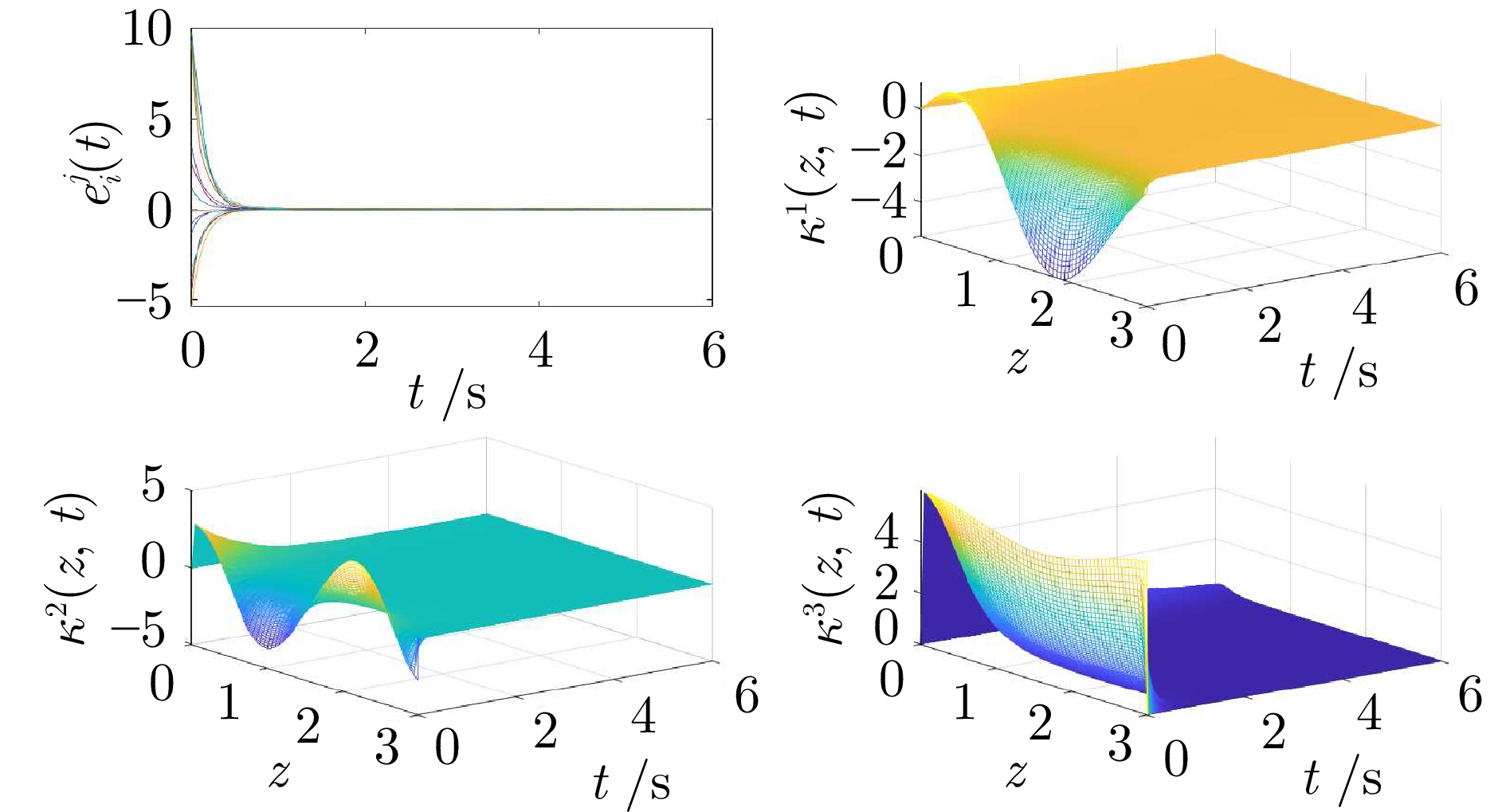
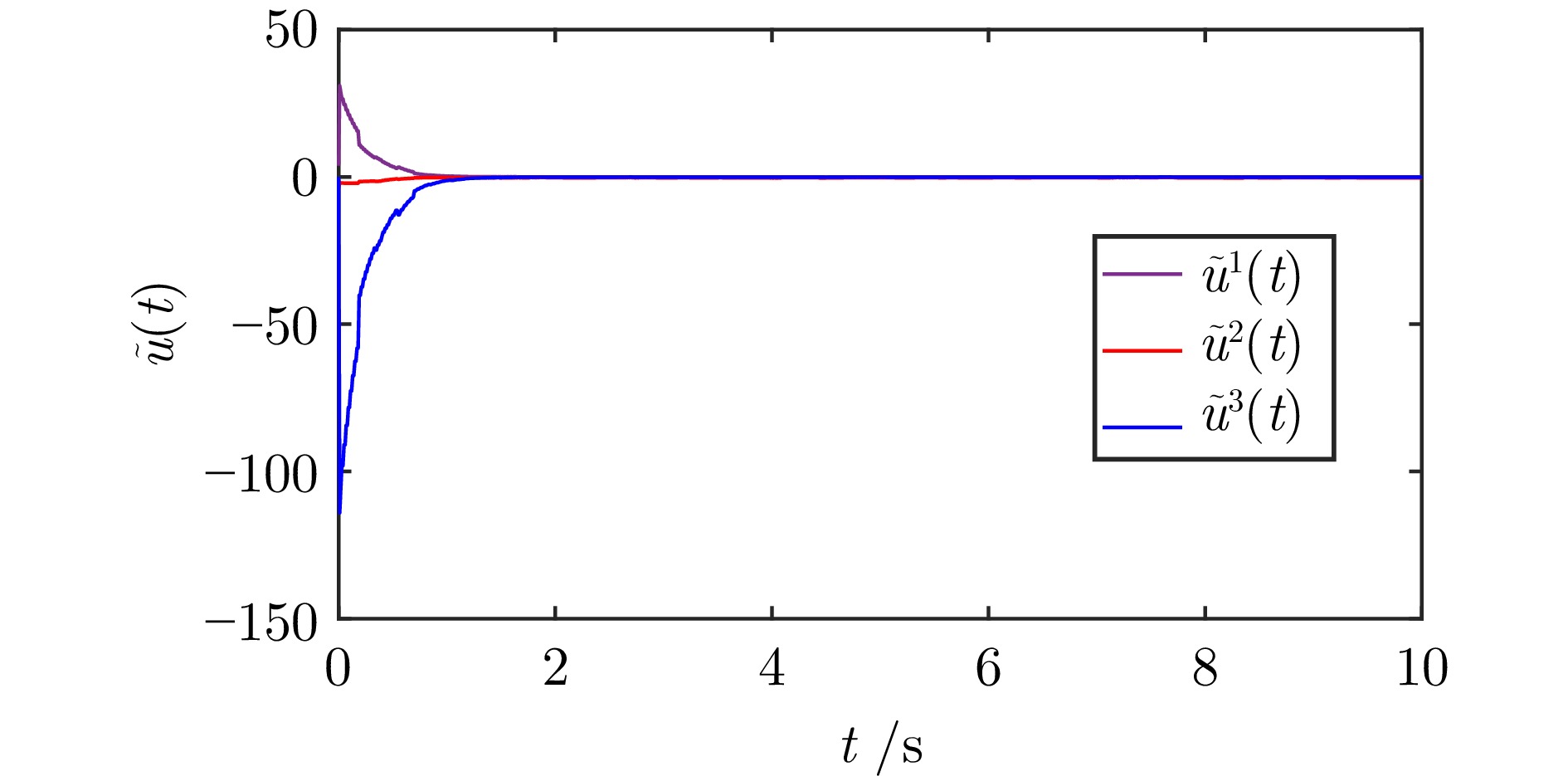
|
[1]
|
Oh K K, Park M C, Ahn H S. A survey of multi-agent formation control. Automatica, 2015, 53 (C): 424−440 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.022
|
|
[2]
|
Qin D D, Jin Z H, Liu A D, Zhang W A, Yu L. Event-triggered distributed predictive cooperation control for multi-agent systems subject to bounded disturbances. Automatica, 2023, 157: Article No. 111230 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.111230
|
|
[3]
|
范泉涌, 张乃宗, 唐勇, 许斌. 基于动态事件触发通信协议的多智能体系统自适应可靠控制. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(5): 924−936Fan Quan-Yong, Zhang Nai-Zong, Tang Yong, Xu Bin. Adaptive reliable control of multi-agent systems based on dynamic event-triggered communication protocol. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(5): 924−936
|
|
[4]
|
Ferrari-Trecate G, Buffa A, Gati M. Analysis of coordination in multi-agent systems through partial difference equations. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2006, 51(6): 1058−1063 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2006.876805
|
|
[5]
|
Freudenthaler G, Meurer T. PDE-based multi-agent formation control using flatness and backstepping: Analysis, design and robot experiments. Automatica, 2020, 115: Article No. 108897 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2020.108897
|
|
[6]
|
Wei J Q, Fridman E, Johansson K H. A PDE approach to deployment of mobile agents under leader relative position measurements. Automatica, 2019, 106: 47−53 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.04.040
|
|
[7]
|
Su H S, Xu Q J. Deployment of second-order networked mobile agents over a smooth curve. Automatica, 2022, 146: Article No. 110645 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110645
|
|
[8]
|
Terushkin M, Fridman E. Network-based deployment of nonlinear multi agents over open curves: A PDE approach. Automatica, 2021, 129: Article No. 109697 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.109697
|
|
[9]
|
Qi J, Wang S S, Fang J A, Diagne M. Control of multi-agent systems with input delay via PDE-based method. Automatica, 2019, 106: 91−100 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.04.032
|
|
[10]
|
Wang S S, Diagne M, Qi J. Delay-adaptive compensation for 3-D formation control of leader-actuated multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2024, 164: Article No. 111645 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2024.111645
|
|
[11]
|
刘凡, 杨洪勇, 杨怡泽, 李玉玲, 刘远山. 带有不匹配干扰的多智能体系统有限时间积分滑模控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(4): 749−758Liu Fan, Yang Hong-Yong, Yang Yi-Ze, Li Yu-Ling, Liu Yuan-Shan. Finite-time integral sliding-mode control for multi-agent systems with mismatched disturbances. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(4): 749−758
|
|
[12]
|
Meurer T, Krstic M. Finite-time multi-agent deployment: A nonlinear PDE motion planning approach. Automatica, 2011, 47(11): 2534−42 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.08.045
|
|
[13]
|
Man J T, Sheng Y, Chen C Y, Zeng Z G. PDE-based finite-time deployment of heterogeneous multi-agent systems subject to multiple asynchronous semi-Markov chains. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2023, 71(2): 885−897
|
|
[14]
|
孙梦薇, 任璐, 刘剑, 孙长银. 切换拓扑下动态事件触发多智能体系统固定时间一致性. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(6): 1295−1305Sun Meng-Wei, Ren Lu, Liu Jian, Sun Chang-Yin. Dynamic event-triggered fixed-time consensus control of multi-agent systems under switching topologies. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(6): 1295−1305
|
|
[15]
|
Wang F Y, Gong J Y, Liu Z X, Chen Z Q. Finite-time output tracking control for random multi-agent systems with mismatched disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2024, 21(4): 7516−7526
|
|
[16]
|
Liu X D, Deng F Q, Wei W, Wan F Z. Formation tracking control of networked systems with time-varying delays and sampling under fixed and Markovian switching topology. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2022, 9(2): 601−612 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2022.3158817
|
|
[17]
|
Li B Q, Wen G G, Peng Z X, Huang T W, Rahmani A. Fully distributed consensus tracking of stochastic nonlinear multiagent systems with Markovian switching topologies via intermittent control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 52(5): 3200−3209
|
|
[18]
|
郑维, 张志明, 刘和鑫, 张明泉, 孙富春. 基于线性变换的领导−跟随多智能体系统动态反馈均方一致性控制. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(10): 2474−2485Zheng Wei, Zhang Zhi-Ming, Liu He-Xin, Zhang Ming-Quan, Sun Fu-Chun. Dynamic feedback mean square consensus control based on linear transformation for leader-follower multi-agent systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(10): 2474−2485
|
|
[19]
|
Liang H J, Zhang L C, Sun Y H, Huang T W. Containment control of semi-Markovian multiagent systems with switching topologies. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 51(6): 3889−3899
|
|
[20]
|
Hu Z H, Mu X W. Impulsive consensus of stochastic multi-agent systems under semi-Markovian switching topologies and application. Automatica, 2023, 150: Article No. 110871 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.110871
|
|
[21]
|
Stone L D. Necessary and sufficient conditions for optimal control of semi-Markov jump processes. SIAM Journal on Control, 1973, 11(2): 187−201 doi: 10.1137/0311017
|
|
[22]
|
Zhu Z, Xia Y Q, Fu M Y. Attitude stabilization of rigid spacecraft with finite-time convergence. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2011, 21(6): 686−702 doi: 10.1002/rnc.1624
|
|
[23]
|
Tao Y Y, Che W W, Wu Z G, Xu Y, Dong S L. Asynchronous control of 2-D Markov jump Roesser systems with nonideal transition probabilities. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(11): 6643−6652
|
|
[24]
|
Wang L K, Zhao Y H, Xie X P, Lam H K. A switching asynchronous control approach for Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy Markov jump systems with time-varying delay. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2024, 32(2): 595−606 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2023.3302134
|
|
[25]
|
Tao J, Wu Z Y, Xiao Z H, Rao H X, Xu Y, Shi P. Synchronization of Markov jump neural networks with communication constraints via asynchronous output feedback control. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(11): 15724−15734
|
|
[26]
|
Hardy G H, Littlewood J E, Pólya G. Inequalities. Cambridge University Press, 1952.
|
|
[27]
|
Wang F, Chen B, Sun Y M, Gao Y L, Lin C. Finite-time fuzzy control of stochastic nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 50(6): 2617−2626
|
|
[28]
|
Wei Y L, Park J H, Qiu J B, Wu L G, Jung H Y. Sliding mode control for semi-Markovian jump systems via output feedback. Automatica, 2017, 81: 133−141 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.03.032
|




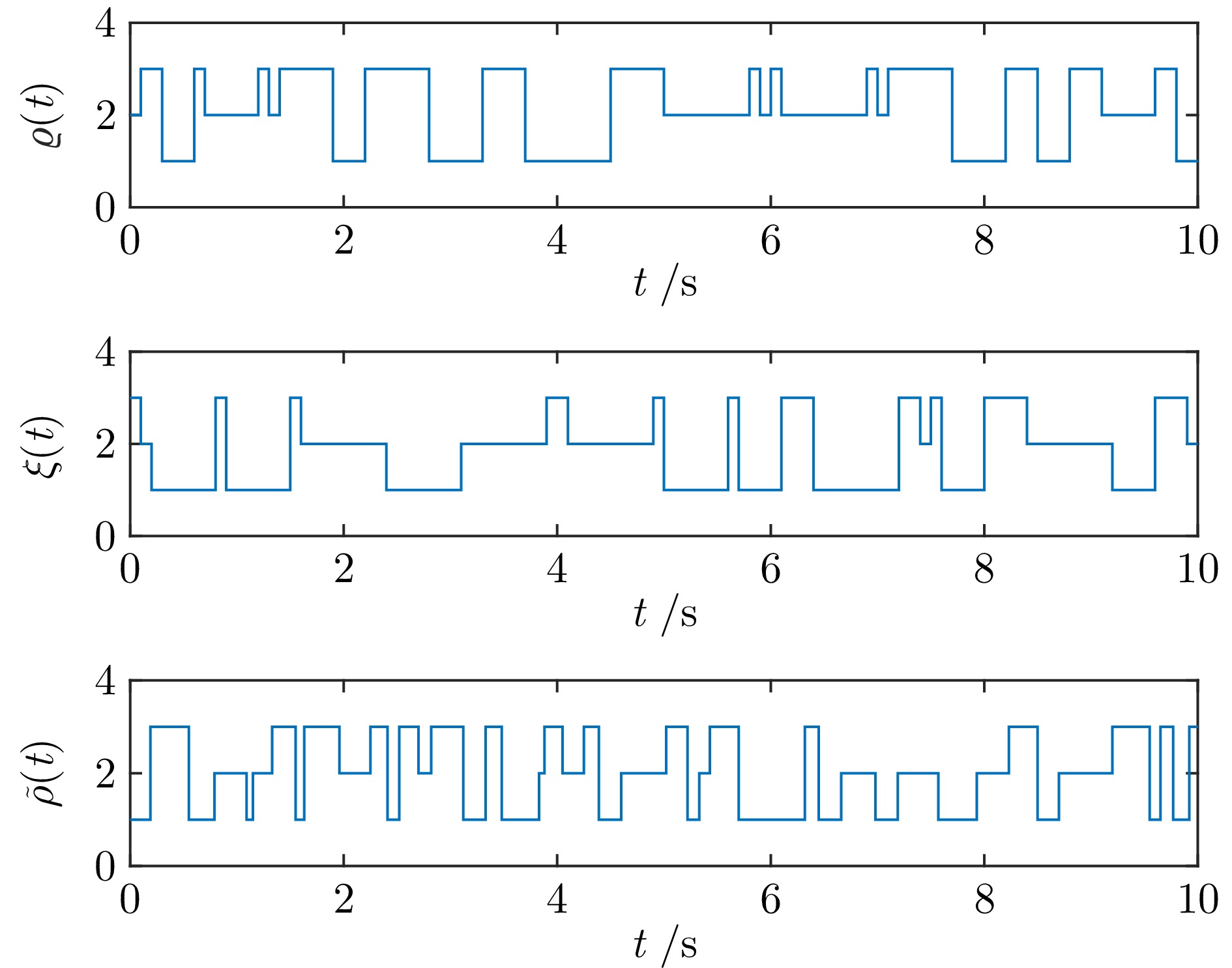
 下载:
下载: