Finite-time Identification and Adaptive Consensus Control of Uncertain Parametric Systems Over Directed Graphs
-
摘要: 针对有向图上一类不确定性多智能体系统, 研究一体化参数辨识与一致性控制策略. 在现有模型参考自适应一致性(Model reference adaptive consensus, MRACon)框架基础上, 结合动态回归因子扩张与融合(Dynamic regressor extension and mixing, DREM)技术, 提出两类改进的MRACon控制协议, 即固定耦合DREM-MRACon和自适应耦合DREM-MRACon. 其中, 自适应耦合DREM-MRACon在有向支撑树结构上具有时变的耦合增益. 与MRACon相比, 此两类改进算法均能保证系统未知参数的有限时间辨识. 此外, 固定耦合DREM-MRACon保证了多智能体系统的指数时间一致性, 而自适应耦合DREM-MRACon则克服了对于全局网络拓扑特征信息的依赖性. 最后, 通过数值仿真验证了理论成果的有效性.Abstract: The paper addresses an integrated parameter identification and consensus control problem of a class of uncertain multi-agent systems over directed graphs. Based on the existing model reference adaptive consensus (MRACon) framework and by leveraging dynamic regressor extension and mixing (DREM) techniques, two improved MRACon protocols are established, namely fixed-coupling DREM-MRACon and adaptive-coupling DREM-MRACon. The latter protocol contains time-varying coupling gains along a directed spanning tree. As compared to the baseline MRACon, both of the proposed protocols ensure finite-time identification of the system's unknown parameters. Additionally, fixed-coupling DREM-MRACon achieves exponential consensus of the agents, while adaptive-coupling DREM-MRACon overcomes the requirement of global information on the network topology. Finally, numerical simulations are conducted to verify the effectiveness of the theoretical results.
-
Key words:
- Multi-agent systems /
- adaptive control /
- parameter identification /
- directed graphs /
- adaptive consensus
-
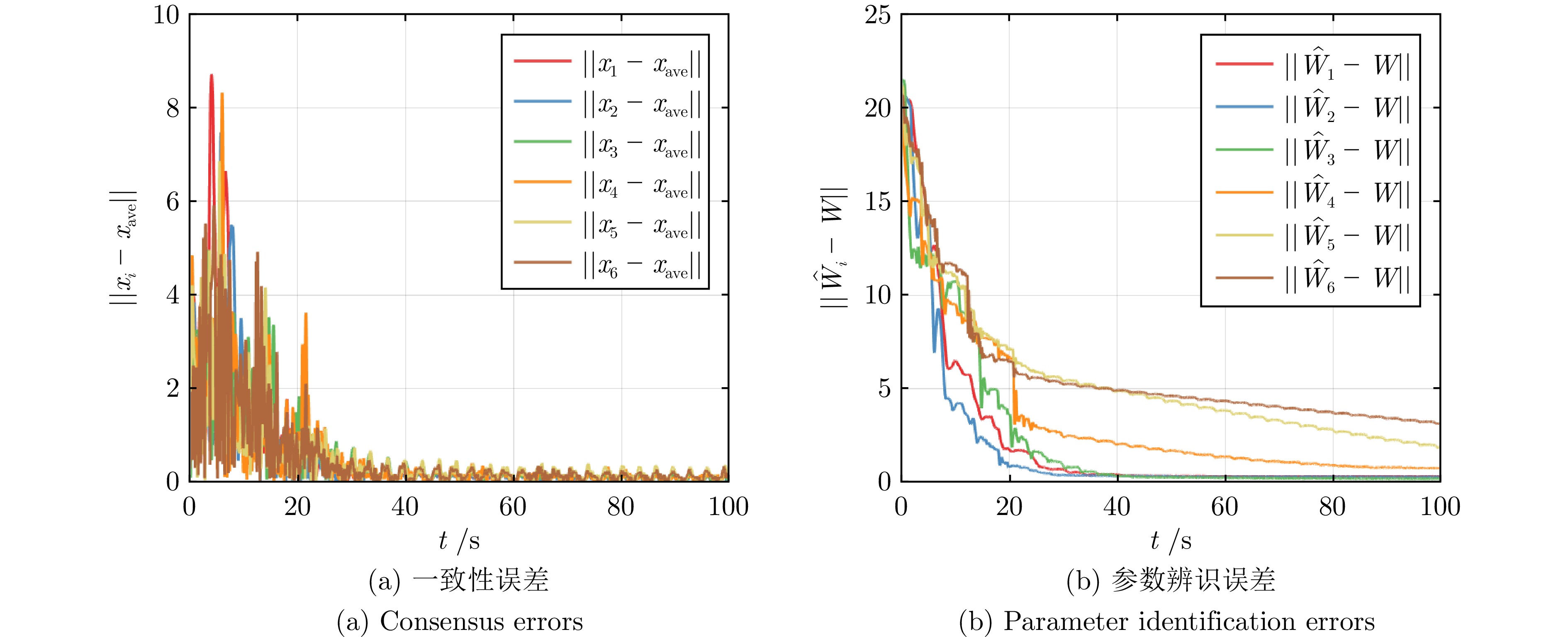
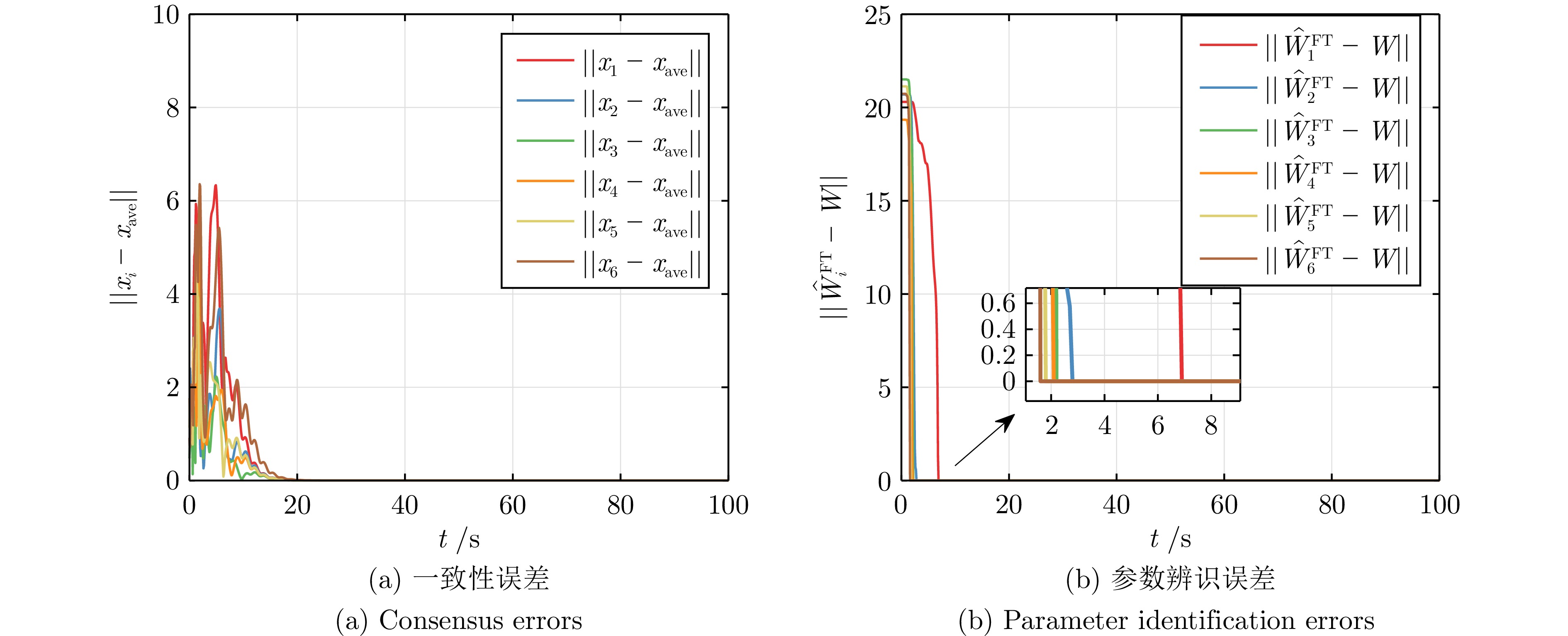
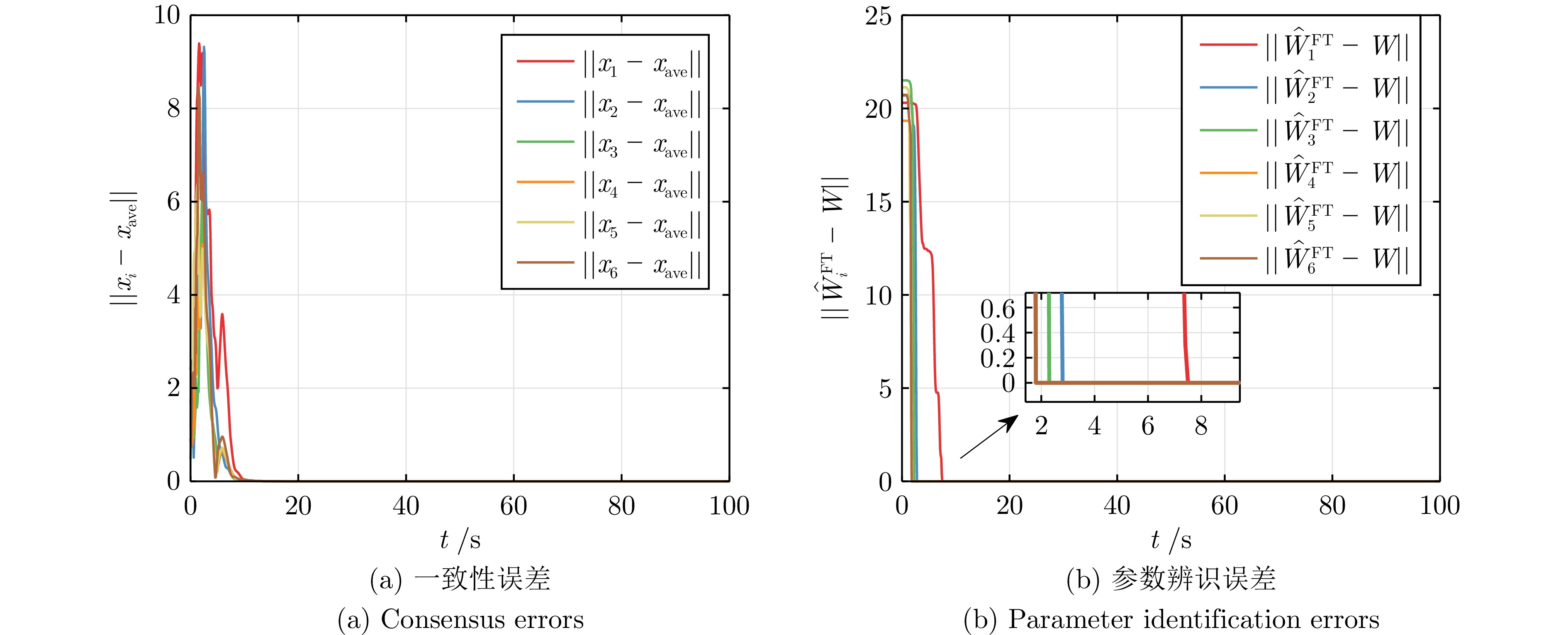
表 1 参数辨识的精确时刻$ T_i $
Table 1 The exact time $T_i$ for parameter identification
智能体序号 MRACon[30] 固定耦合
DREM-MRACon自适应耦合
DREM-MRACon1 — 6.84 7.43 2 — 2.77 2.75 3 — 2.16 2.26 4 — 2.03 1.74 5 — 1.74 1.78 6 — 1.55 1.74 -
[1] Chen W S, Wen C Y, Hua S Y, Sun C Y. Distributed cooperative adaptive identification and control for a group of continuous-time systems with a cooperative PE condition via consensus. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(1): 91−106 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2013.2278135 [2] Papusha I, Lavretsky E, Murray R M. Collaborative system identification via parameter consensus. In: Proceedings of American Control Conference (ACC). Portland, USA: IEEE, 2014, 13−19 [3] Wei G L, Li W Y, Ding D R, Liu Y R. Stability analysis of covariance intersection-based kalman consensus filtering for time-varying systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 50(11): 4611−4622 [4] Gao C, Wang Z D, Hu J, Liu Y, He X. Consensus-based distributed state estimation over sensor networks with encoding-decoding scheme: Accommodating bandwidth constraints. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022, 9(6): 4051−4064 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3195283 [5] 田磊, 董希旺, 赵启伦, 李清东, 吕金虎, 任章. 异构集群系统分布式自适应输出时变编队跟踪控制. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(10): 2386−2401Tian Lei, Dong Xi-Wang, Zhao Qi-Lun, Li Qing-Dong, Lv Jin-Hu, Ren Zhang. Distributed adaptive time-varying output formation tracking for heterogeneous swarm systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(10): 2386−2401 [6] Xu X, Gu G Y, Xiong Z H, Sheng X J, Zhu X Y. Development of a decentralized multi-axis synchronous control approach for real-time networks. ISA Transactions, 2017, 68: 116−126 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2017.03.012 [7] Liu W J, Sun J, Wang G, Bullo F, Chen J. Data-driven resilient predictive control under denial-of-service. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(8): 4722−4737 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3209399 [8] Wang X, Sun J, Wang G, Allgöwer F, Chen J. Data-driven control of distributed event-triggered network systems. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(2): 351−364 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123225 [9] Xu W Y, Wang Z D, Hu G Q, Kurths J. Hybrid nash equilibrium seeking under partial-decision information: An adaptive dynamic event-triggered approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(10): 5862−5876 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3226142 [10] Peng Z H, Wang D, Zhang H W, Sun G. Distributed neural network control for adaptive synchronization of uncertain dynamical multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(8): 1508−1519 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2293499 [11] Yue D D, Cao J D, Li Q, Liu Q S. Neural-network-based fully distributed adaptive consensus for a class of uncertain multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(7): 2965−2977 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3009098 [12] 王庆领, 王雪娆. 切换拓扑下非线性多智能体系统自适应神经网络一致性. 控制理论与应用, 2023, 40(4): 633−640 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.10847Wang Qing-Ling, Wang Xue-Rao. Adaptive NN consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems under switching topologies. Control Theory and Technology, 2023, 40(4): 633−640 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.10847 [13] Mao B, Wu X Q, Lv J H, Chen G R. Predefined-time bounded consensus of multiagent systems with unknown nonlinearity via distributed adaptive fuzzy control. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(4): 2622−2635 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3163755 [14] Wang Y J, Song Y D, Lewis F L. Robust adaptive fault-tolerant control of multiagent systems with uncertain nonidentical dynamics and undetectable actuation failures. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6): 3978−3988 [15] 范泉涌, 张乃宗, 唐勇, 许斌. 基于动态事件触发通信协议的多智能体系统自适应可靠控制. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(5): 924−936Fan Quan-Yong, Zhang Nai-Zong, Tang Yong, Xu Bin. Adaptive reliable control of multi-agent systems based on dynamic event-triggered communication protocol. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(5): 924−936 [16] Li Z K, Ren W, Liu X D, Xie L H. Distributed consensus of linear multi-agent systems with adaptive dynamic protocols. Automatica, 2013, 49(7): 1986−1995 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.03.015 [17] Lv Y Z, Li Z K, Duan Z S, Feng G. Novel distributed robust adaptive consensus protocols for linear multi-agent systems with directed graphs and external disturbances. International Journal of Control, 2017, 90(2): 137−147 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2016.1172259 [18] Li Z H, Ding Z T, Sun J Y, Li Z K. Distributed adaptive convex optimization on directed graphs via continuous-time algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 63(5): 1434−1441 [19] Yue D D, Baldi S, Cao J D, Li Q, DeSchutter B. Distributed adaptive resource allocation: An uncertain saddle-point dynamics viewpoint. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(12): 2209−2221 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123402 [20] Ye M J, Hu G Q. Adaptive approaches for fully distributed nash equilibrium seeking in networked games. Automatica, 2021, 129: Article No. 109661 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.109661 [21] Baldi S, Yuan S, Frasca P. Output synchronization of unknown heterogeneous agents via distributed model reference adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2018, 6(2): 515−525 [22] Azzollini I A, Yu W W, Yuan S, Baldi S. Adaptive leader-follower synchronization over heterogeneous and uncertain networks of linear systems without distributed observer. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 66(4): 1925−1931 [23] Goel R, Garg T, Roy S B. Closed-loop reference model based distributed MRAC using cooperative initial excitation and distributed reference input estimation. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2022, 9(1): 37−49 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2022.3141015 [24] Agha R, Rehan M, Ahn C K, Mustafa G, Ahmad S. Adaptive distributed consensus control of one-sided lipschitz nonlinear multiagents. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2017, 49(3): 568−578 [25] Mei J, Ren W, Chen J. Distributed consensus of second-order multi-agent systems with heterogeneous unknown inertias and control gains under a directed graph. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(8): 2019−2034 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2480336 [26] Lv Y Z, Li Z K. Is fully distributed adaptive protocol applicable to graphs containing a directed spanning tree? Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(8): Article No. 189203 doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3129-1 [27] Yu Z Y, Huang D, Jiang H J, Hu C, Yu W W. Distributed consensus for multiagent systems via directed spanning tree based adaptive control. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2018, 56(3): 2189−2217 doi: 10.1137/16M1088685 [28] Yue D D, Baldi S, Cao J D, Li Q, DeSchutter B. A directed spanning tree adaptive control solution to time-varying formations. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2021, 8(2): 690−701 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2021.3050332 [29] Yue D D, Baldi S, Cao J D, Li Q, DeSchutter B. Distributed adaptive optimization with weight-balancing. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(4): 2068−2075 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3071651 [30] Mei J, Ren W, Song Y D. A unified framework for adaptive leaderless consensus of uncertain multi-agent systems under directed graphs. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(12): 6179−6186 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3062594 [31] Wang X Y, Xu Y J, Cao Y, Li S H. A hierarchical design framework for distributed control of multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2024, 160: Article No. 111402 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.111402 [32] 柴天佑, 岳恒. 自适应控制. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016.Chai Tian-You, Yue Heng. Adaptive Control. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016. [33] Ioannou P A, Sun J. Robust Adaptive Control. New York: Dover Publications, Inc., 2012. [34] Aranovskiy S, Bobtsov A, Ortega R, Pyrkin A. Parameters estimation via dynamic regressor extension and mixing. In: Proceedings of American Control Conference (ACC). Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2016. 6971−6976 [35] Ortega R, Nikiforov V, Gerasimov D. On modified parameter estimators for identification and adaptive control. A unified framework and some new schemes. Annual Reviews in Control, 2020, 50: 278−293 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2020.06.002 [36] Wang L, Ortega R, Bobtsov A. Observability is sufficient for the design of globally exponentially stable state observers for state-affine nonlinear systems. Automatica, 2023, 149: Article No. 110838 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110838 [37] Ortega R, Gerasimov D N, Barabanov N E, Nikiforov V O. Adaptive control of linear multivariable systems using dynamic regressor extension and mixing estimators: Removing the high-frequency gain assumptions. Automatica, 2019, 110: Article No. 108589 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108589 [38] Wang S B, Lv B, Wen S P, Shi K B, Zhu S, Huang T W. Robust adaptive safety-critical control for unknown systems with finite-time elementwise parameter estimation. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(3): 1607−1617 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3203176 [39] Shadab S, Revati G, Wagh S, Singh N. Finite-time parameter estimation for an online monitoring of transformer: A system identification perspective. International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems, 2023, 145: Article No. 108639 [40] Matveev A S, Almodarresi M, Ortega R, Pyrkin A, Xie S Y. Diffusion-based distributed parameter estimation through directed graphs with switching topology: Application of dynamic regressor extension and mixing. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(8): 4256−4263 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3115075 [41] Ren W, Beard R W. Distributed Consensus in Multi-Vehicle Cooperative Control. London: Springer London, 2008. [42] Na J, Herrmann G, Zhang K Q. Improving transient performance of adaptive control via a modified reference model and novel adaptation. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2017, 27(8): 1351−1372 doi: 10.1002/rnc.3636 [43] Garg T, Roy S B. Distributed adaptive estimation without persistence of excitation: An online optimization perspective. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2023, 37(5): 1117−1134 doi: 10.1002/acs.3563 [44] Cai H, Lewis F L, Hu G Q, Huang J. The adaptive distributed observer approach to the cooperative output regulation of linear multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2017, 75: 299−305 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.09.038 [45] Yuan C Z, Stegagno P, He H B, Ren W. Cooperative adaptive containment control with parameter convergence via cooperative finite-time excitation. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(11): 5612−5618 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3056336 [46] Hou Q H, Dong J X. Cooperative output regulation of linear multiagent systems with parameter convergence. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 53(1): 518−528 [47] Sun Z Y, Rantzer A, Li Z K, Robertsson A. Distributed adaptive stabilization. Automatica, 2021, 129: Article No. 109616 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.109616 [48] Shen Y, Wang J. Robustness analysis of global exponential stability collaborative system identificationof recurrent neural networks in the presence of time delays and random disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2011, 23(1): 87−96 [49] Yu W W, Lv J H, Yu X H, Chen G R. Distributed adaptive control for synchronization in directed complex networks. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2015, 53(5): 2980−3005 doi: 10.1137/140970781 -




 下载:
下载: