Multi-robot Collaborative Perception and Capture Based on Variational Sparse Gaussian Process
-
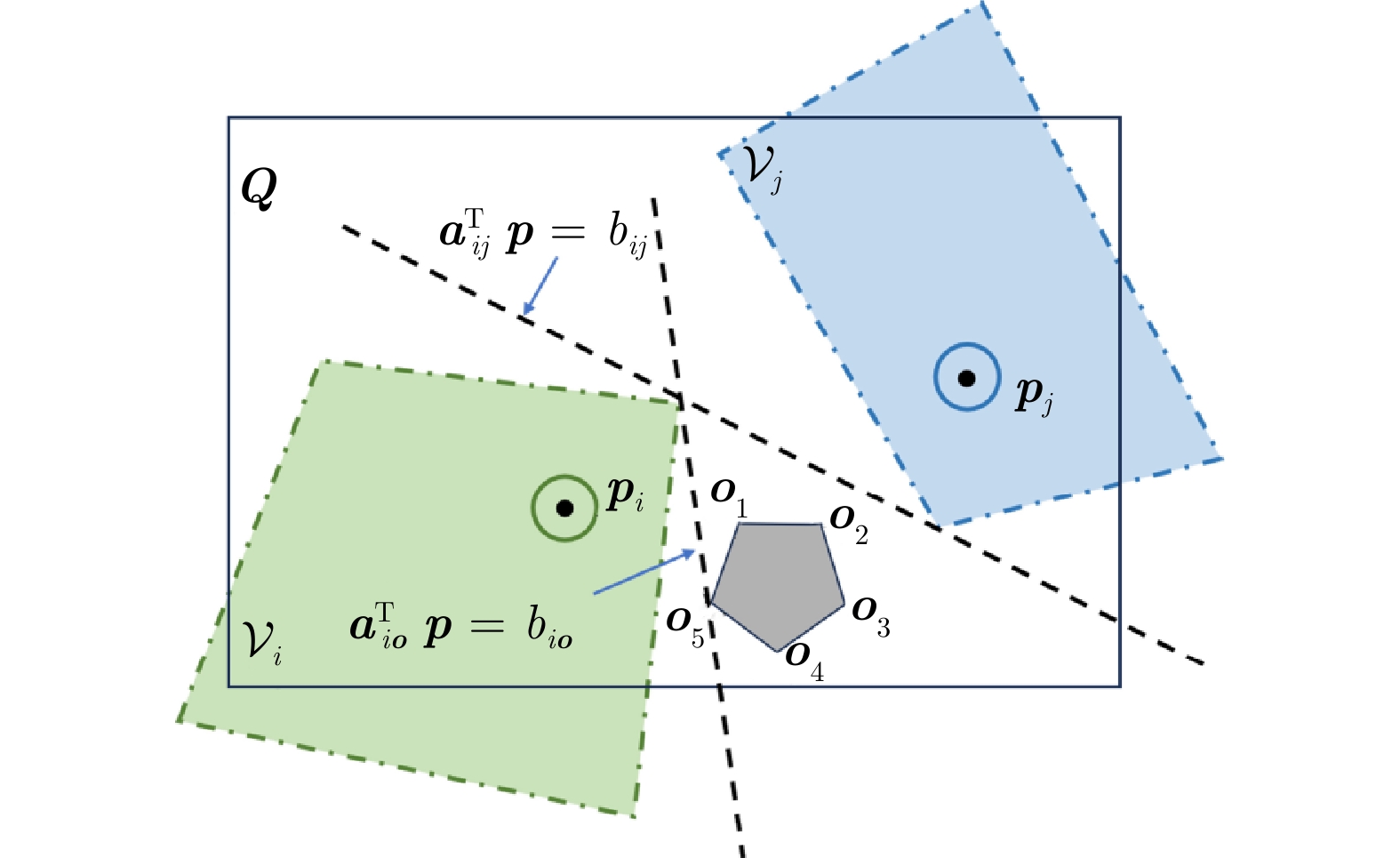
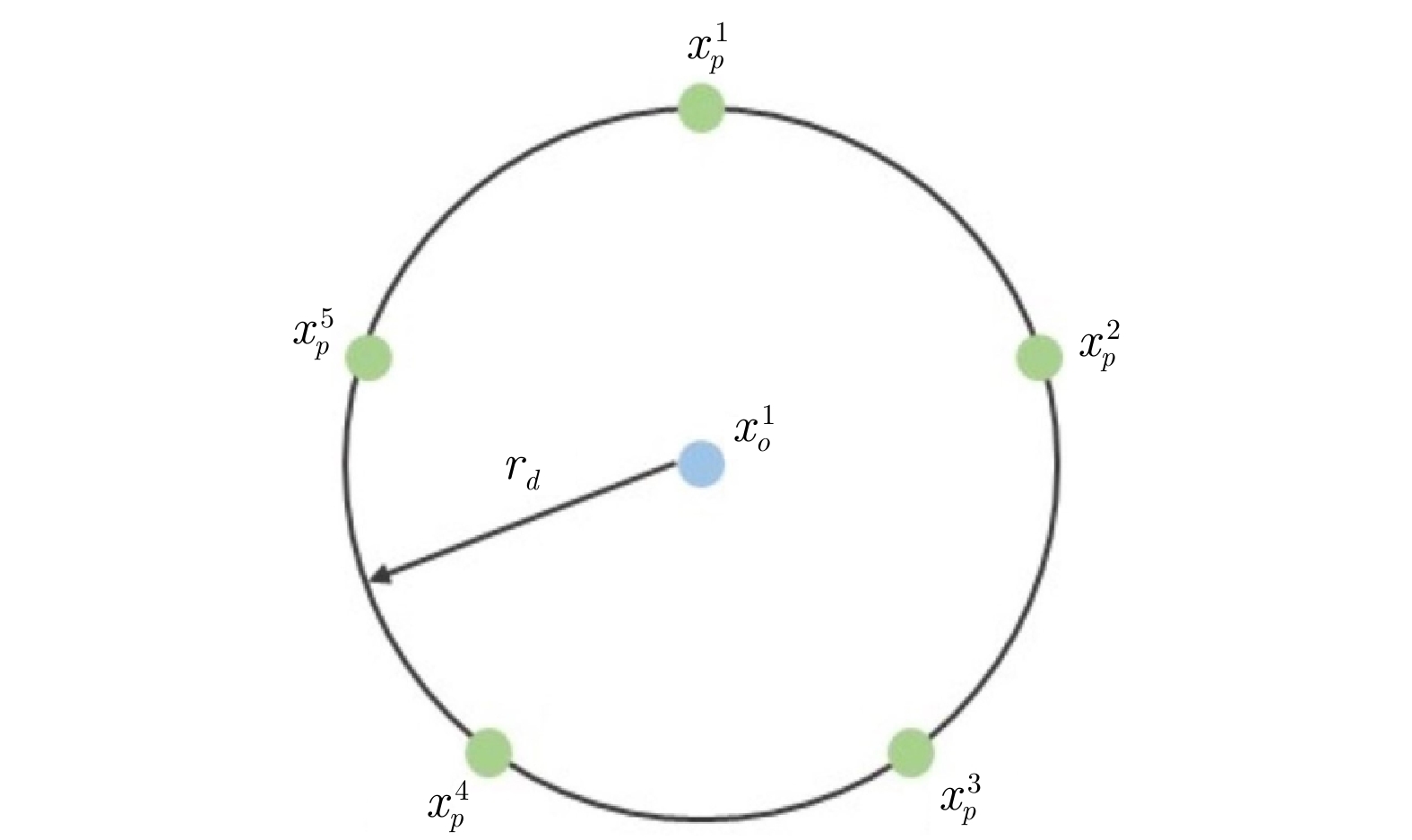
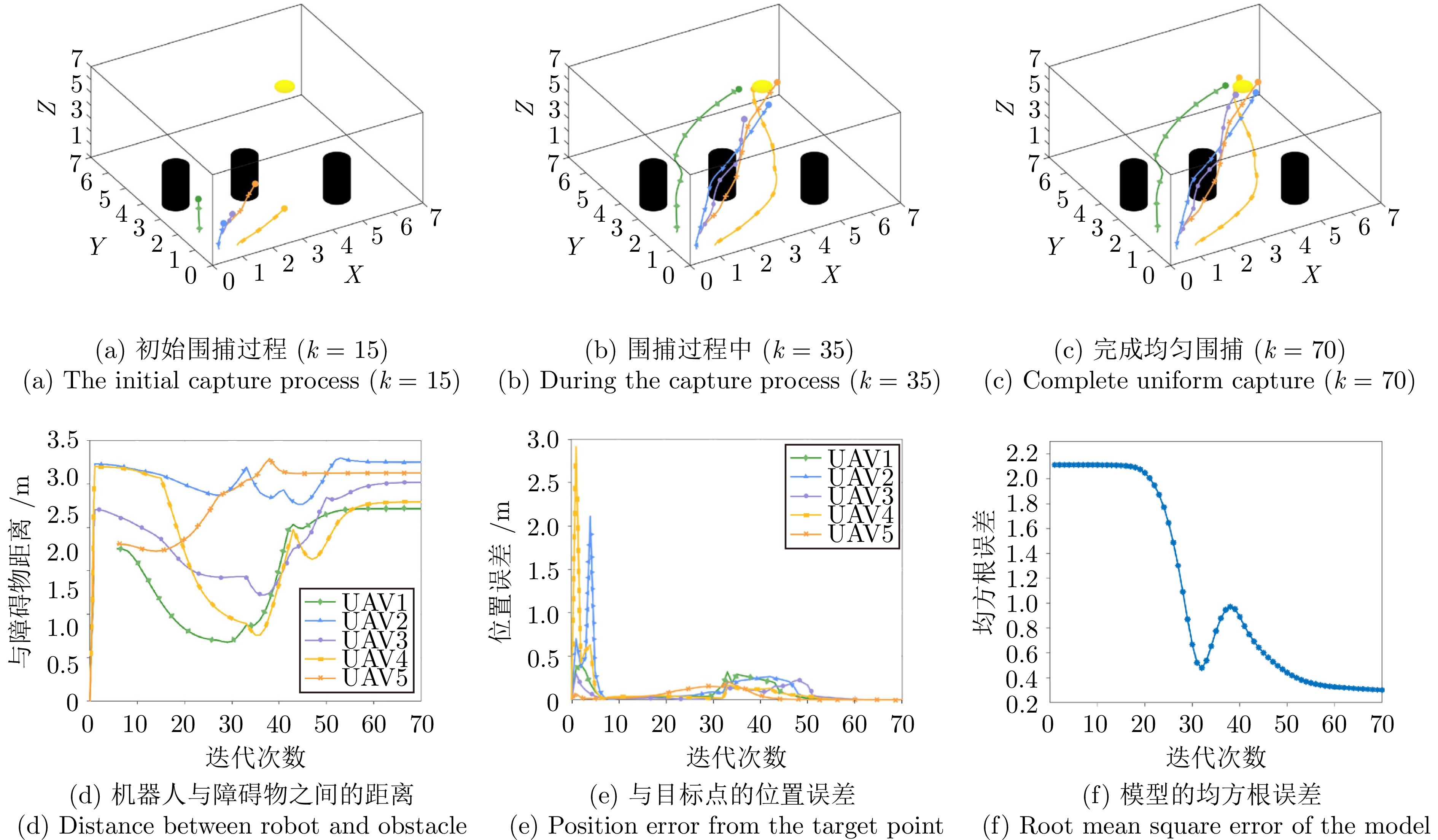
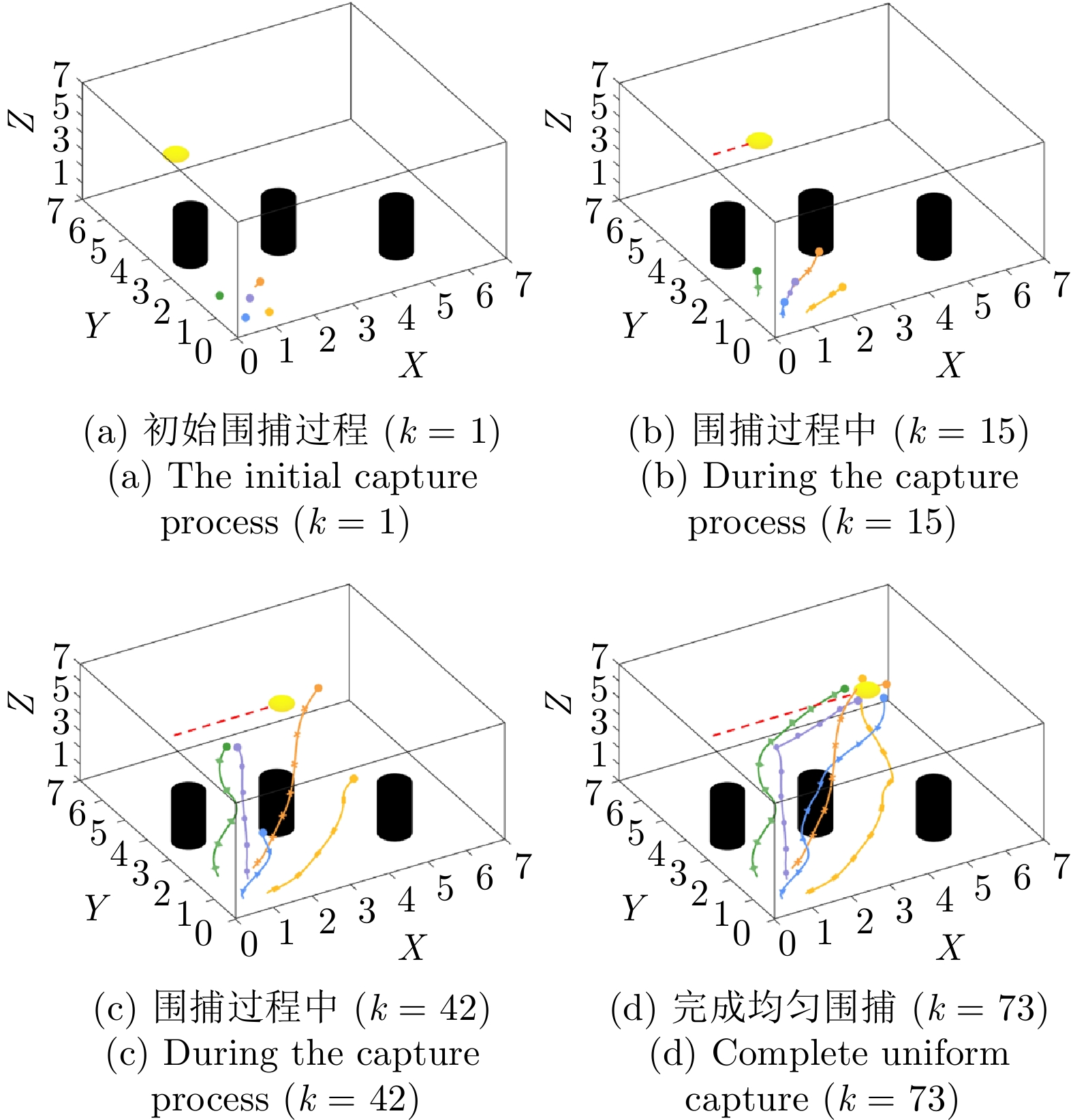
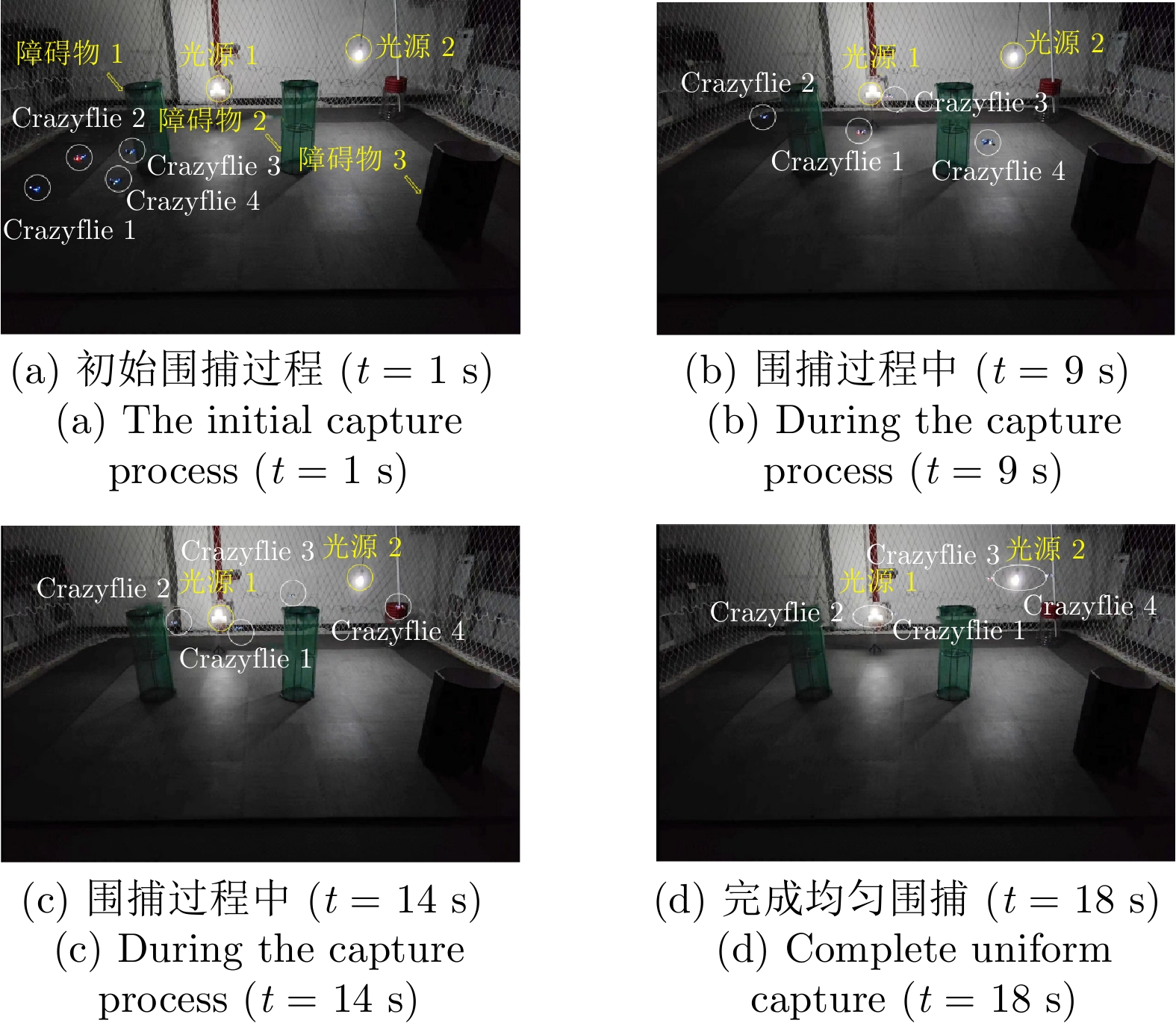
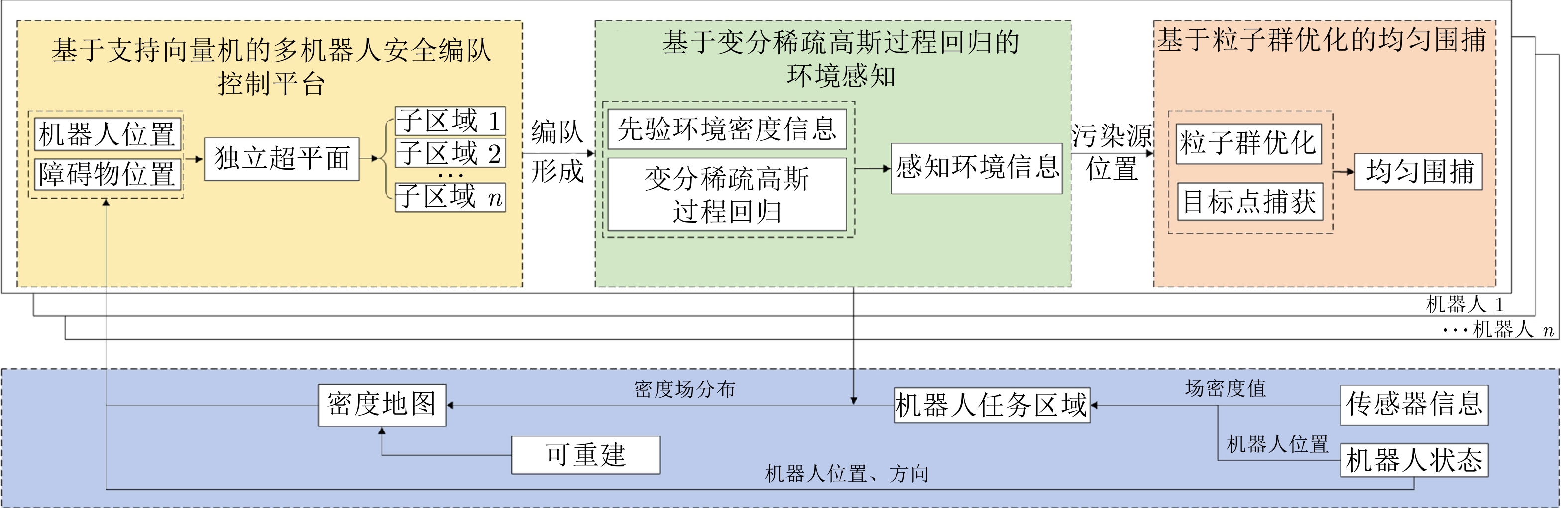
摘要: 针对未知环境下的多机器人环境感知和围捕问题, 提出一种基于变分稀疏高斯过程回归的分布式感知与围捕算法. 考虑到传统高斯过程回归不适合处理大量数据的问题, 在这项工作中, 首先考虑障碍物的影响, 以引入分离超平面的质心维诺划分算法为机器人动态规划任务区域; 其次, 利用多机器人在任务区域中的移动探索获取环境信息, 并通过变分自由方法来近似模型的后验分布, 完成对未知环境的感知; 最后, 基于粒子群优算法为围捕机器人动态分配围捕点, 实现多机器人的全方位均匀围捕. 通过仿真实验证明, 该算法能够适用于单源、多源以及动态源的围捕, 且能够在保证多机器人编队安全性的同时, 实现较高的迭代速度, 最终成功实现均匀围捕.
-
关键词:
- 多机器人 /
- 质心维诺划分 /
- 变分稀疏高斯过程回归 /
- 围捕 /
- 协同感知
Abstract: To solve the problem of multi-robot environmental perception and capture in unknown environments. Proposing a distributed perception and capture algorithm based on variational sparse Gaussian process regression. Considering the issue that traditional Gaussian process regression is not suitable for handling large amounts of data, in this paper, the influence of obstacles is first taken into account to introduce the centroidal Voronoi tessinations algorithm with separating hyperplanes for dynamic planning of the task area for robots; Secondly, the movement exploration of multi-robot in the task area is used to obtain environmental information, and the variational free energy method is used to approximate the posterior distribution of the model to complete the perception of the unknown environment; Finally, the particleswarm optimization algorithm is used to dynamically assign capture points for the capturing robots, achieving all-round uniform capture of multi-robot. Simulation experiments prove that this algorithm is applicable to single-source, multi-source and dynamic source environments, and can achieve high iteration speed while ensuring the safety of the multi-robot formation, ultimately successfully achieving uniform capture. -
表 1 分类指标及相关工作
Table 1 The classification indicators and related work
表 2 仿真参数设置
Table 2 Simulation parameter settings
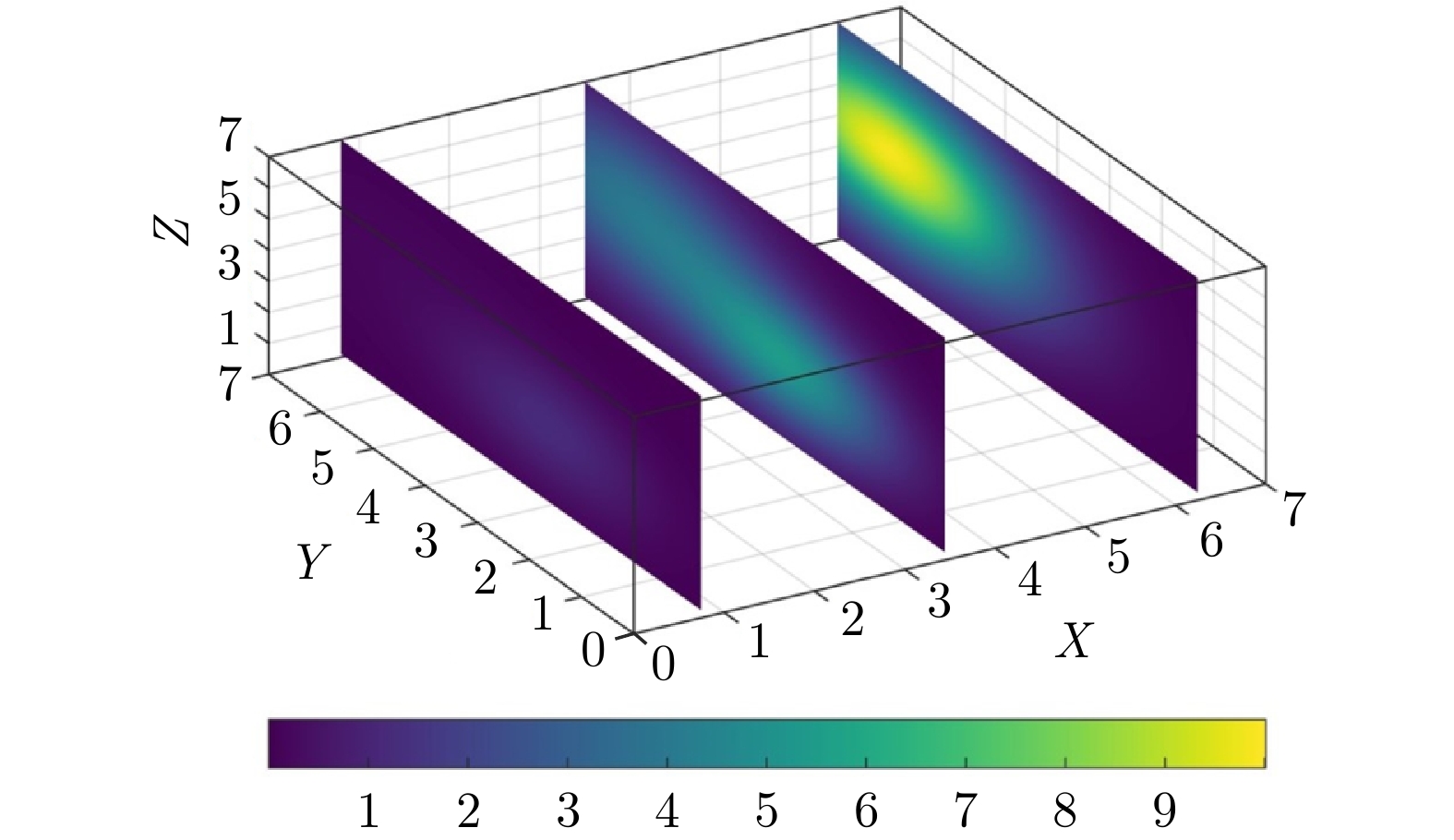
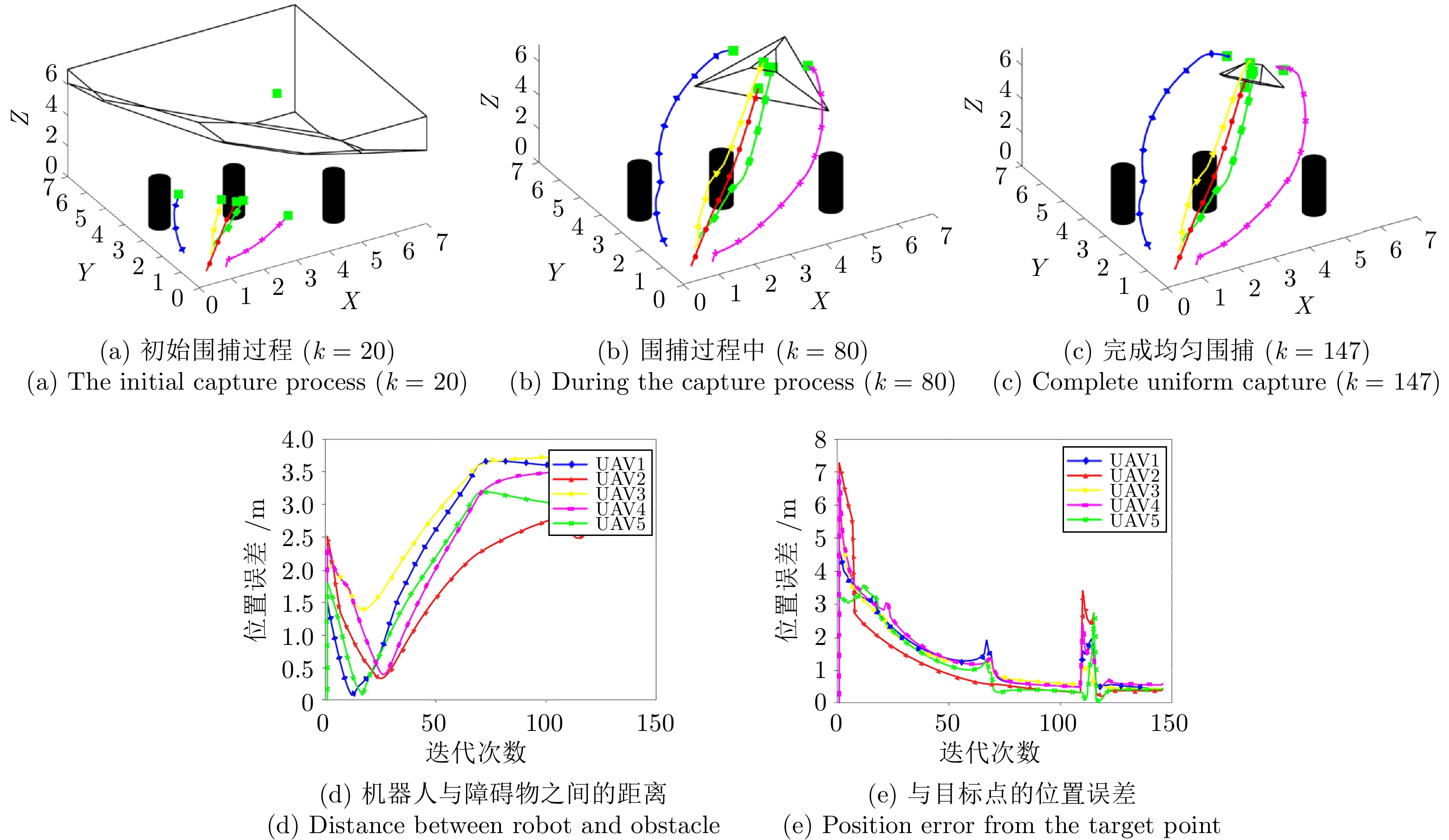
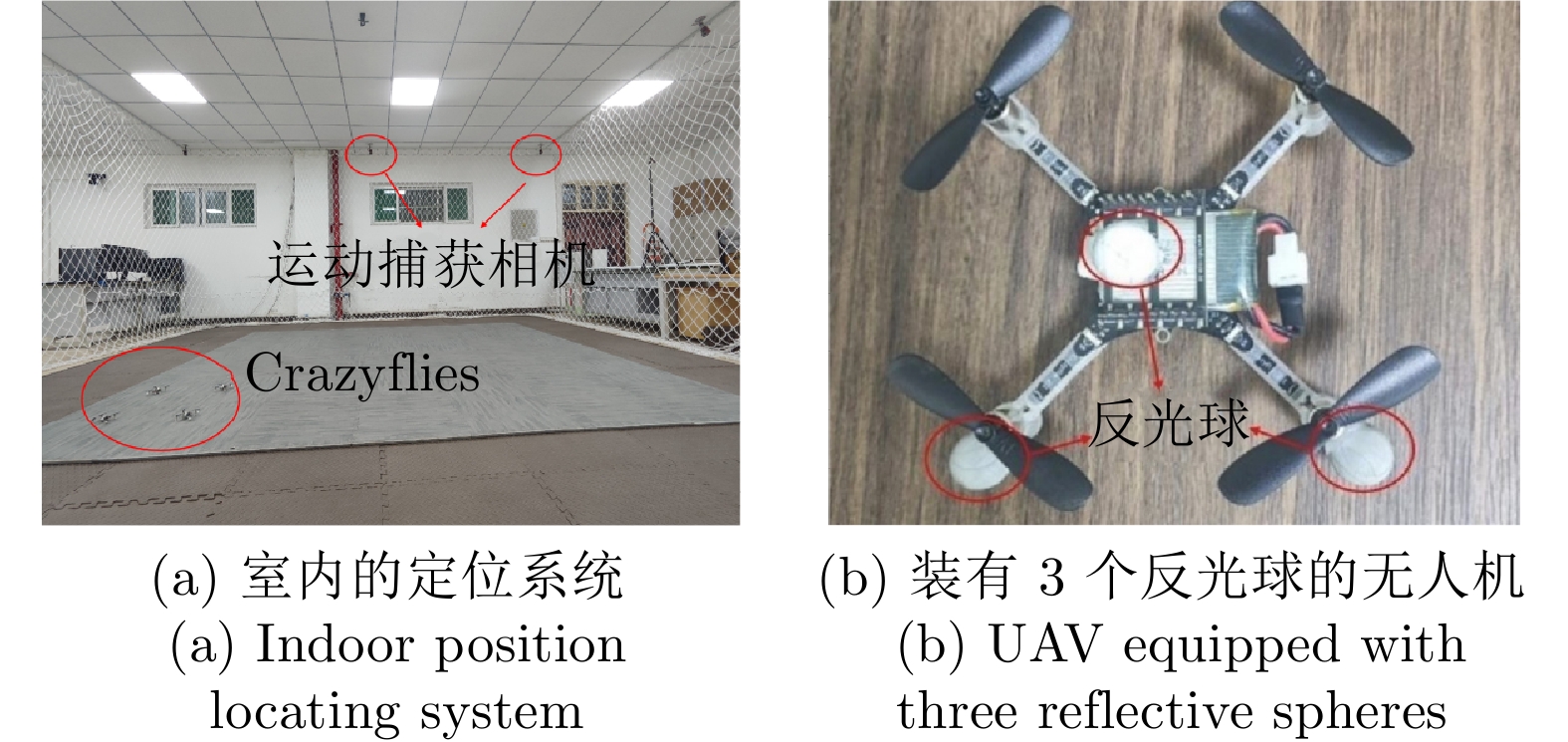
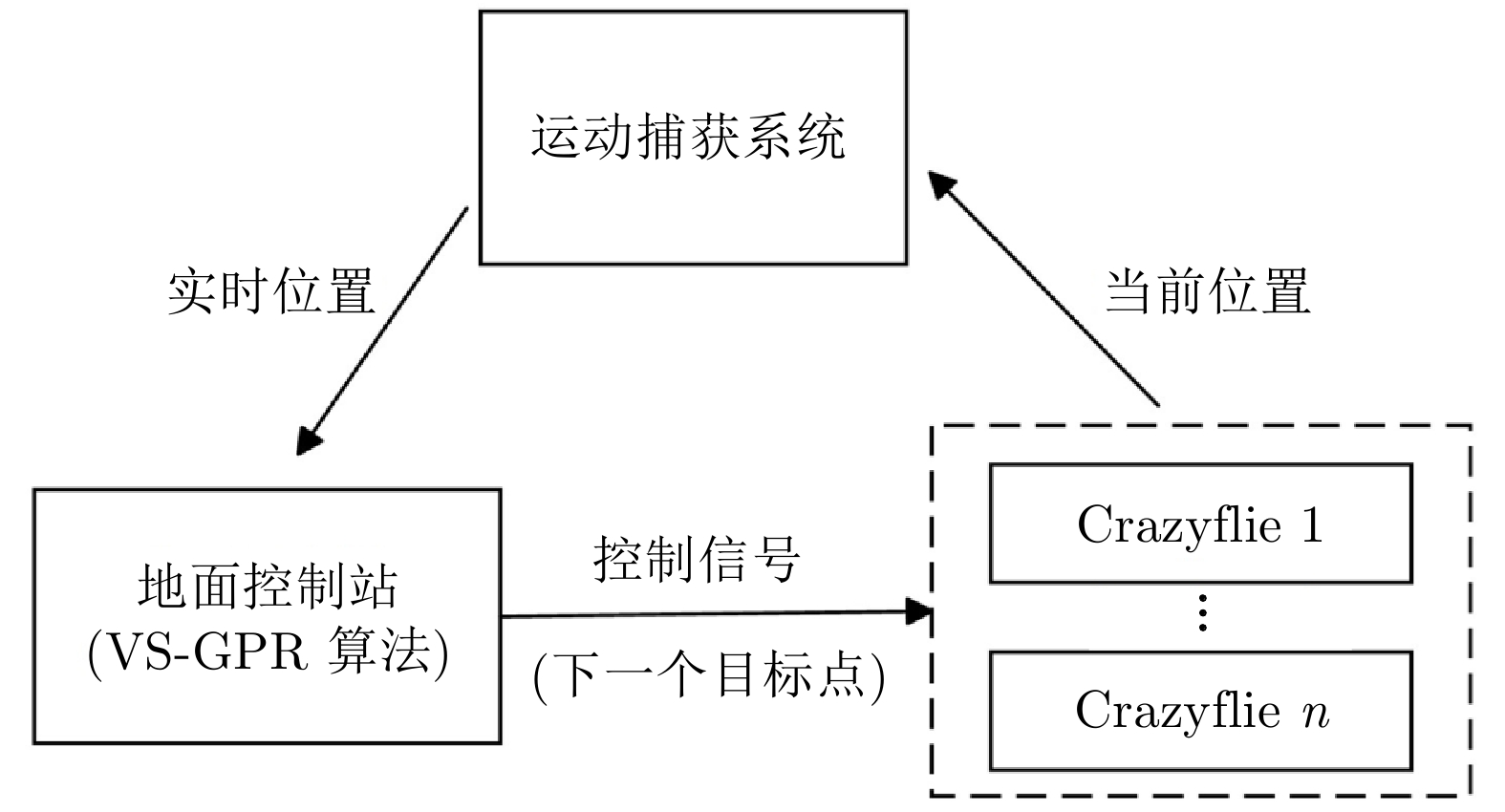
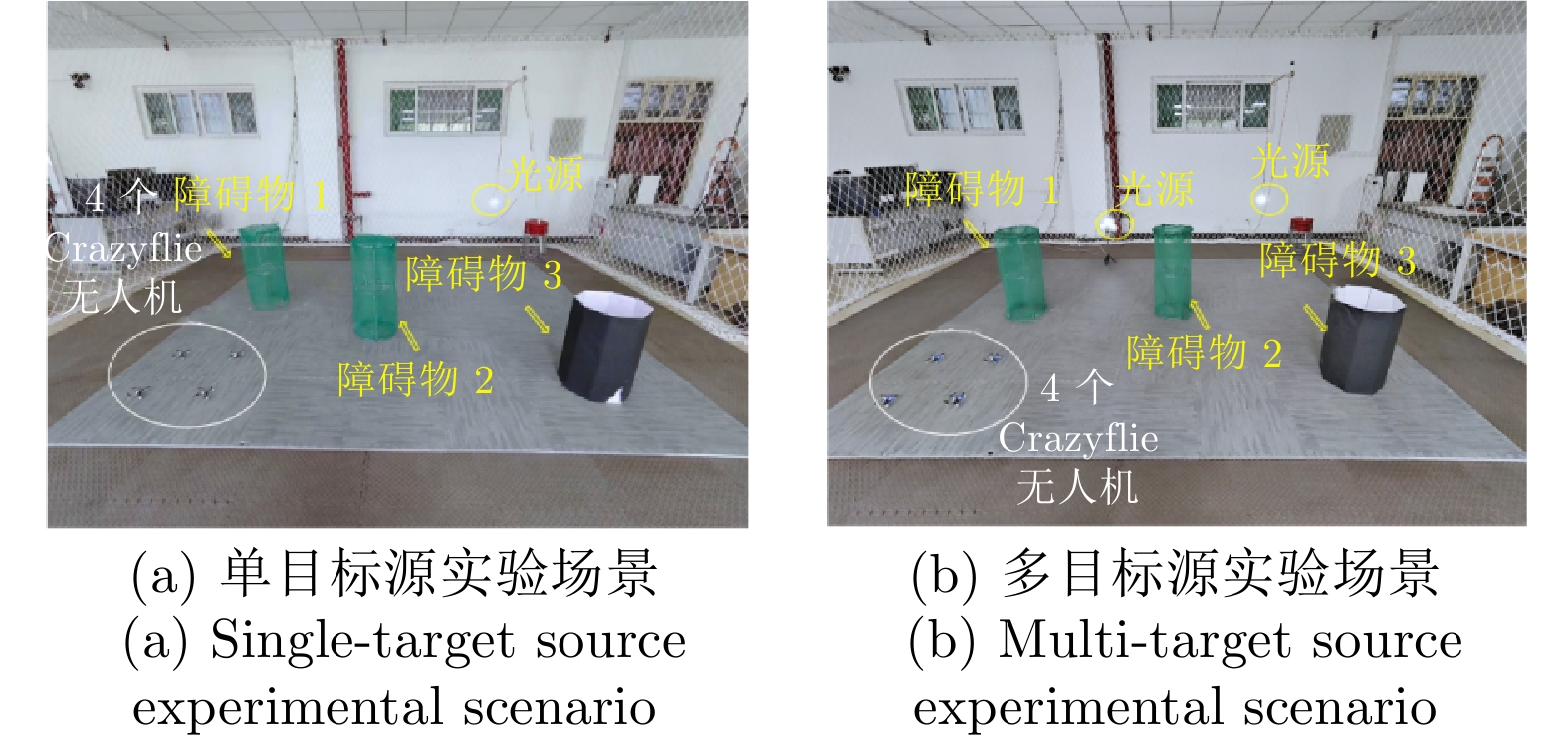
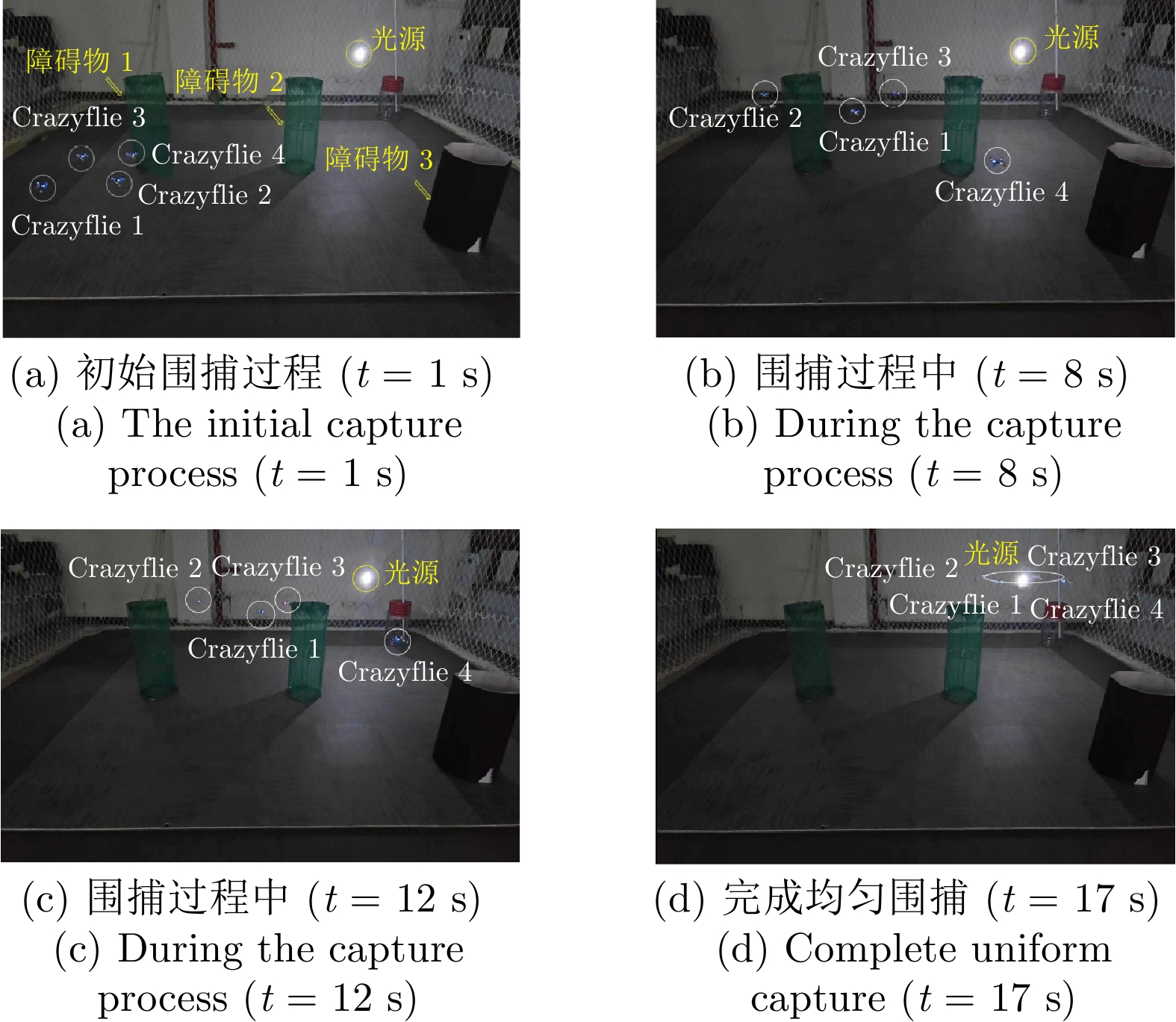
参数名称 参数值 任务切换阈值 4.5 障碍物的二维坐标(m) (5.0, 1.5), (1.2, 3.5), (4.0, 5.0) 障碍物尺寸 0.5 m$\times$0.5 m$\times$3.0 m UAV最大速度 0.3 m/s 机器人和待围捕点最小距离 0.5 m 表 3 单污染源下两种围捕方法对比
Table 3 Comparison of two capture strategies for a single pollution source
围捕方法 运行时间(s) 迭代次数 ODMV围捕 197.62 180 VS-GPR围捕 102.67 70 表 4 多机器人围捕多污染源用时对比
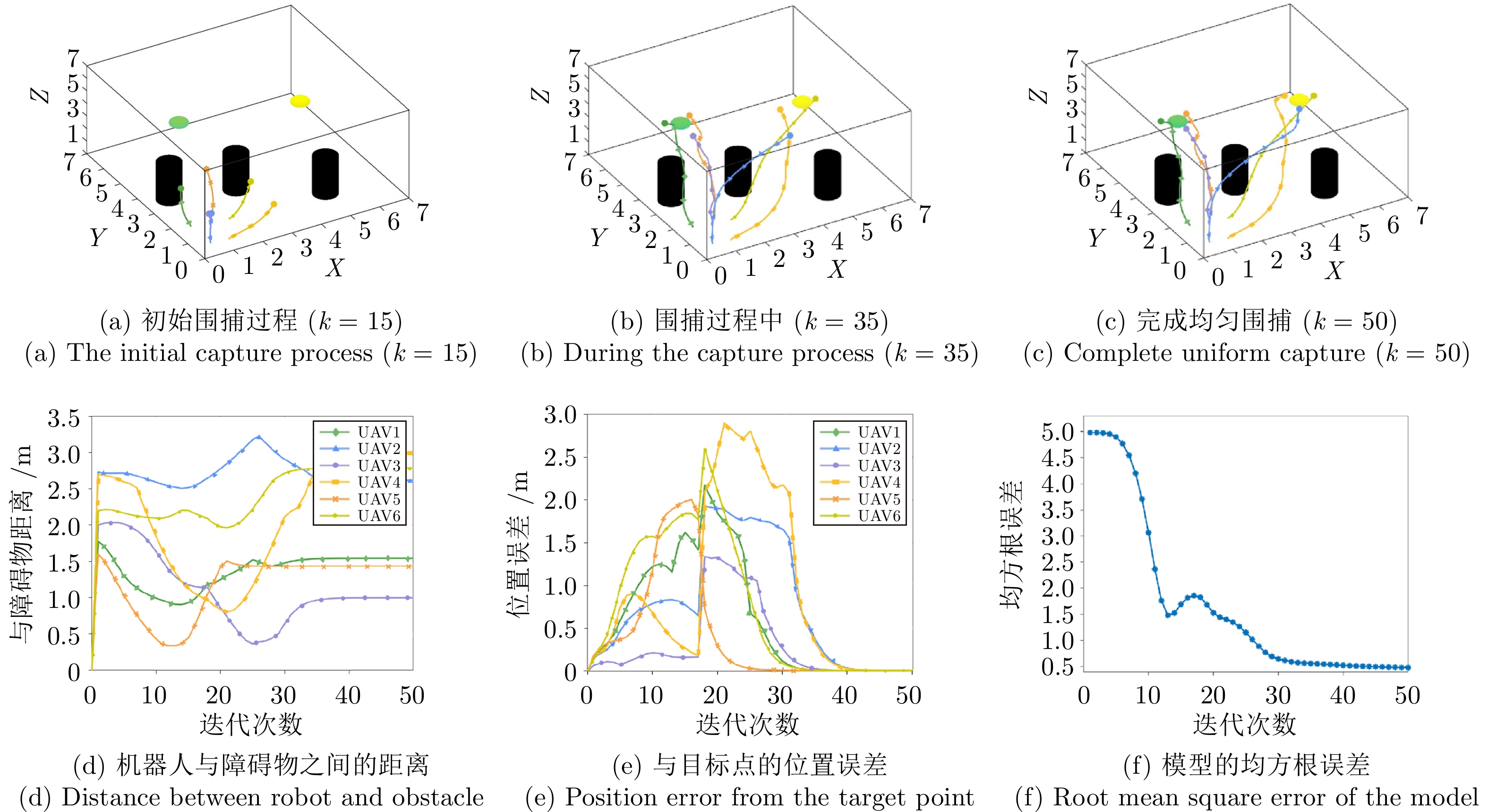
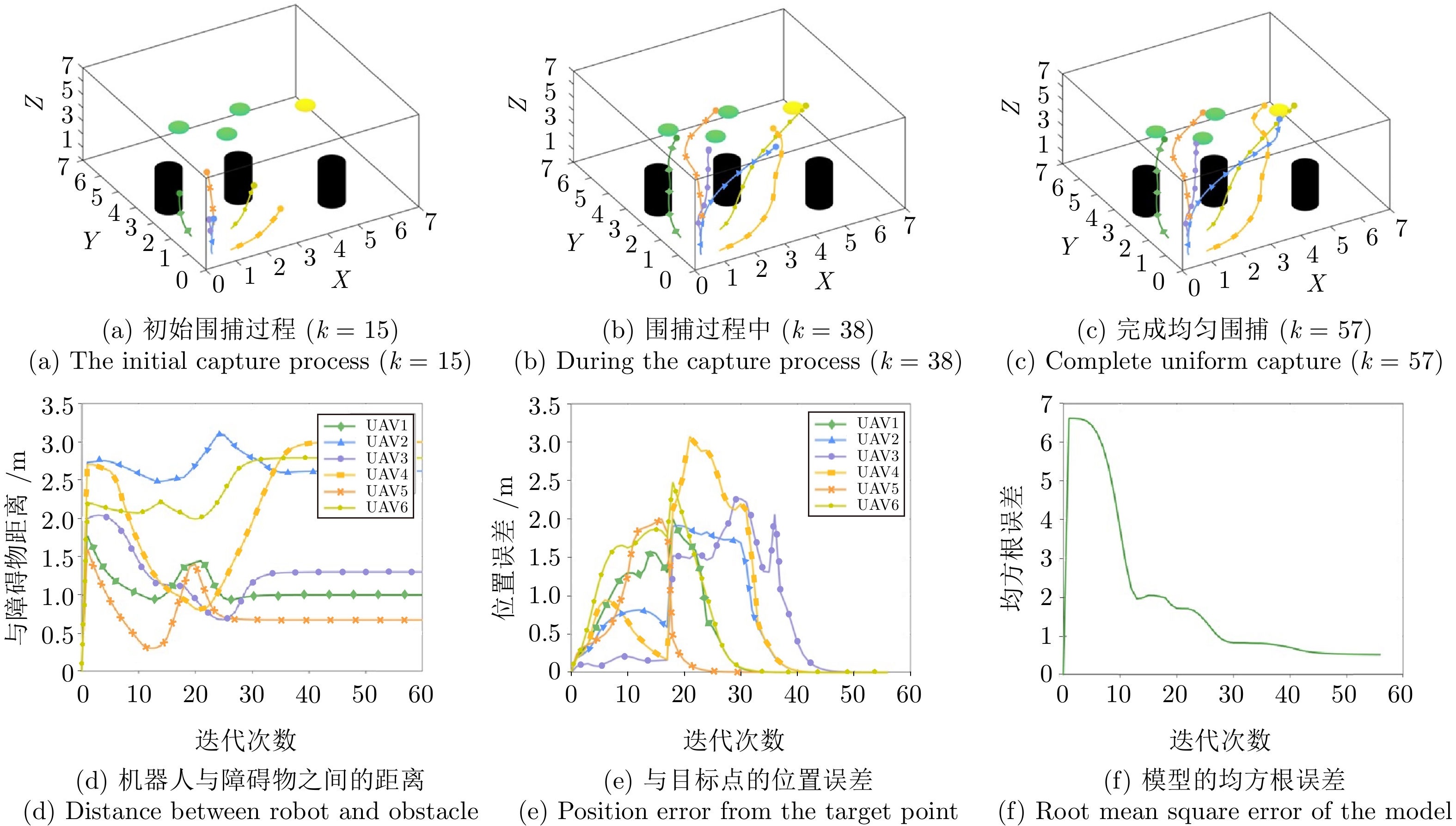
Table 4 Comparison of time consumption for multi-robot capture multi-pollution source
污染源数量 GPR耗时(s) VS-GPR耗时(s) 2个 278.63 102.67 3个 319.37 113.41 4个 345.56 118.32 5个 352.17 118.84 -
[1] 蒲志强, 易建强, 刘振, 丘腾海, 孙金林, 李非墨. 知识和数据协同驱动的群体智能决策方法研究综述. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(3): 627−643Pu Zhi-Qiang, Yi Jian-Qiang, Liu Zhen, Qiu Teng-Hai, Sun Jin-Lin, Li Fei-Mo. A review of the research on swarm intelligence decision-making methods driven by knowledge and data collaboration. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 627−643 [2] Chung T H, Hollinger G A, Isler V. Search and pursuit-evasion in mobile robotics: A survey. Autonomous Robots, 2011, 31(4): 299−316 doi: 10.1007/s10514-011-9241-4 [3] Zhang J, Lu Y, Wu Y, Wang C, Zang D, Abusorrah A, et al. PSO-based sparse source location in large-scale environments with a UAV swarm. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(5): 5249−5258 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3237570 [4] Karagüzel T A, Turgut A E, Eiben A E, Ferrante E. Collective gradient perception with a flying robot swarm. Swarm Intelligence, 2023, 17(1): 117−146 [5] Jang H, Park M, Oh H. Improved Socialtaxis for information-theoretic source search using cooperative multiple agents in turbulent environments. Expert Systems With Applications, 2023, 225: Article No. 120033 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120033 [6] Chen L, Zhou C, Wang Y, Zong Y, Lu T, Chen C. Autonomous search investigation for radioactive leaked source based on an updated infotaxis method during nuclear emergency rescue. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2024, 416: Article No. 112769 doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2023.112769 [7] Ma H, Zhang T, Wu Y, Calmon F P, Li N. Gaussian max-value entropy search for multi-agent Bayesian optimization. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Detroit MI, USA: IEEE, 2023. 10028−10035 [8] Xu Y, Zheng R, Zhang S, Liu M, Huang S. CARE: Confidence-rich autonomous robot exploration using Bayesian kernel inference and optimization. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023, 8(10): 6755−6762 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3313054 [9] Jabeen M, Meng Q H, Jing T, Hou H R. Robot odor source localization in indoor environments based on gradient adaptive extremum seeking search. Building and Environment, 2023, 229: Article No. 109983 doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.109983 [10] Li H, Yuan J, Yuan H. An active olfaction approach using deep reinforcement learning for indoor attenuation odor source localization. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(9): 14561−14572 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3373610 [11] Latif E, Parasuraman R. Communication-efficient multi-robot exploration using coverage-biased distributed Q-learning. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024, 9(3): 2622−2629 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3358095 [12] Liao Y, Chen A, Cai H, Lu J, Zhang W, Lin B, et al. An experimental study on locating time-varying pollutant sources in a dynamic indoor environment with mechanical ventilation based on multi-robot cooperation. Journal of Building Engineering, 2023, 67: Article No. 105962 doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2023.105962 [13] Yu L, Huo S, Wang Z, Li K. Hybrid attention-oriented experience replay for deep reinforcement learning and its application to a multi-robot cooperative hunting problem. Neurocomputing, 2023, 523: 44−57 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.12.020 [14] Qu X, Gan W, Song D, Zhou L. Pursuit-evasion game strategy of USV based on deep reinforcement learning in complex multi-obstacle environment. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 273: Article No. 114016 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114016 [15] Zhao Z, Hu Q, Feng H, Feng X, Su W. A cooperative hunting method for multi-AUV swarm in underwater weak information environment with obstacles. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2022, 10(9): Article No. 1266 doi: 10.3390/jmse10091266 [16] Zhou M, Wang Z, Wang J, Cao Z. Multi-robot collaborative hunting in cluttered environments with obstacle-avoiding Voronoi cells. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(7): 1643−1655 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.124041 [17] Wang X, Xi L, Ding Y, Chen B M. Distributed encirclement and capture of multiple pursuers with collision avoidance. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 71(7): 7520−7530 [18] Li B, Wang J M, Song C, Yang Z P, Wan K F, Zhang Q F. Multi-UAV roundup strategy method based on deep reinforcement learning CEL-MADDPG algorithm. Expert Systems With Applications, 2024, 245: Article No. 123018 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.123018 [19] Zhao Z Y, Zhang Y Z, Feng X L, Jiang C, Su W B, Hu Q. A dynamic velocity potential field method for multi-AUV cooperative hunting tasks. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 295: Article No. 116813 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.116813 [20] Fu X W, Zhang Y X, Zhu J D, Wang Q L. Bioinspired cooperative control method of a pursuer group vs. a faster evader in a limited area. Applied Intelligence, 2023, 53(6): 6736−6752 doi: 10.1007/s10489-022-03892-8 [21] Tian B, Li P, Lu H, Zong Q, He L. Distributed pursuit of an evader with collision and obstacle avoidance. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 52(12): 13512−13520 [22] Cao K, Chen Y Q, Gao S, Yan K, Zhang J H, An D. Omni-directional capture for multi-drone based on 3D-Voronoi tessellation. Drones, 2023, 7(7): Article No. 458 doi: 10.3390/drones7070458 -




 下载:
下载: