Hybrid Underwater Image Enhancement Based on Color Transfer and Adaptive Gain Control
-
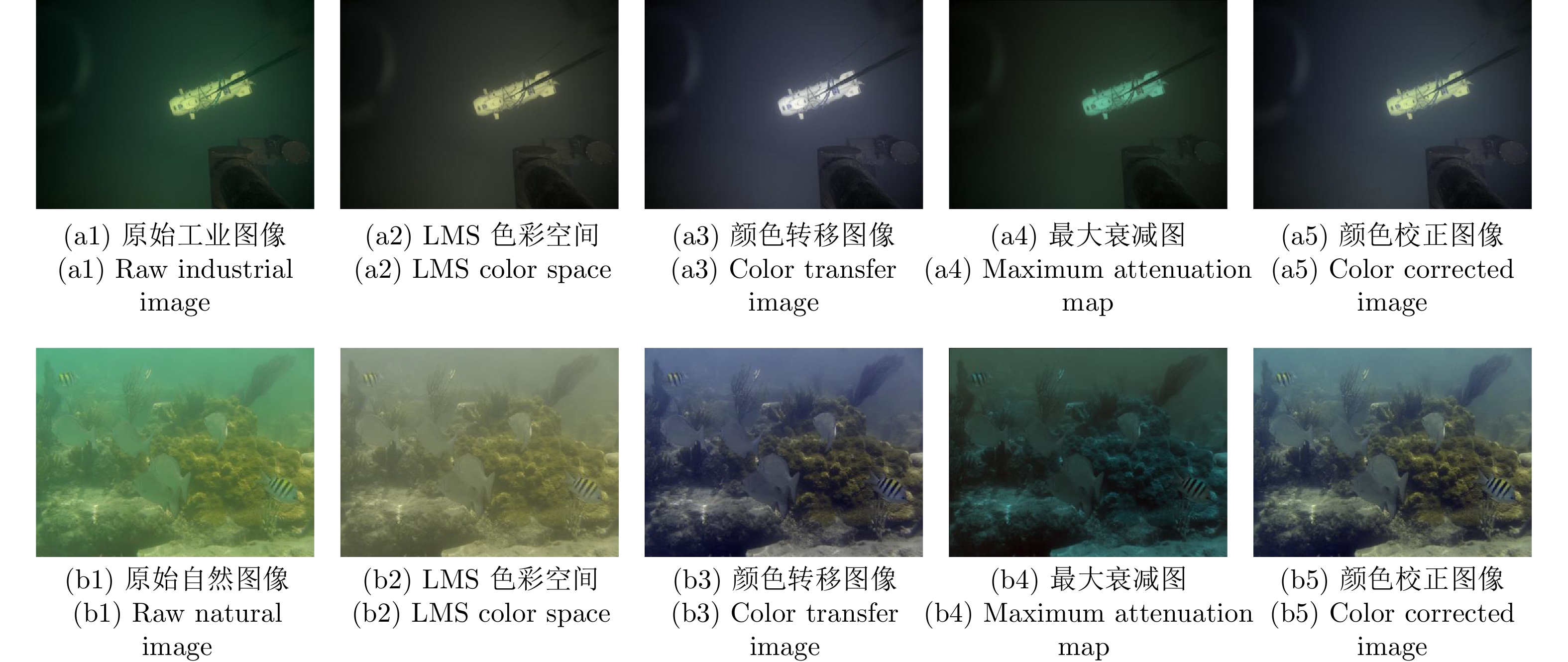
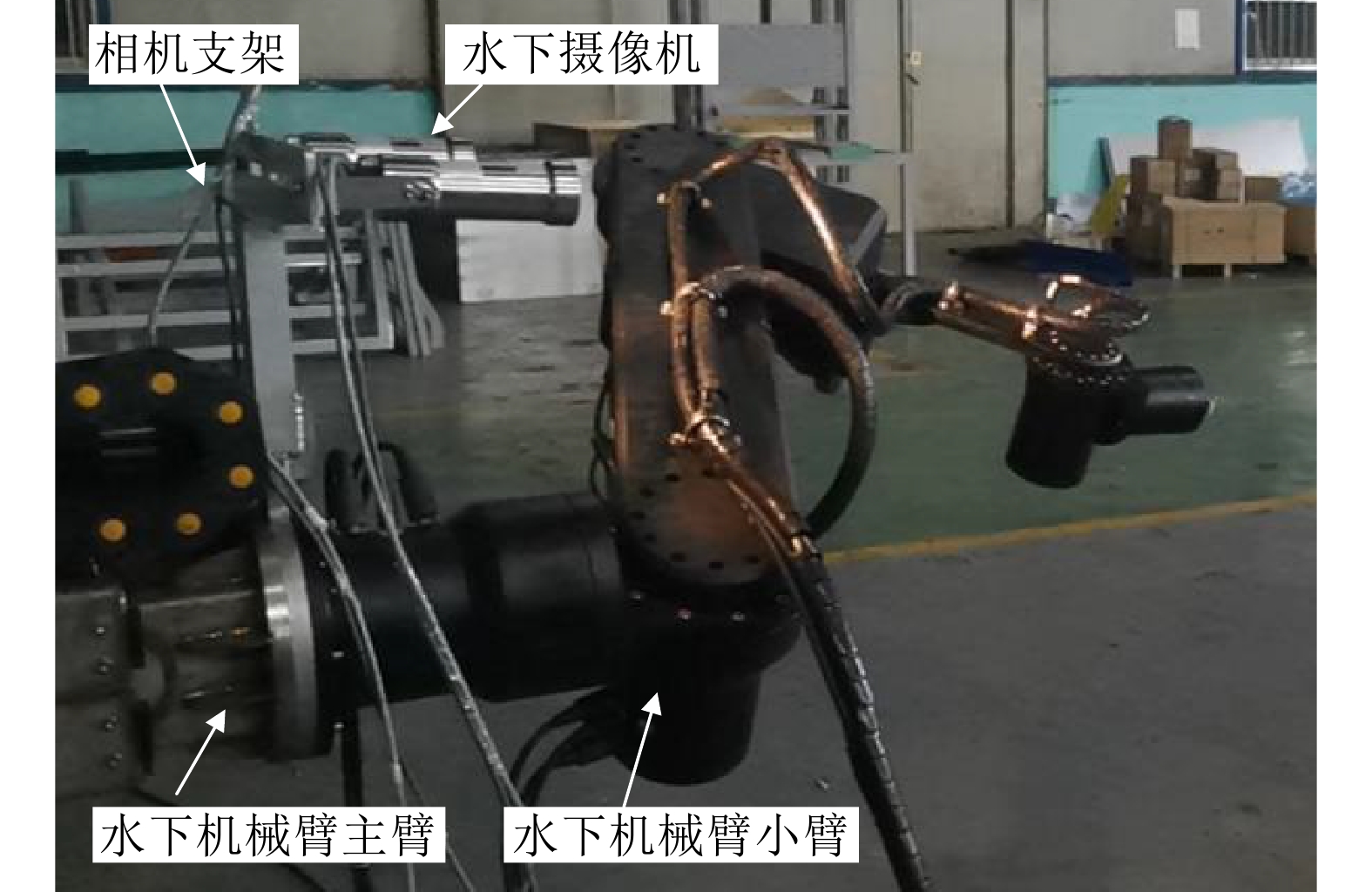
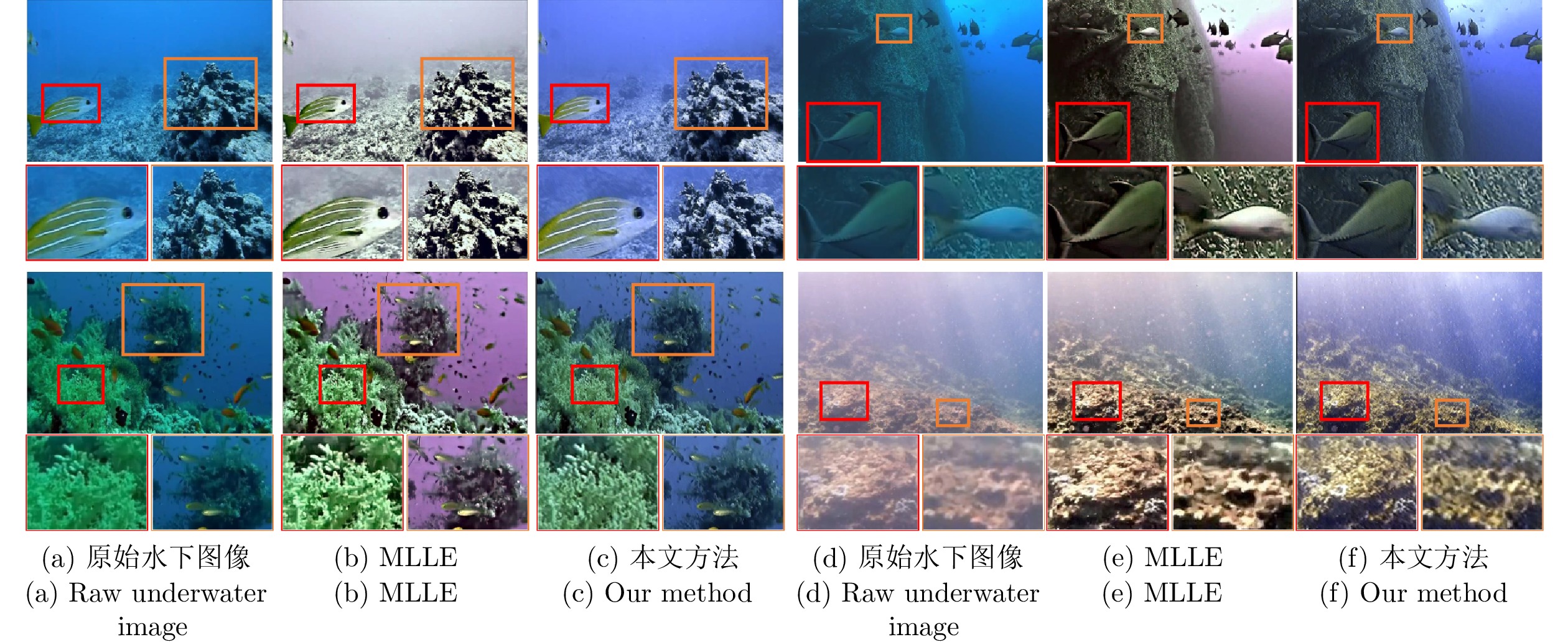
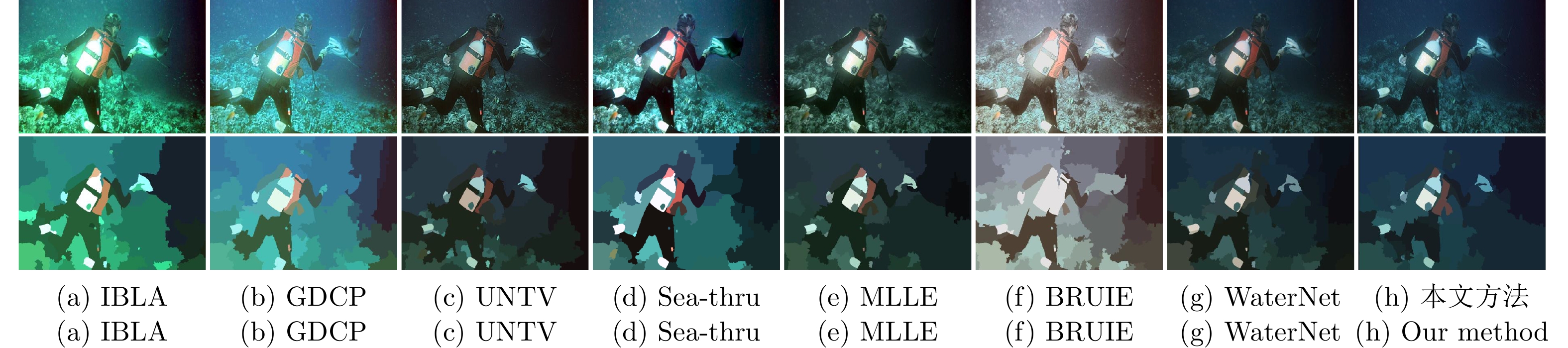
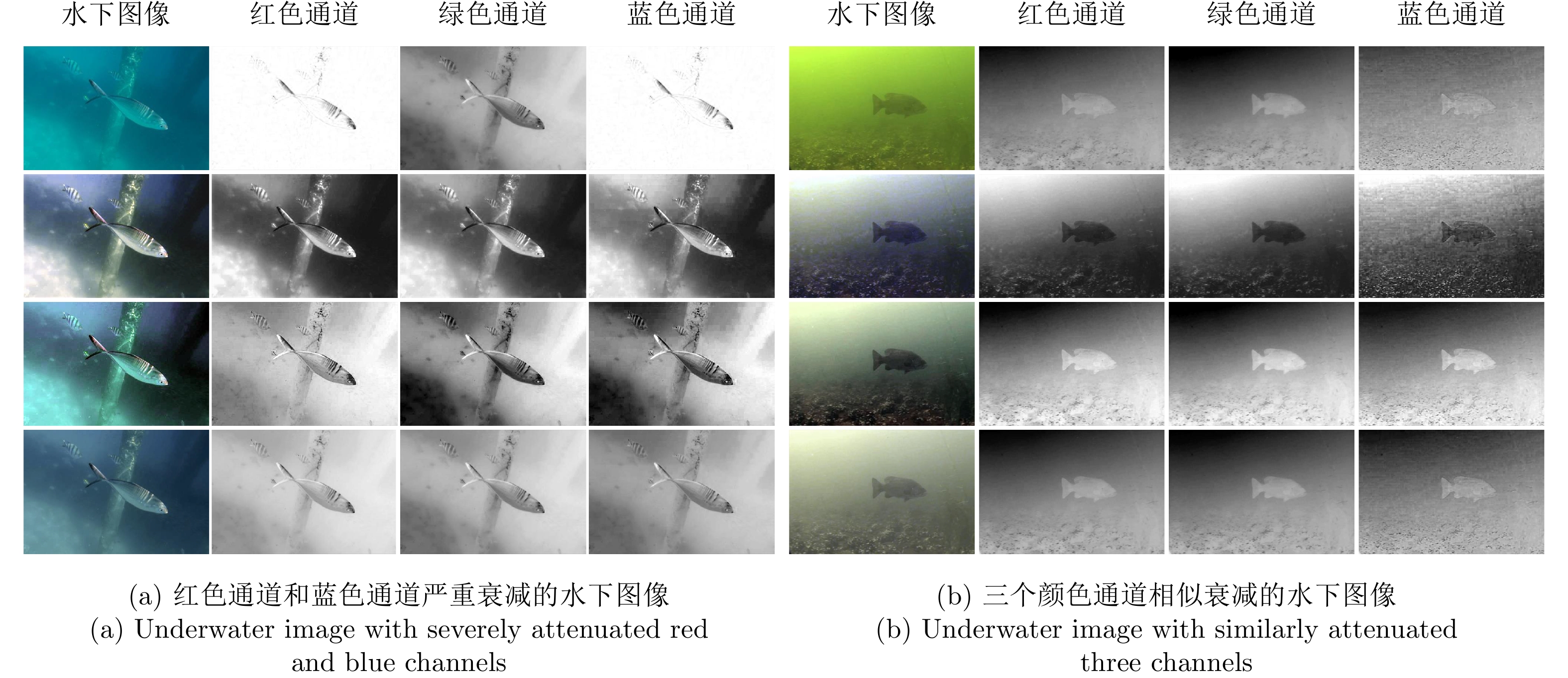
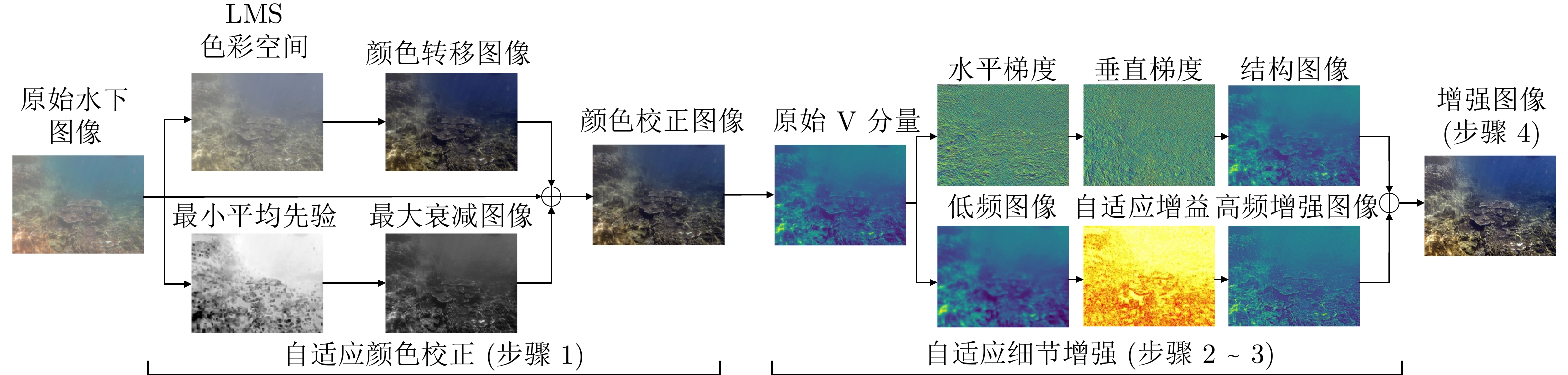
摘要: 针对水下图像的颜色偏差和低对比度等退化问题, 提出一种基于颜色转移和自适应增益控制的混合水下图像增强方法. 首先, 根据颜色转移图像和最大衰减图引导的融合策略校正水下图像的颜色偏差. 其次, 利用一阶原始对偶方法对V通道进行滤波以有效地抑制噪声的干扰, 获得结构图像; 并且提出自适应增益控制, 根据图像的高频信息自适应调整增益, 以获得细节图像. 最后, 通过加权融合结构图像与细节图像, 得到高质量的水下图像. 实验结果表明, 针对不同自然和工业环境下的水下图像: 1) 所提方法可以有效地校正颜色失真现象; 2) 显著提高水下图像的对比度并且抑制噪声干扰; 3) 在定量评价指标和高级视觉任务(目标检测、图像分割、关键点检测和水下双目测距)中优于其他主流水下图像增强方法, 为水下目标抓取等工程应用提供了有益的参考.Abstract: Aiming at handling the degradation problems of color deviation and low contrast in underwater images, a hybrid underwater image enhancement method based on color transfer and adaptive gain control is proposed. Firstly, the color transfer image and the maximum attenuation map-guided fusion strategy are used to correct the color deviation of underwater images. Secondly, the structure image of the V channel is obtained based on the first-order primal-dual algorithm to effectively suppress the noise interference. Furthermore, adaptive gain control based on the high-frequency information of the image is proposed to adaptively adjust the gain to obtain detailed image. Finally, the structure image and the detail image are weighted fused to obtain a high-quality underwater image. The experimental results demonstrate that for underwater images with various natural and industrial environments, 1) The outputs of the proposed method can effectively correct the color distortion; 2) It can improve the contrast of underwater images and suppress the noise interference; 3) The quantitative metrics and high-level visual tasks (object detection, image segmentation, key-point detection, and underwater binocular distance measurement) are superior to other state-of-the-art underwater enhancement methods, which provides a useful reference for engineering applications such as underwater automated grasping.
-
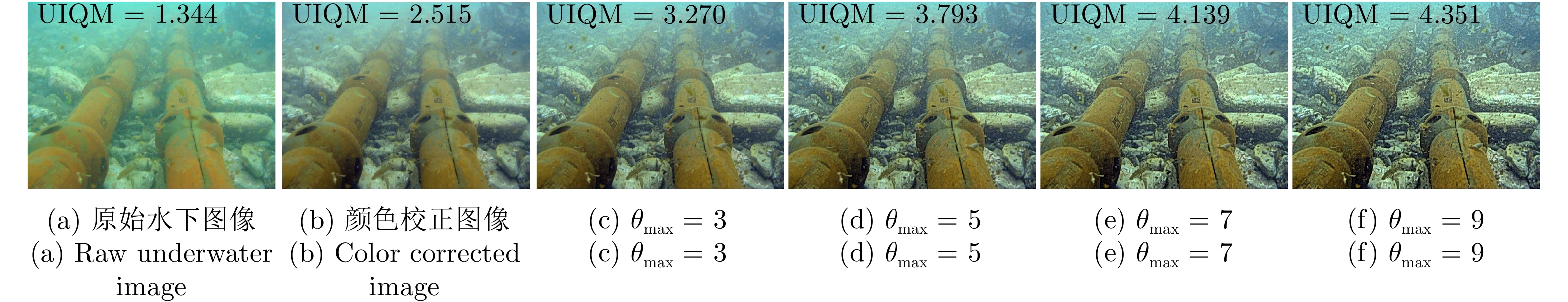
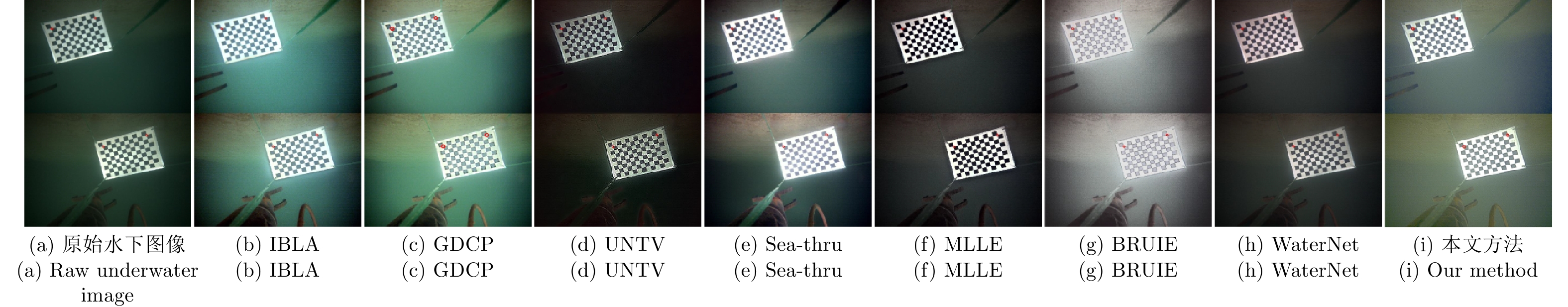
表 1 基于UIQM指标的定量结果
Table 1 Quantitative results based on UIQM metrics
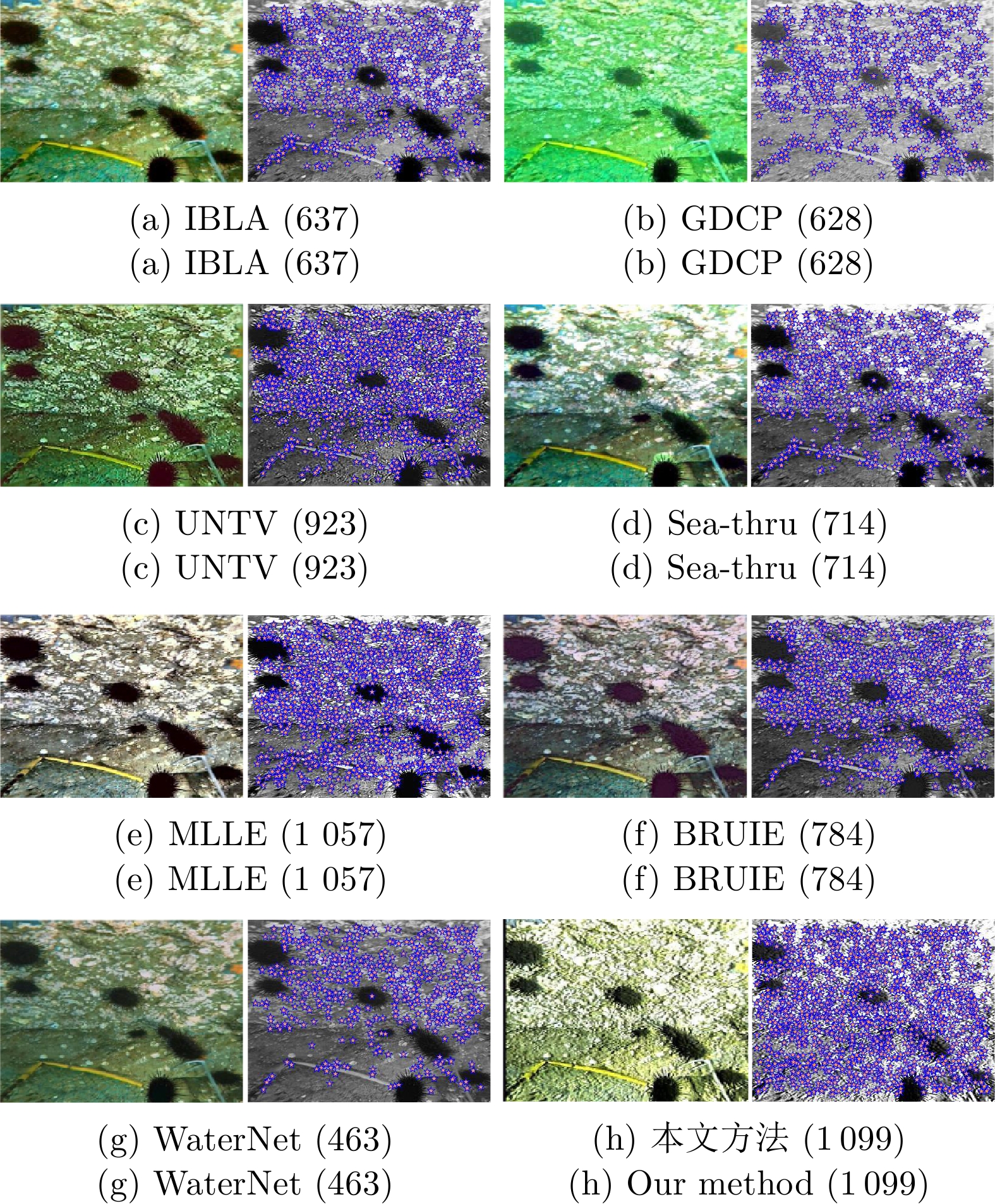
IBLA GDCP UNTV Sea-thru MLLE BRUIE WaterNet 本文方法 Image 1 3.739 3.425 3.868 4.340 4.751 5.183 4.307 4.971 Image 2 4.693 5.174 3.719 4.665 4.149 4.742 3.631 4.848 Image 3 2.451 1.223 3.696 2.876 3.545 3.995 3.057 3.834 Image 4 1.991 2.906 2.992 2.551 2.776 4.002 2.787 2.862 Image 5 2.510 1.762 5.768 4.395 4.841 5.113 4.580 5.313 Image 6 3.300 1.727 4.883 4.460 4.701 5.259 3.971 5.110 Image 7 4.052 1.781 4.862 4.333 4.756 5.248 4.078 4.902 Image 8 3.514 2.771 5.118 5.019 4.745 5.242 4.493 5.396 注: 粗体表示最高的定量指标, 斜体表示次高的定量指标. 表 2 定量比较不同主流方法在目标检测上的性能
Table 2 Quantitative comparison of the performance of different mainstream methods on object detection
$AP$ $AP_{50}$ $AP_{75}$ $AR_{1}$ $AR_{10}$ $AR_{100}$ IBLA 0.502 0.856 0.524 0.168 0.554 0.618 GDCP 0.493 0.854 0.516 0.159 0.531 0.588 UNTV 0.509 0.873 0.513 0.168 0.552 0.606 Sea-thru 0.499 0.862 0.506 0.164 0.548 0.601 MLLE 0.509 0.871 0.530 0.161 0.550 0.599 BRUIE 0.499 0.859 0.529 0.154 0.538 0.597 WaterNet 0.501 0.862 0.515 0.162 0.532 0.591 本文方法 0.514 0.871 0.558 0.167 0.551 0.609 注: 粗体表示最高的检测准确率, 斜体表示次高的检测准确率. 表 3 各组件的定量消融结果
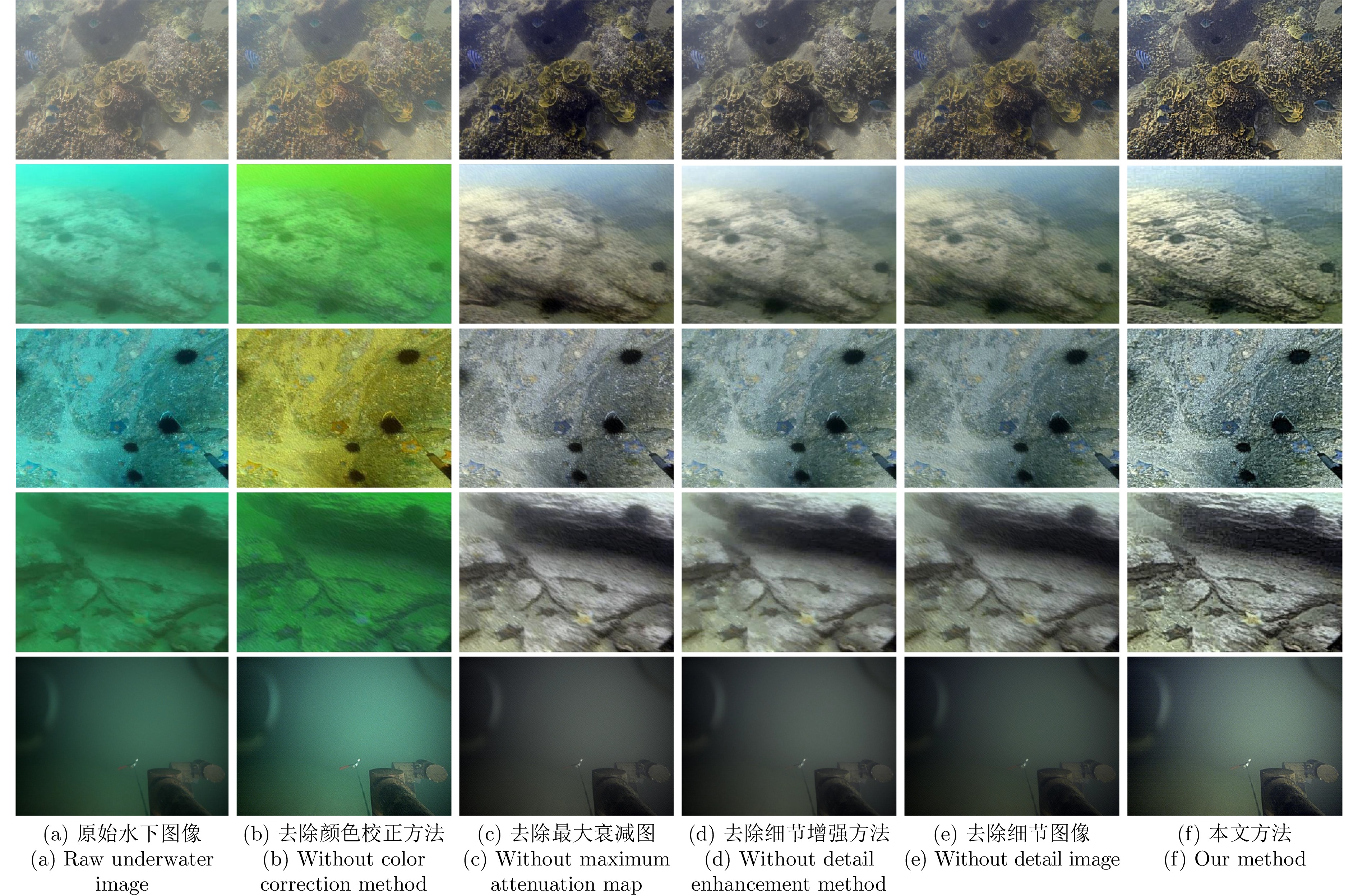
Table 3 Quantitative ablation results of each component
Image 1 Image 2 Image 3 Image 4 Image 5 无颜色校正方法 4.539 0.475 4.804 1.573 3.584 无最大衰减图 5.160 3.802 5.013 4.465 4.474 无细节增强方法 4.356 2.465 4.244 3.277 4.152 无细节图像 4.991 3.402 4.517 4.188 4.434 完整方法 5.246 4.131 5.029 4.921 4.517 注: 粗体表示最高的定量指标. 表 4 水下视觉测量
Table 4 Measurement of underwater vision
Raw IBLA GDCP UNTV Sea-thru MLLE BRUIE WaterNet 本文方法 RE (像素) 0.16 0.18 0.17 0.32 0.22 0.16 0.18 0.17 0.13 AD (mm) 28.38 28.57 28.60 26.59 28.65 28.38 28.62 28.56 28.87 注: 粗体表示最高的定量指标. -
[1] Raveendran S, Patil M D, Birajdar G K. Underwater image enhancement: A comprehensive review, recent trends, challenges and applications. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2021, 54: 5413−5467 doi: 10.1007/s10462-021-10025-z [2] 刘妹琴, 韩学艳, 张森林, 郑荣濠, 兰剑. 基于水下传感器网络的目标跟踪技术研究现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(2): 235−251Liu Mei-Qin, Han Xue-Yan, Zhang Sen-Lin, Zheng Rong-Hao, Lan Jian. Research status and prospect of target tracking technologies via underwater sensor networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(2): 235−251 [3] Yang M, Hu J T, Li C Y, Gustavo R, Du Y X, Hu K. An in-depth survey of underwater image enhancement and restoration. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 123638−123657 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2932611 [4] 徐璠, 王贺升. 软体机械臂水下自适应鲁棒视觉伺服. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(4): 744−753Xu Fan, Wang He-Sheng. Adaptive robust visual servoing control of a soft manipulator in underwater environment. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(4): 744−753 [5] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341−2353 [6] Drews P, Nascimento E, Moraes F, Botelho S, Campos M. Transmission estimation in underwater single images. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 825−830 [7] Galdran A, Pardo D, Picón A, Alvarez A. Automatic red-channel underwater image restoration. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2015, 26: 132−145 doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2014.11.006 [8] 谢昊伶, 彭国华, 王凡, 杨成. 基于背景光估计与暗通道先验的水下图像复原. 光学学报, 2018, 38(1): 18−27Xie Hao-Ling, Peng Guo-Hua, Wang Fan, Yang Cheng. Underwater image restoration based on background light estimation and dark channel prior. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(1): 18−27 [9] Carlevaris-Bianco N, Mohan A, Eustice R M. Initial results in underwater single image dehazing. In: Proceedings of the 2010 OCEANS. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2010. 1−8 [10] Peng Y T, Cosman P C. Underwater image restoration based on image blurriness and light absorption. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(4): 1579−1594 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2663846 [11] Berman D, Levy D, Avidan S, Treibitz T. Underwater single image color restoration using haze-lines and a new quantitative dataset. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 43(8): 2822−2837 [12] Xie J, Hou G J, Wang G D, Pan Z K. A variational framework for underwater image dehazing and deblurring. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 32(6): 3514−3526 [13] Ancuti C O, Ancuti C, de Vleeschouwer C, Bekaert P. Color balance and fusion for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(1): 379−393 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2759252 [14] Zhang W, Zhuang P, Sun H H, Li G H, Kwong S, Li C Y. Underwater image enhancement via minimal color loss and locally adaptive contrast enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 3997−4010 [15] Zhuang P X, Li C Y, Wu J M. Bayesian retinex underwater image enhancement. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 101: Article No. 104171 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104171 [16] Ghani A S A, Isa N A M. Underwater image quality enhancement through Rayleigh-stretching and averaging image planes. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, 2014, 6(4): 840−866 doi: 10.2478/IJNAOE-2013-0217 [17] 杨淼, 纪志成. 基于模糊形态筛和四元数的水下彩色图像增强. 仪器仪表学报, 2012, 33(7): 1601−1605Yang Miao, Ji Zhi-Cheng. Underwater color image enhancement based on quaternion and fuzzy morphological sieves. Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2012, 33(7): 1601−1605 [18] 李庆忠, 白文秀, 牛炯. 基于改进CycleGAN的水下图像颜色校正与增强. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(4): 820−829Li Qing-Zhong, Bai Wen-Xiu, Niu Jiong. Underwater image color correction and enhancement based on improved cycle-consistent generative adversarial networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(4): 820−829 [19] Li C Y, Guo C L, Ren W Q, Cong R M, Hou J H, Kwang S, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 4376−4389 [20] Islam M J, Xia Y, Sattar J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3227−3234 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2974710 [21] McGlamery B L. A computer model for underwater camera systems. In: Proceedings of the Ocean Optics VI. Bellingham: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers, 1980. 221−231 [22] Jaffe J S. Computer modeling and the design of optimal underwater imaging systems. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1990, 15(2): 101−111 [23] Reinhard E, Adhikhmin M, Gooch B, Shirley P. Color transfer between images. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 2001, 21(5): 34−41 [24] Chambolle A, Pock T. A first-order primal-dual algorithm for convex problems with applications to imaging. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2011, 40: 120−145 doi: 10.1007/s10851-010-0251-1 [25] Tarik A, Salih D, Yucel A. A histogram modification framework and its application for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(9): 1921−1935 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2021548 [26] Deng G. A generalized unsharp masking algorithm. IEEE transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 20(5): 1249−1261 [27] Peng Y T, Cao K, Cosman P C. Generalization of the dark channel prior for single image restoration. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(6): 2856−2868 [28] Akkaynak D, Treibitz T. Sea-thru: A method for removing water from underwater images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1682−1691 [29] Ranftl R, Lasinger K, Hafner D, Schindler K, Koltun V. Towards robust monocular depth estimation: Mixing datasets for zero-shot cross-dataset transfer. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 44(3): 1623−1637 [30] Panetta K, Gao C, Agaian S. Human-visual-system-inspired underwater image quality measures. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2015, 41(3): 541−551 [31] Li C Y, Li L L, Jiang H L, Weng K H, Geng Y F, Li L, et al. YOLOv6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arxiv preprint arXiv: 2209.02976, 2022. [32] Jiang L H, Wang Y, Jia Q, Xu S W, Liu Y, Fan X, et al. Underwater species detection using channel sharpening attention. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Chengdu, China: ACM, 2021. 4259−4267 [33] Lei T, Jia X H, Zhang Y N, Liu S G, Meng H Y, Nandi A K. Superpixel-based fast fuzzy C-means clustering for color image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(9): 1753−1766 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2889018 [34] Bay H, Tuytelaars T, van Gool L. Surf: Speeded up robust features. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Graz, Austria: Springer, 2006. 404−417 [35] Pedersen M, Bengtson S H, Gade R, Madsen N, Mieslund T B. Camera calibration for underwater 3D reconstruction based on ray tracing using snell's Law. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1410−1417 -




 下载:
下载: