Privacy-preserving Distributed Optimization Algorithm Based on Elliptic Curve ELGamal
-
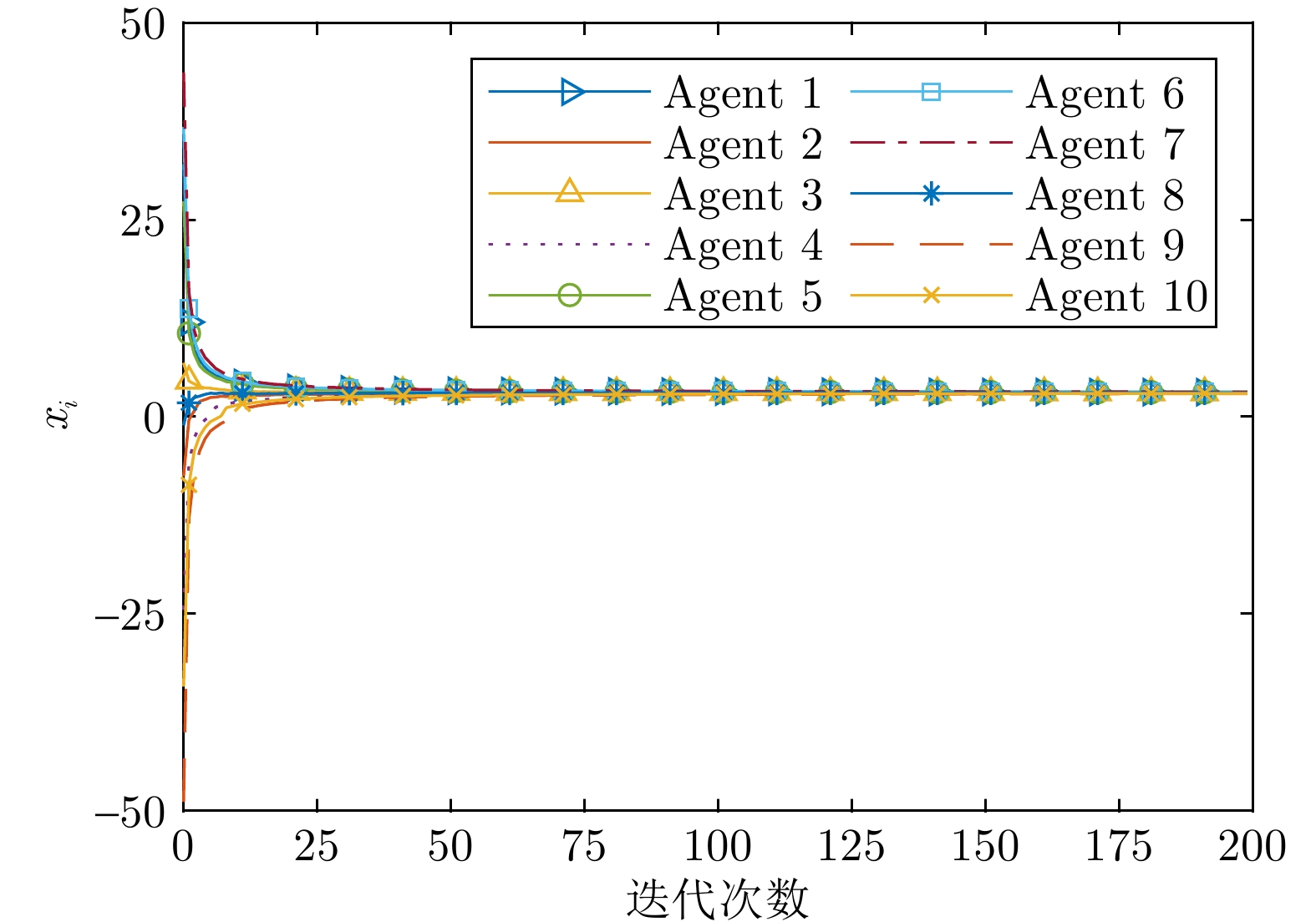
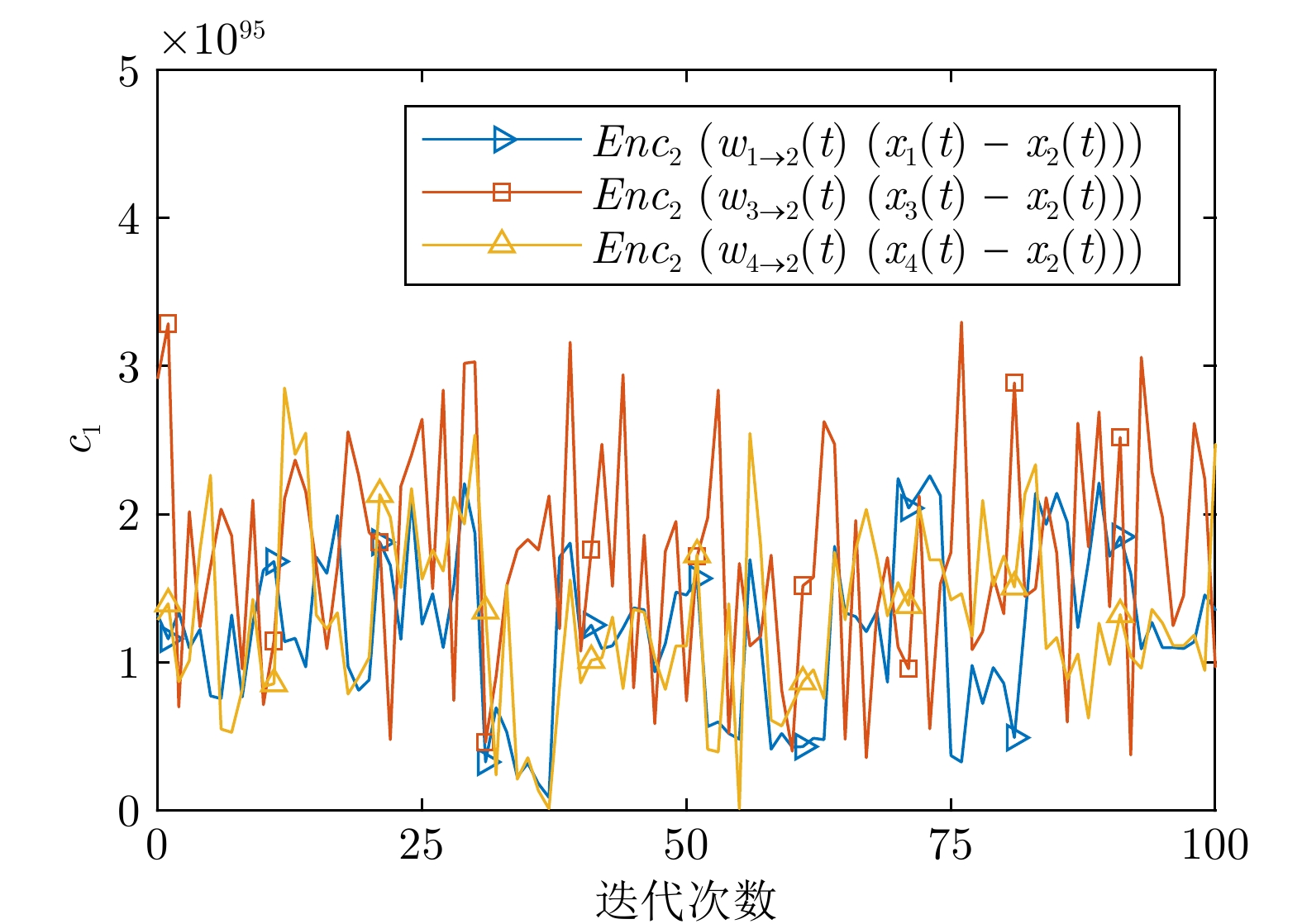
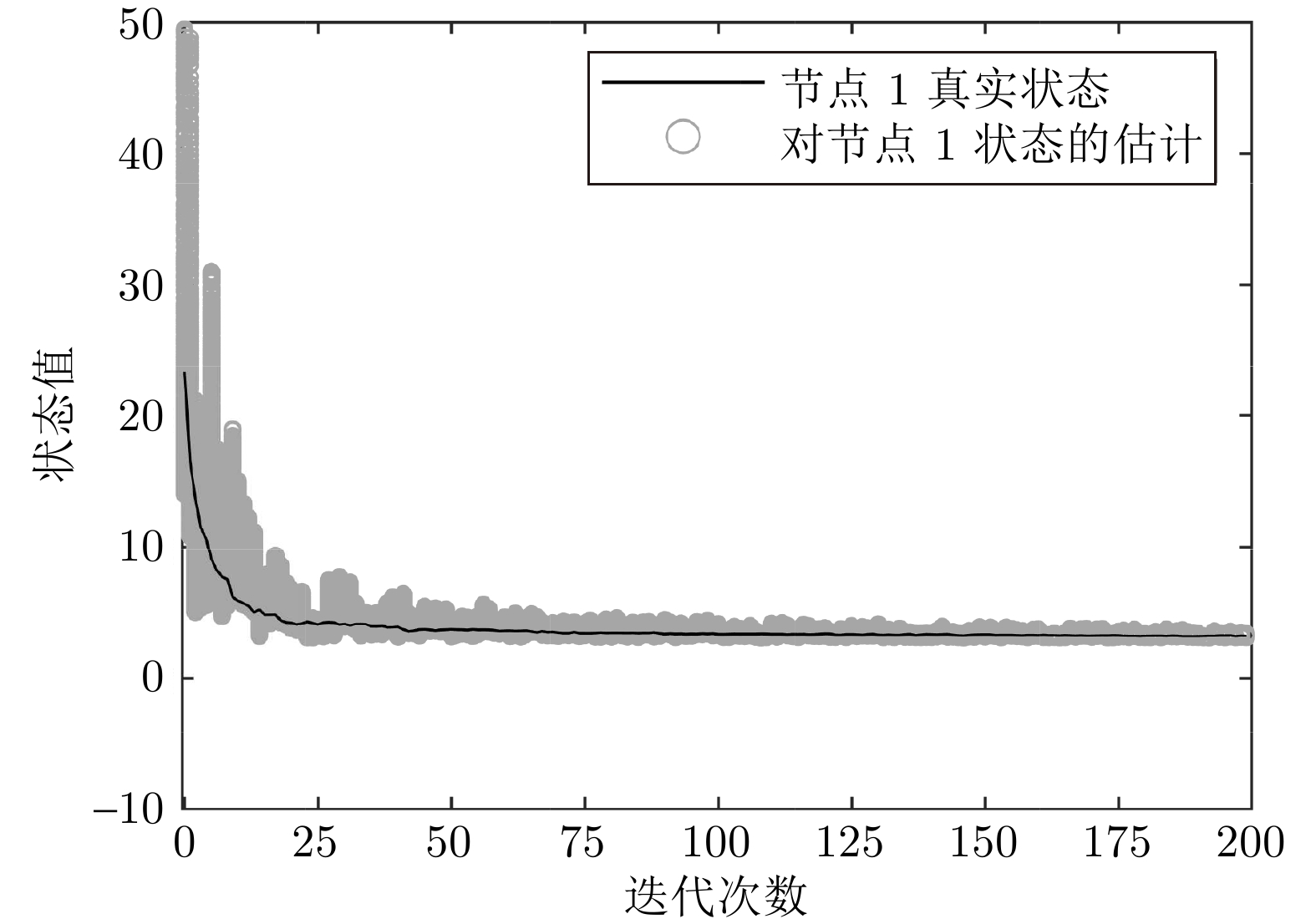
摘要: 研究一类考虑节点隐私保护的分布式优化问题, 目标为保护各智能体的隐私信息不被泄露, 并最小化所有智能体局部成本函数之和. 首先, 针对无向连通图, 提出一种基于椭圆曲线密码机制的分布式凸优化算法. 通过设计底层权重矩阵, 将基于椭圆曲线的ELGamal同态加密和数字签名与分布式次梯度算法相结合, 克服了椭圆曲线密码机制与分布式一致性策略无法结合的难点. 在无第三方或聚合器的场景下, 该算法实现了系统的隐私保护. 理论分析表明, 该算法能够渐近收敛至全局最优解, 并适用于时变通信拓扑的动态环境. 此外, 算法能有效保护智能体的状态和成本函数不受来自诚实但好奇攻击者、外部窃听者和篡改攻击者的威胁. 最后, 通过数值仿真验证了算法的有效性.Abstract: In this paper, we investigate a class of distributed optimization problems considering node privacy protection, aiming to prevent the disclosure of private information of each agent while minimizing the sum of local cost functions across all agents. Firstly, for an undirected connected graph, a distributed convex optimization algorithm based on elliptic curve cryptography is proposed. By designing the underlying weight matrix, elliptic curve-based ELGamal homomorphic encryption and digital signatures are combined with the distributed subgradient algorithm, overcoming the difficulty of integrating elliptic curve cryptosystems with distributed consensus strategies. Without the need for a third party or aggregator, our algorithm achieves system privacy protection. Theoretical analysis shows that the algorithm can asymptotically converge to the global optimal solution and is suitable for dynamic environments with time-varying communication topologies. Moreover, the algorithm effectively safeguards the state and cost functions of agents from threats posed by curious but honest attackers, external eavesdroppers, and adversaries attempting tampering attacks. Finally, the effectiveness of the algorithm is validated through numerical simulations.
-
Key words:
- Distributed optimization /
- privacy protection /
- homomorphic encryption /
- elliptic curve
-
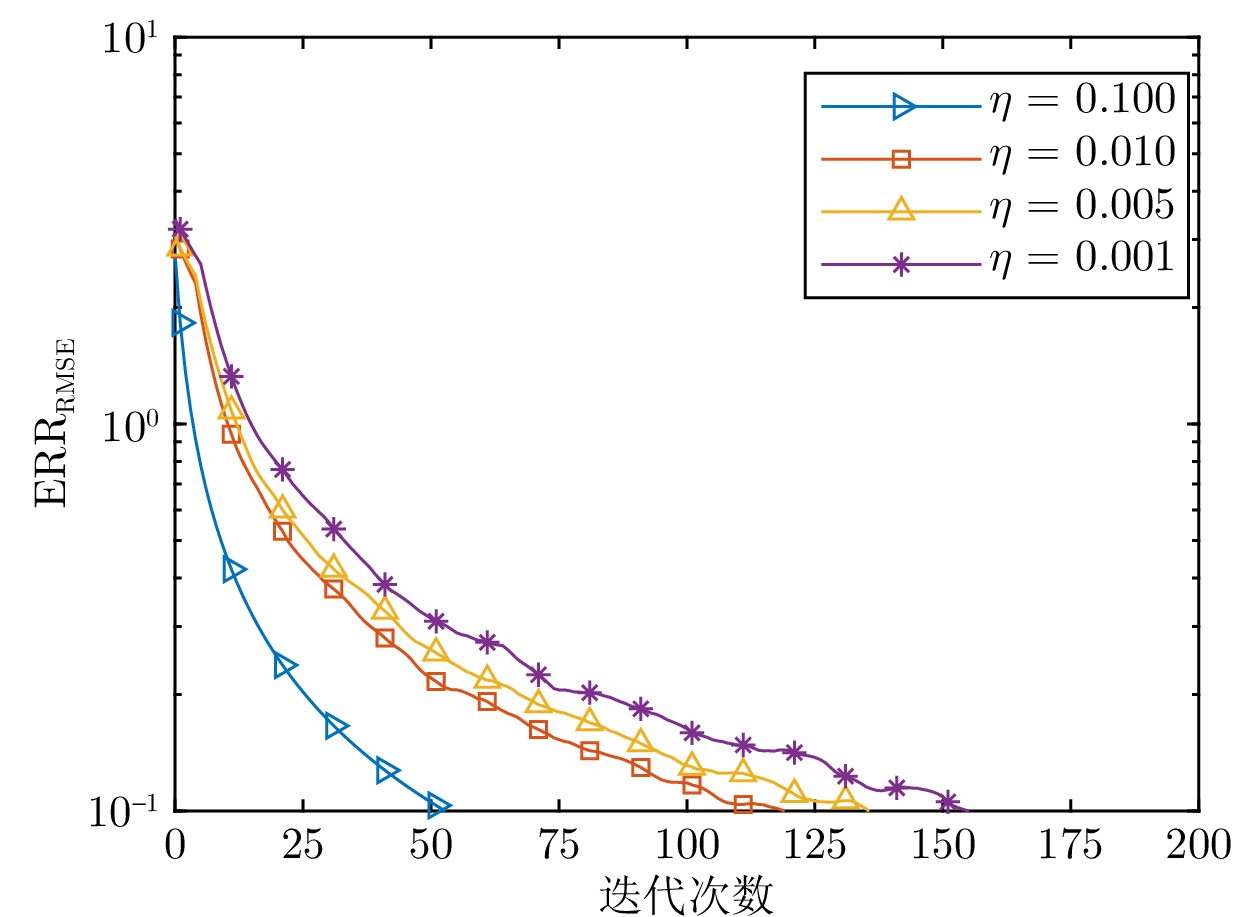
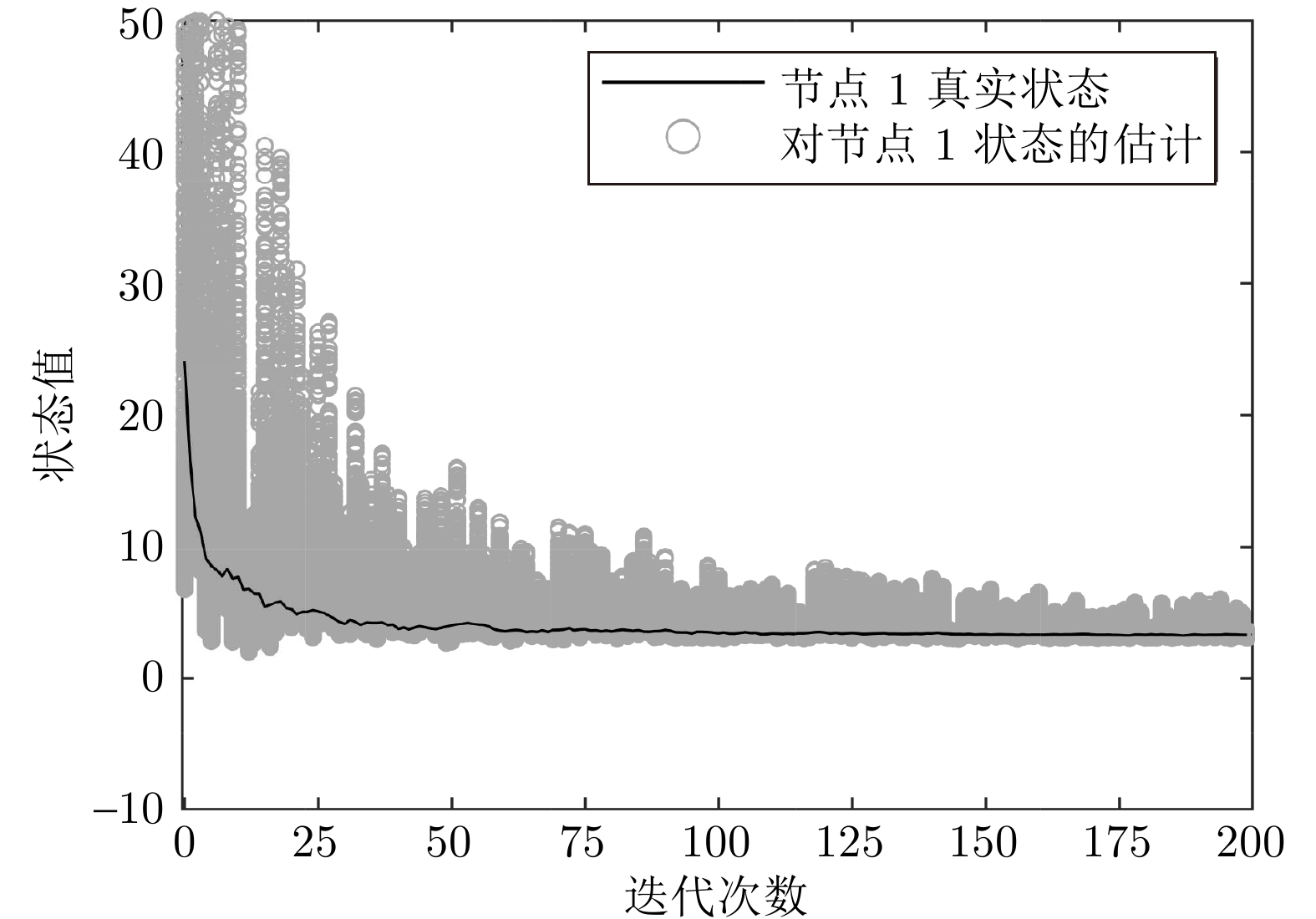
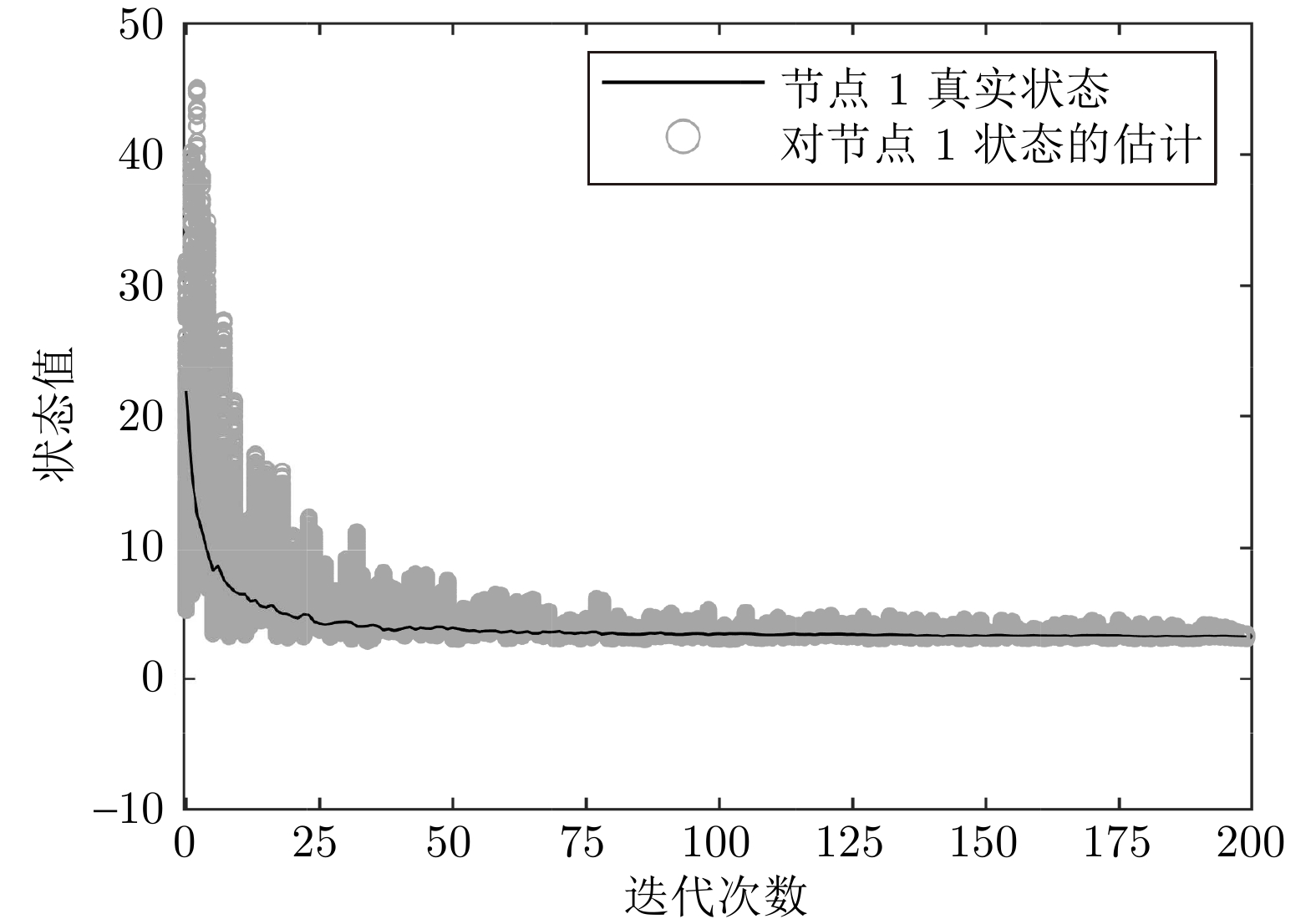
表 1 不同$\eta$值下算法1的均方根误差
Table 1 Root mean square error of algorithm 1 under different $\eta$ values
$\eta$ $\mathrm{ERR_{\mathrm{RMSE}}}$ $0.100$ $5.47 \times 10^{-4}$ $0.010$ $1.16 \times 10^{-3}$ $0.005$ $1.42 \times 10^{-3}$ $0.001$ $1.47 \times 10^{-3}$ 表 2 $N=5$时各种同态加密方案的计算时间 (s)
Table 2 Computation time of various homomorphic encryption schemes for $N=5$ (s)
表 3 $N=10$时各种同态加密方案的计算时间 (s)
Table 3 Computation time of various homomorphic encryption schemes for $N=10$ (s)
-
[1] Yang T, Yi X L, Wu J F, Yuan Y, Wu D, Meng Z Y, et al. A survey of distributed optimization. Annual Reviews in Control, 2019, 47: 278−305 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2019.05.006 [2] Guo F H, Wen C Y, Mao J F, Song Y D. Distributed economic dispatch for smart grids with random wind power. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(3): 1572−1583 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2015.2434831 [3] 李远征, 倪质先, 段钧韬, 徐磊, 杨涛, 曾志刚. 面向高比例新能源电网的重大耗能企业需求响应调度. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(4): 754−768Li Yuan-Zheng, Ni Zhi-Xian, Duan Jun-Tao, Xu Lei, Yang Tao, Zeng Zhi-Gang. Demand response scheduling of major energy-consuming enterprises based on a high proportion of renewable energy power grid. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(4): 754−768 [4] Nedić A. Distributed gradient methods for convex machine learning problems in networks: distributed optimization. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(3): 92−101 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2975210 [5] Tao W, Pan Z L, Wu G W, Tao Q. The strength of nesterov's extrapolation in the individual convergence of nonsmooth optimization. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(7): 2557−2568 [6] Wu M, Xiong N X, Vasilakos A V, Leung V C M, Chen C L P. RNN-K: A reinforced newton method for consensus-based distributed optimization and control over multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(5): 4012−4026 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3011819 [7] Zhou X, Zou S L, Wang P, Ma Z J. ADMM-based coordination of electric vehicles in constrained distribution networks considering fast charging and degradation. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(1): 565−578 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3015122 [8] Gao F K, Yang B, Chen C L, Guan X P, Zhang Y. Distributed urban freeway traffic optimization considering congestion propagation. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(14): 12155−12165 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3133877 [9] Zhang S Y, Zhang S Y, Yeung L K, Yu J J Q. Urban internet of electric vehicle parking system for vehicle-to-grid scheduling: Formulation and distributed algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(1): 67−79 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3304718 [10] 杨涛, 徐磊, 易新蕾, 张圣军, 陈蕊娟, 李渝哲. 基于事件触发的分布式优化算法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 133−143Yang Tao, Xu Lei, Yi Xin-Lei, Zhang Sheng-Jun, Chen Rui-Juan, Li Yu-Zhe. Event-triggered distributed optimization algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 133−143 [11] 王龙, 卢开红, 关永强. 分布式优化的多智能体方法. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(11): 1820−1833 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90502Wang Long, Lu Kai-Hong, Guan Yong-Qiang. Distributed optimization via multi-agent systems. Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 36(11): 1820−1833 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90502 [12] 谢佩, 游科友, 洪奕光, 谢立华. 网络化分布式凸优化算法研究进展. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(7): 918−927 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.80205Xie Pei, You Ke-You, Hong Yi-Guang, Xie Li-Hua. A survey of distributed convex optimization algorithms over networks. Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 35(7): 918−927 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.80205 [13] Nedić A, Ozdaglar A. Distributed subgradient methods for multi-agent optimization. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(1): 48−61 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2008.2009515 [14] Shi W, Ling Q, Yuan K, Wu G, Yin W T. On the linear convergence of the ADMM in decentralized consensus optimization. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(7): 1750−1761 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2304432 [15] Iutzeler F, Bianchi P, Ciblat P, Hachem W. Explicit convergence rate of a distributed alternating direction method of multipliers. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(4): 892−904 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2448011 [16] Gratton C, Venkategowda N K D, Arablouei R, Werner S. Privacy-preserved distributed learning with zeroth-order optimization. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 265−279 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3139267 [17] Lü Q G, Liao X F, Xiang T, Li H Q, Huang T W. Privacy masking stochastic subgradient-push algorithm for distributed online optimization. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(6): 3224−3237 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2973221 [18] Wei M L, Yang J, Zhao Z Y, Zhang X G, Li J S, Deng Z L. DeFedHDP: Fully decentralized online federated learning for heart disease prediction in computational health systems. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2024, 11(5): 6854−6867 doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2024.3406528 [19] Lagendijk R L, Erkin Z, Barni M. Encrypted signal processing for privacy protection: Conveying the utility of homomorphic encryption and multiparty computation. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2013, 30(1): 82−105 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2012.2219653 [20] Gong Y M, Cai Y, Guo Y X, Fang Y G. A Privacy-preserving scheme for incentive-based demand response in the smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(3): 1304−1313 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2015.2412091 [21] Wei W Q, Liu L. Gradient leakage attack resilient deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 303−316 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3139777 [22] Zhang T, Zhu Q Y. Dynamic differential privacy for ADMM-based distributed classification learning. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 12(1): 172−187 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2607691 [23] Huo X, Liu M X. Encrypted decentralized multi-agent optimization for privacy preservation in cyber-physical systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(1): 750−761 doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3132940 [24] Mo Y L, Murray R M. Privacy preserving average consensus. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(2): 753−765 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2564339 [25] Gade S, Vaidya N H. Privacy-preserving distributed learning via obfuscated stochastic gradients. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Decision and Control. Miami, USA: IEEE, 2018. 184−191 [26] He J P, Cai L, Cheng P, Pan J P, Shi L. Distributed privacy-preserving data aggregation against dishonest nodes in network systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 1462−1470 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2834544 [27] Lu Y, Zhu M H. Privacy preserving distributed optimization using homomorphic encryption. Automatica, 2018, 96: 314−325 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.07.005 [28] Lu Y, Zhu M H. Game-theoretic distributed control with information-theoretic security guarantees. In: Proceedings of the 5th IFAC Workshop on Distributed Estimation and Control in Networked Systems. Philadelphia, USA: IFAC, 2015. 264−269 [29] Ruan M H, Gao H, Wang Y Q. Secure and privacy-preserving consensus. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(10): 4035−4049 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2890887 [30] Chen Z Y, Ye F, Cao X H, Chow M Y. A homomorphic encryption-based private collaborative distributed energy management system. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2021, 12(6): 5233−5243 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2021.3091624 [31] Yuan Z P, Li P, Li Z L, Xia J. A fully distributed privacy-preserving energy management system for networked microgrid cluster based on homomorphic encryption. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2024, 15(2): 1735−1748 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2023.3309405 [32] Zhang C L, Ahmad M, Wang Y Q. ADMM based privacy-preserving decentralized optimization. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(3): 565−580 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2855169 [33] 唐飞, 凌国玮, 单进勇. 基于国密SM2和SM9的加法同态加密方案. 密码学报, 2022, 9(3): 535−549Tang Fei, Ling Guo-Wei, Shan Jin-Yong. Additive homomorphic encryption schemes based on SM2 and SM9. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2022, 9(3): 535−549 [34] Zhang C L, Wang Y Q. Enabling privacy-preservation in decentralized optimization. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2019, 6(2): 679−689 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2018.2873152 [35] Nedić A, Ozdaglar A, Parrilo P A. Constrained consensus and optimization in multi-agent networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010, 55(4): 922−938 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2041686 [36] Tsiounis Y, Yung M. On the security of ELGamal based encryption. In: Proceedings of International Workshop on Public Key Cryptography. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 1998. 117−134 [37] Johnson D, Menezes A, Vanstone S. The elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA). International Journal of Information Security, 2001, 1(1): 36−63 doi: 10.1007/s102070100002 [38] Su Y, Yang B L, Yang C, Zhao S Y. ReMCA: A reconfigurable multi-core architecture for full RNS variant of BFV homomorphic evaluation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2022, 69(7): 2857−2870 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3163970 -




 下载:
下载: