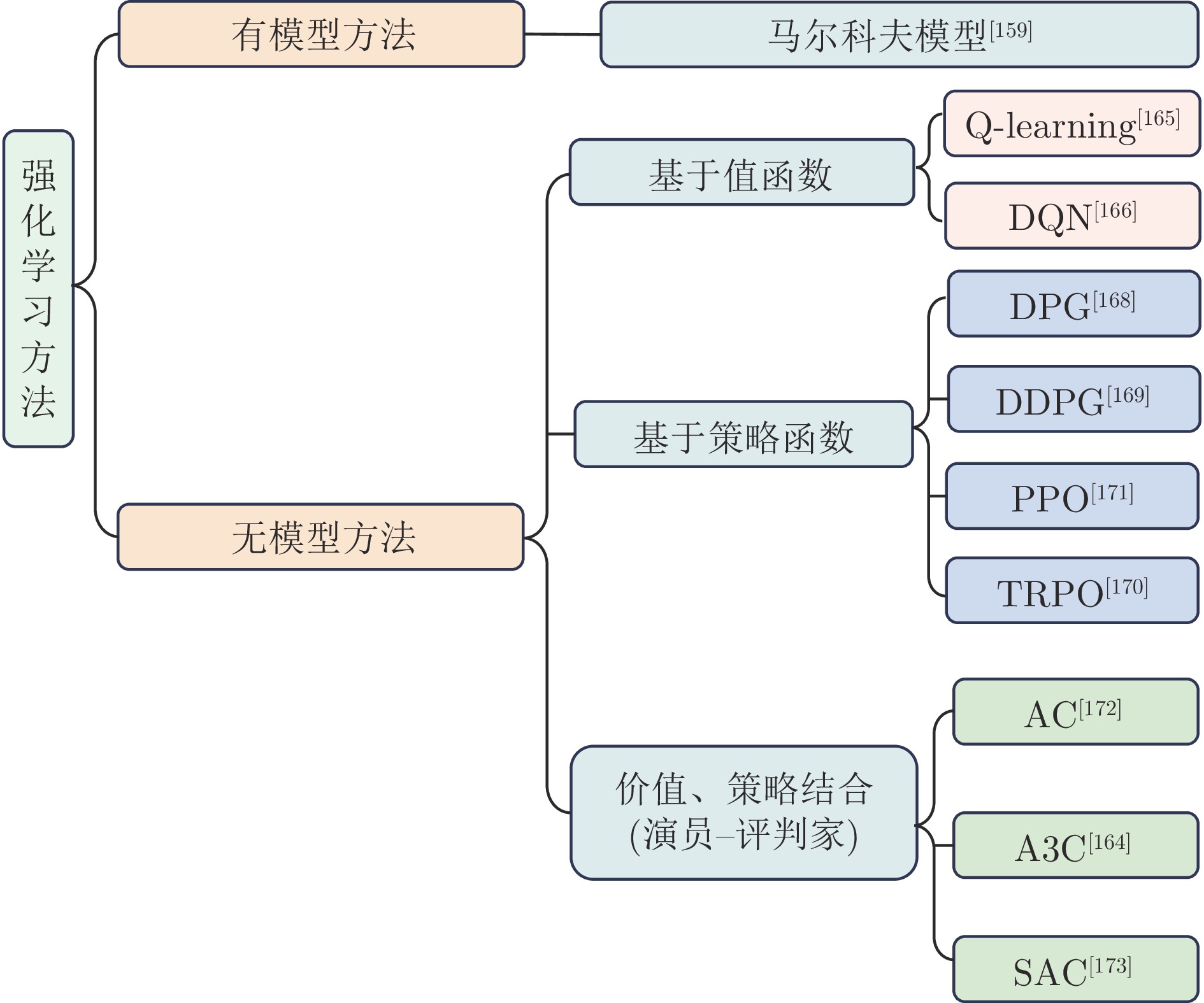
-
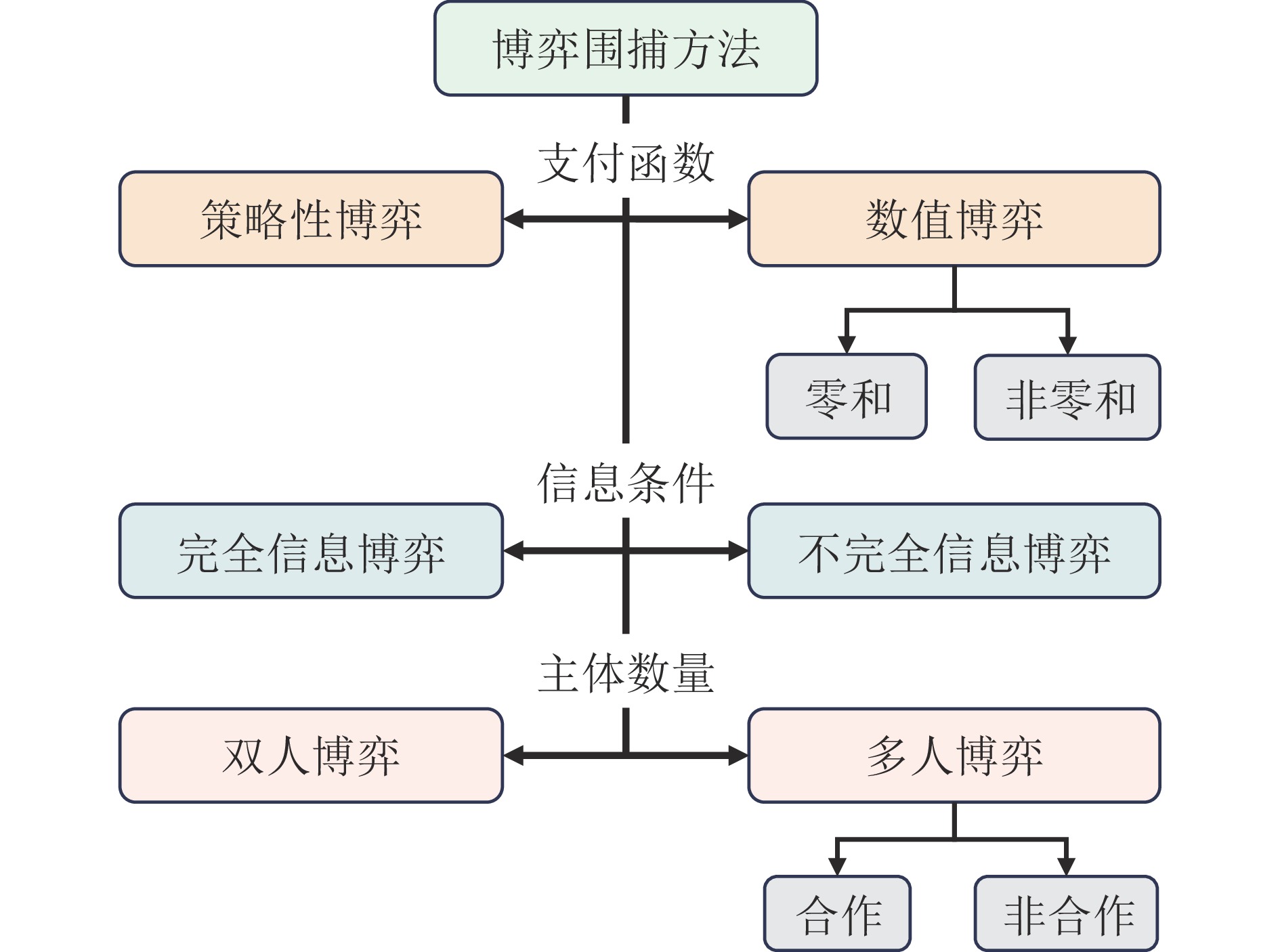
摘要: 多机协同围捕作为多机器人协同领域的一项重要分支, 着重研究多个机器人通过相互协作对动态可疑目标实现有效的追踪与围捕, 在军事侦查、紧急救援、协同探测等领域具有重要的研究意义与实际应用价值. 首先通过国内外科学引文数据库对多机协同围捕领域相关的文献进行全面检索, 深入剖析目前该领域前沿技术的发展现状与研究热点. 接下来从理论与技术层面分别针对多机协同围捕领域中的目标协同搜索、多机任务分配、协同围捕控制等方面进行全面总结, 重点阐述各研究内容常用方法与技术的工作原理、优缺点及适用范围等. 最后对该领域的发展现状进行总结, 并分析探讨目前尚未解决的难点, 对未来的发展方向提出展望.Abstract: As a significant branch of multi-robot coordination, multi-robot cooperative hunting mainly focuses on tracking and capturing dynamic suspicious targets effectively through cooperation. It has important significance and has been applied in various fields, such as military reconnaissance, emergency rescue, and collaborative detection. This paper conducts a comprehensive search of relevant literature in the field of multi-robot cooperative hunting through domestic and foreign scientific citation databases. It then thoroughly analyzes the current development status and research hotspots of frontier technologies in this field. Following this, the paper offers a thorough summary of research in the field of multi-robot cooperative hunting, covering theoretical and technical aspects, which concentrates on target cooperative search, multi-robot task allocation, and cooperative hunting control, etc.. The working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and application ranges of commonly used methods and technologies in each research aspect are introduced in detail. Finally, this paper summarizes the current state of development and unresolved challenges in this field, and suggests potential directions for future development.
-
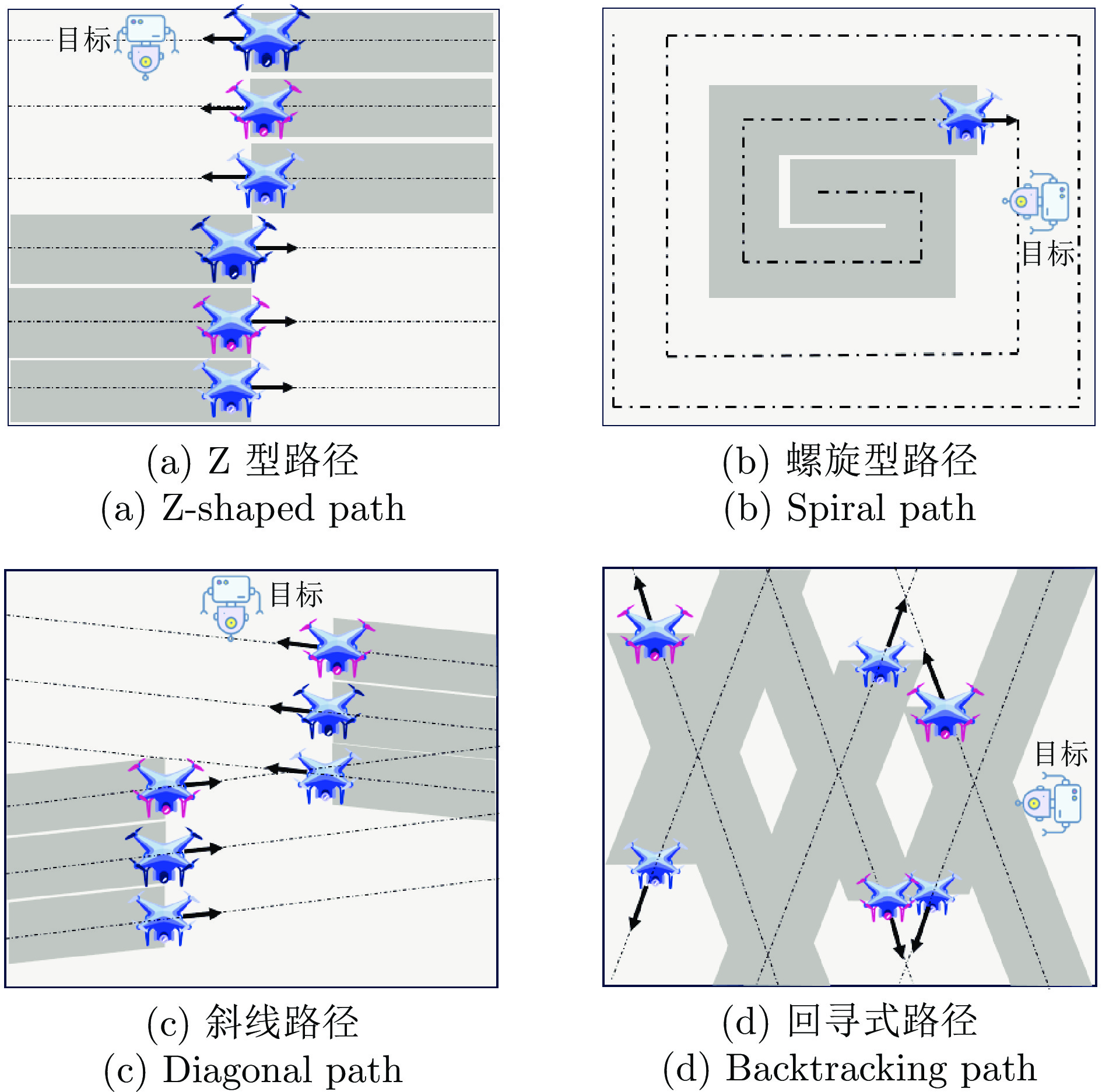
表 1 多机协同搜索方法总结
Table 1 Summary of multi-robot cooperative search methods
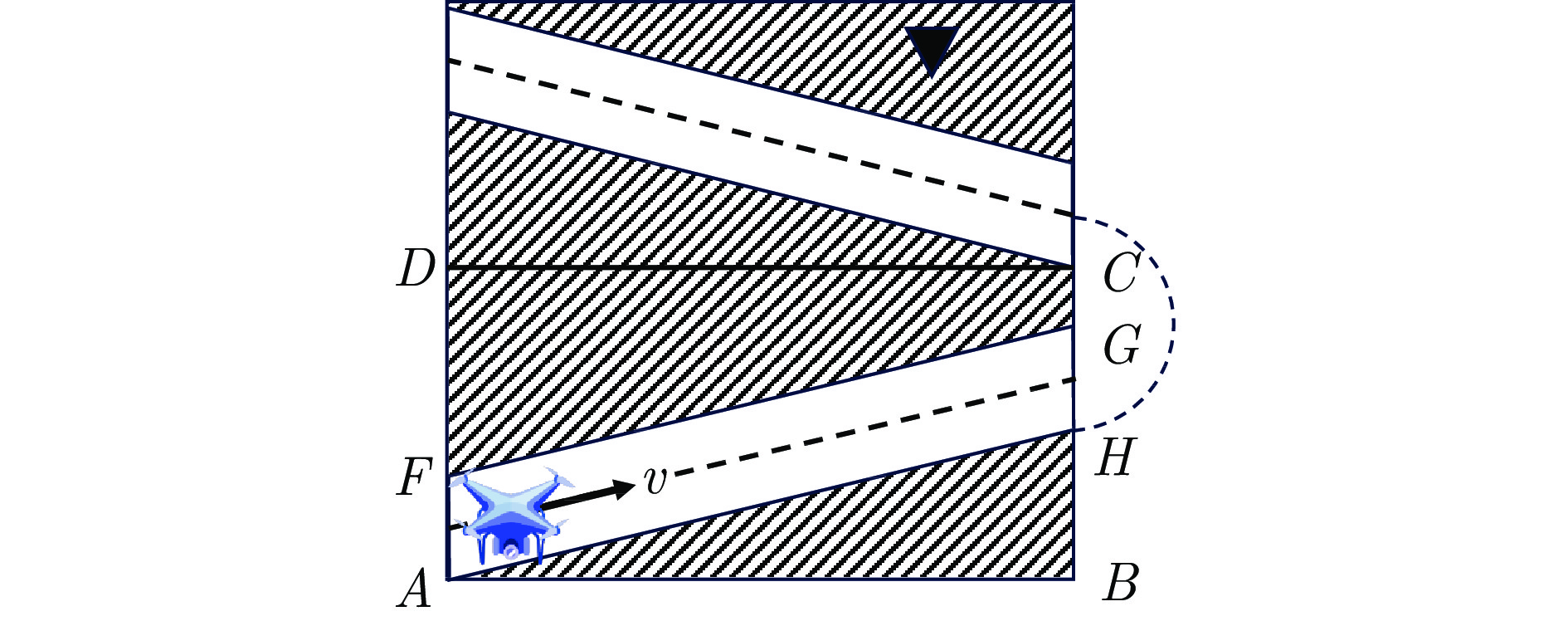
表 2 围捕机器人常见运动学与动力学约束
Table 2 Common kinematic and dynamic constraints of hunting robots
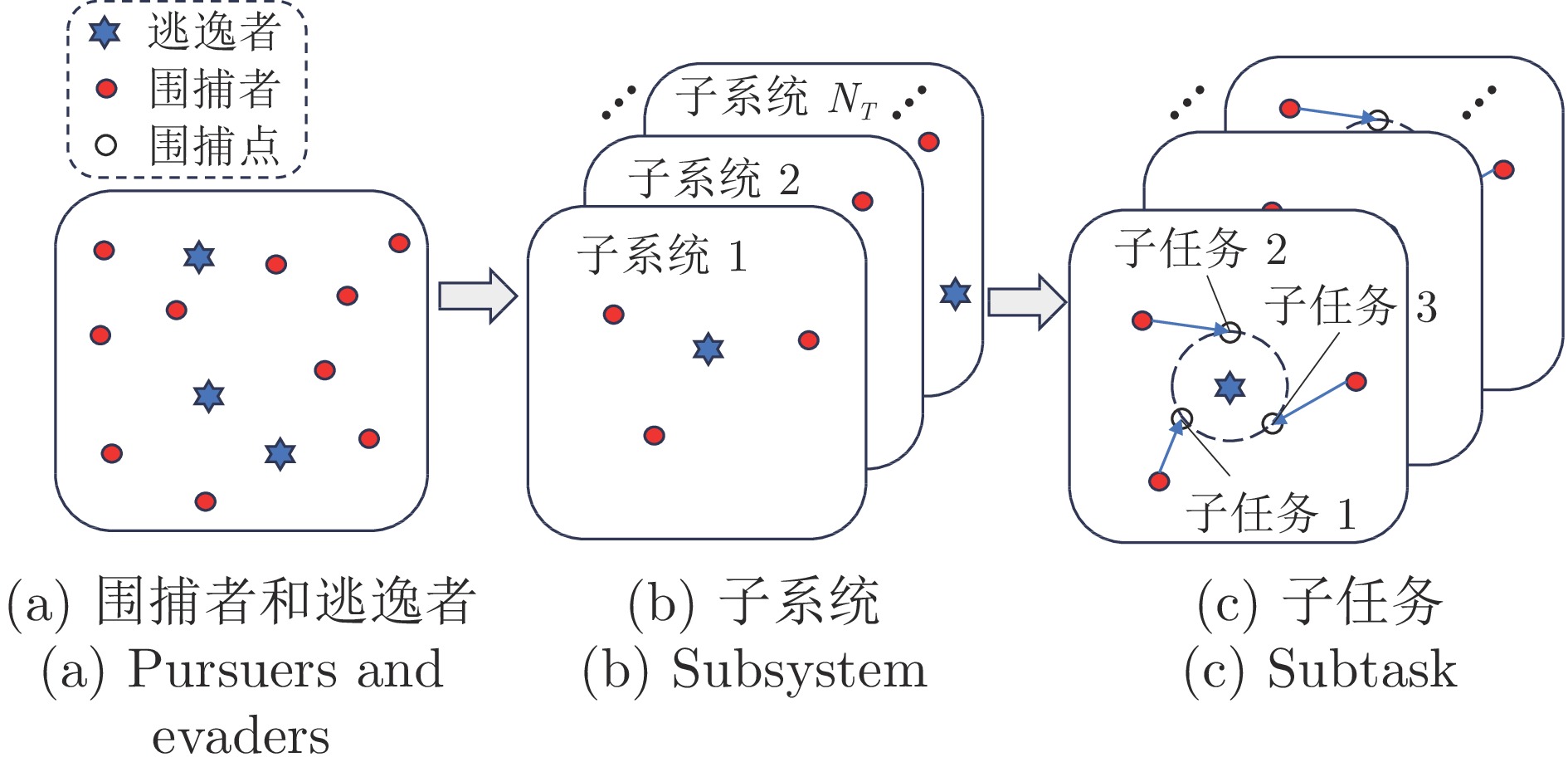
运动学与动力学约束 约束描述 最小、最大运动速度约束 围捕机器人速度须介于最小速度和最大速度之间 最小、最大运动加速度约束 围捕机器人加速度须介于最小加速度和最大加速度之间 最小步长约束 围捕机器人轨迹从当前状态到改变行进方向的下一状态之间的直线运动距离须大于最小步长 最小转弯半径约束 围捕机器人轨迹的转弯半径须大于最小转弯半径 最大航偏角约束 围捕机器人运动过程中的航偏角须小于最大航偏角 表 3 多机器人协同围捕任务分配方法总结
Table 3 Summary of multi-robot cooperative hunting task allocation methods
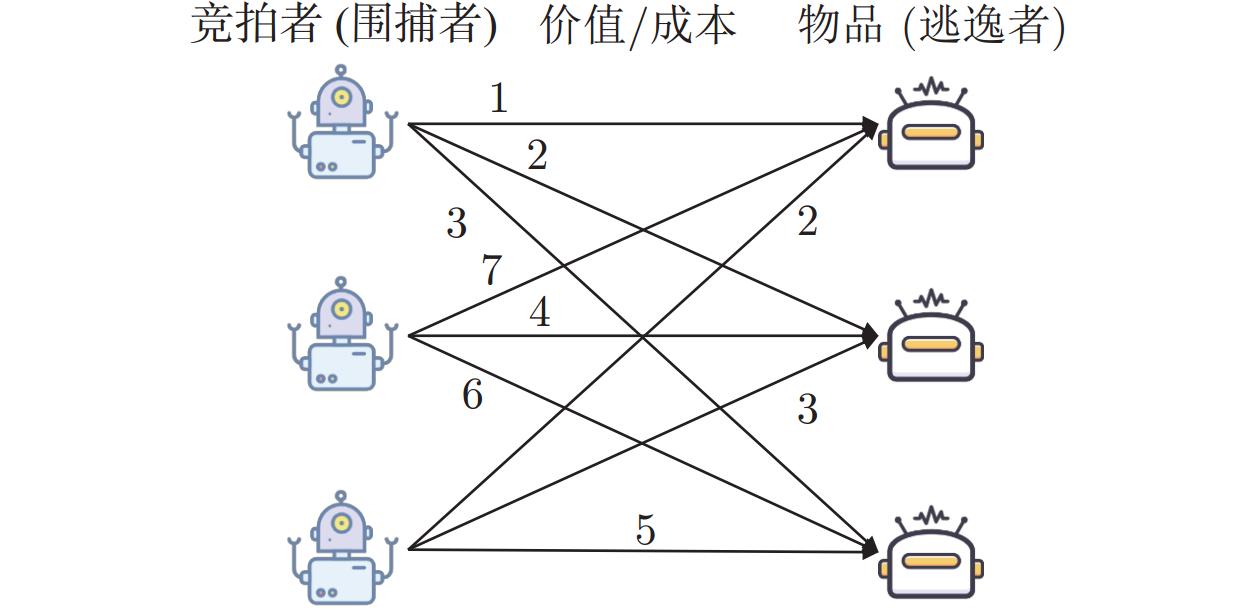
任务分配算法 架构特点 优点 缺点 贪婪算法[91] 集中式 实时性高, 简单易实现 局部最优解, “死锁”分配 匈牙利算法[74−75] 集中式 效率高, 局部最优解, 简单易实现 不适合大规模任务分配场景, 只适合一对一分配 遗传算法[81] 集中式 全局搜索能力, 适应性和鲁棒性, 并行性 计算成本高, 难以收敛, 参数设置敏感, 编码方式选择困难 粒子群算法[88, 90] 集中式 快速收敛, 简单易实现, 适应性强 过早收敛, 参数敏感 契约合同网络方法[95−96] 分布式 分布式协作, 动态灵活性, 适应性 高复杂性和通讯开销大, 信任建立和信息共享困难 拍卖算法[106−107] 分布式 分布式协作, 灵活性, 任务动态调整 竞争激烈可能导致效率下降, 存在信息不对称, 对于大规模问题不再适用 表 4 生物启发式神经网络方法分析
Table 4 Biologically inspired neural network method analysis
领域 内容 优点 缺点 路径规划[125−126, 128] 解决机器人路径规划、防碰撞问题 实时性好 仅适用于二维平面 多机围捕[137] 首次将围捕问题与生物神经网络模型对应 兼顾围捕任务目标搜索、任务分配过程 模型设计复杂 路径规划[129] 引入假想非障碍物相邻点, 考虑转角因素 解决路径错判问题 计算效率低 路径规划[130] 模型考虑相邻神经元权值影响 使模型更具网络特性 增加碰撞检测计算节点 路径规划[131−132] 决策项考虑洋流影响 使方法更贴合实际环境 缺乏高效任务分配方法 多机围捕[133−134] 决策项考虑洋流影响 使方法更贴合实际环境 规划路径可能并非最优解 多机围捕[135] 设计基于协商思想的任务分配方法 增加围捕任务效率 仅适用于低维环境 多机围捕[136] 将方法拓展至三维环境 增强方法的可拓展性 奖励函数设计复杂、计算效率低 -
[1] Motes J, Chen T, Bretl T, Aguirre M M, Amato N M. Hypergraph-based multi-robot task and motion planning. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2023, 39(5): 4166−4186 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2023.3297011 [2] Liu W H, Hu J W, Zhang H, Wang M Y, Xiong Z H. A novel graph-based motion planner of multi-mobile robot systems with formation and obstacle constraints. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2024, 40: 714−728 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2023.3339989 [3] Robin C, Lacroix S. Multi-robot target detection and tracking: Taxonomy and survey. Autonomous Robots, 2016, 40(4): 729−760 doi: 10.1007/s10514-015-9491-7 [4] 寇立伟, 项基. 基于输出反馈线性化的多移动机器人目标包围控制. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(5): 1285−1291Kou Li-Wei, Xiang Ji. Target fencing control of multiple mobile robots using output feedback linearization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(5): 1285−1291 [5] Duberg D, Jensfelt P. UFOExplorer: Fast and scalable sampling-based exploration with a graph-based planning structure. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 2487−2494 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3142923 [6] Li Q B, Lin W Z, Liu Z, Prorok A. Message-aware graph attention networks for large-scale multi-robot path planning. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(3): 5533−5540 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3077863 [7] Hu J W, Xie L H, Lum K Y, Xu J. Multiagent information fusion and cooperative control in target search. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2013, 21(4): 1223−1235 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2012.2198650 [8] Lin Y C, Saripalli S. Sampling-based path planning for UAV collision avoidance. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(11): 3179−3192 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2673778 [9] Phung M D, Ha Q P. Safety-enhanced UAV path planning with spherical vector-based particle swarm optimization. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 107: Article No. 107376 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107376 [10] 彭辉, 沈林成, 霍霄华. 多UAV协同区域覆盖搜索研究. 系统仿真学报, 2007, 19(11): 2472−2476 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2007.11.022Peng Hui, Shen Lin-Cheng, Huo Xiao-Hua. Research on multiple UAV cooperative area coverage searching. Journal of System Simulation, 2007, 19(11): 2472−2476 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2007.11.022 [11] 王洪民, 田家强, 韦凌云, 庄育锋. 多运动目标的多无人机协同搜索追踪策略. 控制理论与应用, 2021, 38(7): 971−978 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.00565Wang Hong-Min, Tian Jia-Qiang, Wei Ling-Yun, Zhuang Yu-Feng. Multi-unmanned aerial vehicles cooperative searching and tracking strategy for multiple moving targets. Control Theory & Applications, 2021, 38(7): 971−978 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.00565 [12] Sun L, Baek S, Pack D. Distributed probabilistic search and tracking of agile mobile ground targets using a network of unmanned aerial vehicles. Human Behavior Understanding in Networked Sensing: Theory and Applications of Networks of Sensors. Cham: Springer, 2014. 301–319 [13] 轩永波, 黄长强, 吴文超, 王勇, 翁兴伟, 李望西. 多无人机协同搜索随机目标决策. 控制与决策, 2013, 28(5): 711−715Xuan Yong-Bo, Huang Chang-Qiang, Wu Wen-Chao, Wang Yong, Weng Xing-Wei, Li Wang-Xi. Cooperative search stategies of multi-UAVs for random targets. Control and Decision, 2013, 28(5): 711−715 [14] El-Hady Kassem M A, El-Hadidy M A A. Optimal multiplicative Bayesian search for a lost target. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2014, 247: 795−802 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2014.09.039 [15] Xu X L, Yang L X, Meng W, Cai Q Q, Fu M Y. Multi-agent coverage search in unknown environments with obstacles: A survey. In: Proceedings of the Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Guangzhou, China: IEEE, 2019. 2317–2322 [16] 张世勇, 张雪波, 苑晶, 方勇纯. 旋翼无人机环境覆盖与探索规划方法综述. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(3): 513−529Zhang Shi-Yong, Zhang Xue-Bo, Yuan Jing, Fang Yong-Chun. A survey on coverage and exploration path planning with multi-rotor micro aerial vehicles. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(3): 513−529 [17] Barrientos A, Colorado J, del Cerro J, Martinez A, Rossi C, Sanz D, et al. Aerial remote sensing in agriculture: A practical approach to area coverage and path planning for fleets of mini aerial robots. Journal of Field Robotics, 2011, 28(5): 667−689 doi: 10.1002/rob.20403 [18] Bast H, Hert S. The area partitioning problem. In: Proceedings of the 12th Annual Canadian Conference on Computational Geometry (CCCG-00). Fredericton, Canada: University of New Brunswick, 2000. 163–171 [19] Chen J C, Du C L, Zhang Y, Han P C, Wei W. A clustering-based coverage path planning method for autonomous heterogeneous UAVs. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(12): 25546−25556 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3066240 [20] Mei Y G, Lu Y H, Hu Y C, Lee C S G. Deployment of mobile robots with energy and timing constraints. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2006, 22(3): 507−522 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2006.875494 [21] Bouzid Y, Bestaoui Y, Siguerdidjane H. Quadrotor-UAV optimal coverage path planning in cluttered environment with a limited onboard energy. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 979–984 [22] 轩永波, 黄长强, 吴文超, 于文波, 王勇, 翁兴伟. 运动目标的多无人机编队覆盖搜索决策. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(3): 539−544 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.03.15Xuan Yong-Bo, Huang Chang-Qiang, Wu Wen-Chao, Yu Wen-Bo, Wang Yong, Weng Xing-Wei. Coverage search strategies for moving targets using multiple unmanned aerial vehicle teams. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(3): 539−544 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.03.15 [23] 王勋, 姚佩阳, 梅权. 多无人机协同运动目标搜索问题研究. 电光与控制, 2016, 23(8): 18−22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2016.08.005Wang Xun, Yao Pei-Yang, Mei Quan. On multi-UAV cooperation for moving target searching. Electronics Optics & Control, 2016, 23(8): 18−22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2016.08.005 [24] 曾国奇, 白宇, 林伟, 丁文锐. 地面运动目标的多UAV协同搜索方法. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(7): 1498−1505 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.07.13Zeng Guo-Qi, Bai Yu, Lin Wei, Ding Wen-Rui. Multi-UAV cooperative search method for ground moving targets. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(7): 1498−1505 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.07.13 [25] Nam L H, Huang L L, Li X J, Xu J F. An approach for coverage path planning for UAVs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 14th International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control (AMC). Auckland, New Zealand: IEEE, 2016. 411–416 [26] Xing C, Wang J L, Xu Y M. Overlap analysis of the images from unmanned aerial vehicles. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical and Control Engineering. Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2010. 1459–1462 [27] Valente J, Sanz D, del Cerro J, Barrientos A, de Frutos M Á. Near-optimal coverage trajectories for image mosaicing using a mini quad-rotor over irregular-shaped fields. Precision Agriculture, 2013, 14(1): 115−132 doi: 10.1007/s11119-012-9287-0 [28] di Franco C, Buttazzo G. Coverage path planning for UAVs photogrammetry with energy and resolution constraints. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2016, 83(3): 445−462 [29] Cabreira T M, di Franco C, Ferreira P R, Buttazzo G C. Energy-aware spiral coverage path planning for UAV photogrammetric applications. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(4): 3662−3668 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2854967 [30] 赵发, 綦秀利, 余晓晗, 张所娟, 李本凌. 基于多无人机自主协作任务规划的区域搜索与目标围捕问题研究. 电子技术与软件工程, 2022(11): 141−146Zhao Fa, Qi Xiu-Li, Yu Xiao-Han, Zhang Suo-Juan, Li Ben-Ling. Research on area search and target rounding problem based on multi-UAV autonomous collaborative mission planning. Electronic Technology & Software Engineering, 2022(11): 141−146 [31] 刘云辉, 石永康. 未知环境下多无人机协同搜索与围捕策略研究. 现代电子技术, 2023, 46(6): 98−104Liu Yun-Hui, Shi Yong-Kang. Research on cooperative search and round up strategy of multiple-UAV in unknown environment. Modern Electronics Technique, 2023, 46(6): 98−104 [32] Sauter J, Matthews R, Parunak H, Brueckner S. Demonstration of digital pheromone swarming control of multiple unmanned air vehicles. In: Proceedings of the Infotech@Aerospace. Arlington, Virginia: AIAA, 2005. Article No. 7046 [33] Aznar F, Pujol M, Rizo R, Rizo C. Modelling multi-rotor UAVs swarm deployment using virtual pheromones. PLoS One, 2018, 13(1): Article No. e0190692 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190692 [34] 甄子洋. 无人机集群作战协同控制与决策. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2022.Zhen Zi-Yang. Cooperative Control and Decision of UAV Swarm Operations. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2022. [35] 高炳霞, 张波涛, 王坚, 吴秋轩. 一种基于概率地图的移动机器人最优期望时间目标搜索. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(4): 944−952Gao Bing-Xia, Zhang Bo-Tao, Wang Jian, Wu Qiu-Xuan. An expected-time optimal target search method based on probabilistic maps. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(4): 944−952 [36] Hu J W, Xie L H, Xu J, Xu Z. Multi-agent cooperative target search. Sensors, 2014, 14(6): 9408−9428 doi: 10.3390/s140609408 [37] Sharma R, Yoder J, Kwon H, Pack D. Vision based mobile target geo-localization and target discrimination using Bayes detection theory. Distributed Autonomous Robotic Systems: The 11th International Symposium. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2014. 59–71 [38] 黄书召, 田军委, 乔路, 王沁, 苏宇. 基于改进遗传算法的无人机路径规. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(2): 390−397Huang Shu-Zhao, Tian Jun-Wei, Qiao Lu, Wang Qin, Su Yu. Unmanned aerial vehicle path planning based on improved genetic algorithm. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(2): 390−397 [39] 朱梦圆, 吕娜, 陈柯帆, 钟赟, 刘创, 高维廷. 航空集群协同搜索马尔科夫运动目标方法. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(9): 2041−2047 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.17Zhu Meng-Yuan, Lv Na, Chen Ke-Fan, Zhong Yun, Liu Chuang, Gao Wei-Ting. Collaborative aeronautic swarm search of Markov moving targets. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(9): 2041−2047 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.17 [40] Xin Y, Liang H W, Mei T, Huang R L, Du M B, Sun C, et al. A new occupancy grid of the dynamic environment for autonomous vehicles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium Proceedings. Dearborn, USA: IEEE, 2014. 787–792 [41] Sharifi F, Mirzaei M, Zhang Y M, Gordon B W. Cooperative multi-vehicle search and coverage problem in an uncertain environment. Unmanned Systems, 2015, 3(1): 35−47 doi: 10.1142/S230138501550003X [42] 沈东, 魏瑞轩, 祁晓明, 关旭宁. 基于MTPM和DPM的多无人机协同广域目标搜索滚动时域决策. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(7): 1391−1403Shen Dong, Wei Rui-Xuan, Qi Xiao-Ming, Guan Xu-Ning. Receding horizon decision method based on MTPM and DPM for multi-UAVs cooperative large area target search. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(7): 1391−1403 [43] Steyer S, Tanzmeister G, Wollherr D. Grid-based environment estimation using evidential mapping and particle tracking. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2018, 3(3): 384−396 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2018.2843130 [44] Lum C, Rysdyk R, Pongpunwattana A. Occupancy based map searching using heterogeneous teams of autonomous vehicles. In: Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit. Keystone, Colorado: AIAA, 2006. Article No. 6196 [45] Erignac C. An exhaustive swarming search strategy based on distributed pheromone maps. In: Proceedings of the AIAA Infotech@Aerospace 2007 Conference and Exhibit. Rohnert Park, California: AIAA, 2007. Article No. 2822 [46] 范衠, 孙福赞, 马培立, 李文姬, 石泽, 王诏君, 等. 基于共识主动性的群体机器人目标搜索与围捕. 北京理工大学学报, 2022, 42(2): 158−167Fan Zhun, Sun Fu-Zan, Ma Pei-Li, Li Wen-Ji, Shi Ze, Wang Zhao-Jun, et al. Stigmergy-based swarm robots for target search and trapping. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2022, 42(2): 158−167 [47] 彭辉, 沈林成, 朱华勇. 基于分布式模型预测控制的多UAV协同区域搜索. 航空学报, 2010, 31(3): 593−601Peng Hui, Shen Lin-Cheng, Zhu Hua-Yong. Multiple UAV cooperative area search based on distributed model predictive control. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 593−601 [48] 彭辉. 分布式多无人机协同区域搜索中的关键问题研究 [博士学位论文], 国防科学技术大学, 中国, 2009.Peng Hui. A Study of Key Issues in Distributed Multi-UAV Collaborative Area Searches [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, China, 2009. [49] Delight M, Ramakrishnan S, Zambrano T, MacCready T. Developing robotic swarms for ocean surface mapping. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Stockholm, Sweden: IEEE, 2016. 5309–5315 [50] Khan A, Yanmaz E, Rinner B. Information exchange and decision making in micro aerial vehicle networks for cooperative search. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2015, 2(4): 335−347 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2015.2426771 [51] Shen Y K, Wei C, Sun Y B, Duan H B. Bird flocking inspired methods for multi-UAV cooperative target search. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2024, 71(2): 702−706 [52] 郑伟铭, 周贞文, 徐扬, 罗德林. 针对运动目标的多无人机协同鸽群优化搜索方法. 控制理论与应用, 2023, 40(4): 624−632 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.10466Zheng Wei-Ming, Zhou Zhen-Wen, Xu Yang, Luo De-Lin. Multi-UAV cooperative pigeon-inspired optimization search method for moving targets. Control Theory & Applications, 2023, 40(4): 624−632 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.10466 [53] 周鹤翔, 徐扬, 罗德林. 针对动态目标的多无人机协同组合差分进化搜索方法. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(11): 3128−3136Zhou He-Xiang, Xu Yang, Luo De-Lin. A composite differential evolution algorithm for multi-UAV cooperative dynamic target search. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(11): 3128−3136 [54] 岳伟, 辛弘, 林彬, 刘中常, 李莉莉. MAUV协同搜索多智能目标的路径规划. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(11): 2065−2073 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.11140Yue Wei, Xin Hong, Lin Bin, Liu Zhong-Chang, Li Li-Li. Path planning of MAUV cooperative search for multi-intelligent targets. Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 39(11): 2065−2073 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.11140 [55] Zhen Z Y, Chen Y, Wen L D, Han B. An intelligent cooperative mission planning scheme of UAV swarm in uncertain dynamic environment. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 100: Article No. 105826 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105826 [56] 过劲劲, 齐俊桐, 王明明, 吴冲, 徐士博. 未知区域中四旋翼无人机集群协同搜索与围捕算法. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(8): 2001−2010Guo Jin-Jin, Qi Jun-Tong, Wang Ming-Ming, Wu Chong, Xu Shi-Bo. A cooperative search and encirclement algorithm for quadrotors in unknown areas. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(8): 2001−2010 [57] 黄依新, 相晓嘉, 周晗, 闫超, 常远, 孙懿豪. 基于概率图模型的多机器人自组织协同围捕方法. 控制理论与应用, 2023, 40(12): 2225−2235 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2023.30245Huang Yi-Xin, Xiang Xiao-Jia, Zhou Han, Yan Chao, Chang Yuan, Sun Yi-Hao. Multi-robot self-organizing cooperative pursuit method based on probabilistic graphical model. Control Theory & Applications, 2023, 40(12): 2225−2235 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2023.30245 [58] Jiang P Y, Ergu D, Liu F Y, Cai Y, Ma B. A review of Yolo algorithm developments. Procedia Computer Science, 2022, 199: 1066−1073 doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2022.01.135 [59] Wu Z, Tang W L, Chen S J, Jiang L, Fu C W. CIA-SSD: Confident IoU-aware single-stage object detector from point cloud. In: Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI, 2021. 3555–3562 [60] Zhang H K, Chang H, Ma B P, Wang N Y, Chen X L. Dynamic R-CNN: Towards high quality object detection via dynamic training. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 260–275 [61] Qiao L M, Zhao Y X, Li Z Y, Qiu X, Wu J N, Zhang C. DeFRCN: Decoupled faster R-CNN for few-shot object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 8681–8690 [62] Shi J F, Zhang T Q, He G H, Hao F. A review of abnormal personnel behavior detection based on deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP). Queenstown, New Zealand: IEEE, 2023. 1–5 [63] Sabokrou M, Fayyaz M, Fathy M, Moayed Z, Klette R. Deep-anomaly: Fully convolutional neural network for fast anomaly detection in crowded scenes. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2018, 172: 88−97 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2018.02.006 [64] Pang G S, Yan C, Shen C H, van den Hengel A, Bai X. Self-trained deep ordinal regression for end-to-end video anomaly detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 12173–12182 [65] Ramachandra B, Jones M J, Vatsavai R R. Learning a distance function with a Siamese network to localize anomalies in videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Snowmass, USA: IEEE, 2020. 2598–2607 [66] Wu P, Liu J, Shen F. A deep one-class neural network for anomalous event detection in complex scenes. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(7): 2609−2622 [67] Samuel R D J, Fenil E, Manogaran G, Vivekananda G N, Thanjaivadivel T, Jeeva S, et al. Real time violence detection framework for football stadium comprising of big data analysis and deep learning through bidirectional LSTM. Computer Networks, 2019, 151: 191−200 doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2019.01.028 [68] Ravanbakhsh M, Nabi M, Sangineto E, Marcenaro L, Regazzoni C, Sebe N. Abnormal event detection in videos using generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2017. 1577–1581 [69] Ravanbakhsh M, Sangineto E, Nabi M, Sebe N. Training adversarial discriminators for cross-channel abnormal event detection in crowds. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1896–1904 [70] Yang Q, Fu S, Wang H G, Fang H. Machine-learning-enabled cooperative perception for connected autonomous vehicles: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(3): 96−101 doi: 10.1109/MNET.011.2000560 [71] An Q E, Wang Y L, Shen Y. Sensor deployment for visual 3D perception: A perspective of information gains. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(6): 8464−8478 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3050325 [72] 李新德, 杨伟东, Dezert Jean. 一种飞机图像目标多特征信息融合识别方法. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(8): 1298−1307 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01298Li Xin-De, Yang Wei-Dong, Dezert Jean. An airplane image target's multi-feature fusion recognition method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(8): 1298−1307 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01298 [73] 王峰, 黄子路, 韩孟臣, 邢立宁, 王凌. 基于KnCMPSO算法的异构无人机协同多任务分配. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(2): 399−414Wang Feng, Huang Zi-Lu, Han Meng-Chen, Xing Li-Ning, Wang Ling. A knee point based coevolution multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm for heterogeneous UAV cooperative multi-task allocation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(2): 399−414 [74] Liao J, Liu C, Liu H H T. Model predictive control for cooperative hunting in obstacle rich and dynamic environments. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2021. 5089–5095 [75] Zhu J L, Fang B F. Emotional robot pursuit task allocation algorithm based on emotional constraint. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Robotics and Artificial Intelligence. Shanghai, China: ACM, 2017. 110–115 [76] Xia G Q, Sun X X, Xia X M. Multiple task assignment and path planning of a multiple unmanned surface vehicles system based on improved self-organizing mapping and improved genetic algorithm. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(6): Article No. 556 doi: 10.3390/jmse9060556 [77] 杜永浩, 邢立宁, 姚锋, 陈盈果. 航天器任务调度模型、算法与通用求解技术综述. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(12): 2715−2741Du Yong-Hao, Xing Li-Ning, Yao Feng, Chen Ying-Guo. Survey on models, algorithms and general techniques for spacecraft mission scheduling. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(12): 2715−2741 [78] Holland J H. Genetic algorithms. Scientific American, 1992, 267(1): 66−72 doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0792-66 [79] Liau Y Y, Ryu K. Genetic algorithm-based task allocation in multiple modes of human-robot collaboration systems with two cobots. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 119(11−12): 7291−7309 doi: 10.1007/s00170-022-08670-x [80] Saeedvand S, Aghdasi H S, Baltes J. Robust multi-objective multi-humanoid robots task allocation based on novel hybrid metaheuristic algorithm. Applied Intelligence, 2019, 49(12): 4097−4127 doi: 10.1007/s10489-019-01475-8 [81] Ye F, Chen J, Tian Y, Jiang T. Cooperative multiple task assignment of heterogeneous UAVs using a modified genetic algorithm with multi-type-gene chromosome encoding strategy. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2020, 100(2): 615−627 [82] Zhou X, Wang H M, Ding B, Hu T J, Shang S N. Balanced connected task allocations for multi-robot systems: An exact flow-based integer program and an approximate tree-based genetic algorithm. Expert Systems With Applications, 2019, 116: 10−20 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.09.001 [83] Kruekaew B, Kimpan W. Multi-objective task scheduling optimization for load balancing in cloud computing environment using hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm with reinforcement learning. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 17803−17818 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3149955 [84] Pendharkar P C. An ant colony optimization heuristic for constrained task allocation problem. Journal of Computational Science, 2015, 7: 37−47 doi: 10.1016/j.jocs.2015.01.001 [85] de Oca M A M, Stutzle T, Birattari M, Dorigo M. Frankenstein's PSO: A composite particle swarm optimization algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13(5): 1120−1132 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2009.2021465 [86] Geng N, Chen Z T, Nguyen Q A, Gong D W. Particle swarm optimization algorithm for the optimization of rescue task allocation with uncertain time constraints. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 2021, 7(2): 873−890 [87] Wei C Y, Ji Z, Cai B L. Particle swarm optimization for cooperative multi-robot task allocation: A multi-objective approach. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 2530−2537 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2972894 [88] Zhu Z X, Tang B W, Yuan J P. Multirobot task allocation based on an improved particle swarm optimization approach. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2017, 14(3): Article No. 1729881417710312 [89] Kong X J, Gao Y P, Wang T Y, Liu J H, Xu W T. Multi-robot task allocation strategy based on particle swarm optimization and greedy algorithm. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 8th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC). Chongqing, China: IEEE, 2019. 1643–1646 [90] 李炜, 张伟. 基于粒子群算法的多无人机任务分配方法. 控制与决策, 2010, 25(9): 1359−1363Li Wei, Zhang Wei. Method of tasks allocation of multi-UAVs based on particles swarm optimization. Control and Decision, 2010, 25(9): 1359−1363 [91] Pierson A, Wang Z J, Schwager M. Intercepting rogue robots: An algorithm for capturing multiple evaders with multiple pursuers. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 2(2): 530−537 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2016.2645516 [92] 翟政, 何明, 徐鹏, 彭志新. 基于市场机制的无人集群任务分配研究综述. 计算机应用研究, 2023, 40(7): 1921−1928Zhai Zheng, He Ming, Xu Peng, Peng Zhi-Xin. Research review of task allocation for unmanned swarm based on market mechanism. Application Research of Computers, 2023, 40(7): 1921−1928 [93] 李娟, 张昆玉. 基于改进合同网算法的异构多AUV协同任务分配. 水下无人系统学报, 2017, 25(6): 418−423Li Juan, Zhang Kun-Yu. Heterogeneous multi-AUV cooperative task allocation based on improved contract net algorithm. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2017, 25(6): 418−423 [94] Zhen Z Y, Wen L D, Wang B L, Hu Z, Zhang D M. Improved contract network protocol algorithm based cooperative target allocation of heterogeneous UAV swarm. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 119: Article No. 107054 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.107054 [95] 李瑞珍, 杨惠珍, 萧丛杉. 基于动态围捕点的多机器人协同策略. 控制工程, 2019, 26(3): 510−514Li Rui-Zhen, Yang Hui-Zhen, Xiao Cong-Shan. Cooperative hunting strategy for multi-mobile robot systems based on dynamic hunting points. Control Engineering of China, 2019, 26(3): 510−514 [96] 付光远, 李源. 多移动机器人动态联盟围捕策略. 计算机应用, 2019, 39(S1): 1−7Fu Guang-Yuan, Li Yuan. Dynamic alliance pursuit strategy for multiple mobile robots. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(S1): 1−7 [97] 吴蔚楠, 崔乃刚, 郭继峰. 基于目标信息估计的分布式局部协调任务分配方法. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(4): 566−576 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.70172Wu Wei-Nan, Cui Nai-Gang, Guo Ji-Feng. Distributed task assignment method based on local information consensus and target estimation. Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 35(4): 566−576 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.70172 [98] 王孟阳, 张栋, 唐硕, 许斌, 赵军民. 基于动态联盟策略的无人机集群在线任务规划方法. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(8): 2207−2223Wang Meng-Yang, Zhang Dong, Tang Shuo, Xu Bin, Zhao Jun-Min. UAV swarm on-line mission planning method based on dynamic allocation strategy. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(8): 2207−2223 [99] Sujit P B, Manathara J G, Ghose D, de Sousa J B. Decentralized multi-UAV coalition formation with limited communication ranges. Handbook of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Dordrecht: Springer, 2015. 2021–2048 [100] 陈璞, 严飞, 刘钊, 成果达. 通信约束下异构多无人机任务分配方法. 航空学报, 2021, 42(8): Article No. 525844 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.25844Chen Pu, Yan Fei, Liu Zhao, Cheng Guo-Da. Communication-constrained task allocation of heterogeneous UAVs. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(8): Article No. 525844 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.25844 [101] Braquet M, Bakolas E. Greedy decentralized auction-based task allocation for multi-agent systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2021, 54(20): 675−680 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.11.249 [102] Li X H, Liang Y N. An optimal online distributed auction algorithm for multi-UAV task allocation. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Logistics, Informatics and Service Sciences. Springer, 2022. 537–548 [103] Choi H L, Brunet L, How J P. Consensus-based decentralized auctions for robust task allocation. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2009, 25(4): 912−926 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2009.2022423 [104] 唐嘉钰, 李相民, 代进进, 薄宁. 复杂约束条件下异构多智能体联盟任务分配. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(11): 2413−2422 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2020.90868Tang Jia-Yu, Li Xiang-Min, Dai Jin-Jin, Bo Ning. Coalition task allocation of heterogeneous multiple agents with complex constraints. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(11): 2413−2422 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2020.90868 [105] Hunt S, Meng Q G, Hinde C, Huang T W. A consensus-based grouping algorithm for multi-agent cooperative task allocation with complex requirements. Cognitive Computation, 2014, 6(3): 338−350 doi: 10.1007/s12559-014-9265-0 [106] Dong D B, Zhu Y H, Du Z Z, Yu D X. Multi-target dynamic hunting strategy based on improved K-means and auction algorithm. Information Sciences, 2023, 640: Article No. 119072 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.119072 [107] Dong D B, Du Z Z, Min J C, Lu R T, Liu J M, Yu D X. Fuzzy dual-hunting control based on auction algorithm. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 2023, 25(7): 2816−2827 doi: 10.1007/s40815-023-01531-z [108] 潘子双, 苏析超, 韩维, 柳文林, 郁大照, 汪节. 基于动态一致性联盟算法的异构无人机集群协同作战联盟组建. 兵工学报, DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0914Pan Zi-Shuang, Su Xi-Chao, Han Wei, Liu Wen-Lin, Yu Da-Zhao, Wang Jie. Cooperative combat coalition formation with heterogeneous UAV swarm based on dynamic consensus-based grouping algorithm. Acta Armamentarii, DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0914 [109] Zhou M, Wang Z H, Wang J, Cao Z C. Multi-robot collaborative hunting in cluttered environments with obstacle-avoiding Voronoi cells. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(7): 1643−1655 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.124041 [110] Bhattacharya P, Gavrilova M L. Roadmap-based path planning-using the Voronoi diagram for a clearance-based shortest path. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 2008, 15(2): 58−66 [111] Chi W Z, Ding Z Y, Wang J K, Chen G D, Sun L N. A generalized Voronoi diagram-based efficient heuristic path planning method for RRTs in mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(5): 4926−4937 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3078390 [112] Xia N, Wang C, Yu Y T, Du H Z, Xu C N, Zheng J G. A path forming method for water surface mobile sink using Voronoi diagram and dominating set. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(8): 7608−7619 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2832096 [113] Wang J K, Meng M Q H. Optimal path planning using generalized Voronoi graph and multiple potential functions. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(12): 10621−10630 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2962425 [114] Bakolas E, Tsiotras P. Optimal pursuit of moving targets using dynamic Voronoi diagrams. In: Proceedings of the 49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC). Atlanta, USA: IEEE, 2010. 7431–7436 [115] Wang Y, He G H, Ma Y D, Kong G J, Gong J W. Research on multi-robots self-organizing cooperative pursuit algorithm based on Voronoi graph. In: Proceedings of the 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Shenyang, China: IEEE, 2020. 3840–3844 [116] 张云赫, 苏立晨, 董云帆, 刘瑜, 李宇萌. 基于Voronoi图最近邻协商的多机协同追捕方法. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2023, 44(2): 284−291 doi: 10.11990/jheu.202203002Zhang Yun-He, Su Li-Chen, Dong Yun-Fan, Liu Yu, Li Yu-Meng. Cooperative pursuit of multiple UAVs based on Voronoi partition nearest neighbor negotiation. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2023, 44(2): 284−291 doi: 10.11990/jheu.202203002 [117] Zhou D J, Wang Z J, Bandyopadhyay S, Schwager M. Fast, on-line collision avoidance for dynamic vehicles using buffered Voronoi cells. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 2(2): 1047−1054 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2656241 [118] Pierson A, Schwarting W, Karaman S, Rus D. Weighted buffered Voronoi cells for distributed semi-cooperative behavior. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris, France: IEEE, 2020. 5611–5617 [119] Tian B L, Li P P, Lu H C, Zong Q, He L. Distributed pursuit of an evader with collision and obstacle avoidance. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(12): 13512−13520 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3112572 [120] Wang M Y, Schwager M. Distributed collision avoidance of multiple robots with probabilistic buffered Voronoi cells. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Multi-Robot and Multi-Agent Systems (MRS). New Brunswick, USA: IEEE, 2019. 169–175 [121] Zhu H, Alonso-Mora J. B-UAVC: Buffered uncertainty-aware Voronoi cells for probabilistic multi-robot collision avoidance. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Multi-Robot and Multi-Agent Systems (MRS). New Brunswick, USA: IEEE, 2019. 162–168 [122] Zhu H, Brito B, Alonso-Mora J. Decentralized probabilistic multi-robot collision avoidance using buffered uncertainty-aware Voronoi cells. Autonomous Robots, 2022, 46(2): 401−420 doi: 10.1007/s10514-021-10029-2 [123] Hodgkin A L, Huxley A F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. The Journal of Physiology, 1952, 117(4): 500−544 doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764 [124] Grossberg S. Nonlinear neural networks: Principles, mechanisms, and architectures. Neural Networks, 1988, 1(1): 17−61 doi: 10.1016/0893-6080(88)90021-4 [125] Yang S X, Luo C M. A neural network approach to complete coverage path planning. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2004, 34(1): 718−724 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2003.811769 [126] Luo C M, Yang S X. A bioinspired neural network for real-time concurrent map building and complete coverage robot navigation in unknown environments. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2008, 19(7): 1279−1298 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2008.2000394 [127] Yang S X, Meng M Q H. Real-time collision-free motion planning of a mobile robot using a neural dynamics-based approach. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2003, 14(6): 1541−1552 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2003.820618 [128] Öǧmen H, Gagné S. Neural network architectures for motion perception and elementary motion detection in the fly visual system. Neural Networks, 1990, 3(5): 487−505 doi: 10.1016/0893-6080(90)90001-2 [129] 王耀南, 潘琪, 陈彦杰. 改进型生物激励神经网络的路径规划方法. 控制工程, 2018, 25(4): 541−548Wang Yao-Nan, Pan Qi, Chen Yan-Jie. Path planning method based on improved biologically inspired neural network. Control Engineering of China, 2018, 25(4): 541−548 [130] 朱大奇, 孙兵, 李利. 基于生物启发模型的AUV三维自主路径规划与安全避障算法. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(5): 798−806Zhu Da-Qi, Sun Bing, Li Li. Algorithm for AUV's 3-D path planning and safe obstacle avoidance based on biological inspired model. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(5): 798−806 [131] 朱大奇, 刘雨, 孙兵, 刘清沁. 自治水下机器人的自主启发式生物启发神经网络路径规划算法. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(2): 183−191 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.70576Zhu Da-Qi, Liu Yu, Sun Bing, Liu Qing-Qin. Autonomous underwater vehicles path planning based on autonomous inspired Glasius bio-inspired neural network algorithm. Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 36(2): 183−191 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.70576 [132] 刘晨霞, 朱大奇, 周蓓, 顾伟. 海流环境下多AUV多目标生物启发任务分配与路径规划算法. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(11): 2100−2107 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.11019Liu Chen-Xia, Zhu Da-Qi, Zhou Bei, Gu Wei. A novel algorithm of multi-AUVs task assignment and path planning based on biologically inspired neural network for ocean current environment. Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 39(11): 2100−2107 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2022.11019 [133] Lv R F, Gan W Y, Sun B, Zhu D Q. A multi-AUV hunting algorithm with ocean current effect. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER). Shenyang, China: IEEE, 2015. 869–874 [134] Liu Q Q, Sun B, Zhu D Q. A multi-AUVs cooperative hunting algorithm for environment with ocean current. In: Proceedings of the 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2018. 5441–5444 [135] Zhu D Q, Lv R F, Cao X, Yang S X. Multi-AUV hunting algorithm based on bio-inspired neural network in unknown environments. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2015, 12(11): Article No. 166 doi: 10.5772/61555 [136] Huang Z R, Zhu D Q, Sun B. A multi-AUV cooperative hunting method in 3-D underwater environment with obstacle. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2016, 50: 192−200 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2016.01.036 [137] Ni J J, Yang S X. Bioinspired neural network for real-time cooperative hunting by multirobots in unknown environments. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(12): 2062−2077 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2169808 [138] Niu Z Y, Zhong G Q, Yu H. A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning. Neurocomputing, 2021, 452: 48−62 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.03.091 [139] 李登峰. 微分对策及其应用. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2000.Li Deng-Feng. Differential Games and Applications. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2000. [140] 方宝富, 潘启树, 洪炳镕, 丁磊, 蔡则苏. 多追捕者−单一逃跑者追逃问题实现成功捕获的约束条件. 机器人, 2012, 34(3): 282−291 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1218.2012.00282Fang Bao-Fu, Pan Qi-Shu, Hong Bing-Rong, Ding Lei, Cai Ze-Su. Constraint conditions of successful capture in multi-pursuers vs one-evader games. Robot, 2012, 34(3): 282−291 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1218.2012.00282 [141] Bera R, Makkapati V R, Kothari M. A comprehensive differential game theoretic solution to a game of two cars. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2017, 174(3): 818−836 doi: 10.1007/s10957-017-1134-z [142] Pan T Y, Yuan Y. A region-based relay pursuit scheme for a pursuit-evasion game with a single evader and multiple pursuers. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(3): 1958−1969 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3210022 [143] Sun W, Tsiotras P. Sequential pursuit of multiple targets under external disturbances via Zermelo-Voronoi diagrams. Automatica, 2017, 81: 253−260 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.03.015 [144] 罗亚中, 李振瑜, 祝海. 航天器轨道追逃微分对策研究综述. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2020, 50(12): 1533−1545 doi: 10.1360/SST-2019-0174Luo Ya-Zhong, Li Zhen-Yu, Zhu Hai. Survey on spacecraft orbital pursuit-evasion differential games. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2020, 50(12): 1533−1545 doi: 10.1360/SST-2019-0174 [145] Nian X H, Niu F X, Yang Z. Distributed Nash equilibrium seeking for multicluster game under switching communication topologies. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(7): 4105−4116 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3090515 [146] Zhu Y H, Zhao D B. Online minimax Q network learning for two-player zero-sum Markov games. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(3): 1228−1241 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3041469 [147] Li M, Qin J H, Ma Q C, Zheng W X, Kang Y. Hierarchical optimal synchronization for linear systems via reinforcement learning: A stackelberg-Nash game perspective. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(4): 1600−1611 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2985738 [148] Isaacs R. Differential Games. A Mathematical Theory With Applications to Warfare and Pursuit, Control and Optimization. Wiley, 1965. [149] Ramana M V, Kothari M. Pursuit strategy to capture high-speed evaders using multiple pursuers. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2017, 40(1): 139−149 doi: 10.2514/1.G000584 [150] Fang X, Wang C, Xie L H, Chen J. Cooperative pursuit with multi-pursuer and one faster free-moving evader. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(3): 1405−1414 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2958548 [151] García E, Murano D A. State estimation for a class of nonlinear differential games using differential neural networks. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2011. 2486–2491 [152] Xue B, Easwaran A, Cho N J, Fränzle M. Reach-avoid verification for nonlinear systems based on boundary analysis. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(7): 3518−3523 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2615599 [153] Chen M, Bansal S, Fisac J F, Tomlin C J. Robust sequential trajectory planning under disturbances and adversarial intruder. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2019, 27(4): 1566−1582 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2018.2828380 [154] Li W. Formulation of a Cooperative-Confinement-Escape problem of multiple cooperative defenders against an evader escaping from a circular region. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2016, 39: 442−457 doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2016.02.042 [155] Li W. Escape analysis on the confinement-escape problem of a defender against an evader escaping from a circular region. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(9): 2166−2172 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2541158 [156] Fisac J F, Sastry S S. The pursuit-evasion-defense differential game in dynamic constrained environments. In: Proceedings of the 54th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC). Osaka, Japan: IEEE, 2015. 4549–4556 [157] Zhang H G, Cui L L, Luo Y H. Near-optimal control for nonzero-sum differential games of continuous-time nonlinear systems using single-network ADP. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2013, 43(1): 206−216 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2012.2203336 [158] Zhao D B, Zhang Q C, Wang D, Zhu Y H. Experience replay for optimal control of nonzero-sum game systems with unknown dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(3): 854−865 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2488680 [159] 王龙, 黄锋. 多智能体博弈、学习与控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 580−613Wang Long, Huang Feng. An interdisciplinary survey of multi-agent games, learning, and control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 580−613 [160] Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (Second edition). Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018. [161] Kaelbling L P, Littman M L, Moore A W. Reinforcement learning: A survey. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 1996, 4: 237−285 doi: 10.1613/jair.301 [162] Zhang K Q, Yang Z R, Basar T. Multi-agent reinforcement learning: A selective overview of theories and algorithms. Handbook of Reinforcement Learning and Control. Cham: Springer, 2021. 321–384 [163] Yang Y D, Wang J. An overview of multi-agent reinforcement learning from game theoretical perspective. arXiv: 2011.00583, 2020. [164] Xie S, Chu X M, Zheng M, Liu C G. A composite learning method for multi-ship collision avoidance based on reinforcement learning and inverse control. Neurocomputing, 2020, 411: 375−392 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.089 [165] Watkins C J C H, Dayan P. Q-learning. Machine Learning, 1992, 8(3): 279−292 [166] Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Rusu A A, Veness J, Bellemare M G, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529−533 doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [167] Kocsis L, Szepesvári C. Bandit based Monte-Carlo planning. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Machine Learning. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2006. 282–293 [168] Shi X T, Li Y J, Hu W X, Du C L, Chen C Y, Gui W H. Optimal lateral path-tracking control of vehicles with partial unknown dynamics via DPG-based reinforcement learning methods. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 9(1): 1701−1710 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3319642 [169] Gao H H, Wang X J, Wei W, Al-Dulaimi A, Xu Y S. Com-DDPG: Task offloading based on multiagent reinforcement learning for information-communication-enhanced mobile edge computing in the internet of vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(1): 348−361 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3309321 [170] Centurelli A, Arleo L, Rizzo A, Tolu S, Laschi C, Falotico E. Closed-loop dynamic control of a soft manipulator using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 4741−4748 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3146903 [171] Guo D L, Tang L, Zhang X G, Liang Y C. Joint optimization of handover control and power allocation based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(11): 13124−13138 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3020400 [172] Han M H, Zhang L X, Wang J, Pan W. Actor-critic reinforcement learning for control with stability guarantee. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(4): 6217−6224 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.3011351 [173] Ge H W, Gao D W, Sun L, Hou Y Q, Yu C, Wang Y X, et al. Multi-agent transfer reinforcement learning with multi-view encoder for adaptive traffic signal control. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(8): 12572−12587 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3115240 [174] Wang Y D, Dong L, Sun C Y. Cooperative control for multi-player pursuit-evasion games with reinforcement learning. Neurocomputing, 2020, 412: 101−114 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.06.031 [175] Lowe R, Wu Y, Tamar A, Harb J, Abbeel P, Mordatch I. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 6382–6393 [176] Yu L L, Huo S X, Wang Z J, Li K Y. Hybrid attention-oriented experience replay for deep reinforcement learning and its application to a multi-robot cooperative hunting problem. Neurocomputing, 2023, 523: 44−57 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.12.020 [177] 夏家伟, 朱旭芳, 张建强, 罗亚松, 刘忠. 基于多智能体强化学习的无人艇协同围捕方法. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(5): 1438−1447Xia Jia-Wei, Zhu Xu-Fang, Zhang Jian-Qiang, Luo Ya-Song, Liu Zhong. Research on cooperative hunting method of unmanned surface vehicle based on multi-agent reinforcement learning. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(5): 1438−1447 [178] Bilgin A T, Kadioglu-Urtis E. An approach to multi-agent pursuit evasion games using reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR). Istanbul, Turkey: IEEE, 2015. 164–169 [179] Vlahov B, Squires E, Strickland L, Pippin C. On developing a UAV pursuit-evasion policy using reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA). Orlando, USA: IEEE, 2018. 859–864 [180] de Souza C, Newbury R, Cosgun A, Castillo P, Vidolov B, Kulić D. Decentralized multi-agent pursuit using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(3): 4552−4559 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3068952 [181] Xia J W, Luo Y S, Liu Z K, Zhang Y L, Shi H R, Liu Z. Cooperative multi-target hunting by unmanned surface vehicles based on multi-agent reinforcement learning. Defence Technology, 2023, 29: 80−94 doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2022.09.014 [182] Awheda M D, Schwartz H M. A fuzzy reinforcement learning algorithm using a predictor for pursuit-evasion games. In: Proceedings of the Annual IEEE Systems Conference (SysCon). Orlando, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1–8 [183] Cao X, Zuo F. A fuzzy-based potential field hierarchical reinforcement learning approach for target hunting by multi-AUV in 3-D underwater environments. International Journal of Control, 2021, 94(5): 1334−1343 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2019.1648875 [184] Wang L X, Wang M L, Yue T. A fuzzy deterministic policy gradient algorithm for pursuit-evasion differential games. Neurocomputing, 2019, 362: 106−117 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.07.038 [185] Foerster J, Farquhar G, Afouras T, Nardelli N, Whiteson S. Counterfactual multi-agent policy gradients. In: Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New Orleans, USA: AAAI, 2018. [186] Zhang Z, Wang X H, Zhang Q R, Hu T J. Multi-robot cooperative pursuit via potential field-enhanced reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Philadelphia, USA: IEEE, 2022. 8808–8814 [187] Fang B F, Zhu J L, Zhang H, Wang H, Wang Z J. Multi self-interested robot pursuit based on quantum game theory. In: Proceedings of the Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). Jinan, China: IEEE, 2017. 7368–7373 [188] 晏亚林. 基于博弈论的多机器人追捕问题的研究 [硕士学位论文], 哈尔滨工程大学, 中国, 2014.Yan Ya-Lin. Research on Multi-Robot Pursuit-Evasion Problem Based on Game Theory [Master thesis], Harbin Engineering University, China, 2014. [189] 郑延斌, 樊文鑫, 韩梦云, 陶雪丽. 基于博弈论及Q学习的多Agent协作追捕算法. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(6): 1613−1620Zheng Yan-Bin, Fan Wen-Xin, Han Meng-Yun, Tao Xue-Li. Multi-agent collaborative pursuit algorithm based on game theory and Q-learning. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 40(6): 1613−1620 [190] Qu X Q, Gan W H, Song D L, Zhou L Q. Pursuit-evasion game strategy of USV based on deep reinforcement learning in complex multi-obstacle environment. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 273: Article No. 114016 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114016 [191] Zhang R L, Zong Q, Zhang X Y, Dou L Q, Tian B L. Game of drones: Multi-UAV pursuit-evasion game with online motion planning by deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(10): 7900−7909 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3146976 [192] Gao Z K, Dai X Y, Yao M B, Xiao X M. A data enhancement strategy for multi-agent cooperative hunting based on deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 6th International Conference on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS). Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2023. 1–8 [193] Asl Z D, Derhami V, Yazdian-Dehkordi M. A new approach on multi-agent multi-objective reinforcement learning based on agents' preferences. In: Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Signal Processing Conference (AISP). Shiraz, Iran: IEEE, 2017. 75–79 [194] Du B, Lin B, Zhang C M, Dong B T, Zhang W D. Safe deep reinforcement learning-based adaptive control for USV interception mission. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 246: Article No. 110477 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.110477 [195] Deghat M, Davis E, See T, Shames I, Anderson B D O, Yu C B. Target localization and circumnavigation by a non-holonomic robot. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal: IEEE, 2012. 1227–1232 [196] Deghat M, Shames I, Anderson B D O, Yu C B. Localization and circumnavigation of a slowly moving target using bearing measurements. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(8): 2182−2188 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2299011 [197] Zheng R H, Liu Y H, Sun D. Enclosing a target by nonholonomic mobile robots with bearing-only measurements. Automatica, 2015, 53: 400−407 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2015.01.014 [198] Lee B H, Ahn H S. Distributed formation control via global orientation estimation. Automatica, 2016, 73: 125−129 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.06.030 [199] Yu X, Xu X, Liu L, Feng G. Circular formation of networked dynamic unicycles by a distributed dynamic control law. Automatica, 2018, 89: 1−7 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.11.021 [200] Yamamoto Y, Yun X P. Coordinating locomotion and manipulation of a mobile manipulator. In: Proceedings of the 31st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Tucson, USA: IEEE, 1992. 2643–2648 [201] Zhao S Y, Pan Y N, Du P H, Liang H J. Adaptive control for non-affine nonlinear systems with input saturation and output dead zone. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2020, 386: Article No. 125506 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2020.125506 [202] Chen M, Ge S S, Ren B B. Adaptive tracking control of uncertain MIMO nonlinear systems with input constraints. Automatica, 2011, 47(3): 452−465 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.01.025 [203] 张红强, 章兢, 周少武, 曾照福, 吴亮红. 基于简化虚拟受力模型的未知复杂环境下群机器人围捕. 电子学报, 2015, 43(4): 665−674 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2015.04.007Zhang Hong-Qiang, Zhang Jing, Zhou Shao-Wu, Zeng Zhao-Fu, Wu Liang-Hong. Hunting in unknown complex environments by swarm robots based on simplified virtual-force model. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2015, 43(4): 665−674 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2015.04.007 [204] 张红强, 章兢, 周少武, 曾照福, 吴亮红. 未知动态环境下非完整移动群机器人围捕. 控制理论与应用, 2014, 31(9): 1151−1165 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2014.31243Zhang Hong-Qiang, Zhang Jing, Zhou Shao-Wu, Zeng Zhao-Fu, Wu Liang-Hong. Nonholonomic mobile swarm robots hunting in unknown dynamic environments. Control Theory & Applications, 2014, 31(9): 1151−1165 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2014.31243 [205] 张红强, 吴亮红, 周游, 章兢, 周少武, 刘朝华. 复杂环境下群机器人自组织协同多目标围捕. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(5): 1054−1062 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90015Zhang Hong-Qiang, Wu Liang-Hong, Zhou You, Zhang Jing, Zhou Shao-Wu, Liu Zhao-Hua. Self-organizing cooperative multi-target hunting by swarm robots in complex environments. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(5): 1054−1062 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90015 [206] 罗家祥, 许博喆, 刘海明, 蔡鹤, 高焕丽, 姚瞻楠. 感知范围受限的群机器人自主围捕算法. 控制理论与应用, 2021, 38(7): 933−946 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.00715Luo Jia-Xiang, Xu Bo-Zhe, Liu Hai-Ming, Cai He, Gao Huan-Li, Yao Zhan-Nan. Autonomous hunting algorithm for swarm robots subject to limited sensing range. Control Theory & Applications, 2021, 38(7): 933−946 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.00715 [207] 黄天云, 陈雪波, 徐望宝, 周自维, 任志勇. 基于松散偏好规则的群体机器人系统自组织协作围捕. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(1): 57−68 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60007-5Huang Tian-Yun, Chen Xue-Bo, Xu Wang-Bao, Zhou Zi-Wei, Ren Zhi-Yong. A self-organizing cooperative hunting by swarm robotic systems based on loose-preference rule. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(1): 57−68 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60007-5 [208] Yu X, Liu L, Feng G. Distributed circular formation control of nonholonomic vehicles without direct distance measurements. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(8): 2730−2737 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2790259 [209] Su Y X. Comments on “Controller design for rigid spacecraft attitude tracking with actuator saturation”. Information Sciences, 2016, 342: 150−152 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.12.040 [210] Wen G X, Ge S S, Chen C L P, Tu F W, Wang S N. Adaptive tracking control of surface vessel using optimized backstepping technique. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(9): 3420−3431 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2844177 [211] Zheng K M, Zhang Q J, Hu Y M, Wu B. Design of fuzzy system-fuzzy neural network-backstepping control for complex robot system. Information Sciences, 2021, 546: 1230−1255 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.08.110 [212] Ding S H, Park J H, Chen C C. Second-order sliding mode controller design with output constraint. Automatica, 2020, 112: Article No. 108704 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108704 [213] Huang C R, Fujisawa S, de Lima T F, Tait A N, Blow E C, Tian Y, et al. A silicon photonic-electronic neural network for fibre nonlinearity compensation. Nature Electronics, 2021, 4(11): 837−844 doi: 10.1038/s41928-021-00661-2 [214] Ma H, Ren H R, Zhou Q, Lu R Q, Li H Y. Approximation-based Nussbaum gain adaptive control of nonlinear systems with periodic disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(4): 2591−2600 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3050993 [215] Sun Y M, Chen B, Lin C, Wang H H, Zhou S W. Adaptive neural control for a class of stochastic nonlinear systems by backstepping approach. Information Sciences, 2016, 369: 748−764 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.06.010 [216] Ghommam J, Saad M, Mnif F. Finite-time circular formation around a moving target with multiple underactuated ODIN vehicles. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2021, 180: 230−250 doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2020.08.026 [217] Duan Y, Huang X, Yu X. Multi-robot dynamic virtual potential point hunting strategy based on FIS. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference (CGNCC). Nanjing, China: IEEE, 2016. 332–335 [218] Beke A, Kumbasar T. Game of spheros: A real-world pursuit-evasion game with type-2 fuzzy logic. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE). Naples, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1–6 [219] 胡俊, 朱庆保. 基于动态预测目标轨迹和围捕点的多机器人围捕算法. 电子学报, 2011, 39(11): 2480−2485Hu Jun, Zhu Qing-Bao. A multi-robot hunting algorithm based on dynamic prediction for trajectory of the moving target and hunting points. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(11): 2480−2485 [220] Wu Z Y, Cao Z Q, Yu Y Y, Pang L, Zhou C, Chen E K. A multi-robot cooperative hunting approach based on dynamic prediction of target motion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). Macao, China: IEEE, 2017. 587–592 [221] Cui J F, Li D C, Liu P, Qin J, Ma Y D, Lu Z G. Game-model prediction hybrid path planning algorithm for multiple mobile robots in pursuit evasion game. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2021. 925–930 [222] Cao X, Xu X Y. Hunting algorithm for multi-AUV based on dynamic prediction of target trajectory in 3D underwater environment. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 138529−138538 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3013032 [223] Huang G Q. Visual-inertial navigation: A concise review. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2019. 9572–9582 [224] Yu H, Zhen W K, Yang W, Zhang J, Scherer S. Monocular camera localization in prior LiDAR maps with 2D-3D line correspondences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2020. 4588–4594 [225] Kim Y, Jeong J, Kim A. Stereo camera localization in 3D LiDAR maps. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Madrid, Spain: IEEE, 2018. 1–9 [226] Srivastava S, Kumar M S, Mishra A, Chopra S, Jagannatham A K, Hanzo L. Sparse doubly-selective channel estimation techniques for OSTBC MIMO-OFDM systems: A hierarchical Bayesian Kalman filter based approach. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(8): 4844−4858 doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2995585 [227] 张梦轩, 苏治宝, 索旭东. 移动机器人定位方法研究综述. 车辆与动力技术, 2023(4): 56−62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4687.2023.04.010Zhang Meng-Xuan, Su Zhi-Bao, Suo Xu-Dong. Overview of research on localization methods for mobile robots. Vehicle & Power Technology, 2023(4): 56−62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4687.2023.04.010 [228] 王耀南, 江一鸣, 姜娇, 张辉, 谭浩然, 彭伟星, 等. 机器人感知与控制关键技术及其智能制造应用. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 494−513Wang Yao-Nan, Jiang Yi-Ming, Jiang Jiao, Zhang Hui, Tan Hao-Ran, Peng Wei-Xing, et al. Key technologies of robot perception and control and its intelligent manufacturing applications. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 494−513 [229] Yan T M, Gan Y Z, Xia Z Y, Zhao Q F. Segment-based disparity refinement with occlusion handling for stereo matching. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(8): 3885−3897 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2903318 [230] Yang L, Xu Y, Wang S R, Yuan C F, Zhang Z Q, Li B, et al. PDNet: Toward better one-stage object detection with prediction decoupling. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 5121−5133 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3193223 [231] Chen Q, Tang S H, Yang Q, Fu S. Cooper: Cooperative perception for connected autonomous vehicles based on 3D point clouds. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 39th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS). Dallas, USA: IEEE, 2019. 514–524 [232] Du Y C, Qin B H, Zhao C, Zhu Y F, Cao J, Ji Y X. A novel spatio-temporal synchronization method of roadside asynchronous MMW radar-camera for sensor fusion. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(11): 22278−22289 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3119079 [233] 孙志娟. 多机器人协同通信技术研究 [硕士学位论文], 广西科技大学, 中国, 2019.Sun Zhi-Juan. Research on Multi-Robot Cooperative Communication Technology [Master thesis], Guangxi University of Science and Technology, China, 2019. [234] 李莹莹, 刘云辉, 樊玮虹, 蔡宣平, 李波. 基于移动通信网络的机器人遥操作. 通信学报, 2006, 27(5): 52−59 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-436X.2006.05.010Li Ying-Ying, Liu Yun-Hui, Fan Wei-Hong, Cai Xuan-Ping, Li Bo. Teleoperation of robots via the mobile communication networks. Journal on Communications, 2006, 27(5): 52−59 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-436X.2006.05.010 [235] Marangoz S, Amasyal M F, Uslu E, Çakmak F, Altuntaş N, Yavuz S. More scalable solution for multi-robot-multi-target assignment problem. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2019, 113: 174−185 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2019.01.005 [236] Lin E S, Agmon N, Kraus S. Multi-robot adversarial patrolling: Handling sequential attacks. Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 274: 1−25 doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2019.02.004 -




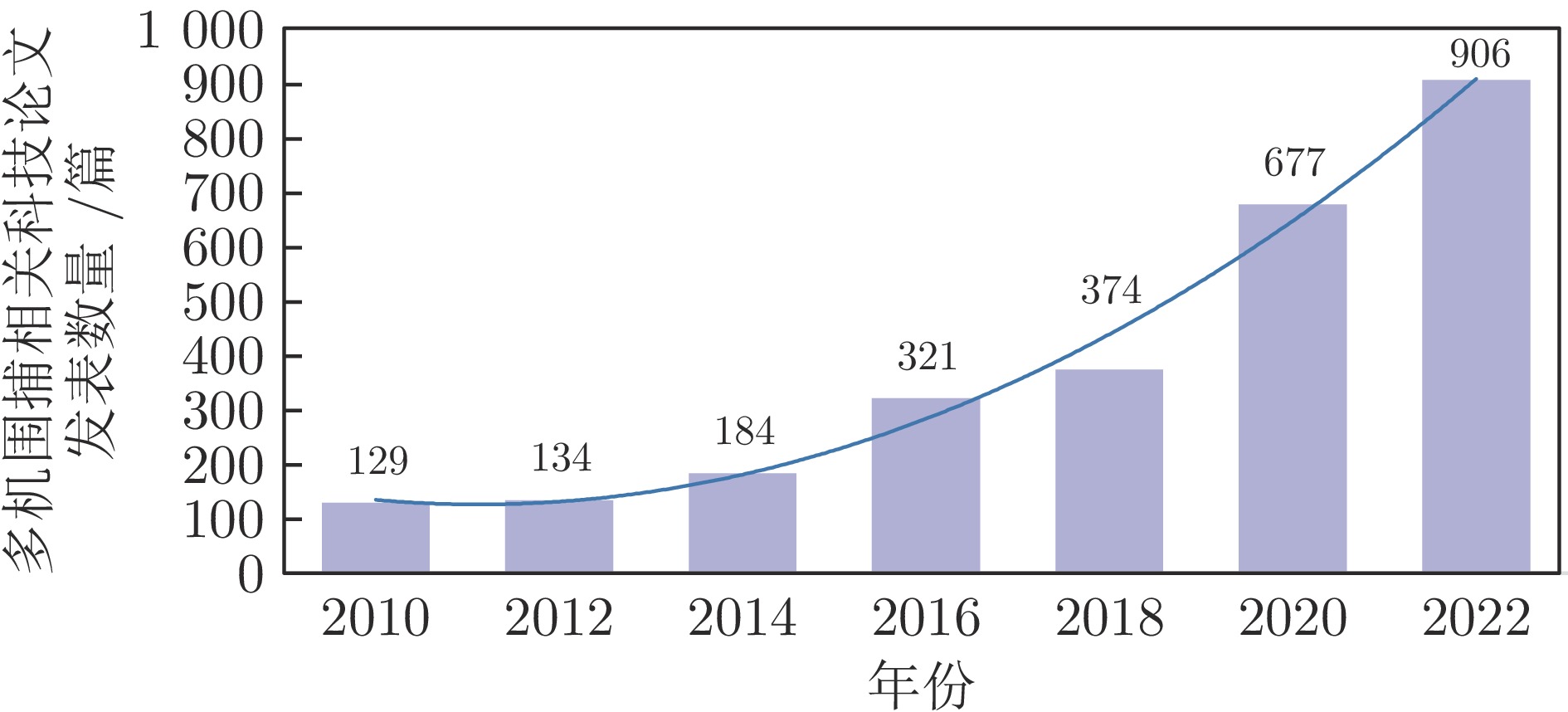
 下载:
下载: