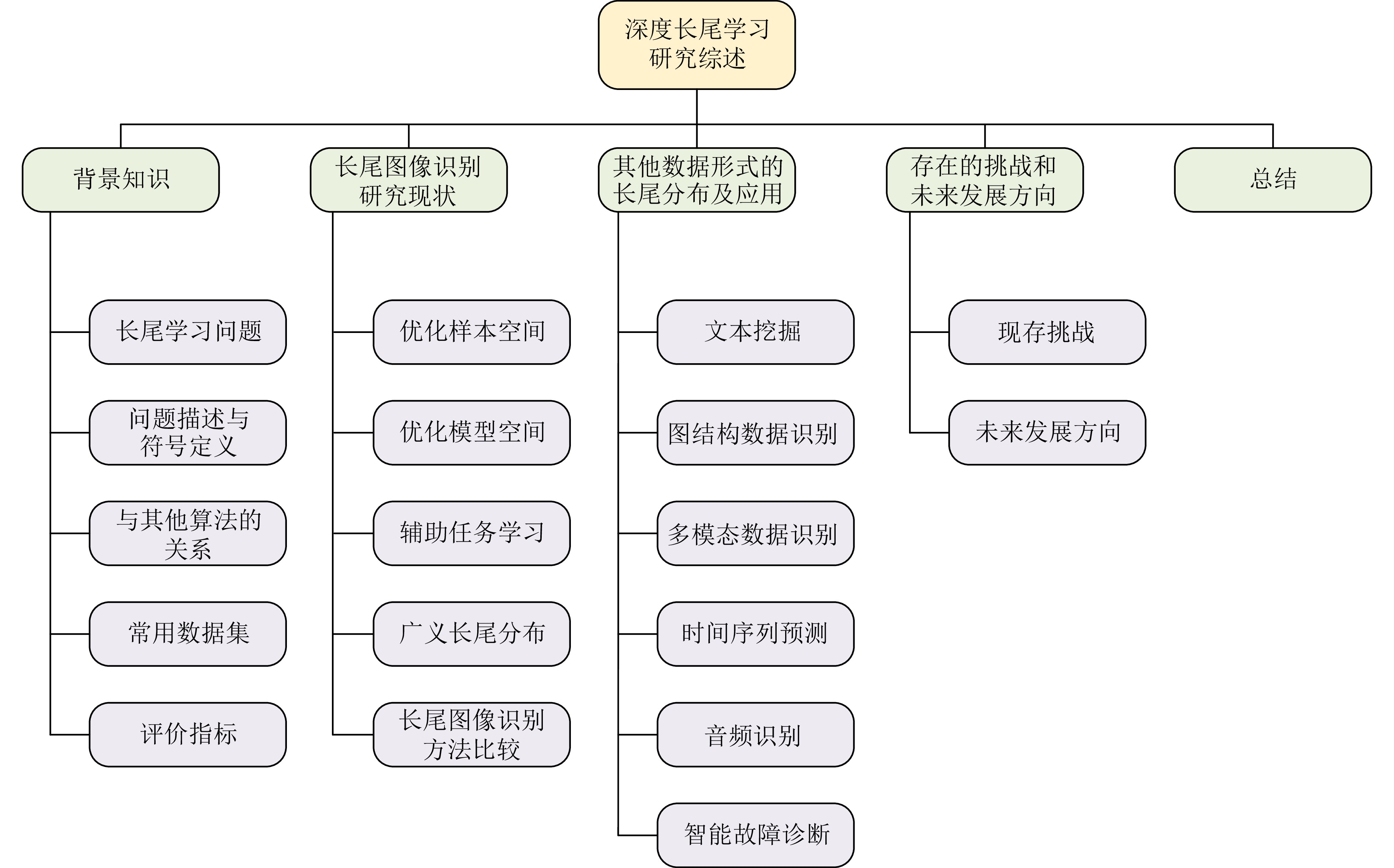
-
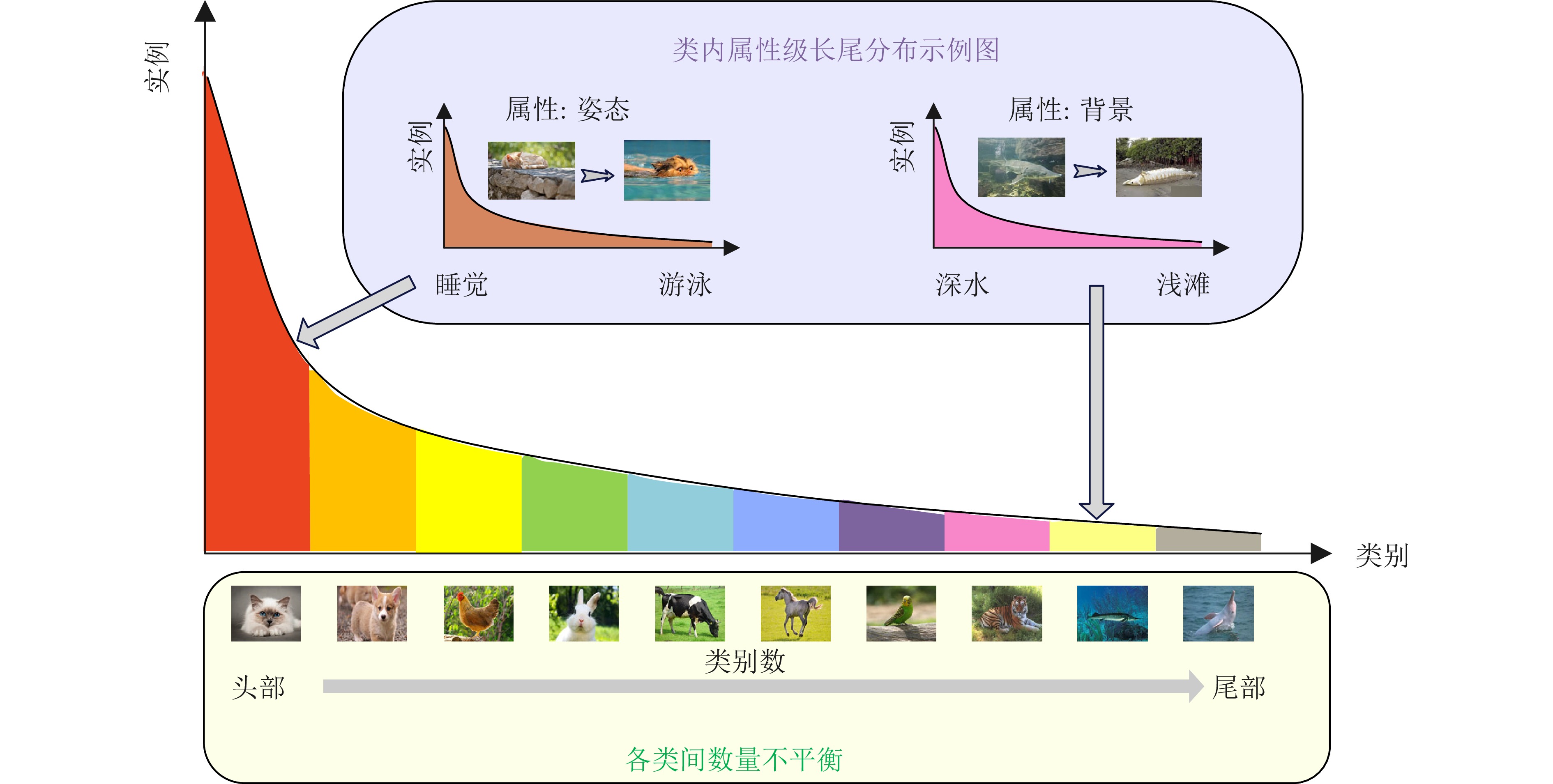
摘要: 深度学习是一门依赖于数据的科学, 传统深度学习方法假定在平衡数据集上训练模型, 然而, 现实世界中大规模数据集通常表现出长尾分布现象, 样本数量众多的少量头部类主导模型训练, 而大量尾部类样本数量过少, 难以得到充分学习. 近年来, 长尾学习掀起学术界的研究热潮. 本文综合梳理和分析近年来发表在高水平会议或期刊上的文献, 对长尾学习进行全面综述. 具体而言, 根据深度学习模型设计流程, 将图像识别领域的长尾学习算法分为丰富样本数量与语义信息的优化样本空间方法, 关注特征提取器、分类器、logits和损失函数这四个基本组成部分的优化模型方法, 以及通过引入辅助任务来帮助模型训练并在多个空间共同优化长尾学习模型的辅助任务学习3大类, 根据提出的分类方法综合对比分析每类长尾学习方法的优缺点. 然后, 进一步将基于样本数量的狭义长尾学习概念推广至多尺度广义长尾学习. 此外, 对文本数据、语音数据等其他数据形式下的长尾学习算法进行简要评述. 最后, 讨论目前长尾学习面临的可解释性较差、数据质量较低等挑战, 并展望如多模态长尾学习、半监督长尾学习等未来具有潜力的发展方向.Abstract: Deep learning is a science that depends on data. Traditional deep learning methods unrealistically assume that the training models are on balanced datasets. In real-world large-scale datasets, a long-tailed distribution often occurs, with a few head classes having many samples dominating model training, while many tail classes have too few samples to be adequately learned. In recent years, the long-tailed learning has set off a research upsurge in academic circles. In this paper, we comb and analyze the literature published in high-level conferences or journals to provide a comprehensive survey of long-tailed learning. Specifically, we categorize long-tailed learning algorithms in the field of image recognition into three main types according to the design process of deep learning models: Optimizing the sample space by enriching the quantity and semantic information of samples, optimizing the model by focusing on the four fundamental components of feature extractor, classifier, logits and loss function, and auxiliary task learning, which involves introducing auxiliary tasks to aid model training and jointly optimizing long-tailed learning models across multiple spaces. Additionally, a comprehensive comparative analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of each category is conducted based on the proposed classification method. We further extend the concept of narrow long-tail learning based on the number of samples to multi-scale generalized long-tailed learning. In addition, we briefly review long-tailed learning algorithms in other data forms, such as text data and voice data. Finally, we discuss the current challenges faced by long-tailed learning, such as poor interpretability and low data quality, and look forward to the future development directions, such as multimodal long-tailed learning and semi-supervised long-tailed learning.
-
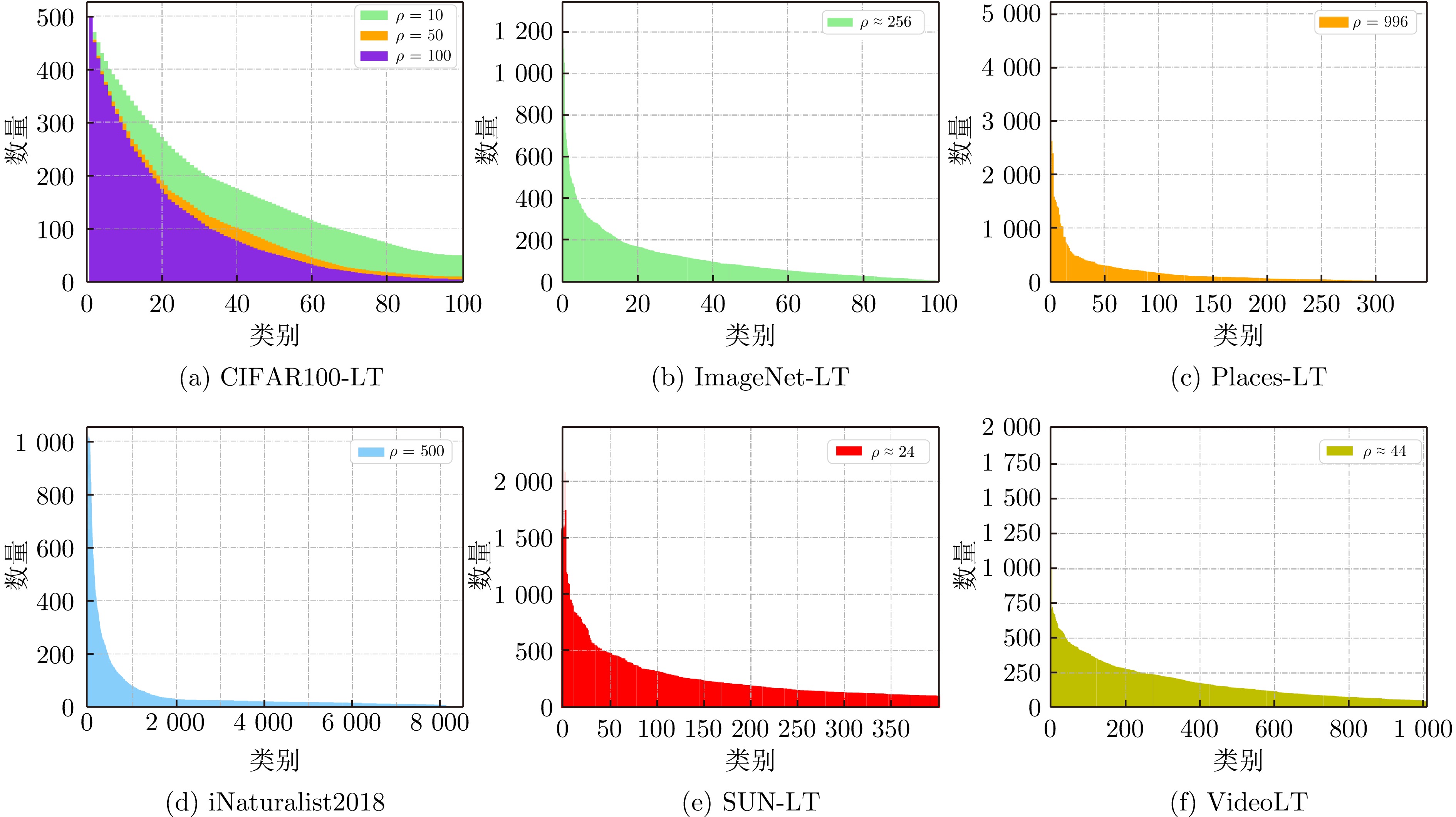
表 1 常见长尾数据集基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of common long-tailed datasets
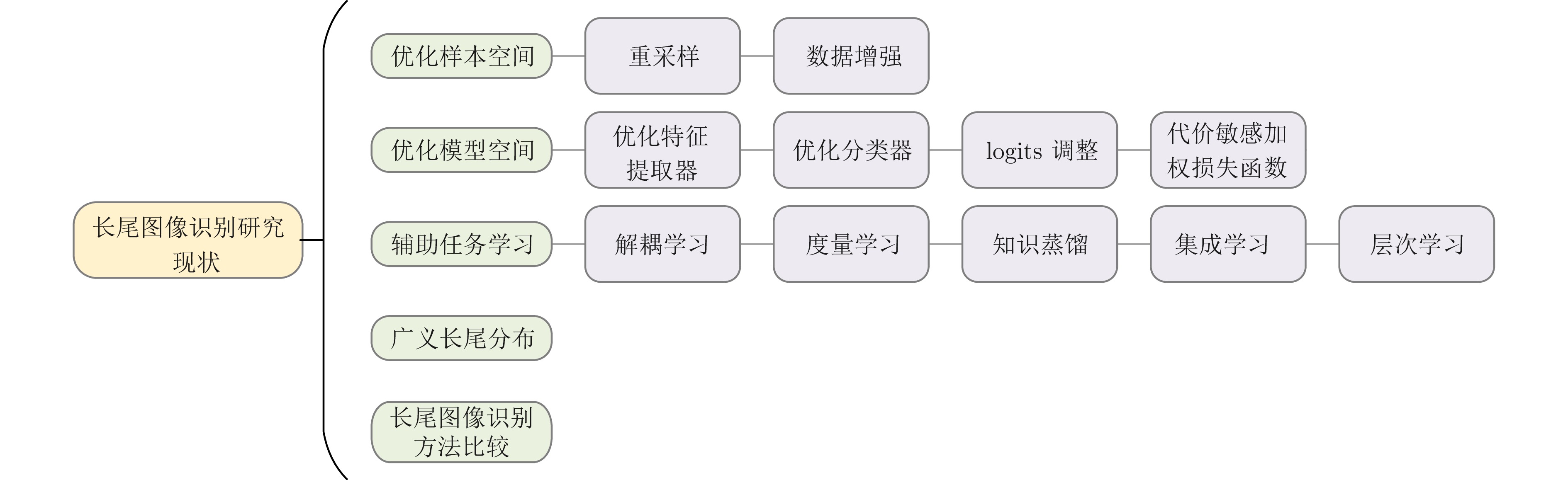
类型 数据集 类别数量 训练集样本数量 测试集样本数量 最大类样本数量 最小类样本数量 图像分类 CIFAR10-LT[13] 10 50000 10000 5000 $5\;( \rho=100)$, $50\;( \rho=10)$ 图像分类 CIFAR100-LT[13] 100 50000 10000 500 $5\;( \rho=100)$, $50\;(\rho=10)$ 目标检测 ImageNet-LT[66] 1000 115846 50000 1280 5 场景识别 Places-LT[66] 365 62500 36500 4980 5 目标检测 iNaturalist2017[69] 5089 579184 182707 196613 381 目标检测 iNaturalist2018[69] 8142 437513 24426 127551 19 实例分割 LVIS v0.5[70] 1230 57000 20000 26148 1 实例分割 LVIS v1[70] 1203 100170 19822 50552 1 场景理解 SUN-LT[71] 397 4084 2868 12 2 人脸识别 MS1M-LT[66] 74500 (ID)887530 3530 598 1 目标检测 AWA-LT[71] 50 6713 6092 720 2 鸟类识别 CUB-LT[71] 200 2945 2348 43 2或3 图像分类 STL10-LT[72] 10 5000 8000 500 $5\;( \rho=100)$, $50\;( \rho=10)$ 目标检测 VOC-LT[73] 20 1142 4952 775 4 视频分类 VideoLT[74] 1004 179352 51244 1912 44 表 2 长尾图像识别方法比较
Table 2 Comparison of long-tailed image recognition methods
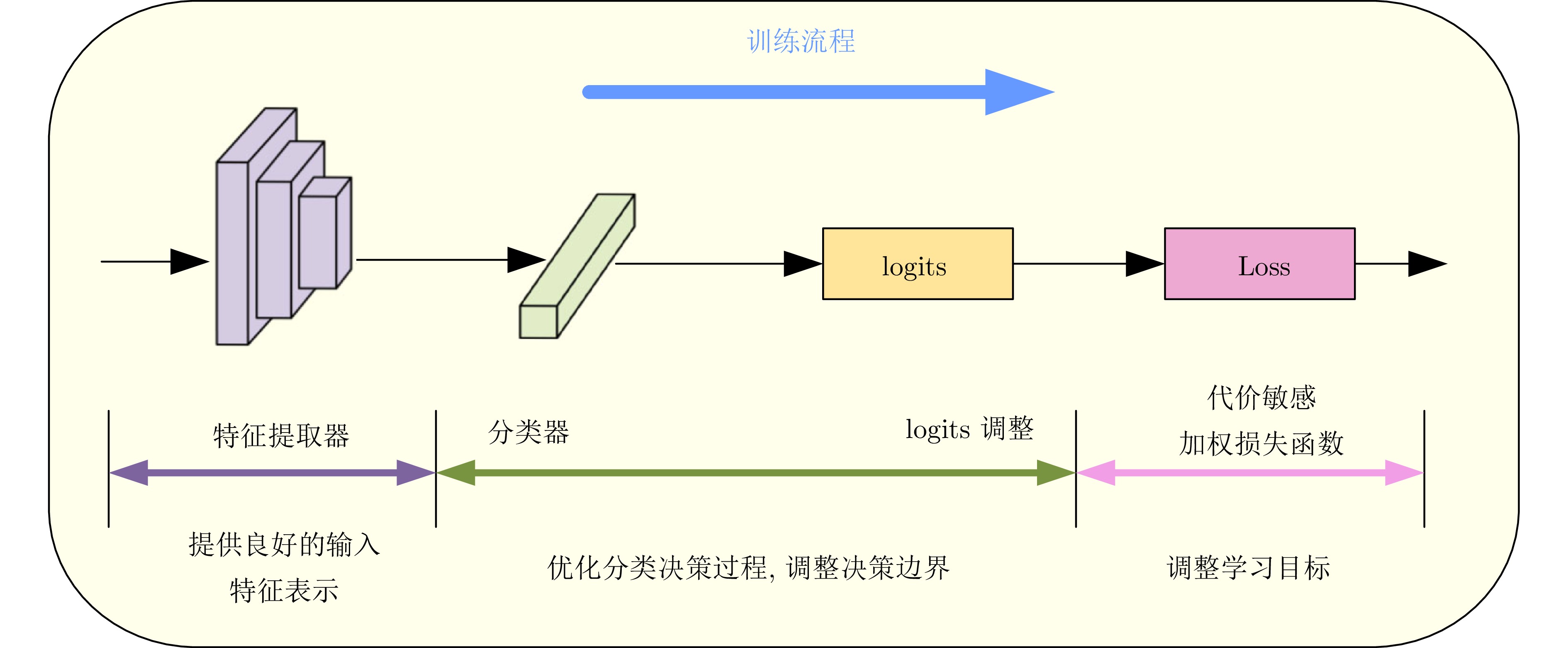
分类 代表性文献 优点 缺点 优化样本空间 重采样 [1, 2, 30, 56, 63, 82, 84, 173] 简单通用, 理论直观, 易于操作 1)会丢弃大量头部类有效信息
2)重复采样尾部类不能增加有效信息, 并容易引发过拟合
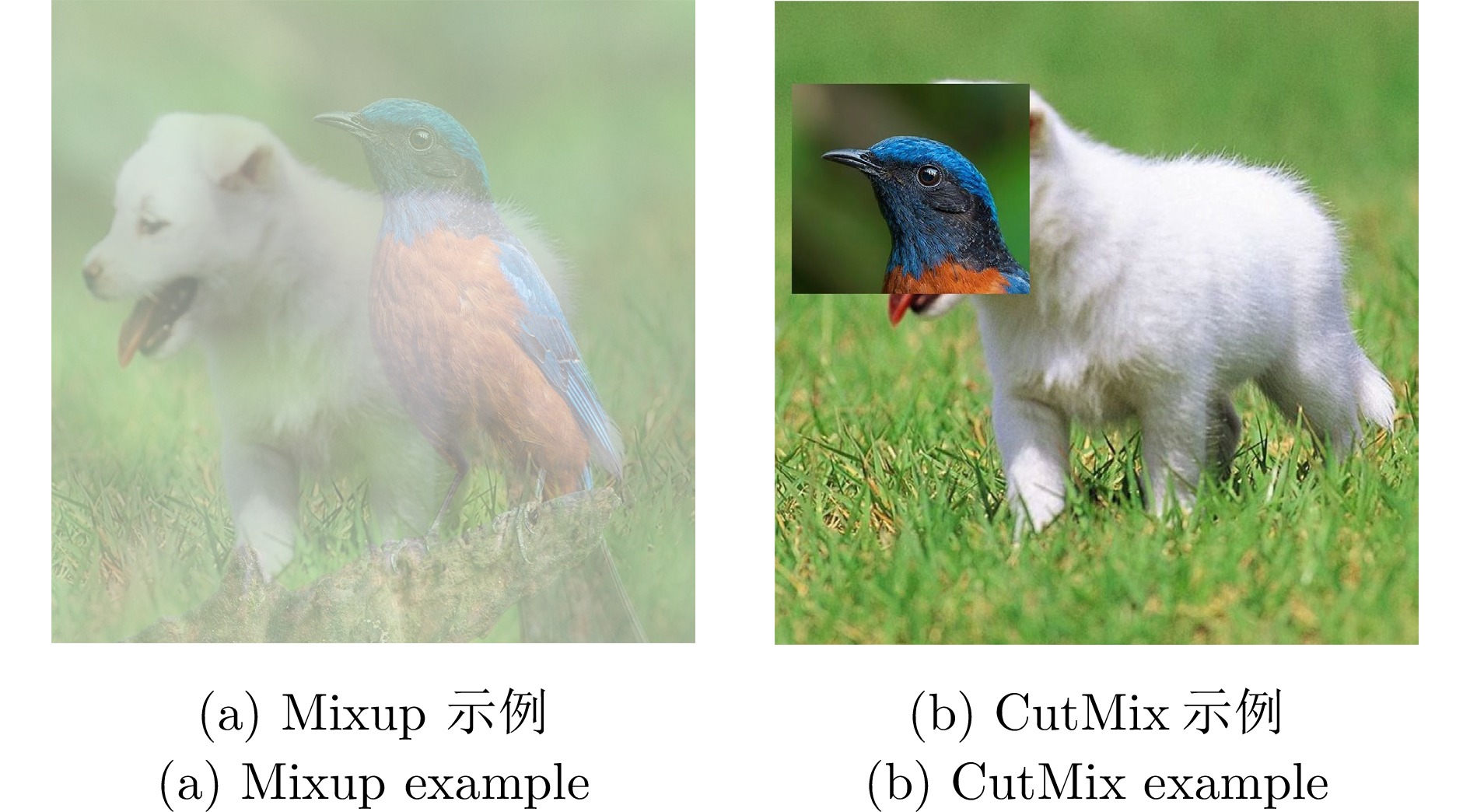
3)易引入其他噪声数据增强 [2, 8−9, 15, 85, 92−93, 98−99] 样本变换法成本较低, 易与其他方法结合, 灵活性较高. 语义增强法丰富尾部样本的语义信息, 生成具有现实意义的新样本 1)样本变换法引入大量新数据, 增加模型训练成本, 且可能生成毫无意义的样本, 鲁棒性较差
2)语义增强方法需设计专门的模型结构, 操作复杂. 并过于依赖头部类数据质量, 易给模型带来新的偏置优化模型空间 优化特征提取器 [111−113, 115−116, 174] 有效增强样本上下文语义特征, 帮助模型学到无偏的特征表示 1)引入大量参数, 占用内存, 降低训练效率
2)可解释性较差优化分类器 [1, 16, 26, 117, 119−120, 122−123] 计算开销小, 训练稳定无需设计额外的损失函数或存储单元 1)对超参数和优化器的选择敏感, 试错代价高
2)灵活性较低, 在目标检测与实例分割任务上表现不佳logits调整 [12, 28, 30, 55, 64, 124, 126] 既能优化训练过程, 又能进行事后修正. 计算开销较低, 泛化性能良好, 易与其他方法结合 1)依赖于数据集的先验分布
2)修正后的边际分布可能不满足期望分布代价敏感加权损失函数 [11−12, 54, 65, 131, 133, 137] 操作简单, 易于实现, 计算开销较小, 适应于实际应用场景 1)优化困难, 参数敏感, 难以处理大规模真实场景
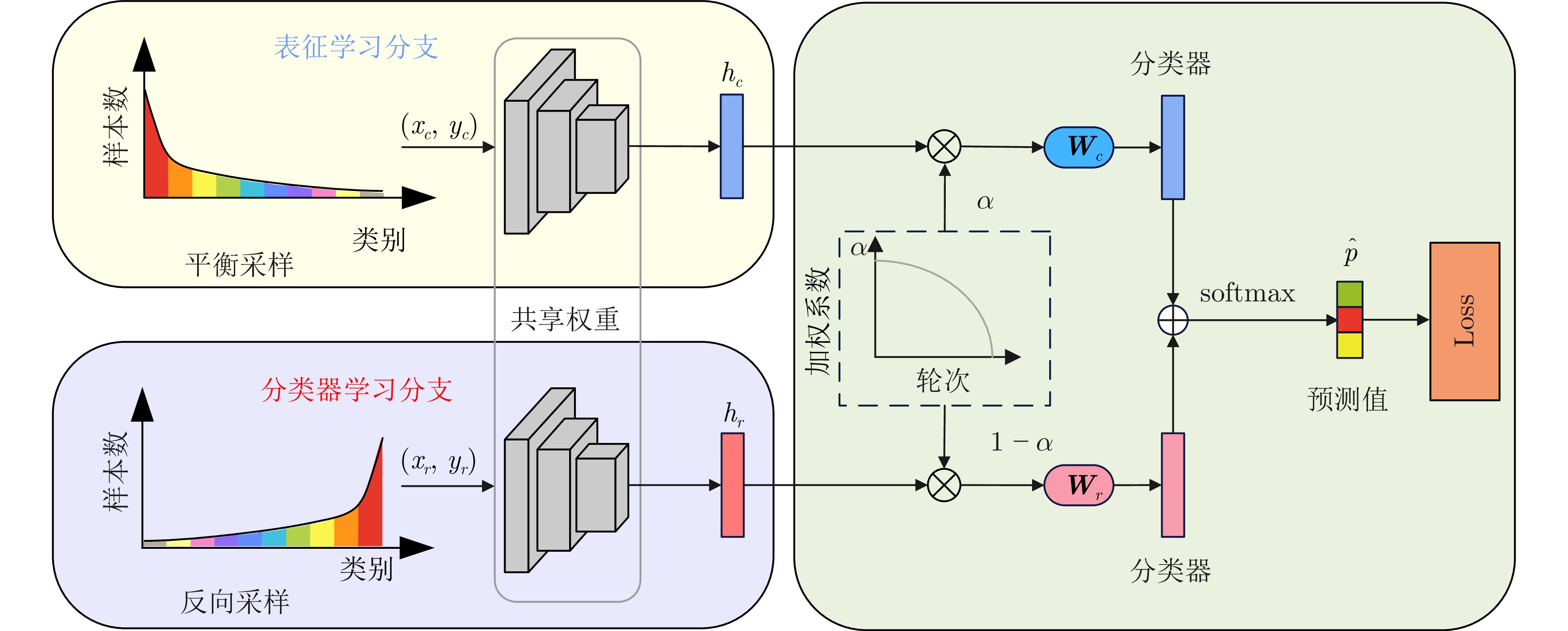
2)头尾性能像“跷跷板”, 无法从本质上解决信息缺乏问题辅助任务学习 解耦学习 [1, 14, 138−139, 142−143] 利用大量头部类数据生成泛化能力良好的特征表示, 能够有效提升模型性能且计算成本较低 1)两阶段方法不利于端到端的模型训练与部署
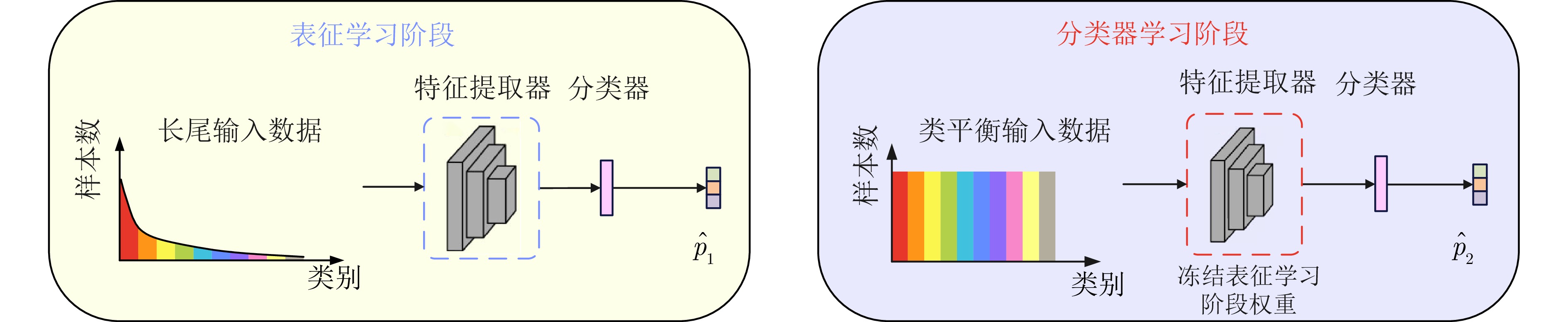
2)对数据依赖性较强
3)与其他算法结合使用时需重新设计, 实用性不强度量学习 [40, 58−59, 131, 149, 152, 154] 便于公式化与构建一个正样本接近、负样本远离的特征空间, 优化决策边界 1)尾部类样本极少的情况下性能很差
2)依赖于度量损失函数的设计知识蒸馏 [17, 19, 36, 149, 157, 159] 重用模型资源, 充分利用数据集蕴含的知识, 稳定尾部类学习过程 1)计算开销大, 优化成本相对过高, 对超参数敏感
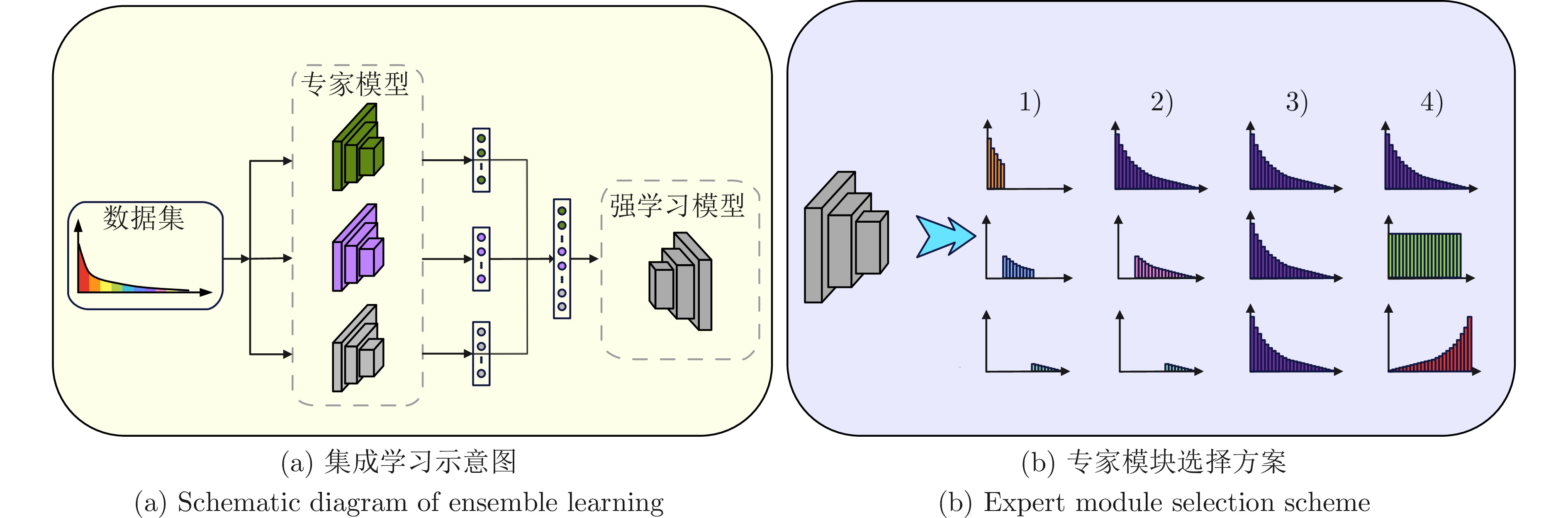
2)易出现师生不匹配问题, 整体性能过于依赖教师模型的学习情况集成学习 [18−20, 162−163, 165] 在头部类和尾部类上都能保持良好性能, 泛化能力良好, 能够处理未知分布的测试集 1)计算和存储负担过大, 框架部署复杂
2)专家之间存在相互影响的情况, 难以有效整合专家层次学习 [23−25, 166] 对数据间的关系进行多粒度建模, 捕捉类间隐式语义关系, 有助于头尾知识迁移 1)模型设计复杂, 训练成本较高
2)依赖于高质量数据, 有时需要数据集提供外部信息
3)层次划分步骤对后续训练产生过大影响 -
[1] Kang B Y, Xie S N, Rohrbach M, Yan Z C, Gordo A, Feng J S, et al. Decoupling representation and classifier for long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: OpenReview.net, 2020. [2] Zhang Y S, Wei X S, Zhou B Y, Wu J X. Bag of tricks for long-tailed visual recognition with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2021. 3447–3455 [3] Wang J Q, Zhang W W, Zang Y H, Cao Y H, Pang J M, Gong T, et al. Seesaw loss for long-tailed instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 9695–9704 [4] Fu Y, Xiang L Y, Zahid Y, Ding G G, Mei T, Shen Q, et al. Long-tailed visual recognition with deep models: A methodological survey and evaluation. Neurocomputing, 2022, 509: 290−309 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.08.031 [5] Yang L, Jiang H, Song Q, Guo J. A survey on long-tailed visual recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2022, 130(7): 1837−1872 doi: 10.1007/s11263-022-01622-8 [6] Drummond C, Holte R C. C4.5, class imbalance, and cost sensitivity: Why under-sampling beats over-sampling. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Learning from Imbalanced Datasets II. Washington, USA: ICML, 2003. 1–8 [7] Shen L, Lin Z C, Huang Q M. Relay backpropagation for effective learning of deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 467–482 [8] Chou H P, Chang S C, Pan J Y, Wei W, Juan D C. Remix: Rebalanced mixup. In: Proceedings of the Computer Vision——ECCV 2020 Workshops. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 95–110 [9] Kim J, Jeong J, Shin J. M2m: Imbalanced classification via major-to-minor translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 13896–13905 [10] Chu P, Bian X, Liu S P, Ling H B. Feature space augmentation for long-tailed data. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 694–710 [11] Cui Y, Jia M L, Lin T Y, Song Y, Belongie S. Class-balanced loss based on effective number of samples. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 9268–9277 [12] Tan J R, Wang C B, Li B Y, Li Q Q, Ouyang W L, Yin C Q, et al. Equalization loss for long-tailed object recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 11662–11671 [13] Cao K D, Wei C L, Gaidon A, Arechiga N, Ma T Y. Learning imbalanced datasets with label-distribution-aware margin loss. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2019. Article No. 140 [14] Zhou B Y, Cui Q, Wei X S, Chen Z M. BBN: Bilateral-branch network with cumulative learning for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 9719–9728 [15] Zhou A, Tajwar F, Robey A, Knowles T, Pappas G J, Hassani H, et al. Do deep networks transfer invariances across classes? arXiv preprint arXiv: 2203.09739, 2022. [16] Liu B, Li H X, Kang H, Hua G, Vasconcelos N. GistNet: A geometric structure transfer network for long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 8209–8218 [17] Zhang S Y, Chen C, Hu X Y, Peng S L. Balanced knowledge distillation for long-tailed learning. Neurocomputing, 2023, 527: 36−46 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.01.063 [18] Sharma S, Yu N, Fritz M, Schiele B. Long-tailed recognition using class-balanced experts. In: Proceedings of the 42nd DAGM German Conference on Pattern Recognition. Tübingen, Germany: Springer, 2021. 86–100 [19] Xiang L Y, Ding G G, Han J G. Learning from multiple experts: Self-paced knowledge distillation for long-tailed classification. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 247–263 [20] Cai J R, Wang Y Z, Hwang J N. ACE: Ally complementary experts for solving long-tailed recognition in one-shot. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 112–121 [21] Cai J R, Wang Y Z, Hsu H M, Hwang J N, Magrane K, Rose C. LUNA: Localizing unfamiliarity near acquaintance for open-set long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2022. 131–139 [22] Liu X T, Zhang J F, Hu T Y, Cao H, Yao Y, Pan L J. Inducing neural collapse in deep long-tailed learning. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Palau de Congressos, Spain: PMLR, 2023. 11534–11544 [23] Wu J L, Song L C, Zhang Q, Yang M, Yuan J S. ForestDet: Large-vocabulary long-tailed object detection and instance segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2022, 24: 3693−3705 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2021.3106096 [24] Ouyang W L, Wang X G, Zhang C, Yang X K. Factors in finetuning deep model for object detection with long-tail distribution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 864–873 [25] Li B H. Adaptive hierarchical representation learning for long-tailed object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 2313–2322 [26] Tang K H, Huang J Q, Zhang H W. Long-tailed classification by keeping the good and removing the bad momentum causal effect. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2009.12991, 2021. [27] Zhu B E, Niu Y L, Hua X S, Zhang H W. Cross-domain empirical risk minimization for unbiased long-tailed classification. In: Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2022. 3589–3597 [28] Wu T, Liu Z W, Huang Q Q, Wang Y, Lin D H. Adversarial robustness under long-tailed distribution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 8659–8668 [29] Wang Y X, Ramanan D, Hebert M. Learning to model the tail. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 7032–7042 [30] Ren J W, Yu C J, Sheng S N, Ma X, Zhao H Y, Yi S, et al. Balanced meta-softmax for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 351 [31] Dong B W, Zhou P, Yan S C, Zuo W M. LPT: Long-tailed prompt tuning for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Learning Representations. Kigali, Rwanda: OpenReview.net, 2023. [32] Tang K H, Tao M Y, Qi J X, Liu Z G, Zhang H W. Invariant feature learning for generalized long-tailed classification. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision. Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 709–726 [33] Zhang R R, E H H, Yuan L F, He J W, Zhang H X, Zhang S J, et al. MBNM: Multi-branch network based on memory features for long-tailed medical image recognition. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2021, 212: Article No. 106448 doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106448 [34] Ju L, Yu Z, Wang L, Zhao X, Wang X, Bonnington P, et al. Hierarchical knowledge guided learning for real-world retinal disease recognition. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2024, 43(1): 335−350 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2023.3302473 [35] Yang Z X, Pan J W, Yang Y Z, Shi X Z, Zhou H Y, Zhang Z C, et al. ProCo: Prototype-aware contrastive learning for long-tailed medical image classification. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Singapore: Springer, 2022. 173–182 [36] Zhao W D, Liu J N, Liu Y, Zhao F, He Y, Lu H C. Teaching teachers first and then student: Hierarchical distillation to improve long-tailed object recognition in aerial images. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: Article No. 5624412 [37] Li G Z, Pan L P, Qiu L W, Tan Z W, Xie F Y, Zhang H P. A two-stage shake-shake network for long-tailed recognition of SAR aerial view objects. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPRW). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 249–256 [38] Jiao W P, Zhang J L. Sonar images classification while facing long-tail and few-shot. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: Article No. 4210420 [39] Guo S, Liu R J, Wang M J, Zhang M, Nie S J, Lina S, et al. Exploiting the tail data for long-tailed face recognition. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 97945−97953 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3206040 [40] Zhang X, Fang Z Y, Wen Y D, Li Z F, Qiao Y. Range loss for deep face recognition with long-tailed training data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 5419–5428 [41] Moon W, Seong H S, Heo J P. Minority-oriented vicinity expansion with attentive aggregation for video long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Washington, USA: AAAI Press, 2023. 1931–1939 [42] Zhang C, Ren L, Wang J G, Wu W, Song D W. Making pretrained language models good long-tailed learners. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: ACL, 2022. 3298–3312 [43] Li Y, Shen T, Long G D, Jiang J, Zhou T Y, Zhang C Q. Improving long-tail relation extraction with collaborating relation-augmented attention. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Barcelona, Spain: ACL, 2020. 1653–1664 [44] Huang Y, Giledereli B, Köksal A, Özgür A, Ozkirimli E. Balancing methods for multi-label text classification with long-tailed class distribution. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Punta Cana, Dominican Republic: ACL, 2021. 8153–8161 [45] Li X Y, Sun X F, Meng Y X, Liang J J, Wu F, Li J W. Dice loss for data-imbalanced NLP tasks. In: Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. ACL, 2020. 465–476 [46] Conde M V, Choi U J. Few-shot long-tailed bird audio recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2206.11260, 2022. [47] Chen Z H, Chen J L, Xie Z L, Xu E Y, Feng Y, Liu S. Multi-expert attention network with unsupervised aggregation for long-tailed fault diagnosis under speed variation. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 252: Article No. 109393 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109393 [48] Sreepada R S, Patra B K. Mitigating long tail effect in recommendations using few shot learning technique. Expert Systems With Applications, 2020, 140: Article No. 112887 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.112887 [49] Chaudhary A, Gupta H P, Shukla K K. Real-time activities of daily living recognition under long-tailed class distribution. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2022, 6(4): 740−750 doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2022.3150757 [50] Zhang Y F, Kang B Y, Hooi B, Yan S C, Feng J S. Deep long-tailed learning: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(9): 10795−10816 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3268118 [51] Pareto V. Cours D'Économie Politique. Genève: Librairie Droz, 1964. [52] Zipf G K. The meaning-frequency relationship of words. The Journal of General Psychology, 1945, 33(2): 251−256 doi: 10.1080/00221309.1945.10544509 [53] Hitt M A. The long tail: Why the future of business is selling less of more. Academy of Management Perspectives, 2007, 21(2): 83−85 doi: 10.5465/amp.2007.25356519 [54] Tan J R, Lu X, Zhang G, Yin C Q, Li Q Q. Equalization loss v2: A new gradient balance approach for long-tailed object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 1685–1694 [55] Zhang S Y, Li Z M, Yan S P, He X M, Sun J. Distribution alignment: A unified framework for long-tail visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 2361–2370 [56] Sinha S, Ohashi H, Nakamura K. Class-difficulty based methods for long-tailed visual recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2022, 130(10): 2517−2531 doi: 10.1007/s11263-022-01643-3 [57] Cui J Q, Zhong Z S, Liu S, Yu B, Jia J Y. Parametric contrastive learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 715–724 [58] Kang B Y, Li Y, Xie S, Yuan Z H, Feng J S. Exploring balanced feature spaces for representation learning. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2021. [59] Li T H, Cao P, Yuan Y, Fan L J, Yang Y Z, Feris R, et al. Targeted supervised contrastive learning for long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEEE, 2022. 6918–6928 [60] 叶志飞, 文益民, 吕宝粮. 不平衡分类问题研究综述. 智能系统学报, 2009, 4(2): 148−156 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4785.2009.02.010Ye Zhi-Fei, Wen Yi-Min, Lv Bao-Liang. A survey of imbalanced pattern classification problems. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2009, 4(2): 148−156 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4785.2009.02.010 [61] 赵凯琳, 靳小龙, 王元卓. 小样本学习研究综述. 软件学报, 2021, 32(2): 349−369Zhao Kai-Lin, Jin Xiao-Long, Wang Yuan-Zhuo. Survey on few-shot learning. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(2): 349−369 [62] Feng C J, Zhong Y J, Huang W L. Exploring classification equilibrium in long-tailed object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 3417–3426 [63] Shrivastava A, Gupta A, Girshick R. Training region-based object detectors with online hard example mining. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 761–769 [64] Zhao Y, Chen W C, Tan X, Huang K, Zhu J H. Adaptive logit adjustment loss for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2022. 3472–3480 [65] Chen Z, Casser V, Kretzschmar H, Anguelov D. GradTail: Learning long-tailed data using gradient-based sample weighting. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2201.05938, 2022. [66] Liu Z W, Miao Z Q, Zhan X H, Wang J Y, Gong B Q, Yu S X. Large-scale long-tailed recognition in an open world. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 2537–2546 [67] Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L J, Li K, Li F F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, USA: IEEE, 2009. 248–255 [68] Zhou B L, Lapedriza A, Khosla A, Oliva A, Torralba A. Places: A 10 million image database for scene recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(6): 1452−1464 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2723009 [69] van Horn G, mac Aodha O, Song Y, Cui Y, Sun C, Shepard A, et al. The iNaturalist species classification and detection dataset. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 8769–8778 [70] Gupta A, Dollár P, Girshick R. LVIS: A dataset for large vocabulary instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 5356–5364 [71] Samuel D, Atzmon Y, Chechik G. From generalized zero-shot learning to long-tail with class descriptors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2021. 286–295 [72] Oh Y, Kim D J, Kweon I S. DASO: Distribution-aware semantics-oriented pseudo-label for imbalanced semi-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 9786–9796 [73] Wu T, Huang Q Q, Liu Z W, Wang Y, Lin D H. Distribution-balanced loss for multi-label classification in long-tailed datasets. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 162–178 [74] Zhang X, Wu Z X, Weng Z J, Fu H Z, Chen J J, Jiang Y G, et al. VideoLT: Large-scale long-tailed video recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 7960–7969 [75] Lampert C H, Nickisch H, Harmeling S. Attribute-based classifcation for zero-shot visual object categorization. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(3): 453−465 [76] Wah C, Branson S, Welinder P, Perona P, Belongie S. The caltech-UCSD birds-200-2011 dataset [Online], available: https://authors.library.caltech.edu/records/cvm3y-5hh21, March 14, 2025 [77] Coates A, Ng A Y, Lee H. An analysis of single-layer networks in unsupervised feature learning. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Lauderdale, USA: JMLR.org, 2011. 215–223 [78] Everingham M, van Gool L, Williams C K I, Winn J, Zisserman A. The PASCAL visual object classes (VOC) challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88: 303−338 [79] Li B L, Han Z B, Li H N, Fu H Z, Zhang C Q. Trustworthy long-tailed classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6970–6979 [80] Huang J, Ling C X. Using AUC and accuracy in evaluating learning algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2005, 17(3): 299−310 [81] Wang T, Zhu Y S, Chen Y Y, Zhao C Y, Yu B, Wang J Q, et al. C2AM Loss: Chasing a better decision boundary for long-tail object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6980–6989 [82] Buda M, Maki A, Mazurowski M A. A systematic study of the class imbalance problem in convolutional neural networks. Neural Networks, 2018, 106: 249−259 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2018.07.011 [83] Guo H X, Li Y J, Shang J, Gu M Y, Huang Y Y, Gong B. Learning from class-imbalanced data: Review of methods and applications. Expert Systems With Applications, 2017, 73: 220−239 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2016.12.035 [84] Chawla N V, Bowyer K W, Hall L O, Kegelmeyer W P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2002, 16: 321−357 doi: 10.1613/jair.953 [85] Zang Y H, Huang C, Loy C C. FASA: Feature augmentation and sampling adaptation for long-tailed instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 3457–3466 [86] Jaiswal A, Babu A R, Zadeh M Z, Banerjee D, Makedon F. A survey on contrastive self-supervised learning. Technologies, 2020, 9(1): Article No. 2 doi: 10.3390/technologies9010002 [87] Zhang H Y, Cissé M, Dauphin Y N, Lopez-Paz D. Mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1710.09412, 2017. [88] Yun S, Han D, Oh S J, Yoo Y, Choe J. CutMix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019. 6023–6032 [89] Verma V, Lamb A, Beckham C, Najafi A, Mitliagkas I, Lopez-Paz D, et al. Manifold mixup: Better representations by interpolating hidden states. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach, USA: PMLR, 2019. 6438–6447 [90] Zhang S Y, Chen C, Zhang X J, Peng S L. Label-occurrence-balanced mixup for long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Singapore: IEEE, 2022. 3224–3228 [91] Park S, Hong Y, Heo B, Yun S, Choi J Y. The majority can help the minority: Context-rich minority oversampling for long-tailed classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6887–6896 [92] Zhang C, Pan T Y, Li Y D, Hu H X, Xuan D, Changpinyo S, et al. MosaicOS: A simple and effective use of object-centric images for long-tailed object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 417–427 [93] Liu B, Li H X, Kang H, Hua G, Vasconcelos N. Breadcrumbs: Adversarial class-balanced sampling for long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision. Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 637–653 [94] Liu J L, Li W H, Sun Y F. Memory-based jitter: Improving visual recognition on long-tailed data with diversity in memory. In: Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2022. 1720–1728 [95] Kingma D P, Welling M. An introduction to variational autoencoders. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2019, 12(4): 307−392 [96] Rangwani H, Jaswani N, Karmali T, Jampani V, Babu R V. Improving GANs for long-tailed data through group spectral regularization. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision. Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 426–442 [97] Gomez-Rodriguez M, Balduzzi D, Schölkopf B. Uncovering the temporal dynamics of diffusion networks. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning. Bellevue, USA: Omnipress, 2011. [98] Liu B, Li H X, Kang H, Vasconcelos N, Hua G. Semi-supervised long-tailed recognition using alternate sampling. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2105.00133, 2021. [99] Wei C, Sohn K, Mellina C, Yuille A, Yang F. CReST: A class-rebalancing self-training framework for imbalanced semi-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 10857–10866 [100] Wang W Q, Zhao Z C, Wang P Y, Su F, Meng H Y. Attentive feature augmentation for long-tailed visual recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(9): 5803−5816 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3161427 [101] Wang Y L, Pan X R, Song S J, Zhang H, Wu C, Huang G. Implicit semantic data augmentation for deep networks. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2019. Article No. 1132 [102] Li S, Gong K X, Liu C H, Wang Y L, Qiao F, Cheng X J. MetaSAug: Meta semantic augmentation for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 5212–5221 [103] Zhao Y, Chen W C, Huang K, Zhu J H. Feature re-balancing for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Padua, Italy: IEEE, 2022. 1–8 [104] Vigneswaran R, Law M T, Balasubramanian V N, Tapaswi M. Feature generation for long-tail classification. In: Proceedings of the 12th Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing. Jodhpur, India: ACM, 2021. Article No. 41 [105] Liu J L, Sun Y F, Han C C, Dou Z P, Li W H. Deep representation learning on long-tailed data: A learnable embedding augmentation perspective. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 2970–2979 [106] LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278−2324 doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [107] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770–778 [108] Xie S N, Girshick R, Dollár P, Tu Z W, He K M. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1492–1500 [109] He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R. Mask R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2961–2969 [110] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2015. 91–99 [111] Long A, Yin W, Ajanthan T, Nguyen V, Purkait P, Garg R, et al. Retrieval augmented classification for long-tail visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans: IEEE, 2022. 6959–6969 [112] Zhou J X, Li J, Yan Y B, Wu L, Xu H. Mixing global and local features for long-tailed expression recognition. Information, 2023, 14(2): Article No. 83 doi: 10.3390/info14020083 [113] Zhao W, Su Y L, Hu M J, Zhao H. Hybrid ResNet based on joint basic and attention modules for long-tailed classification. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2022, 150: 83−97 doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2022.08.007 [114] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez A N, et al. Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 6000–6010 [115] Chen J, Agarwal A, Abdelkarim S, Zhu D, Elhoseiny M. RelTransformer: A transformer-based long-tail visual relationship recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 19507–19517 [116] Hou Z, Yu B S, Tao D C. BatchFormer: Learning to explore sample relationships for robust representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 7256–7266 [117] Ye H J, Chen H Y, Zhan D C, Chao W L. Identifying and compensating for feature deviation in imbalanced deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2001.01385, 2020. [118] Djouadi A, Bouktache E. A fast algorithm for the nearest-neighbor classifier. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1997, 19(3): 277−282 doi: 10.1109/34.584107 [119] Wei X S, Xu S L, Chen H, Xiao L, Peng Y X. Prototype-based classifier learning for long-tailed visual recognition. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(6): Article No. 160105 doi: 10.1007/s11432-021-3489-1 [120] Parisot S, Esperança P M, McDonagh S, Madarasz T J, Yang Y X, Li Z G. Long-tail recognition via compositional knowledge transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans: IEEE, 2022. 6939–6948 [121] Wu T Y, Morgado P, Wang P, Ho C H, Vasconcelos N. Solving long-tailed recognition with deep realistic taxonomic classifier. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 171–189 [122] Jia Y H, Peng X R, Wang R, Zhang M L. Long-tailed partial label learning by head classifier and tail classifier cooperation. In: Proceedings of the 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2024. [123] Duggal R, Freitas S, Dhamnani S, Chau D H, Sun J M. ELF: An early-exiting framework for long-tailed classification. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2006.11979, 2020. [124] Menon A K, Jayasumana S, Rawat A S, Jain H, Veit A, Kumar S. Long-tail learning via logit adjustment. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2007.07314, 2020. [125] Wang Y D, Zhang B W, Hou W X, Wu Z, Wang J D, Shinozaki T. Margin calibration for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 14th Asian Conference on Machine Learning. Hyderabad, India: PMLR, 2023. 1101–1116 [126] Li M K, Cheung Y M, Lu Y. Long-tailed visual recognition via Gaussian clouded logit adjustment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6929–6938 [127] Hong Y, Han S, Choi K, Seo S, Kim B, Chang B. Disentangling label distribution for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 6626–6636 [128] Xu Z Z, Yang S, Wang X J, Yuan C. Rethink long-tailed recognition with vision transforms. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Rhodes Island, Greece: IEEE, 2023. 1–5 [129] He Y Y, Zhang P Z, Wei X S, Zhang X Y, Sun J. Relieving long-tailed instance segmentation via pairwise class balance. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 7000–7009 [130] Long H X, Zhang X L, Liu Y B, Luo Z T, Liu J B. Mutual exclusive modulator for long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPRW). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 4890–4899 [131] Huang C, Li Y N, Loy C C, Tang X O. Learning deep representation for imbalanced classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 5375–5384 [132] Jamal M A, Brown M, Yang M H, Wang L Q, Gong B Q. Rethinking class-balanced methods for long-tailed visual recognition from a domain adaptation perspective. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 7610–7619 [133] Hsieh T I, Robb E, Chen H T, Huang J B. DropLoss for long-tail instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2021. 1549–1557 [134] Park S, Lim J, Jeon Y, Choi J Y. Influence-balanced loss for imbalanced visual classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 735–744 [135] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K M, Dollár P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2980–2988 [136] Smith L N. Cyclical focal loss. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2202.08978, 2022. [137] Li B, Yao Y Q, Tan J R, Zhang G, Yu F W, Lu J W, et al. Equalized focal loss for dense long-tailed object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6990–6999 [138] Wang T, Li Y, Kang B Y, Li J N, Liew J, Tang S, et al. The devil is in classification: A simple framework for long-tail instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 728–744 [139] Li Y, Wang T, Kang B Y, Tang S, Wang C F, Li J T, et al. Overcoming classifier imbalance for long-tail object detection with balanced group softmax. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 10991–11000 [140] Zhong Z S, Cui J Q, Liu S, Jia J Y. Improving calibration for long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 16489–16498 [141] Fan S, Zhang X M, Song Z H, Shao W M. Cumulative dual-branch network framework for long-tailed multi-class classification. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 114: Article No. 105080 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105080 [142] Guo H, Wang S. Long-tailed multi-label visual recognition by collaborative training on uniform and re-balanced samplings. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 15089–15098 [143] Bengio Y, Lamblin P, Popovici D, Larochelle H. Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: MIT Press, 2006. 153–160 [144] Alshammari S, Wang Y X, Ramanan D, Kong S. Long-tailed recognition via weight balancing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6897–6907 [145] Zhu Z H, Xing H L, Xu Y G. Easy balanced mixing for long-tailed data. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 248: Article No. 108816 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108816 [146] Yang Y Z, Xu Z. Rethinking the value of labels for improving class-imbalanced learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 1618 [147] Liu X L, Hu Y S, Cao X S, Bagdanov A D, Li K, Cheng M M. Long-tailed class incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision. Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 495–512 [148] Dong Q, Gong S G, Zhu X T. Imbalanced deep learning by minority class incremental rectifcation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(6): 1367−1381 [149] Wang Y R, Gan W H, Yang J, Wu W, Yan J J. Dynamic curriculum learning for imbalanced data classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019. 5017–5026 [150] Wei T, Shi J X, Tu W W, Li Y F. Robust long-tailed learning under label noise. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2108.11569, 2021. [151] Chen T, Kornblith S, Norouzi M, Hinton G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. Virtual Event: PMLR, 2020. Article No. 149 [152] Wang P, Han K, Wei X S, Zhang L, Wang L. Contrastive learning based hybrid networks for long-tailed image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 943–952 [153] Fu S M, Chu H P, He X X, Wang H L, Yang Z Y, Hu H J. Meta-prototype decoupled training for long-tailed learning. In: Proceedings of the 16th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Macao, China: Springer, 2023. 569–585 [154] Zhong Z S, Cui J Q, Li Z M, Lo E, Sun J, Jia J Y. Rebalanced Siamese contrastive mining for long-tailed recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2203.11506, 2022. [155] Zhu J G, Wang Z, Chen J J, Chen Y P P, Jiang Y G. Balanced contrastive learning for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6908–6917 [156] Hinton G, Vinyals O, Dean J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1503.02531, 2015. [157] Iscen A, Araújo A, Gong B Q, Schmid C. Class-balanced distillation for long-tailed visual recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2104.05279, 2021. [158] He Y Y, Wu J X, Wei X S. Distilling virtual examples for long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 235–244 [159] Li T H, Wang L M, Wu G S. Self supervision to distillation for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 630–639 [160] Xia Y L, Zhang S, Wang J, Zou W, Zhou J X, Wen B. One-stage self-distillation guided knowledge transfer for long-tailed visual recognition. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2022, 37(12): 11893−11908 doi: 10.1002/int.23068 [161] Yang C Y, Hsu H M, Cai J R, Hwang J N. Long-tailed recognition of SAR aerial view objects by cascading and paralleling experts. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 142–148 [162] Cui J Q, Liu S, Tian Z T, Zhong Z S, Jia J Y. ResLT: Residual learning for long-tailed recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(3): 3695−3706 [163] Wang X D, Lian L, Miao Z Q, Liu Z W, Yu S X. Long-tailed recognition by routing diverse distribution-aware experts. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2010.01809, 2020. [164] Li J, Tan Z C, Wan J, Lei Z, Guo G D. Nested collaborative learning for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 6949–6958 [165] Zhang Y F, Hooi B, Hong L Q, Feng J S. Self-supervised aggregation of diverse experts for test-agnostic long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 2470 [166] Chen Q, Liu Q F, Lin E L. A knowledge-guide hierarchical learning method for long-tailed image classification. Neurocomputing, 2021, 459: 408−418 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.07.008 [167] Li Z Y, Zhao H, Lin Y J. Multi-task convolutional neural network with coarse-to-fine knowledge transfer for long-tailed classification. Information Sciences, 2022, 608: 900−916 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.07.015 [168] Wen Y D, Zhang K P, Li Z, Qiao Y. A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 499–515 [169] Cao D, Zhu X Y, Huang X Y, Guo J Z, Lei Z. Domain balancing: Face recognition on long-tailed domains. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 5671–5679 [170] Ma Y B, Jiao L C, Liu F, Li Y X, Yang S Y, Liu X. Delving into semantic scale imbalance. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2212.14613, 2022. [171] Park B, Kim J, Cho S, Kim H, Kim C. Balancing domain experts for long-tailed camera-trap recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2202.07215, 2022. [172] Wang W T, Wang M, Wang S, Long G D, Yao L N, Qi G L, et al. One-shot learning for long-tail visual relation detection. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI Press, 2020. 12225–12232 [173] Chang N, Yu Z D, Wang Y X, Anandkumar A, Fidler S, Álvarez J M. Image-level or object-level? A tale of two resampling strategies for long-tailed detection. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. Virtual Event: PMLR, 2021. 1463–1472 [174] Zhang C, Lin G S, Lai L L, Ding H H, Wu Q Y. Calibrating class activation maps for long-tailed visual recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2108.12757, 2021. [175] Cao Y X, Kuang J, Gao M, Zhou A Y, Wen Y G, Chua T S. Learning relation prototype from unlabeled texts for long-tail relation extraction. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2023, 35(2): 1761−1774 [176] Zhang G X, Liang R J, Yu Z Y, Zhang S C. Rumour detection on social media with long-tail strategy. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Padua, Italy: IEEE, 2022. 1–8 [177] Mottaghi A, Sarma P K, Amatriain X, Yeung S, Kannan A. Medical symptom recognition from patient text: An active learning approach for long-tailed multilabel distributions. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2011.06874, 2020. [178] Scarselli F, Gori M, Tsoi A C, Hagenbuchner M, Monfardini G. The graph neural network model. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(1): 61−80 [179] Shi C, Hu B B, Zhao W X, Yu P S. Heterogeneous information network embedding for recommendation. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2019, 31(2): 357−370 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2018.2833443 [180] Zhao T X, Zhang X, Wang S H. GraphSMOTE: Imbalanced node classification on graphs with graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. Israel: ACM, 2021. 833–841 [181] Park J, Song J, Yang E. GraphENS: Neighbor-aware ego network synthesis for class-imbalanced node classification. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2022. [182] Yun S, Kim K, Yoon K, Park C. LTE4G: Long-tail experts for graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management. Atlanta, USA: ACM, 2022. 2434–2443 [183] Hu Z N, Dong Y X, Wang K S, Chang K W, Sun Y Z. GPT-GNN: Generative pre-training of graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. Virtual Event: ACM, 2020. 1857–1867 [184] Liu Z M, Nguyen T K, Fang Y. Tail-GNN: Tail-node graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. Singapore: ACM, 2021. 1109–1119 [185] Perrett T, Sinha S, Burghardt T, Mirmehdi M, Damen D. Use your head: Improving long-tail video recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 2415–2425 [186] Tian C Y, Wang W H, Zhu X Z, Dai J F, Qiao Y. VL-LTR: Learning class-wise visual-linguistic representation for long-tailed visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision. Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 73–91 [187] Ma T L, Geng S J, Wang M M, Shao J, Lu J S, Li H S, et al. A simple long-tailed recognition baseline via vision-language model. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2111.14745, 2021. [188] Wang R M, Yu G X, Domeniconi C, Zhang X L. Meta cross-modal hashing on long-tailed data. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2111.04086, 2021. [189] Wang P K, Wang X, Wang B W, Zhang Y D, Bai L, Wang Y. Long-tailed time series classification via feature space rebalancing. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications. Tianjin, China: Springer, 2023. 151–166 [190] Deng J L, Chen X S, Jiang R H, Song X, Tsang I W. ST-norm: Spatial and temporal normalization for multi-variate time series forecasting. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. Singapore: ACM, 2021. 269–278 [191] Craw S, Horsburgh B, Massie S. Music recommendation: Audio neighbourhoods to discover music in the long tail. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Case-Based Reasoning Research and Development. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Springer, 2015. 73–87 [192] Deng K Q, Cheng G F, Yang R Y, Yan Y H. Alleviating ASR long-tailed problem by decoupling the learning of representation and classification. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2022, 30: 340−354 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2021.3138707 [193] Winata G I, Wang G S, Xiong C M, Hoi S C H. Adapt-and-adjust: Overcoming the long-tail problem of multilingual speech recognition. In: Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Brno, Czechia: ISCA, 2021. 2451–2455 [194] Peng P, Lu J X, Tao S T, Ma K, Zhang Y, Wang H W, et al. Progressively balanced supervised contrastive representation learning for long-tailed fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: Article No. 3506112 [195] Deng S Q, Lei Z J, Liu J X, Liu Z M, Su Y, Feng K, et al. A cost-sensitive dense network for fault diagnosis under data imbalance. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Sensing, Measurement & Data Analytics in the Era of Artificial Intelligence (ICSMD). Harbin, China: IEEE, 2022. 1–6 [196] Shao J, Zhu K, Zhang H X, Wu J X. DiffuLT: How to make diffusion model useful for long-tail recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2403.05170, 2024. [197] Xian Y, Zhuang J X, Yu F. Solution for large-scale long-tailed recognition with noisy labels. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2106.10683, 2021. [198] Kabir H M D. Reduction of class activation uncertainty with background information. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2305.03238, 2023. [199] Du F, Yang P, Jia Q, Nan F T, Chen X T, Yang Y. Global and local mixture consistency cumulative learning for long-tailed visual recognitions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 15814–15823 [200] Chen X N, Liang C, Huang D, Real E, Wang K Y, Pham H, et al. Symbolic discovery of optimization algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 2140 [201] Cui J Q, Zhong Z S, Tian Z T, Liu S, Yu B, Jia J Y. Generalized parametric contrastive learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(12): 7463−7474 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3278694 [202] Shi J X, Wei T, Zhou Z, Han X Y, Shao J J, Li Y F. Parameter-efficient long-tailed recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2309.10019, 2023. [203] Hendrycks D, Gimpel K. A baseline for detecting misclassified and out-of-distribution examples in neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1610.02136, 2016. [204] Liu W T, Wang X Y, Owens J D, Li Y X. Energy-based out-of-distribution detection. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 1802 [205] Yang Y Z, Wang H, Katabi D. On multi-domain long-tailed recognition, imbalanced domain generalization and beyond. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision. Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 57–75 [206] Kim C D, Jeong J, Kim G. Imbalanced continual learning with partitioning reservoir sampling. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 411–428 [207] Ditzler G, Polikar R, Chawla N. An incremental learning algorithm for non-stationary environments and class imbalance. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Istanbul, Turkey: IEEE, 2010. 2997–3000 [208] Kharbanda S, Gupta D, Schultheis E, Banerjee A, Hsieh C J, Babbar R. Gandalf: Learning label-label correlations in extreme multi-label classification via label features. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2024. 1360–1371 [209] Zhang Y, Cao S C, Mi S Y, Bian Y L. Learning sample representativeness for class-imbalanced multi-label classification. Pattern Analysis and Applications, 2024, 27(2): Article No. 62 doi: 10.1007/s10044-024-01209-8 [210] Shi J X, Wei T, Li Y F. Residual diverse ensemble for long-tailed multi-label text classification. Science China Information Sciences, 2024, 67(11): Article No. 212102 doi: 10.1007/s11432-022-3915-6 [211] Du C Q, Han Y Z, Huang G. SimPro: A simple probabilistic framework towards realistic long-tailed semi-supervised learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2402.13505, 2024. [212] Ma C C, Elezi I, Deng J K, Dong W M, Xu C S. Three heads are better than one: Complementary experts for long-tailed semi-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2024. 14229–14237 [213] Shang X Y, Lu Y, Huang G, Wang H Z. Federated learning on heterogeneous and long-tailed data via classifier re-training with federated features. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2204.13399, 2022. [214] Kou X, Xu C H, Yang X, Deng C. Attention-guided contrastive hashing for long-tailed image retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vienna, Austria: IJCAI, 2022. 1017–1023 [215] Geifman Y, El-Yaniv R. Deep active learning over the long tail. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1711.00941, 2017. -




 下载:
下载: