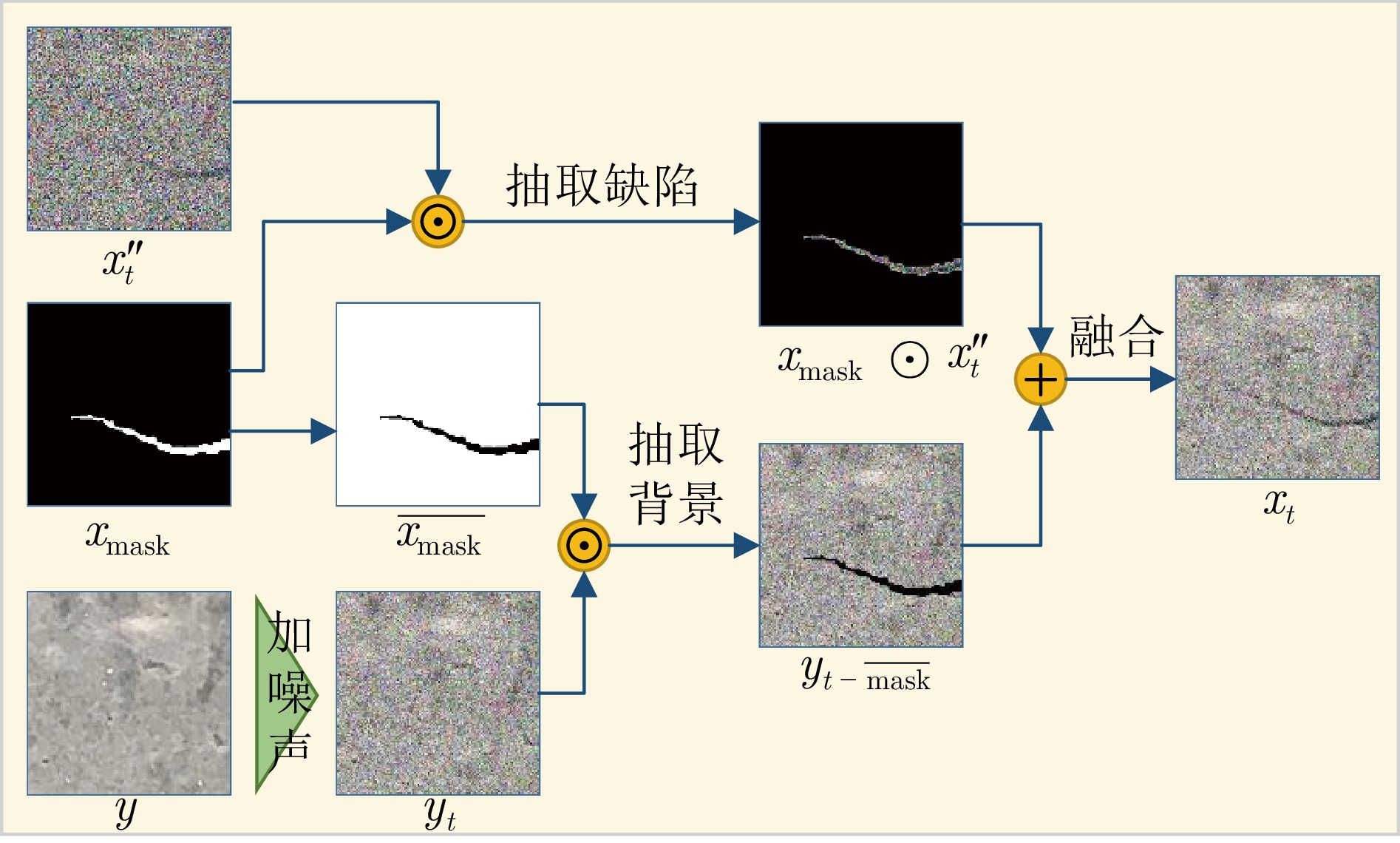
-
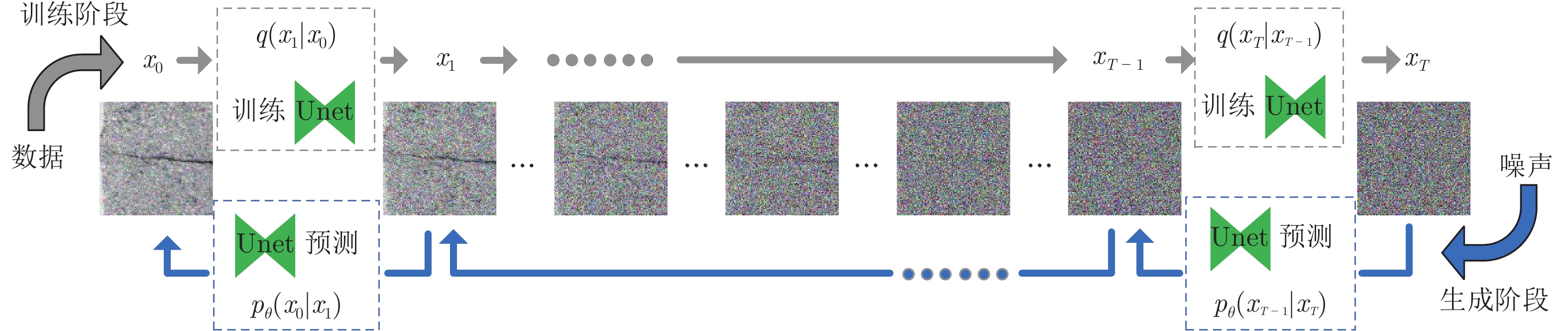
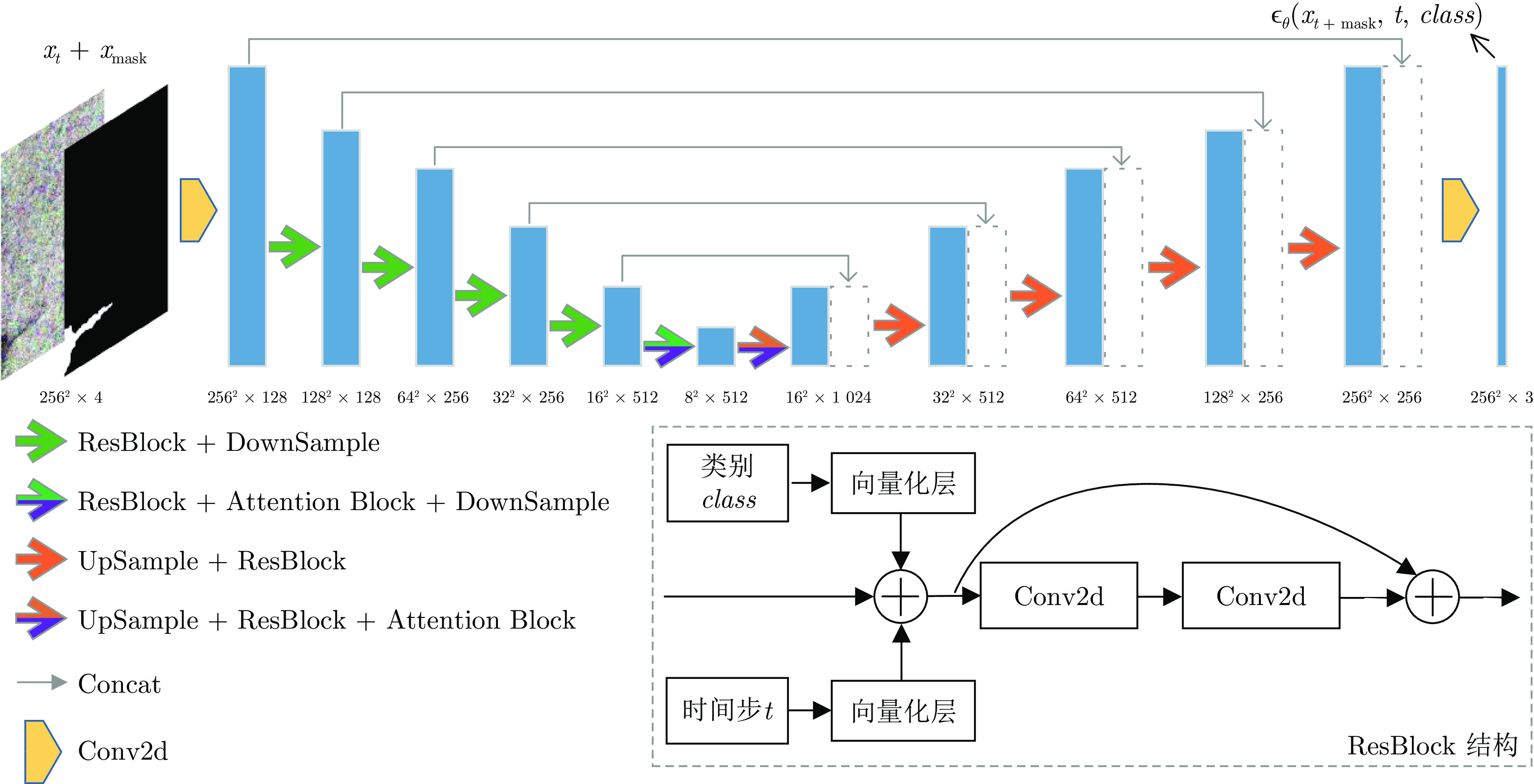
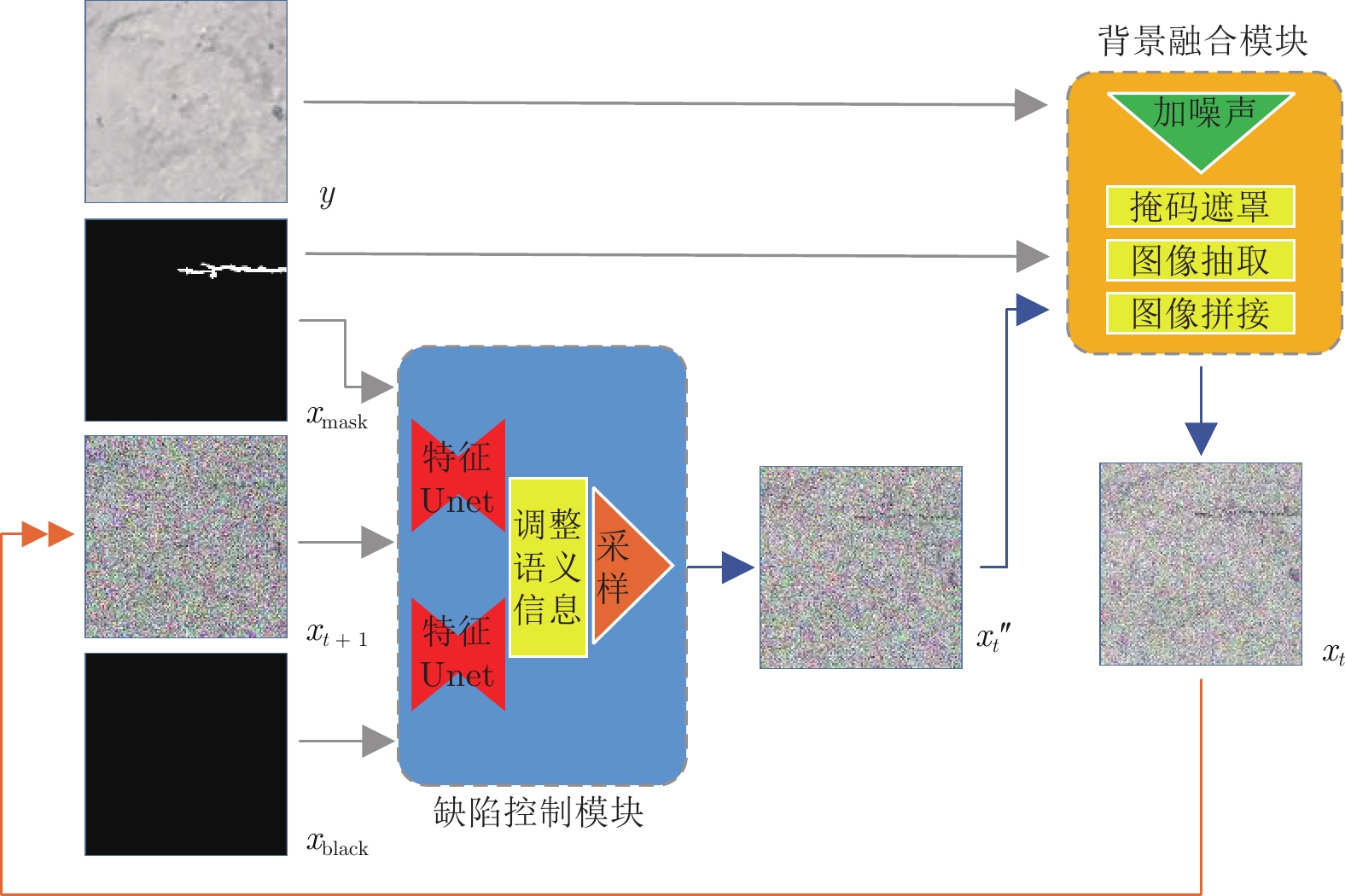
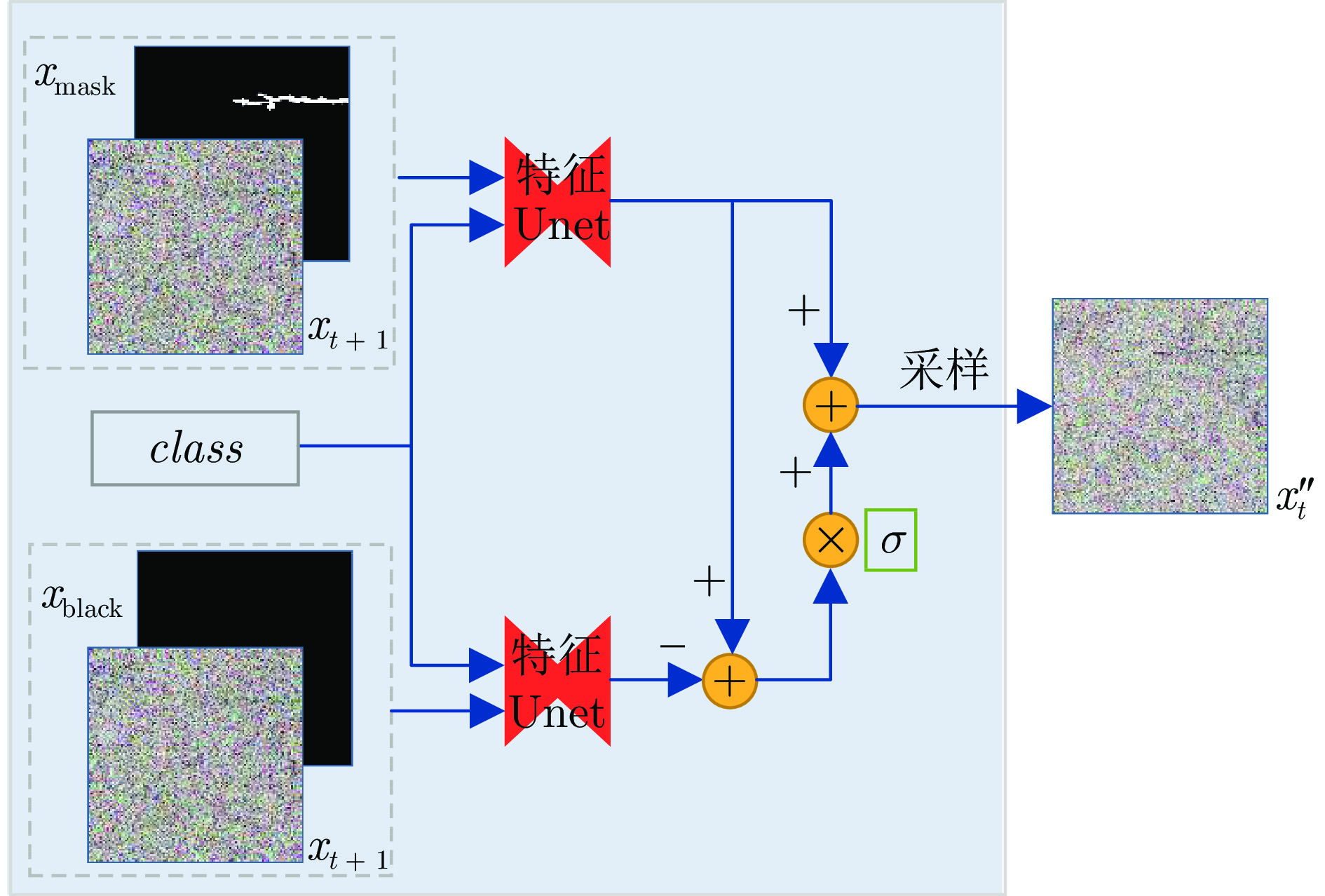
摘要: 基于深度学习的表面缺陷检测技术是工业上的一项重要应用, 而缺陷图像数据集质量对缺陷检测性能有重要影响. 为解决实际工业生产过程中缺陷样本获取成本高、缺陷数据量少的痛点, 提出了一种基于去噪扩散概率模型(Denoising diffusion probabilistic model, DDPM)的缺陷图像生成方法. 该方法在训练过程中加强了模型对缺陷部位和无缺陷背景的差异化学习. 在生成过程中通过缺陷控制模块对生成缺陷的类别、形态、显著性等特征进行精准控制, 通过背景融合模块, 能将缺陷在不同的无缺陷背景上进行迁移, 大大降低新背景上缺陷样本的获取难度. 实验验证了该模型的缺陷控制和缺陷迁移能力, 其生成结果能有效扩充训练数据集, 提升下游缺陷检测任务的准确率.Abstract: Surface defect detection technology based on deep learning is an important application in industry and the quality of defect image dataset has a significant impact on defect detection performance. A defect image generation method based on denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM) is designed to address the pain points of high cost of obtaining defect samples and low amount of defect data in actual industrial production processes. This method enhances the model's differential learning of defect locations and defect free backgrounds during the training process. Through the defect control module during the generation process, this method accurately controls the category, morphology, saliency and other features of generated defects. Through the background fusion module, defects can be migrated on different defect free backgrounds, which greatly reducing the difficulty of obtaining defect samples on new backgrounds. The experiment has verified the defect control and defect migration capabilities of the model, and its generated results can effectively expand the training dataset and improve the accuracy of downstream defect detection tasks.
-
Key words:
- Data augmentation /
- dataset expansion /
- defect image generation /
- deep learning
-
表 1 评价指标统计
Table 1 Statistics of evaluation metrics
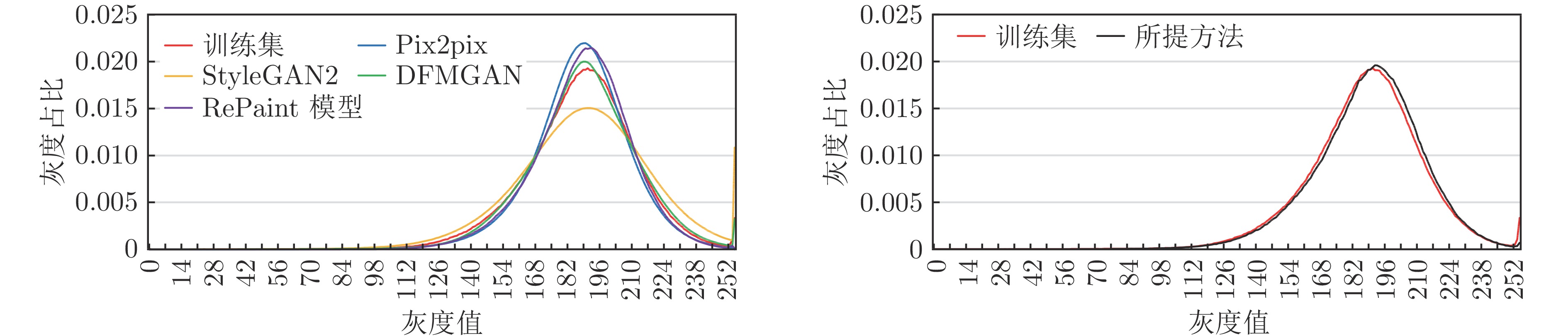
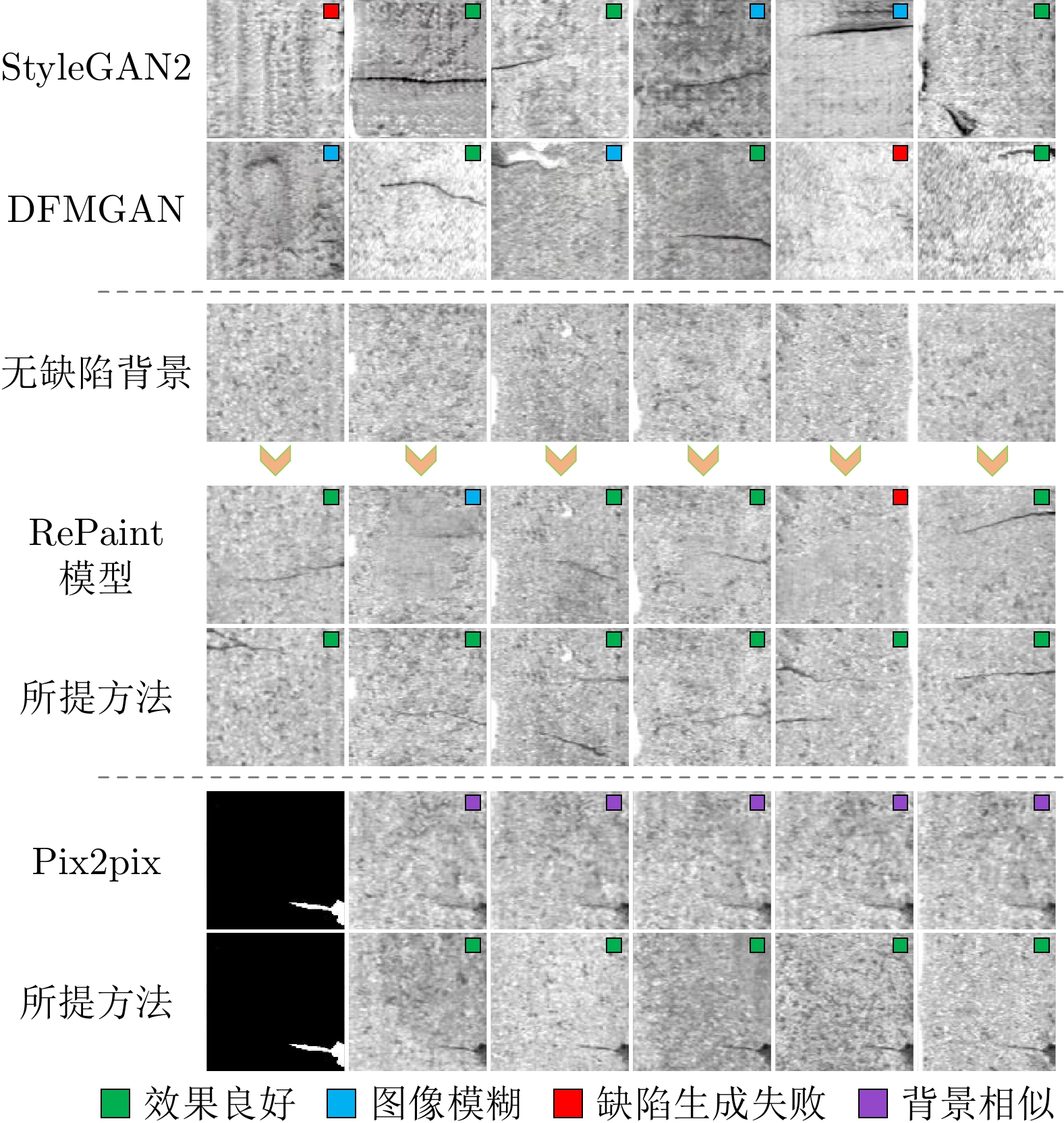
评价指标 Pix2pix StyleGAN2 DFMGAN RePaint模型 所提方法 IS↑ 1.388 1.368 1.301 1.474 1.541 FID↓ 59.056 124.748 96.783 72.750 57.650 KID↓ 0.024 0.098 0.053 0.044 0.020 MS-SSIM↓ 0.189 0.161 0.174 0.187 0.159 PSNR↓ 28.308 28.284 28.357 28.273 28.223 注: 1) RePaint模型使用裂纹掩码生成缺陷效果差, 改为区块掩码; 2) 箭头标识评价指标得分更好的方向. 表 2 分类结果统计(%)
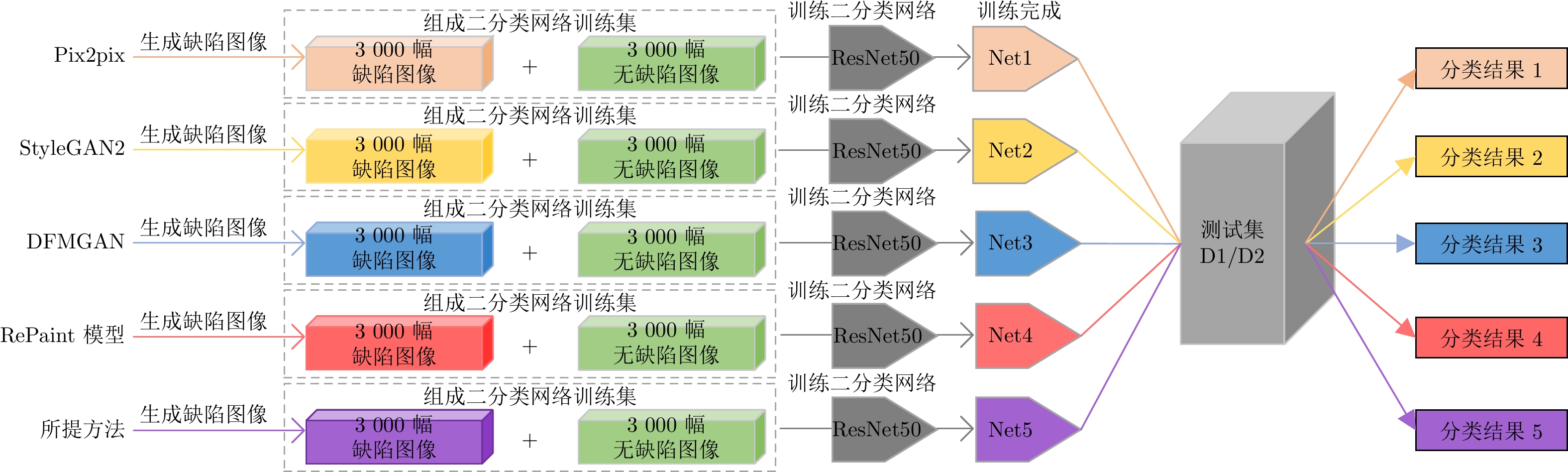
Table 2 Statistics of classification results (%)
测试集 Pix2pix StyleGAN2 DFMGAN RePaint模型 所提方法 缺陷检出率 总正确率 缺陷检出率 总正确率 缺陷检出率 总正确率 缺陷检出率 总正确率 缺陷检出率 总正确率 D1 30.77 65.38 26.92 63.46 7.69 53.85 13.46 54.81 88.46 94.23 D2 54.46 77.07 49.94 74.97 32.26 66.13 45.76 70.99 88.32 93.76 注: RePaint模型使用裂纹掩码生成缺陷效果差, 改为区块掩码. -
[1] 张辉, 张邹铨, 陈煜嵘, 吴天月, 钟杭, 王耀南. 工业铸件缺陷无损检测技术的应用进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(4): 935−956Zhang Hui, Zhang Zou-Quan, Chen Yu-Rong, Wu Tian-Yue, Zhong Hang, Wang Yao-Nan. Application advance and prospect of nondestructive testing technology for industrial casting defects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(4): 935−956 [2] 罗东亮, 蔡雨萱, 杨子豪, 章哲彦, 周瑜, 白翔. 工业缺陷检测深度学习方法综述. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2022, 52(6): 1002−1039 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0336Luo Dong-Liang, Cai Yu-Xuan, Yang Zi-Hao, Zhang Zhe-Yan, Zhou Yu, Bai Xiang. Survey on industrial defect detection with deep learning. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2022, 52(6): 1002−1039 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0336 [3] 陶晓天, 何博侠, 张鹏辉, 田德旭. 基于深度学习的航天密封圈表面缺陷检测. 仪器仪表学报, 2021, 42(1): 199−206Tao Xiao-Tian, He Bo-Xia, Zhang Peng-Hui, Tian De-Xu. Surface defect detection of aerospace sealing rings based on deep learning. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2021, 42(1): 199−206 [4] 田娟秀, 刘国才, 谷珊珊, 鞠忠建, 刘劲光, 顾冬冬. 医学图像分析深度学习方法研究与挑战. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 401−424Tian Juan-Xiu, Liu Guo-Cai, Gu Shan-Shan, Ju Zhong-Jian, Liu Jin-Guang, Gu Dong-Dong. Deep learning in medical image analysis and its challenges. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 401−424 [5] 王国力, 孙宇, 魏本征. 医学图像图深度学习分割算法综述. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(12): 37−50 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2112-0225Wang Guo-Li, Sun Yu, Wei Ben-Zheng. Systematic review on graph deep learning in medical image segmentation. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022, 58(12): 37−50 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2112-0225 [6] 李书林, 冯朝路, 于鲲, 刘鑫, 江鑫, 赵大哲. 基于深度学习的心脏磁共振影像超分辨率前沿进展. 中国图象图形学报, 2022, 27(3): 704−721 doi: 10.11834/j.issn.1006-8961.2022.3.zgtxtxxb-a202203005Li Shu-Lin, Feng Chao-Lu, Yu Kun, Liu Xin, Jiang Xin, Zhao Da-Zhe. Critical review of human cardiac magnetic resonance image super resolution reconstruction based on deep learning method. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2022, 27(3): 704−721 doi: 10.11834/j.issn.1006-8961.2022.3.zgtxtxxb-a202203005 [7] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779−788 [8] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C Y, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 21−37 [9] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137−1149 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [10] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. [11] Santos C F G D, Papa J P. Avoiding overfitting: A survey on regularization methods for convolutional neural networks. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2022, 54(S10): Article No. 20 [12] 陶显, 侯伟, 徐德. 基于深度学习的表面缺陷检测方法综述. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(5): 1017−1034Tao Xian, Hou Wei, Xu De. A survey of surface defect detection methods based on deep learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(5): 1017−1034 [13] Niu S L, Li B, Wang X G, Lin H. Defect image sample generation with GAN for improving defect recognition. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(3): 1611−1622 [14] 伍麟, 郝鸿宇, 宋友. 基于计算机视觉的工业金属表面缺陷检测综述. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(7): 1261−1283Wu Lin, Hao Hong-Yu, Song You. A review of metal surface defect detection based on computer vision. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(7): 1261−1283 [15] Rippel O, Müller M, Merhof D. GAN-based defect synthesis for anomaly detection in fabrics. In: Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA). Vienna, Austria: IEEE, 2020. 534−540 [16] Zhang G J, Cui K W, Hung T Y, Lu S J. Defect-GAN: High-fidelity defect synthesis for automated defect inspection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2021. 2523−2533 [17] Zhang H B, Pan D, Liu J H, Jiang Z H. A novel MAS-GAN-based data synthesis method for object surface defect detection. Neurocomputing, 2022, 499: 106−114 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.05.021 [18] Wang R Y, Hoppe S, Monari E, Huber M F. Defect transfer GAN: Diverse defect synthesis for data augmentation. In: Proceedings of the 33rd British Machine Vision Conference. London, UK: BMVA Press, 2023. Article No. 445 [19] 丁鹏, 卢文壮, 刘杰, 袁志响. 基于生成对抗网络的叶片表面缺陷图像数据增强. 组合机床与自动化加工技术, 2022, (7): 18−21Ding Peng, Lu Wen-Zhuang, Liu Jie, Yuan Zhi-Xiang. Image data augmentation of blade surface defects based on generative adversarial network. Modular Machine Tool and Automatic Manufacturing Technique, 2022, (7): 18−21 [20] Dhariwal P, Nichol A. Diffusion models beat GANs on image synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates Inc., 2021. Article No. 672Dhariwal P, Nichol A. Diffusion models beat GANs on image synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates Inc., 2021. Article No. 672 [21] Carlini N, Hayes J, Nasr M, Jagielski M, Sehwag V, Tramér F, et al. Extracting training data from diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the 32nd USENIX Security Symposium. Anaheim, USA: USENIX Association, 2023. 5253−5270 [22] Jain S, Seth G, Paruthi A, Soni U, Kumar G. Synthetic data augmentation for surface defect detection and classification using deep learning. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2022, 33(4): 1007−1020 doi: 10.1007/s10845-020-01710-x [23] Zhang H Y, Cisse M, Dauphin Y N, Lopez-Paz D. mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada: ICLR, 2018. [24] Zhang L J, Deng Z, Kawaguchi K, Ghorbani A, Zou J. How does mixup help with robustness and generalization? In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Austria: ICLR, 2021.Zhang L J, Deng Z, Kawaguchi K, Ghorbani A, Zou J. How does mixup help with robustness and generalization? In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Austria: ICLR, 2021. [25] Chou H P, Chang S C, Pan J Y, Wei W, Juan D C. Remix: Rebalanced mixup. In: Proceedings of the Computer Vision-ECCV 2020 Workshops. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 95−110 [26] Ren X Y, Lin W Y, Yang X Q, Yu X H, Gao H J. Data augmentation in defect detection of sanitary ceramics in small and non-i.i.d datasets. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(11): 8669−8678 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3152245 [27] Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T, Efros A A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5967−5976 [28] Duan Y X, Hong Y, Niu L, Zhang L Q. Few-shot defect image generation via defect-aware feature manipulation. In: Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Washington, USA: AAAI, 2023. 571−578 [29] Sohl-Dickstein J, Weiss E, Maheswaranathan N, Ganguli S. Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: PMLR, 2015. 2256−2265 [30] Ho J, Jain A, Abbeel P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 574 [31] Ho J, Salimans T. Classifier-free diffusion guidance. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2207.12598, 2022.Ho J, Salimans T. Classifier-free diffusion guidance. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2207.12598, 2022. [32] Saharia C, Ho J, Chan W, Salimans T, Fleet D J, Norouzi M. Image super-resolution via iterative refinement. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 45(4): 4713−4726 [33] Lugmayr A, Danelljan M, Romero A, Yu F, Timofte R, Van Gool L. RePaint: Inpainting using denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 11451−11461 [34] Wang W L, Bao J M, Zhou W G, Chen D D, Chen D, Yuan L, et al. Semantic image synthesis via diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2207.00050, 2022.Wang W L, Bao J M, Zhou W G, Chen D D, Chen D, Yuan L, et al. Semantic image synthesis via diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2207.00050, 2022. [35] Nichol A Q, Dhariwal P, Ramesh A, Shyam P, Mishkin P, Mcgrew B, et al. GLIDE: Towards photorealistic image generation and editing with text-guided diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 16784−16804 [36] Ramesh A, Dhariwal P, Nichol A, Chu C, Chen M. Hierarchical text-conditional image generation with CLIP latents. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2204.06125, 2022.Ramesh A, Dhariwal P, Nichol A, Chu C, Chen M. Hierarchical text-conditional image generation with CLIP latents. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2204.06125, 2022. [37] Rombach R, Blattmann A, Lorenz D, Esser P, Ommer B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 10674−10685 [38] Song Y, Sohl-Dickstein J, Kingma D P, Kumar A, Ermon S, Poole B. Score-based generative modeling through stochastic differential equations. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Austria: ICLR, 2020.Song Y, Sohl-Dickstein J, Kingma D P, Kumar A, Ermon S, Poole B. Score-based generative modeling through stochastic differential equations. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Austria: ICLR, 2020. [39] Tabernik D, Šela S, Skvarč J, Skočaj D. Segmentation-based deep-learning approach for surface-defect detection. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2020, 31(3): 759−776 doi: 10.1007/s10845-019-01476-x [40] Wieler M, Hahn T, Hamprecht F A. Weakly supervised learning for industrial optical inspection [Online], available: https://hci.iwr.uni-heidelberg.de/content/weakly-supervised-learning-industrial-optical-inspection, February 20, 2024 [41] Song K C, Yan Y H. A noise robust method based on completed local binary patterns for hot-rolled steel strip surface defects. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 285: 858−864 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.09.002 [42] Karras T, Laine S, Aittala M, Hellsten J, Lehtinen J, Aila T. Analyzing and improving the image quality of StyleGAN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 8107−8116 [43] Barratt S, Sharma R. A note on the inception score. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.01973, 2018.Barratt S, Sharma R. A note on the inception score. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.01973, 2018. [44] Heusel M, Ramsauer H, Unterthiner T, Nessler B, Hochreiter S. GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 6629−6640 [45] Bińkowski M, Sutherland D J, Arbel M, Gretton A. Demystifying MMD GANs. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada: ICLR, 2018. [46] Wang Z, Simoncelli E P, Bovik A C. Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the 37th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers. Pacific Grove, USA: IEEE, 2003. 1398−1402 [47] Huynh-Thu Q, Ghanbari M. Scope of validity of PSNR in image/video quality assessment. Electronics Letters, 2008, 44(13): 800−801 doi: 10.1049/el:20080522 -





 下载:
下载: