-
摘要: 传统机器人经过长时间的研究和发展, 已经在生产和生活的多个领域得到了广泛的应用, 但在复杂多变的环境中依然缺乏与真实生物类似的灵活性、稳定性和适应能力. 类脑智能作为一种新型的机器智能, 使用计算建模的方法模拟生物神经系统的各类特性, 进而实现对各类信息的推理和决策, 近年来受到了学术界的广泛关注. 鉴于此, 综述了国内外面向机器人系统的类脑智能研究现状, 并对类脑智能方法在机器人感知、决策和控制三个研究方向的成果进行了整理、归纳和分析, 最后从软硬件层面分别指出了机器人类脑智能目前存在的主要问题和未来的发展方向.Abstract: After a long time of research and development, traditional robots have been widely used in many fields of production and life, but they still lack the flexibility, stability and adaptability similar to real organisms in complex and changing environments. As a new type of machine intelligence, brain-inspired intelligence uses computational modeling methods to simulate various characteristics of biological nervous systems and realize the reasoning and decision-making based on all kinds of information. In recent years, it has received extensive attention from the academic community. The main applications of brain-inspired intelligence methods in robot perception, decision-making and control problems are introduced. The related research results are analyzed and summarized. Finally, the main problems of software and hardware are pointed out and future development directions of robotic brain-inspired intelligence are proposed.
-
Key words:
- Robot /
- brain-inspired robot /
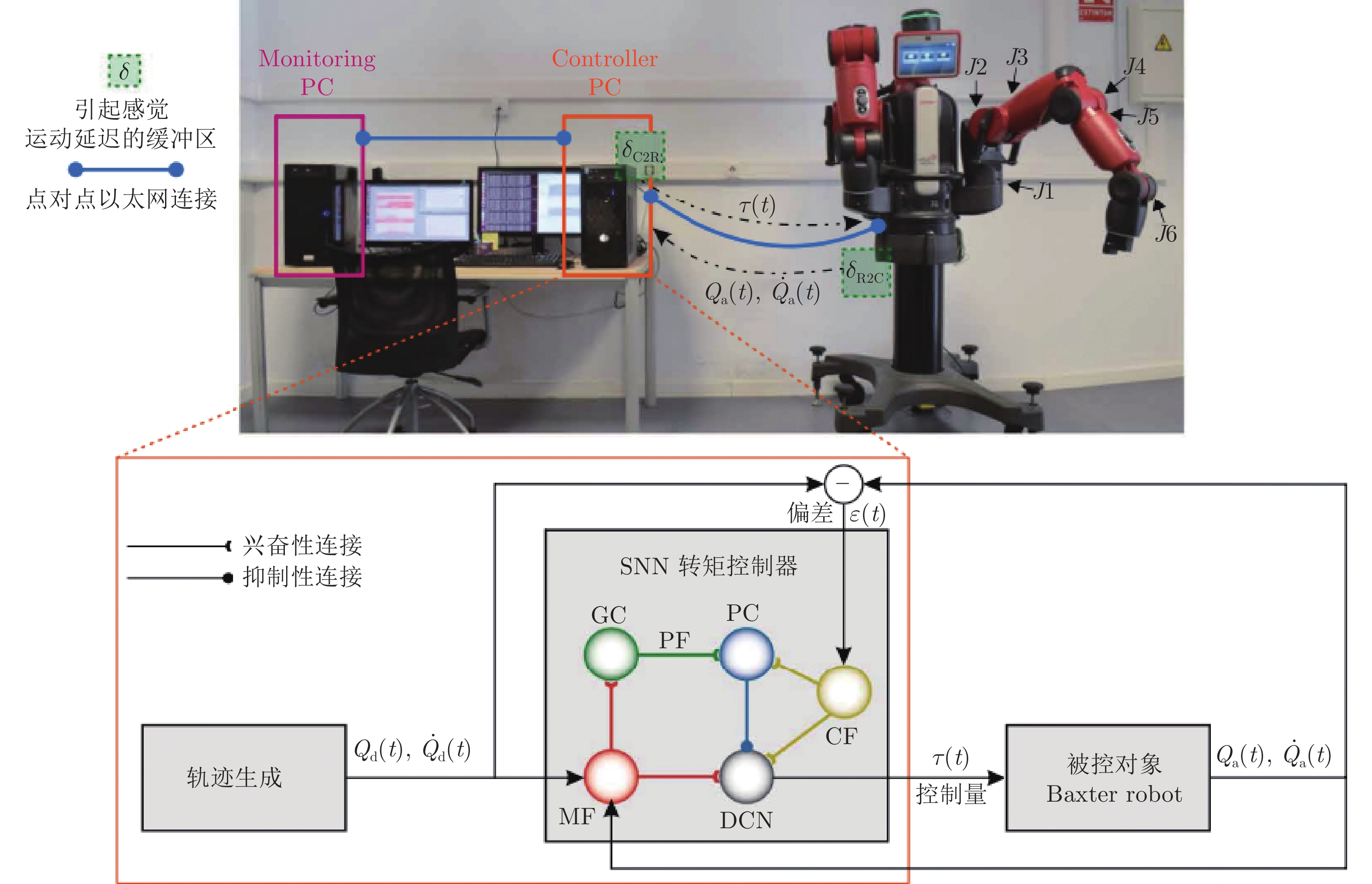
- brain-inspired intelligence /
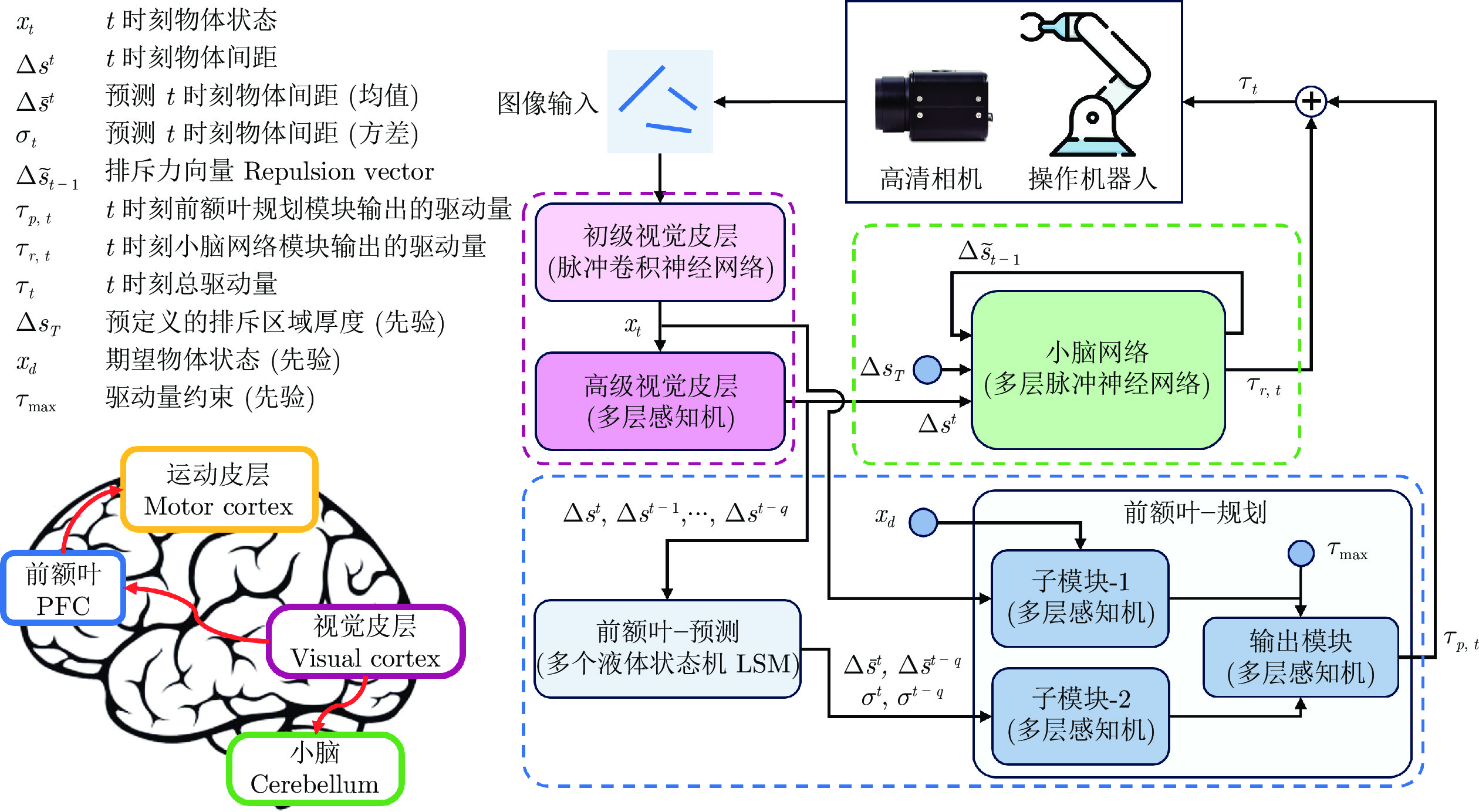
- spiking neural network (SNN)
-
表 1 机器人类脑感知方向文献总结
Table 1 Summary of the literature of robotic brain-inspired perception
模态 研究团队 传感器种类 网络结构 主要功能 视觉 Kreiser 等[41] 相机
(iCub机器人)仿脑内回路 识别物体并将注意力转移到感兴趣的物体上 Zhou等[20] 激光雷达 (LiDAR)
(文中未确切指明)层式 感知物体的三维轮廓 Ambrosano等[46] 相机
(iCub机器人)仿视网膜回路 机器人视线追踪 Li等[21] 相机 层式 手势识别和意图推断 Qiao等[25] 相机 层式 物体 (人脸)识别 Tang等[43] 距离传感器和RGB相机 多网络融合 SLAM Yoon等[42] 相机 仿脑内回路 SLAM Hussaini等[22] 相机
(文中未确切指明)层式 地点识别
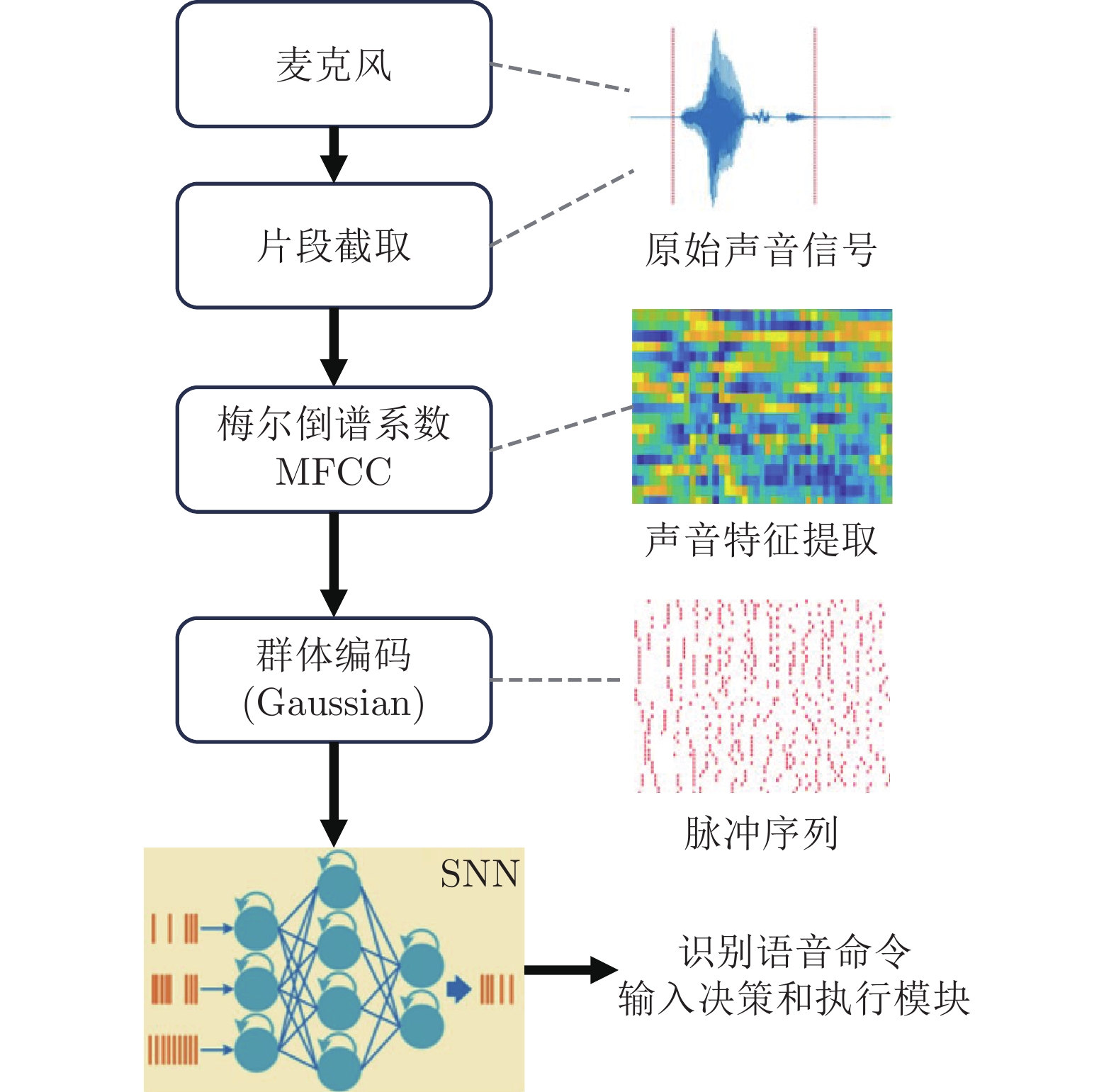
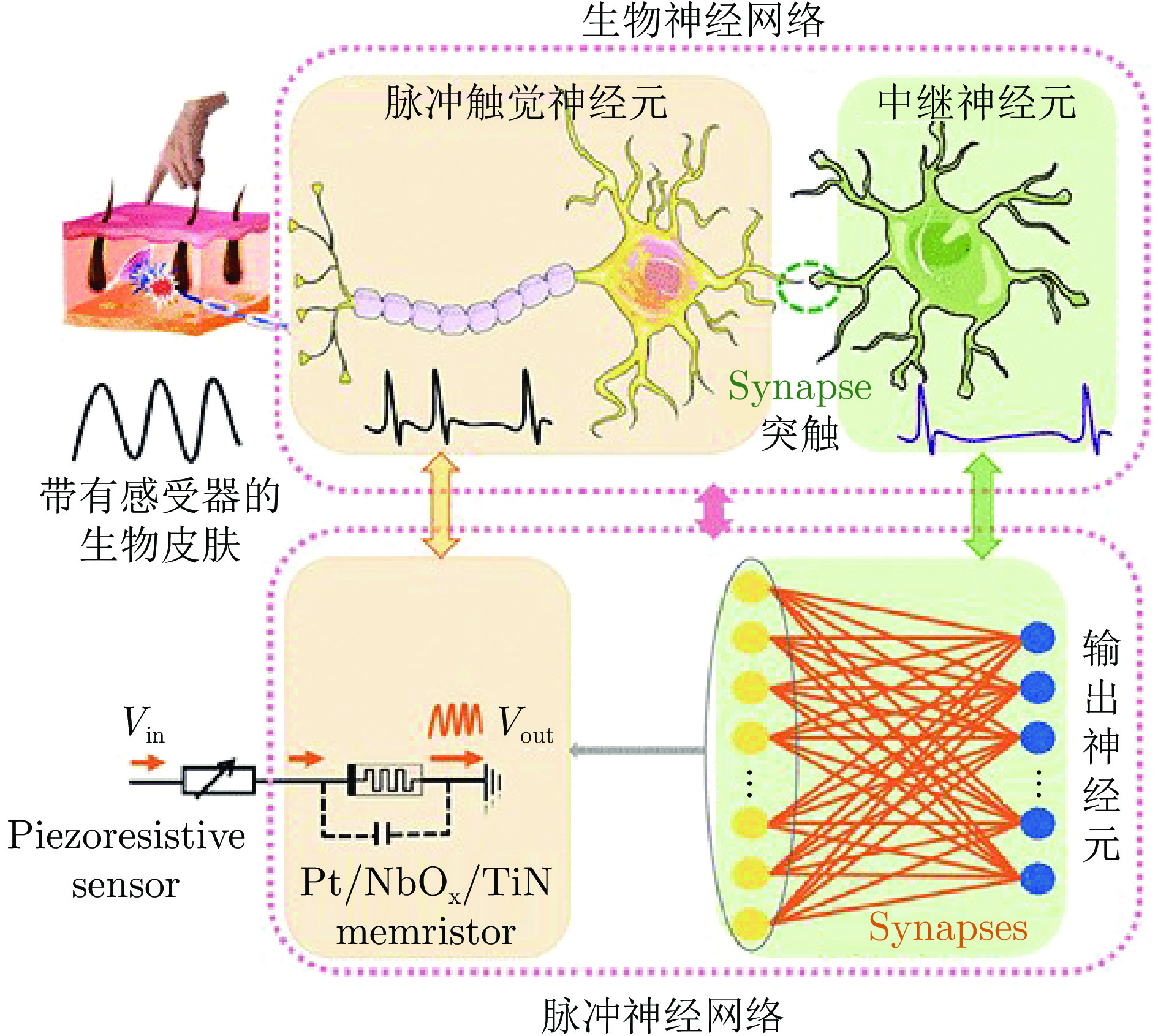
(Place recognition)听觉 Deng等[27, 47] 麦克风 层式 语音分类 Zou等[4] 麦克风 层式 语音识别 Gao等[29] 麦克风 阵列式 声源定位 Liu等[28] 麦克风 仿脑内回路 声源定位 触觉 Chou等[30] 触觉传感器
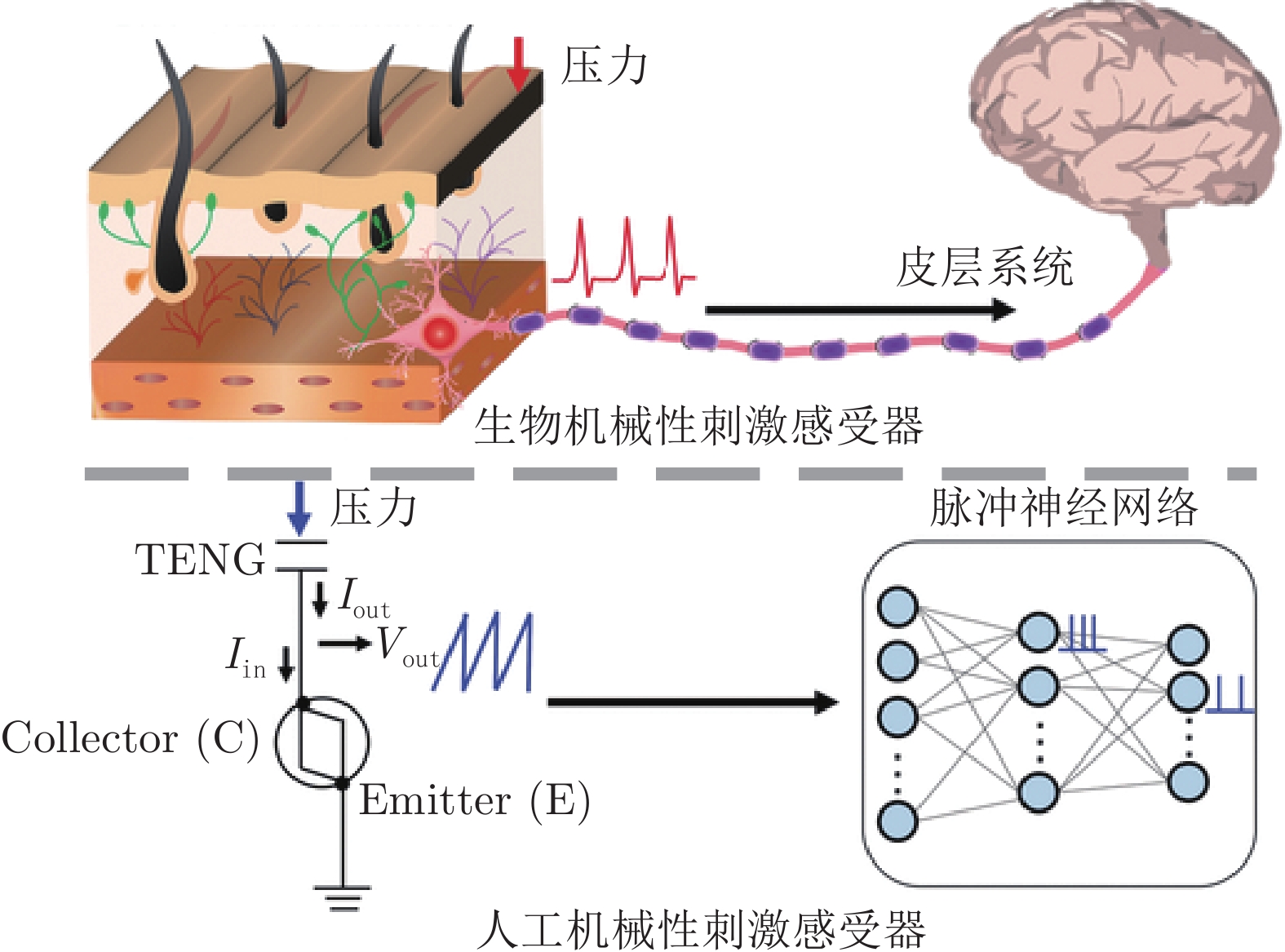
(文中未确切指明)仿脑内回路 感知人类的轻抚动作 Feng等[31] 多传感器融合 仿脑内回路 机器人的“痛觉”感知 张超凡等[32] GelStereo触觉传感器 层式 触觉滑动感知 Liu等[39] 基于晶体管的电子皮肤 仿生物触觉回路 触觉记忆与学习
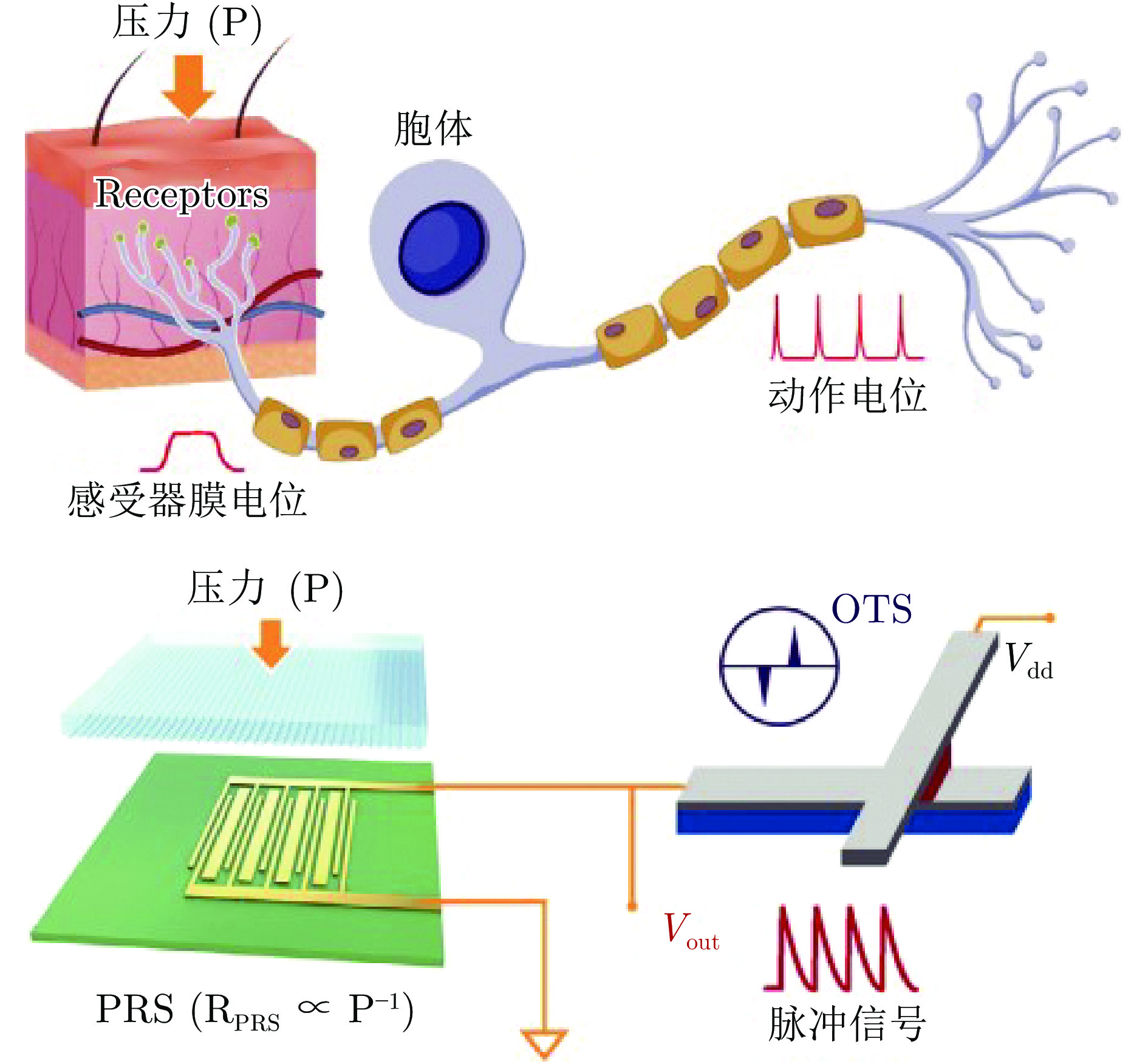
(以痛觉反射为例)Dabbous等[33] 压阻式传感器阵列 层式 触觉模态分类 Jiang等[34] 压电传感器 层式 表面粗糙度感知 Lee等[38] 基于压阻器和忆阻器的触觉神经元 库网络
(Reservoir)生物组织硬度感知 Han等[37] 基于摩擦纳米发电器的人工触觉感受器 层式 广范围 (3 kPa)触觉感知
(以呼吸状态辨识为例)Kang等[35] 事件驱动触觉传感器
NeuTouch[48]层式 触觉对象识别
触觉滑动检测Wen等[40] 基于压阻器和忆阻器的触觉神经元 层式 触觉感知和识别
(以MNIST分类为例)表 2 机器人类脑决策方向文献总结
Table 2 Summary of the literature of robotic brain-inspired decision
模型结构 研究团队 模型输入 模型输出 主要功能 循环结构 Rueckert等[56] 某一时刻Agent的状态
(例如空间位置)未来一段时间内的位置规划
(位置序列)有限和无限时间范围的任务规划问题 仿脑内回路 Zhao等[53] 视觉图像信息
(State)动作决策
(无人机的前进、后退、向左、向右)无人机飞行 (穿过窗户)过程决策任务 Daglarli等[55] 视觉信息
听觉信息机器人行为序列
决策奖励信号机器人的类人决策
(情感、注意力、意图等推理)左国玉等[50] 关于任务、记忆、 观测Affordance
和标签的词语该物品的Affordance (可以抓取)
或者该物品所需Affordance
的建议 (不可抓取)根据不同的任务选择合适的
物品和抓取位置Robertazzi等[52] 模拟视觉刺激
(方波信号)机器人动作
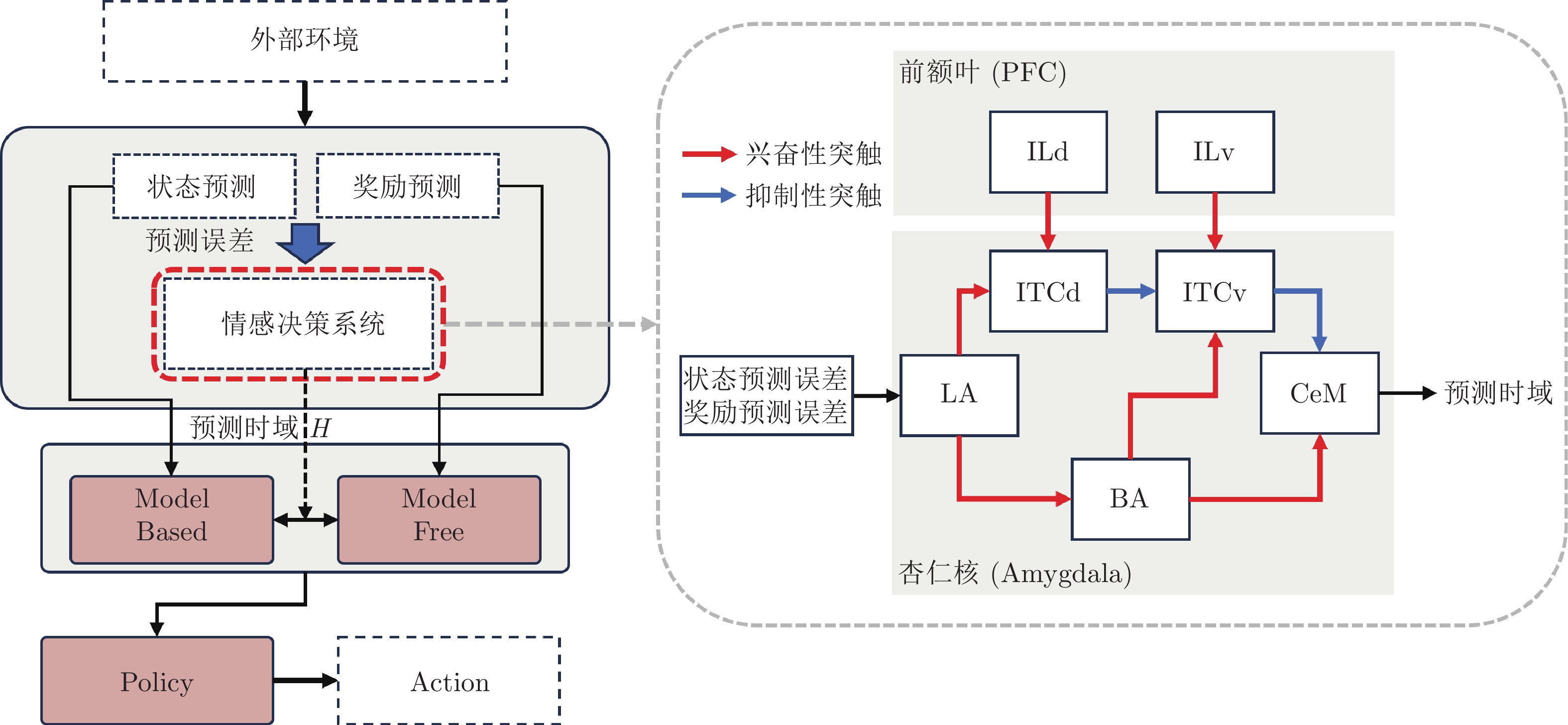
(向左、向右、保持不动)实现机器人在指定任务需求下的“动作抑制” Huang等[59] 状态预测误差
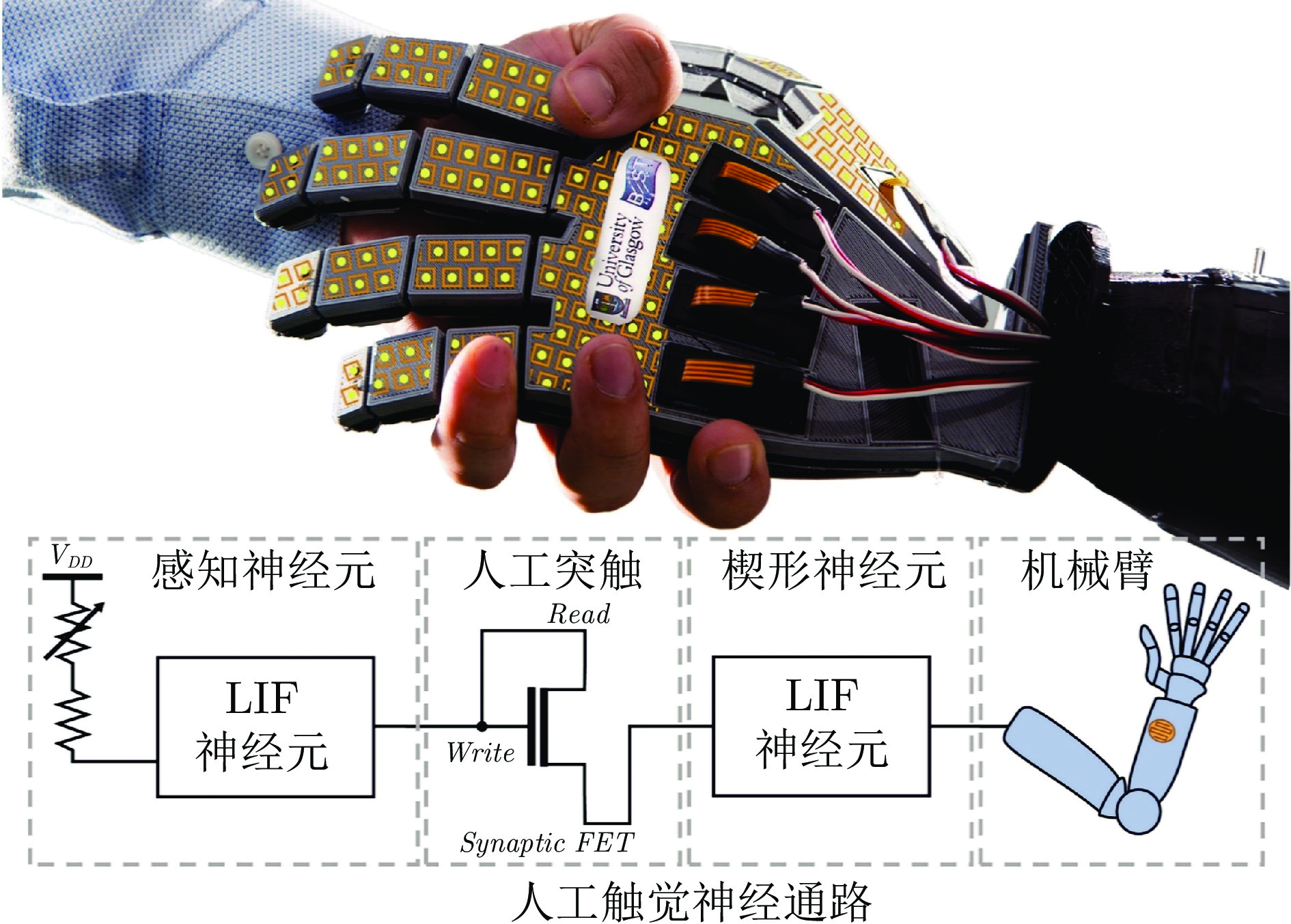
奖励预测误差预测时域调整量 在MB和MF控制之间
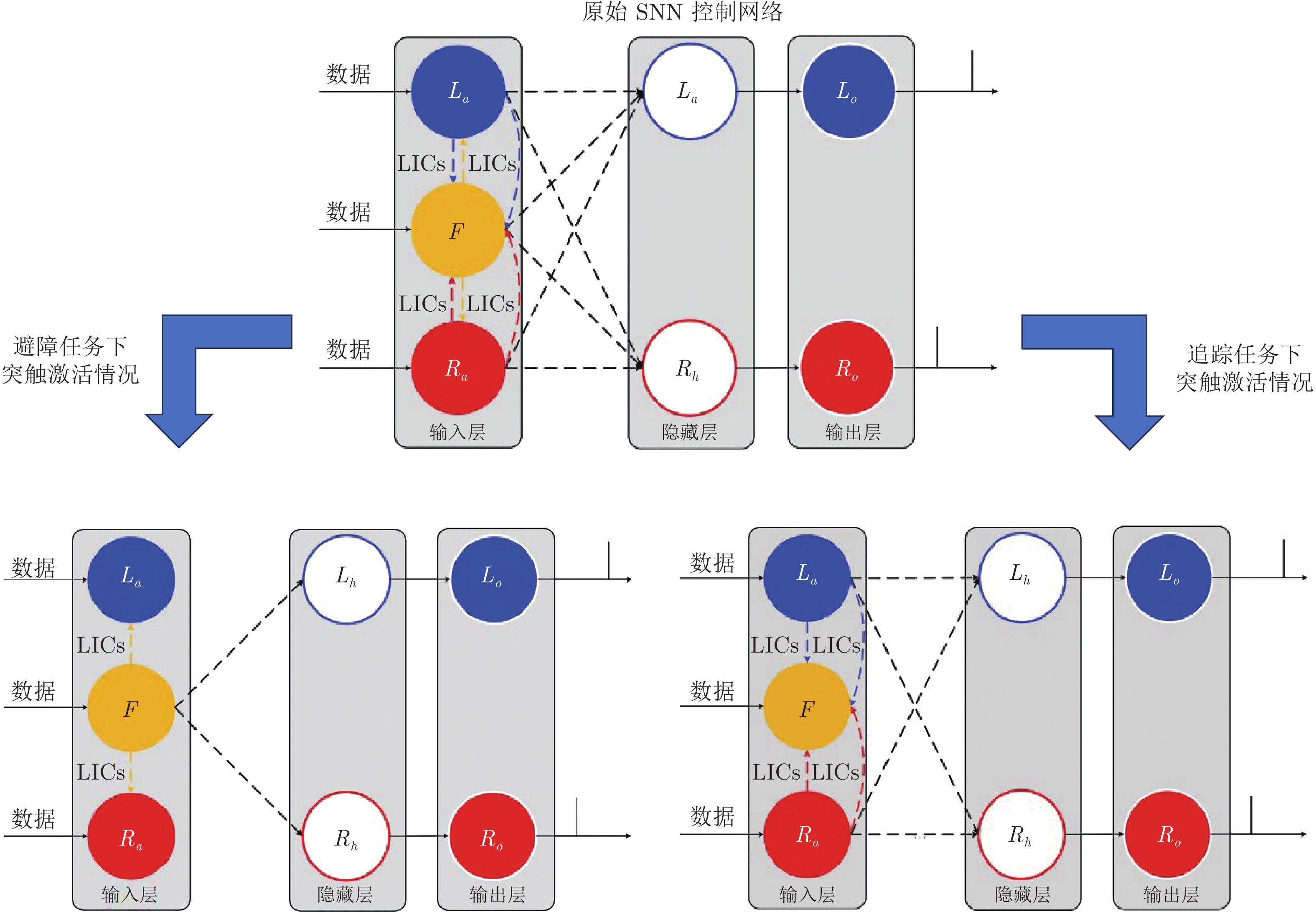
切换 (图9)层式 Liu等[58] 传感器感知到的数据 (转换为脉冲序列) 机器人控制量 (左右轮速度) 针对不同的任务需求激活不同的突触
实现控制策略的切换Skorheim等[57] 视觉感知信息
(7×7矩阵)运动决策信息
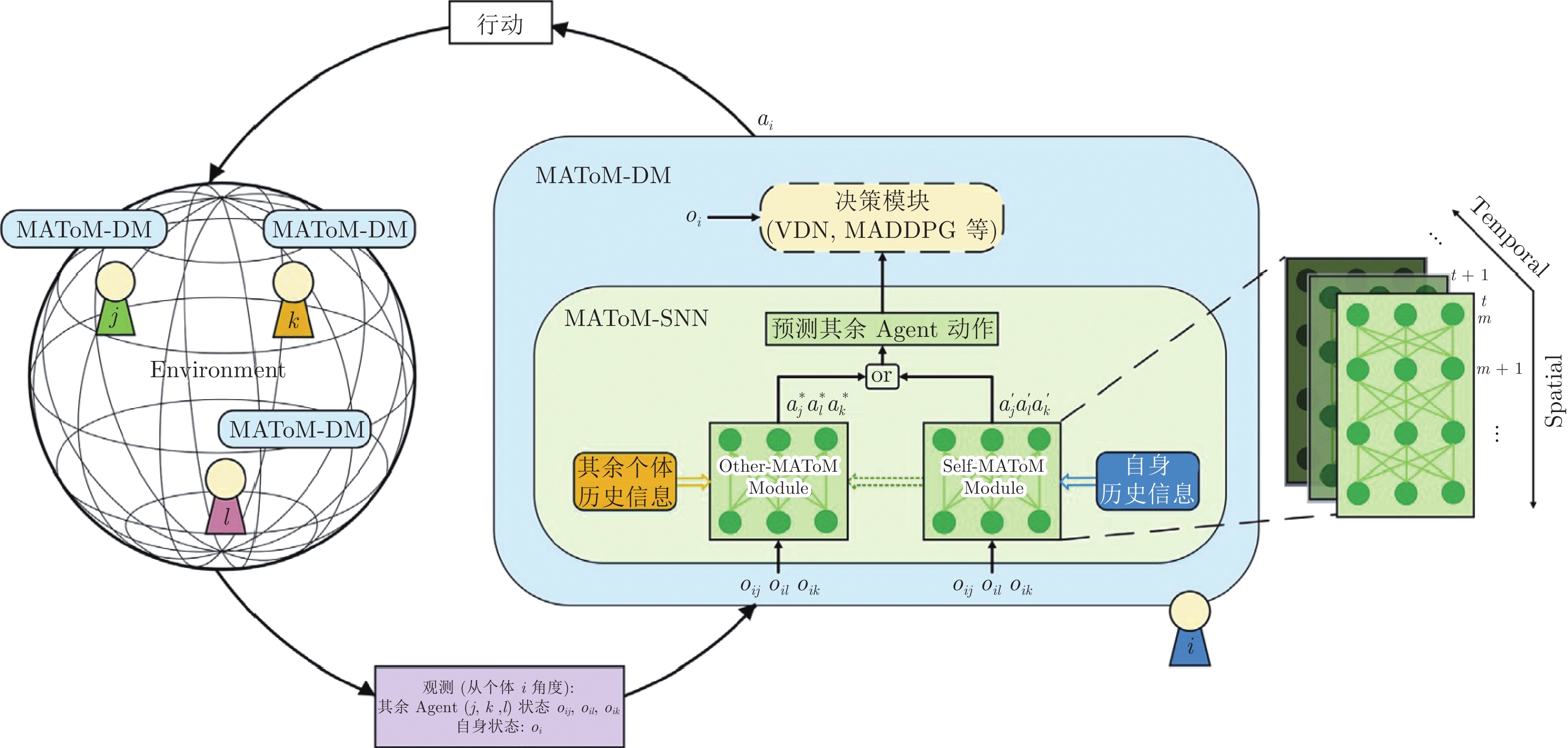
(3×3矩阵)实现虚拟环境中Agent的觅食决策 Zhao等[49] 环境上下文信息与对其他
个体状态和行为的观测对其他个体未来行为的预测 多智能体协同决策 表 3 机器人类脑控制方向文献总结
Table 3 Summary of the literature of robotic brain-inspired control
机器人类型 研究团队 网络输入 网络输出 主要功能 移动机器人 Lobov等[75]
(2-DoF)超声传感器信息
触觉传感器信息控制信号
(电机驱动量)移动控制
(避障)Wang等[68]
(2-DoF)声纳传感器信息 控制信号
(电机驱动量)移动控制
(避障、追踪、沿墙行走)Bing等[65]
(2-DoF)DVS图像信息 控制信号 (电机转速) 移动控制
(车道保持)Liu等[70]
(4-DoF)超声传感器 控制指令
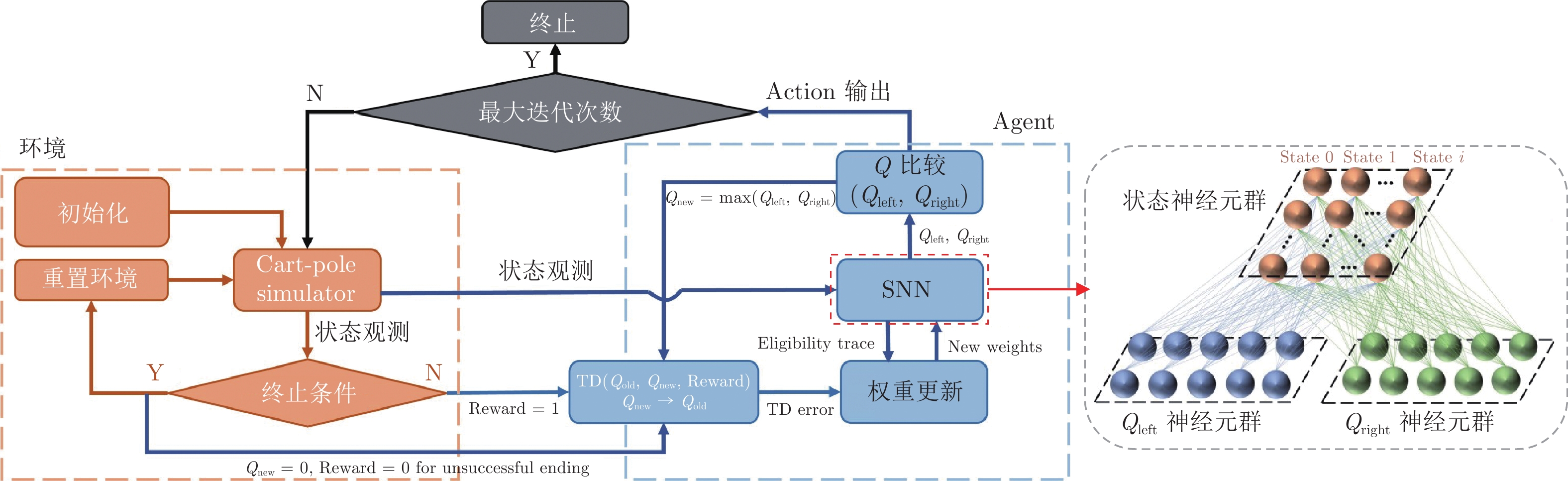
(左、右、前进)移动控制
(避障)Lu等[64]
(4-DoF)超声传感器感知到的距离信息 控制信号 (转换为
左右轮转速)移动控制
(避障)机械臂 Xing等[7]
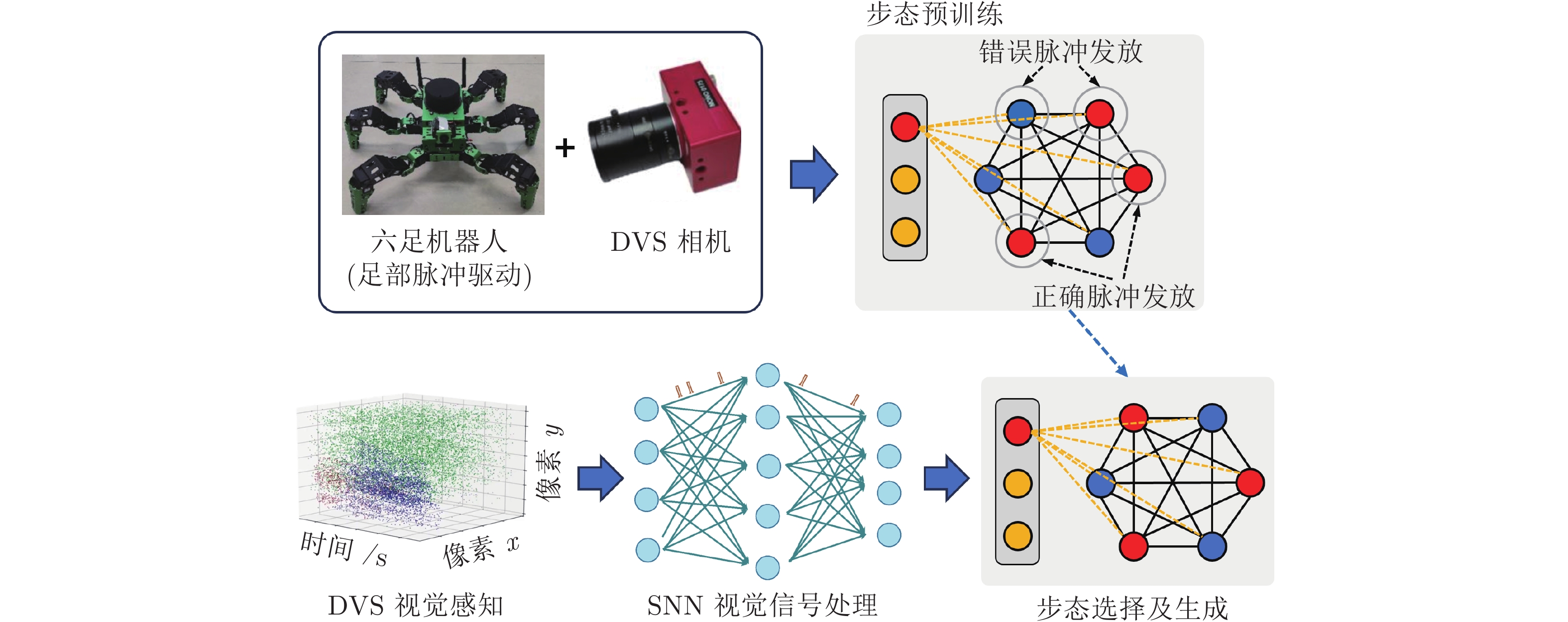
(未说明)其他网络输出的运动参数 关节驱动力矩 对小空间操作机器人
实现精确控制Chen等[86]
(1-DoF)期望角度与传感器信息 控制信号补偿量 提高机械臂的适应性和鲁棒性 IAbadia等[6]
(6-DoF)轨迹规划器生成的轨迹参数 机械臂控制力矩 通过预测运动指令实现对
指令延迟的鲁棒性Zahra等[87]
(6-DoF)目标运动状态与机械臂内部传感器信息 机械臂驱动量 提高机械臂在操作任务中的
精度和运动协调性Carrillo等[77]
(2-DoF)期望机械臂状态与目标信息 肩部与肘部驱动转动的调整量 机械臂运动控制 Zahra等[82]
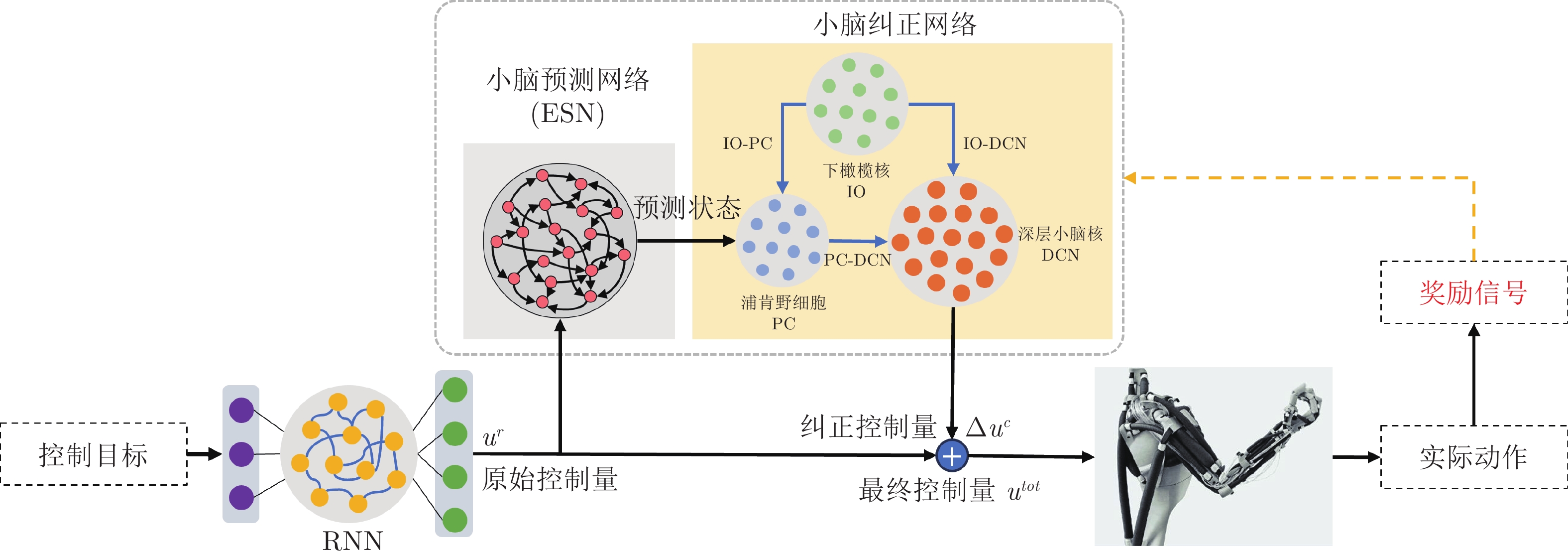
(6-DoF)关节角速度变化量 机器人状态预测 降低机械臂的运动误差和执行时间 Zhang等[80]
(2-DoF)原始控制信号 控制信号纠正量 提升机械臂的运动精度 仿生机器人 Naveros等[88]
(3-DoF)感知运动信号
(Sensory-motor signal)眼球转动量 根据机器人头部转动控制机器人
眼球转动 (前庭眼反射)Naya等[5]
(24-DoF)状态观测量
(State)行动
(Action)考虑能耗成本的步态学习 Lele等[62]
(6-DoF)DVS图像信息 步态选择 移动控制 (捕猎) Espinal等[89]
(12-DoF)− 步态生成 作为CPG生成指定的步态 Jiang等[60]
(未说明)NVS图像信息 (神经形态视觉传感器) 控制信号
(传递给CPG生成对应的步态)移动控制
(目标追踪)− Wilson等[83] 控制信号 控制对象的状态预测 实现一般线性系统的自适应控制 注: DoF (Degree of freedom)为对应文献中机器人的自由度. -
[1] 于振中, 李强, 樊启高. 智能仿生算法在移动机器人路径规划优化中的应用综述. 计算机应用研究, 2019, 36(11): 3210−3219Yu Zhen-Zhong, Li Qiang, Fan Qi-Gao. Survey on application of bioinspired intelligent algorithms in path planning optimization of mobile robots. Application Research of Computers, 2019, 36(11): 3210−3219 [2] 蔡灿, 刘璇, 张建华, 张明路. 工业机器人避碰算法研究与展望. 机械设计, 2018, 35(4): 1−7Cai Can, Liu Xuan, Zhang Jian-Hua, Zhang Ming-Lu. Research and prospect of collision avoidance algorithm for industrial robots. Journal of Machine Design, 2018, 35(4): 1−7 [3] 黄海丰, 刘培森, 李擎, 于欣波. 协作机器人智能控制与人机交互研究综述. 工程科学学报, 2022, 44(4): 780−791 doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1001-053X.2022.4.bjkjdxxb202204028Huang Hai-Feng, Liu Pei-Sen, Li Qing, Yu Xin-Bo. Review: Intelligent control and human-robot interaction for collaborative robots. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2022, 44(4): 780−791 doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1001-053X.2022.4.bjkjdxxb202204028 [4] Zou Z, Zhao R, Wu Y J, Yang Z Y, Tian L, Wu S, et al. A hybrid and scalable brain-inspired robotic platform. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): Article No. 18160 doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73366-9 [5] Naya K, Kutsuzawa K, Owaki D, Hayashibe M. Spiking neural network discovers energy-efficient hexapod motion in deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 150345−150354 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3126311 [6] Abadia I, Naveros F, Ros E, Carrillo R R, Luque N R. A cerebellar-based solution to the nondeterministic time delay problem in robotic control. Science Robotics, 2021, 6(58): Article No. eabf2756 doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.abf2756 [7] Xing D P, Li J L, Zhang T L, Xu B. A brain-inspired approach for collision-free movement planning in the small operational space. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(5): 2094−2105 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3111051 [8] Qiao H, Chen J H, Huang X. A survey of brain-inspired intelligent robots: Integration of vision, decision, motion control, and musculoskeletal systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(10): 11267−11280 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3071312 [9] Qiao H, Wu Y X, Zhong S L, Yin P J, Chen J H. Brain-inspired intelligent robotics: Theoretical analysis and systematic application. Machine Intelligence Research, 2023, 20(1): 1−18 doi: 10.1007/s11633-022-1390-8 [10] Qiao H, Zhong S L, Chen Z Y, Wang H Z. Improving performance of robots using human-inspired approaches: A survey. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(12): Article No. 221201 doi: 10.1007/s11432-022-3606-1 [11] Maass W. Networks of spiking neurons: The third generation of neural network models. Neural Networks, 1997, 10(9): 1659−1671 doi: 10.1016/S0893-6080(97)00011-7 [12] Roy K, Jaiswal A, Panda P. Towards spike-based machine intelligence with neuromorphic computing. Nature, 2019, 575(7784): 607−617 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1677-2 [13] Neftci E O. Data and power efficient intelligence with neuromorphic learning machines. iScience, 2018, 5: 52−68 doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.06.010 [14] Bing Z S, Meschede C, Röhrbein F, Huang K, Knoll A C. A survey of robotics control based on learning-inspired spiking neural networks. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2018, 12: Article No. 35 doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2018.00035 [15] 朱祥维, 沈丹, 肖凯, 马岳鑫, 廖祥, 古富强, 等. 类脑导航的机理、算法、实现与展望. 航空学报, 2023, 44(19): 1−33 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.28569Zhu Xiang-Wei, Shen Dan, Xiao Kai, Ma Yue-Xin, Liao Xiang, Gu Fu-Qiang, et al. Mechanisms, algorithms, implementation and perspectives of brain-inspired navigation. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(19): 1−33 doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.28569 [16] Zheng H L, Wu Y J, Deng L, Hu Y F, Li G Q. Going deeper with directly-trained larger spiking neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI, 2021. 11062−11070 [17] Wu Y J, Deng L, Li G Q, Zhu J, Xie Y, Shi L P. Direct training for spiking neural networks: Faster, larger, better. In: Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Honolulu, USA: AAAI, 2019. 1311−1318 [18] Wu Y J, Deng L, Li G Q, Zhu J, Shi L P. Spatio-temporal backpropagation for training high-performance spiking neural networks. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2018, 12: Article No. 331 doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00331 [19] Niu L Y, Wei Y, Liu W B, Long J Y, Xue T H. Research progress of spiking neural network in image classification: A review. Applied Intelligence, 2023, 53(16): 19466−19490 doi: 10.1007/s10489-023-04553-0 [20] Zhou S B, Chen Y, Li X H, Sanyal A. Deep SCNN-based real-time object detection for self-driving vehicles using LiDAR temporal data. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 76903−76912 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990416 [21] Li J X, Li D J, Jiang R H, Xiao R, Tang H J, Tan K C. Vision-action semantic associative learning based on spiking neural networks for cognitive robot. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2022, 17(4): 27−38 doi: 10.1109/MCI.2022.3199623 [22] Hussaini S, Milford M, Fischer T. Spiking neural networks for visual place recognition via weighted neuronal assignments. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 4094−4101 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3149030 [23] Cao Y Q, Chen Y, Khosla D. Spiking deep convolutional neural networks for energy-efficient object recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 113(1): 54−66 doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0788-3 [24] Rast A D, Adams S V, Davidson S, Davies S, Hopkins M, Rowley A, et al. Behavioral learning in a cognitive neuromorphic robot: An integrative approach. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(12): 6132−6144 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2816518 [25] Qiao H, Xi X Y, Li Y L, Wu W, Li F F. Biologically inspired visual model with preliminary cognition and active attention adjustment. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(11): 2612−2624 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2377196 [26] Qiao H, Li Y L, Li F F, Xi X Y, Wu W. Biologically inspired model for visual cognition achieving unsupervised episodic and semantic feature learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(10): 2335−2347 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2476706 [27] Deng B, Fan Y R, Wang J, Yang S M. Reconstruction of a fully paralleled auditory spiking neural network and FPGA implementation. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2021, 15(6): 1320−1331 [28] Liu J D, Perez-Gonzalez D, Rees A, Erwin H, Wermter S. A biologically inspired spiking neural network model of the auditory midbrain for sound source localisation. Neurocomputing, 2010, 74(1−3): 129−139 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2009.10.030 [29] Gao B, Zhou Y, Zhang Q T, Zhang S L, Yao P, Xi Y, et al. Memristor-based analogue computing for brain-inspired sound localization with in situ training. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): Article No. 2026 doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29712-8 [30] Chou T S, Bucci L D, Krichmar J L. Learning touch preferences with a tactile robot using dopamine modulated STDP in a model of insular cortex. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2015, 9: Article No. 6 [31] Feng H, Zeng Y. A brain-inspired robot pain model based on a spiking neural network. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2022, 16: Article No. 1025338 doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2022.1025338 [32] 张超凡, 乔一铭, 曹露, 王志刚, 崔少伟, 王硕. 基于神经形态的触觉滑动感知方法. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2023, 57(4): 683−692 doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2023.04.005Zhang Chao-Fan, Qiao Yi-Ming, Cao Lu, Wang Zhi-Gang, Cui Shao-Wei, Wang Shuo. Tactile slip detection method based on neuromorphic modeling. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2023, 57(4): 683−692 doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2023.04.005 [33] Dabbous A, Ibrahim A, Valle M. Feed-forward SNN for touch modality prediction. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on System-Integrated Intelligence. Genova, Italy: Springer, 2022. 215−222 [34] Jiang C M, Yang L, Zhang Y L. A spiking neural network with spike-timing-dependent plasticity for surface roughness analysis. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(1): 438−445 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3120845 [35] Kang P, Banerjee S, Chopp H, Katsaggelos A, Cossairt O. Boost event-driven tactile learning with location spiking neurons. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2023, 17: Article No. 1127537 doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1127537 [36] Navaraj W, Dahiya R. Fingerprint-enhanced capacitive-piezoelectric flexible sensing skin to discriminate static and dynamic tactile stimuli. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2019, 1(7): Article No. 1900051 doi: 10.1002/aisy.201900051 [37] Han J K, Tcho I W, Jeon S B, Yu J M, Kim W G, Choi Y K. Self-powered artificial mechanoreceptor based on triboelectrification for a neuromorphic tactile system. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(9): Article No. 2105076 doi: 10.1002/advs.202105076 [38] Lee J, Kim S, Park S, Lee J, Hwang W, Cho S W, et al. An artificial tactile neuron enabling spiking representation of stiffness and disease diagnosis. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(24): Article No. 2201608 doi: 10.1002/adma.202201608 [39] Liu F Y, Deswal S, Christou A, Baghini M S, Chirila R, Shakthivel D, et al. Printed synaptic transistor-based electronic skin for robots to feel and learn. Science Robotics, 2022, 7(67): Article No. eabl7286 doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.abl7286 [40] Wen J, Zhang L, Wang Y Z, Guo X. Artificial tactile perception system based on spiking tactile neurons and spiking neural networks. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(1): 998−1004 [41] Kreiser R, Waibel G, Armengol N, Renner A, Sandamirskaya Y. Error estimation and correction in a spiking neural network for map formation in neuromorphic hardware. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Paris, France: IEEE, 2020. 6134−6140 [42] Yoon J H, Raychowdhury A. NeuroSLAM: A 65-nm 7.25-to-8.79-TOPS/W mixed-signal oscillator-based SLAM accelerator for edge robotics. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2021, 56(1): 66−78 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3028298 [43] Tang G Z, Shah A, Michmizos K P. Spiking neural network on neuromorphic hardware for energy-efficient unidimensional SLAM. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Macao, China: IEEE, 2019. 4176−4181 [44] Wang H, Li Y F. Bioinspired membrane learnable spiking neural network for autonomous vehicle sensors fault diagnosis under open environments. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2023, 233: Article No. 109102 [45] Lopez-Randulfe J, Duswald T, Bing Z S, Knoll A. Spiking neural network for fourier transform and object detection for automotive radar. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2021, 15: Article No. 688344 doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2021.688344 [46] Ambrosano A, Vannucci L, Albanese U, Kirtay M, Falotico E, Martínez-Cañada P, et al. Retina color-opponency based pursuit implemented through spiking neural networks in the neurorobotics platform. In: Proceedings of the 5th Conference on Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems. Edinburgh, UK: Springer, 2016. 16−27 [47] Deng B, Fan Y R, Wang J, Yang S M. Auditory perception architecture with spiking neural network and implementation on FPGA. Neural Networks, 2023, 165: 31−42 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2023.05.026 [48] Taunyazov T, Sng W, Lim B, See H H, Kuan J, Ansari A F, et al. Event-driven visual-tactile sensing and learning for robots. In: Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Robotics: Science and Systems. Corvalis, USA: 2020. [49] Zhao Z Y, Zhao F F, Zhao Y X, Zeng Y, Sun Y Q. A brain-inspired theory of mind spiking neural network improves multi-agent cooperation and competition. Patterns, 2023, 4(8): Article No. 100775 doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2023.100775 [50] 左国玉, 刘洪星, 龚道雄, 阮晓钢. 受脑启发的机器人认知抓取决策模型. 北京工业大学学报, 2021, 47(8): 863−873 doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2020120034Zuo Guo-Yu, Liu Hong-Xing, Gong Dao-Xiong, Ruan Xiao-Gang. Brain-inspired decision-making model for robot cognitive grasping. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2021, 47(8): 863−873 doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2020120034 [51] Sun T J, Gao Z H, Chang Z Y, Zhao K H. Brain-like intelligent decision-making based on basal ganglia and its application in automatic car-following. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2021, 18(6): 1439−1451 doi: 10.1007/s42235-021-00113-9 [52] Robertazzi F, Vissani M, Schillaci G, Falotico E. Brain-inspired meta-reinforcement learning cognitive control in conflictual inhibition decision-making task for artificial agents. Neural Networks, 2022, 154: 283−302 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2022.06.020 [53] Zhao F F, Zeng Y, Wang G X, Bai J, Xu B. A brain-inspired decision making model based on top-down biasing of prefrontal cortex to basal ganglia and its application in autonomous UAV explorations. Cognitive Computation, 2018, 10(2): 296−306 doi: 10.1007/s12559-017-9511-3 [54] Zhao F F, Zeng Y, Xu B. A brain-inspired decision-making spiking neural network and its application in unmanned aerial vehicle. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2018, 12: Article No. 56 doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2018.00056 [55] Daglarli E. Computational modeling of prefrontal cortex for meta-cognition of a humanoid robot. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 98491−98507 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2998396 [56] Rueckert E, Kappel D, Tanneberg D, Pecevski D, Peters J. Recurrent spiking networks solve planning tasks. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): Article No. 21142 doi: 10.1038/srep21142 [57] Skorheim S, Lonjers P, Bazhenov M. A spiking network model of decision making employing rewarded STDP. PLoS One, 2014, 9(3): Article No. e90821 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090821 [58] Liu J X, Lu H, Luo Y L, Yang S. Spiking neural network-based multi-task autonomous learning for mobile robots. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 104: Article No. 104362 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104362 [59] Huang X, Wu W, Qiao H. Connecting model-based and model-free control with emotion modulation in learning systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(8): 4624−4638 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2933152 [60] Jiang Z Y, Bing Z S, Huang K, Knoll A. Retina-based pipe-like object tracking implemented through spiking neural network on a snake robot. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2019, 13: Article No. 29 doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2019.00029 [61] Wang M, Zhang Y Y, Yu J Z. An SNN-CPG hybrid locomotion control for biomimetic robotic fish. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2022, 105(2): Article No. 45 [62] Lele A, Fang Y, Ting J, Raychowdhury A. An end-to-end spiking neural network platform for edge robotics: From event-cameras to central pattern generation. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2022, 14(3): 1092−1103 doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2021.3097675 [63] Cao Z Q, Cheng L, Zhou C, Gu N, Wang X, Tan M. Spiking neural network-based target tracking control for autonomous mobile robots. Neural Computing and Applications, 2015, 26(8): 1839−1847 doi: 10.1007/s00521-015-1848-5 [64] Lu H, Liu J X, Luo Y L, Hua Y F, Qiu S H, Huang Y C. An autonomous learning mobile robot using biological reward modulate STDP. Neurocomputing, 2021, 458: 308−318 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.06.027 [65] Bing Z S, Meschede C, Chen G, Knoll A, Huang K. Indirect and direct training of spiking neural networks for end-to-end control of a lane-keeping vehicle. Neural Networks, 2020, 121: 21−36 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.05.019 [66] Bing Z S, Baumann I, Jiang Z Y, Huang K, Cai C X, Knoll A. Supervised learning in snn via reward-modulated spike-timing-dependent plasticity for a target reaching vehicle. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2019, 13: Article No. 18 doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2019.00018 [67] Nichols E, McDaid L J, Siddique N H. Case study on a self-organizing spiking neural network for robot navigation. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2010, 20(6): 501−508 doi: 10.1142/S0129065710002577 [68] Wang X Q, Hou Z G, Lv F, Tan M, Wang Y J. Mobile robots' modular navigation controller using spiking neural networks. Neurocomputing, 2014, 134: 230−238 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.07.055 [69] Bing Z S, Jiang Z Y, Cheng L, Cai C X, Huang K, Knoll A. End to end learning of a multi-layered SNN based on R-STDP for a target tracking snake-like robot. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2019. 9645−9651 [70] Liu J X, Hua Y F, Yang R X, Luo Y L, Lu H, Wang Y H, et al. Bio-inspired autonomous learning algorithm with application to mobile robot obstacle avoidance. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2022, 16: Article No. 905596 doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.905596 [71] Guerrero-Criollo R J, Castaño-López J A, Hurtado-López J, Ramirez-Moreno D F. Bio-inspired neural networks for decision-making mechanisms and neuromodulation for motor control in a differential robot. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2023, 17: Article No. 1078074 doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2023.1078074 [72] Guerrero-Criollo R J, Castaño-López J A, Díaz-Cuchala R E, Rozo-Giraldo Y D, Ramirez-Moreno D F. Design and simulation of a bio-inspired neural network for the motor control of a mobile automaton. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Colombian Conference on Applications of Computational Intelligence. Cali, Colombia: IEEE, 2022. 1−6 [73] Abadía I, Naveros F, Garrido J A, Ros E, Luque N R. On robot compliance: A cerebellar control approach. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(5): 2476−2489 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2945498 [74] 戴嘉伟, 熊智, 晁丽君, 杨闯. 基于STDP奖励调节的类脑面向目标导航. 导航定位与授时, 2023, 10(2): 47−56Dai Jia-Wei, Xiong Zhi, Chao Li-Jun, Yang Chuang. Brain-inspired target-driven navigation based on STDP reward modulation. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2023, 10(2): 47−56 [75] Lobov S A, Mikhaylov A N, Shamshin M, Makarov V A, Kazantsev V B. Spatial properties of STDP in a self-learning spiking neural network enable controlling a mobile robot. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2020, 14: Article No. 88 doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00088 [76] Sathyanesan A, Zhou J, Scafidi J, Heck D H, Sillitoe R V, Gallo V. Emerging connections between cerebellar development, behaviour and complex brain disorders. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2019, 20(5): 298−313 doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0152-2 [77] Carrillo R R, Ros E, Boucheny C, Coenen O J M D. A real-time spiking cerebellum model for learning robot control. Biosystems, 2008, 94(1−2): 18−27 doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2008.05.008 [78] Oikonomou K M, Kansizoglou I, Gasteratos A. A hybrid spiking neural network reinforcement learning agent for energy-efficient object manipulation. Machines, 2023, 11(2): Article No. 162 doi: 10.3390/machines11020162 [79] Liu Y X, Pan W. Spiking neural-networks-based data-driven control. Electronics, 2023, 12(2): Article No. 310 doi: 10.3390/electronics12020310 [80] Zhang J H, Chen J H, Wu W, Qiao H. A cerebellum-inspired prediction and correction model for motion control of a musculoskeletal robot. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2023, 15(3): 1209−1223 doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2022.3200839 [81] Cao Y, Huang J, Ding G Z, Wang Y J. Design of nonlinear predictive control for pneumatic muscle actuator based on echo state gaussian process. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2017, 50(1): 1952−1957 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.390 [82] Zahra O, Navarro-Alarcon D, Tolu S. Vision-based control for robots by a fully spiking neural system relying on cerebellar predictive learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2011.01641, 2020. [83] Wilson E D, Assaf T, Pearson M J, Rossiter J M, Dean P, Anderson S R, et al. Biohybrid control of general linear systems using the adaptive filter model of cerebellum. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2015, 9: Article No. 5 [84] Lechner M, Hasani R, Amini A, Henzinger T A, Rus D, Grosu R. Neural circuit policies enabling auditable autonomy. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2020, 2(10): 642−652 doi: 10.1038/s42256-020-00237-3 [85] Hasani R, Lechner M, Amini A, Liebenwein L, Ray A, Tschaikowski M, et al. Closed-form continuous-time neural networks. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2022, 4(11): 992−1003 doi: 10.1038/s42256-022-00556-7 [86] Chen X Y, Zhu W X, Liang W Y, Lang Y L, Ren Q Y. Control of antagonistic McKibben muscles via a bio-inspired approach. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2022, 19(6): 1771−1789 doi: 10.1007/s42235-022-00225-w [87] Zahra O, Navarro-Alarcon D, Tolu S. A neurorobotic embodiment for exploring the dynamical interactions of a spiking cerebellar model and a robot arm during vision-based manipulation tasks. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2022, 32(8): Article No. 2150028 doi: 10.1142/S0129065721500283 [88] Naveros F, Luque N R, Ros E, Arleo A. VOR adaptation on a humanoid iCub robot using a spiking cerebellar model. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(11): 4744−4757 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2899246 [89] Espinal A, Rostro-Gonzalez H, Carpio M, Guerra-Hernandez E I, Ornelas-Rodriguez M, Puga-Soberanes H J, et al. Quadrupedal robot locomotion: A biologically inspired approach and its hardware implementation. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2016, 2016: Article No. 5615618 [90] Aitsam M, Davies S, Di Nuovo A. Neuromorphic computing for interactive robotics: A systematic review. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 122261−122279 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3219440 [91] Guo Y F, Huang X H, Ma Z. Direct learning-based deep spiking neural networks: A review. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2023, 17: Article No. 1209795 doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1209795 [92] Shen G B, Zhao D C, Dong Y T, Zeng Y. Brain-inspired neural circuit evolution for spiking neural networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(39): Article No. e2218173120 [93] Javanshir A, Nguyen T T, Mahmud M A P, Kouzani A Z. Advancements in algorithms and neuromorphic hardware for spiking neural networks. Neural Computation, 2022, 34(6): 1289−1328 doi: 10.1162/neco_a_01499 [94] Quintana F M, Perez-Peña F, Galindo P L. Bio-plausible digital implementation of a reward modulated STDP synapse. Neural Computing and Applications, 2022, 34(18): 15649−15660 doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07220-6 [95] 胡金岭. 机械臂类脑控制平台的设计与实现研究 [硕士学位论文], 天津大学, 中国, 2019.Hu Jin-Ling. Design and Implementation of Brain-inspired Control Platform for Manipulator [Master thesis], Tianjin University, China, 2019. -





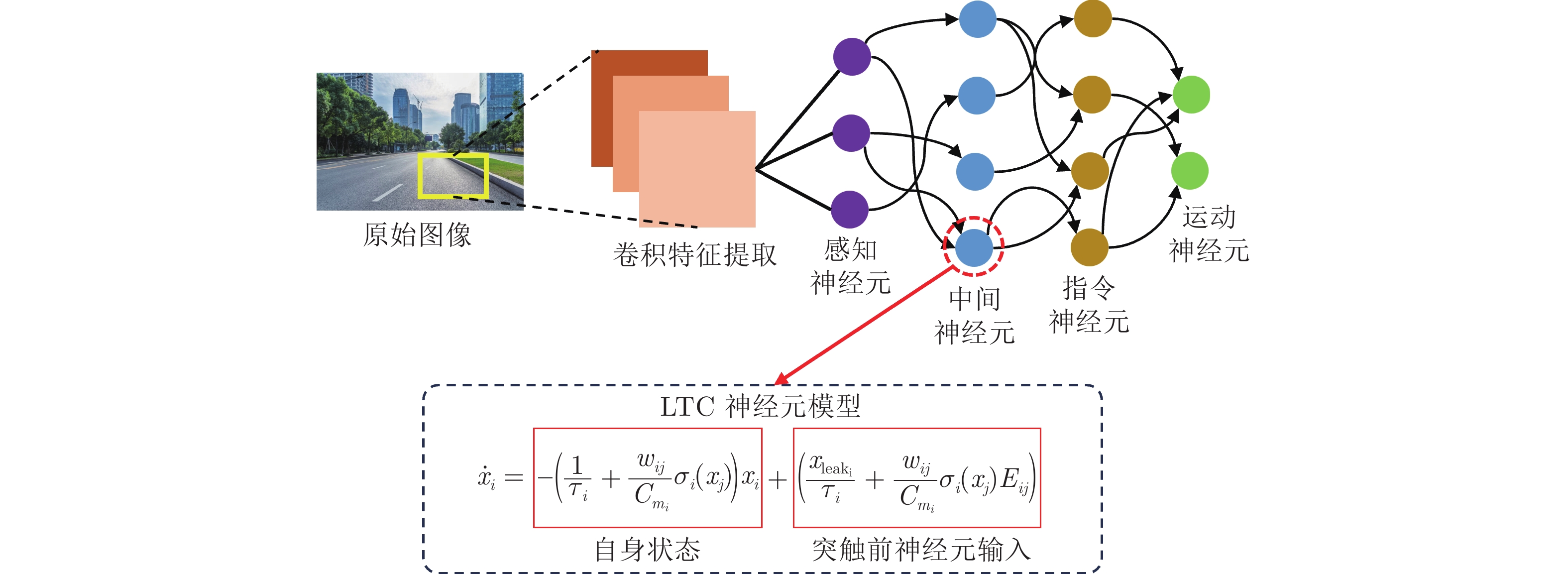
 下载:
下载: