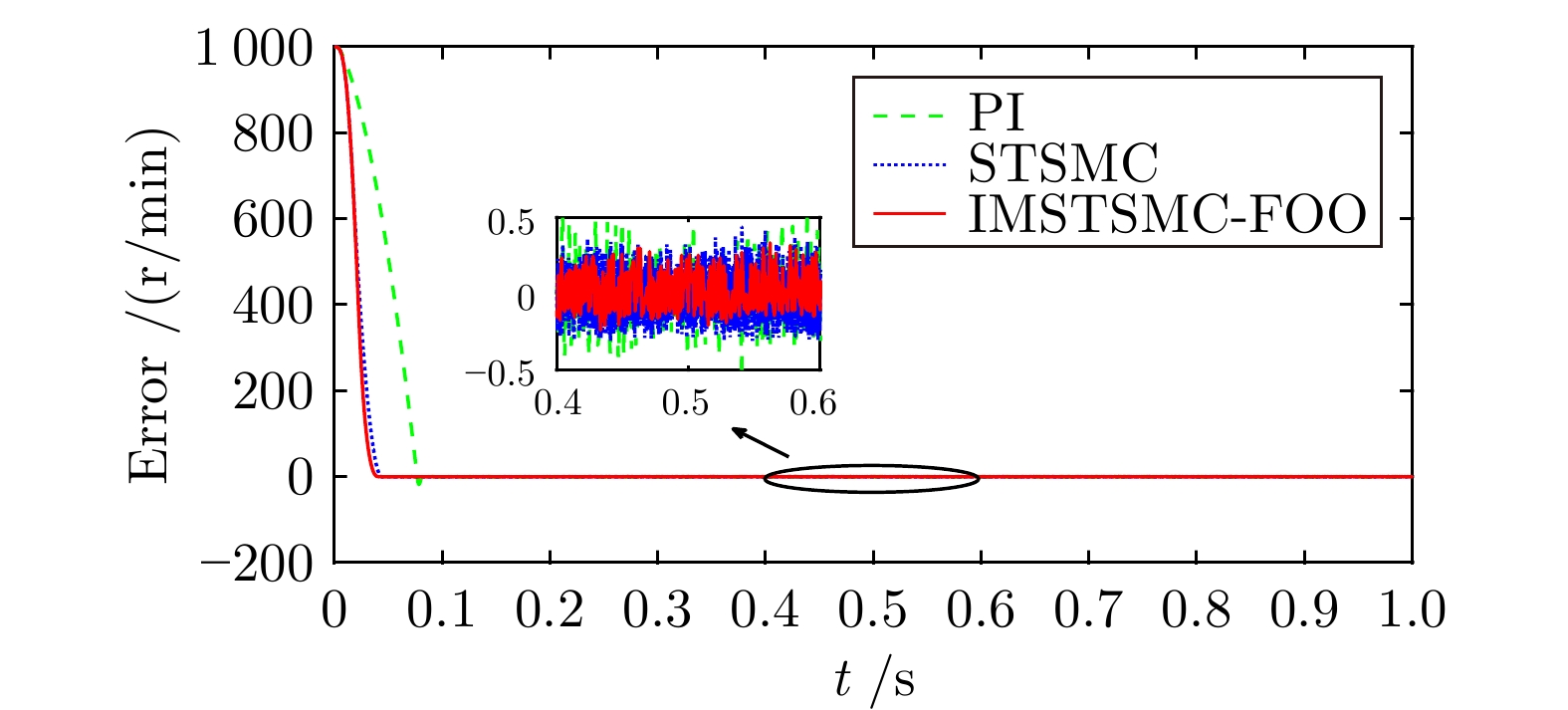
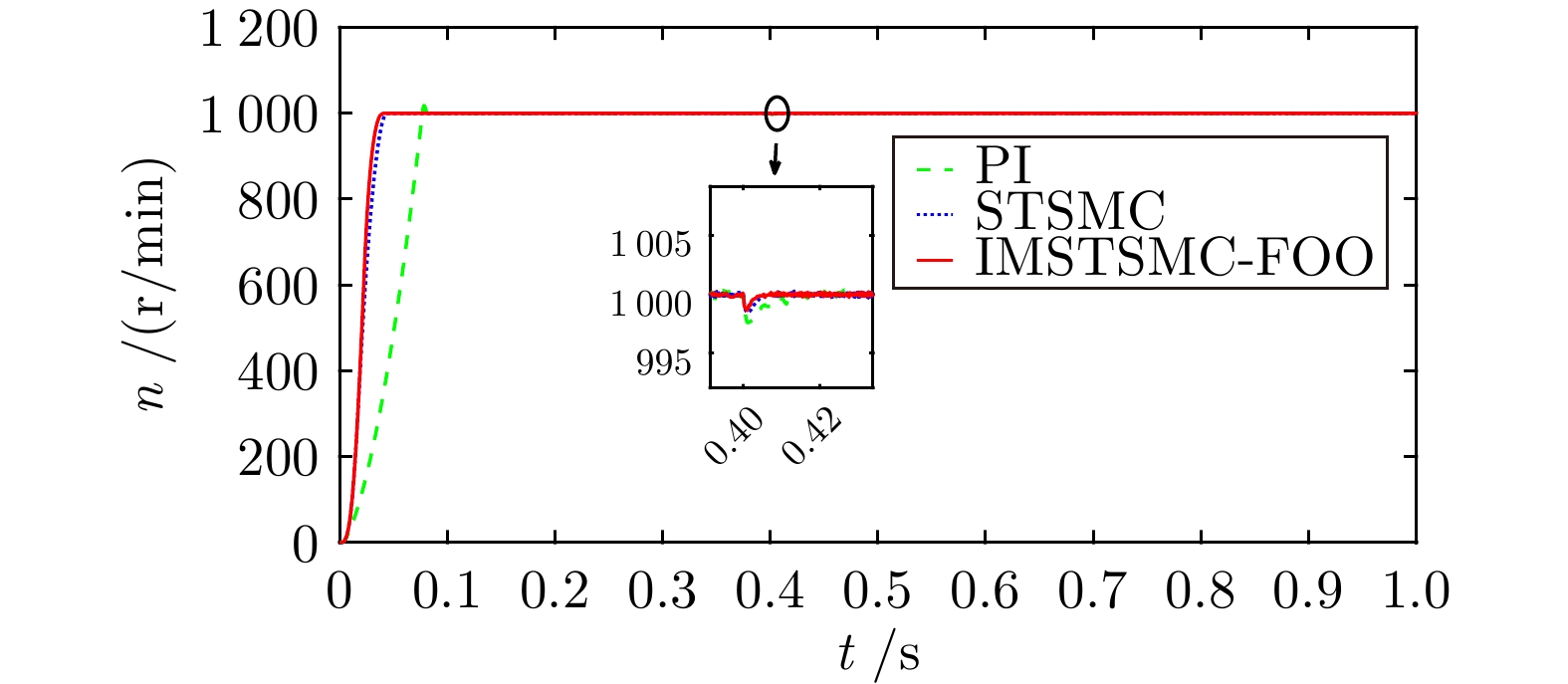
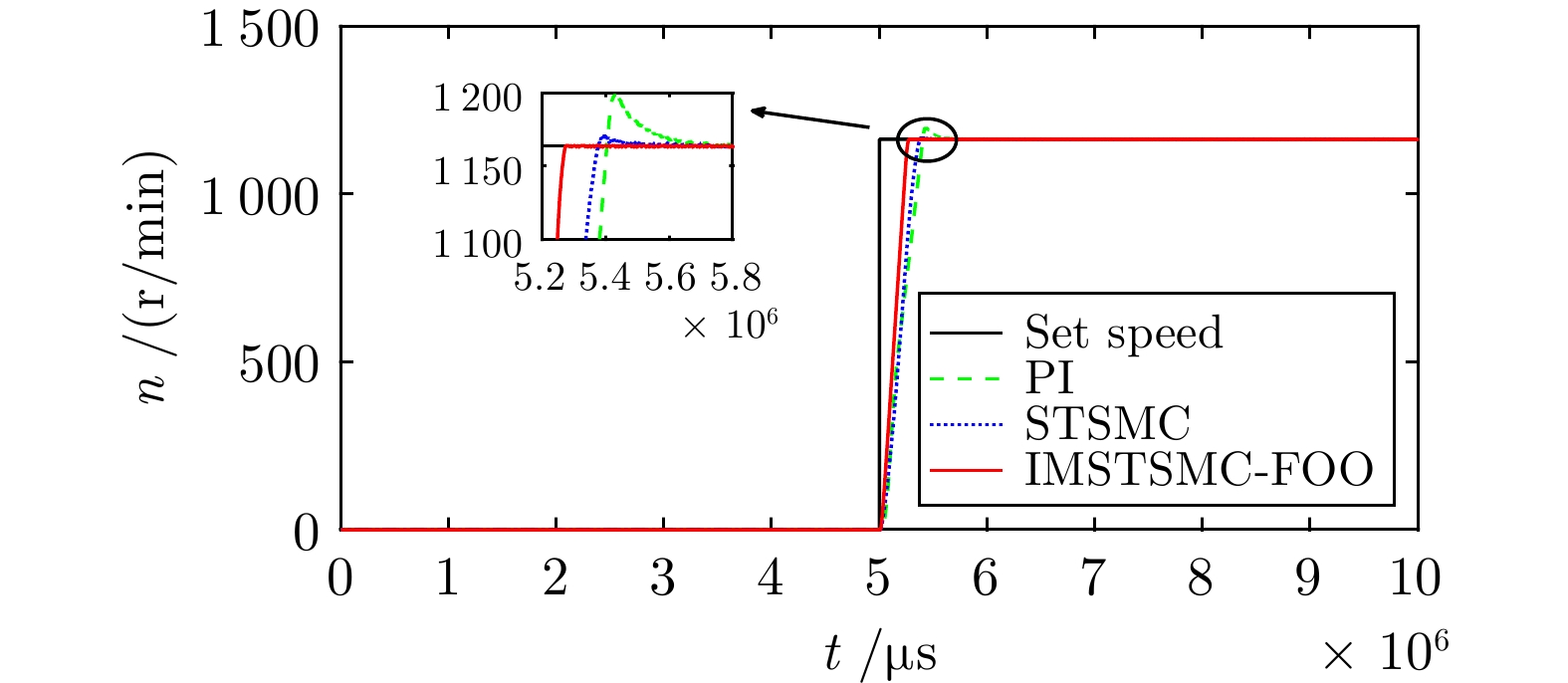
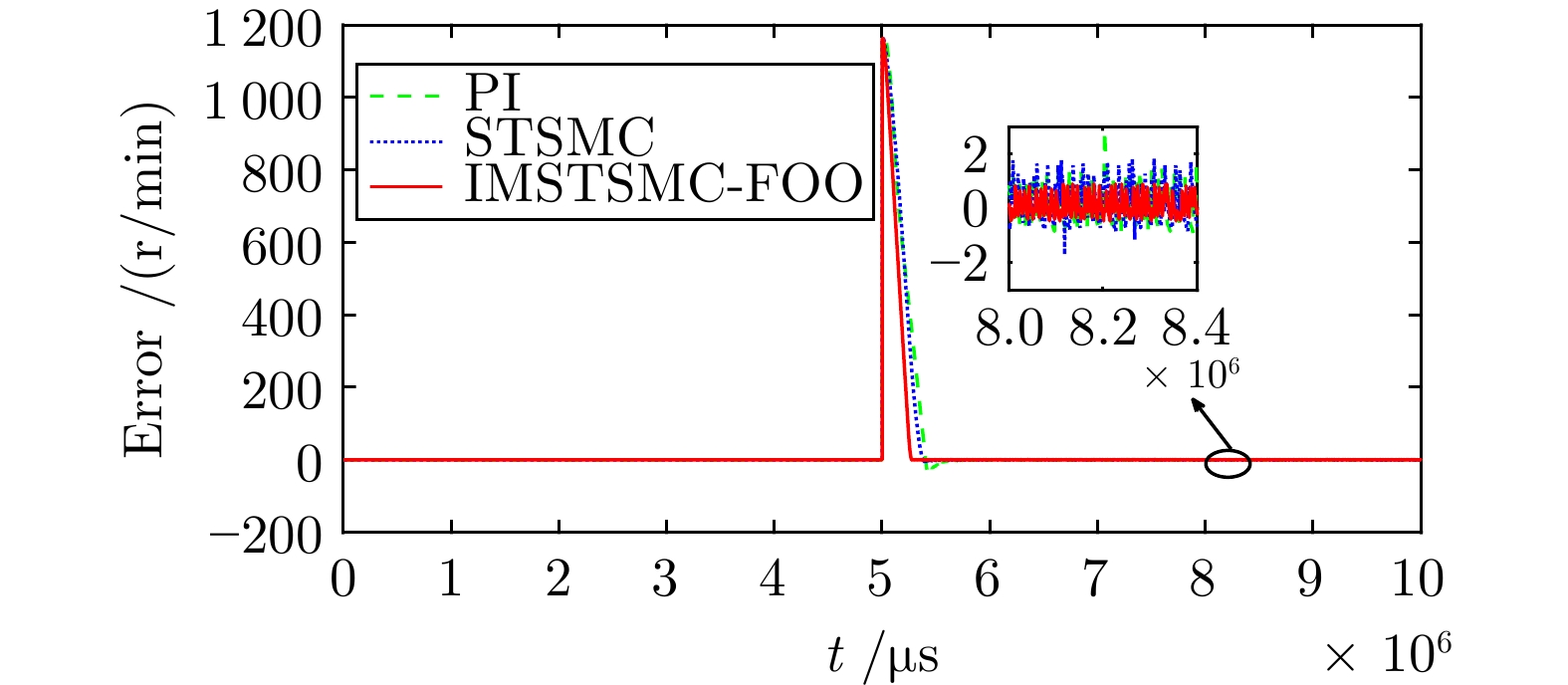
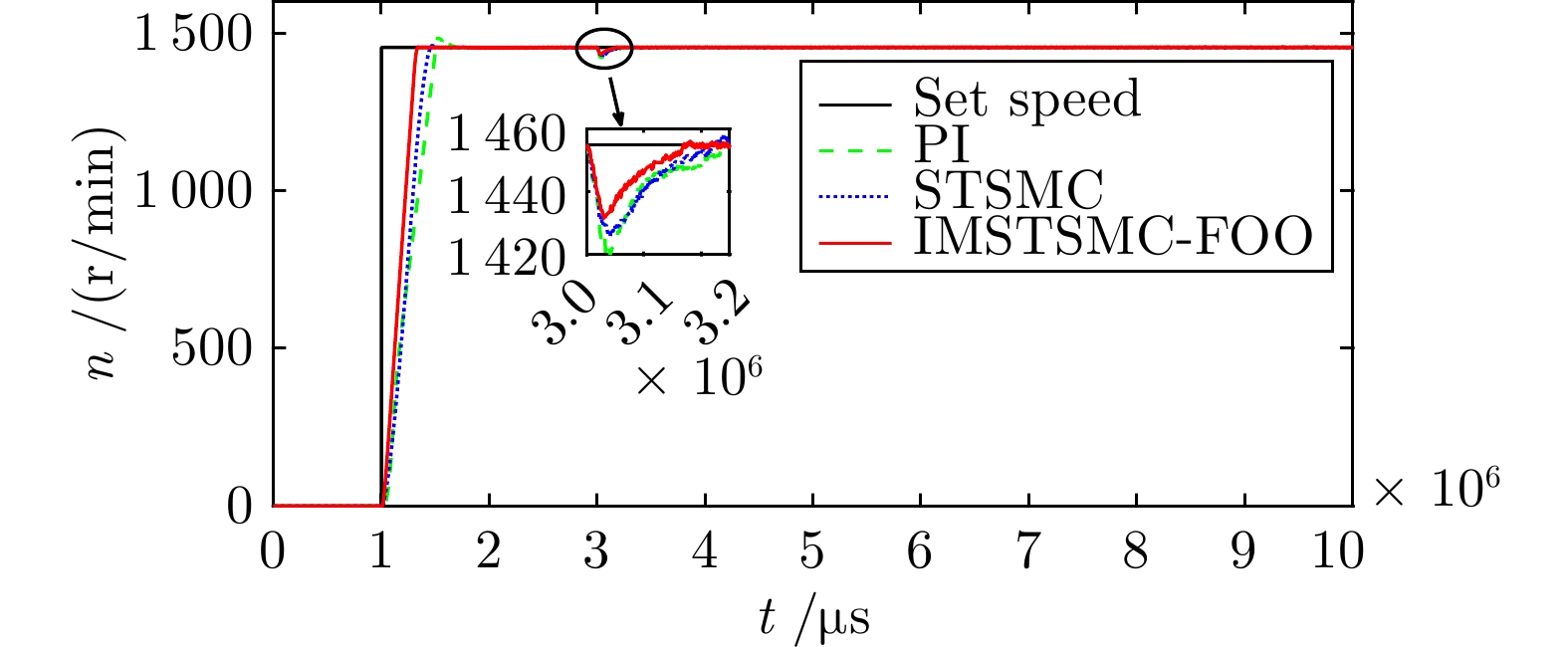
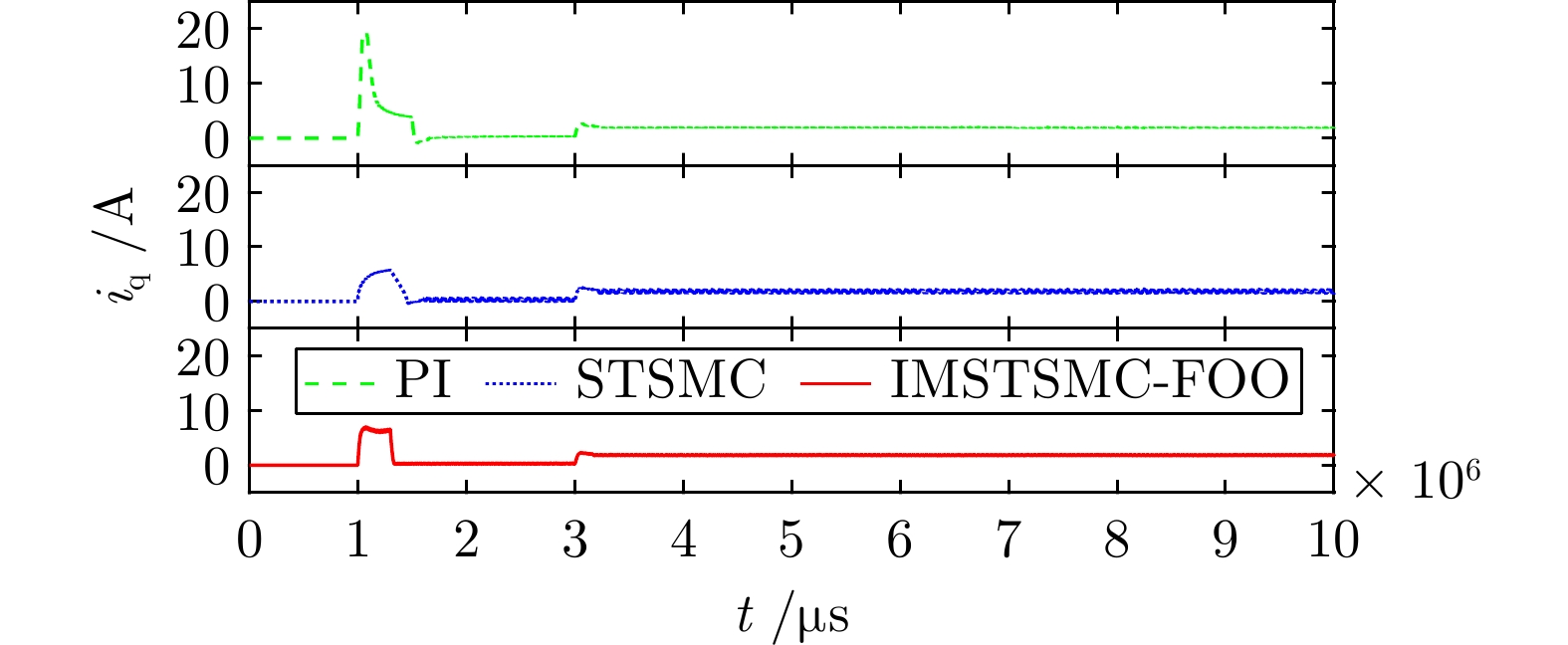
控制方式 收敛时间(s) 超调量(%) 转速波动(r/min) PI 5.722 3.040 ± 3.0 STSMC 5.510 0.653 ± 2.0 IMSTSMC-FOO 5.276 0.039 ± 1.0 表 4 三种控制方案下的突变转速控制性能表
Table 4 The performance table of sudden change speed control under three control schemes
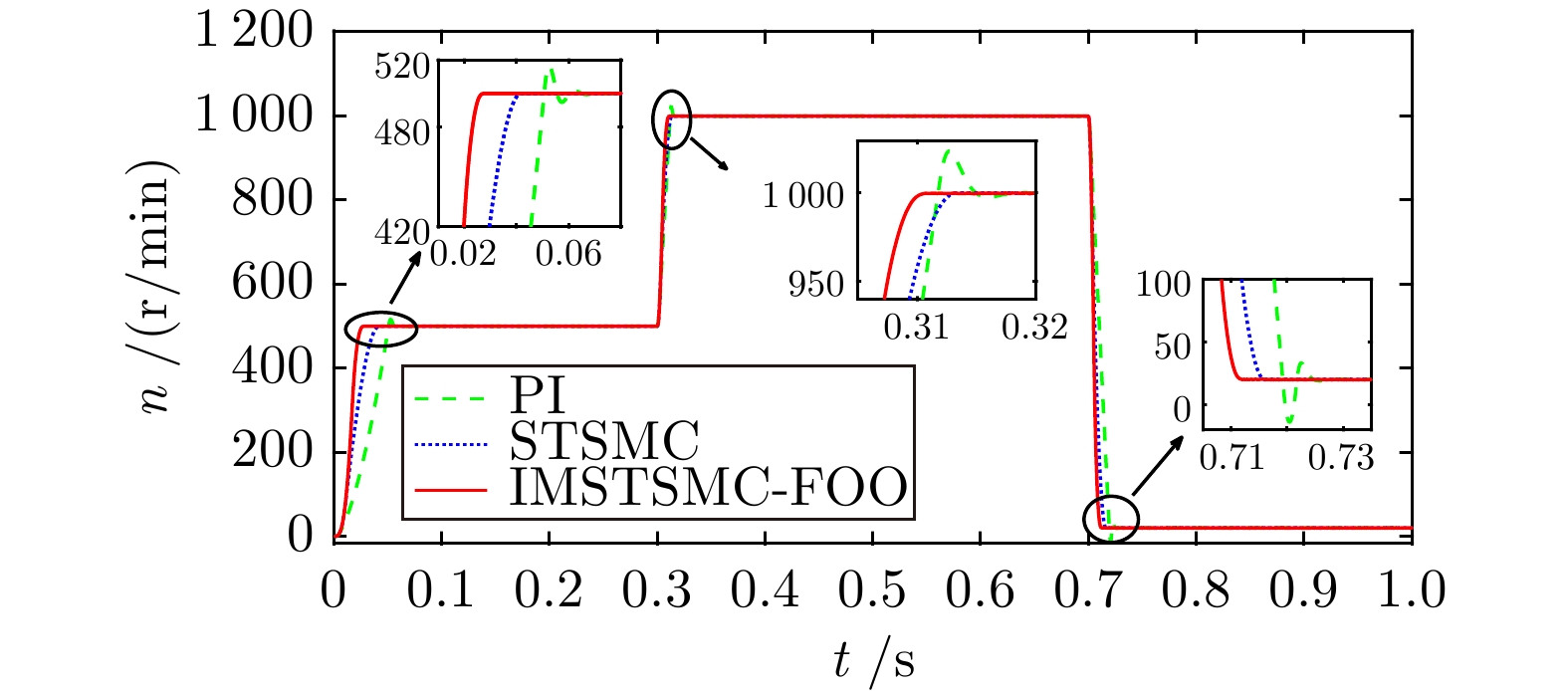
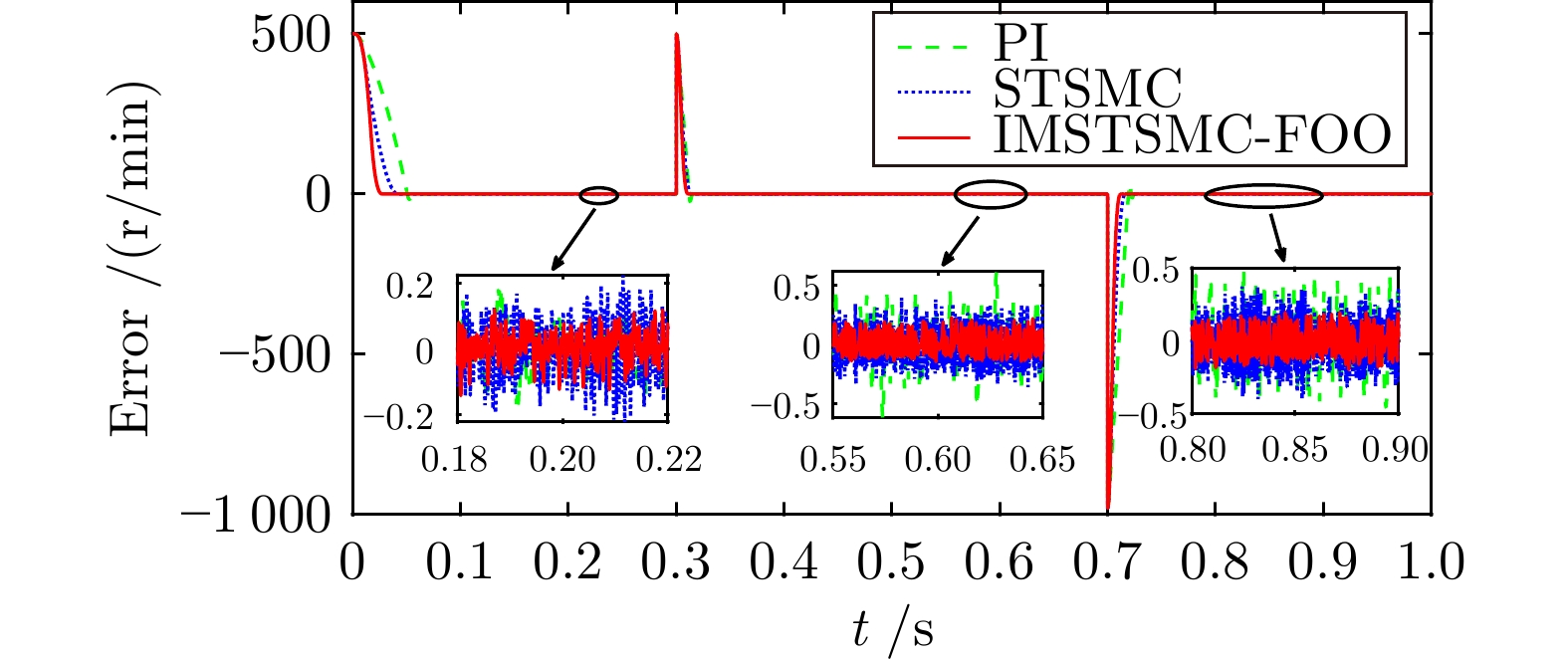
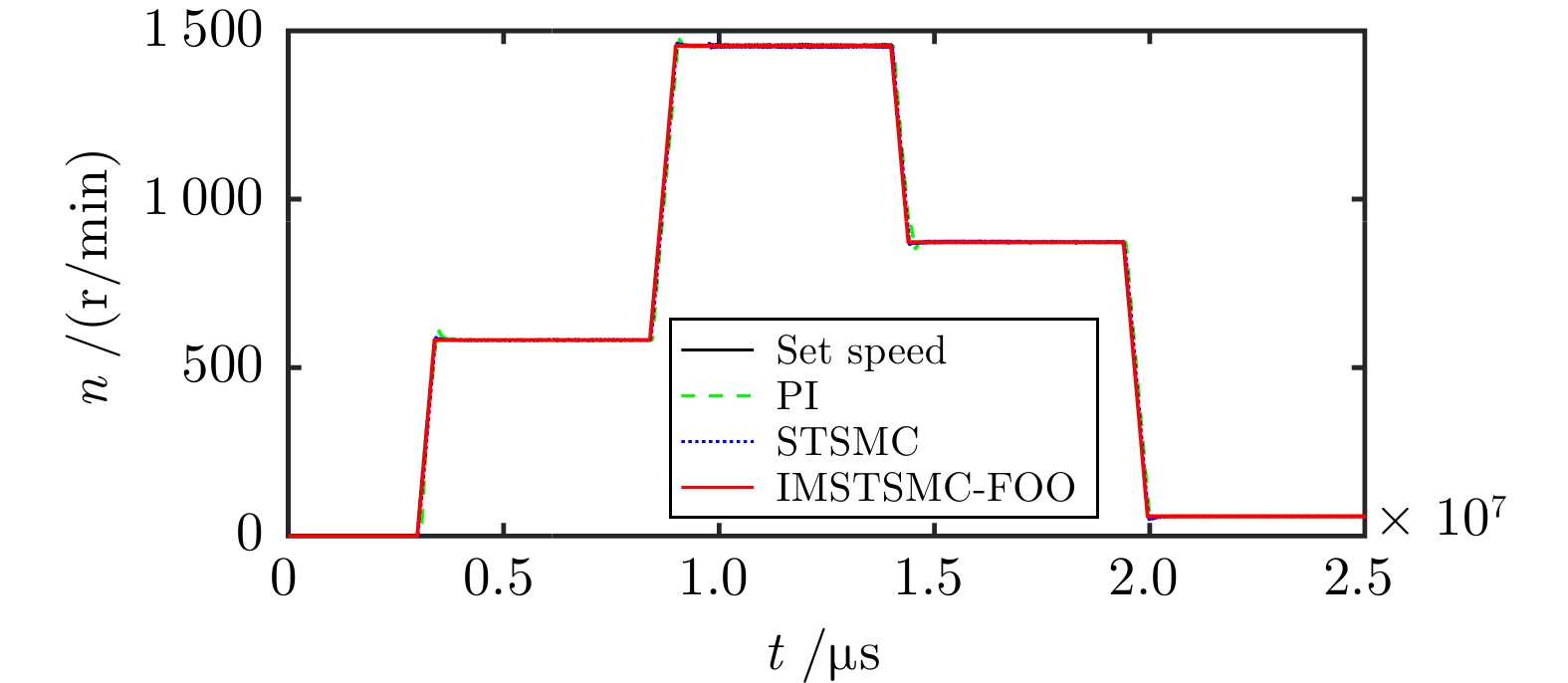
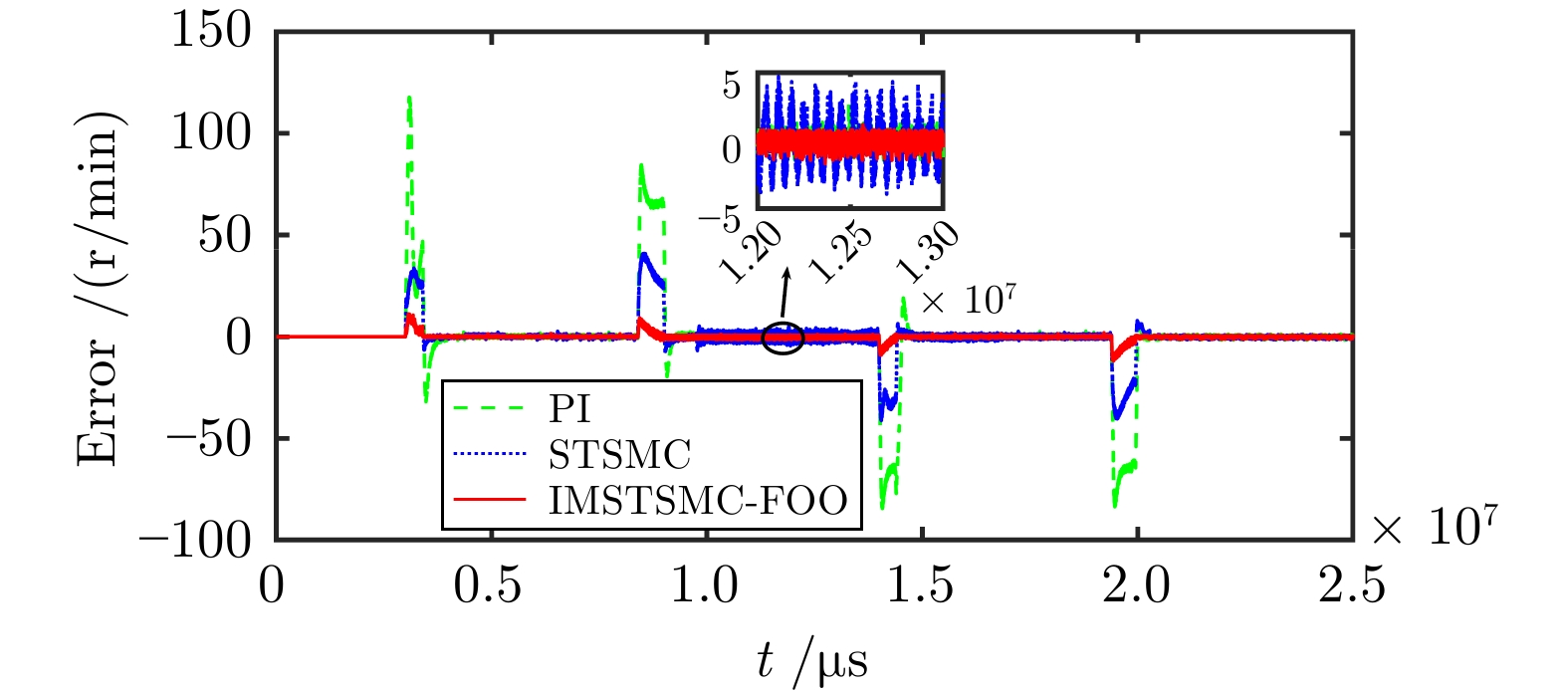
控制方式 收敛时间(s) 超调量(%) 转速波动(r/min) 第1段 PI 4.028 5.493 ± 2.0 STSMC 3.658 1.178 ± 2.0 IMSTSMC-FOO 3.420 0.067 ± 1.5 第2段 PI 9.516 1.347 ± 3.0 STSMC 9.284 0.544 ± 4.0 IMSTSMC-FOO 9.013 0.096 ± 1.5 第3段 PI 14.741 2.184 ± 2.5 STSMC 14.548 0.774 ± 2.0 IMSTSMC-FOO 14.405 0.055 ± 1.0 第4段 PI 20.117 12.992 ± 1.5 STSMC 20.193 14.167 ± 1.5 IMSTSMC-FOO 19.972 1.128 ± 1.0 表 5 三种控制方案下的突增负载转速控制性能表
Table 5 The performance table of sudden load increase speed control under three control schemes
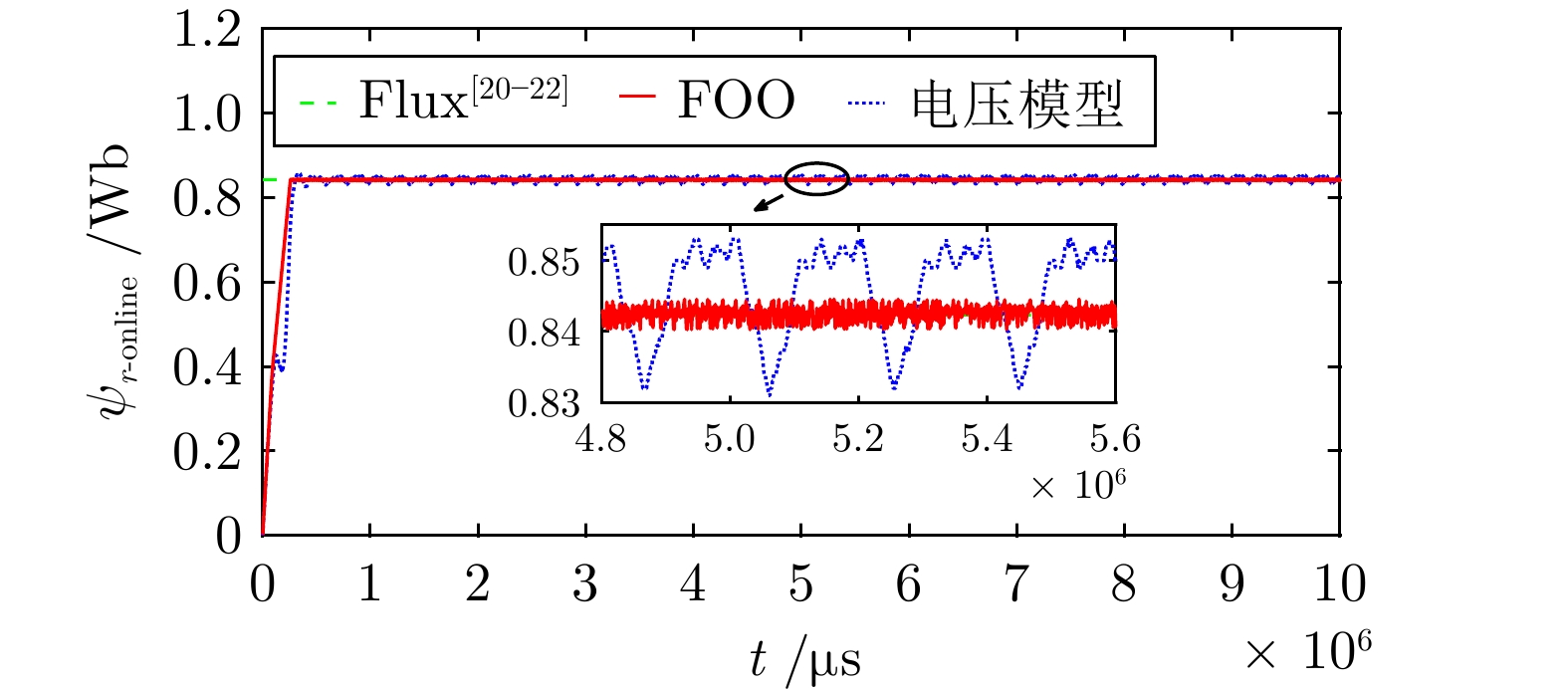
控制方式 恢复时长(s) 掉落量(r/min) PI 0.241 33.7 STSMC 0.219 29.2 IMSTSMC-FOO 0.184 23.1 -
[1] Zhang J, Yu J, Chen X, Liu J. Discrete-time adaptive fuzzy event-triggered command filtered control for induction motors with input saturation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2023, 71(3): 1271−1275 [2] Jung C, Torrico C R C, Carati E G. Adaptive loss model control for robustness and efficiency improvement of induction motor drives. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(11): 10893−10903 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3125648 [3] Luo C, Wang B, Yu Y. Decoupled stator resistance estimation for speed-sensorless induction motor drives considering speed and load torque variations. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2019, 8(2): 1193−1207 [4] 刘乐, 刘鹏, 王馨. 基于龙伯格观测器的感应电机预设性能位置跟踪优化控制. 控制理论与应用, 2023, 40(6): 1043−1052 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.11194Liu Le, Liu Peng, Wang Xin. Position tracking optimization control of induction motor with prescribed performance based on Luenberger observer. Control Theory and Applications, 2023, 40(6): 1043−1052 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.11194 [5] 王淑平, 张国山. 基于PI控制器的线性系统的鲁棒耗散控制. 控制与决策, 2012, 27(8): 1139−1144Wang Shu-Ping, Zhang Guo-Shan. Robust dissipative control for linear systems via PI controller. Control and Decision, 2012, 27(8): 1139−1144 [6] Gunabalam R, Subbiah V. Speed sensorless vector control of induction motor drive with PI and fuzzy controller. International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems, 2015, 5(3): 315−325 [7] Zhang Y, Yin Z, Li W. Adaptive sliding-mode-based speed control in finite control set model predictive torque control for induction motors. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(7): 8076−8087 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.3042181 [8] 王正齐, 刘贤兴. 基于神经网络逆系统的无轴承异步电机非线性内模控制. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(4): 433−439 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60043-9Wang Zheng-Qi, Liu Xian-Xing. Nonlinear internal model control for bearingless induction motor based on neural network inversion. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 433−439 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60043-9 [9] Ma P, Yu J, Wang Q G. Filter-and observer-based finite-time adaptive fuzzy control for induction motors systems considering stochastic disturbance and load variation. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2023, 38(2): 1599−1609 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2022.3211412 [10] Ei-Sousy F F M, Amin M M, Mohammed O A. Robust adaptive neural network tracking control with optimized super-twisting sliding-mode technique for induction motor drive system. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2022, 58(3): 4134−4157 doi: 10.1109/TIA.2022.3160136 [11] 陈闯, 王勃, 于泳. 基于改进指数趋近律的感应电机滑模转速观测器研究. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(S1): 155−163Chen Chuang, Wang Bo, Yu Yong. An improved exponential reaching law based-sliding mode observer for speed-sensorless induction motor drives. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(S1): 155−163 [12] 李中奇, 周靓, 杨辉. 高速动车组数据驱动无模型自适应积分滑模预测控制. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(1): 194−210Li Zhong-Qi, Zhou Liang, Yang Hui. Data-driven model-free adaptive integral sliding mode predictive control for high-speed electric multiple unit. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(1): 194−210 [13] 蔡运颂, 许璟, 牛玉刚. 基于自适应多尺度超螺旋算法的无人机集群姿态同步控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(8): 1656−1666Cai Yun-Song, Xu Jing, Niu Yu-Gang. Attitude consensus control of UAV swarm based on adaptive multi-scale super-twisting algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(8): 1656−1666 [14] Lian S, Meng W, Shao K, Zheng J, Zhu S, Li H. Full attitude control of a quadrotor using fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode with angular velocity planning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 70(4): 3975−3984 [15] Krim S, Gdaim S, Mtibaa A. FPGA-based real-time implementation of a direct torque control with second-order sliding mode control and input-output feedback linearisation for an induction motor drive. IET Electric Power Applications, 2020, 14(3): 480−491 doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2018.5829 [16] 刘陆, 丁世宏, 李世华. 高阶滑模控制理论综述. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(12): 2193−2201Liu Lu, Ding Shi-Hong, Li Shi-Hua. A survey for high-order sliding mode control theory. Control Theory and Applications, 2022, 39(12): 2193−2201 [17] Kali Y, Ayala M, Rodas J. Time delay estimation based discrete-time super-twisting current control for a six-phase induction motor. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(11): 12570−12580 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.2995773 [18] Nurettin A, Ínanç N. High-performance induction motor speed control using a robust hybrid controller with a supertwisting sliding mode load disturbance observer. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 70(8): 7743−7752 [19] Halimi H, Elgarouaz M, Lazrak L. High-order sliding mode control with hyperbolic evaluation function for improving performances of a squirrel-cage induction motor fed by a two-level inverter. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2024, 12(8): 2929−2943 doi: 10.1007/s40435-023-01378-0 [20] 宁博文, 周凤星, 卢少武. 基于高阶滑模速度控制器的异步电机模型预测转矩控制. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(4): 953−958Ning Bo-Wen, Zhou Feng-Xing, Lu Shao-Wu. A model predictive torque control for induction motor based on high order sliding mode speed controller. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(4): 953−958 [21] Wang B, Wang T, Yu Y. Second-order terminal sliding-mode speed controller for induction motor drives with nonlinear control gain. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(11): 10923−10934 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3231248 [22] Teja A V R, Chakraborty C, Pal B C. Disturbance rejection analysis and FPGA-based implementation of a second-order sliding mode controller fed induction motor drive. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2018, 33(3): 1453−1462 doi: 10.1109/TEC.2018.2808325 [23] 张杰, 柴建云, 孙旭东. 基于反电动势与磁链正交性的异步电机电压模型积分改进算法. 电工技术学报, 2014, 29(3): 41−49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2014.03.006Zhang Jie, Chai Jian-Yun, Sun Xu-Dong. An improved voltage model integral algorithm of induction motors based on the orthogonality between back EMF and flux. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2014, 29(3): 41−49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2014.03.006 [24] Devanshu A, Singh M, Kumar N. An improved nonlinear flux observer based sensorless FOC IM drive with adaptive predictive current control. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(1): 652−666 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2019.2912265 [25] Jo G J, Choi J W. Rotor flux estimator design with offset extractor for sensorless-driven induction motors. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 37(4): 4497−4510 [26] 何志明, 廖勇, 向大为. 定子磁链观测器低通滤波器的改进. 中国电机工程学报, 2008, 28(18): 61−65He Zhi-Ming, Liao Yong, Xiang Da-Wei. Improvement of low-pass filter algorithm for stator flux estimator. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2008, 28(18): 61−65 [27] 孙宇新, 唐敬伟, 施凯. 改进型MRAS无速度传感器的无轴承异步电机矢量控制. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(6): 939−950Sun Yu-Xin, Tang Jing-Wei, Shi Kai. Vector control of speed sedsorless bearingless induction motors using improved MRAS. Control Theory and Applications, 2019, 36(6): 939−950 [28] Çavuş B, Aktaş M. A new adaptive terminal sliding mode speed control in flux weakening region for DTC controlled induction motor drive. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2023, 39(1): 449−458 [29] Jiang D, Yu W, Wang J. Dynamic analysis of DFIG fault detection and its suppression using sliding mode control. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2020, 11(1): 643−656 [30] Seeber R, Horn M. Stability proof for a well-established super-twisting parameter setting. Automatica, 2017, 84: 241−243 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.07.002 [31] Wang Z. Adaptive smooth second-order sliding mode control method with application to missile guidance. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2017, 39(6): 848−860 doi: 10.1177/0142331215621616 [32] Jo G J, Choi J W. Gopinath model-based voltage model flux observer design for field-oriented control of induction motor. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2018, 34(5): 4581−4592 -




 下载:
下载: