A Two-stage Domain Generalization Learning Framework for Fault Diagnosis of Bearings
-
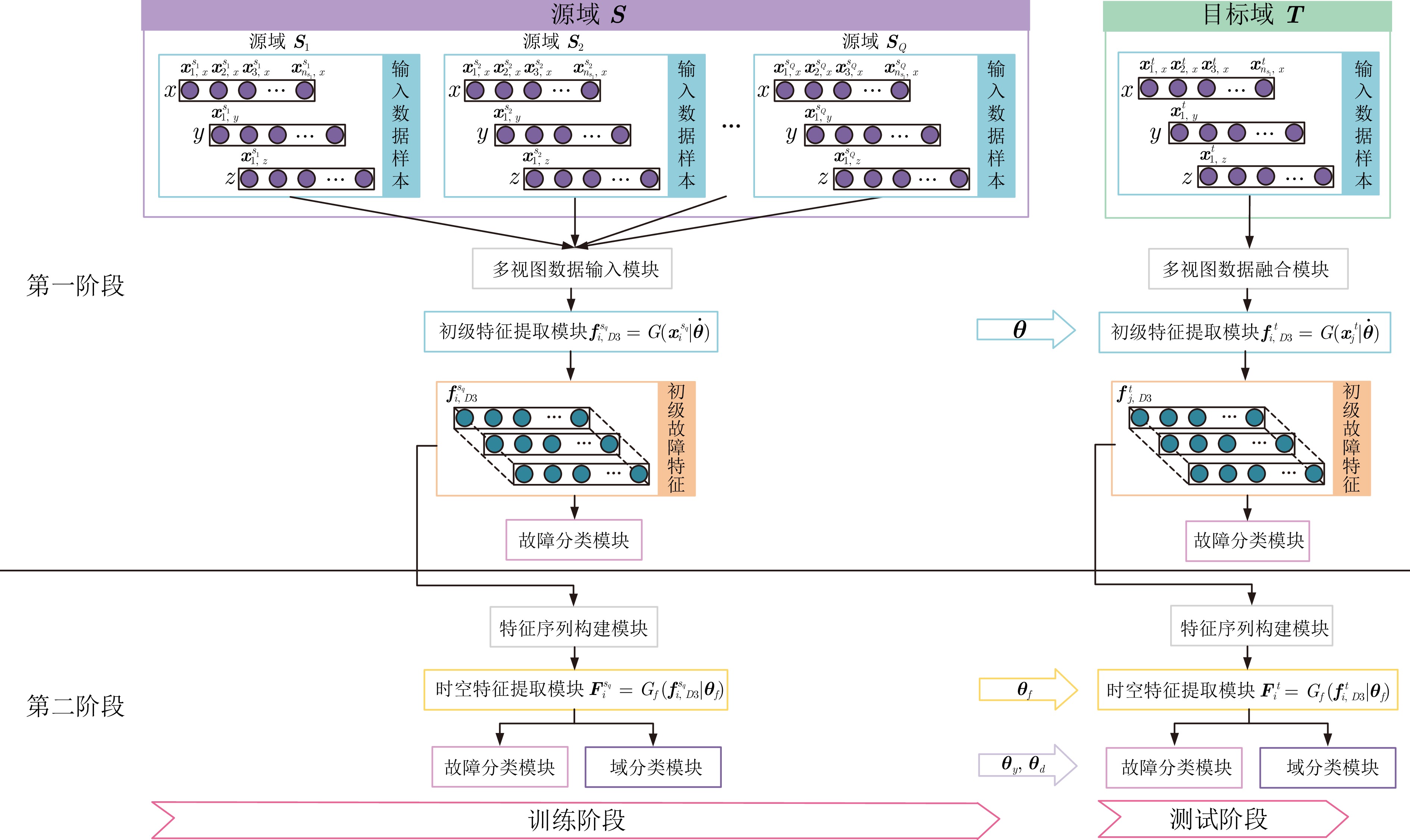
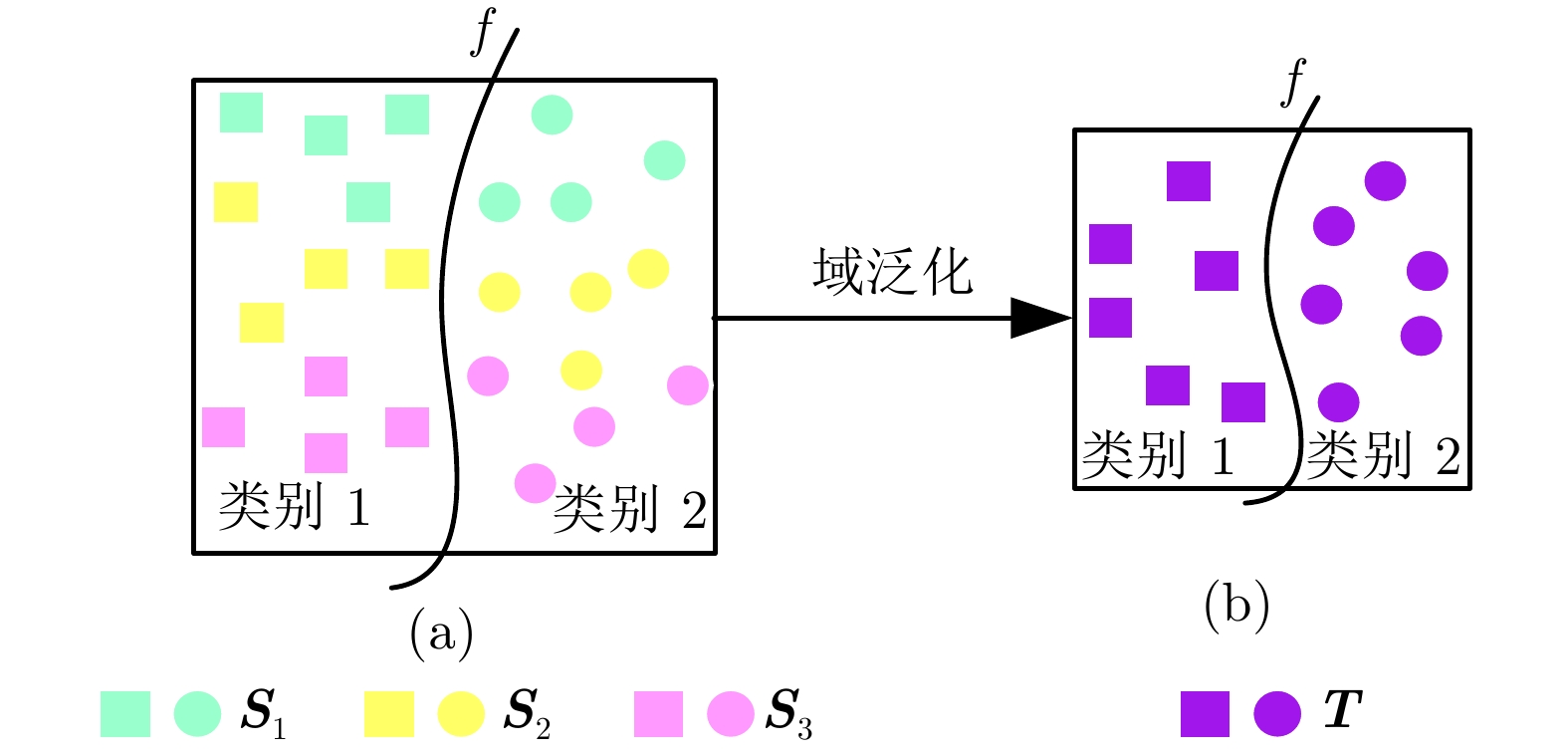
摘要: 设备在实际运行过程中工况复杂多变, 导致振动信号分布存在较大差异. 现有的多数方法通过添加度量指标来约束特征提取过程, 提取源域和目标域的相似特征以解决从单一源域到目标域的诊断问题. 然而, 实际运行过程往往包含多个源域数据, 且目标域信息在不同源域中存在较大差异, 难以有效学习不同域之间的域不变特征. 针对上述问题, 提出了一种基于两阶段域泛化学习框架的轴承故障诊断方法. 在第一阶段, 利用大尺寸卷积特征提取模型对多视图振动信号进行预训练, 提取多个源域数据之间的初级故障特征. 在第二阶段, 将初级故障特征输入动静双态融合的时空图卷积模型中, 捕捉随时间变化的动态特征和全局时空特征. 通过两阶段的学习, 将多个源域的数据映射到一个共有特征空间, 提取判别性和泛化性特征. 实验结果表明, 该方法在多源域轴承故障诊断任务中具有较高的诊断精度和较强的泛化能力.Abstract: During the actual operation of the equipment, the working conditions are complex and changeable, resulting in large differences in vibration signal distribution. Many existing methods constrain the feature extraction process by incorporating measurement metrics, aiming to extract similar features from both the source and target domains to address diagnostic problems from a single source domain to a target domain. However, the actual operational process often involves data from multiple source domains, and the target domain information exhibits significant differences across these various source domains, making it difficult to extract the domain invariant feature. In response to the above problems, this paper proposes a two-stage domain generalization learning framework for fault diagnosis of bearings. In the first stage, the large-scale convolutional feature extraction model is used to pre-train multi-view vibration signals to extract primary fault features between multiple source domain data. In the second stage, the primary fault features are input into the spatial-temporal graph convolutional model for dynamic and static two-state fusion combining dynamic and static states to capture the dynamic features and global spatiotemporal features that change over time. Through two-stage learning, data from multiple source domains are mapped to a common feature space, and discriminative and generalization features are extracted. Experimental results show that this method has high diagnostic accuracy and strong generalization ability in multi-source domain bearing fault diagnosis tasks.
-
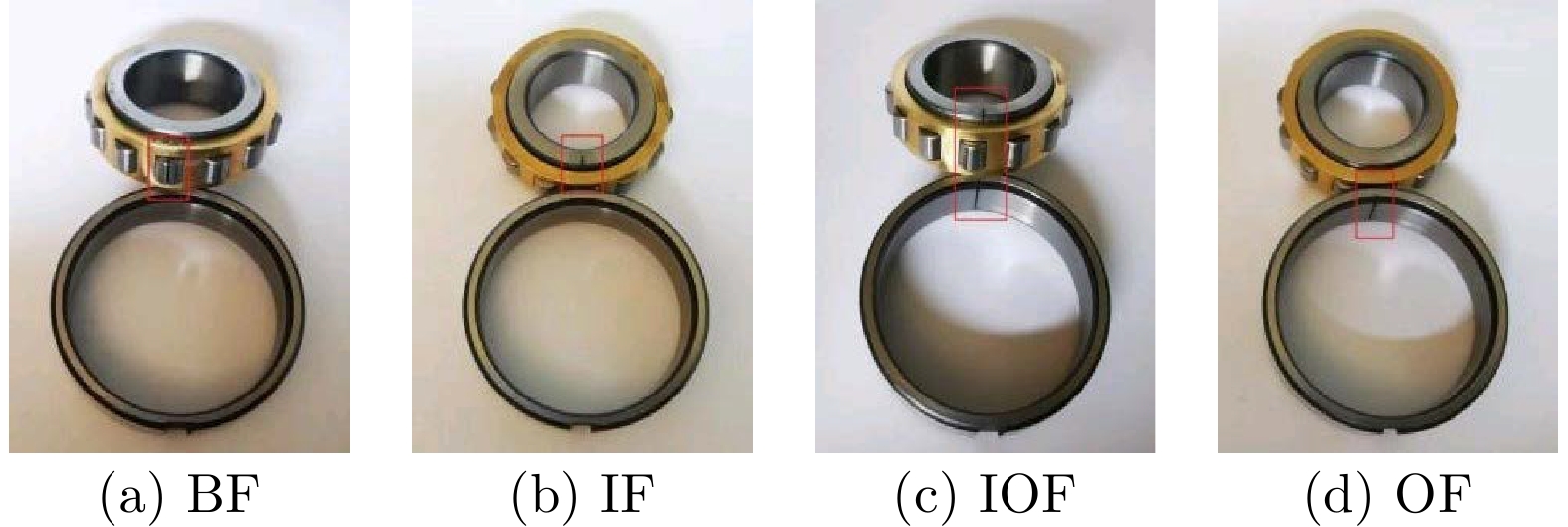
表 1 不同域泛化任务的轴承数据说明
Table 1 Bearing data description of different domain generalization tasks
域泛化任务 源域 目标域 转速(rpm) 总样本数 特征序列数 转速(rpm) 总样本数 特征序列数 任务1 B-C-D→A 600、900、 1200 30000 29988 300 10000 9996 任务2 A-C-D→B 300、900、 1200 30000 29988 600 10000 9996 任务3 A-B-D→C 300、600、 1200 30000 29988 900 10000 9996 任务4 A-B-C→D 300、600、900 30000 29988 1200 10000 9996 表 2 结构参数设计
Table 2 Structural parameter design
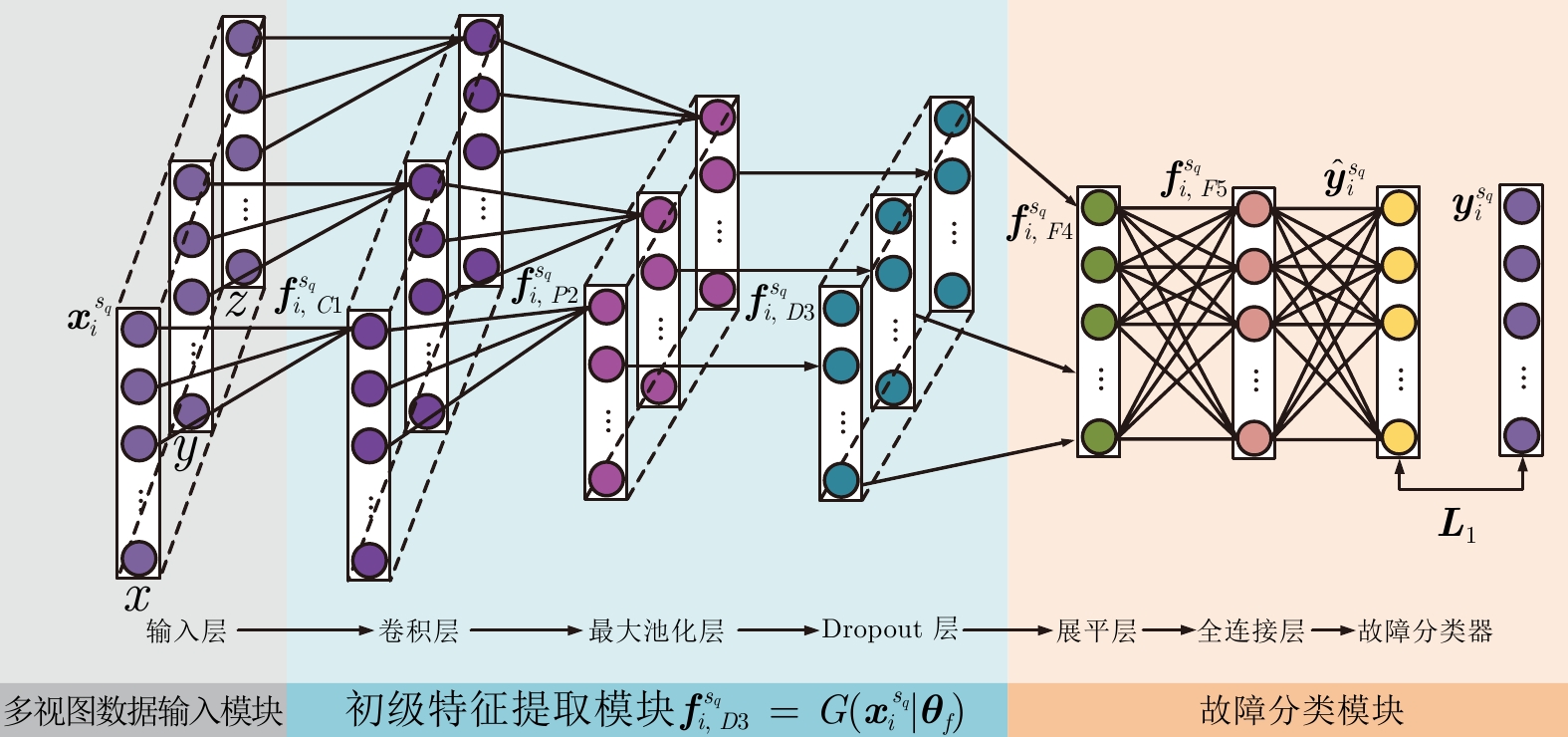
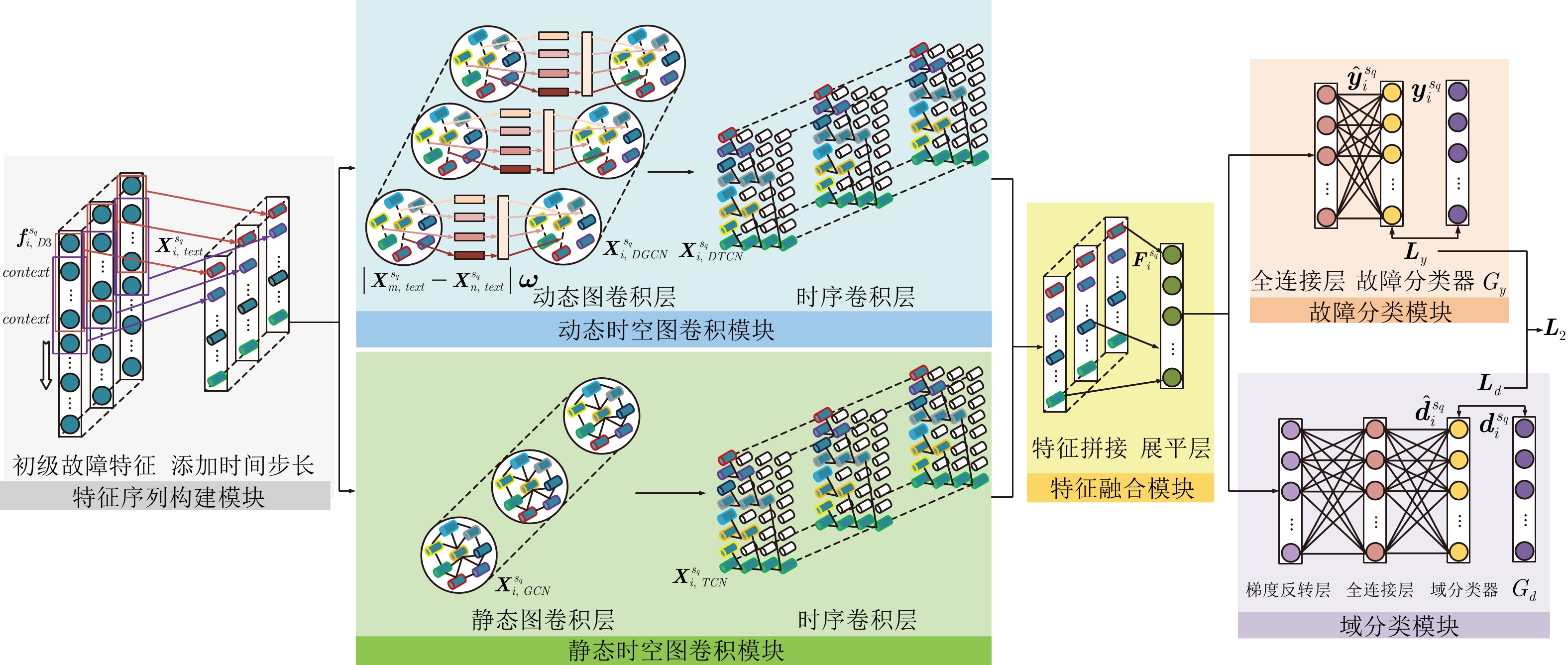
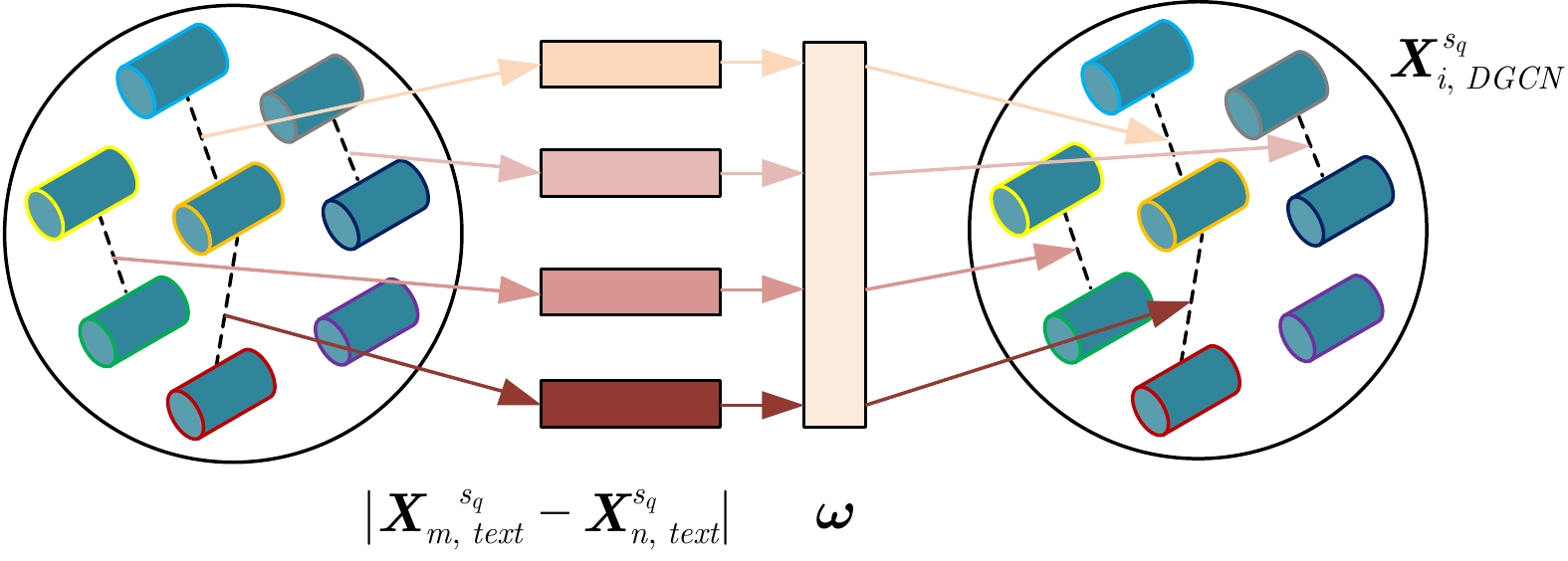
网络结构 输入尺寸 输出尺寸 参数设置 填充方式 第一阶段 输入层 64×3× 1024 64×3× 1024 ×1— — 卷积层(C1) 64×3× 1024 ×164×3×13×64 kernel_size=400, filter=64, stride=50 same 最大池化层(P2) 64×3×13×64 64×3×2×64 pool_size=5, strides=5 valid Dropout层(D3) 64×3×2×64 64×3×2×64 p=0.5 — 展平层(F4) 64×3×2×64 64×3×128 — — 全连接层(F5) 64×3×128 64×384 — — 故障分类器 64×384 64×5 — — 第二阶段 输入层 64×3×128 64×3×128 — — 添加时间步 64×3×128 64×5×3×128 — — 动态图卷积层 64×5×3×128 64×5×3×64 k=3, filter=64, $ \lambda =0.001 $ valid 时序卷积层 64×5×3×64 64×5×3×64 filter=64, stride=(1,1), kernel=(3,1) same 静态图卷积层 64×5×3×128 64×5×3×64 k=3, filter=64 valid 时序卷积层 64×5×3×64 64×5×3×64 filter=64, stride=(1,1), kernel=(3,1) same 全连接层 64×5×3×64, 64×5×3×64 64×5×3×128 — — 展平层 64×5×3×128 64× 1920 — — 故障分类 全连接层 64× 1920 64×64 — — 故障分类器 64×64 64×5 — — 域分类 梯度反转层 64× 1920 64× 1920 $ \beta =0.01 $ — 全连接层 64× 1920 64×64 — — 域分类器 64×64 64×4 — — 表 3 五种健康状态分类结果统计表
Table 3 Table of classification results of five health states
健康状态 准确率(%) F1得分(%) 精确率(%) 召回率(%) 滚子故障 97.05±2.32 97.39±2.02 95.95±2.87 99.96±0.01 内圈故障 99.06±0.10 99.06±0.10 99.80±0.01 98.33±0.57 内外圈故障 92.27±1.05 97.61±1.31 99.98±0.01 96.34±0.07 外圈故障 99.15±0.04 99.15±0.01 98.44±0.18 99.20±0.50 正常状态 99.98±0.01 99.98±0.01 99.97±0.01 99.99±0.01 平均值 98.77±0.36 98.77±0.38 98.83±0.53 98.77±0.32 表 4 不同的多视图数据组合对性能的影响统计表
Table 4 Table of the impact of different multi-view data combinations on performance
不同视图组合 准确率(%) F1得分(%) 精确率(%) 召回率(%) $ xz $ 90.75±0.50 90.24±0.62 92.06±0.76 90.42±0.61 $ xy $ 92.31±0.71 92.67±0.62 93.18±0.45 92.31±0.71 $ yz $ 94.78±2.23 94.57±2.55 95.70±1.33 94.76±2.54 $ xyz $ 98.77±0.36 98.77±0.38 98.83±0.53 98.77±0.32 表 5 动静双态融合的时空图卷积模型不同组成结构对性能的影响统计表
Table 5 Table of the impact of different structures of the spatial-temporal graph convolutional model for dynamic and static two-state fusion on performance
动态时空图卷积模块 静态时空图卷积模块 准确率(%) F1 得分(%) 精确率(%) 召回率(%) 动态图卷积层 时序卷积层 静态图卷积层 时序卷积层 √ × √ × 90.36±0.63 90.32±0.52 90.87±2.40 90.36±0.37 × √ × √ 92.58±4.35 92.66±4.13 93.57±2.01 92.25±4.35 × × √ √ 90.69±3.12 90.75±3.24 92.35±1.05 90.70±4.49 √ √ × × 90.35±0.51 90.34±0.51 91.91±0.56 90.35±0.59 √ √ √ √ 98.77±0.36 98.77±0.38 98.83±0.53 98.77±0.32 表 6 不同特征可视化效果的量化指标统计表
Table 6 Table of quantitative indicators of different feature visualization effects
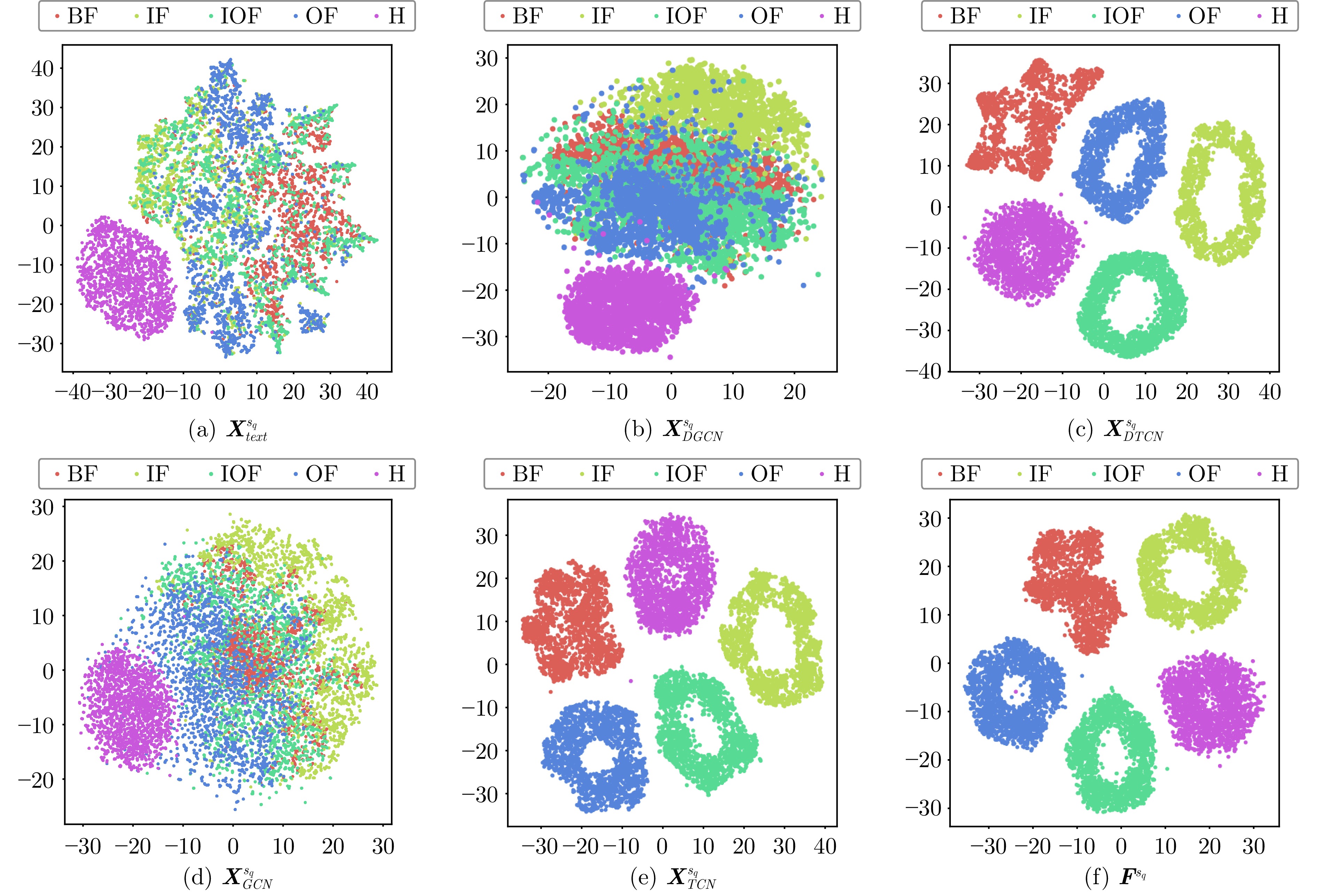
量化指标 $ {\boldsymbol{X}}_{text}^{{{s}_{q}}} $ $ {\boldsymbol{X}}_{DGCN}^{{{s}_{q}}} $ $ {\boldsymbol{X}}_{DTCN}^{{{s}_{q}}} $ $ {\boldsymbol{X}}_{GCN}^{{{s}_{q}}} $ $ {\boldsymbol{X}}_{TCN}^{{{s}_{q}}} $ $ {{{\boldsymbol{F}}}^{{{s}_{q}}}} $ 轮廓系数 0.0828 0.1134 0.4807 0.1920 0.5021 0.5431 CH指数 1194.49 2336.10 13642.92 5208.58 14917.97 17765.84 表 7 不同方法的诊断结果统计表
Table 7 Table of statistics of diagnostic results of different methods
评估指标 域泛化任务B-C-D→A CNN WDCNN GCN TCN DAGCN CVC-Net 所提方法 准确率(%) 60.24±9.14 63.20±6.51 59.77±8.56 62.64±5.38 85.01±6.75 86.31±5.25 95.14±1.75 F1得分(%) 64.01±6.86 65.70±5.30 54.85±5.17 57.37±7.54 83.30±8.21 85.11±4.50 95.81±0.86 精确率(%) 63.61±8.43 61.86±6.46 57.38±6.52 61.15±8.64 90.98±3.83 80.04±3.59 95.95±1.98 召回率(%) 61.13±7.25 63.19±5.43 59.07±7.89 62.32±7.95 85.37±9.47 86.67±5.58 95.03±0.85 表 8 不同方法特征可视化效果的量化指标统计表
Table 8 Table of quantitative indicators of feature visualization effects of different methods
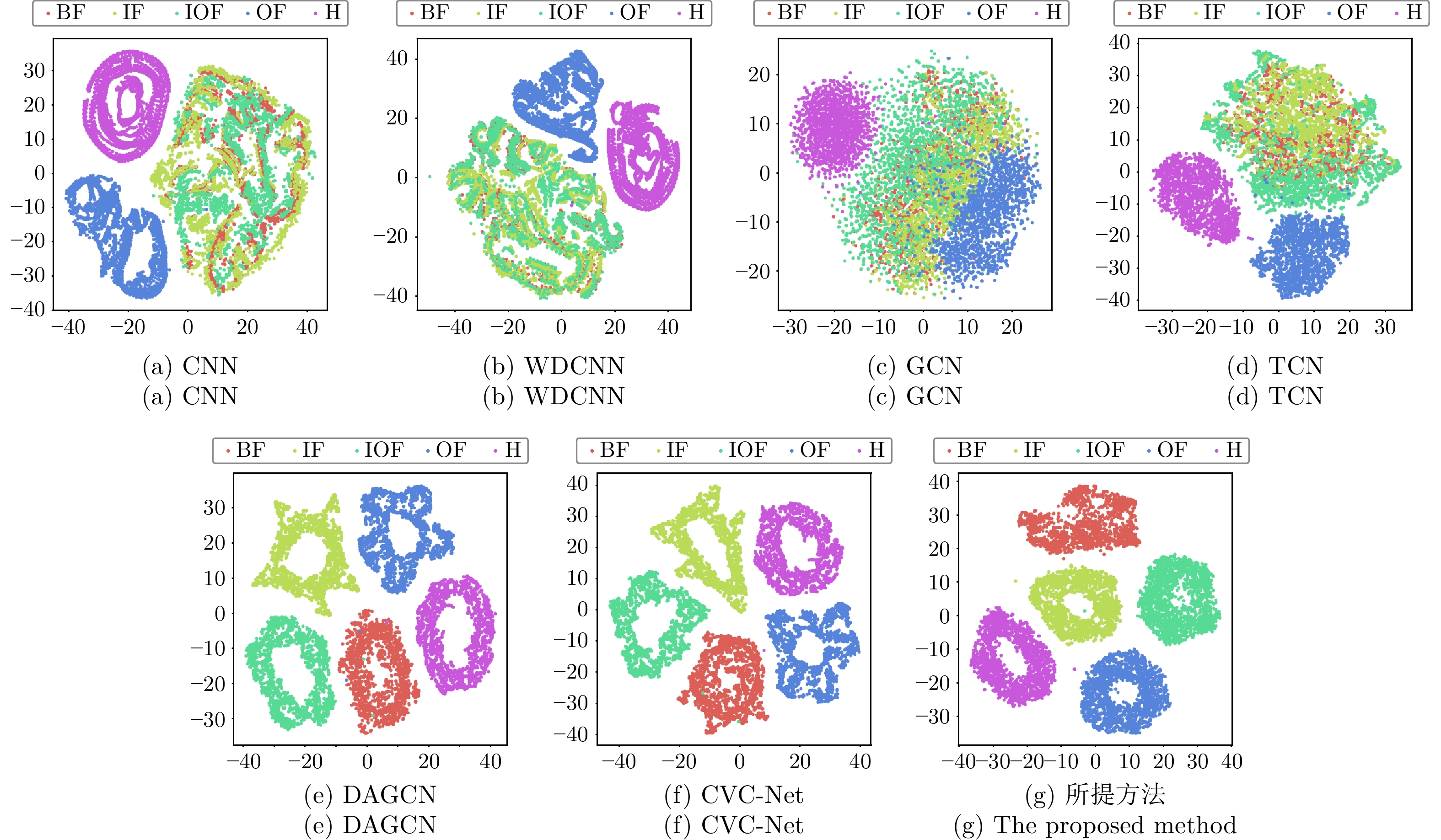
量化指标 CNN WDCNN GCN TCN DAGCN CVC-Net 所提方法 轮廓系数 0.2164 0.1926 0.1843 0.2390 0.4440 0.4602 0.5082 CH指数 3920.27 3484.86 3483.51 4795.91 12051.26 11544.79 14780.77 -
[1] 刘建昌, 权贺, 于霞, 何侃, 李镇华. 基于参数优化VMD和样本熵的滚动轴承故障诊断. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(3): 808−819Liu Jian-Chang, Quan He, Yu Xia, He Kan, Li Zhen-Hua. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on parameter optimization vmd and sample entropy. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 808−819 [2] Xin G, Zhong Q T, Jin Y Q, Li Z, Chen Y F, Li Y F, et al. Autonomous bearing fault diagnosis based on fault-induced envelope spectrum and moving peaks-over-threshold approach. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 1−12 [3] Ma Z P, Fu L, Dun G, Tan D P, Xu F, Zhang L B. A robust domain distribution alignment discriminative network driven by physical samples for rotor-bearing fault diagnosis. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2024, 300(27): 1−15 [4] Pu H X, Zhang K, An Y Y. Restricted sparse networks for rolling bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(11): 11139−11149 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3243929 [5] 范苍宁, 刘鹏, 肖婷, 赵巍, 唐降龙. 深度域适应综述: 一般情况与复杂情况. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(25): 515−548Fan Cang-Ning, Liu Peng, Xiao Ting, Zhao Wei, Tang Jiang-Long. A review of deep domain adaptation: General situation and complex situation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(25): 515−548 [6] Wang J D, Lan C L, Liu C, Ouyang Y D, Qin T, Lu W, et al. Generalizing to unseen domains: A survey on domain generalization. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2022, 35(8): 8052−8072 [7] Huo C R, Xu W Y, Jiang Q S, Shen Y H, Zhu Q X, Zhang Q K. An unsupervised transfer learning approach for rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on dual pseudo-label screening. Structural Health Monitoring, 2024, 23(4): 2288−2309 doi: 10.1177/14759217231206579 [8] An Y Y, Zhang K, Chai Y, Liu Q, Huang X H. Bearing fault diagnosis under variable working conditions base on contrastive domain adaptation method. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 1−11 [9] An Y Y, Zhang K, Chai Y, Zhu Z Q, Liu Q. Gaussian mixture variational based transformer domain adaptation fault diagnosis method and its application in bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 20(1): 615−625 [10] Ding Y F, Jia M P, Zhuang J C, Cao Y D, Zhao X L, Lee C G. Deep imbalanced domain adaptation for transfer learning fault diagnosis of bearings under multiple working conditions. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2023, 230: Article No. 108890 [11] 叶楠, 常佩泽, 张露予, 王嘉. 基于改进后半监督深度信念网络的多工况轴承故障诊断研究. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(15): 80−90 doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.15.080Ye Nan, Chang Pei-Ze, Zhang Lu-Yu, Wang Jia. Research on multi-condition bearing fault diagnosis based on improved semi-supervised deep belief network. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(15): 80−90 doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.15.080 [12] 黄星华, 吴天舒, 杨龙玉, 胡友强, 柴毅. 一种面向旋转机械的基于Transformer特征提取的域自适应故障诊断. 仪器仪表学报, 2022, 43(11): 210−218Huang Xing-Hua, Wu Tian-Shu, Yang Long-Yu, Hu You-Qiang, Chai Yi. Domain adaptive fault diagnosis based on transformer feature extraction for rotating machinery. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2022, 43(11): 210−218 [13] 陈仁祥, 唐林林, 胡小林, 胡友强, 柴毅. 不同转速下基于深度注意力迁移学习的滚动轴承故障诊断方法. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(12): 95−101, 195Chen Ren-Xiang, Tang Lin-Lin, Hu Xiao-Lin, Hu You-Qiang, Chai Yi. A rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on deep attention transfer learning at different rotations. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(12): 95−101, 195 [14] Chen Z Y, Liao Y X, Li J P, Huang R Y, Xu L, Jin G, et al. A multi-source weighted deep transfer network for open-set fault diagnosis of rotary machinery. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 53(3): 1982−1993 [15] 吕鹏飞, 闫云聚, 荔越. 基于马氏距离的改进核Fisher化工故障诊断研究. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(11): 2379−2391Lv Peng-Fei, Yan Yun-Ju, Li Yue. Research on fault diagnosis of improved kernel Fisher based on Mahalanobis distance in the field of chemical industry. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(11): 2379−2391 [16] Li X Y, Zhang Z, Gao L, Wen L. A new semi-supervised fault diagnosis method via deep coral and transfer component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2021, 6(3): 690−699 [17] Li X Q, Jiang H K, Xie M, Wang T Q, Wang R X, Wu Z H. A reinforcement ensemble deep transfer learning network for rolling bearing fault diagnosis with multi-source domains. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2022, 51: Article No. 101480 doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2021.101480 [18] Yang B, Xu S C, Lei Y G, Lee C G, Stewart E, Roberts C. Multi-source transfer learning network to complement knowledge for intelligent diagnosis of machines with unseen faults. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 162: Article No. 108095 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2021.108095 [19] Zhou K Y, Liu Z W, Qiao Y, Xiang T, Loy C C. Domain generalization: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 45 (4): 4396−4415. [20] Bhatti U A, Tang H, Wu G L, Marjan S, Hussain A. Deep learning with graph convolutional networks: An overview and latest applications in computational intelligence. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2023, 2023(1): Article No. 8342104 [21] Liu X L, Hou F, Qin H, Hao A M. Multi-view multi-scale CNNs for lung nodule type classification from CT images. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 77: 262−275 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.12.022 [22] Jia Z Y, Lin Y F, Wang J, Ning X J, He Y L, Zhou R H, et al. Multi-view spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks with domain generalization for sleep stage classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2021, 29: 1977−1986 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3110665 [23] Huang R Y, Li J P, Liao Y X, Chen J B, Wang Z, Li W H. Deep adversarial capsule network for compound fault diagnosis of machinery toward multidomain generalization task. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 1−11 [24] Zhao D F, Liu S L, Miao Z H, Zhang H L, Dou W. Subdomain adaptation joint attention network enabled two-stage strategy towards few-shot fault diagnosis of LRE turbopump. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2024, 60: Article No. 102366 doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2024.102366 [25] Luo F, Poslad S, Budanese E. Temporal convolutional networks for multiperson activity recognition using a 2-D LIDAR. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(8): 7432−7442 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2984544 [26] Guo Q G, Li J, Zhou F D, Li G L, Lin J L. An open-set fault diagnosis framework for mmcs based on optimized temporal convolutional network. Applied Soft Computing, 2023, 133: Article No. 109959 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109959 [27] Yang Y J, Zhang T X, Li G Y, Kim T, Wang G H. An unsupervised domain adaptation model based on dual-module adversarial training. Neurocomputing, 2022, 475: 102−111 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.12.060 [28] Bagirov A M, Aliguliyev R M, Sultanova N. Finding compact and well-separated clusters: Clustering using silhouette coefficients. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 135: Article No. 109144 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109144 [29] Gonzalez K, Misra S. Unsupervised learning monitors the carbon-dioxide plume in the subsurface carbon storage reservoir. Expert Systems With Applications, 2022, 201: Article No. 117216 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117216 [30] Gao D W, Huang K, Zhu Y S, Zhu L P, Yan K, Ren Z J, et al. Semi-supervised small sample fault diagnosis under a wide range of speed variation conditions based on uncertainty analysis. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2024, 242: Article No. 109746 [31] Li T, Zhao Z, Sun C, Yan R, Chen X. Domain adversarial graph convolutional network for fault diagnosis under variable working conditions. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 1−10 [32] Li X, Wang Y, Yao J, Li M, Gao Z. Multi-sensor fusion fault diagnosis method of wind turbine bearing based on adaptive convergent viewable neural networks. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2024, 245: Article No. 109980 -




 下载:
下载: