-
摘要: 自适应评判技术已经广泛应用于求解复杂非线性系统的最优控制问题, 但利用其求解离散时间非线性随机系统的无限时域最优控制问题还存在一定局限性. 本文融合自适应评判技术, 建立一种数据驱动的离散随机系统折扣最优调节方法. 首先, 针对宽松假设下的非线性随机系统, 研究带有折扣因子的无限时域最优控制问题. 所提的随机系统 Q-learning 算法能够将初始的容许策略单调不增地优化至最优策略. 基于数据驱动思想, 随机系统 Q-learning 算法在不建立模型的情况下直接利用数据进行策略优化. 其次, 利用执行−评判神经网络方案, 实现了随机系统 Q-learning 算法. 最后, 通过两个基准系统, 验证本文提出的随机系统 Q-learning 算法的有效性.Abstract: Adaptive critic technology has been widely employed to solve the optimal control problems of complicated nonlinear systems, but there are some limitations to solve the infinite-horizon optimal problems of discrete-time nonlinear stochastic systems. In this paper, we establish a data-driven discounted optimal regulation method for discrete-time stochastic systems involving adaptive critic technology. First, we investigate the infinite-horizon optimal problems with the discount factor for stochastic systems under the relaxed assumption. The developed stochastic Q-learning algorithm can optimize an initial admissible policy to the optimal one in a monotonically nonincreasing way. Based on the data-driven idea, the policy optimization of the stochastic Q-learning algorithm is executed without a dynamic model. Then, the stochastic Q-learning algorithm is implemented by utilizing the actor-critic neural networks. Finally, two nonlinear benchmarks are given to demonstrate the overall performance of the developed stochastic Q-learning algorithm.
-
表 1 随机 Q-learning 算法的主要参数
Table 1 Main parameters of the stochastic Q-learning algorithm
算法参数 $\mathcal{Q}$ $\mathcal{R}$ ${\rho}_{\max}$ $\lambda$ $\epsilon$ 基准系统I $2I_2$ 2.0 300 0.97 0.01 基准系统II $0.1I_4$ 0.1 500 0.99 0.01 表 2 球台平衡系统的主要参数
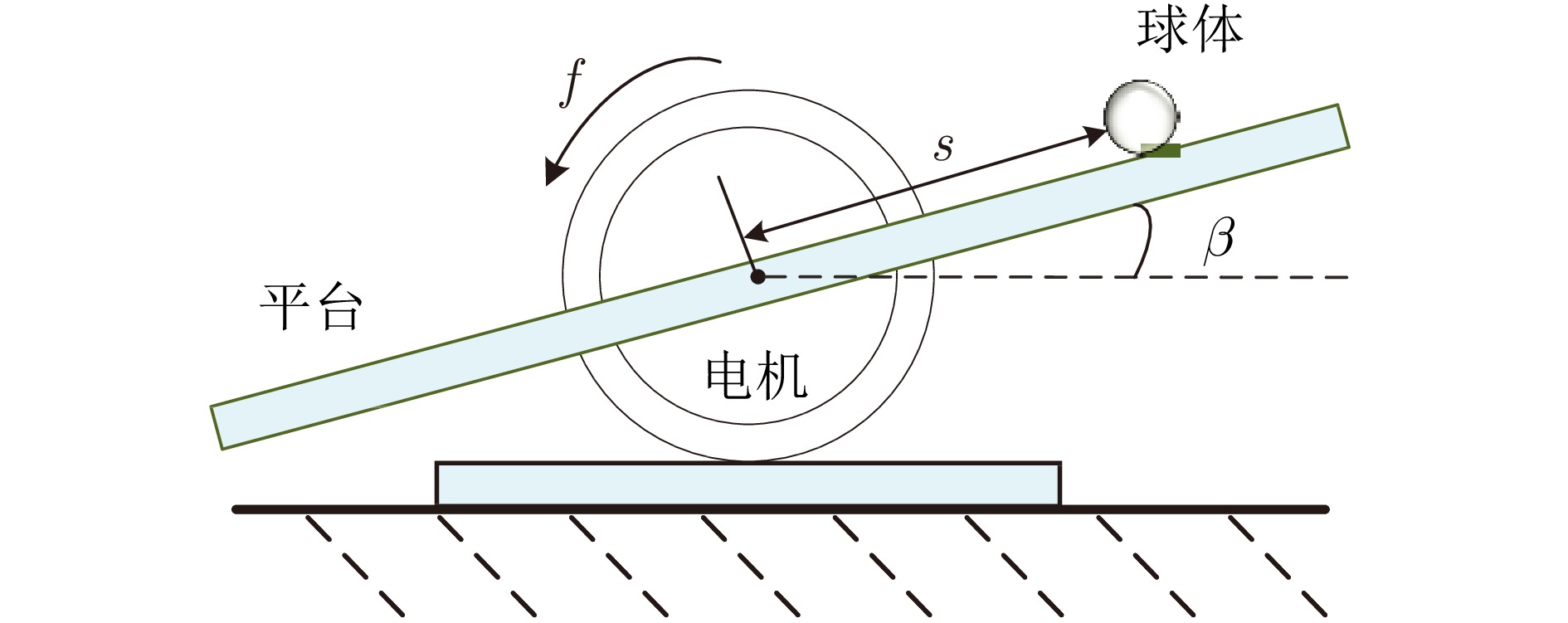
Table 2 Main parameters of the ball-and-beam system
符号及取值 物理意义 $S_t=0.001 \;{\rm{N}}/ {\rm{m}}$ 驱动机械刚度 $L_\omega =0.5\; {\rm{m}}$ 平台半径 $L =0.48 \; {\rm{m}}$ 电机作用半径 $f_c= 1\; {\rm{N_s/ m}}$ 驱动电机的机械摩擦系数 $I_\omega = 0.140\;25 \;{\rm{kg} }\cdot {\rm{m} }^2$ 平台惯性矩 $g = 9.8\; {\rm{m/s}}^2$ 重力加速度 $\varpi =0.016\;2 \;{\rm{kg} }$ 球体质量 $\tau =0.02 \;{\rm{m}}$ 球体滚动半径 $I_b=4.32\times10^{-5} \;{\rm{kg}}\cdot {\rm{m}}^2$ 球体转动惯量 -
[1] Liu D R, Xue S, Zhao B, Luo B, Wei Q L. Adaptive dynamic programming for control: A survey and recent advances. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(1): 142−160 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3042876 [2] Bellman R. Dynamic programming. Science, 1966, 153(3731): 34−37 doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.34 [3] Wang F Y, Zhang H G, Liu D R. Adaptive dynamic programming: An introduction. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2009, 4(2): 39−47 doi: 10.1109/MCI.2009.932261 [4] Prokhorov D V, Wunsch D C. Adaptive critic designs. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1997, 8(5): 997−1007 doi: 10.1109/72.623201 [5] Zhao M M, Wang D, Qiao J F, Ha M M, Ren J. Advanced value iteration for discrete-time intelligent critic control: A survey. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2023, 56(10): 12315−12346 doi: 10.1007/s10462-023-10497-1 [6] Wang D, Gao N, Liu D R, Li J N, Lewis F L. Recent progress in reinforcement learning and adaptive dynamic programming for advanced control applications. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(1): 18−36 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123843 [7] Liu T, Tian B, Ai Y F, Li L, Cao D P, Wang F Y. Parallel reinforcement learning: A framework and case study. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2018, 5(4): 827−835 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2018.7511144 [8] Miao Q H, Lv Y S, Huang M, Wang X, Wang F Y. Parallel learning: Overview and perspective for computational learning across Syn2Real and Sim2Real. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(3): 603−631 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123375 [9] Zhao M M, Wang D, Ha M M, Qiao J F. Evolving and incremental value iteration schemes for nonlinear discrete-time zero-sum games. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(7): 4487−4499 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3198078 [10] 王鼎, 胡凌治, 赵明明, 哈明鸣, 乔俊飞. 未知非线性零和博弈最优跟踪的事件触发控制设计. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(1): 91−101Wang Ding, Hu Ling-Zhi, Zhao Ming-Ming, Ha Ming-Ming, Qiao Jun-Fei. Event-triggered control design for optimal tracking of unknown nonlinear zero-sum games. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 91−101 [11] 王鼎. 一类离散动态系统基于事件的迭代神经控制. 工程科学学报, 2022, 44(3): 411−419Wang Ding. Event-based iterative neural control for a type of discrete dynamic plant. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2022, 44(3): 411−419 [12] Wang D, Hu L Z, Zhao M M, Qiao J F. Dual event-triggered constrained control through adaptive critic for discrete-time zero-sum games. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(3): 1584−1595 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3201671 [13] Wang D, Li X, Zhao M M, Qiao J F. Adaptive critic control design with knowledge transfer for wastewater treatment applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, DOI: 10.1109/TⅡ.2023.3278875 [14] 王鼎, 赵慧玲, 李鑫. 基于多目标粒子群优化的污水处理系统自适应评判控制. 工程科学学报, 2024, 46(5): 908−917Wang Ding, Zhao Hui-Ling, Li Xin. Adaptive critic control for wastewater treatment systems based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2024, 46(5): 908−917 [15] Wu T Y, He S Z, Liu J P, Sun S Q, Liu K, Han Q L, et al. A brief overview of ChatGPT: The history, status quo and potential future development. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(5): 1122−1136 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123618 [16] Luo B, Liu D R, Wu H N, Wang D, Lewis F L. Policy gradient adaptive dynamic programming for data-based optimal control. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(10): 3341−3354 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2623859 [17] Luo B, Yang Y, Liu D R. Policy iteration Q-learning for data-based two-player zero-sum game of linear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(7): 3630−3640 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2970969 [18] Lin M D, Zhao B, Liu D R. Policy gradient adaptive critic designs for model-free optimal tracking control with experience replay. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(6): 3692−3703 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3071968 [19] Su S, Zhu Q Y, Liu J Q, Tang T, Wei Q L, Cao Y. A data-driven iterative learning approach for optimizing the train control strategy. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(7): 7885−7893 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3195888 [20] Wei Q L, Song R Z, Yan P F. Data-driven zero-sum neuro-optimal control for a class of continuous-time unknown nonlinear systems with disturbance using ADP. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(2): 444−458 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2464080 [21] Liang M M, Wang D, Liu D R. Improved value iteration for neural-network-based stochastic optimal control design. Neural Networks, 2020, 124: 280−295 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.01.004 [22] Pang B, Jiang Z P. Reinforcement learning for adaptive optimal stationary control of linear stochastic systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(4): 2383−2390 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3172250 [23] Wei Q L, Zhou T M, Lu J W, Liu Y, Su S, Xiao J. Continuous-time stochastic policy iteration of adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(10): 6375−6387 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3284612 [24] Lee J, Haddad W M, Lanchares M. Finite time stability and optimal finite time stabilization for discrete-time stochastic dynamical systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(7): 3978−3991 [25] Liang M M, Wang D, Liu D R. Neuro-optimal control for discrete stochastic processes via a novel policy iteration algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(11): 3972−3985 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2907991 [26] 王鼎, 赵明明, 哈明鸣, 乔俊飞. 基于折扣广义值迭代的智能最优跟 踪及应用验证. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 182−193Wang Ding, Zhao Ming-Ming, Ha Ming-Ming, Qiao Jun-Fei. Intelligent optimal tracking with application verifications via discounted generalized value iteration. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 182−193 [27] Wang D, Ren J, Ha M M, Qiao J F. System stability of learning-based linear optimal control with general discounted value iteration. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(9): 6504−6514 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3137524 [28] Lincoln B, Rantzer A. Relaxing dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2006, 51(8): 1249−1260 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2006.878720 [29] Ha M M, Wang D, Liu D R. Generalized value iteration for discounted optimal control with stability analysis. Systems & Control Letters, 2021, 147: Article No. 104847 [30] Ha M M, Wang D, Liu D R. Discounted iterative adaptive critic designs with novel stability analysis for tracking control. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2022, 9(7): 1262−1272 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2022.105692 [31] Yang X, Wei Q L. Adaptive critic designs for optimal event-driven control of a CSTR system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(1): 484−493 doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2972383 [32] Heydari A. Revisiting approximate dynamic programming and its convergence. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(12): 2733−2743 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2314612 [33] Ha M M, Wang D, Liu D R. Neural-network-based discounted optimal control via an integrated value iteration with accuracy guarantee. Neural Networks, 2021, 144: 176−186 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2021.08.025 [34] Wang D, Wang J Y, Zhao M M, Xin P, Qiao J F. Adaptive multi-step evaluation design with stability guarantee for discrete-time optimal learning control. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(9): 1797−1809 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123684 [35] Liu D R, Wei Q L. Policy iteration adaptive dynamic programming algorithm for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(3): 621−634 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2281663 [36] Zhong X N, Ni Z, He H B. Gr-GDHP: A new architecture for globalized dual heuristic dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(10): 3318−3330 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2598282 [37] Ha M M, Wang D, Liu D R. A novel value iteration scheme with adjustable convergence rate. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(10): 7430−7442 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3143527 -




 下载:
下载: