Hierarchical-based Prescribed-time Optimal Fault-tolerant Control for Air-ground Cooperative System
-
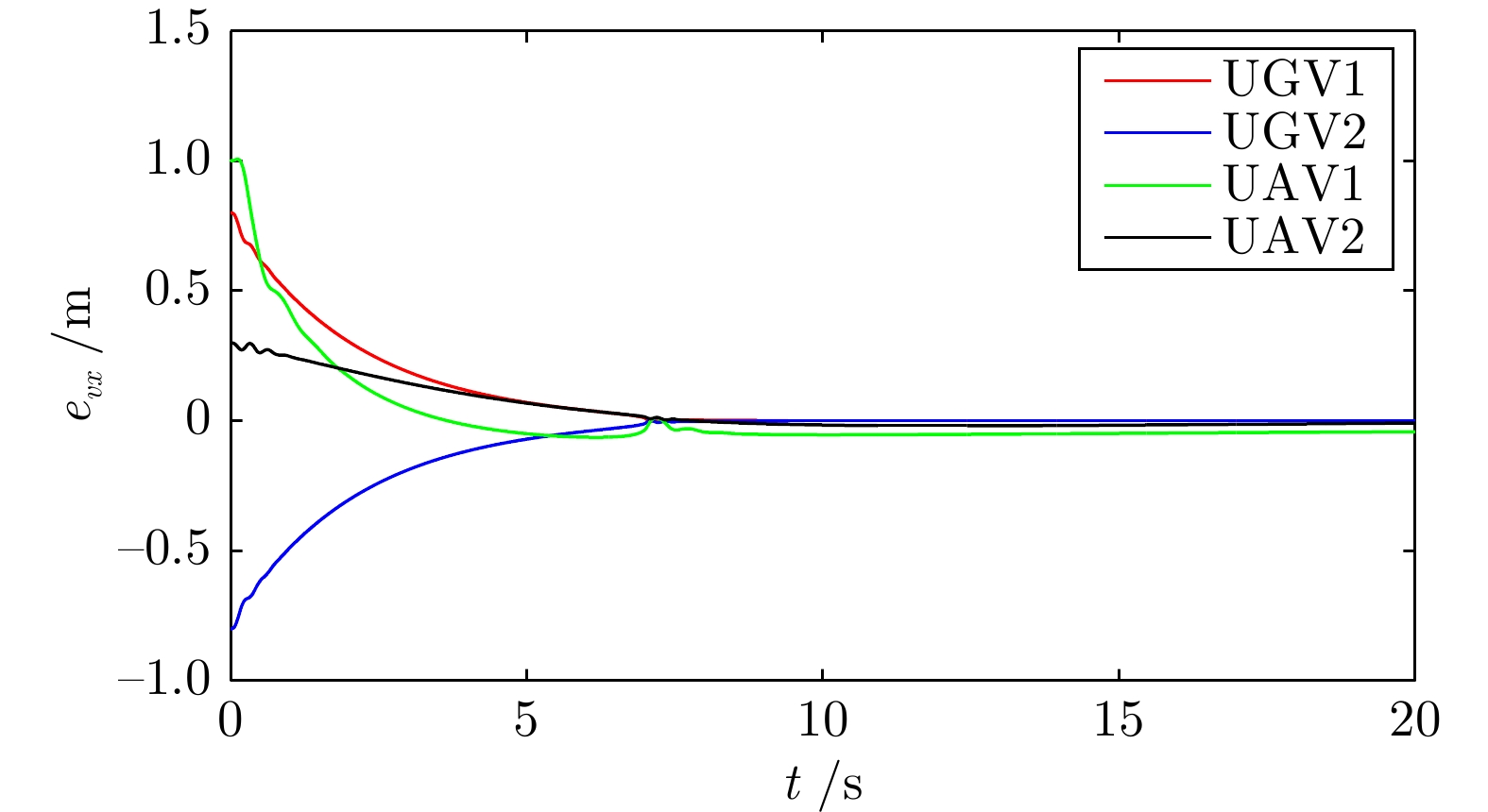
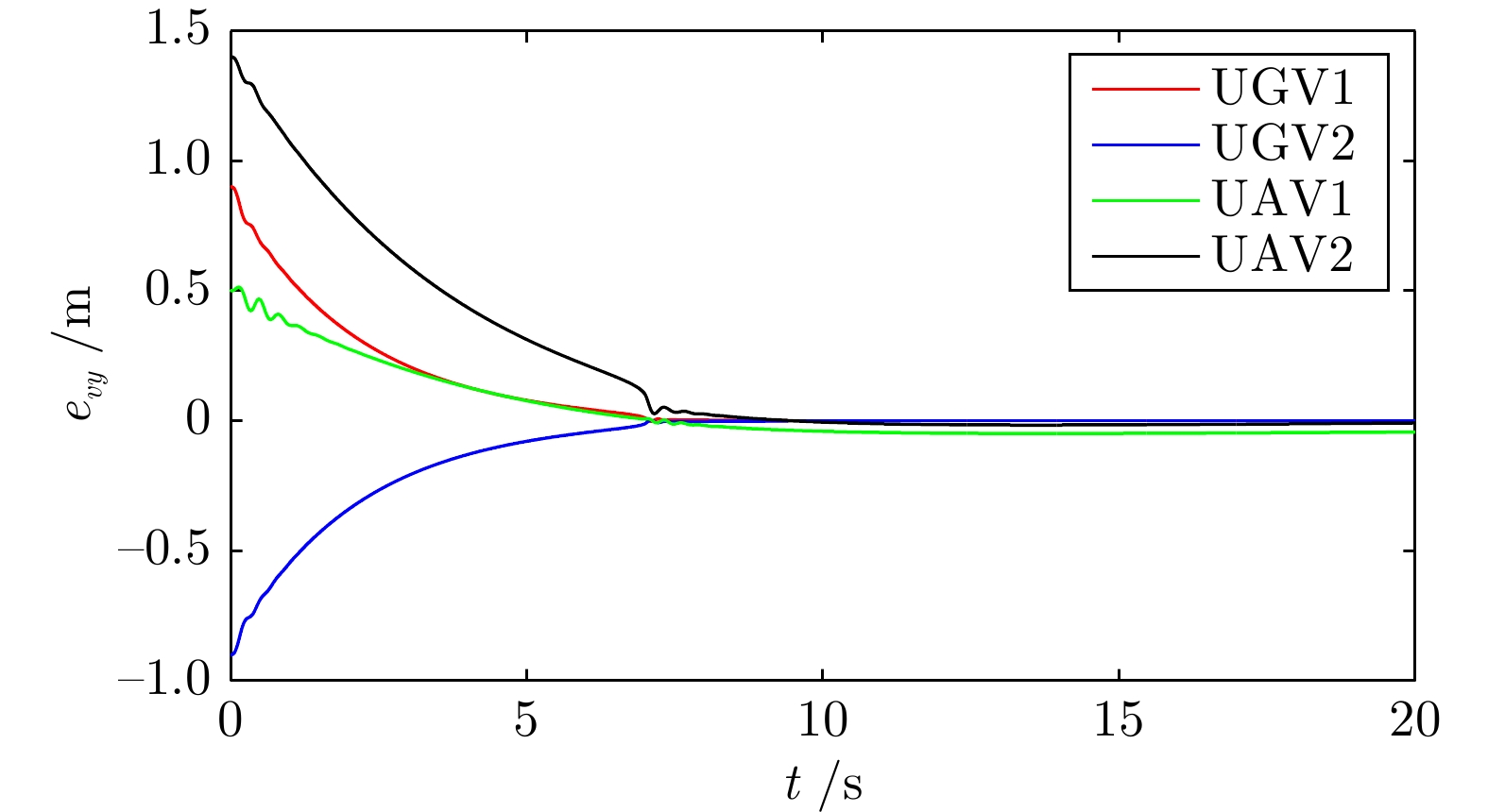
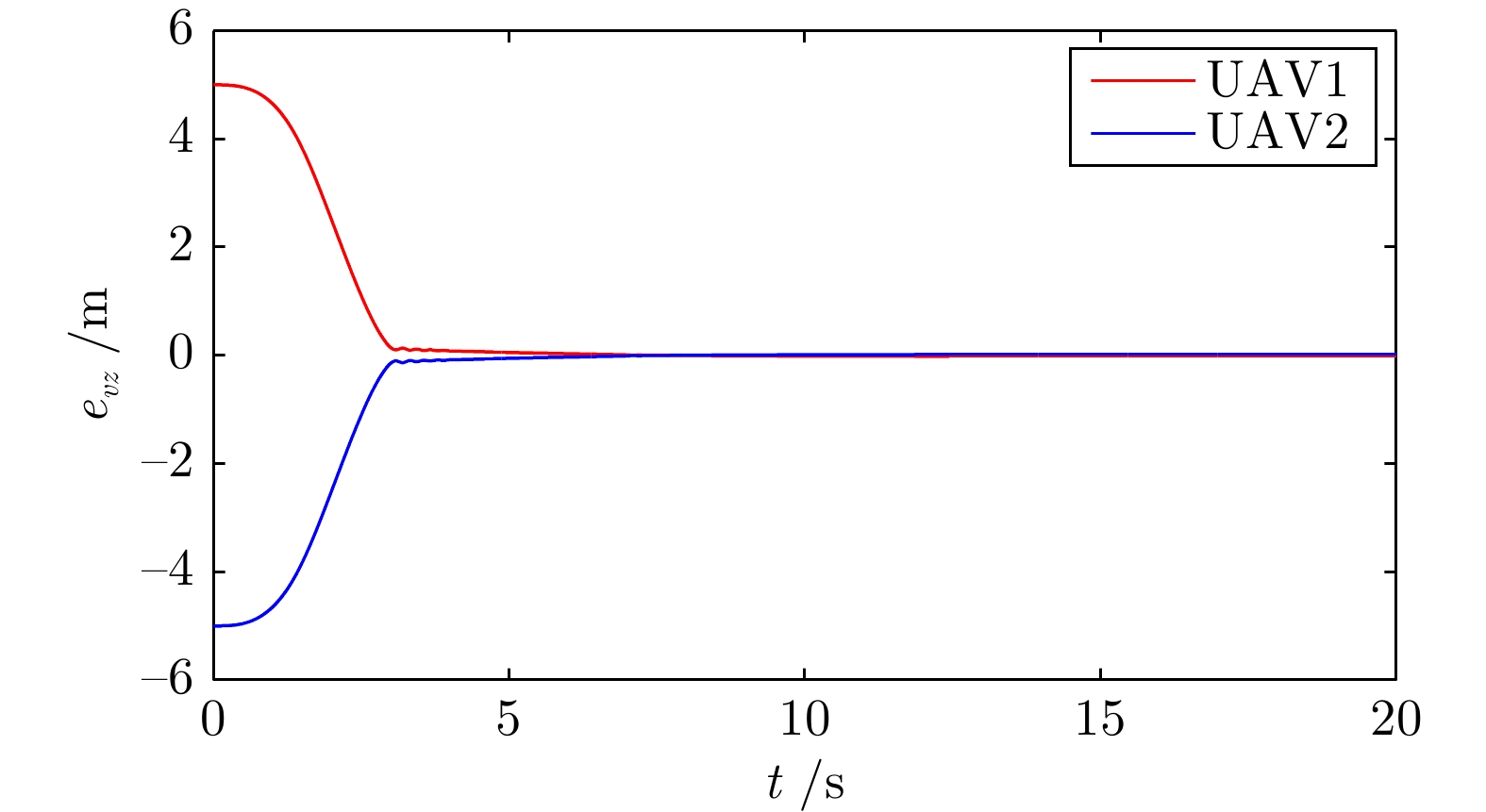
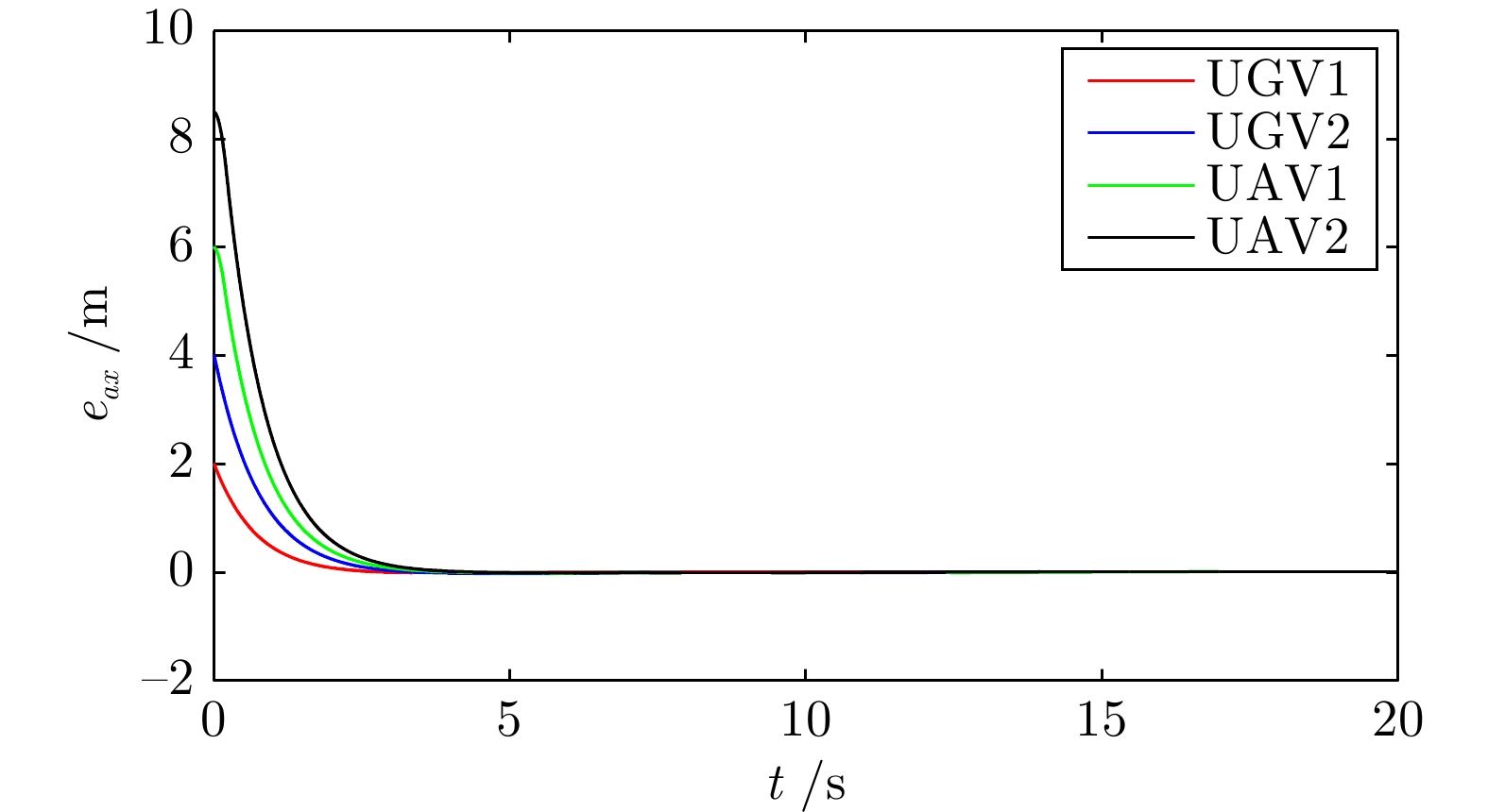
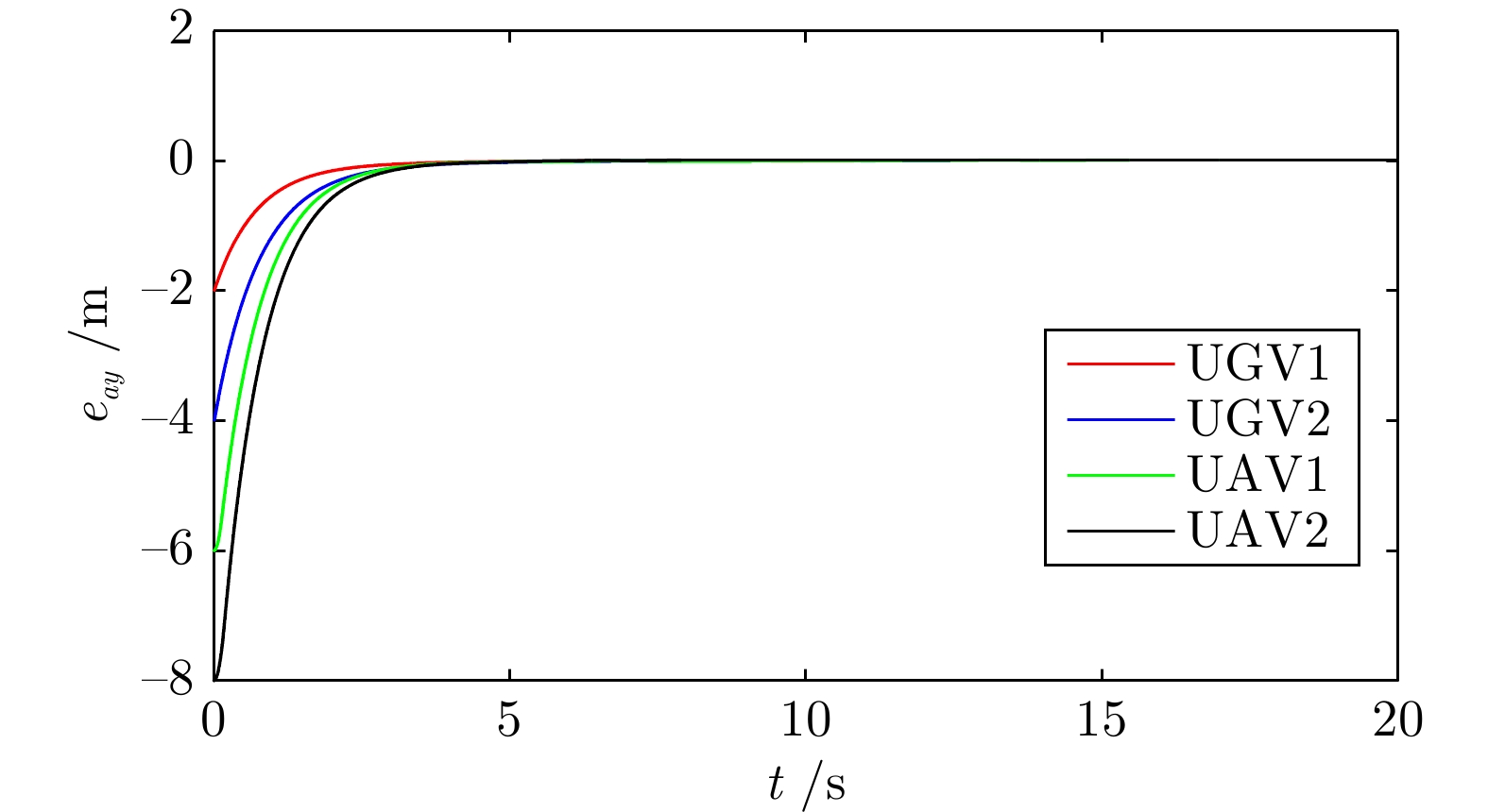
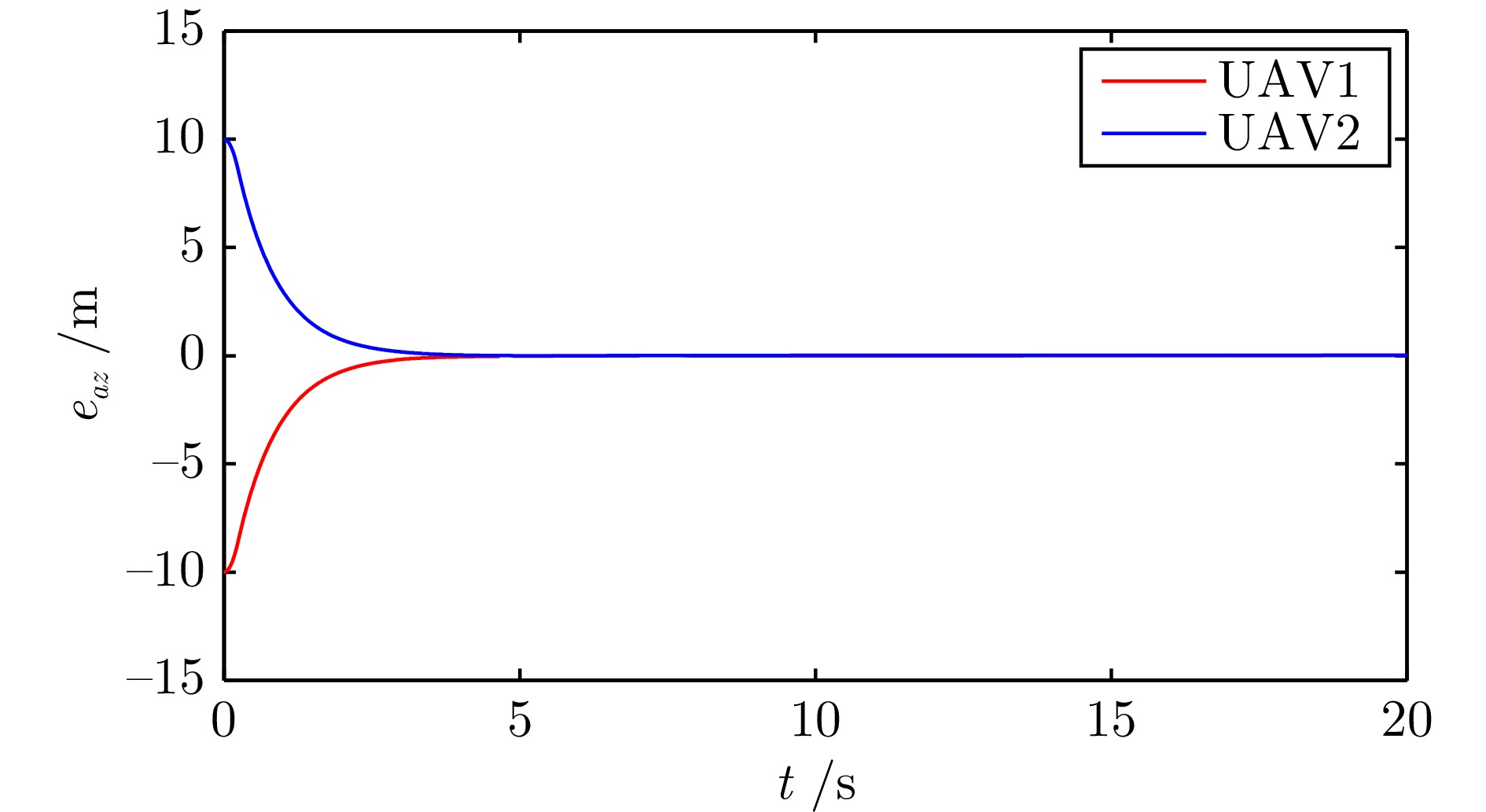
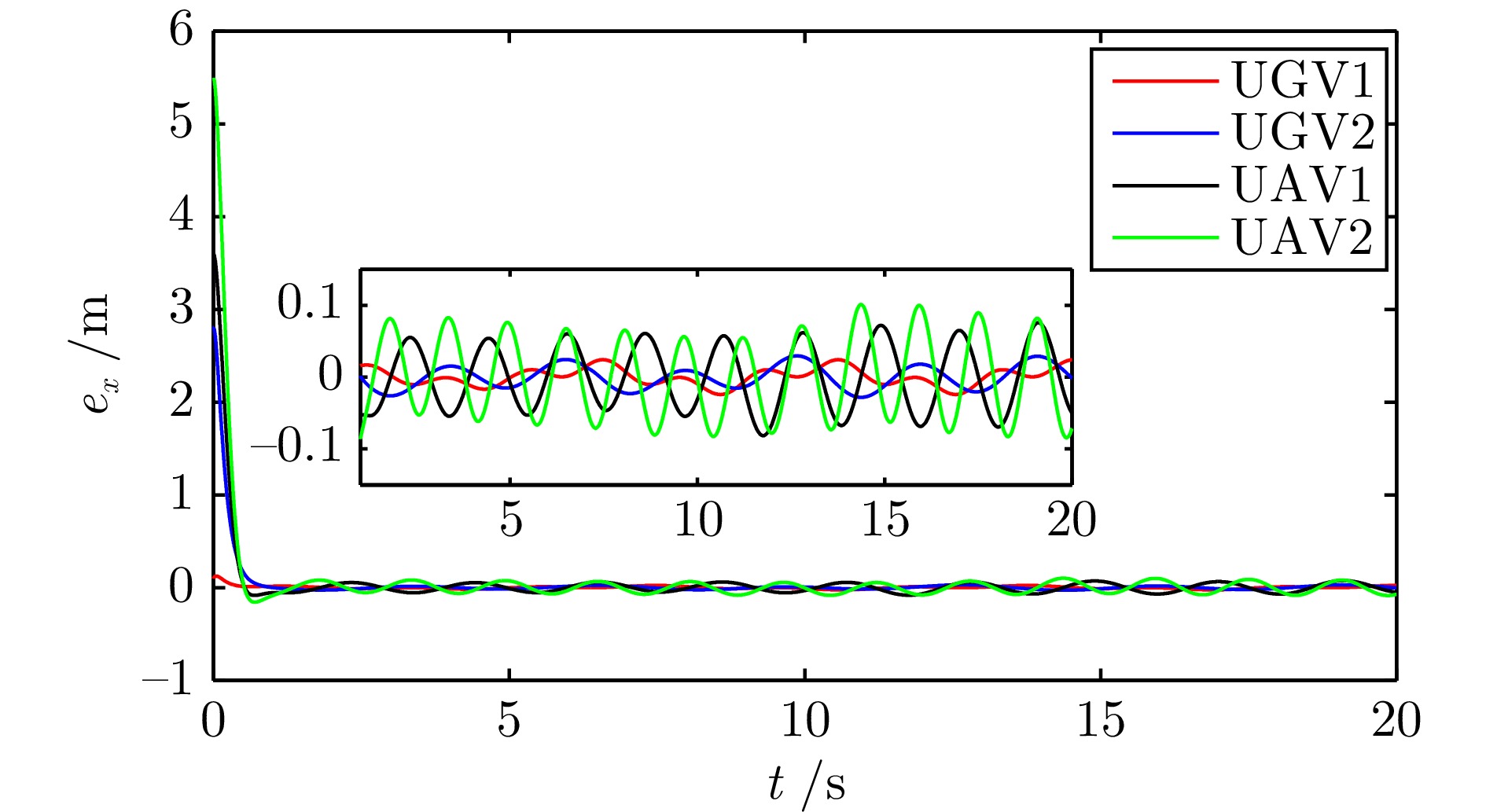
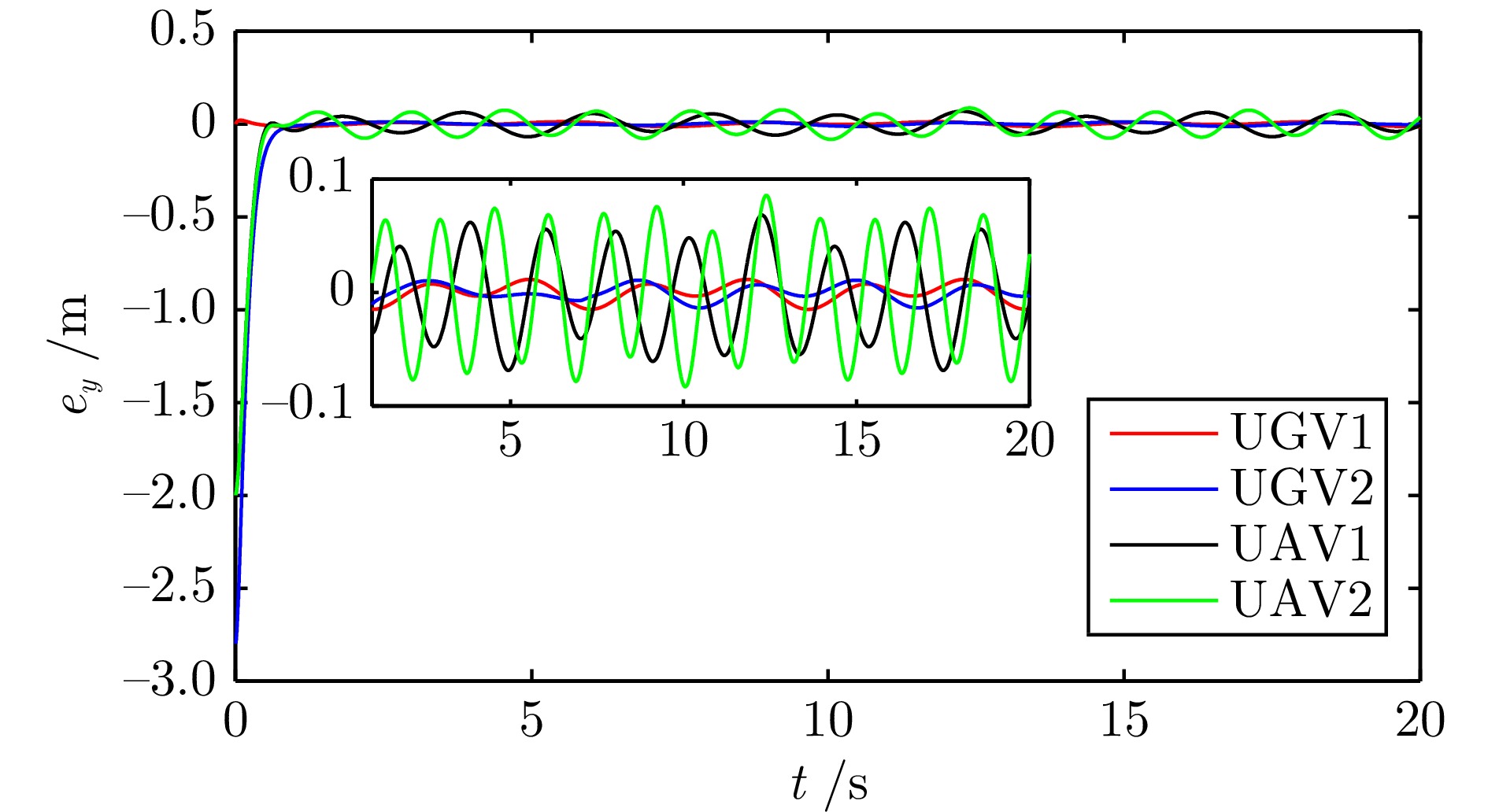
摘要: 研究了发生执行器故障的无人机−无人车异构编队系统的层级预设时间最优编队控制问题. 以保容错性能和收敛速度的优化控制为研究主线, 以层级控制、图博弈理论和预设时间控制为技术基础, 构建了一种预设时间最优容错控制算法. 虚拟层设计了基于一致性跟踪误差和能量消耗的二次型性能指标函数, 借助耦合哈密顿−雅克比−贝尔曼(Hanmilton-Jacobi-Bellman, HJB)方程和强化学习求解近似最优控制策略, 实现多智能体的同步最优控制和交互纳什均衡. 实际控制层基于最优信号并利用滑模控制和自适应技术, 设计了预设时间容错跟踪控制器, 实现对最优编队轨迹的有限时间跟踪. 在保证全局收敛时间完全不依赖于系统的初始状态和控制器参数的同时, 也有效实现对执行器故障参数的逼近. 最后, 通过仿真实验验证了所提控制策略的有效性.Abstract: This article investigates the hierarchical structure-based optimal formation control problem of a heterogeneous formation system of unmanned aerial vehicles and unmanned ground vehicles. This article focuses on the optimization control with fault-tolerant performance and fast convergence speed, and constructs a prescribed-time optimal fault-tolerant control algorithm based on hierarchical control, graphical game theory, and prescribed-time control method. In virtual layer, an quadratic performance index function based on consistency tracking error and energy consumption is designed, and approximate optimal control strategy is obtained by using coupled Hanmilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) equation and reinforcement learning, which achieves synchronous optimal control and interactive Nash equilibrium of multiagent systems. In actual control layer, a prescribed-time fault-tolerant tracking controller is designed based on the optimal signal, sliding-mode and adaptive technologies, which realizes the finite-time tracking of the optimal formation trajectory. The proposed method ensures that the global convergence time is completely independent of the initial states of the system and controller parameters, while also effectively approximating the actuator fault parameters. Finally, the effectiveness of the constructed control strategy is verified through simulation experiment.
-
Key words:
- Air-ground cooperation /
- actuator faults /
- prescribed-time formation /
- graphical game /
- optimal control
-
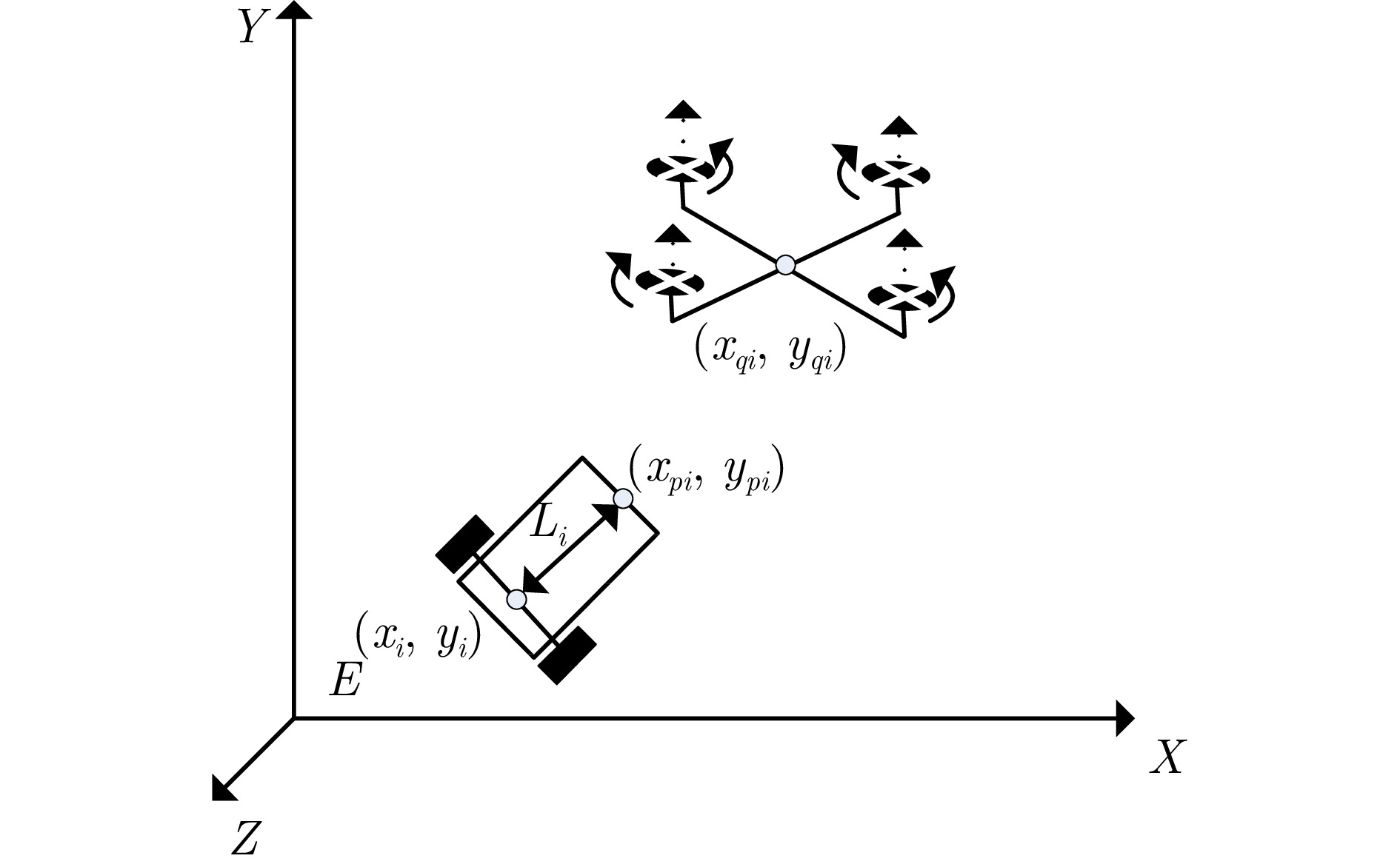
表 1 无人机和无人车的模型参数
Table 1 Model parameters of UAVs and UGVs
序号 参数 数值 1 ${\xi _{xi}},\;{\xi _{yi}},\;{\xi _{zi}}$ $1.2 \times {10^{ - 2}}\ {\rm{N}}\cdot{\rm{s}}/{\rm{rad}}$ 2 $L_i$ $0.5\ {\rm{m}}$ 3 $m_i$ $2\ {\rm{kg}}$ 4 ${\kappa _i}$ $2.98 \times {10^{ - 6}}\ {\rm{N}}\cdot{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}{\rm{/ra}}{{\rm{d}}^{\rm{2}}}$ -
[1] Yan B, Shi P, Lim C C. Robust formation control for nonlinear heterogeneous multiagent systems based on adaptive event-triggered strategy. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(4): 2788−2800 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2021.3103877 [2] Zhang L L, Gao F, Deng F, Xi L L, Chen J. Distributed estimation of a layered architecture for collaborative air-ground target geolocation in outdoor environments. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(3): 2822−2832 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3165245 [3] Loria A, Nuno E, Panteley E. Observerless output-feedback consensus-based formation control of second-order nonholonomic systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(12): 6934−6939 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3136140 [4] Oh K K, Park M C, Ahn H S. A survey of muitiagent formation control. Automatica, 2015, 53: 424−440 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.022 [5] Hua Y Z, Dong X W, Hu G Q, Li Q D, Ren Z. Distributed time-varying output formation tracking for heterogeneous linear multiagent systems with a nonautonomous leader of unknown input. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(10): 4292−4299 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2893978 [6] Jiang P W, Zhang W, Yan C H, Hu Z. Fully distributed event-triggered bipartite output formation control for heterogeneous MASs with directed graphs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2023, 70(6): 2072−2076 [7] 周思全, 化永朝, 董希旺, 李清东, 任章. 面向空地协同作战的无人机无人车异构时变编队跟踪控制. 航空兵器, 2019, 26(4): 54−59Zhou Si-Quan, Hua Yong-Zhao, Dong Xi-Wang, Li Qing-Dong, Ren Zhang. Air-ground time varying formation tracking control for heterogeneous UAV-UGV swarm system. Aero Weaponry, 2019, 26(4): 54−59 [8] Shi J L, Hu B, Chen L, Zhang D X, He D X, Huang J, et al. Formation tracking of heterogeneous UGV-UAV systems with switching directed topologies. In: Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics. Osaka, Japan: IEEE, 2019. 970−975 [9] Vallejo-Alarcon M A, Castro-Linares R, Velasco-Villa M. Unicycle-type robot and quadrotor leader-follower formation backstepping control. IFAC-Papers Online, 2015, 48(19): 51−56 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2015.12.009 [10] Hua H A, Fang Y C, Zhang X T, Lu B A. A novel robust observer-based nonlinear trajectory tracking control strategy for quadrotors. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2021, 29(5): 1952−1963 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2020.3024805 [11] Fan Q Y, Deng C, Ge X H, Wang C C. Distributed adaptive fault-tolerant control for heterogeneous multiagent systems with time-varying communication delays. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(7): 4362−4372 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3095263 [12] Zhang K, Jiang B, Shi P. Adjustable parameter-based distributed fault estimation observer design for multiagent systems with directed graphs. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(2): 306−314 [13] Jiang B, Zhang K, Shi P. Integrated fault estimation and accommodation design for discrete-time Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems with actuator faults. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2011, 19(2): 291−304 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2010.2095861 [14] Zhang K, Jiang B, Staroswiecki M. Dynamic output feedback-fault tolerant controller design for Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems with actuator faults. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2010, 18(1): 194−201 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2009.2036005 [15] Wang Y, Qi R, He C. Trajectory and attitude cooperative formation control for air-ground collaborative systems under communication faults. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Autonomous Systems. Nanjing, China: 2023. 1−6 [16] Zhao W, Liu H, Gao Q, Lu J. Robust optimal formation control of heterogeneous air-ground vehicles under communication faults via reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Guidance. Harbin, China: 2022. 4145−4155 [17] Zhao W B, Liu H, Valavanis K P, Lewis F L. Fault-tolerant formation control for heterogeneous vehicles via reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 2796−2806 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3139260 [18] Kamel M, Ghamry K, Zhang Y M. Real-time fault-tolerant cooperative control of multiple UAVs-UGVs in the presence of actuator faults. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, 2017, 88(2−4): 469−480 doi: 10.1007/s10846-016-0463-8 [19] Cheng W L, Jiang B, Zhang K, Ding S X. Robust finite-time cooperative formation control of UGV-UAV with model uncertainties and actuator faults. Journal of the Franklin Institute-Engineering and Applied Mathematics, 2021, 358(17): 8811−8837 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.08.038 [20] Cheng W L, Jiang B, Zhang K, Ding S X. Fixed-time fault-tolerant formation control for heterogeneous multi-agent systems with parameter uncertainties and disturbances. IEEE Transactions On Circuits and Systems I. Regular Papers, 2021, 68(5): 2121−2133 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2021.3061386 [21] Song Y D, Wang Y J, Holloway J, Krstic M A. Time-varying feedback for regulation of normal-form nonlinear systems in prescribed finite time. Automatica, 2017, 83: 243−251 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.06.008 [22] Wang Z W, Liang B, Sun Y C, Zhang T. Adaptive fault-tolerant prescribed-time control for teleoperation systems with position error constraints. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 16(7): 4889−4899 [23] 王龙, 黄锋. 多智能体博弈、学习与控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 580−613Wang Long, Huang Feng. An interdisciplinary survey of multi-agent games, learning, and control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 580−613 [24] Han X, Zhao X, Sun T, Wu Y, Xu N, Zong G. Event-triggered optimal control for discrete-time switched nonlinear systems with constrained control input. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(12): 7850−7859 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.2987136 [25] Wang Y, Zhang J, Liu J, Sun J. Optimal synchronization for multiagent systems under directed graphs by scalable distributed event-triggered control. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2023, 70(12): 4539−4543 [26] Li H, Wu Y, Chen M. Adaptive fault-tolerant tracking control for discrete-time multiagent systems via reinforcement learning algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(3): 1163−1174 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2982168 [27] Li Z, Song Y, Wen G. Reinforcement learning based optimized sliding-mode consensus control of high-order nonlinear canonical dynamic multiagent system. IEEE Systems Journal, 2023, 17(4): 6302−6311 [28] Wang X, Wang G, Li S. Distributed finite-time optimization for disturbed second-order multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(9): 4634−4547 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2988490 [29] Cao S, Sun L, Jiang J, Zuo Z. Reinforcement learning-based fixed-time trajectory tracking control for uncertain robotic manipulators with input saturation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(8): 4584−4595 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3116713 [30] Tang Y T, Yi P. Nash equilibrium seeking for high-order multiagent systems with unknown dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2023, 10(1): 321−332 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2022.3203362 [31] 于镝. 基于零和博弈的多智能体网络鲁棒包容控制. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(8): 1841−1848Yu Di. Robust containment control of multi-agent networks based on zero-sum game. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(8): 1841−1848 [32] Zhao J, Yang C, Wang W D, Xu B, Li Y, Yang L Q, et al. A game-learning-based smooth path planning strategy for intelligent air-ground vehicle considering mode switching. IEEE Transac tions on Transportation Electrification, 2022, 8(3): 3349−3366 doi: 10.1109/TTE.2022.3142150 [33] Wen G, Li B. Optimized leader-follower consensus control using reinforcement learning for a class of second-order nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(9): 5546−5555 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3130070 [34] Dong H, Zhao X, Yang H. Reinforcement learning-based approximate optimal control for attitude reorientation under state constraints. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2021, 29(4): 1664−1673 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2020.3007401 [35] Cao Z, Guo G. Fixed-time sliding mode formation control of AUVs based on a disturbance observer. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(2): 539−545 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003057 [36] Chen F Y, Jiang R, Zhang K, Jiang B, Tao G. Robust backstepping sliding-mode control and observer-based fault estimation for a quadrotor UAV. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(8): 5044−5056 -




 下载:
下载: