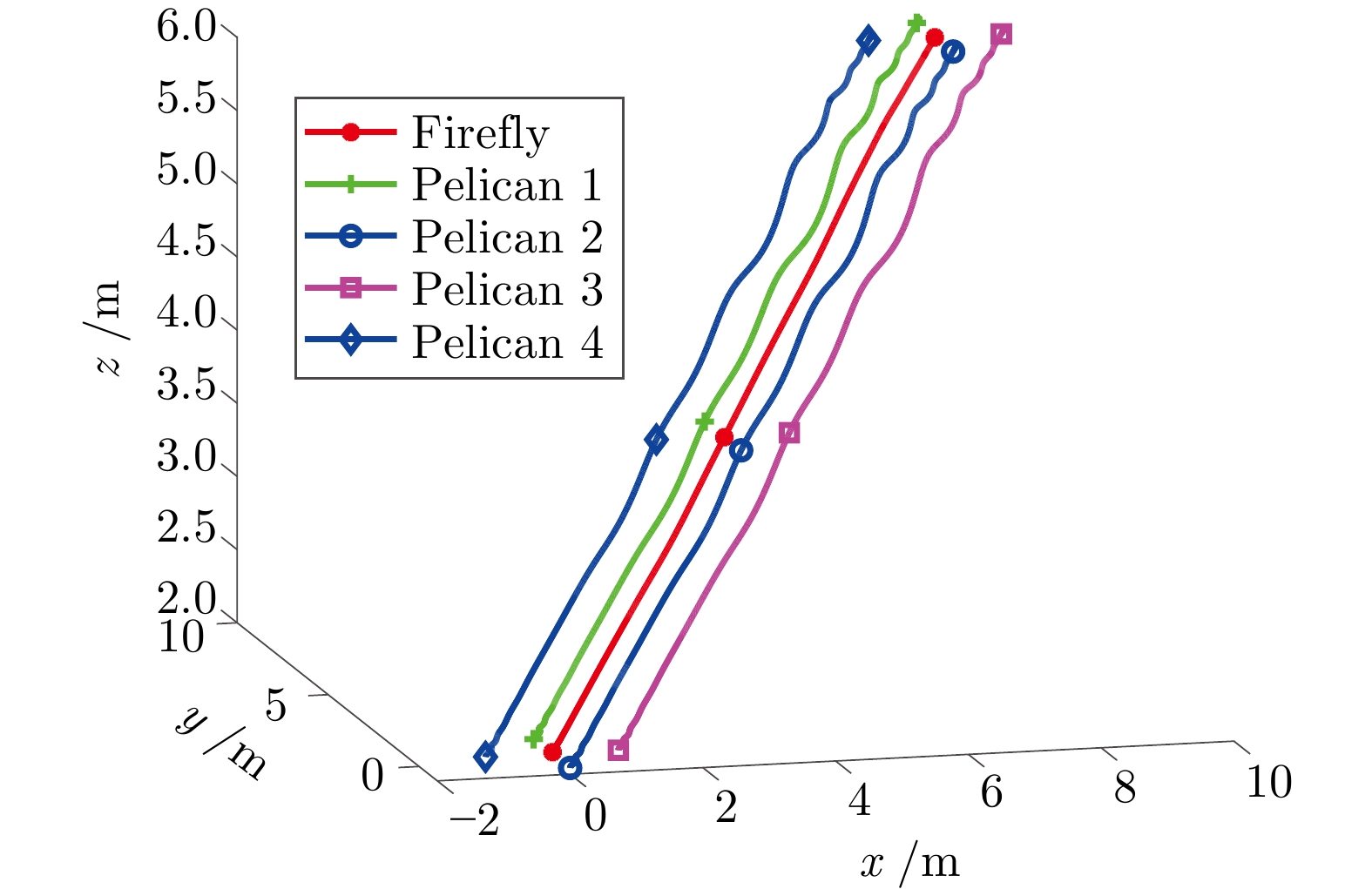
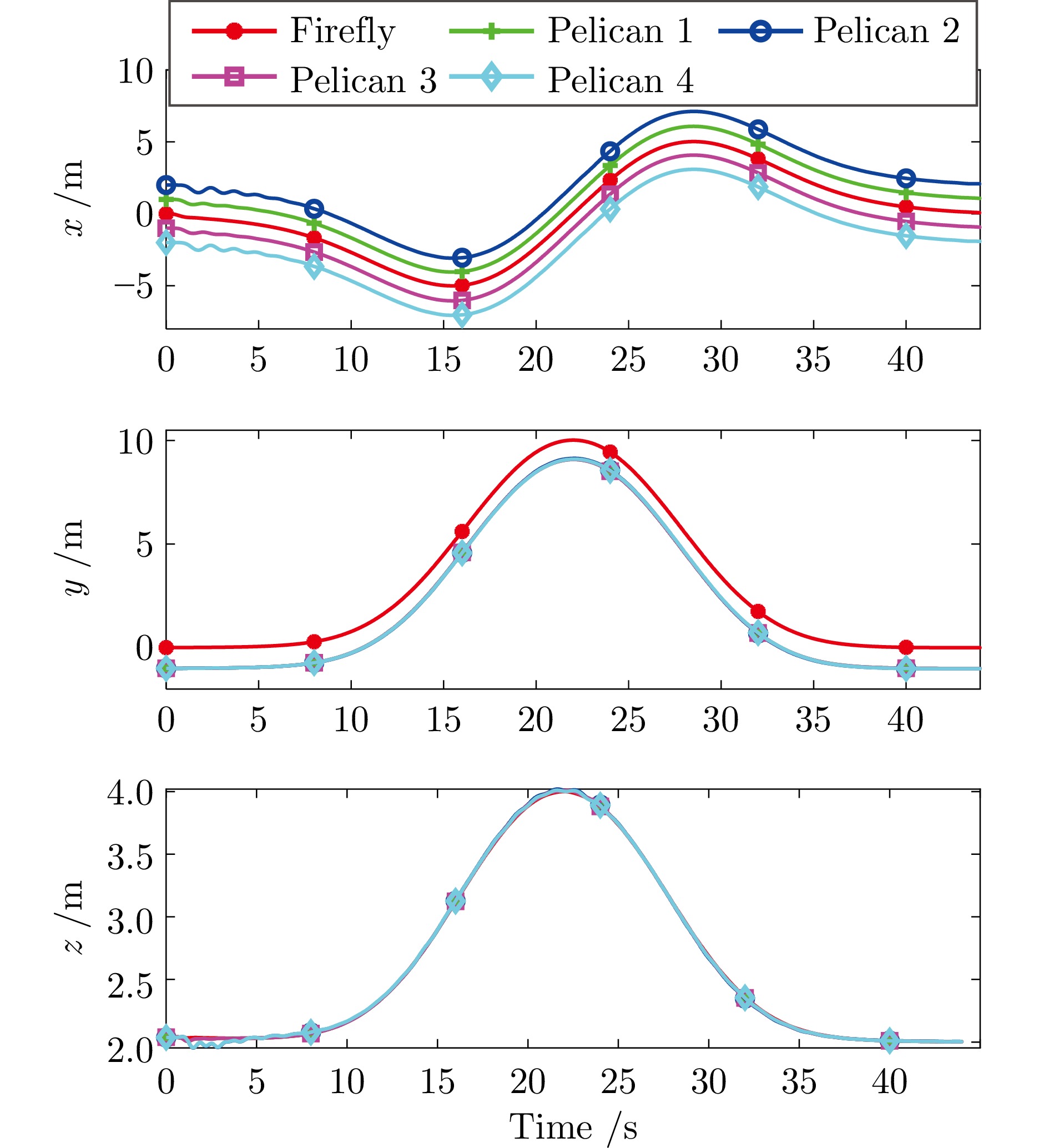
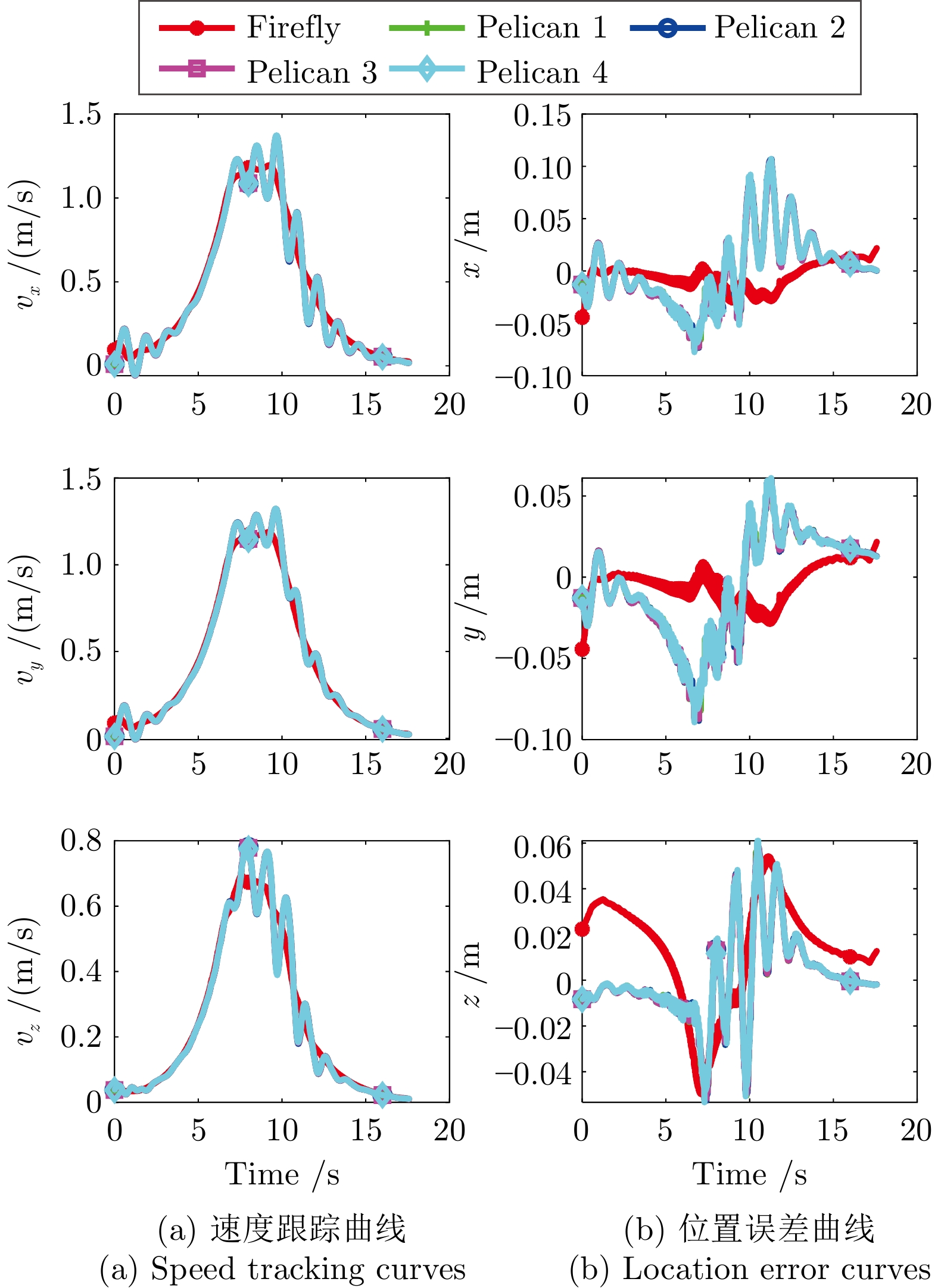
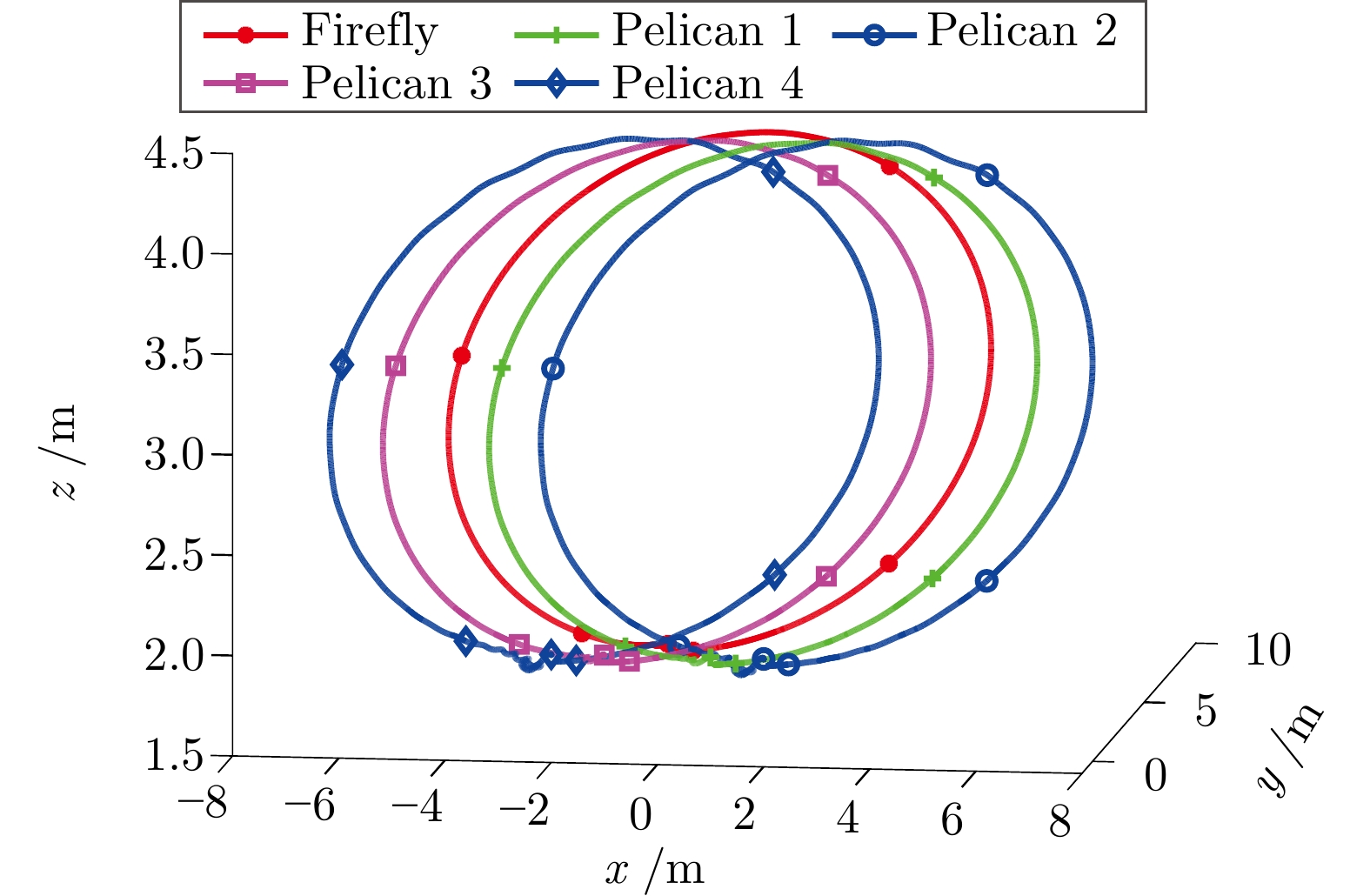
-
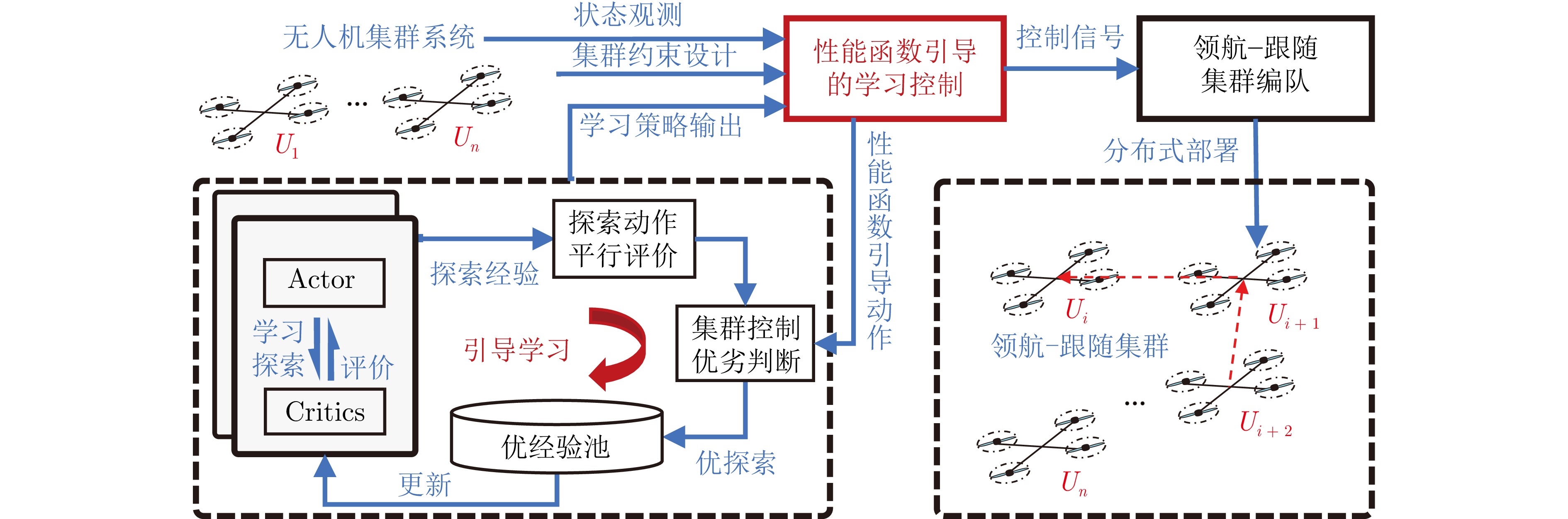
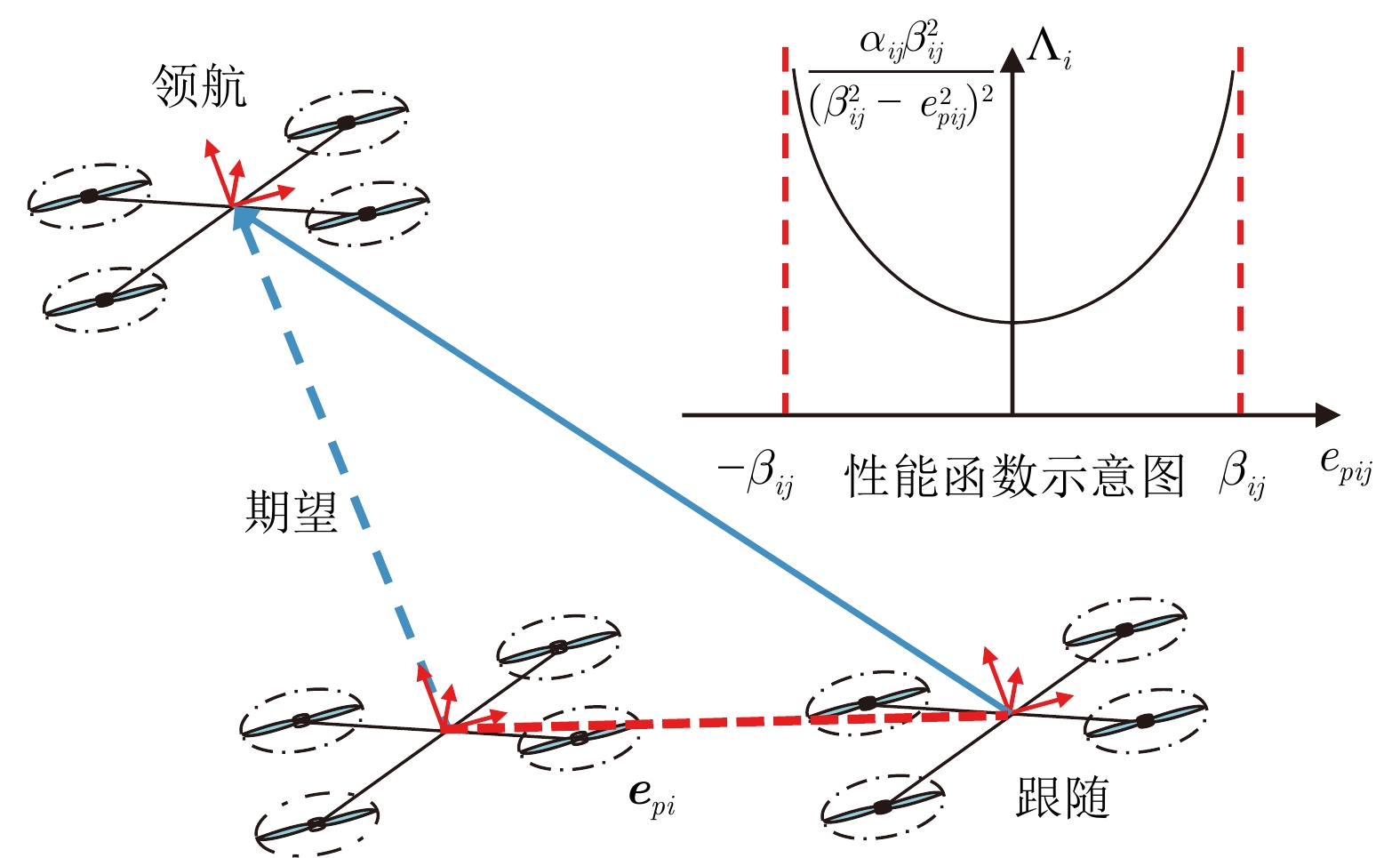
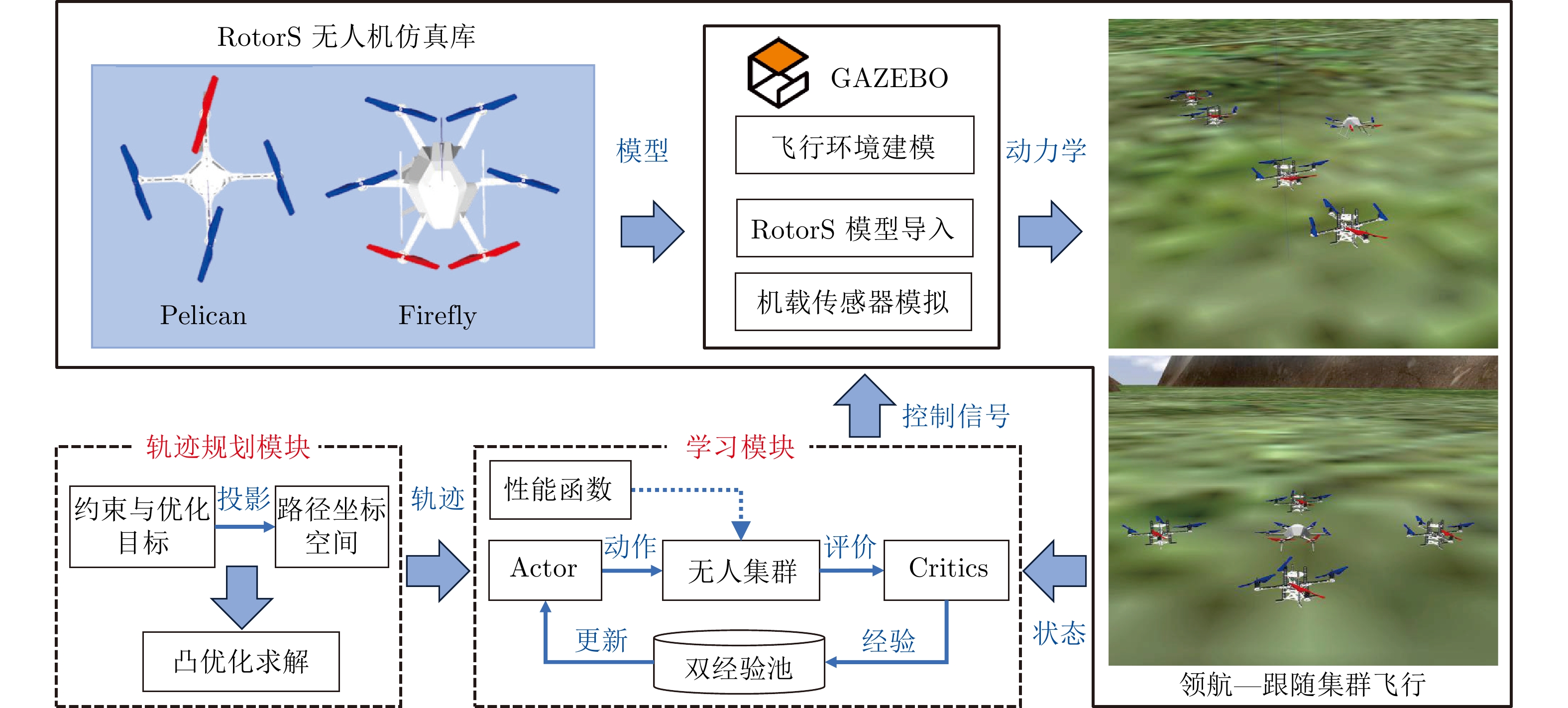
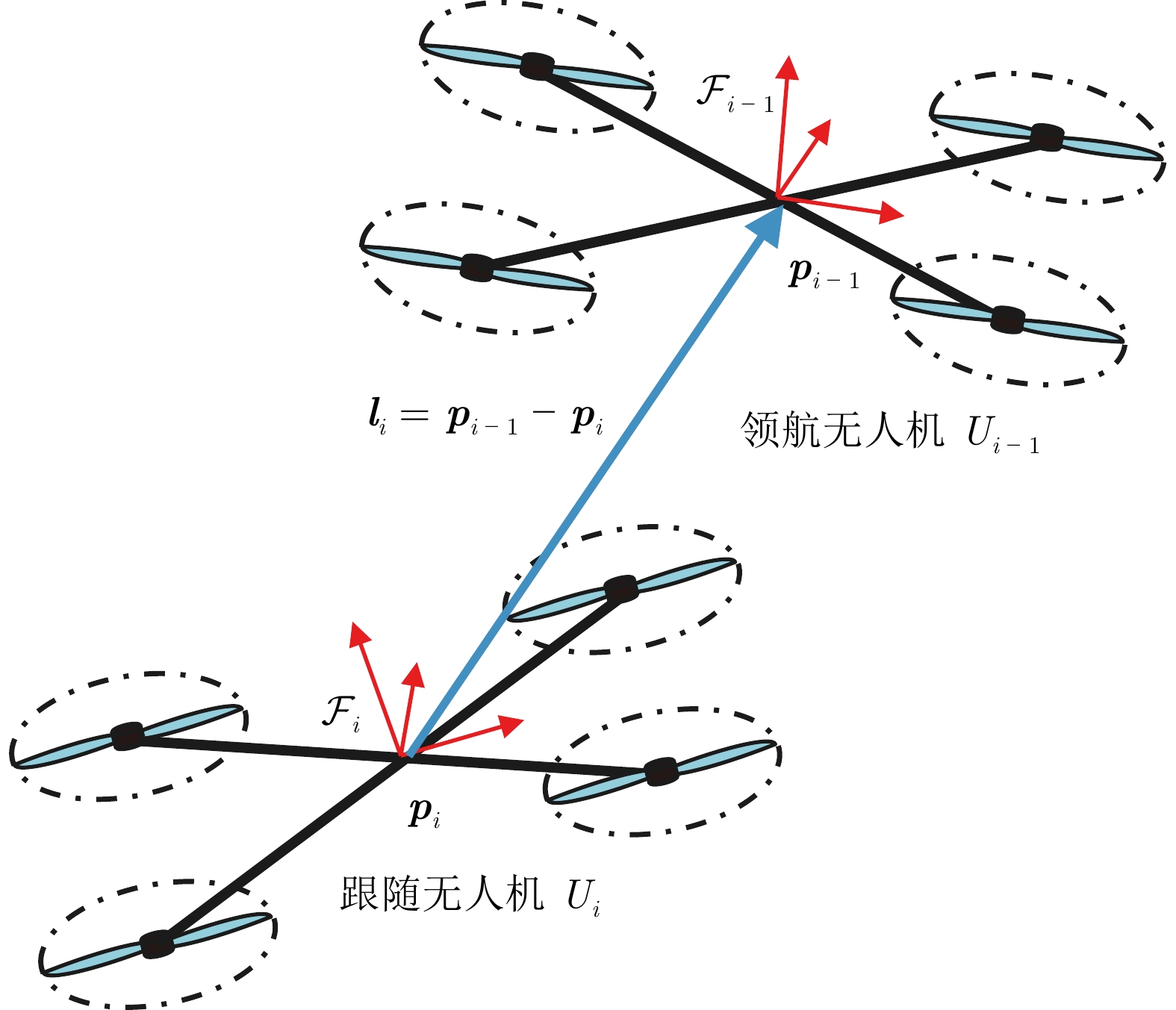
摘要: 针对无人机集群系统, 提出一种性能函数引导的深度强化学习控制方法, 同时评估性能函数的示范经验与学习策略的探索动作, 保证高效可靠的策略更新, 实现无人机集群系统的高性能控制. 首先, 利用领航–跟随集群框架, 将无人机集群的控制问题转化为领航–跟随框架下的跟踪问题, 进而提出基于模型的跟踪控制方法, 利用性能函数将集群编队误差约束在给定范围内, 实现无人机集群的模型驱动控制. 接下来, 为解决复杂工况下性能函数极易失效难题, 将深度强化学习方法和性能函数驱动方法结合, 提出性能函数引导的深度强化学习控制方法, 利用性能函数的示范经验辅助训练强化学习网络, 通过同时评估探索与示范动作, 保证学习策略显著优于性能函数驱动控制方法, 有效提高无人机编队控制精度与鲁棒性. 实验结果表明, 该方法能够显著提升无人机集群的控制性能, 实现兼顾鲁棒性与飞行精度的高性能集群控制.Abstract: A novel performance function-guided deep reinforcement learning control method is proposed for the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) swarm system, which simultaneously evaluates both the demonstration experience from the performance function and exploratory actions from the learning strategy to guarantee efficient and reliable policy updating, achieving high-performance control of the UAV swarm system. Firstly, based on the leader-follower framework, the UAV swarm control problem is transformed into a tracking problem under the leader–follower paradigm, and then, the model-based tracking control is proposed, where the performance function is designed to constrain the tracking error within a given range, thereby achieving UAV model-driven formation control. Then, to address the invalid problem of performance function under complex working conditions, the deep reinforcement learning and the performance function-driven methods are combined to propose the performance-function-guided deep reinforcement learning control method, where the demonstration of performance function is used to assist in training the reinforcement learning network. By jointly evaluating exploratory and demonstrative actions, the proposed method ensures a learned policy that significantly outperforms the performance function-driven control alone, effectively enhancing the accuracy and robustness of UAV formation control. Comparative experimental results show that the proposed method significantly improves the control performance of UAV swarms, realizing high-performance swarm control with both robustness and flight accuracy.
-
表 1 训练参数
Table 1 Training parameters
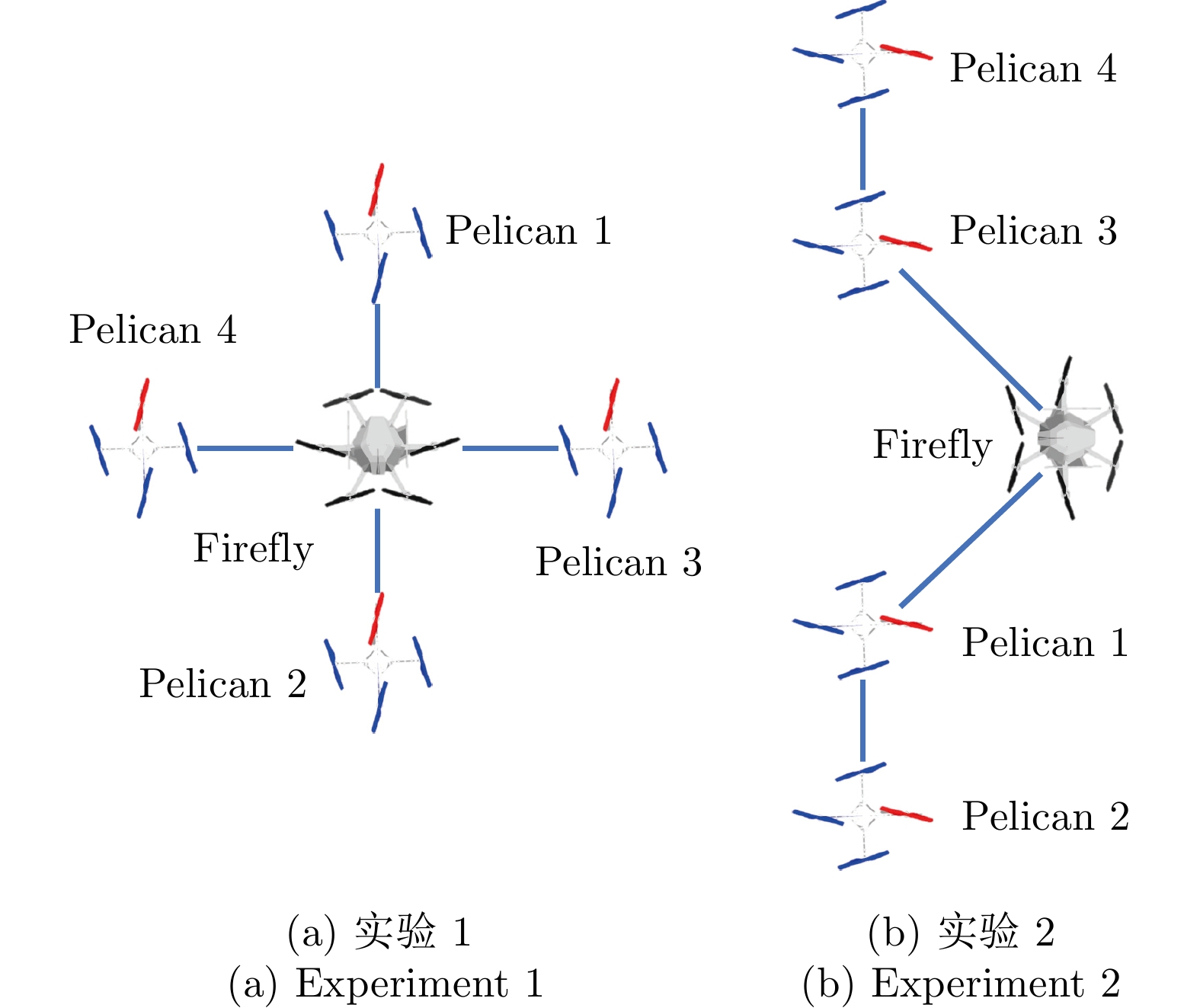
参数 值 无人机质量$ {m}_i $ $ {m}_1 = 1.6\;\text{kg},\;{m}_{2} = {m}_{3}= {m}_{4}= {m}_{5}=1.0 \;\text{kg} $ 无人机转动惯量$ \mathrm{II}_i $ $ \text{diag}\left\{0.01\,\;\,\;0.01\,\;\,\;0.01\right\}\;\text{kg}\cdot \text{m}^2 $ 重力加速度 $ 9.8\;\text{m}/\text{s}^2 $ 学习率$ \lambda_{\alpha_{1,\;2,\;3}} $ $ 1,\;2,\;2\times 10^{-4} $ 训练回合数$ M_\text{max} $ $ 100 $ 训练步数$ N_\text{max} $ $ 500 $ 经验池大小$ \mathcal{B}_{1,\;2} $ $ 10\;000,\; 10\;000 $ 采样数据量$ {N_m} $ $ 128 $ 训练折扣因子$ \gamma $ $ 0.95 $ 探索与平滑系数$ \sigma_{1,\;2} $ $ 0.1,\;0.05 $ 控制策略交互频率 $ 100 $ Hz 引导策略参数$ k_{\varphi ij},\;\beta_{ij} $ $ 0.2,\; 0.3 $ 辅助增益矩阵$ K_{pi} $ $ \text{diag}\left\{4\ 4\ 4\right\} $ 辅助增益矩阵$ K_{Ri} $ $ \text{diag}\left\{1.5\ 1.5\ 1.5\right\} $ 外环控制参数$ K_{\zeta i} $ $ \text{diag}\left\{2\ 2\ 2\right\} $ 内环控制参数 $ k_{\eta i} $ $ \text{diag}\left\{1.5\ 1.5\ 1.5\right\} $ 内环控制参数$ k_i $ $ \text{diag}\left\{2\ 2\ 2\right\} $ -
[1] 陈谋, 马浩翔, 雍可南, 吴颖. 无人机安全飞行控制综述. 机器人, 2023, 45(3): 345−366Chen Mou, Ma Hao-Xiang, Yong Ke-Nan, Wu Ying. Safety flight control of UAV: A survey. Robot, 2023, 45(3): 345−366 [2] Erskine J, Briot S, Fantoni I, Chriette A. Singularity analysis of rigid directed bearing graphs for quadrotor formations. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2024, 40: 139−157 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2023.3324198 [3] 代波, 何玉庆, 谷丰, 王骞翰, 徐卫良. 基于加速度反馈增强的旋翼无人机抗风扰控制. 机器人, 2020, 42(1): 79−88Dai Bo, He Yu-Qing, Gu Feng, Wang Qian-Han, Xu Wei-Liang. Acceleration feedback enhanced controller for wind disturbance rejection of rotor unmanned aerial vehicle. Robot, 2020, 42(1): 79−88 [4] 蔡运颂, 许璟, 牛玉刚. 基于自适应多尺度超螺旋算法的无人机集群姿态同步控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(8): 1656−1666Cai Yun-Song, Xu Jing, Niu Yu-Gang. Attitude consensus control of UAV swarm based on adaptive multi-scale super-twisting algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(8): 1656−1666 [5] Ille M, Namerikawa T. Collision avoidance between multi-UAV-systems considering formation control using MPC. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM). Munich, Germany: IEEE, 2017. 651–656 [6] 茹常剑, 魏瑞轩, 戴静, 沈东, 张立鹏. 基于纳什议价的无人机编队自主重构控制方法. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(8): 1349−1359Ru Chang-Jian, Wei Rui-Xuan, Dai Jing, Shen Dong, Zhang Li-Peng. Autonomous reconfiguration control method for UAV's formation based on Nash bargain. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(8): 1349−1359 [7] Qi J T, Guo J J, Wang M M, Wu C, Ma Z W. Formation tracking and obstacle avoidance for multiple quadrotors with static and dynamic obstacles. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 1713−1720 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3140830 [8] Shi Y, Hua Y Z, Yu J L, Dong X W, Lv J H, Ren Z. Cooperative fault-tolerant formation tracking control for heterogeneous air-ground systems using a learning-based method. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(2): 1505−1518 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3336638 [9] Zhang Y, Ma L, Yang C Y, Zhou L N, Wang G Q, Dai W. Formation control for multiple quadrotors under DoS attacks via singular perturbation. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4753−4762 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3241139 [10] Park B S, Yoo S J. Time-varying formation control with moving obstacle avoidance for input-saturated quadrotors with external disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(5): 3270−3282 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3358345 [11] Du H B, Zhu W W, Wen G H, Duan Z S, Lv J H. Distributed formation control of multiple quadrotor aircraft based on nonsmooth consensus algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(1): 342−353 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2777463 [12] Dong X W, Yu B C, Shi Z Y, Zhong Y S. Time-varying formation control for unmanned aerial vehicles: Theories and applications. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2015, 23(1): 340−348 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2014.2314460 [13] Hu Z J, Jin X. Formation control for an UAV team with environment-aware dynamic constraints. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 9(1): 1465−1480 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3295354 [14] Wang Z X, Zou Y, Liu Y Z, Meng Z Y. Distributed control algorithm for leader-follower formation tracking of multiple quadrotors: Theory and experiment. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2021, 26(2): 1095−1105 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2020.3017816 [15] Liu H, Ma T, Lewis F L, Wan Y. Robust formation trajectory tracking control for multiple quadrotors with communication delays. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2020, 28(6): 2633−2640 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2019.2942277 [16] Wu J, Luo C B, Min G Y, McClean S. Formation control algorithms for multi-UAV systems with unstable topologies and hybrid delays. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(9): 12358−12369 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3383352 [17] Dai S L, He S D, Chen X, Jin X. Adaptive leader-follower formation control of nonholonomic mobile robots with prescribed transient and steady-state performance. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(6): 3662−3671 doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2939263 [18] Shen Y Y, Zhou J, Xu Z D, Zhao F G, Xu J M, Chen J M, et al. Aggressive trajectory generation for a swarm of autonomous racing drones. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Detroit, USA: IEEE, 2023. 7436–7441 [19] Song F L, Li Z, Yu X H. A feedforward quadrotor disturbance rejection method for visually identified gust sources based on transfer reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(5): 6612−6623 [20] Xiao C X, Lu P, He Q Z. Flying through a narrow gap using end-to-end deep reinforcement learning augmented with curriculum learning and Sim2Real. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(5): 2701−2708 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3107742 [21] Han H R, Cheng J, Xi Z L, Yao B C. Cascade flight control of quadrotors based on deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(4): 11134−11141 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3196455 [22] Hua H A, Fang Y C. A novel reinforcement learning-based robust control strategy for a quadrotor. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(3): 2812−2821 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3165288 [23] Zhao W B, Liu H, Lewis F L. Robust formation control for cooperative underactuated quadrotors via reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(10): 4577−4587 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3023711 [24] Hua H A, Fang Y C. A novel learning-based trajectory generation strategy for a quadrotor. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(7): 9068−9079 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3217814 [25] Hwangbo J, Sa I, Siegwart R, Hutter M. Control of a quadrotor with reinforcement learning. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 2(4): 2096−2103 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2720851 [26] Pu Z Q, Wang H M, Liu Z, Yi J Q, Wu S G. Attention enhanced reinforcement learning for multi agent cooperation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(11): 8235−8249 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3146858 [27] Sun Q Y, Fang J B, Zheng W X, Tang Y. Aggressive quadrotor flight using curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(12): 13838−13848 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3144586 [28] Wang Y D, Sun J, He H B, Sun C Y. Deterministic policy gradient with integral compensator for robust quadrotor control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(10): 3713−3725 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2884725 [29] Raja G, Essaky S, Ganapathisubramaniyan A, Baskar Y. Nexus of deep reinforcement learning and leader-follower approach for AIoT enabled aerial networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(8): 9165−9172 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3226529 [30] Yoo J, Jang D, Kim H J, Johansson K H. Hybrid reinforcement learning control for a micro quadrotor flight. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2021, 5(2): 505−510 doi: 10.1109/LCSYS.2020.3001663 [31] Koryakovskiy I, Kudruss M, Vallery H, Babuška R, Caarls W. Model-plant mismatch compensation using reinforcement learning. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(3): 2471−2477 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2800106 [32] Furrer F, Burri M, Achtelik M, Siegwart R. RotorS——A modular gazebo MAV simulator framework. Robot Operating System (ROS). Cham: Springer, 2016. 595–625 [33] Hua H A, Fang Y C, Zhang X T, Qian C. A time-optimal trajectory planning strategy for an aircraft with a suspended payload via optimization and learning approaches. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2022, 30(6): 2333−2343 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2021.3139762 -




 下载:
下载: