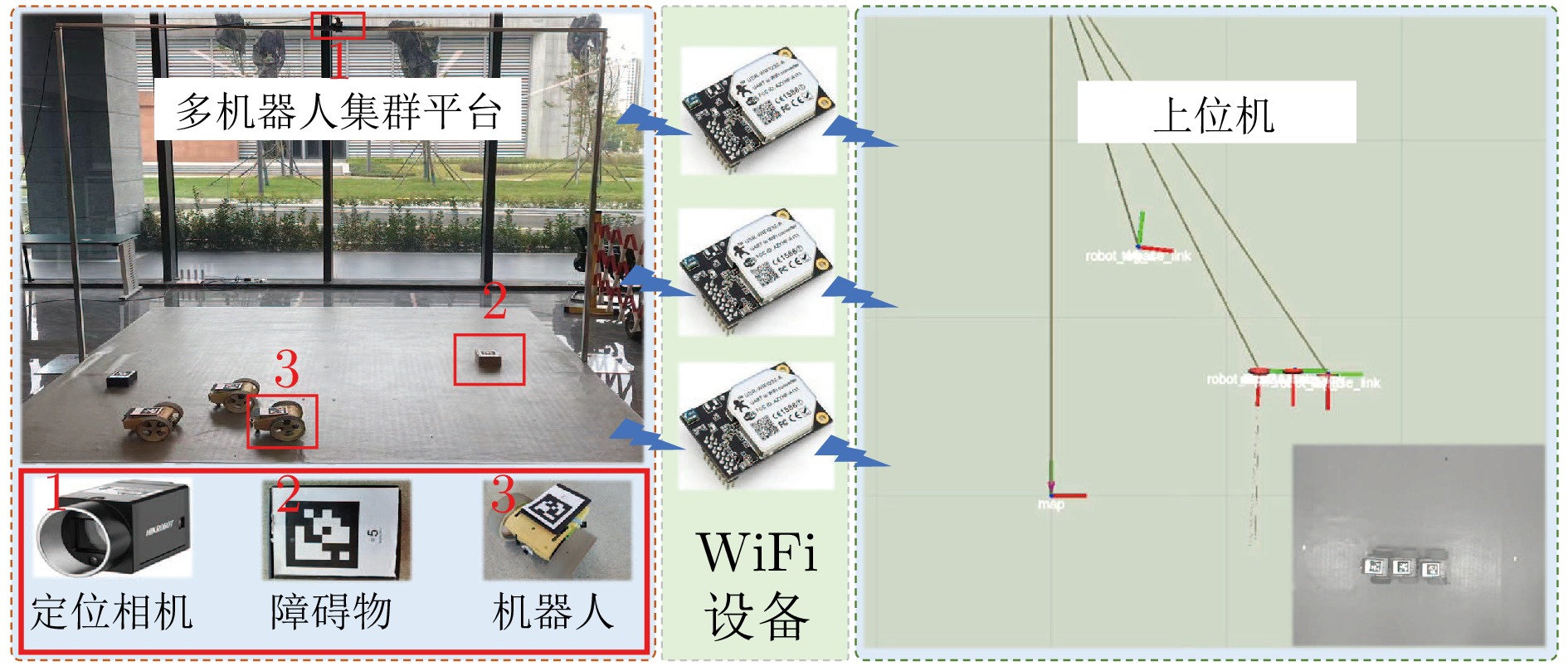
Distributed Multi-mobile Robot Anti-oscillation Safety Formation Control With Nested Motion Saturation
-
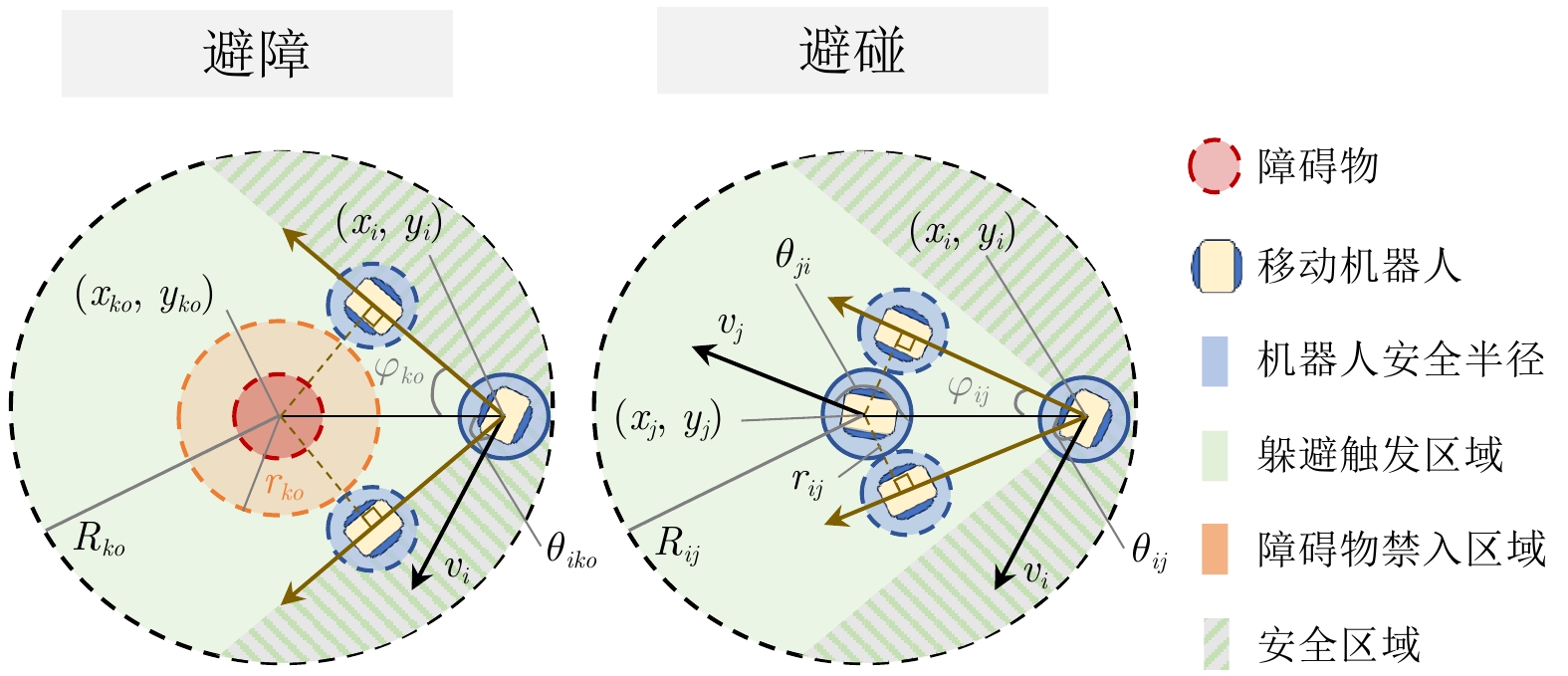
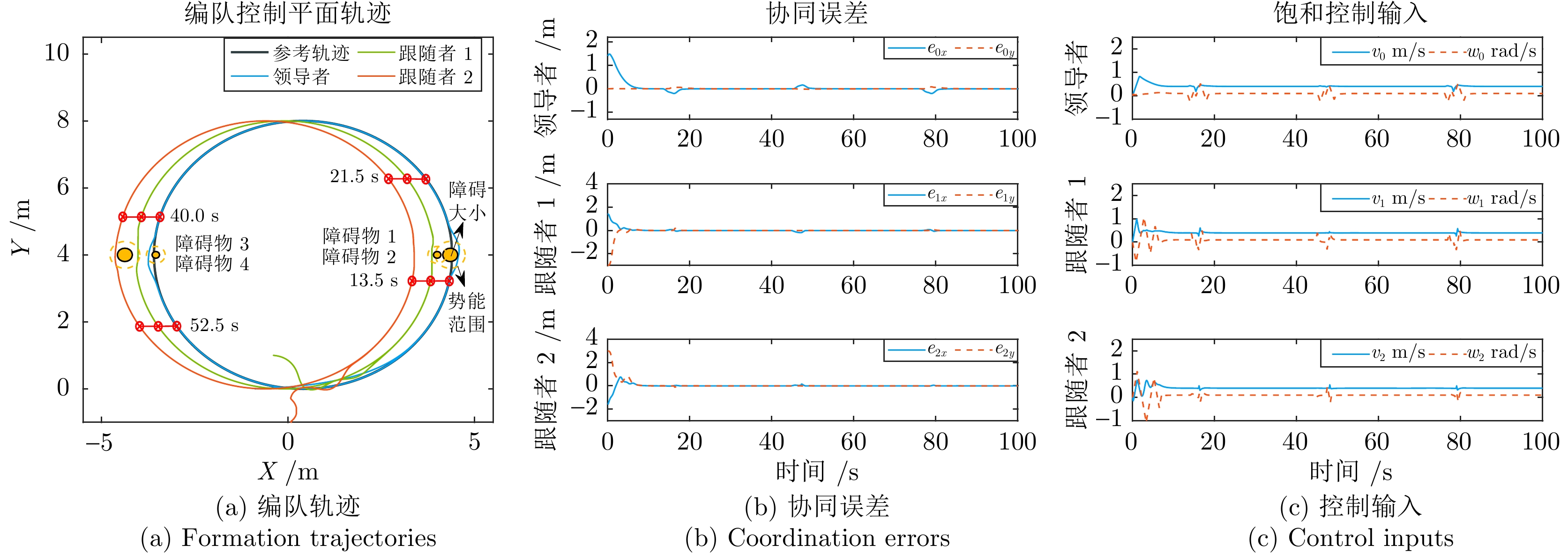
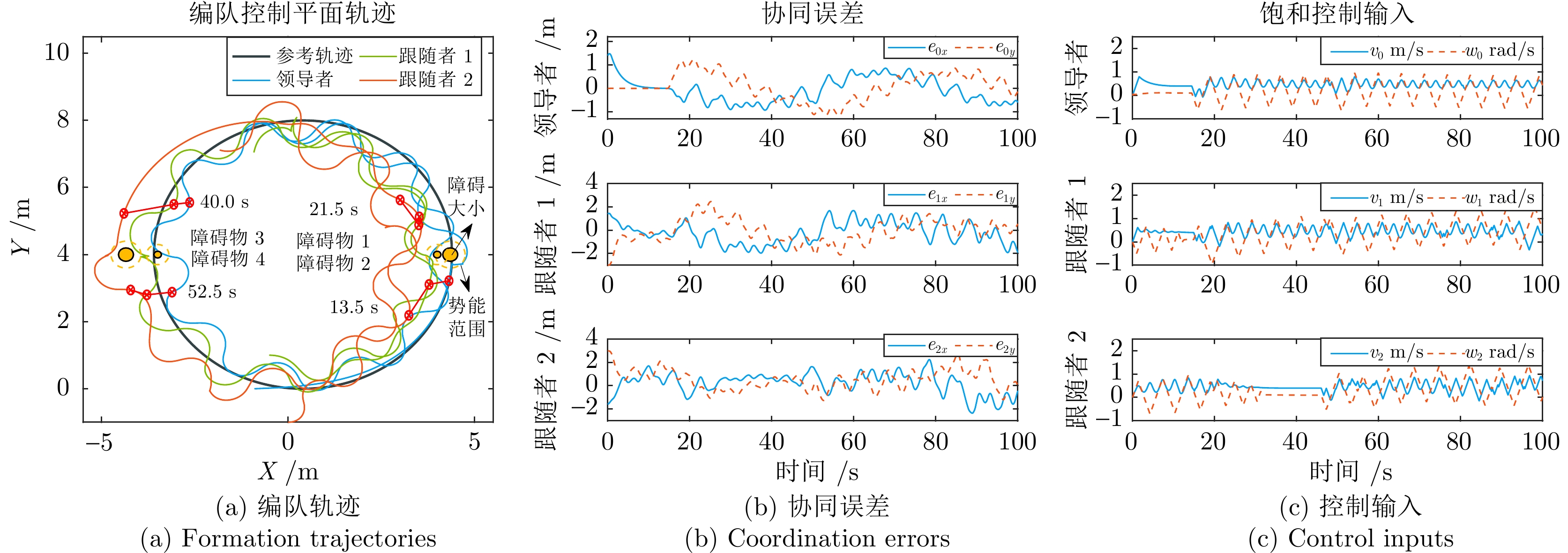
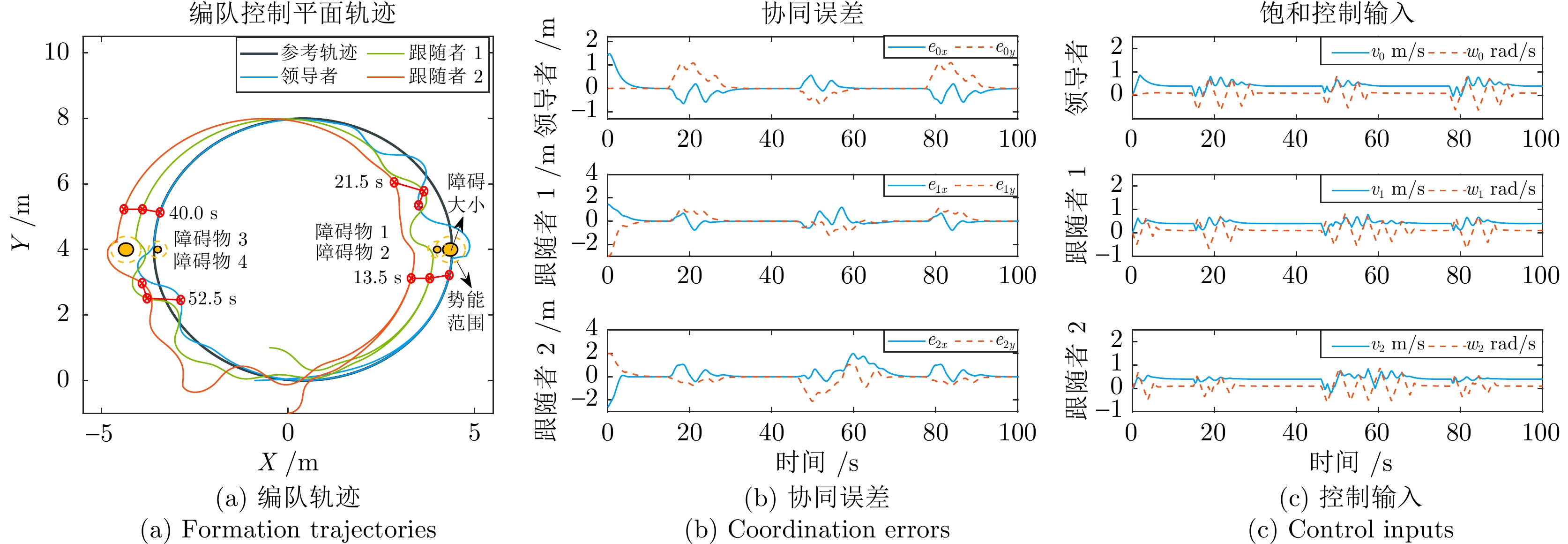
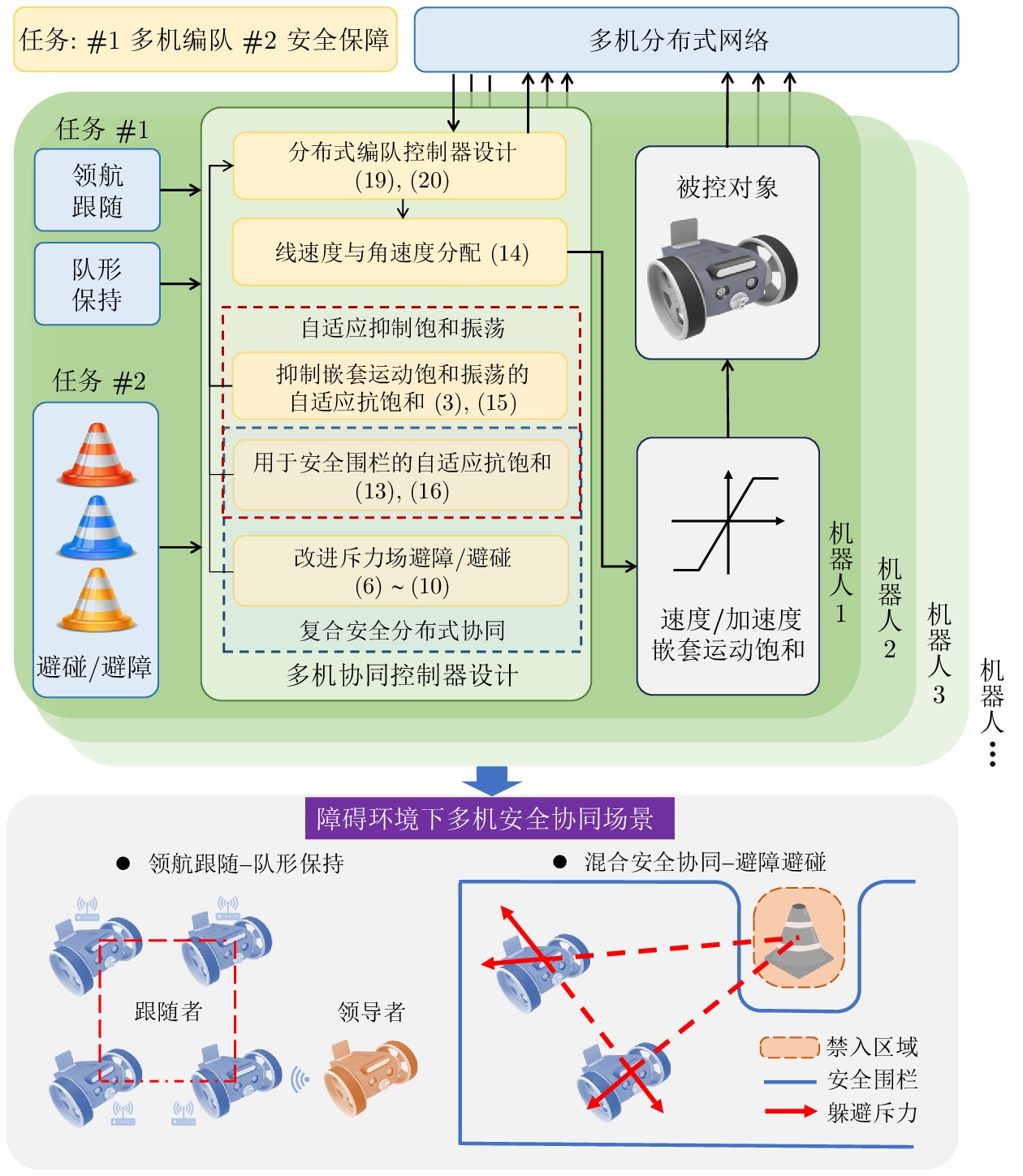
摘要: 运动受速度和加速度嵌套饱和约束, 而反应式躲避安全机制下分布式编队互联的移动机器人更易触发该嵌套饱和, 从而引起编队的剧烈振荡, 所以需要研究该情况下多移动机器人平滑安全协同及其自适应振荡抑制方法. 故以分布式网络中的移动机器人为研究对象, 首先构建基于视线和速度的低触发势能函数, 实现邻近编队机器人近距排斥作用下的避碰保持; 引入驱动机器人绕过障碍物的安全加速度包络, 并复合近距排斥的弱能量、低触发势能, 避免与非合作障碍物的碰撞. 其次, 嵌入复合自适应辅助动态系统, 平滑躲避过程中触发的嵌套运动饱和与安全加速度约束引起的轨迹振荡; 设计复合非线性反馈框架下的分布式编队控制器, 融合混合的躲避和振荡抑制机制, 实现多机器人障碍环境下的安全编队. 最后, 与现有安全编队方法进行对比仿真和实验验证, 结果表明该方法在嵌套运动饱和约束下可显著提升编队的平滑和安全性能.
-
关键词:
- 分布式移动机器人编队 /
- 嵌套运动饱和 /
- 动态安全围栏 /
- 低触发势能函数 /
- 自适应振荡抑制
Abstract: The motion is constrained by nested saturation of velocity and acceleration. Under the reactive avoidance safety mechanism, distributed formation-connected mobile robots are more likely to trigger this nested saturation, causing severe formation oscillations. Thus, it is necessary to study smooth and safe coordination and adaptive oscillation suppression methods for multi-mobile robots under these conditions. Therefore, Mobile robots in a distributed network are taken as the research subjects. Initially, a low-trigger potential function based on line-of-sight and velocity is constructed, enabling collision avoidance while maintaining proximity under the repulsive action of nearby formation robots; A safety acceleration envelope that allows robots to navigate around obstacles is introduced, and it is combined with low-power, low-trigger potential for close-range repulsion, avoiding collisions with non-cooperative obstacles. Secondly, a composite adaptive auxiliary dynamic system is embedded to smooth the trajectory oscillations caused by nested motion saturation and safety acceleration constraint triggered during the smoothing evasion process; A distributed formation controller under a composite nonlinear feedback framework is designed, integrating composite evasion and oscillation suppression mechanisms to achieve safe formation of multiple robots in an obstacle environment. Finally, comparative simulations and experimental validations with existing safe formation methods are conducted, and the results demonstrate that this method can significantly enhance the smoothness and safety performance of the formation under nested motion saturation constraints. -
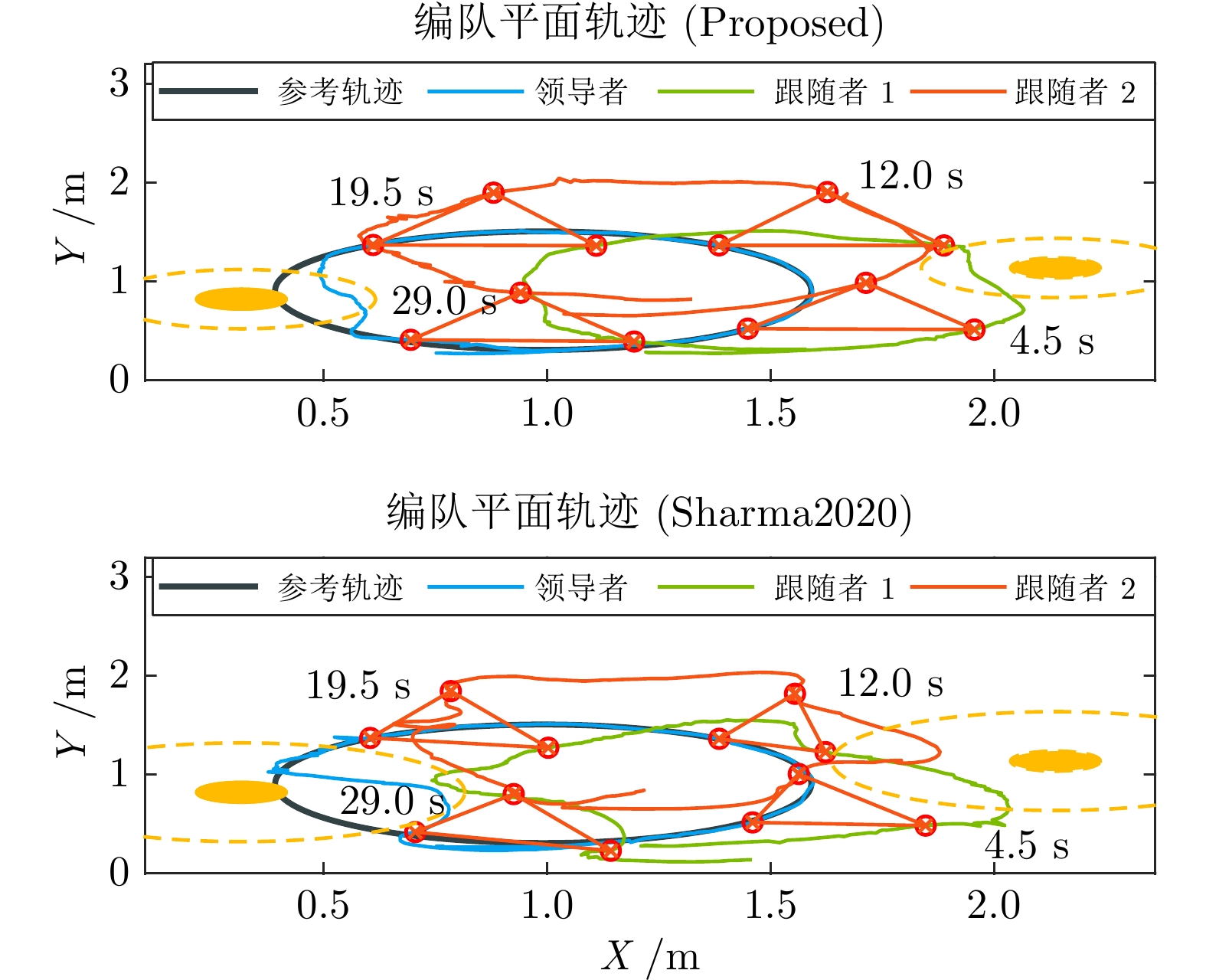
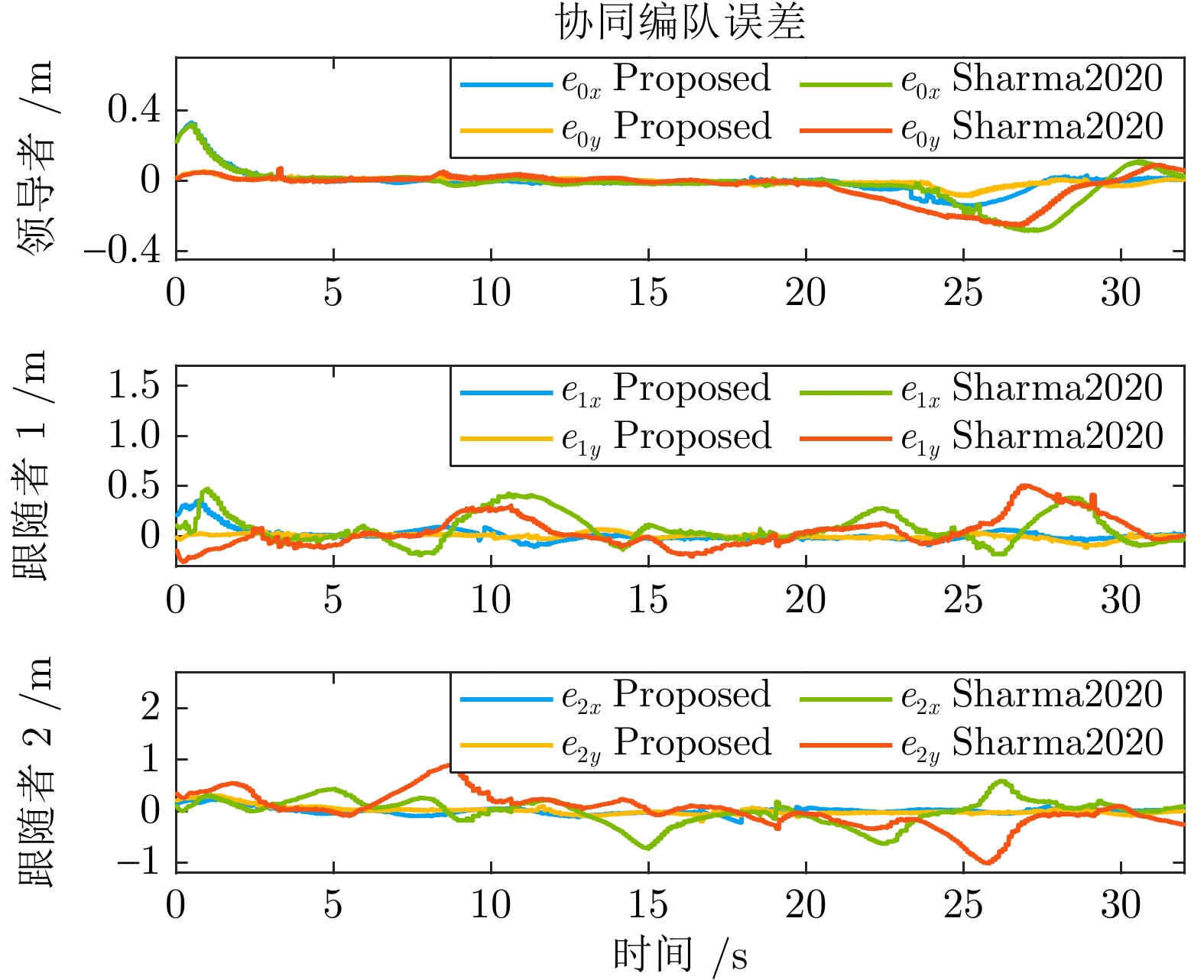
表 1 编队平滑对比指标
Table 1 Formation smoothness comparison index
对比指标 Proposed Sharma2020 第一次躲避跟随者振荡幅值(m) 0.15 0.90 第一次躲避跟随者恢复时间(s) 6.20 — 第二次躲避领导者振荡幅值(m) 0.21 0.52 第二次躲避领导者恢复时间(s) 4.20 11.50 第二次躲避跟随者振荡幅值(m) 0.07 1.20 第二次躲避跟随者恢复时间(s) 0.00 — -
[1] 李润梅, 张立威, 王剑. 基于时变间距和相对角度的无人车跟随控制方法研究. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(11): 2031−2040Li Run-Mei, Zhang Li-Wei, Wang Jian. A control method of unmanned car following under time-varying relative distance and angle. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(11): 2031−2040 [2] 费思远, 鲜斌, 王岭. 基于群集行为的分布式多无人机编队动态避障控制. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39 (1): 1−11Fei Si-Yuan, Xian Bin, Wang Lin. Distributed formation control for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles with dynamic obstacle avoidance based on the flocking behavior. Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 39 (1): 1−11 [3] 李正平, 鲜斌. 基于虚拟结构法的分布式多无人机鲁棒编队控制. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(11): 2423−2431Li Zheng-Ping, Xian Bin. Robust distributed formation control of multiple unmanned aerial vehicles based on virtual structure. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(11): 2423−2431 [4] Zhang K, Huang L, He Y, Wang B, Chen J, Tian Y, et al. A real-time multi-ship collision avoidance decision-making system for autonomous ships considering ship motion uncertainty. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 278 : Article No. 114205 [5] Franzè G, Lucia W, Venturino A. A distributed model predictive control strategy for constrained multi-vehicle systems moving in unknown environments. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vechicles, 2021, 6(2): 343−352 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2020.3029746 [6] Park S, Lee S. Formation reconfiguration control with collision avoidance of nonholonomic mobile robots. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023, 8(12): 7905−7912 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3324593 [7] 林俊亭, 倪铭君. 基于人工势场的虚拟编组自适应模型预测控制.北京航空航天大学学报, DOI: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2023.0544Lin Jun-Ting, Ni Ming-Jun. Adaptive model predictive control of virtual coupled based on artificial potential field. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, DOI: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2023.0544 [8] 黎星华, 刘晓平, 王刚, 吴少波, 李文俊. 面向多智能消防机器人的编队避障控制方法. 机器人, 2024, 46(1): 81−93Li Xing-Hua, Liu Xiao-Ping, Wang Gang, Wu Shao-Bo, Li Wen-Jun. A formation obstacle-avoidance control method for multiple intelligent firefighting robots. Robot, 2024, 46(1): 81−93 [9] 姚瀚晨, 彭建伟, 戴厚德, 林名强. 基于改进弹簧模型的移动机器人柔顺跟随行人方法. 机器人, 2021, 43 (6): 684−693Yao Han-Chen, Peng Jian-Wei, Dai Hou-De, Lin Ming-Qiang. A compliant human following method for mobile robot based on an improved spring model. Robot, 2021, 43 (6): 684−693 [10] Wang G, Wang X, Li S. A guidance module based formation control scheme for multi-mobile robot systems with collision avoidance. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2024, 21(1): 382−393 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2022.3228397 [11] Kamel M, Yu X, Zhang Y. Fault-tolerant cooperative control design of multiple wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2018, 26(2): 756−764 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2017.2679066 [12] Li Y, Dong S, Li K, Tong S. Fuzzy adaptive fault tolerant time-varying formation control for nonholonomic multirobot systems with range constraints. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vechicles, 2023, 8(6): 3668−3679 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3264800 [13] Dai S, He S, Cai H, Yang C. Adaptive leader-follower formation control of underactuated surface vehicles with guaranteed performance. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 52(3): 1997−2008 [14] Dai S, Lu K, Jun F. Fixed-time rigidity-based formation maneuvering for nonholonomic multirobot systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(4): 2129−2141 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3226297 [15] Wang Y, Wang D, Yang S, Shan M. A practical leader-follower tracking control scheme for multiple nonholonomic mobile robots in unknown obstacle environments. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2021, 27(4): 1685−1693 [16] Fathian K, Safaoui S, Summers T H, Gans N R. Robust distributed planar formation control for higher order holonomic and nonholonomic agents. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2022, 52(10): 185−205 [17] Lippay Z S, Hoagg J B. Formation control with time-varying formations, bounded controls, and local collision avoidance. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2022, 30(1): 261−276 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2021.3062824 [18] 张志伟, 滕英元, 杨慧欣, 倪智宇. 具有速度、加速度约束的机器人编队避障控制. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(6): 1388−1396Zhang Zhi-Wei, Teng Ying-Yuan, Yang Hui-Xin, Ni Zhi-Yu. Obstacle avoidance control for robots formation with speed and acceleration constraints. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(6): 1388−1396 [19] Ghaffari A. Analytical design and experimental verification of geofencing control for aerial applications. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2020, 26(2): 1106−1117 [20] Chang S, Wang Y, Zuo Z, Yang H. Fixed-time formation control for wheeled mobile robots with prescribed performance. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2022, 30(2): 844−851 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2021.3069831 [21] Rad S, Khosravi A, Sarhadi P. Pitch autopilot design for an autonomous aerial vehicle in the presence of amplitude and rate saturation. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 108 : Article No. 106371 [22] Li S, Wang X. Finite-time consensus and collision avoidance control algorithms for multiple AUVs. Automatica, 2013, 49: 3359−3367 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.08.003 [23] Sharma R, Mondal A, Behera L. Tracking control of mobile robots in formation in the presence of disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(1): 110−123 doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2983646 -




 下载:
下载: