Event-triggered State Consensus of Heterogeneous Uncertain Second-order Nonlinear Multi-agent Systems
-
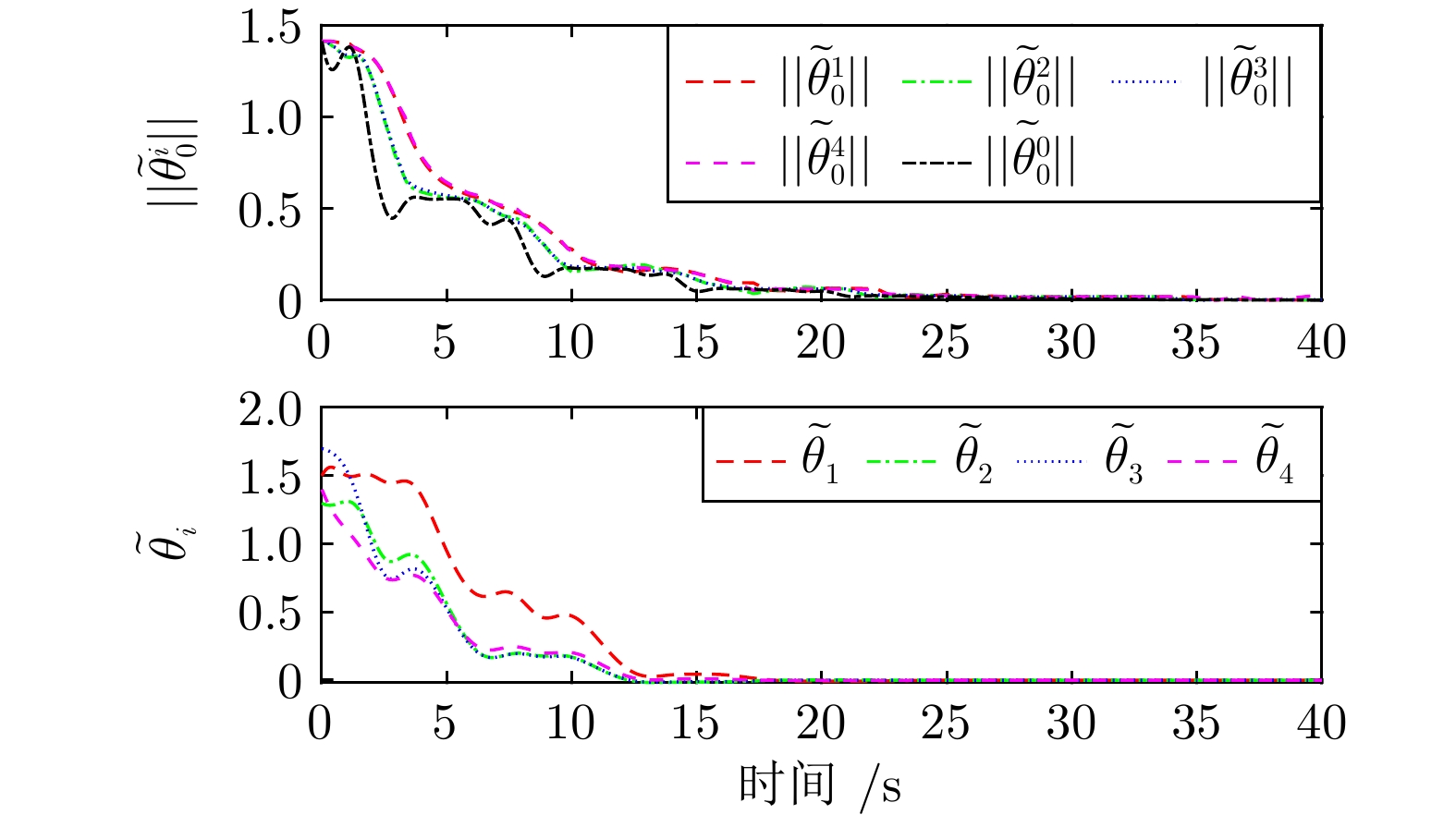
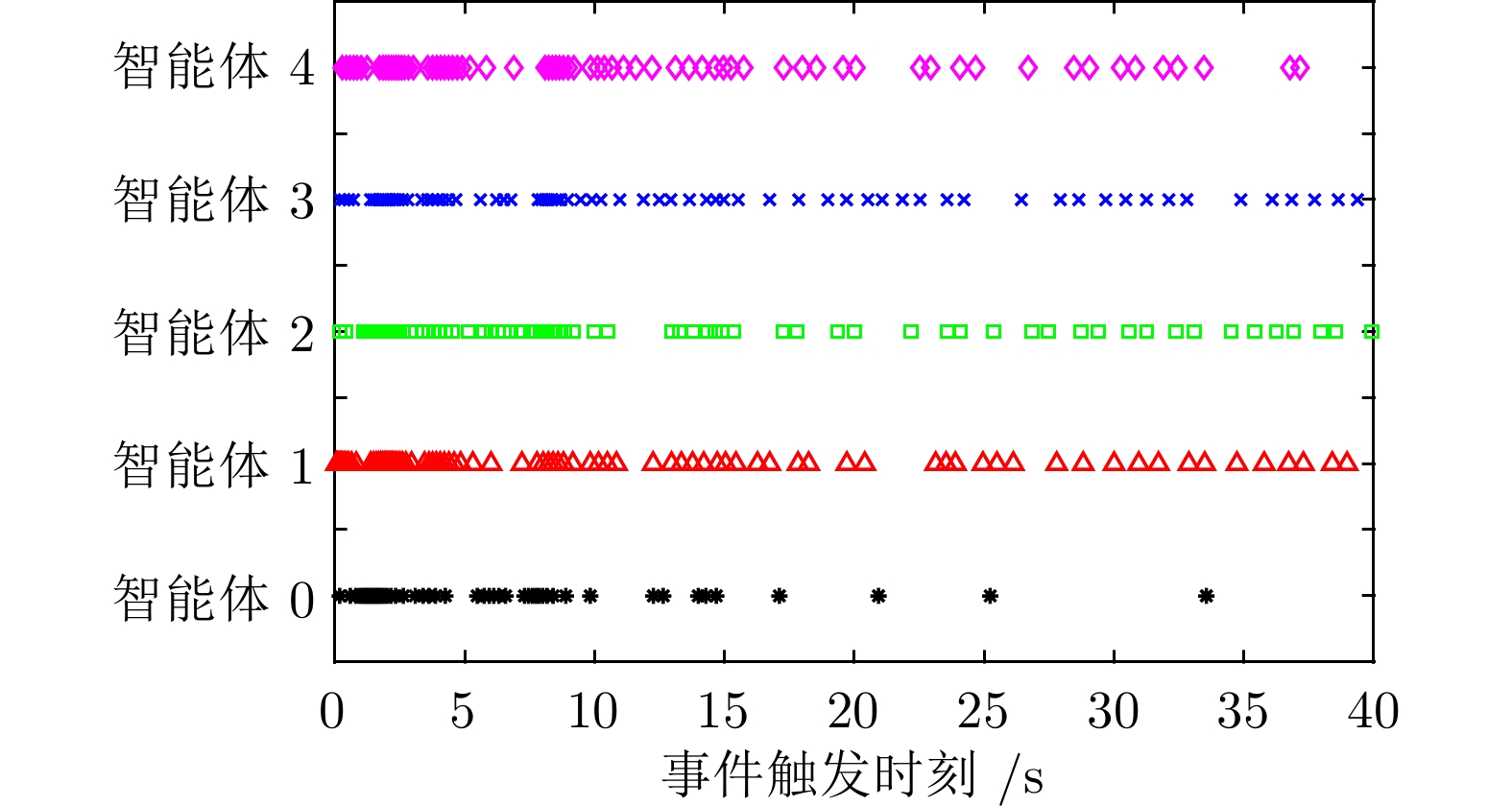
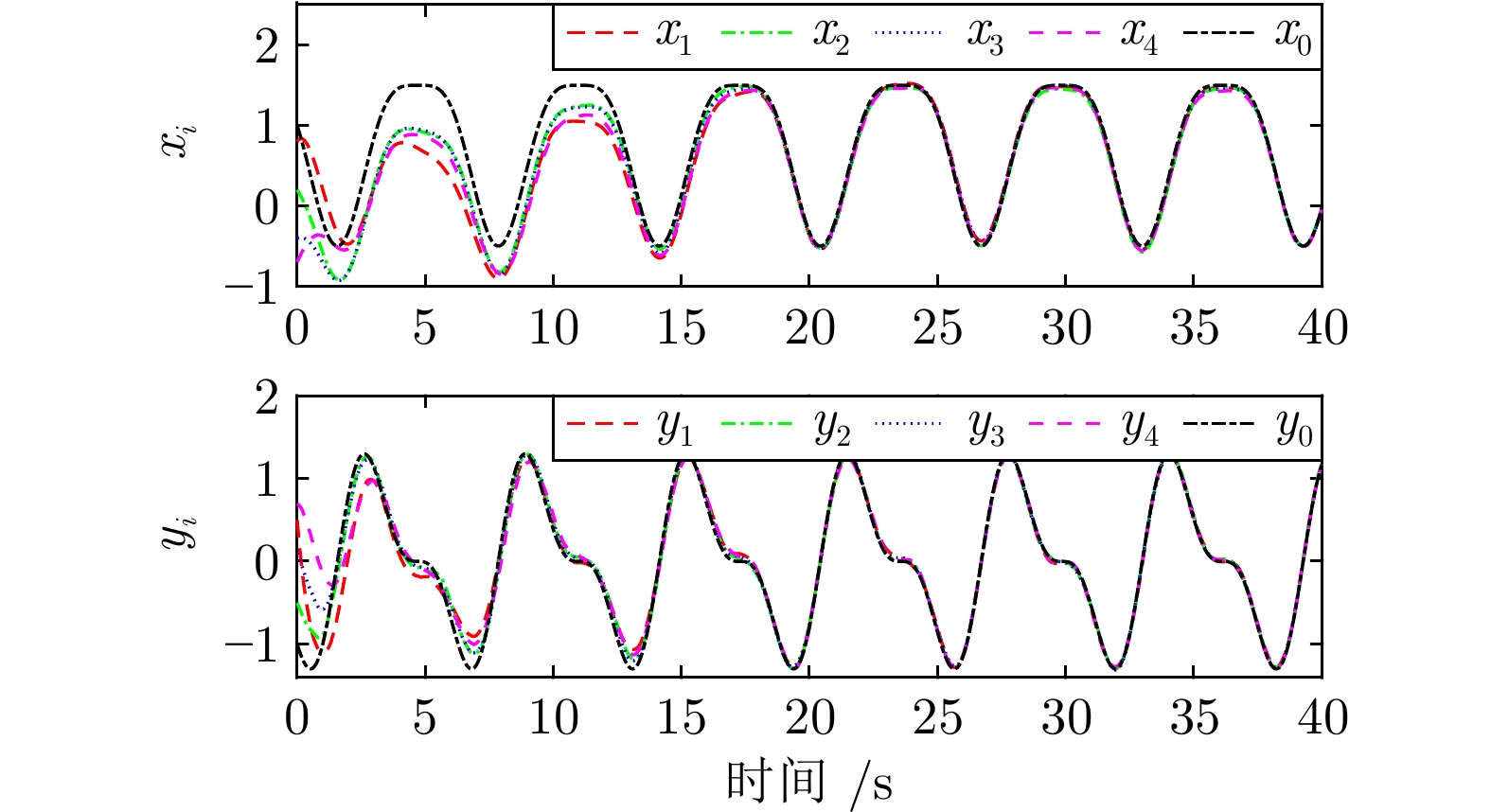
摘要: 研究异构不确定二阶非线性多智能体系统事件触发状态趋同控制问题. 首先, 为每个智能体设计参数观测器, 用以估计不确定参数, 这些观测器可渐近估计不确定参数. 其次, 为每个跟随智能体设计分布式参数观测器, 渐近估计领导智能体不确定参数, 每个智能体利用邻居智能体触发时刻的采样值估计其邻居智能体的状态. 基于估计的参数和邻居状态, 提出完全不依赖智能体间连续信息传输的事件触发趋同算法. 同时, 证明在所给算法的作用下, 多智能体系统能够达到状态趋同且不存在芝诺现象. 最后, 给出一个多单摆系统, 用以验证事件触发趋同算法. 仿真实验结果表明, 跟随智能体的位置和速度可以渐近跟踪领导智能体的位置和速度, 并且整个多智能体系统平均每秒触发8.825次. 对比仿真实验显示, 所提出的事件触发趋同算法可有效减少事件触发次数.
-
关键词:
- 多智能体系统 /
- 事件触发 /
- 不确定二阶非线性系统 /
- 状态趋同 /
- 异构系统
Abstract: This paper studies event-triggered state consensus of heterogeneous uncertain second-order nonlinear multi-agent systems. Firstly, to deal with the uncertain parameter of each agent dynamics, parameter observers are designed for each agent to asymptotically estimate uncertain parameters, these observers can estimate exact values of uncertain parameters. Secondly, distributed parameter observers are designed for each follower agent to asymptotically estimate uncertain parameters of leader agent, and each agent use its neighbors'sampled information at the trigger instant to estimate its neighbors'states. Based on estimated parameters and neighbors'states, an event-triggered consensus algorithm is proposed, which does not rely on any continuous information transmission among agents. Furthermore, it is proved that multi-agent systems can reach state consensus under the proposed algorithm, and there is no Zeno-behavior. Finally, a multi-pendulum system is given to verify event-triggered consensus algorithm. The simulation experiment results show that the position and velocity of follower agents can track that of leader agent asymptotically, and the average trigger number of overall multi-agent systems is 8.825 per second, comparison simulation experiment shows that the proposed event-triggered consensus algorithm can effectively reduce event-triggered number. -
表 1 本文算法的事件触发次数
Table 1 Event-triggered number of the proposed algorithm
智能体 0 1 2 3 4 触发次数 49 84 75 73 72 表 2 组合测量算法的事件触发次数
Table 2 Event-triggered number of the combined measurement algorithm
智能体 0 1 2 3 4 触发次数 139 258 266 255 249 -
[1] Pham V T, Messai N, Nguyen D H, Manamanni N. Robust formation control under state constraints of multi-agent systems in clustered network. Systems & Control Letters, 2020, 140: Article No. 104689 [2] Putra S A, Trilaksono B R, Riyansyah M, Laila D S. Multi-agent architecture for bridge capacity measurement system using wireless sensor network and weight in motion. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 70: Article No. 2502714 [3] Orr J, Dutta A. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for multi-robot applications: A survey. Sensors, 2023, 23(7): Article No. 3625 [4] Tabuada P. Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks. IEEE Transanctions on Automatic Control, 2007, 52(9): 1680−1685 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2007.904277 [5] Dimarogonas D V, Frazzoli E, Johansson K H. Distributed event triggered control for multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(5): 1291−1297 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2174666 [6] Lu W, Han Y, Chen T. Synchronization in networks of linearly coupled dynamical systems via event-triggered diffusions. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(12): 3060−3069 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2402691 [7] Ding L, Han Q L, Ge X, Zhang X M. An overview of recent advances in event-triggered consensus of multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(4): 1110−1123 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2771560 [8] Yang Y, Yue D. NNS-based event-triggered consensus control of a class of uncertain nonlinear multi-agent systems. Asian Journal of Control, 2019, 21(2): 660−673 [9] Yang Y, Li Y F, Yue D, Yue W B. Adaptive event-triggered consensus control of a class of second-order nonlinear multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(12): 5010−5020 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2900266 [10] Li Z X, Yan J, Yu W W, Qiu J L. Adaptive event-triggered control for unknown second-order nonlinear multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(12): 6131−6140 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2964430 [11] Li X W, Tang Y, Karimi H R. Consensus of multi-agent systems via fully distributed event-triggered control. Automatica, 2020, 116: Article No. 108898 [12] Du Z X, Xue H, Ahn C K, Liang H J. Event-triggered adaptive tracking control for high-order multi-agent systems with unknown control directions. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2021, 31: 8937−8960 doi: 10.1002/rnc.5768 [13] Luo Y P, Gao X T, Cao J D, Kashkynbayev A. Event-triggered consensus for delayed second-order leader-following heterogeneous multi-agent systems under input saturated condition. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2023, 29(21−22): 4908−4923 doi: 10.1177/10775463221126313 [14] Chen J J, Jiang P, Chen B S, Zeng Z G. Adaptive neural event-triggered consensus control for unknown nonlinear second-order delayed multi-agent systems. Neurocomputing, 2024, 598 : Article No. 128067 [15] Almeida J, Silvestre C, Pascoal A M. Event-triggered output synchronization of heterogeneous multi-agent systems. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2017, 27(8): 1302−1338 doi: 10.1002/rnc.3629 [16] Wang S H, Zheng S Q, Ahn C K, Shi P, Jiang X W. Event-triggered cooperative control for uncertain multi-agent systems and applications. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2021, 33(12): 7221−7245 [17] Liu W, Huang J. Cooperative global robust output regulation for a class of nonlinear mulit-agent systems by distributed event-triggered control. Automatica, 2018, 93: 138−148 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.03.062 [18] Long J, Wang W, Wen C Y, Huang J S, Lv J H. Output feedback based adaptive consensus tracking for uncertain heterogeneous multi-agent systems with event-triggered communication. Automatica, 2022, 136: Article No. 110049 [19] Liu Y X, Wu X K, Long J, Wang W. Event-triggered distributed adaptive leaderless consensus of uncertain heterogeneous nonlinear multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2024, 71(5): 2694−2698 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2023.3348763 [20] Zhao Y, Xian C X, Wen G H, Huang P F, Ren W. Design of distributed event-triggered average tracking algorithms for homogeneous and heterogeneous multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(3): 1269−1284 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3060714 [21] Wang X, Sun J, Deng F, Wang G, Chen J. Event-triggered consensus control of heterogeneous multi-agent systems: Model and data-based approaches. Science China Information Science, 2023, 66: Article No. 192201 [22] Amini A, Asif A, Mohammadi A. Formation-containment control using dynamic event-triggering mechanism for multi-agent systems. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7 (5): 1235−1248 [23] Choi Y H, Yoo S J. Neural-network-based distributed asynchronous event-triggered consensus tracking of a class of uncertain nonlinear multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(7): 2965−2979 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3047945 [24] Qian Y Y, Liu L, Feng G. Output consensus of heterogeneous linear multi-agent systems with adaptive event-triggered control. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(6): 2606− 2613 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2868997 [25] Yang Q Q, Li X B, Li J. Output consensus for networked heterogeneous nonlinear multi-agent systems by distributed event-triggered control. International Journal of Control, 2022, 95(7): 1850−1863 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2021.1878279 [26] Zheng S Q, Shi P, Zhang H Y. Semiglobal periodic event-triggered output regulation for nonlinear multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(1): 393−399 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3142123 [27] Li Z X, Yan J, Yu W W, Qiu J L. Event-triggered control for a class of nonlinear multi-agent systems with directed graph. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Systems, 2021, 51(11): 6986−6993 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2962827 [28] Khalil H K. Nonlinear Systems (3rd Edition). New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2002. -




 下载:
下载: