A Hierarchical Bio-inspired Neural Network Based Multi-robot Cooperative Area Search Algorithm
-
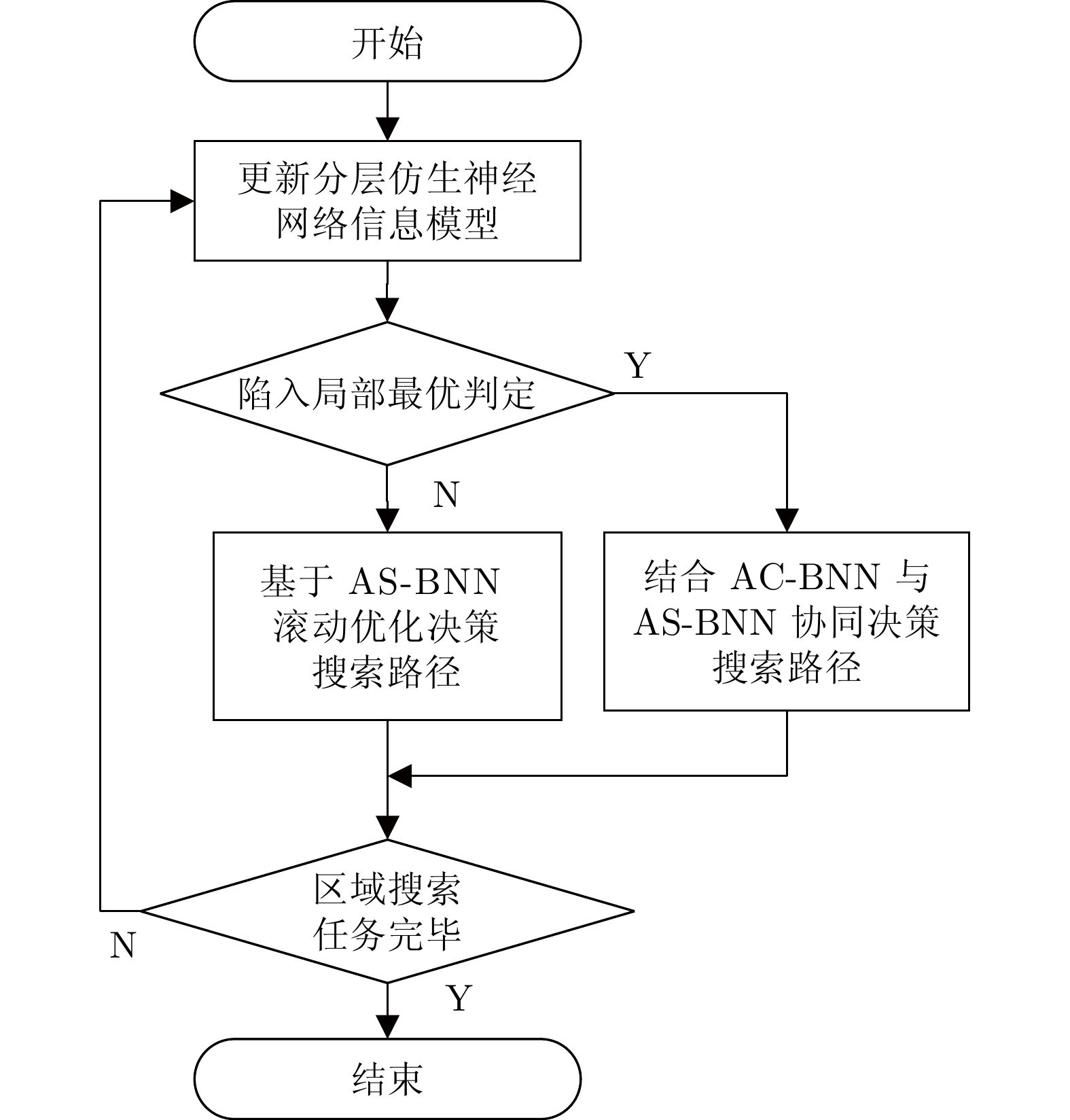
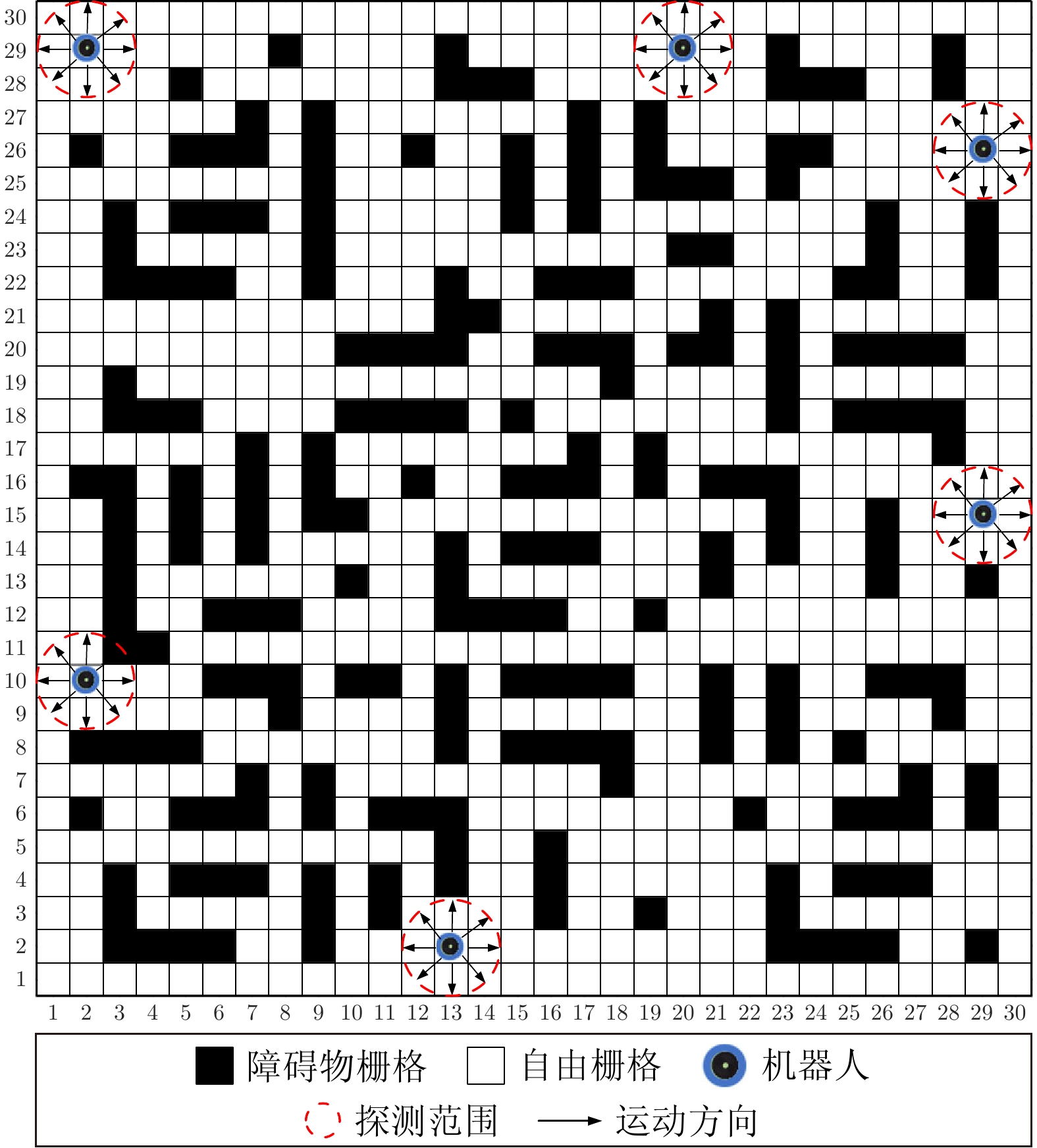
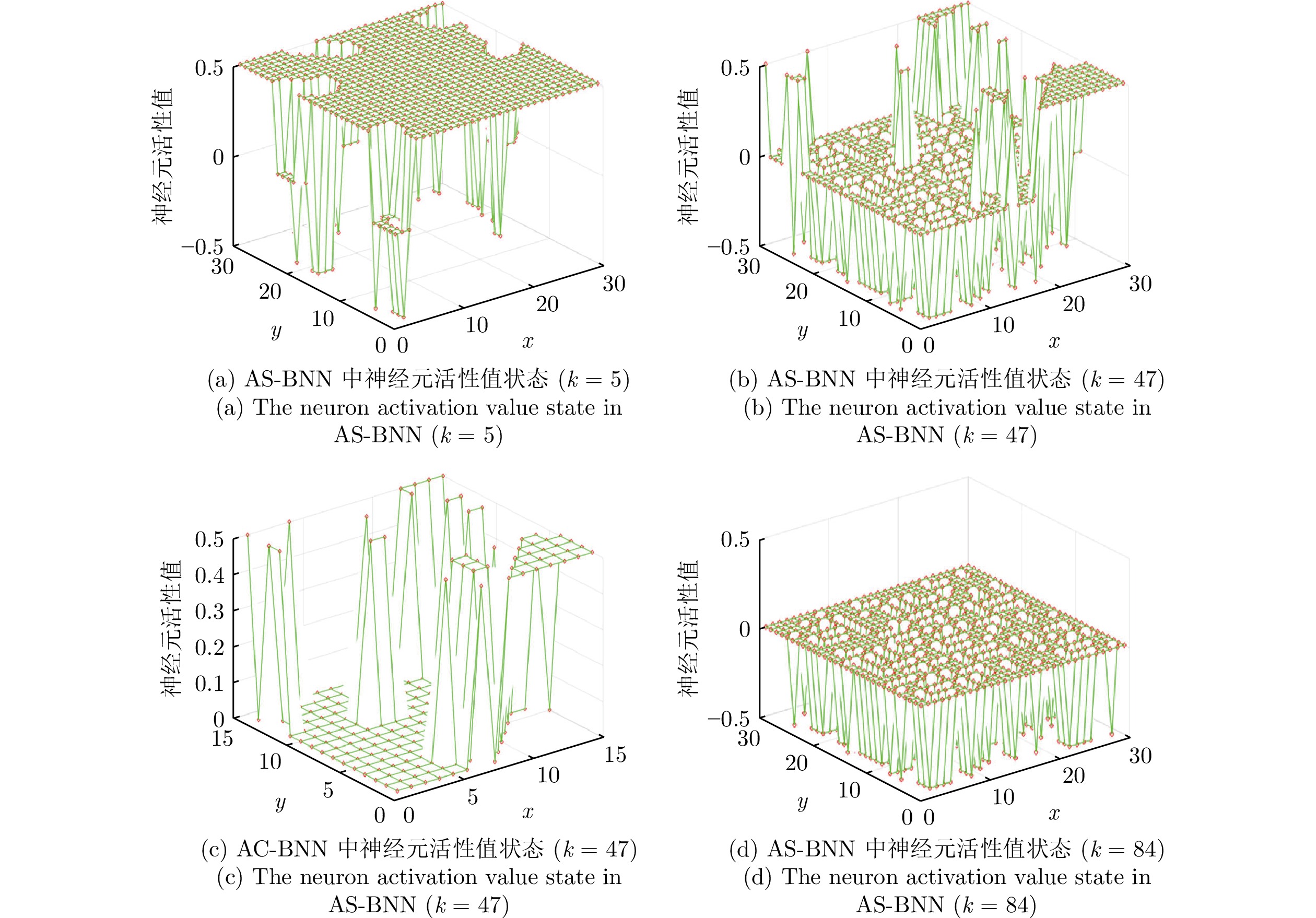
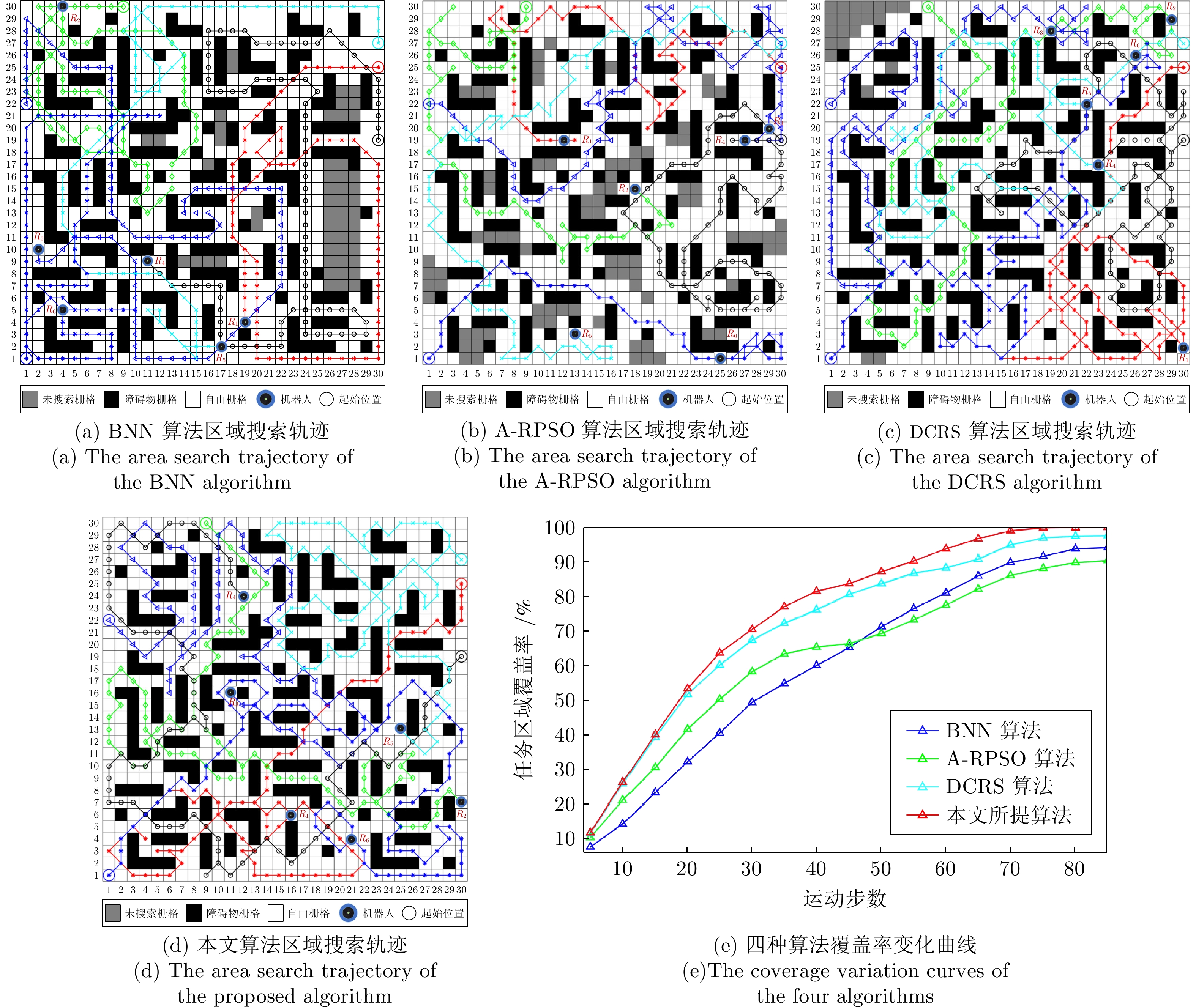
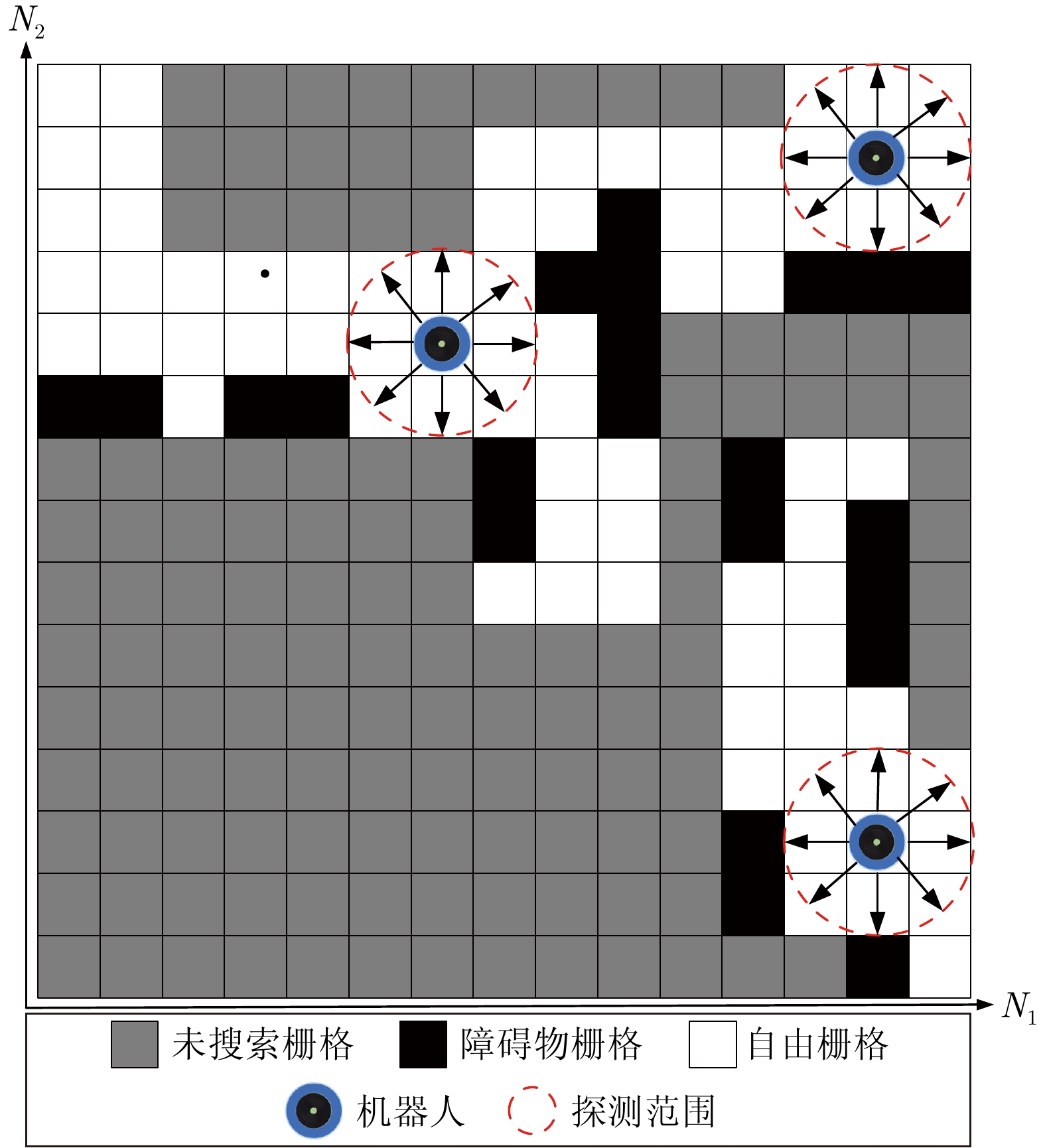
摘要: 针对多机器人系统在战场、灾难现场等复杂未知环境下的区域搜索问题, 提出一种基于分层仿生神经网络的多机器人协同区域搜索算法. 首先将仿生神经网络(Bio-inspired neural network, BNN) 和不同分辨率下的区域栅格地图结合, 构建分层仿生神经网络信息模型, 其中包括区域搜索神经网络信息模型(Area search neural network information model, AS-BNN)和区域覆盖神经网络信息模型(Area coverage neural network information model, AC-BNN). 机器人在任务区域内实时探测到的环境信息将转换为AS-BNN和AC-BNN中神经元的动态活性值. 其次, 在分层仿生神经网络信息模型基础上引入分布式模型预测控制(Distributed model predictive control, DMPC)框架, 并设计多机器人分层协同决策机制. 当机器人处于正常搜索状态时, 基于AS-BNN进行搜索路径滚动优化决策; 当机器人陷入局部最优状态时, 则启用AC-BNN引导机器人快速找到新的未搜索区域. 最后, 在复杂未知环境下进行多机器人区域搜索仿真实验, 并与该领域内的3种算法进行比较. 仿真结果验证了所提算法能够在复杂未知环境下引导多机器人系统高效地完成区域搜索任务.Abstract: Aiming at the problem of multi-robot system area search in complex and unknown environments, such as battlefields and disaster scenes, a multi-robot cooperative area search algorithm based on a hierarchical bio-inspired neural network is proposed. Firstly, a hierarchical bio-inspired neural network (BNN) information model is constructed by combining the bio-inspired neural network with area grid maps at different resolutions, including the area search neural network information model (AS-BNN) and the area coverage neural network information model (AC-BNN). The real-time environmental information detected by the robots in the task area is converted into the dynamic activity values of neurons in both AS-BNN and AC-BNN. Secondly, a distributed model predictive control (DMPC) framework is introduced based on the hierarchical bio-inspired neural network information model, and a multi-robot hierarchical cooperative decision-making mechanism is designed. When the robot is in a normal search state, a rolling optimization decision for the search path is made based on the AS-BNN. If the robot falls into a local optimum state, the AC-BNN is activated to guide it in quickly finding a new unsearched area. Finally, a multi-robot area search simulation experiment is conducted in a complex and unknown environment, comparing the proposed algorithm with three other algorithms in this field. The simulation results verify that the proposed algorithm can guide the multi-robot system to efficiently complete the area search task in complex and unknown environments.
-
表 1 主要符号说明
Table 1 Description of main symbols
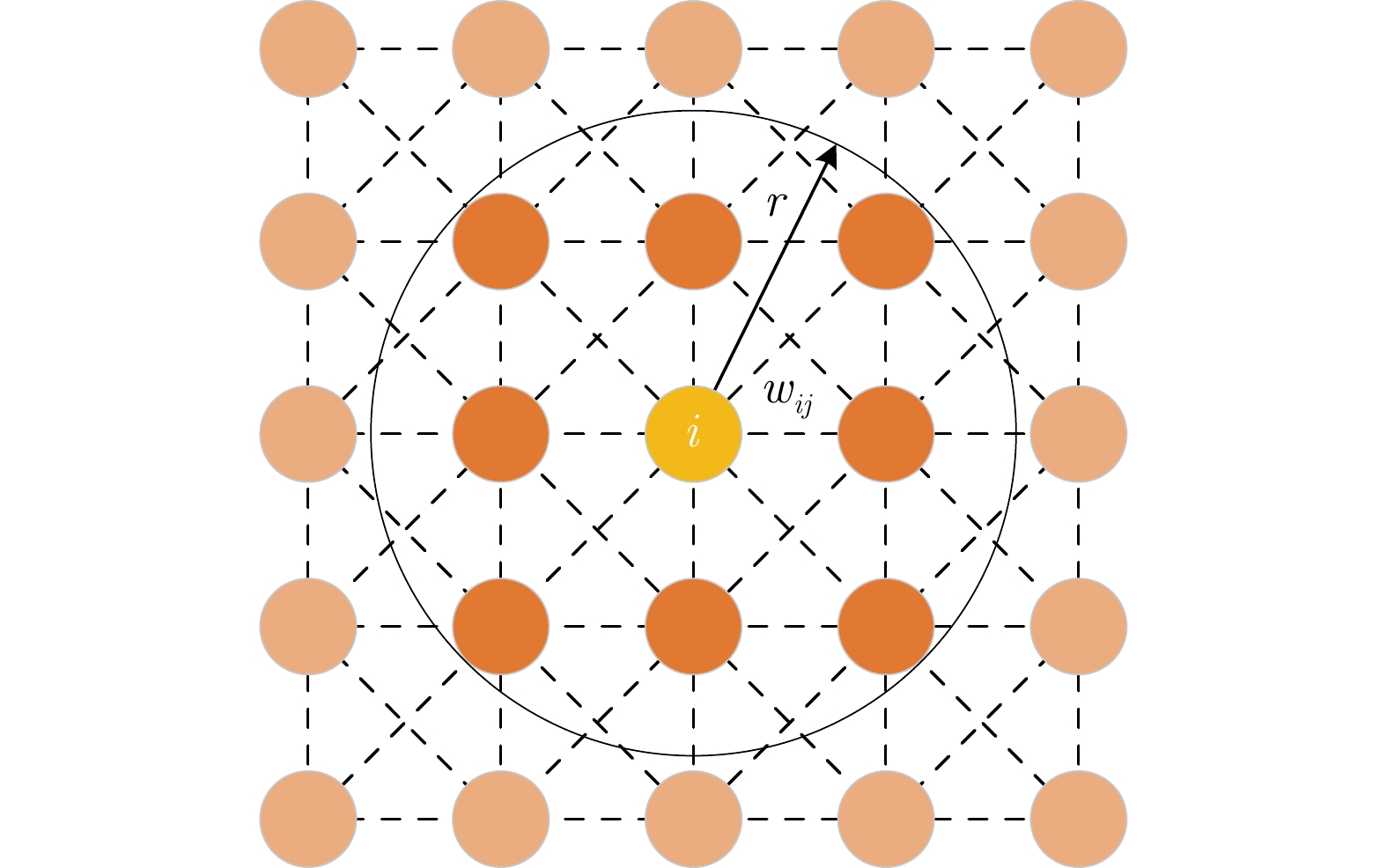
主要符号 具体含义 $ N_r $ 机器人的数量 ${ S}_{{\rm cov}}^{k}$ 第$ k $个机器人搜索的面积大小 ${ S}_{{\rm cov}}^{\rm rep}$ $ N_r $个机器人重复搜索的面积大小 $ { S}(G(x,\;y)) $ 栅格$ G(x,\;y) $的状态 ${ S}(A(\hat{x},\;\hat{y}))$ 子区域$A(\hat{x},\;\hat{y})$的状态 $ K_{\rm u} $ 未搜索栅格状态标记 $ K_{\rm o} $ 障碍物栅格状态标记 $ K_{\rm c} $ 自由栅格状态标记 $ A $ 神经元活性值衰减速率 $ B $ 神经元活性值上限 $ -D $ 神经元活性值下限 $M_r$ 第$i$个神经元的相邻神经元个数 $\psi_{i}$ AS-BNN第$i$个神经元的活性值 $\psi_{i}'$ AC-BNN第$i$个神经元的活性值 $w_{ij} $ 神经元之间连接权重系数 $I_{i}$ AS-BNN神经元外部输入信号 $I_{i}'$ AC-BNN神经元外部输入信号 $L$ DMPC框架下机器人决策预测步长 $h_{s}(k)$ 机器人在栅格地图下位置状态 $h_{s}'(k)$ 机器人在覆盖地图下位置状态 $A(\hat{x}_g,\;\hat{y}_g)$ 机器人局部最优状态下预测的目标子区域 ${x}_s(k),\;{y}_s(k)$ $k$ 时刻机器人在栅格地图所处位置 $\hat{x}_{s}(k),\;\hat{y}_{s}(k)$ $k$ 时刻机器人在覆盖地图所处位置 $J$ 用于机器人正常搜索状态下搜索路径预测的搜索收益函数 $J_E$ 用于机器人局部最优搜索状态下子区域引导路径预测过程的搜索收益函数 $J_H$ 用于机器人局部最优搜索状态下目标子区域搜索路径预测过程的搜索收益函数 $ J^{(L)} $ 机器人$L$步累积搜索收益函数 $J_c$ 神经元活性值增益函数(搜索路径预测) $J_c'$ 神经元活性值增益函数(子区域引导路径预测) $J_t$ 转弯代价函数 $J_g$ 目标子区域引导函数 $\lambda_1$ 函数$J_c$对应的权重系数 $\lambda_2$ 函数$J_t$对应的权重系数 $\lambda_3$ 函数$J_g$对应的权重系数 表 3 不同机器人数量下4种算法区域搜索性能对比
Table 3 Comparison of area search performance of four algorithms under different number of robots
机器人
数量运动
步数BNN算法[26] A-RPSO算法[12] DCRS算法[6] 本文所提算法 AVE-C STD-C MAX-C MIN-C AVE-C STD-C MAX-C MIN-C AVE-C STD-C MAX-C MIN-C AVE-C STD-C MAX-C MIN-C 2 252 84.047% 0.1375 93.556% 72.111% 82.764% 0.0893 94.000% 64.333% 97.164% 0.0330 100.000% 83.556% 99.564% 0.0062 100.000% 98.778% 4 126 84.592% 0.0737 96.556% 76.333% 85.500% 0.0631 96.111% 65.000% 96.836% 0.0232 99.667% 91.111% 99.656% 0.0039 100.000% 99.111% 6 84 86.290% 0.0843 95.667% 75.556% 88.587% 0.0391 93.778% 82.889% 97.438% 0.0162 99.889% 92.778% 99.596% 0.0070 100.000% 98.778% 8 56 82.489% 0.0712 92.444% 71.333% 88.438% 0.0309 93.333% 80.111% 96.106% 0.0231 99.111% 87.444% 99.428% 0.0057 100.000% 98.889% -
[1] Cao X, Li M Y, Tao Y T, Lu P. HMA-SAR: Multi-agent search and rescue for unknown located dynamic targets in completely unknown environments. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024, 9(6): 5567−5574 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3396097 [2] Peng B, Zhang X R, Shang M S. A novel competition-based coordination model with dynamic feedback for multi-robot systems. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(10): 2029−2031 [3] Li K, Zhao K, Song Y D. Adaptive consensus of uncertain multi-agent systems with unified prescribed performance. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(5): 1310−1312 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123723 [4] Huang J H, Zeng J, Chi X M, Sreenath K, Liu Z T, Su H Y. Velocity obstacle for polytopic collision avoidance for distributed multi-robot systems. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023, 8(6): 3502−3509 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3269295 [5] 张方方, 陈波, 班旋旋, 霍本岩, 彭金柱. 基于生物启发神经网络和DMPC的多机器人协同搜索算法. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(11): 2699−2706Zhang Fang-Fang, Chen Bo, Ban Xuan-Xuan, Huo Ben-Yan, Peng Jin-Zhu. Multi-robot cooperative search algorithm based on bio-inspired neural network and DMPC. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(11): 2699−2706 [6] Chen B, Zhang H, Zhang F F, Liu Y H, Tan C, Yu H N, et al. A multirobot distributed collaborative region coverage search algorithm based on Glasius bio-inspired neural network. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2023, 15(3): 1449−1462 doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2022.3218718 [7] Chen B, Zhang H, Zhang F F, Jiang Y M, Miao Z Q, Yu H N, et al. DIBNN: A dual-improved-BNN based algorithm for multi-robot cooperative area search in complex obstacle environments. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, DOI: 10.1109/TASE.2024.3379166 [8] Zheng X M, Jain S, Koenig S, Kempe D. Multi-robot forest coverage. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Edmonton, Canada: IEEE, 2005. 3852−3857 [9] Pehlivanoglu Y V. A new vibrational genetic algorithm enhanced with a Voronoi diagram for path planning of autonomous UAV. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2012, 16(1): 47−55 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2011.02.006 [10] Dong W, Liu S S, Ding Y, Sheng X J, Zhu X Y. An artificially weighted spanning tree coverage algorithm for decentralized flying robots. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(4): 1689−1698 [11] Nair V G, Guruprasad K R. MR-SimExCoverage: Multi-robot simultaneous exploration and coverage. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2020, 85: Article No. 106680 [12] Dadgar M, Jafari S, Hamzeh A. A PSO-based multi-robot cooperation method for target searching in unknown environments. Neurocomputing, 2016, 177: 62−74 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.11.007 [13] Zhang J Q, Lin Y X, Zhou M C. Virtual-source and virtual-swarm-based particle swarm optimizer for large-scale multi-source location via robot swarm. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, DOI: 10.1109/TEVC.2024.3391622 [14] Tang H W, Sun W, Yu H S, Lin A P, Xue M. A multirobot target searching method based on bat algorithm in unknown environments. Expert Systems With Applications, 2020, 141: Article No. 112945 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.112945 [15] Zhou Z W, Luo D L, Shao J, Xu Y, You Y C. Immune genetic algorithm based multi-UAV cooperative target search with event-triggered mechanism. Physical Communication, 2020, 41: Article No. 101103 doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2020.101103 [16] Yang B, Ding Y S, Jin Y C, Hao K R. Self-organized swarm robot for target search and trapping inspired by bacterial chemotaxis. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2015, 72: 83−92 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2015.05.001 [17] Garg V. E2RGWO: Exploration enhanced robotic GWO for cooperative multiple target search for robotic swarms. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2023, 48(8): 9887−9903 doi: 10.1007/s13369-022-07438-5 [18] Hou K, Yang Y J, Yang X R, Lai J Z. Distributed cooperative search algorithm with task assignment and receding horizon predictive control for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 6122−6136 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3048974 [19] Dai W, Lu H M, Xiao J H, Zeng Z W, Zheng Z Q. Multi-robot dynamic task allocation for exploration and destruction. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2020, 98: 455−479 [20] Li J, Tan Y. A two-stage imitation learning framework for the multi-target search problem in swarm robotics. Neurocomputing, 2019, 334: 249−264 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.01.035 [21] Liu B, Wang X P, Zhou W. Multi-UAV collaborative search and strike based on reinforcement learning. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1651 : Article No. 012115 [22] Wang X Y, Fang X. A multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithm with the action preference selection strategy for massive target cooperative search mission planning. Expert Systems With Applications, 2023, 231: Article No. 120643 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120643 [23] Hodgkin A L, Huxley A F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. The Journal of Physiology, 1952, 117(4): 500−544 doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764 [24] Grossberg S. Contour enhancement, short term memory, and constancies in reverberating neural networks. Studies of Mind and Brain: Neural Principles of Learning, Perception, Development, Cognition, and Motor Control, 1982: 332−378 [25] Luo C M, Yang S X, Stacey D A. Real-time path planning with deadlock avoidance of multiple cleaning robots. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 03CH37422). Taipei, China: IEEE, 2003. 4080−4085 [26] Luo C M, Yang S X, Li X D, Meng M Q H. Neural-dynamics-driven complete area coverage navigation through cooperation of multiple mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(1): 750−760 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2609838 [27] Sun B, Zhu D Q, Tian C, Luo C M. Complete coverage autonomous underwater vehicles path planning based on Glasius bio-inspired neural network algorithm for discrete and centralized programming. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2019, 11(1): 73−84 [28] Muthugala M A V J, Samarakoon S M B P, Elara M R. Toward energy-efficient online complete coverage path planning of a ship hull maintenance robot based on Glasius bio-inspired neural network. Expert Systems With Applications, 2022, 187: Article No. 115940 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115940 [29] Zhao L, Li R, Han J D, Zhang J L. A distributed model predictive control-based method for multidifferent-target search in unknown environments. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2023, 27(1): 111−125 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2022.3161942 [30] Conte C, Jones C N, Morari M, Zeilinger M N. Distributed synthesis and stability of cooperative distributed model predictive control for linear systems. Automatica, 2016, 69: 117−125 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.02.009 [31] Qiao K J, Liang J, Yu K J, Yue C T, Lin H Y, Zhang D Z, et al. Evolutionary constrained multiobjective optimization: Scalable high-dimensional constraint benchmarks and algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2024, 28(4): 965−979 [32] Grossberg S. Nonlinear neural networks: Principles, mechanisms, and architectures. Neural Networks, 1988, 1(1): 17−61 [33] Ni J J, Yang S X. Bioinspired neural network for real-time cooperative hunting by multirobots in unknown environments. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(12): 2062−2077 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2169808 -




 下载:
下载: