Cooperative Optimal Output Regulation Under Quantized Communication Based on Adaptive Dynamic Programming
-
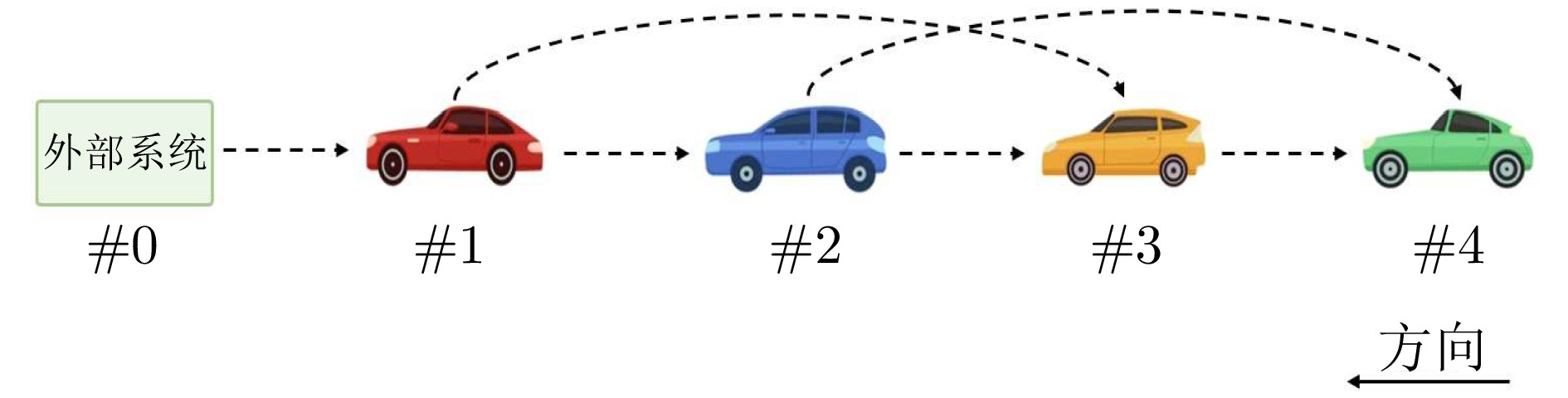
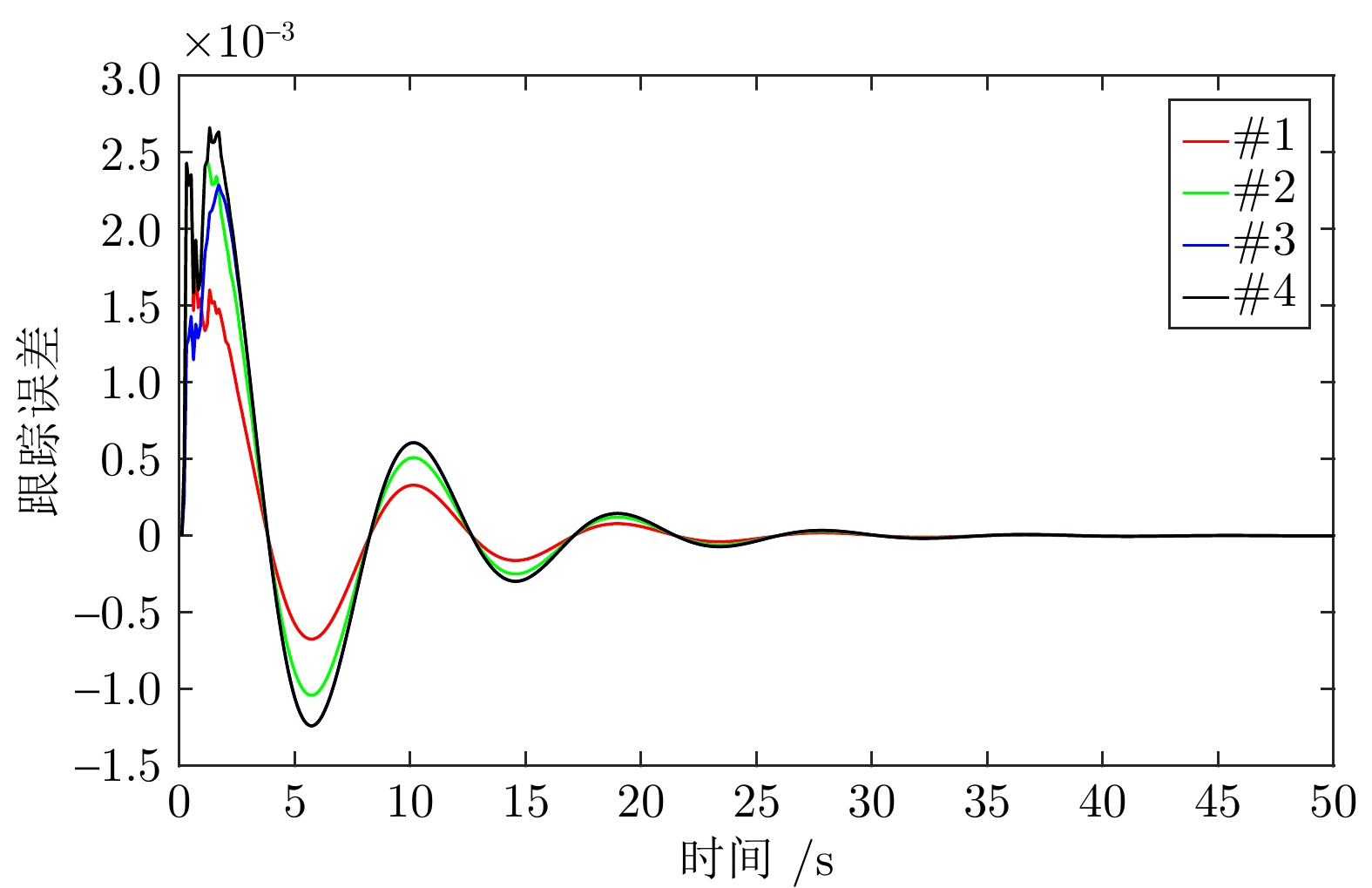
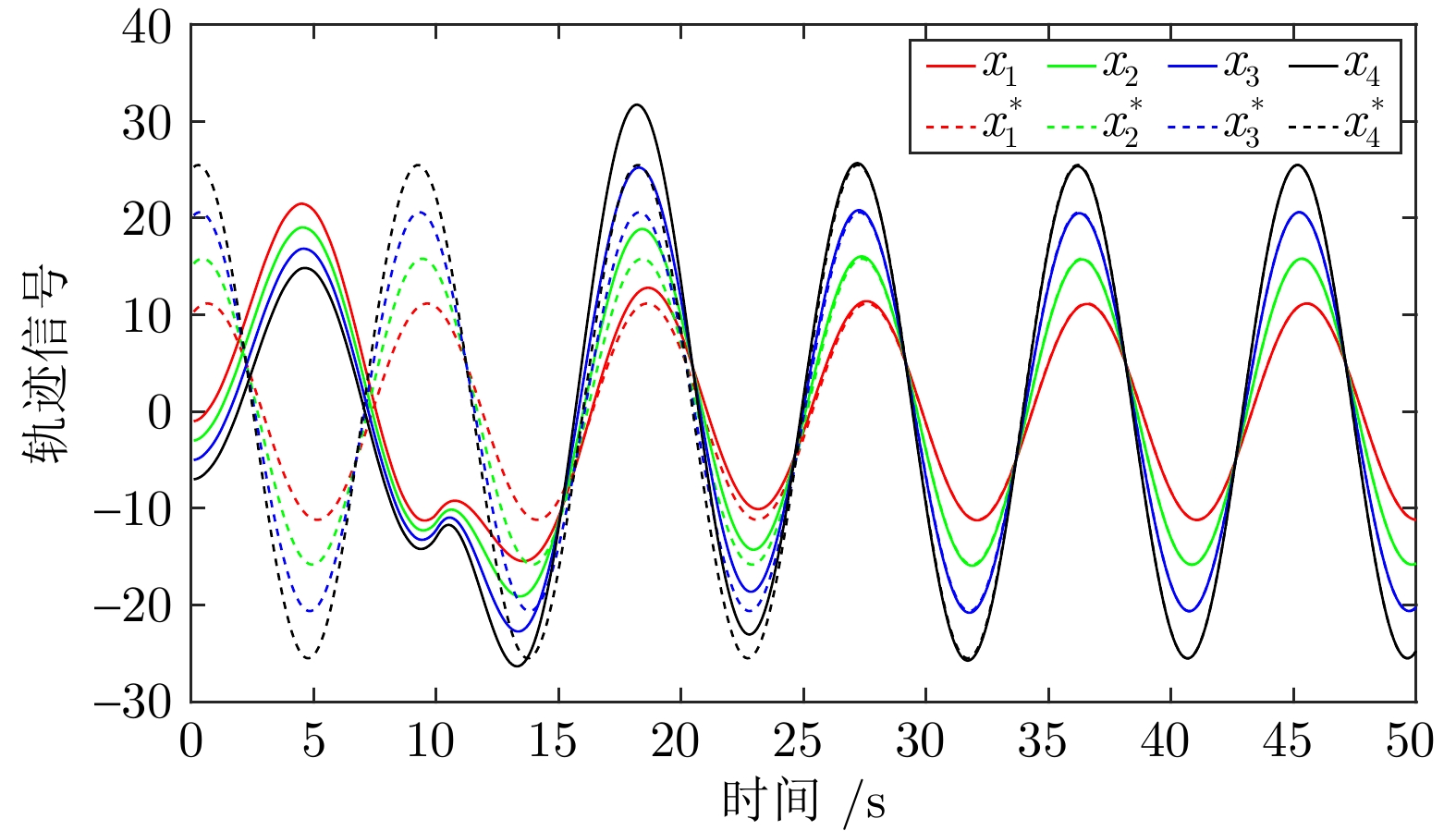
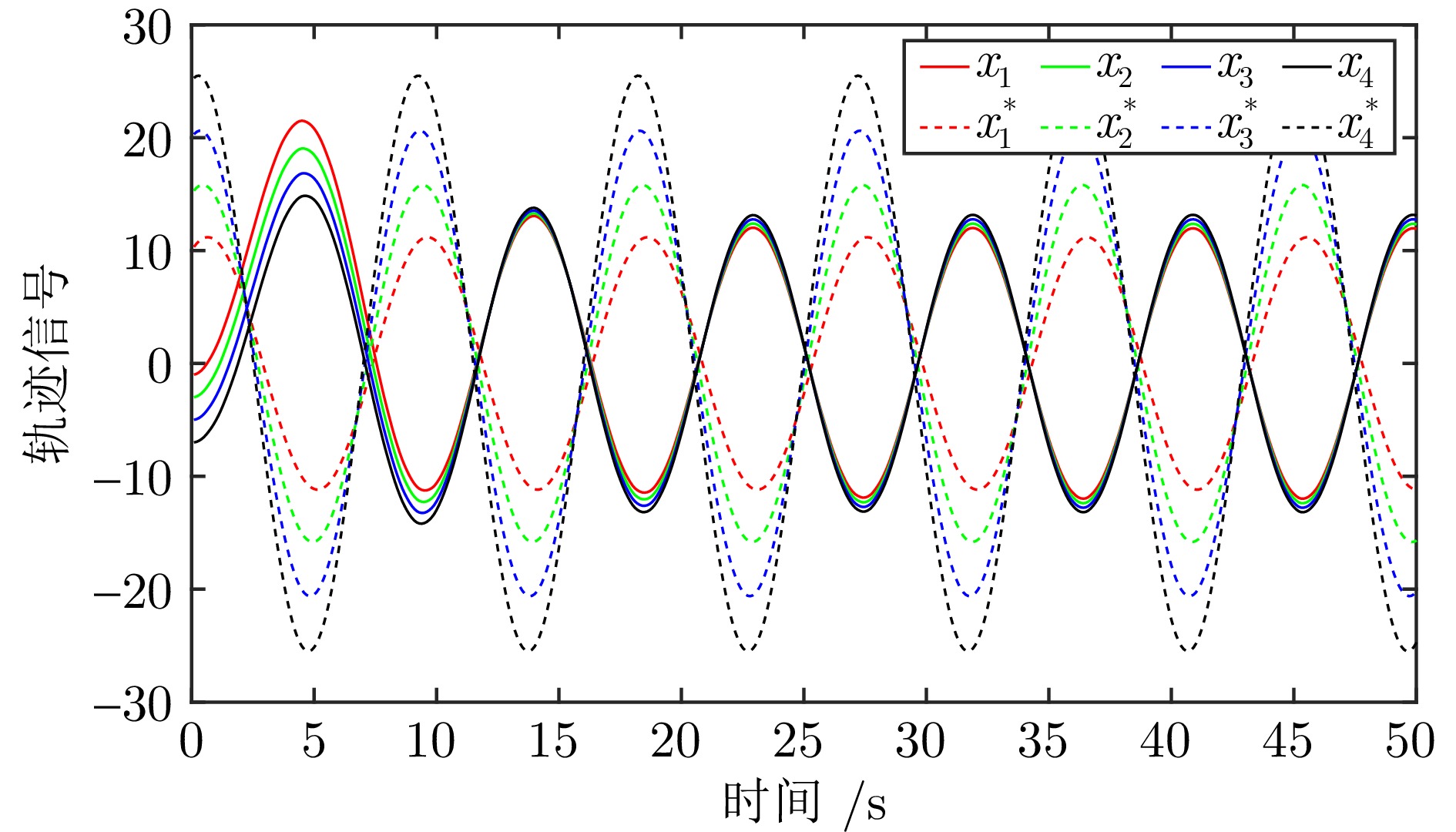
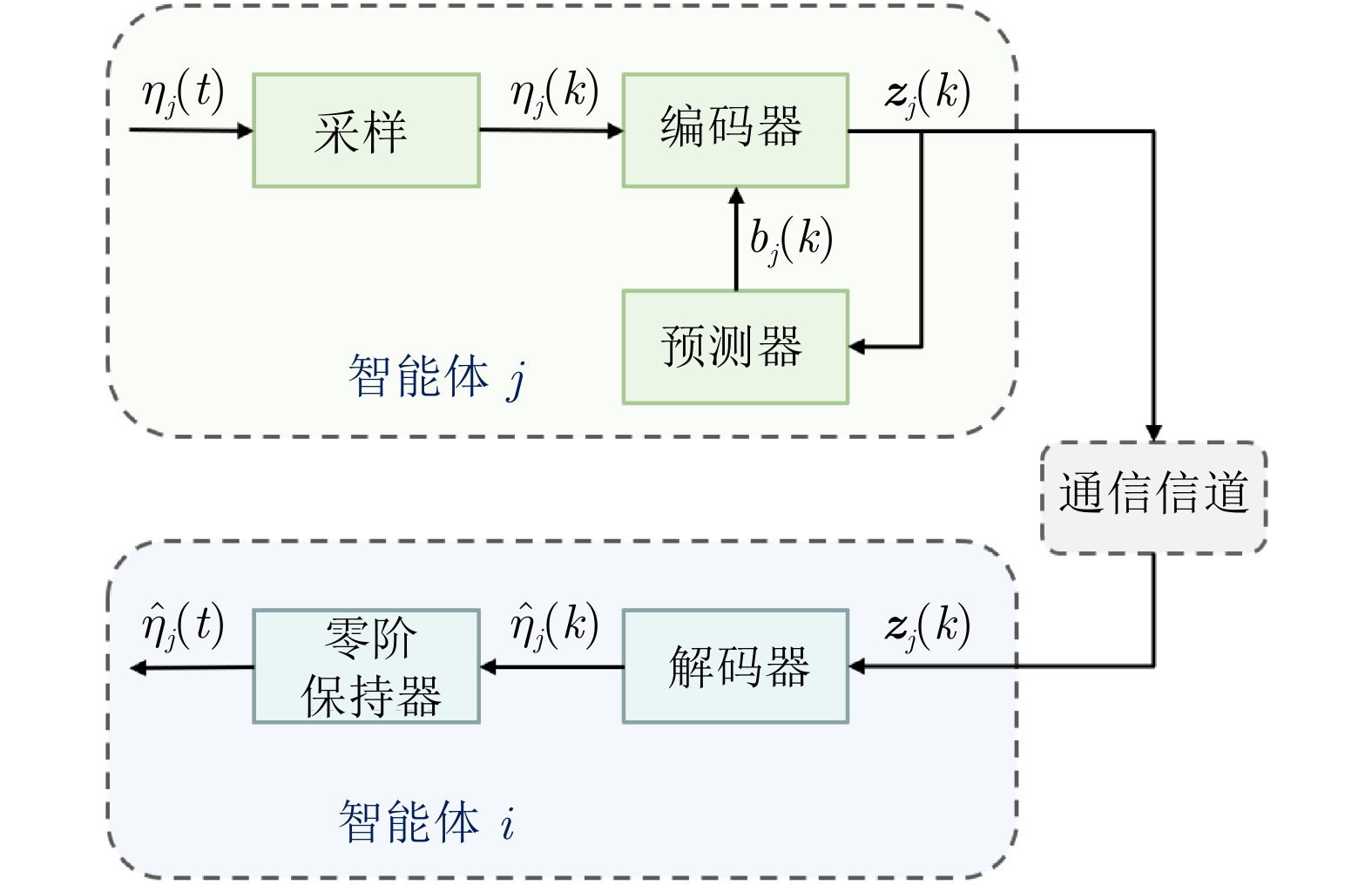
摘要: 考虑了量化通信下多智能体系统的协同最优输出调节问题. 为降低通信负担, 利用取整量化器将智能体之间传输的浮点数数据转化为整数, 从而减少通信信道中传输数据的比特数. 通过将量化器引入编码−解码方案中, 设计分布式量化观测器, 保证在量化通信下, 每个跟随者对外部系统状态的估计误差渐近收敛至零. 在此基础上, 在多智能体系统动态未知的情况下, 提出基于自适应动态规划的数据驱动算法, 在线学习次优控制策略, 解决协同最优输出调节问题, 保证每个跟随者的输出信号渐近跟踪参考信号, 并抑制由外部系统产生的干扰信号. 最后, 在智能车联网自适应巡航控制系统上进行仿真实验并验证了所提方法的有效性. 结果表明与精确通信相比, 量化通信下比特数降低了58.33%.Abstract: This paper considers the cooperative optimal output regulation problem of multi-agent systems under quantized communication. To reduce the communication burden, this paper uses the rounding quantizer to convert floating point data transmitted among agents into integers, reducing the number of bits of data transmitted in the communication channel. By introducing the quantizer into the encoder-decoder scheme, a distributed quantized observer for each follower agent is designed to ensure that the estimation error of the exosystem's state asymptotically converges to zero under quantized communication. On this basis, a data-driven algorithm based on adaptive dynamic programming is proposed to learn the suboptimal control strategy online with unknown multi-agent system dynamics. The algorithm solves the cooperative optimal output regulation problem, ensuring that each follower's output signal asymptotically tracks the reference signal and rejects disturbance signal generated by the exosystem. Finally, the simulation on the adaptive cruise control system of intelligent vehicle networking verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method. The results show that 58.33% of the bits are reduced under quantized communication compared with exact communication.
-
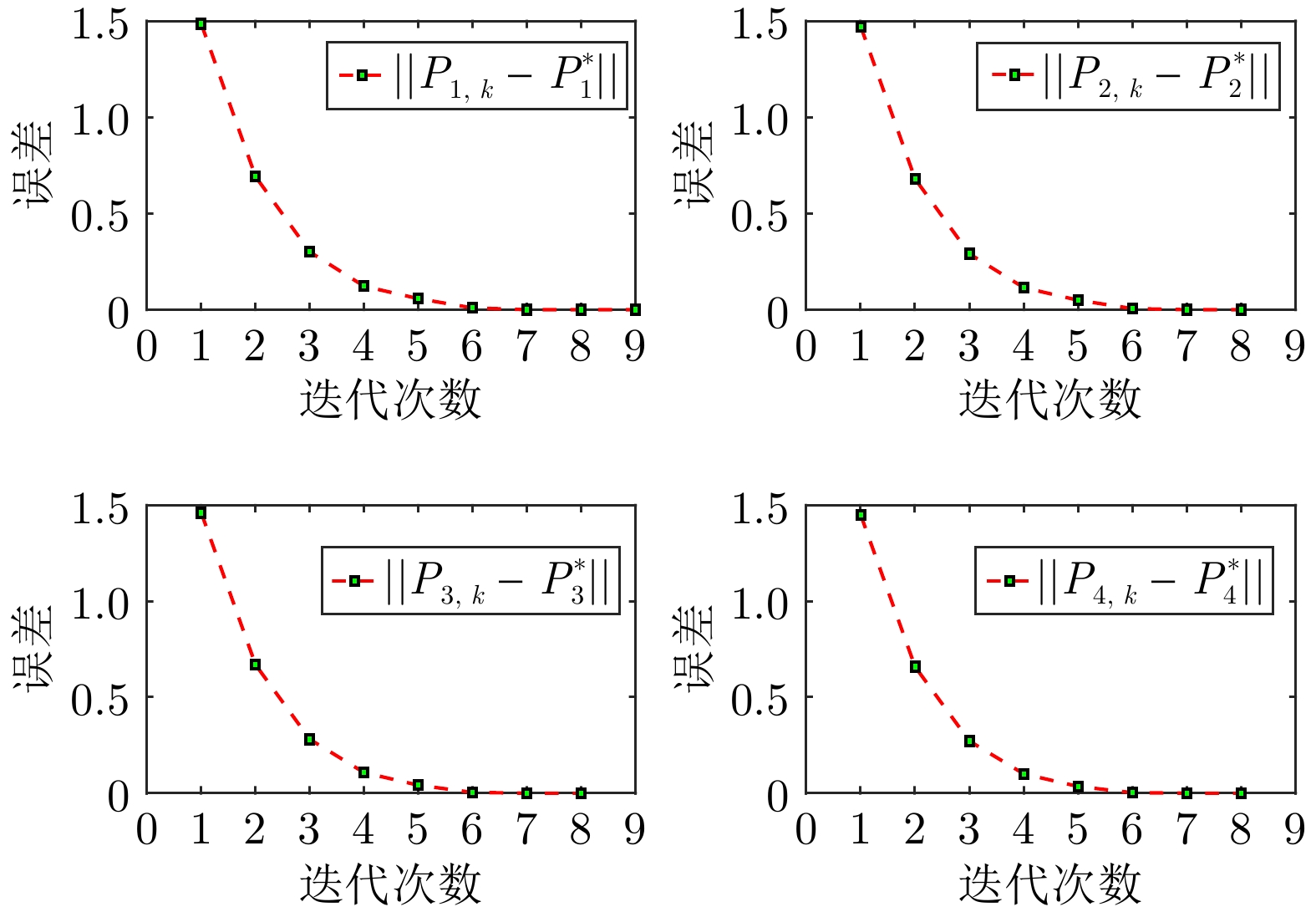
表 1 达到$ ||P_{i,\;k}-P_{i}^{*}||<10^{-4} $有、无量化通信传输的比特数
Table 1 Transmitted bits with and without quantized communication to reach $ ||P_{i,\;k}-P_{i}^{*}||<10^{-4} $
算法1下传输的比特数 无量化通信传输的比特数[3] 降低百分比 80000 192000 58.33% -
[1] Liu L. Adaptive cooperative output regulation for a class of nonlinear multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 60(6): 1677−1682 [2] Cai H, Huang J. The leader-following attitude control of multiple rigid spacecraft systems. Automatica, 2014, 50(4): 1109−1115 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.01.003 [3] Gao W N, Jiang Z P, Lewis F L, Wang Y B. Cooperative optimal output regulation of multi-agent systems using adaptive dynamic programming. In: Proceedings of American Control Conference. Seattle, USA: 2017. 2674−2679 [4] Huang J. Nonlinear Output Regulation: Theory and Applications. Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2004. [5] 吴苗苗, 张皓, 严怀成, 陈世明. 异步切换多智能体系统的协同输出调节. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(5): 735−742Wu Miao-Miao, Zhang Hao, Yan Huai-Cheng, Chen Shi-Ming. Cooperative output regulation for asynchronously switched multi-agent systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5): 735−742 [6] 刘娟, 张皓, 王祝萍. 基于自触发的异构多智能体协同输出调节. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(10): 1893−1902Liu Juan, Zhang Hao, Wang Zhu-Ping. Cooperative output regulation of heterogeneous multi-agent systems by self-triggered. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(10): 1893−1902 [7] Wang S M, Zhang H W, Chen Z Y. Adaptive cooperative tracking and parameter estimation of an uncertain leader over general directed graphs. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 68(7): 3888−3901 [8] Su Y, Huang J. Cooperative output regulation of linear multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 57(4): 1062−1066 [9] Xie K D, Zheng Y W, Jiang Y, Lan W Y, Yu X. Optimal dynamic output feedback control of unknown linear continuous-time systems by adaptive dynamic programming. Automatica, 2024, 163: Article No. 111601 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2024.111601 [10] Fu C C, Zhang H, Huang C, Wang Z P, Yan H C. Cooperative output regulation for continuous-time linear periodic systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69 (11): 7956−7963 [11] Cai H, Lewis F L, Hu G Q, Huang J. The adaptive distributed observer approach to the cooperative output regulation of linear multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2017, 75: 299−305 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.09.038 [12] Rego F, Pascoal A. Cooperative single-beacon multiple AUV navigation under stringent communication bandwidth constraints. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2021, 54(16): 216−223 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.10.096 [13] Hu Q L, Shi Y X. Event-based coordinated control of spacecraft formation flying under limited communication. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2020, 99(3): 2139−2159 doi: 10.1007/s11071-019-05396-6 [14] Zhang J, Liu S, Zhang X F. Output-feedback distributed consensus for nonlinear multi-agent systems with quantization. Information Sciences, 2022, 585: 246−261 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.11.022 [15] Xu L, Yi X L, Sun J Y, Shi Y, Johansson K H, Yang T. Quantized distributed nonconvex optimization algorithms with linear convergence under the Polyak-Łojasiewicz condition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2207.08106, 2022. [16] Xu L, Yi X L, Deng C, Shi Y, Chai T Y, Yang T. Quantized zeroth-order gradient tracking algorithm for distributed nonconvex optimization under Polyak-Łojasiewicz condition. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024. [17] Huang X, Dong J X. Reliable leader-to-follower formation control of multiagent systems under communication quantization and attacks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 50(1): 89−99 [18] Zhou Y J, Wang X Y, Li T. Distributed online optimization under dynamic adaptive quantization. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2024, 71 (7): 3453−3457 [19] Dong S L, Liu L, Feng G, Liu M Q, Wu Z G. Quantized fuzzy cooperative output regulation for heterogeneous nonlinear multiagent systems with directed fixed/switching topologies. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 52(11): 12393−12402 [20] Ma J, Yu X, Liu L, Ji H B, Feng G. Global cooperative output regulation of linear multiagent systems with limited bandwidth. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2021, 9(2): 1017−1028 [21] Ma J, Yang B, Qiu J Y, Chen Z Q, Hu W F. Quantized cooperative output regulation of continuous-time multi-agent systems over switching graph. Kybernetika, 2024, 60(2): 210−227 [22] Wang X L, Sun Y, Ding D R. Adaptive dynamic programming for networked control systems under communication constraints: A survey of trends and techniques. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence, 2022, 1(1): 85−98 [23] Zhang Y, Ma L, Yang C Y, Zhou L N, Wang G Q, Dai W. Formation control for multiple quadrotors under DoS attacks via singular perturbation. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4753−4762 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3241139 [24] Viel C, Kieffer M, Piet-Lahanier H, Bertrand S. Distributed event-triggered formation control for multi-agent systems in presence of packet losses. Automatica, 2022, 141: Article No. 110215 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110215 [25] Gao W N, Jiang Z P. Learning-based adaptive optimal output regulation of linear and nonlinear systems: An overview. Control Theory and Technology, 2022, 20(1): 1−19 doi: 10.1007/s11768-022-00081-3 [26] 温广辉, 杨涛, 周佳玲, 付俊杰, 徐磊. 强化学习与自适应动态规划: 从基础理论到多智能体系统中的应用进展综述. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(5): 1200−1230Wen Guang-Hui, Yang Tao, Zhou Jia-Ling, Fu Jun-Jie, Xu Lei. Reinforcement learning and adaptive/approximate dynamic programming: A survey from theory to applications in multi-agent systems. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(5): 1200−1230 [27] Liu D R, Xue S, Zhao B, Luo B, Wei Q L. Adaptive dynamic programming for control: A survey and recent advances. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 51(1): 142−160 [28] Shi X T, Li Y J, Du C L, Shi Y, Yang C H, Gui W H. Fully distributed event-triggered control of nonlinear multi-agent systems under directed graphs: A model-free DRL approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 70 (1): 603−610 [29] Lu J W, Wei Q L, Wang F Y. Parallel control for optimal tracking via adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(6): 1662−1674 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003426 [30] Gao W N, Jiang Z P. Adaptive dynamic programming and adaptive optimal output regulation of linear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(12): 4164−4169 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2548662 [31] Sun J Y, Ming Z Y. Cooperative differential game-based distributed optimal synchronization control of heterogeneous nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(12): 7933−7942 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2023.3240983 [32] Gao W N, Mynuddin M, Wunsch D C, Jiang Z P. Reinforcement learning-based cooperative optimal output regulation via distributed adaptive internal model. IEEE Transactions on Neural Nnetworks and Learning Systems, 2021, 33(10): 5229−5240 [33] Xie K D, Jiang Y, Yu X, Lan W Y. Data-driven cooperative optimal output regulation for linear discrete-time multi-agent systems by online distributed adaptive internal model approach. Science China Information Sciences, 2023, 66(7): Article No. 170202 doi: 10.1007/s11432-022-3687-1 [34] Qasem O, Davari M, Gao W N, Kirk D R, Chai T Y. Hybrid iteration ADP algorithm to solve cooperative, optimal output regulation problem for continuous-time, linear, multiagent systems: Theory and application in islanded modern microgrids with IBRs. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 71(1): 834−845 [35] Krener A J. The construction of optimal linear and nonlinear regulators. Systems, Models and Feedback: Theory and Applications. New York: Springer, 1992. 301−322 [36] Kleinman D. On an iterative technique for Riccati equation computations. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1968, 13(1): 114−115 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1968.1098829 [37] Gray R M, Neuhoff D L. Quantization. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1998, 44(6): 2325−2383 doi: 10.1109/18.720541 [38] Chen C T. Linear System Theory and Design. Rochester City: Saunders College, 1984. [39] Khalil H K. Nonlinear Systems. New York: Prentice Hall, 2002. [40] Stankovic S S, Stanojevic M J, Siljak D D. Decentralized overlapping control of a platoon of vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2000, 8(5): 816−832 doi: 10.1109/87.865854 -




 下载:
下载: