Intelligent Operational Optimization of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Process Based on Multi-objective Particle Swarm Algorithm
-
摘要: 城市固废焚烧(Municipal solid waste incineration, MSWI)技术因兼具减量化、无害化、资源化等特点, 已成为治理固废污染的主要方式. 由于城市固废成分复杂, 含水率、热值动态波动, 固废燃烧、余热利用、烟气净化等环节耦合冲突, 实际工业过程难以高效运行. 为此, 本文提出了一种基于多目标粒子群算法的城市固废焚烧过程智能操作优化方法, 以期实现燃烧效率和烟气净化效率的协同优化. 首先, 设计自组织径向基函数(Self-organizing radial basis function, SORBF)神经网络建立运行指标模型, 实现城市固废焚烧过程运行性能的在线评价; 其次, 引入区域拥挤度指标提出了一种改进的多目标粒子群优化算法, 以获取操作变量的Pareto解集; 然后, 利用熵权法确定操作变量最佳设定值, 实现城市固废焚烧过程高效运行; 最后, 通过北京某城市固废焚烧厂的实际运行数据对所提方法进行验证, 实验结果表明基于多目标粒子群算法的智能操作优化方法可以实现燃烧效率与脱硝效率的协同提升.Abstract: Municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) technology has become the main way to address solid waste pollution due to its characteristics of reduction, harmlessness, and resource utilization. However, it is difficult for actual industries to operate efficiently due to the complex composition of municipal solid waste, dynamic fluctuations in moisture content and calorific value, coupling conflicts in solid waste combustion, waste heat utilization and flue gas purification. To enhance combustion efficiency and flue gas purification efficiency, this paper proposes an intelligent operational optimization method of MSWI process based on multi-objective particle swarm algorithm. First, operational index models are established by designing self-organizing radial basis function (SORBF) neural networks to achieve online evaluation of operational performance in MSWI process. Second, an improved multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm is presented by incorporating regional congestion degree index to obtain the Pareto solutions of operating variables. Then, the entropy weight method is employed to determine the optimal set value of operating variables, achieving efficient operation of MSWI process. Finally, the proposed method is verified through actual operational data from a MSWI plant in Beijing, and the experimental results demonstrate that the intelligent operational optimization method based on multi-objective particle swarm algorithm can improve combustion efficiency and reduce nitrogen oxide emissions.
-
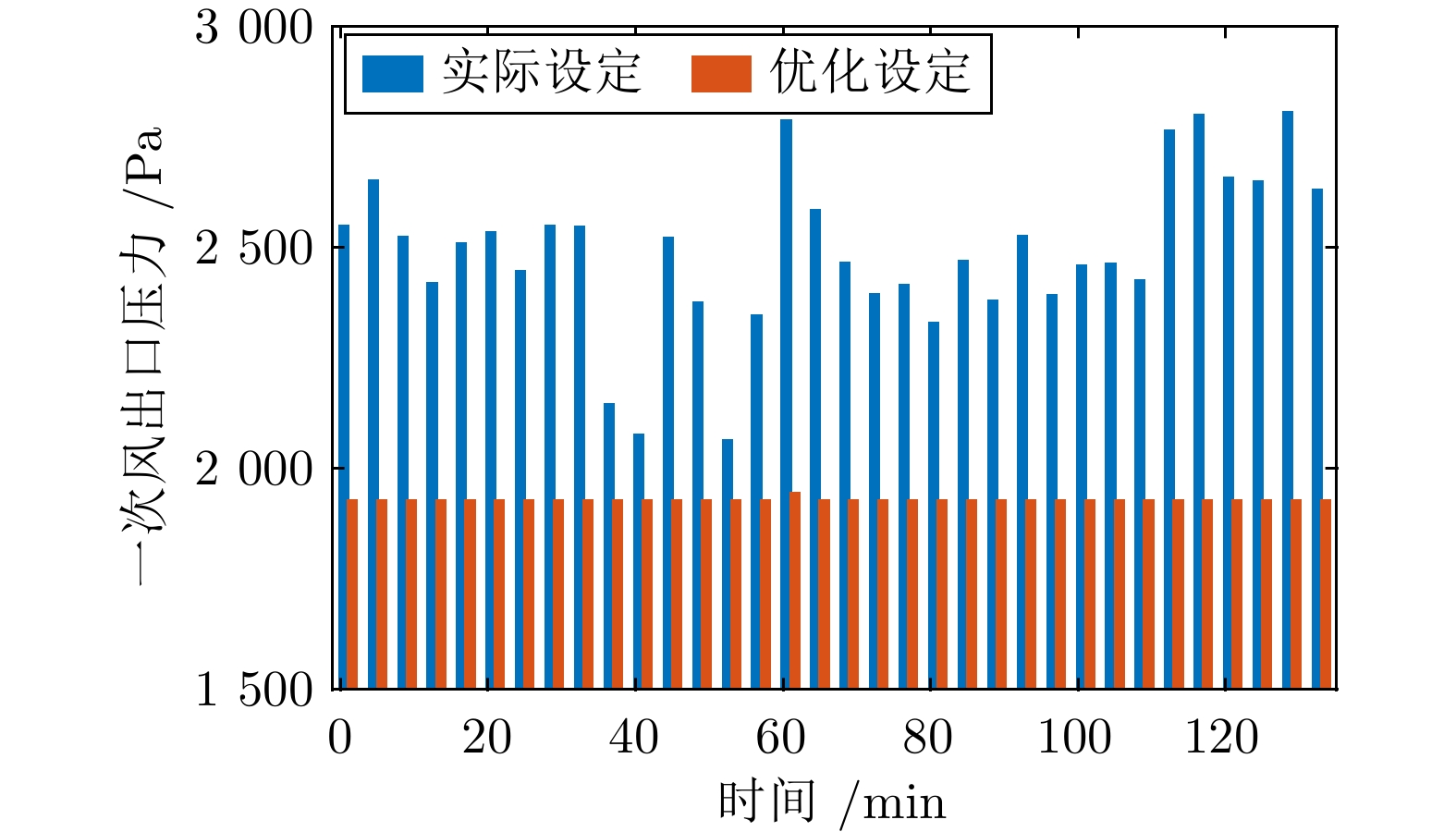
表 1 实验数据基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of experimental data
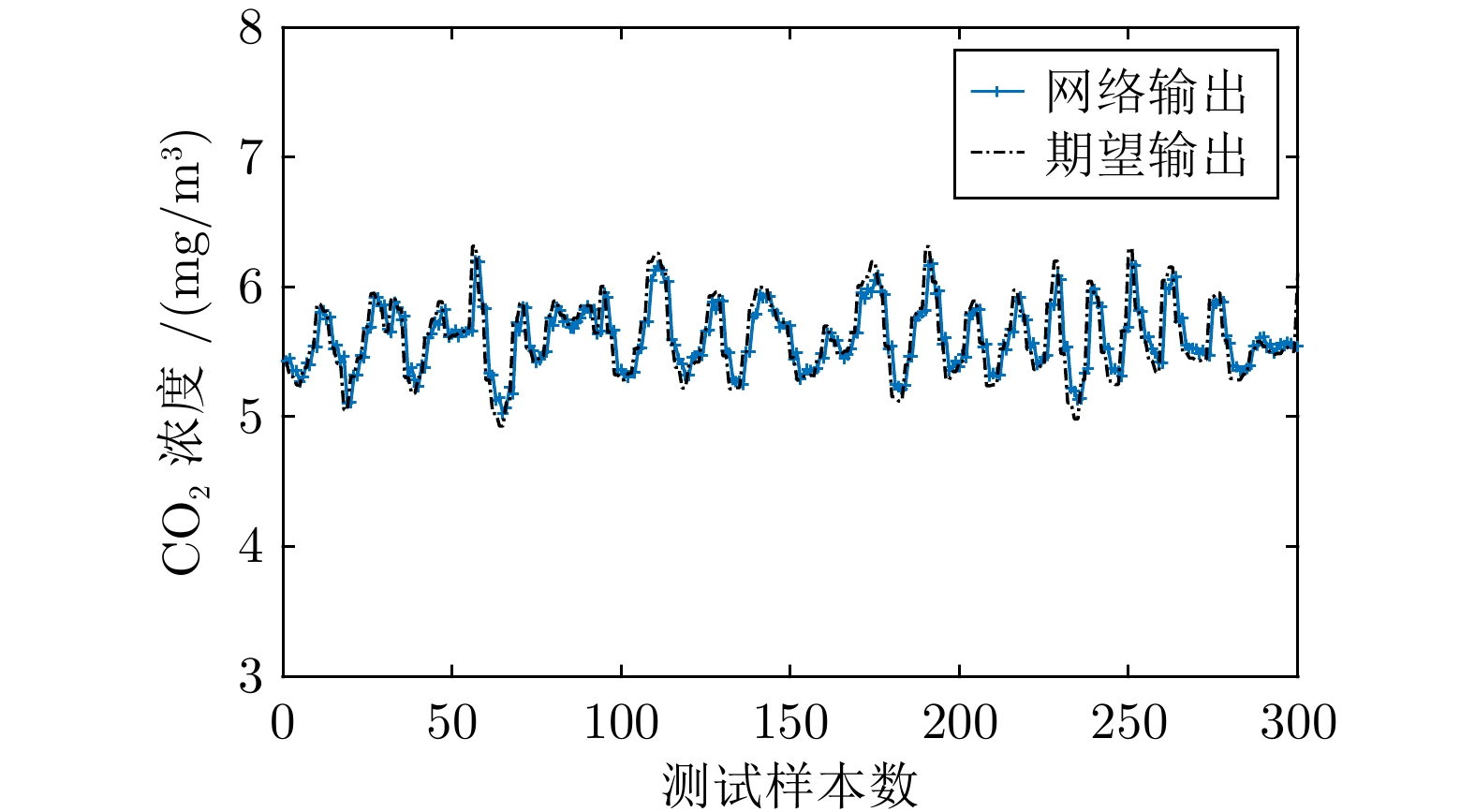
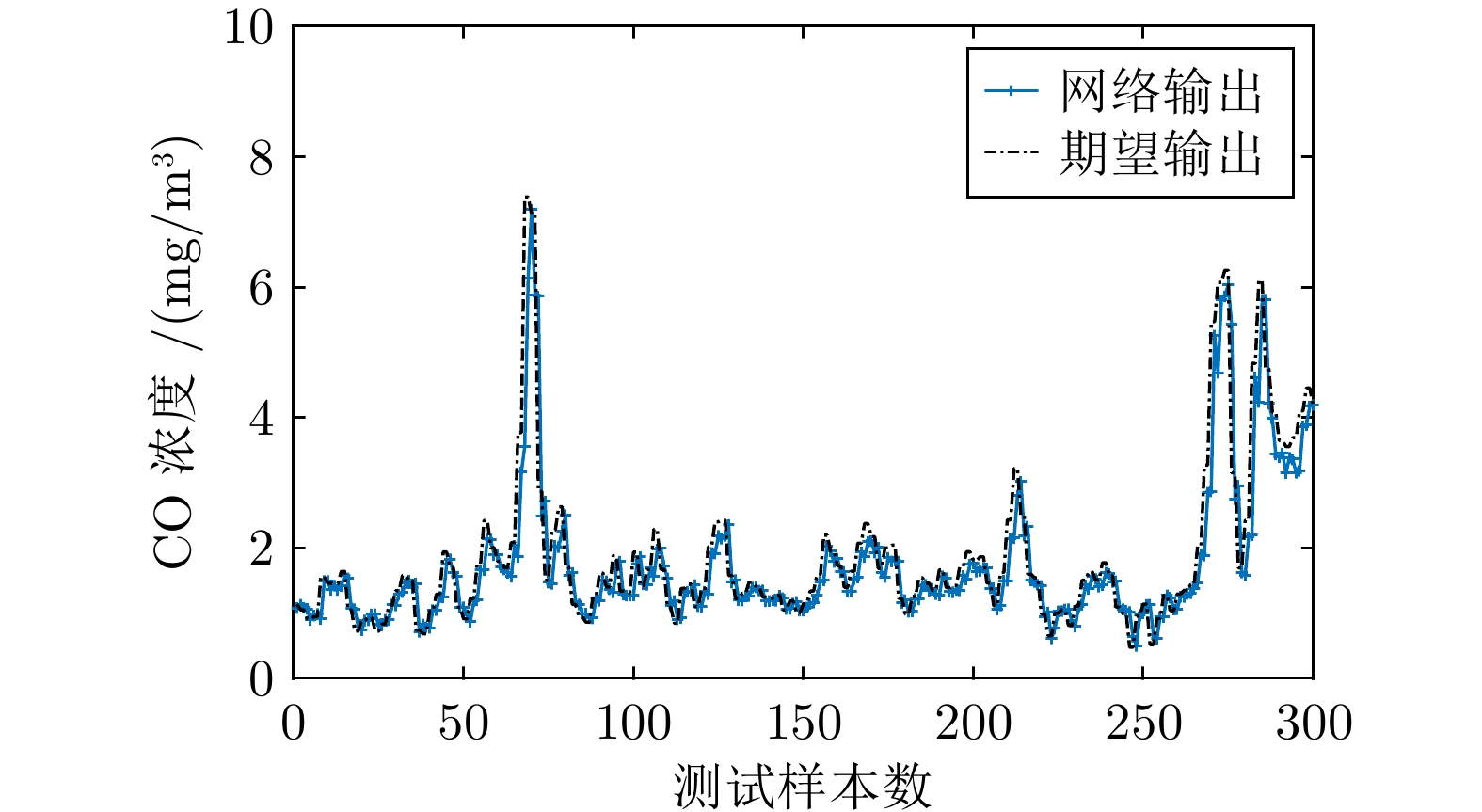
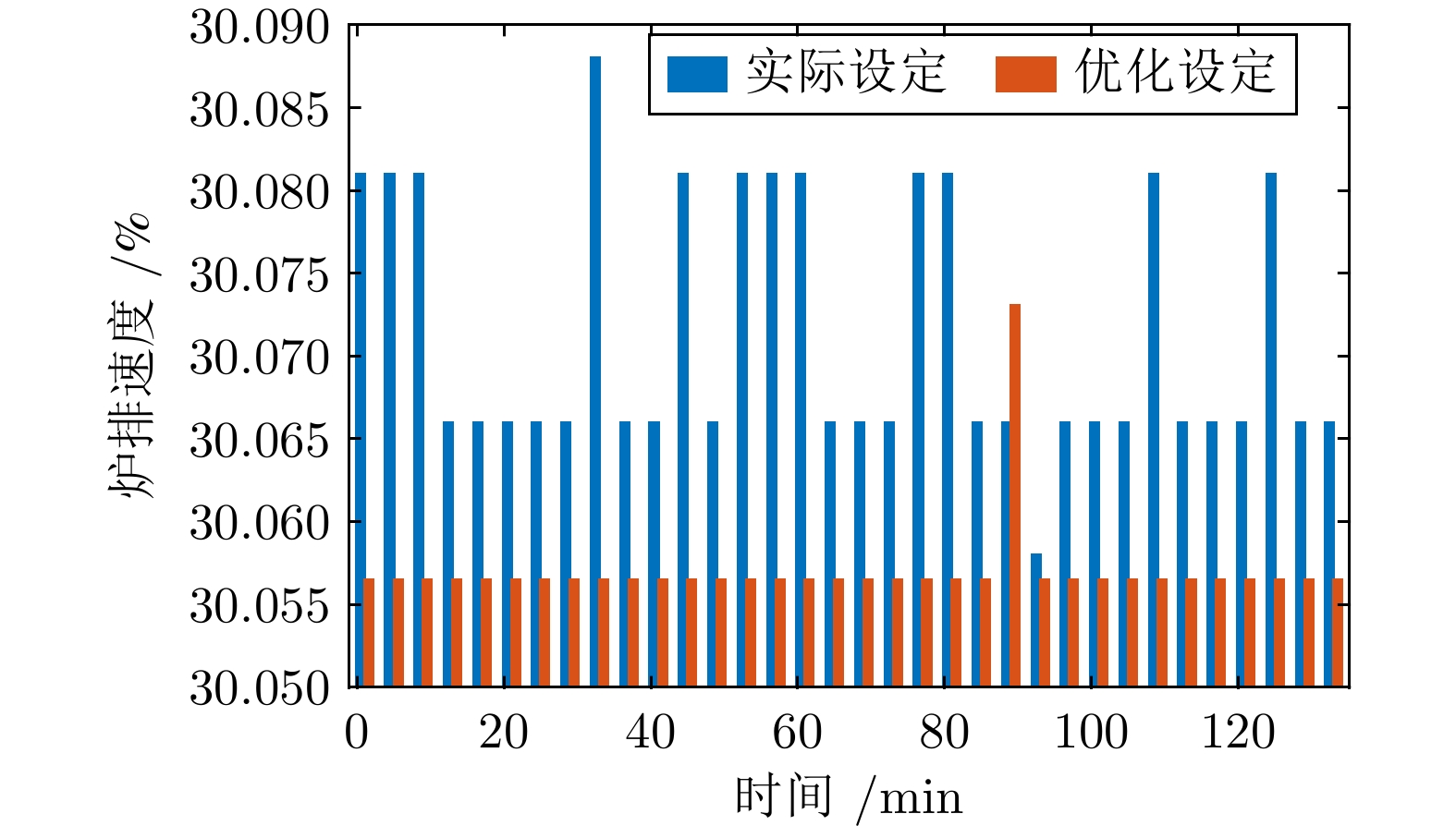
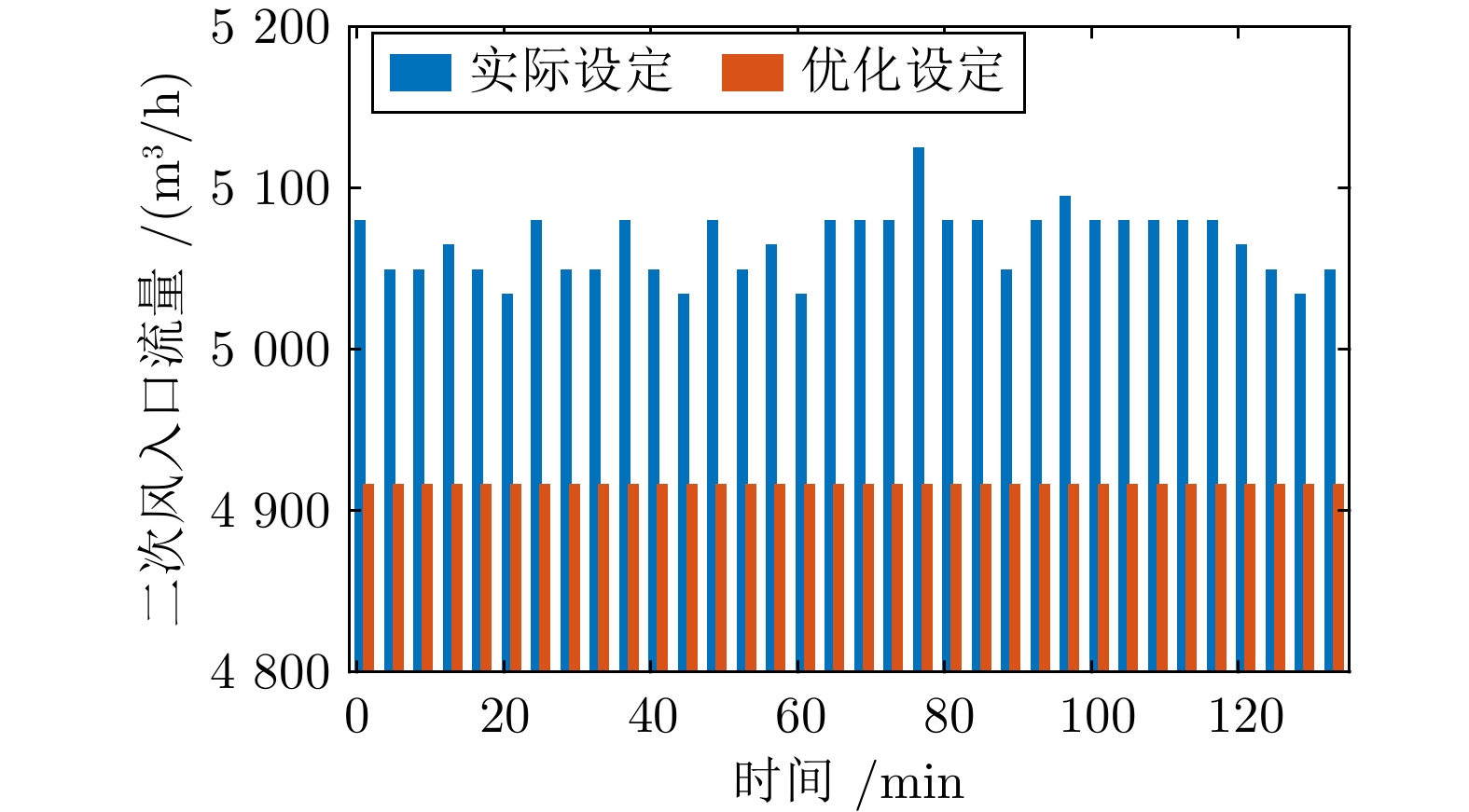
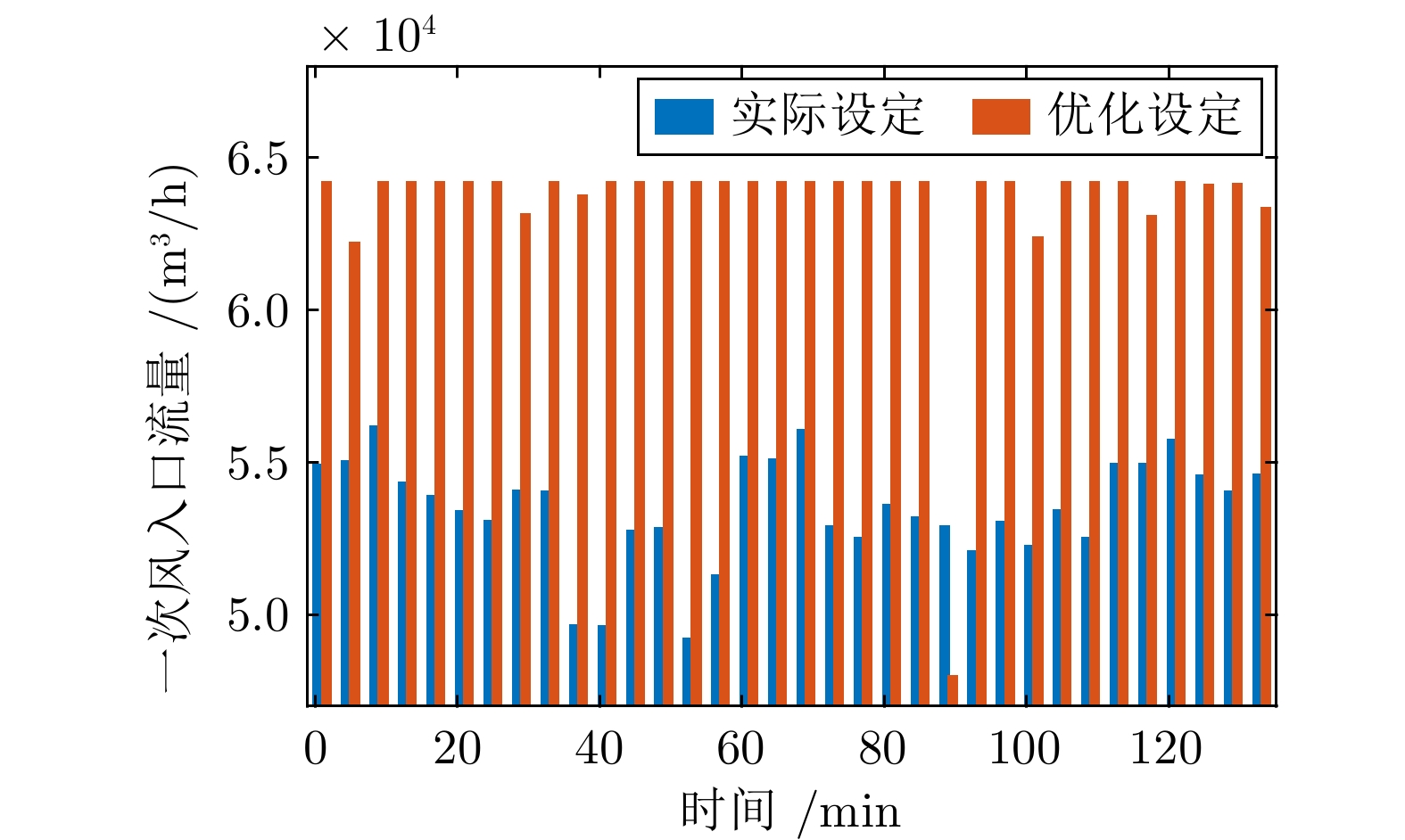
变量名称 取值范围 单位 炉排速度 30.05 ~ 30.08 % 一次风入口流量 47698.32 ~63444.03 m3/h 一次风出口压力 1988.02 ~3189.73 Pa 二次风入口流量 4924.86 ~5124.70 m3/h NOx排放浓度 79.21 ~ 231.27 mg/m3 CO排放浓度 0.39 ~ 7.38 mg/m3 CO2排放浓度 4.80 ~ 6.55 mg/m3 表 2 不同指标模型精度
Table 2 Accuracy of different index models
方法 NOx指标模型 CO指标模型 CO2指标模型 RMSE MAPE (%) RMSE MAPE (%) RMSE MAPE (%) LSSVR 11.2729 7.0716 0.6281 17.8164 0.1970 2.6587 Kriging 10.3483 6.1612 0.5376 15.5635 0.1967 2.5834 RBF 11.6462 7.3384 0.5595 16.5597 0.1908 2.4366 SORBF 9.3939 5.5603 0.5368 15.4444 0.1866 2.2523 表 3 不同算法优化结果均值比较
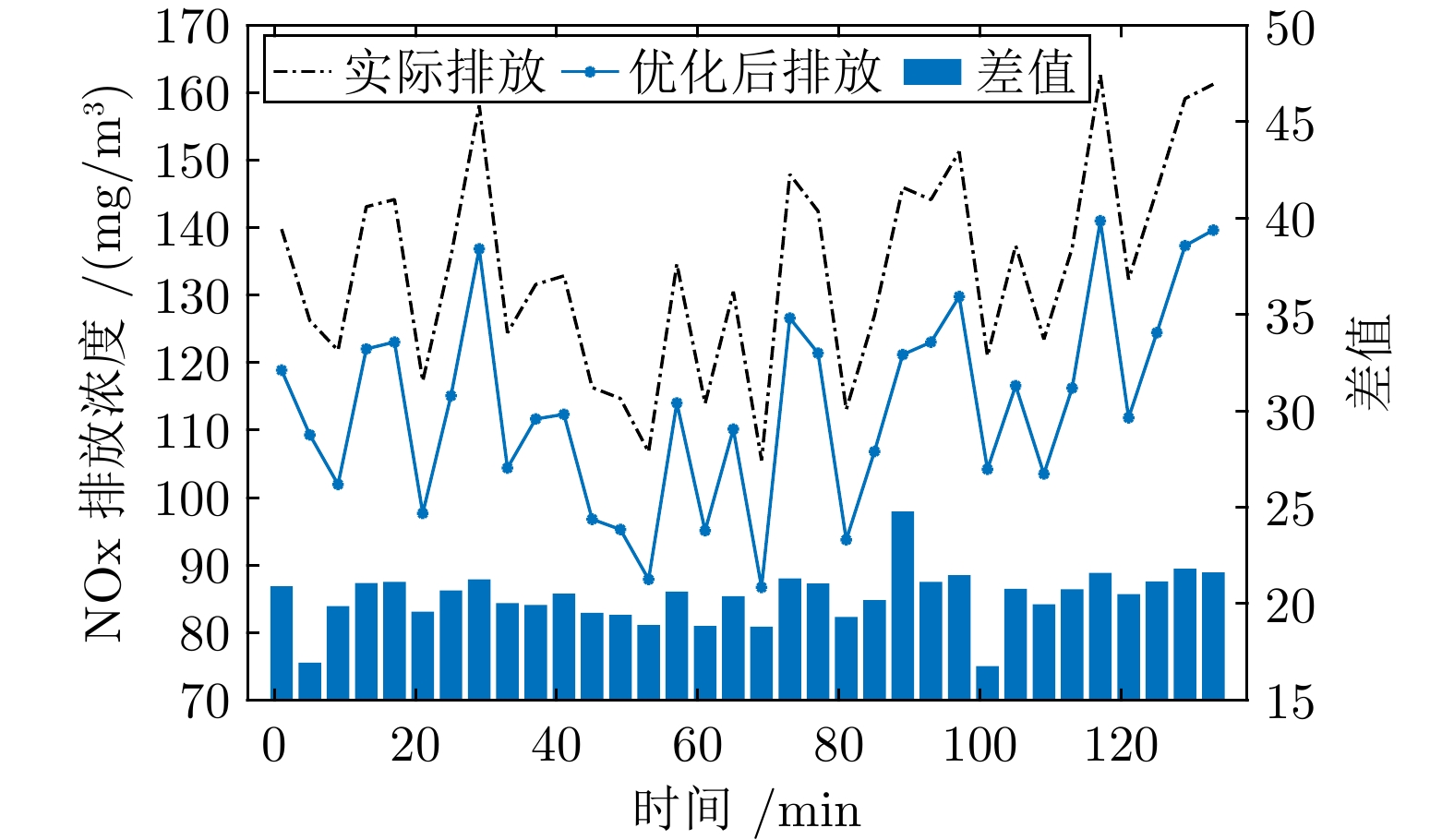
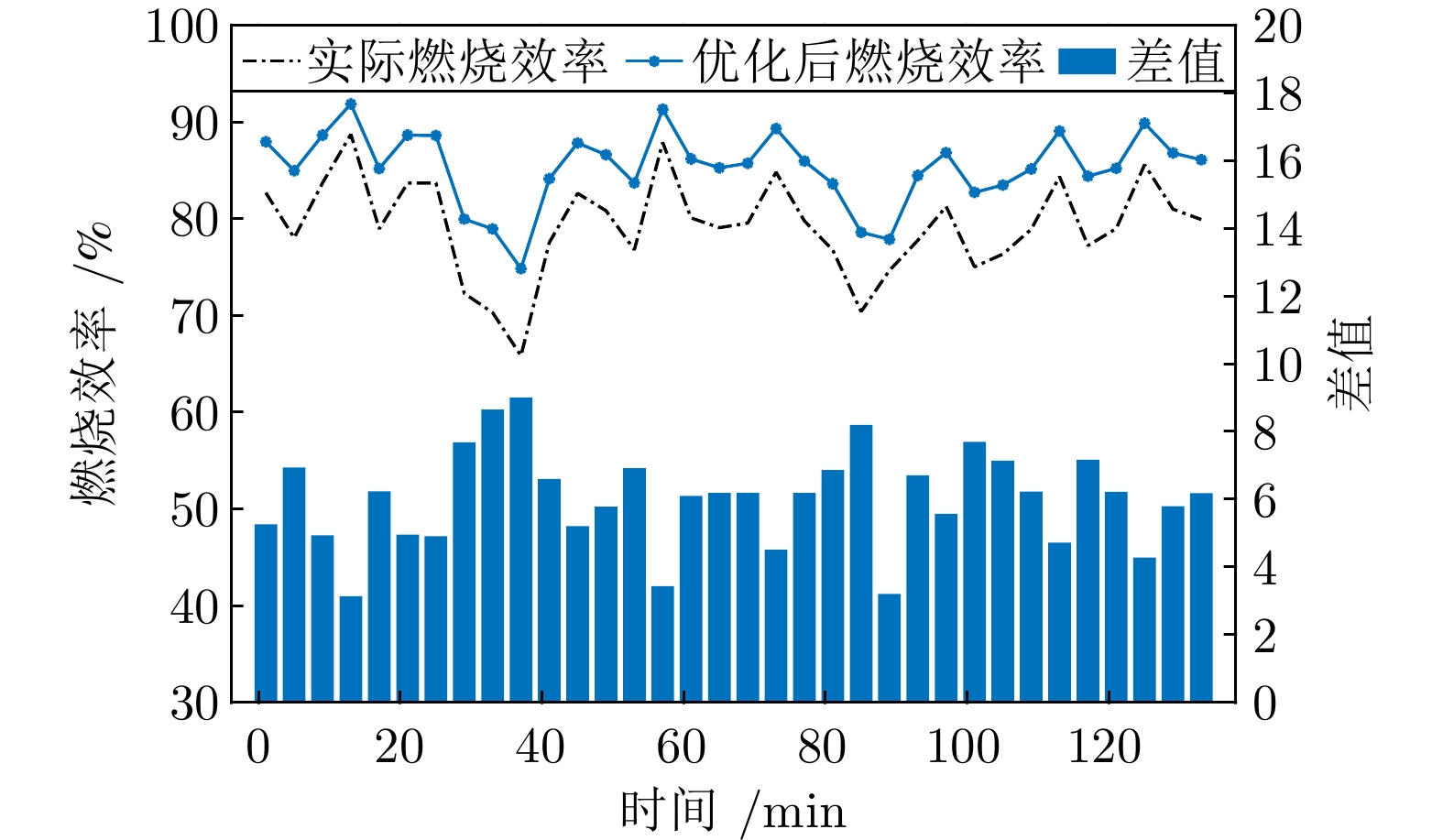
Table 3 Comparison of mean optimization results using different algorithms
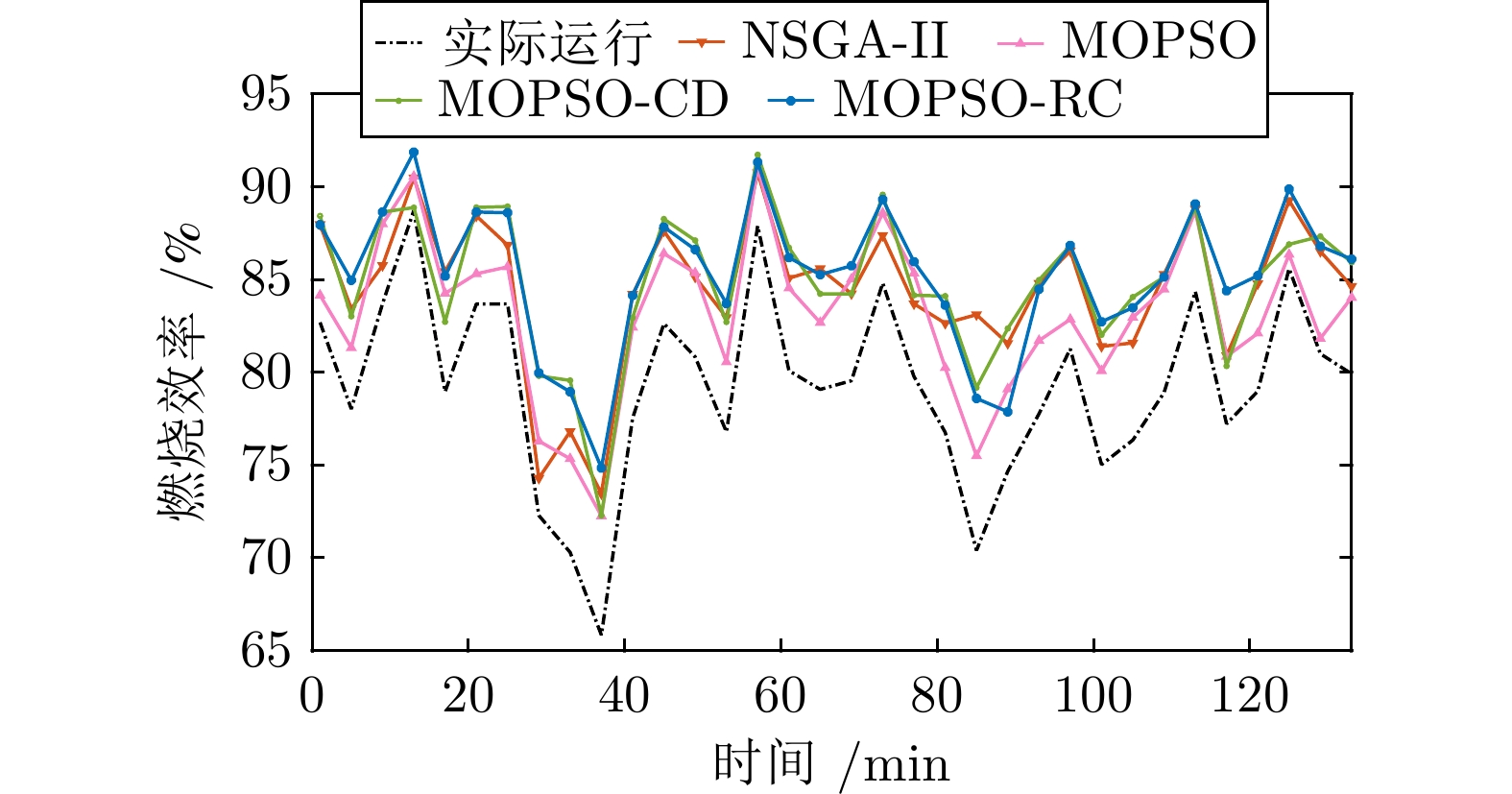
不同优化算法 NOx排放(mg/m3) 燃烧效率(%) 实际运行 133.840 2 79.274 0 NSGA-II 123.567 4 84.460 1 MOPSO 121.792 7 83.122 0 MOPSO-CD 119.997 0 84.890 7 MOPSO-RC 113.462 5 85.299 0 -
[1] Maalouf A, Mavropoulos A, El-Fadel M. Global municipal solid waste infrastructure: Delivery and forecast of uncontrolled disposal. Waste Management & Research, 2020, 38(9): 1028−1036 [2] 汤健, 夏恒, 余文, 乔俊飞. 城市固废焚烧过程智能优化控制研究现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(10): 2019−2059Tang Jian, Xia Heng, Yu Wen, Qiao Jun-Fei. Research status and prospects of intelligent optimization control for municipal solid waste incineration process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(10): 2019−2059 [3] Frey H H, Peters B, Hunsinger H, Vehlow J. Characterization of municipal solid waste combustion in a grate furnace. Waste Management, 2003, 23(8): 689−701 doi: 10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00070-3 [4] Shin D, Choi S. The combustion of simulated waste particles in a fixed bed. Combustion and Flame, 2000, 121(1−2): 167−180 doi: 10.1016/S0010-2180(99)00124-8 [5] Yang Y B, Goh Y R, Zakaria R, Nasserzadeh V, Swithenbank J. Mathematical modelling of MSW incineration on a travelling bed. Waste Management, 2002, 22(4): 369−380 doi: 10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00019-3 [6] Liang Z, Ma X. Mathematical modeling of MSW combustion and SNCR in a full-scale municipal incinerator and effects of grate speed and oxygen-enriched atmospheres on operating conditions. Waste Management, 2010, 30(12): 2520−2529 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2010.05.006 [7] Xia Z, Li J, Wu T, Chen C, Zhang X. CFD simulation of MSW combustion and SNCR in a commercial incinerator. Waste Management, 2014, 34(9): 1609−1618 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2014.04.015 [8] Hu Z, Jiang E, Ma X. Numerical simulation on operating parameters of SNCR process in a municipal solid waste incinerator. Fuel, 2019, 245: 160−173 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.02.071 [9] Yang X, Liao Y, Ma X, Zhou J. Effects of air supply optimization on NOx reduction in a structurally modified municipal solid waste incinerator. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 201: Article No. 117706 doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.117706 [10] Huai X L, Xu W L, Qu Z Y, Li Z G, Zhang F P, Xiang G M, et al. Numerical simulation of municipal solid waste combustion in a novel two-stage reciprocating incinerator. Waste Management, 2008, 28(1): 15−29 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2006.11.010 [11] Han H, Liu Y, Hou Y, Qiao J. Multi-modal multi-objective particle swarm optimization with self-adjusting strategy. Information Sciences, 2023, 629: 580−598 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.02.019 [12] Zhou P, Wang X, Chai T. Multiobjective operation optimization of wastewater treatment process based on reinforcement self-learning and knowledge guidance. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(11): 6896−6909 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3164476 [13] 丁进良, 陈佳鑫, 马欣然. 基于自适应差分进化的常压塔轻质油产量多目标优化. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(3): 604−612Ding Jin-Liang, Chen Jia-Xin, Ma Xin-Ran. Multi-objective optimization of light oil production in atmospheric distillation column based on self-adaptive differential evolution. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(3): 604−612 [14] 阳春华, 孙备, 李勇刚, 黄科科, 桂卫华. 复杂生产流程协同优化与智能控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 528−539Yang Chun-Hua, Sun Bei, Li Yong-Gang, Huang Ke-Ke, Gui Wei-Hua. Cooperative optimization and intelligent control of complex production processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 528−539 [15] Huang W, Mohammad M. Development, exergoeconomic assessment and optimization of a novel municipal solid waste-incineration and solar thermal energy based integrated power plant: An effort to improve the performance of the power plant. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023, 172: 562−578 doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2023.02.016 [16] Costa M, Indrizzi V, Massarotti N, Mauro A. Modeling and optimization of an incinerator plant for the reduction of the environmental impact. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow, 2015, 25(6): 1463−1487 [17] Pan M, Chen X, Li X. Multi-objective analysis and optimization of cascade supercritical CO2 cycle and organic Rankine cycle systems for waste-to-energy power plant. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 214: Article No. 118882 doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.118882 [18] Özahi E, Tozlu A, Abuşoğlu A. Thermoeconomic multi-objective optimization of an organic Rankine cycle (ORC) adapted to an existing solid waste power plant. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 168: 308−319 doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2018.04.103 [19] Mayanti B, Songok J, Helo P. Multi-objective optimization to improve energy, economic and, environmental life cycle assessment in waste-to-energy plant. Waste Management, 2021, 127: 147−157 doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2021.04.042 [20] Tang Z, Zhang Z. The multi-objective optimization of combustion system operations based on deep data-driven models. Energy, 2019, 182: 37−47 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.06.051 [21] Chai T, Zhang J, Yang T. Demand forecasting of the fused magnesia smelting process with system identification and deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(12): 8387−8396 doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3065930 [22] Anderson S R, Kadirkamanathan V, Chipperfield A, Sharifi V, Swithenbank J. Multi-objective optimization of operational variables in a waste incineration plant. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2005, 29(5): 1121−1130 [23] 崔莺莺, 蒙西, 乔俊飞. 城市固废焚烧过程风量智能优化设定方法. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(2): 318−326Cui Ying-Ying, Meng Xi, Qiao Jun-Fei. The intelligent optimization setting method of air flow for municipal solid wastes incineration process. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(2): 318−326 [24] Sun J, Meng X, Qiao J. Data-driven optimal control for municipal solid waste incineration process. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(12): 11444−11454 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3246467 [25] 孙剑, 蒙西, 乔俊飞. 城市固废焚烧过程烟气含氧量自适应预测控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(11): 2338−2349Sun Jian, Meng Xi, Qiao Jun-Fei. Adaptive predictive control of oxygen content in flue gas for municipal solid waste incineration process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(11): 2338−2349 [26] 白良成. 生活垃圾焚烧处理工程技术. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社. 2021Bai Liang-Cheng. Engineering Technology for Incineration Treatment of Municipal Solid Waste. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2021. [27] Meng X, Rozycki P, Qiao J, Wilamowski B. Nonlinear system modeling using RBF networks for industrial application. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 14(3): 931−940 [28] Qiao J, Zhou J, Meng X. A multitask learning model for the prediction of NOx emissions in municipal solid waste incineration processes. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 72: 1−14 [29] Zhou W, Li X, Yi J, He H. A novel UKF-RBF method based on adaptive noise factor for fault diagnosis in pumping unit. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 15(3): 1415−1424 [30] Yao F, Zhao J, Li X, Mao L, Qu K. RBF neural network based virtual synchronous generator control with improved frequency stability. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 17(6): 4014−4024 [31] Liu W, Wang Z, Yuan Y, Zeng N, Hone K, Liu X. A novel sigmoid-function-based adaptive weighted particle swarm optimizer. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 51(2): 1085−1093 [32] Smola A, Schölkopf B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Statistics and Computing, 2004, 14(3): 199−222 doi: 10.1023/B:STCO.0000035301.49549.88 [33] Sacks J, Welch W J, Mitchell T J, Wynn H P. Design and analysis of computer experiments. Statistical Seience, 1989, 4(4): 409−423 -





 下载:
下载: