Weapon Deployment Based on Improved Particle Swarm Optimization and Stackelberg Game
-
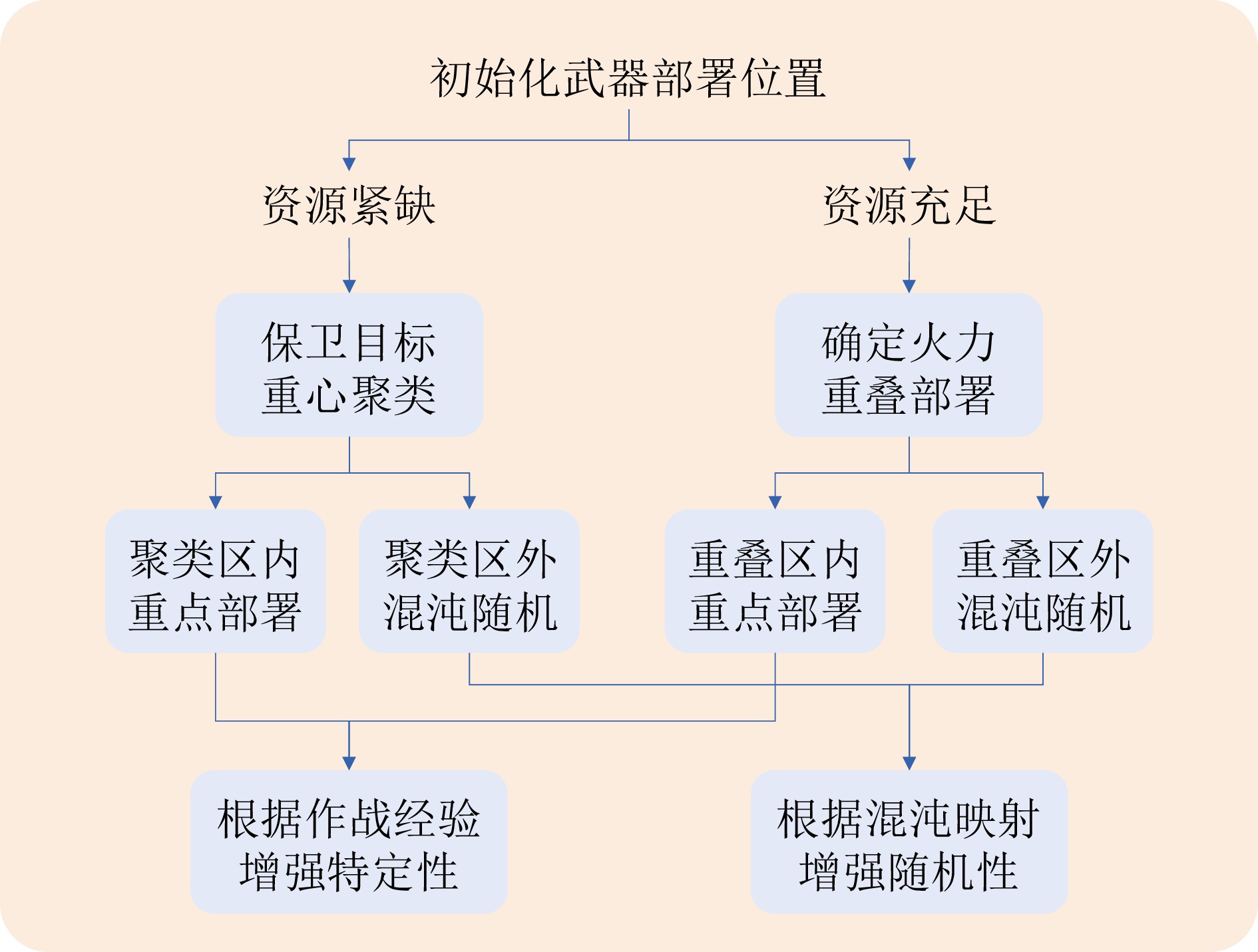
摘要: 为应对来袭目标的机动调整对防区防御能力的影响, 针对性设计全新的部署优化模型和求解算法. 首先, 从战术层面出发, 提出一种考虑攻防信息变化的新型武器部署模型, 该模型能够动态调整部署策略以提高防御系统的整体效能; 其次, 设计基于混沌映射机制和K均值聚类与重心法的算法初始化方案, 以应对资源紧缺和充足两种情况, 降低算法陷入局部最优的风险; 然后, 设计基于Metropolis准则的个体最优更新方法和基于Stackelberg博弈模型的全局最优更新方法用以指导种群的进化方向; 最后, 通过提供多规模场景仿真实验, 验证了新模型和所提算法的有效性. 对比实验结果表明新模型能够更准确地反映部署方案之间的差异, 所提算法在求解质量与收敛性方面均有显著提高.
-
关键词:
- 武器部署 /
- Stackelberg博弈 /
- 粒子群优化 /
- K均值聚类 /
- 重心法
Abstract: In order to cope with the impact of incoming target's maneuvering adjustment on the defensive capability of the defense zone, a new deployment optimization model and a solution algorithm are designed. Firstly, at the tactical level, a new weapon deployment model is proposed that takes into account changes in offensive and defensive information, allowing for dynamic adjustment of the deployment strategy to improve the overall effectiveness of the defense system; Secondly, an initialization scheme for the algorithm, based on chaotic mapping mechanism and K-means clustering and center-of-gravity method, is designed to cope with both limited and ample resources, reducing the risk of the algorithm falling into local optima; Then, an individual optimal renewal method based on the Metropolis criterion and a global optimal renewal method based on the Stackelberg game model are designed to guide the evolutionary directions of the population; Finally, the effectiveness of the new model and the proposed algorithm is verified through multi-scale scenario simulation experiments. The results of the comparative experiments show that the new model reflects deployment scheme differences more accurately and the proposed algorithm significantly improves the solution quality and convergence. -
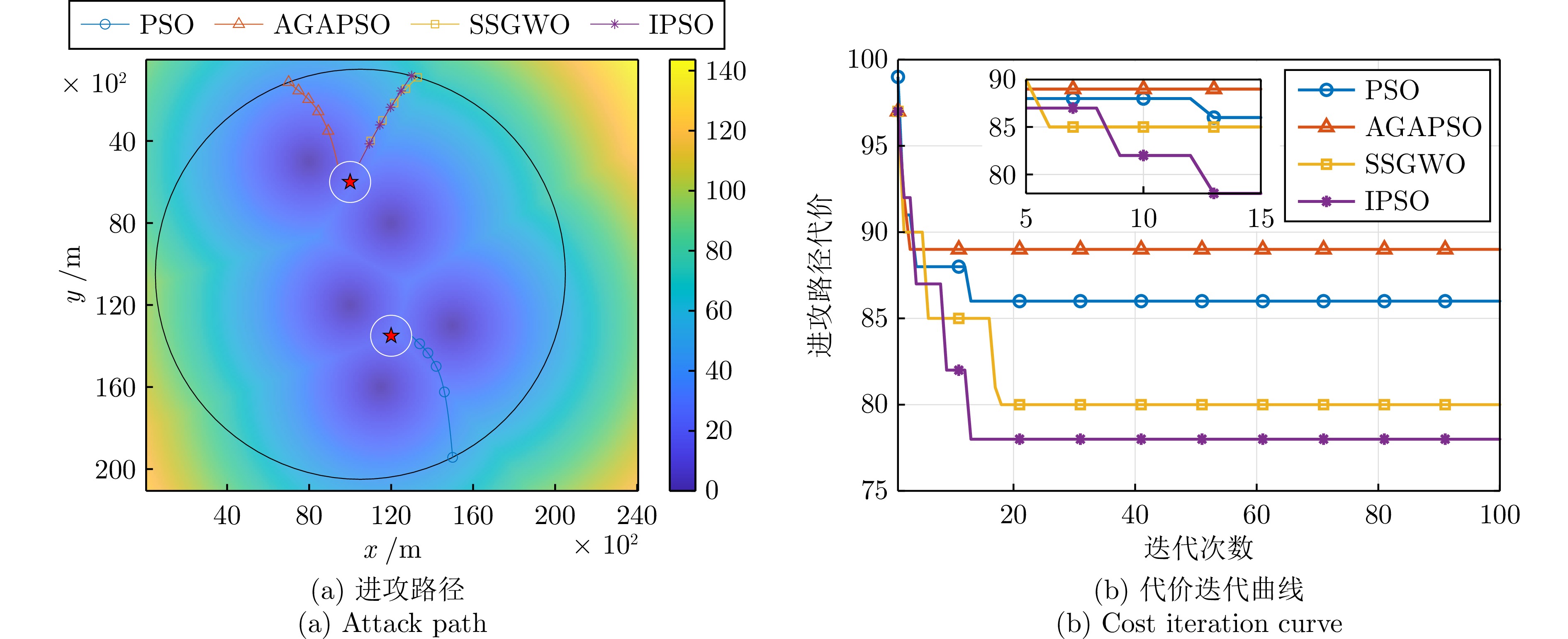
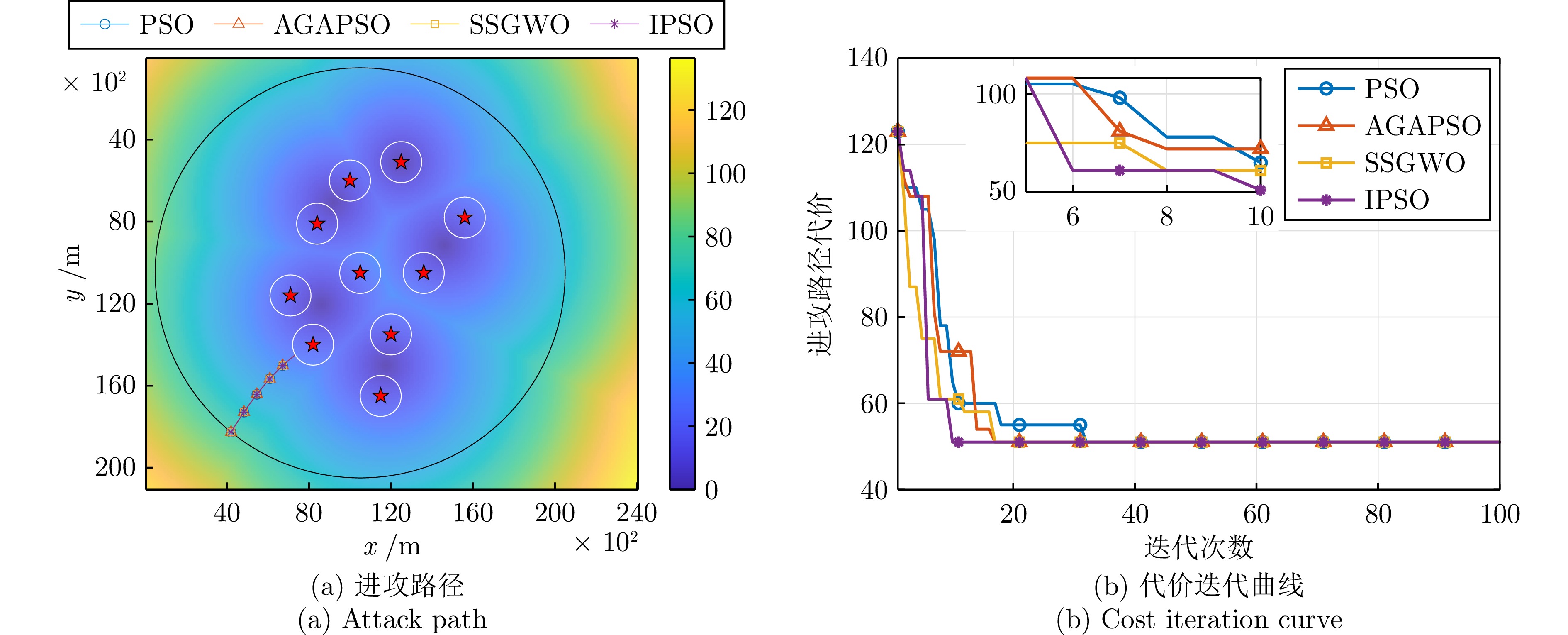
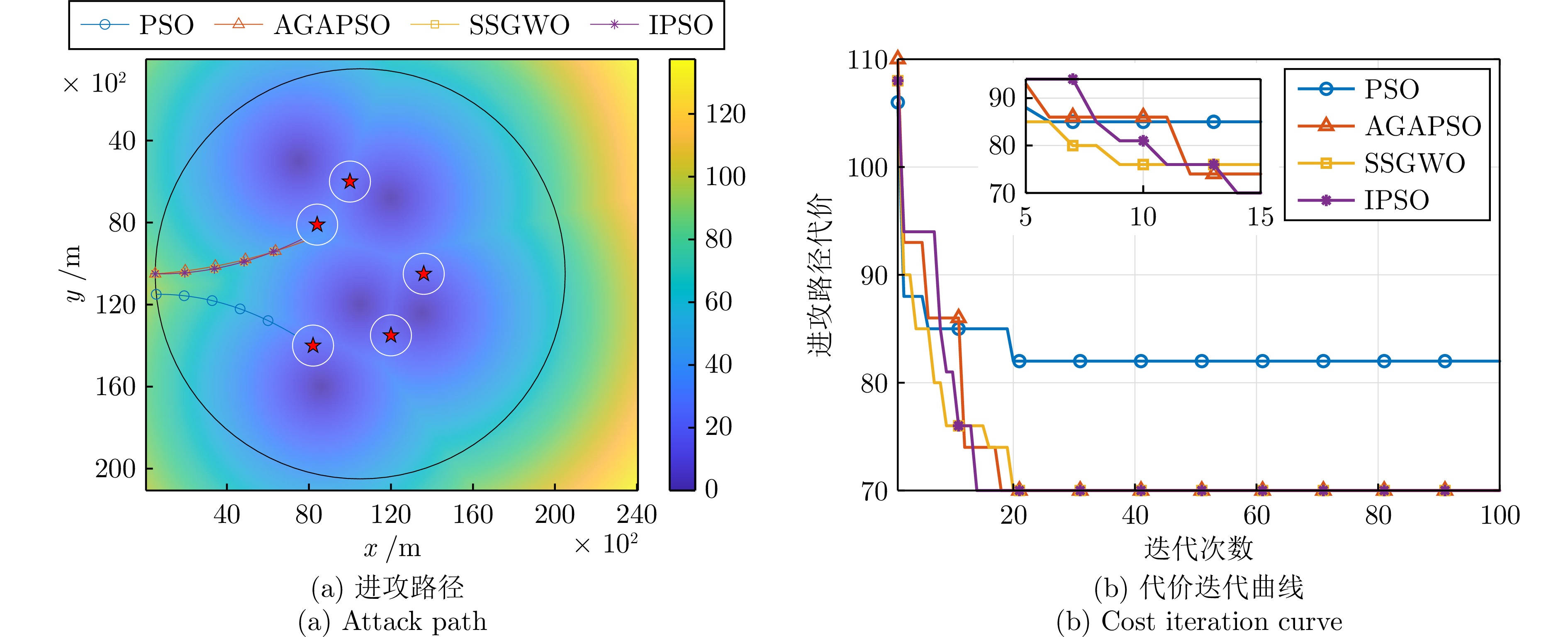
表 1 最优进攻路径代价对比
Table 1 Comparison of optimal attack path costs
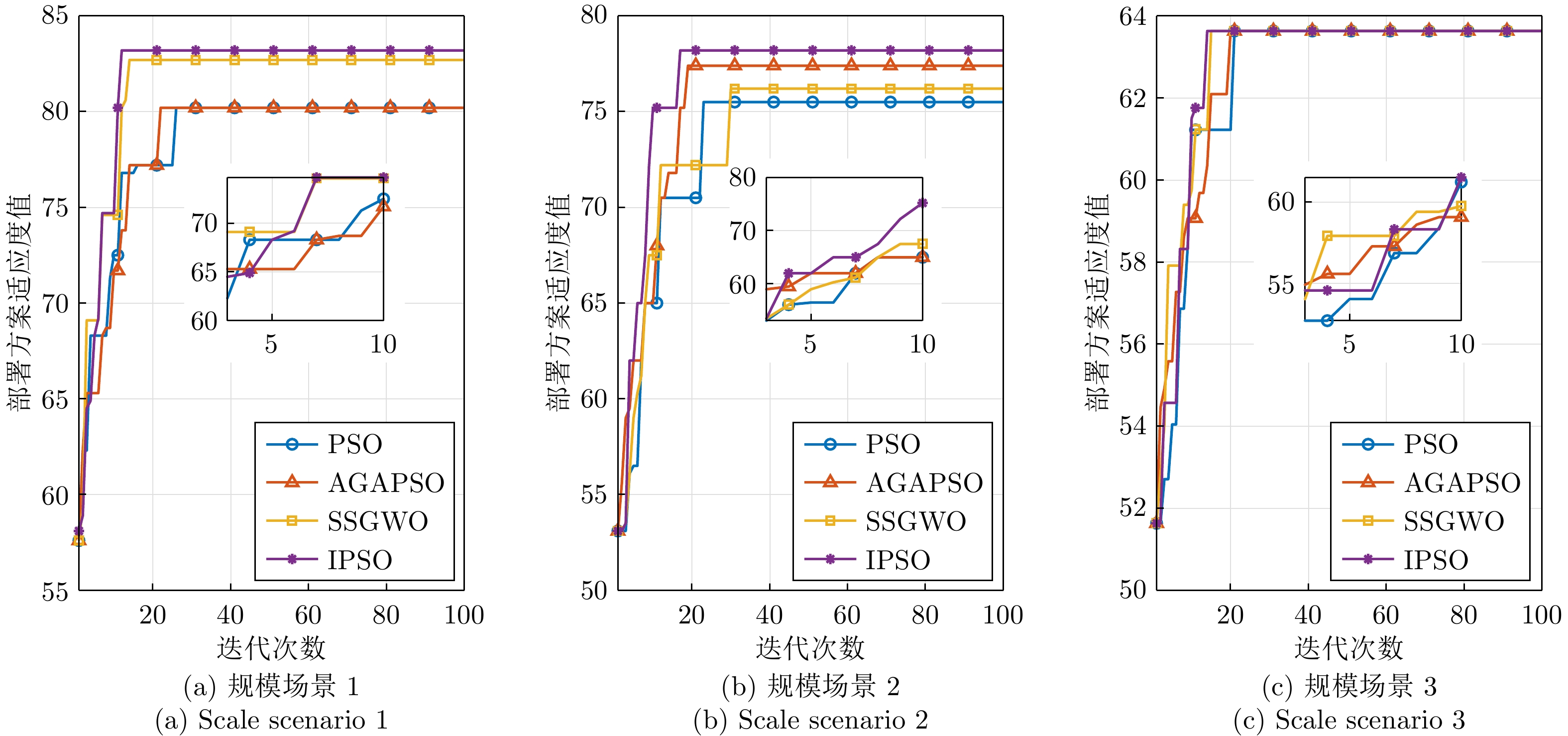
仿真实例 对比指标 PSO AGAPSO SSGWO IPSO 规模场景1 最大值 87.9157 90.1453 83.7577 81.1419 最小值 84.7922 85.7749 79.3922 78.6324 平均值 85.9452 87.0357 81.1712 79.4218 均方差 6.3320 6.9340 7.0318 7.8558 规模场景2 最大值 84.1190 72.7094 72.0462 71.9816 最小值 79.1262 70.2760 70.4387 70.1361 平均值 82.4984 71.6797 71.1869 70.8235 均方差 3.9597 3.6551 4.4898 3.9926 规模场景3 最大值 53.3404 52.7513 52.6991 52.6948 最小值 51.2769 51.2769 51.2769 51.2769 平均值 52.8909 51.9593 51.9407 51.9171 均方差 1.3500 2.8143 2.2543 1.9502 表 2 各算法计算时间对比
Table 2 Comparison of computation time across different algorithms
算法 规模场景1 规模场景2 规模场景3 PSO 0.6864 0.8446 0.9469 AGAPSO 0.6314 0.8430 0.9308 SSGWO 0.6437 0.8236 0.9107 IPSO 0.6357 0.7909 0.8991 表 3 两种模型在对比模型评价指标中的差异
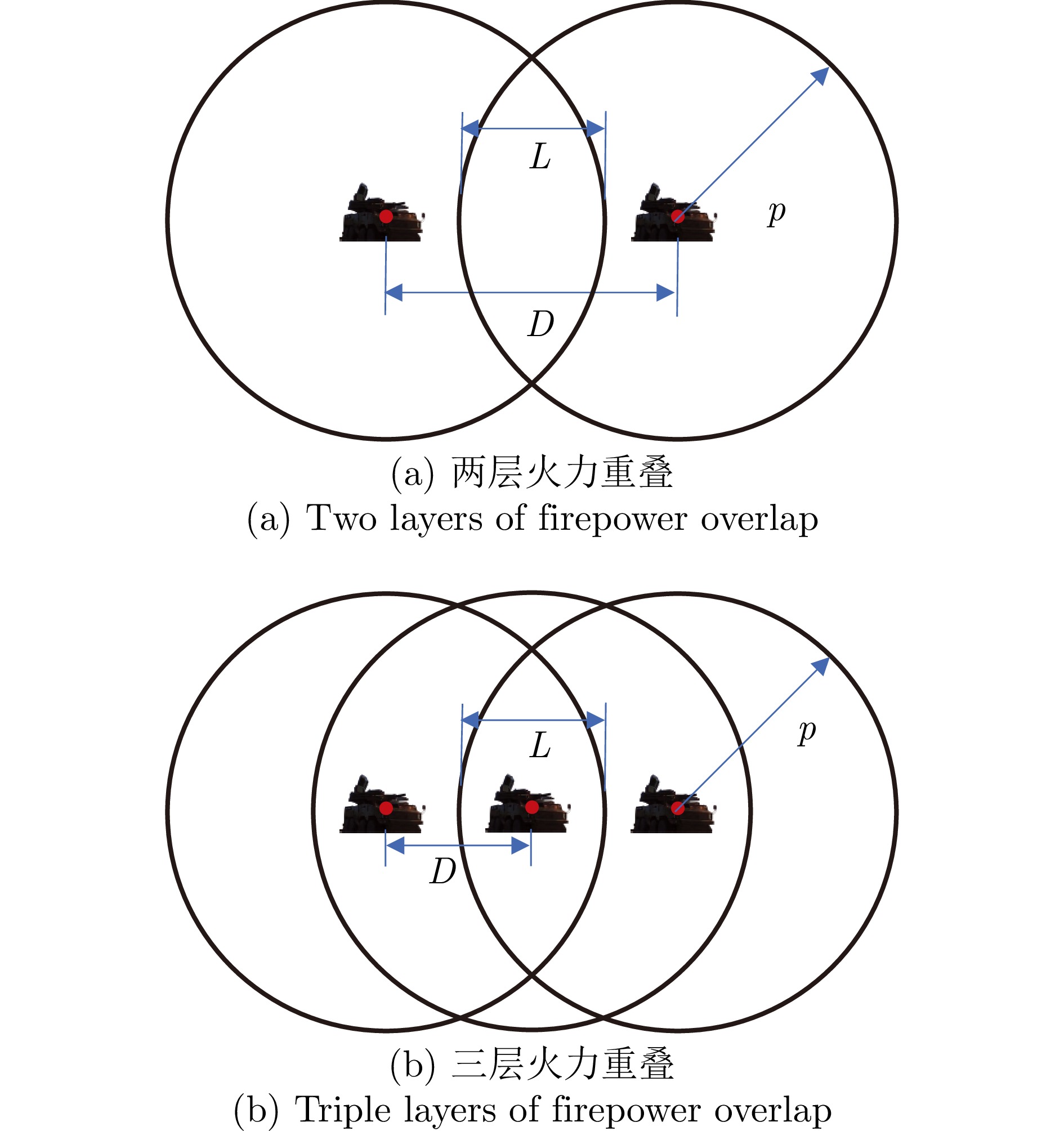
Table 3 Differences between two models in comparative model evaluation indicators
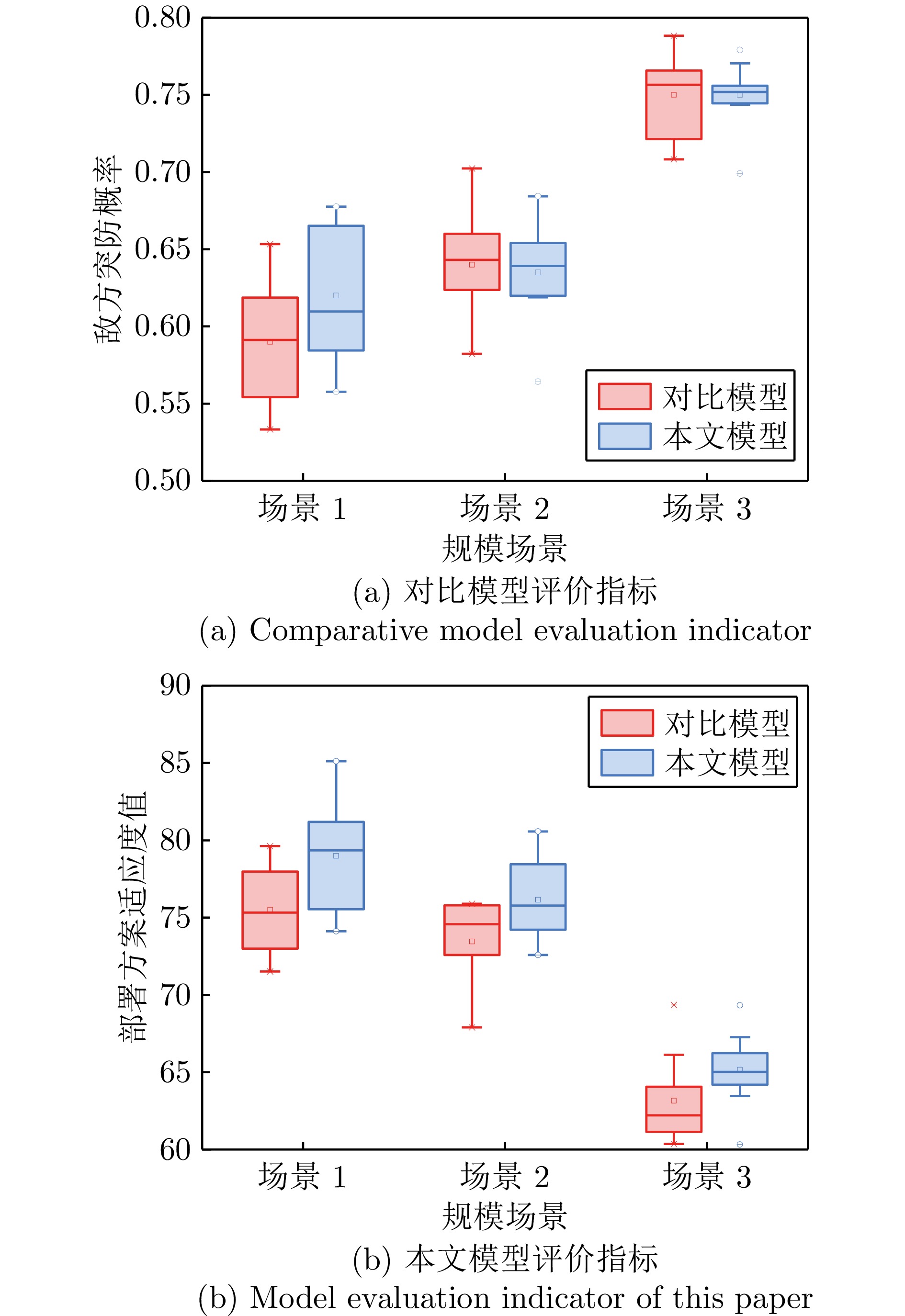
规模 组别 评价指标均值 平均值差 t 显著性 场景1 对比模型 0.5927 0.0288 − 1.6265 0.1212 本文模型 0.6215 场景2 对比模型 0.6438 0.0088 0.3301 0.7451 本文模型 0.6350 场景3 对比模型 0.7500 0.0036 − 0.9334 0.3629 本文模型 0.7536 表 4 两种模型在本文模型评价指标中的差异
Table 4 Differences between two models in the model evaluation indicators of this paper
规模 组别 评价指标均值 平均值差 t 显著性 场景1 对比模型 75.5000 3.5126 − 2.4348 0.0255 *本文模型 79.0126 场景2 对比模型 73.4573 2.6694 2.2003 0.0411 *本文模型 76.1267 场景3 对比模型 63.1573 1.9786 − 1.7206 0.1025 本文模型 65.1359 -
[1] 陈杰, 方浩, 辛斌, 邓方. 数字化陆用武器系统中的建模、优化与控制. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(7): 943−962Chen Jie, Fang Hao, Xin Bin, Deng Fang. Modeling, optimization and control in ground-based digital weapon systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(7): 943−962 [2] 周天颜, 冯小恩, 范云锋, 董诗音, 李玉庆, 金慧中. 避免防空火力过剩的地面兵力防御部署优化模型. 空天防御, 2022, 5(4): 19−23 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4641.2022.04.003Zhou Tian-Yan, Feng Xiao-En, Fan Yun-Feng, Dong Shi-Yin, Li Yu-Qing, Jin Hui-Zhong. Optimization model of ground air defense force deployment to avoid excessive air defense firepower. Air & Space Defense, 2022, 5(4): 19−23 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4641.2022.04.003 [3] 曹伟伟. 高寒山地防空火力配系研究 [硕士学位论文], 国防科技大学, 中国, 2019.Cao Wei-Wei. Study on Air Defense Fire Deployment in Alpine Mountain [Master thesis], National University of Defense Technology, China, 2019. [4] 王凤山, 杨志宏, 郭子曜. 基于三维实景地图的智能兵力部署研究. 舰船电子工程, 2021, 41(10): 107−111 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2021.10.024Wang Feng-Shan, Yang Zhi-Hong, Guo Zi-Yao. Research on intelligent force deployment based on 3D real map. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2021, 41(10): 107−111 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2021.10.024 [5] Bai X S, Fielbaum A, Kronmüller M, Knoedler L, Alonso-Mora J. Group-based distributed auction algorithms for multi-robot task assignment. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(2): 1292−1303 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2022.3175040 [6] Bai X S, Yan W S, Ge S S. Distributed task assignment for multiple robots under limited communication range. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(7): 4259−4271 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3094190 [7] Li Y, Zhang X, Zhao J, Yang X Z, Xi M Y. Position deployment optimization of maneuvering conventional missile based on improved whale optimization algorithm. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2022, 2022: Article No. 4373879 [8] 温包谦, 王涛, 成坤, 张济众. 基于PSO-GA混合算法的末端防御兵力优化部署方法. 兵器装备工程学报, 2019, 40(11): 45−49 doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2019.11.010Wen Bao-Qian, Wang Tao, Cheng Kun, Zhang Ji-Zhong. End-defense force optimization deployment method based on PSO-GA hybrid algorithm. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2019, 40(11): 45−49 doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2019.11.010 [9] Sun W, Cao Z, Wang G, Song Y F, Guo X K. An optimized double-nested anti-missile force deployment based on the deep Kuhn-Munkres algorithm. Mathematics, 2022, 10(23): Article No. 4627 doi: 10.3390/math10234627 [10] 李珂铭, 李定主, 石昊. 基于改进NSGA-Ⅲ 的抗饱和攻击防空编队部署方法. 火力与指挥控制, 2023, 48(4): 153−160 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2023.04.024Li Ke-Ming, Li Ding-Zhu, Shi Hao. Deployment method of air defense formation against saturated attack based on improved NSGA-III. Fire Control & Command Control, 2023, 48(4): 153−160 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2023.04.024 [11] 岳韶华, 何晟, 王刚, 刘伟, 陈晨. 基于改进遗传蜂群算法的武器系统优化部署问题研究. 兵器装备工程学报, 2022, 43(8): 80−86 doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.08.012Yue Shao-Hua, He Sheng, Wang Gang, Liu Wei, Chen Chen. Optimization of weapon system deployment based on improved genetic bee colony algorithm. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2022, 43(8): 80−86 doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.08.012 [12] 张伟, 黄卫民. 基于种群分区的多策略自适应多目标粒子群算法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(10): 2585−2599Zhang Wei, Huang Wei-Min. Multi-strategy adaptive multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on swarm partition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(10): 2585−2599 [13] 刘建华, 刘国买, 杨荣华, 胡文瑜. 粒子群算法的交互性与随机性分析. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(9): 1471−1484 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01471Liu Jian-Hua, Liu Guo-Mai, Yang Rong-Hua, Hu Wen-Yu. Analysis of interactivity and randomness in particle swarm optimization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(9): 1471−1484 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01471 [14] 刘景森, 吉宏远, 李煜. 基于改进蝙蝠算法和三次样条插值的机器人路径规划. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(7): 1710−1719Liu Jing-Sen, Ji Hong-Yuan, Li Yu. Robot path planning based on improved bat algorithm and cubic spline interpolation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(7): 1710−1719 [15] Shi K, Wu W D, Wu Z T, Jiang B P, Karimi H R. Coverage path planning for cleaning robot based on improved simulated annealing algorithm and ant colony algorithm. Signal Image and Video Processing, 2024, 18: 3275−3284 doi: 10.1007/s11760-023-02989-y [16] 刘健. 地空导弹火力单元配置间距计算方法. 弹箭与制导学报, 2007, 27(1): 393−395Liu Jian. A method to calculate the disposition interval of fire units under meeting shooting requests. Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2007, 27(1): 393−395 [17] Xiong R, Wang S L, Huang Q, Yu C M, Fernandez C, Xiao W, et al. Improved cooperative competitive particle swarm optimization and nonlinear coefficient temperature decreasing simulated annealing-back propagation methods for state of health estimation of energy storage batteries. Energy, 2024, 292: Article No. 130594 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2024.130594 [18] Casorrán C, Fortz B, Labbé M, Ordóñez F. A study of general and security Stackelberg game formulations. European Journal of Operational Research, 2019, 278(3): 855−868 doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.05.012 [19] Bo L, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Yang S Q, Wang Y W, Wang Y Y, et al. Research on path planning method of solid backfilling and pushing mechanism based on adaptive genetic particle swarm optimization. Mathematics, 2024, 12(3): Article No. 479 doi: 10.3390/math12030479 [20] Feng J X, Sun C L, Zhang J H, Du Y, Liu Z G, Ding Y M. A UAV path planning method in three-dimensional space based on a hybrid gray wolf optimization algorithm. Electronics, 2024, 13(1): Article No. 68 [21] Chen C, Chen J, Xin B. Hybrid optimization of dynamic deployment for networked fire control system. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 24(6): 954−3961 doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2013.00112 [22] 周宏宇, 王小刚, 单永志, 赵亚丽, 崔乃刚. 基于改进粒子群算法的飞行器协同轨迹规划. 自动化学报, 2022, 148(11): 2670−2676Zhou Hong-Yu, Wang Xiao-Gang, Shan Yong-Zhi, Zhao Ya-Li, Cui Nai-Gang. Synergistic path planning for multiple vehicles based on an improved particle swarm optimization method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 148(11): 2670−2676 -




 下载:
下载: