-
摘要: 本文研究了多智能体时变网络上基于Bandit反馈的分布式在线鞍点问题, 其中每个智能体通过本地计算和局部信息交流去协作最小化全局损失函数. 在Bandit反馈下, 包括梯度在内的损失函数信息是不可用的, 每个智能体仅能获得和使用在某决策或其附近产生的函数值. 为此, 结合单点梯度估计方法和预测映射技术, 提出一种非欧几里得意义上的分布式在线Bandit鞍点优化算法. 以动态鞍点遗憾作为性能指标, 对于一般的凸−凹损失函数, 建立了遗憾上界并在某些预设条件下确保所提算法的次线性收敛. 此外, 考虑到在迭代优化中计算优化子程序的精确解通常较为困难, 进一步扩展一种基于近似计算方法的算法变种, 并严格分析精确度设置对扩展算法遗憾上界的影响. 最后, 通过一个目标跟踪案例对算法的有效性和先进性进行仿真验证.Abstract: This paper studies the distributed online saddle point problem with Bandit feedback over a multi-agent time-varying network, in which each agent collaborates to minimize the global loss function through local calculation and local information exchange. Under Bandit feedback, loss function information including gradients is not available, and each agent can only obtain and use the function value generated by a decision or decisions near it. To this end, a distributed online Bandit saddle point optimization algorithm in a non-Euclidean sense is proposed by combining the one-point gradient estimation method and the predictive mapping technique. Taking the expected dynamic saddle point regret as the performance metric, we establish the related regret upper bound for the general convex-concave loss functions and ensure that the proposed algorithm converges sublinearly under certain preconditions. In addition, considering that computing the exact solutions of the optimization oracles is usually difficult in iterative optimization, this paper further expands an algorithm variant based on an approximate computation method, and rigorously analyzes the impact of precision settings on the regret upper bound of the expanded algorithm. Finally, the effectiveness and advancement of the proposed algorithms are verified through a simulation example of target tracking.
-
表 1 不同步长和精确度下的遗憾界
Table 1 The regret bounds under different step sizes and precisions
$ \alpha_t $ $ \eta_t $ $ \rho_t^x $ $ \rho_t^y $ $ {ESP-Regret}_d^j(T) $ $ \dfrac{1}{\epsilon_1k} t^{-\frac{3}{4}} $ $ \dfrac{1}{\epsilon_2 k} t^{-\frac{3}{4}} $ $ t^{-1} $ $ t^{-1} $ $ {\cal{O}}(\max \{kT^{\frac{7}{8}}, \; kT^{\frac{3}{4}} V_T \}) $ $ t^{-\frac{5}{4}} $ $ t^{-\frac{5}{4}} $ $ {\cal{O}}(kT^{\frac{3}{4}} (1+V_T)) $ $ t^{-2} $ $ t^{-2} $ $ {\cal{O}}(kT^{\frac{3}{4}} (1+V_T)) $ $ \dagger $ $ \dfrac{1}{\epsilon_1k} t^{-\varpi_1} $ $ \dfrac{1}{\epsilon_2 k} t^{-\varpi_1} $ $ t^{-1} $ $ t^{-1} $ ${\cal{O}}(\max \{kT^{\frac{3}{4}}\sqrt{1+V_T}, \; kT^{\frac{7}{8}} (1+V_T)^{-\frac{1}{4}} \})$ $ t^{-\frac{5}{4}} $ $ t^{-\frac{5}{4}} $ $ {\cal{O}}(kT^{\frac{3}{4}} \sqrt{1+V_T}) $ $ t^{-2} $ $ t^{-2} $ $ {\cal{O}}(kT^{\frac{3}{4}} \sqrt{1+V_T}) $ 注: $ \dagger $表示$ \varpi_1=3/4-\log_T {\sqrt{1+V_T}} $. -
[1] Shalev-Shwartz S. Online learning and online convex optimization. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2012, 4(2): 107−194 [2] Hazan E. Introduction to online convex optimization. Foundations and Trends® in Optimization, 2016, 2(3−4): 157−325 [3] Li X X, Xie L H, Li N. A survey on distributed online optimization and online games. Annual Reviews in Control, 2023, 56: Article No. 100904 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2023.100904 [4] 袁德明, 张保勇, 夏建伟. 在线分布式优化研究进展. 聊城大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 36(5): 1−12Yuan De-Ming, Zhang Bao-Yong, Xia Jian-Wei. Recent advance in online distributed optimization. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 36(5): 1−12 [5] Zinkevich M. Online convex programming and generalized infinitesimal gradient ascent. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Washington, USA: AAAI Press, 2003. 928−935 [6] Cao X Y, Liu K J R. Online convex optimization with time-varying constraints and bandit feedback. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(7): 2665−2680 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2884653 [7] 吴庆涛, 朱军龙, 葛泉波, 张明川. 一种基于条件梯度的加速分布式在线学习算法. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(2): 386−402Wu Qing-Tao, Zhu Jun-Long, Ge Quan-Bo, Zhang Ming-Chuan. An accelerated distributed online learning algorithm based on conditional gradient. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(2): 386−402 [8] Yuan D M, Hong Y G, Ho D W C, Xu S Y. Distributed mirror descent for online composite optimization. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(2): 714−729 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.2987379 [9] Yi X L, Li X X, Yang T, Xie L H, Chai T Y, Johansson K H. Distributed bandit online convex optimization with time-varying coupled inequality constraints. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(10): 4620−4635 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3030883 [10] Dixit R, Bedi A S, Rajawat K. Online learning over dynamic graphs via distributed proximal gradient algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(11): 5065−5079 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3033712 [11] Shahrampour S, Jadbabaie A. Distributed online optimization in dynamic environments using mirror descent. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(3): 714−725 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2743462 [12] Beznosikov A, Samokhin V, Gasnikov A. Distributed saddle-point problems: Lower bounds, near-optimal and robust algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2010.13112, 2022. [13] Raghavan K, Garg S, Jagannathan S, Samaranayake V A. Distributed min-max learning scheme for neural networks with applications to high-dimensional classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(10): 4323−4333 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3017434 [14] Akimoto Y, Miyauchi Y, Maki A. Saddle point optimization with approximate minimization oracle and its application to robust berthing control. ACM Transactions on Evolutionary Learning and Optimization, 2022, 2(1): Article No. 2 [15] Ho-Nguyen N, Kılınç-Karzan F. Exploiting problem structure in optimization under uncertainty via online convex optimization. Mathematical Programming, 2019, 177(1−2): 113−147 doi: 10.1007/s10107-018-1262-8 [16] Rivera Cardoso A, Wang H, Xu H. The online saddle point problem and online convex optimization with knapsacks. Mathematics of Operations Research, DOI: 10.1287/moor.2018.0330 [17] Xu Y, Jiang Y, Xie X, Li D Q. An online saddle point optimization algorithm with regularization. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, 569(5): Article No. 052035 [18] Wood K R, Dall'Anese E. Online saddle point tracking with decision-dependent data. In: Proceedings of the 5th Annual Learning for Dynamics and Control Conference. Istanbul, Turkey: PMLR, 2023. 1416−1428 [19] Flaxman A D, Kalai A T, McMahan H B. Online convex optimization in the Bandit setting: Gradient descent without a gradient. In: Proceedings of the 16th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms. Vancouver, Canada: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2005. 385−394 [20] Agarwal A, Dekel O, Xiao L. Optimal algorithms for online convex optimization with multi-point Bandit feedback. In: Proceedings of the 23rd Conference on Learning Theory (COLT). Haifa, Israel: Omnipress, 2010. 28−40 [21] Besbes O, Gur Y, Zeevi A. Non-stationary stochastic optimization. Operations Research, 2015, 63(5): 1227−1244 doi: 10.1287/opre.2015.1408 [22] Roy A, Chen Y F, Balasubramanian K, Mohapatra P. Online and Bandit algorithms for nonstationary stochastic saddle-point optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1912.01698, 2019. [23] Cardoso A R, Abernethy J, Wang H, Xu H. Competing against Nash equilibria in adversarially changing zero-sum games. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Long Beach, USA: PMLR, 2019. 921−930 [24] Yang T, Yi X L, Wu J F, Yuan Y, Wu D, Meng Z Y, et al. A survey of distributed optimization. Annual Reviews in Control, 2019, 47: 278−305 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2019.05.006 [25] Nedic A, Olshevsky A, Ozdaglar A, Tsitsiklis J N. Distributed subgradient methods and quantization effects. In: Proceedings of the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2008. 4177−4184 [26] 洪奕光, 张艳琼. 分布式优化: 算法设计和收敛性分析. 控制理论与应用, 2014, 31(7): 850−857 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2014.40012Hong Yi-Guang, Zhang Yan-Qiong. Distributed optimization: Algorithm design and convergence analysis. Control Theory & Applications, 2014, 31(7): 850−857 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2014.40012 [27] 王龙, 卢开红, 关永强. 分布式优化的多智能体方法. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(11): 1820−1833 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90502Wang Long, Lu Kai-Hong, Guan Yong-Qiang. Distributed optimization via multi-agent systems. Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 36(11): 1820−1833 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90502 [28] 杨涛, 柴天佑. 分布式协同优化的研究现状与展望. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2020, 50(11): 1413−1425Yang Tao, Chai Tian-You. Research status and prospects of distributed collaborative optimization. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2020, 50(11): 1413−1425 [29] 谢佩, 游科友, 洪奕光, 谢立华. 网络化分布式凸优化算法研究进展. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(7): 918−927 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.80205Xie Pei, You Ke-You, Hong Yi-Guang, Xie Li-Hua. A survey of distributed convex optimization algorithms over networks. Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 35(7): 918−927 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.80205 [30] 衣鹏, 洪奕光. 分布式合作优化及其应用. 中国科学: 数学, 2016, 46(10): 1547−1564Yi Peng, Hong Yi-Guang. Distributed cooperative optimization and its applications. Scientia Sinica Mathematica, 2016, 46(10): 1547−1564 [31] 杨涛, 徐磊, 易新蕾, 张圣军, 陈蕊娟, 李渝哲. 基于事件触发的分布式优化算法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 133−143Yang Tao, Xu Lei, Yi Xin-Lei, Zhang Sheng-Jun, Chen Rui-Juan, Li Yu-Zhe. Event-triggered distributed optimization algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 133−143 [32] 刘奕葶, 马铭莙, 付俊. 基于有向图的分布式连续时间非光滑耦合约束凸优化分析. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(1): 66−75Liu Yi-Ting, Ma Ming-Jun, Fu Jun. Distributed continuous-time non-smooth convex optimization analysis with coupled constraints over directed graphs. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(1): 66−75 [33] 时侠圣, 任璐, 孙长银. 自适应分布式聚合博弈广义纳什均衡算法. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(6): 1210−1220Shi Xia-Sheng, Ren Lu, Sun Chang-Yin. Distributed adaptive generalized Nash equilibrium algorithm for aggregative games. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(6): 1210−1220 [34] 陈刚, 李志勇. 集合约束下多智能体系统分布式固定时间优化控制. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(9): 2254−2264Chen Gang, Li Zhi-Yong. Distributed fixed-time optimization control for multi-agent systems with set constraints. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(9): 2254−2264 [35] Xu J M, Zhu S Y, Soh Y C, Xie L H. Convergence of asynchronous distributed gradient methods over stochastic networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(2): 434−448 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2730481 [36] Liu C X, Li H P, Shi Y. Resource-aware exact decentralized optimization using event-triggered broadcasting. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(7): 2961−2974 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3014316 [37] Zhang W T, Shi Y, Zhang B Y, Yuan D M, Xu S Y. Dynamic regret of distributed online saddle point problem. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(4): 2522−2529 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3312033 [38] Zhao P, Wang G H, Zhang L J, Zhou Z H. Bandit convex optimization in non-stationary environments. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Palermo, Italy: PMLR, 2020. 1508−1518 [39] Borwein J M, Lewis A S. Convex Analysis and Nonlinear Optimization: Theory and Examples. New York: Springer, 2000. [40] Zhang Y, Ravier R J, Zavlanos M M, Tarokh V. A distributed online convex optimization algorithm with improved dynamic regret. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 58th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC). Nice, France: IEEE, 2019. 2449−2454 [41] Dai M C, Ho D W C, Zhang B Y, Yuan D M, Xu S Y. Distributed online Bandit linear regressions with differential privacy. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2023, 360(16): 11736−11759 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2023.09.001 [42] Yuan D M, Zhang B Y, Ho D W C, Zheng W X, Xu S Y. Distributed online Bandit optimization under random quantization. Automatica, 2022, 146: Article No. 110590 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110590 [43] Banerjee A, Merugu S, Dhillon I S, Ghosh J. Clustering with Bregman divergences. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2005, 6: 1705−1749 [44] Bauschke H H, Borwein J M. Joint and separate convexity of the Bregman distance. Studies in Computational Mathematics, 2001, 8: 23−36 [45] Dhillon I S, Tropp J A. Matrix nearness problems with Bregman divergences. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2008, 29(4): 1120−1146 doi: 10.1137/060649021 [46] Jadbabaie A, Rakhlin A, Shahrampour S, Sridharan K. Online optimization: Competing with dynamic comparators. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. San Diego, USA: JMLR.org, 2015. 398−406 [47] Li J Y, Li C J, Yu W W, Zhu X M, Yu X H. Distributed online Bandit learning in dynamic environments over unbalanced digraphs. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(4): 3034−3047 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2021.3093536 [48] Yi X L, Li X X, Xie L H, Johansson K H. Distributed online convex optimization with time-varying coupled inequality constraints. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 731−746 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2964200 [49] Xiong M H, Zhang B Y, Ho D W C, Yuan D M, Xu S Y. Event-triggered distributed stochastic mirror descent for convex optimization. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(9): 6480−6491 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3137010 [50] Yu Z, Ho D W C, Yuan D M. Distributed randomized gradient-free mirror descent algorithm for constrained optimization. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(2): 957−964 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3075669 [51] Ben-Tal A, El Ghaoui L, Nemirovski A. Robust Optimization. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2009. [52] Zhang S Q, Choudhury S, Stich S U, Loizou N. Communication-efficient gradient descent-accent methods for distributed variational inequalities: Unified analysis and local updates. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2306.05100, 2024. [53] Thekumparampil K K, He N, Oh S. Lifted primal-dual method for bilinearly coupled smooth minimax optimization. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Valencia, Spain: PMLR, 2022. 4281−4308 -




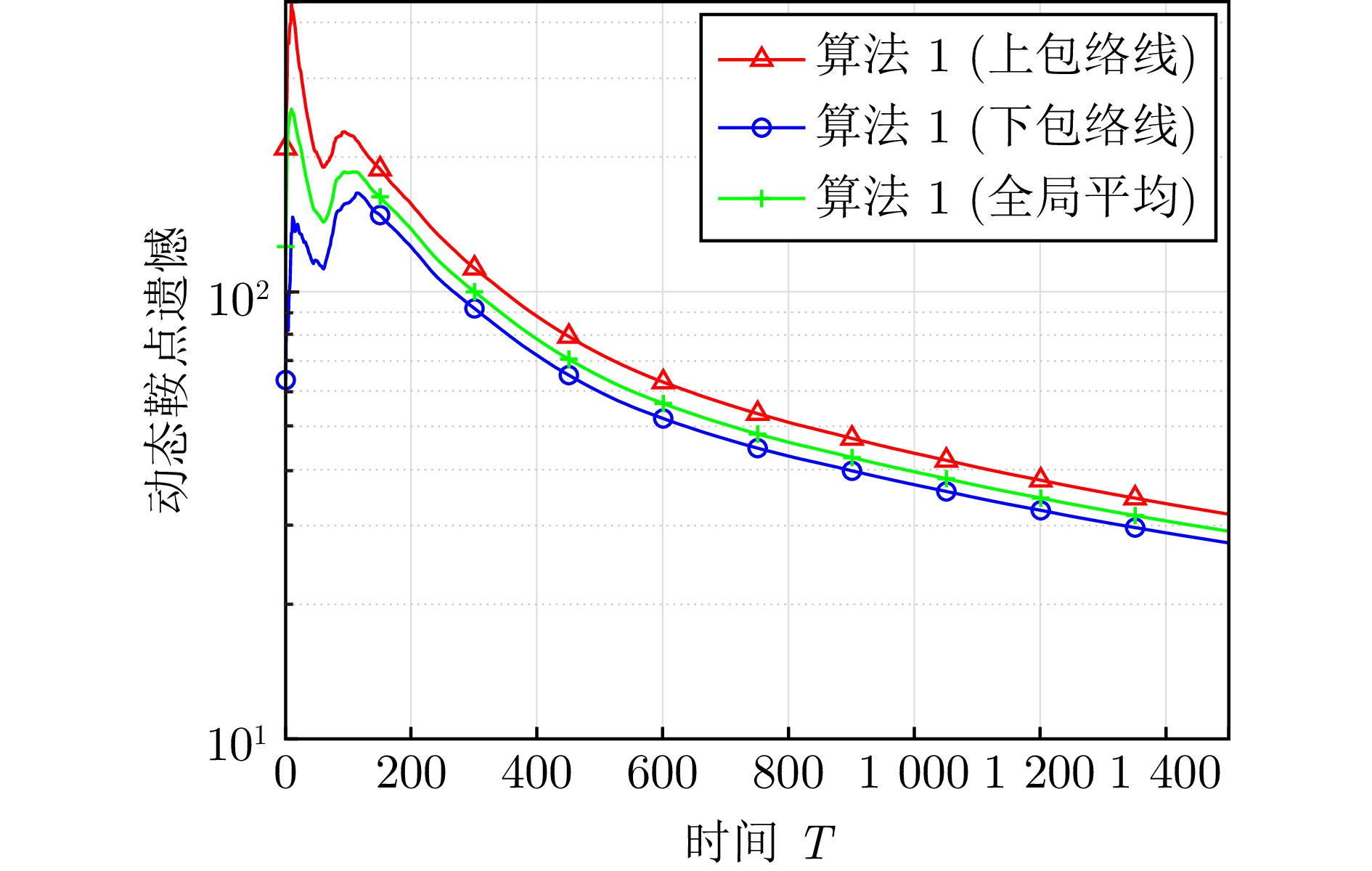
 下载:
下载: