Intelligent Perception and Recognition of Blast Furnace Anomalies via Burden Surface Video Image Analysis
-
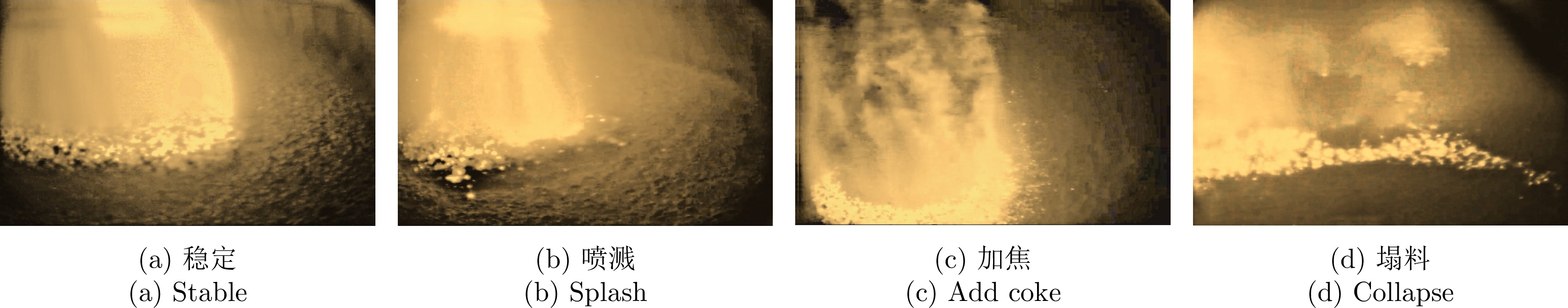
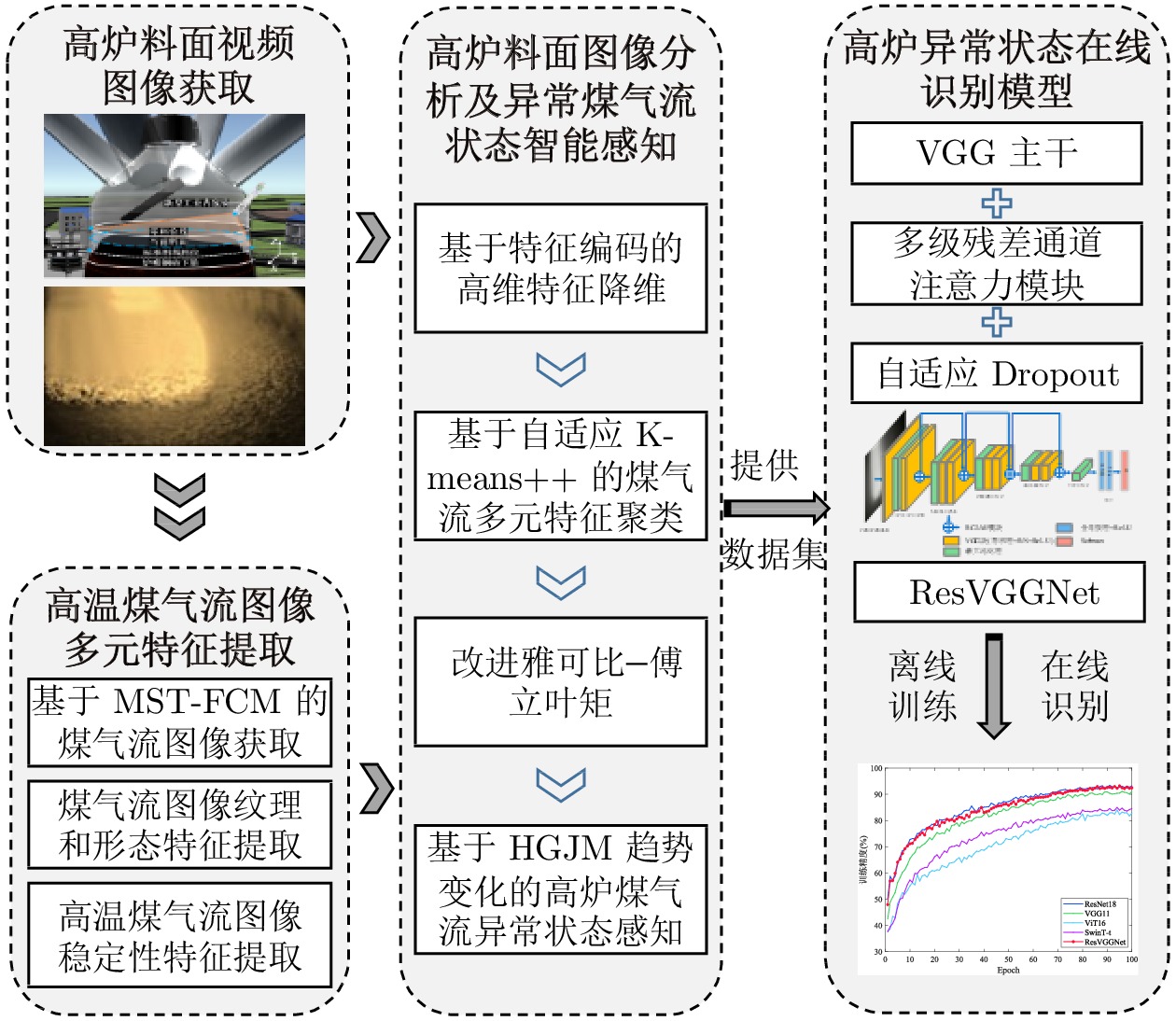
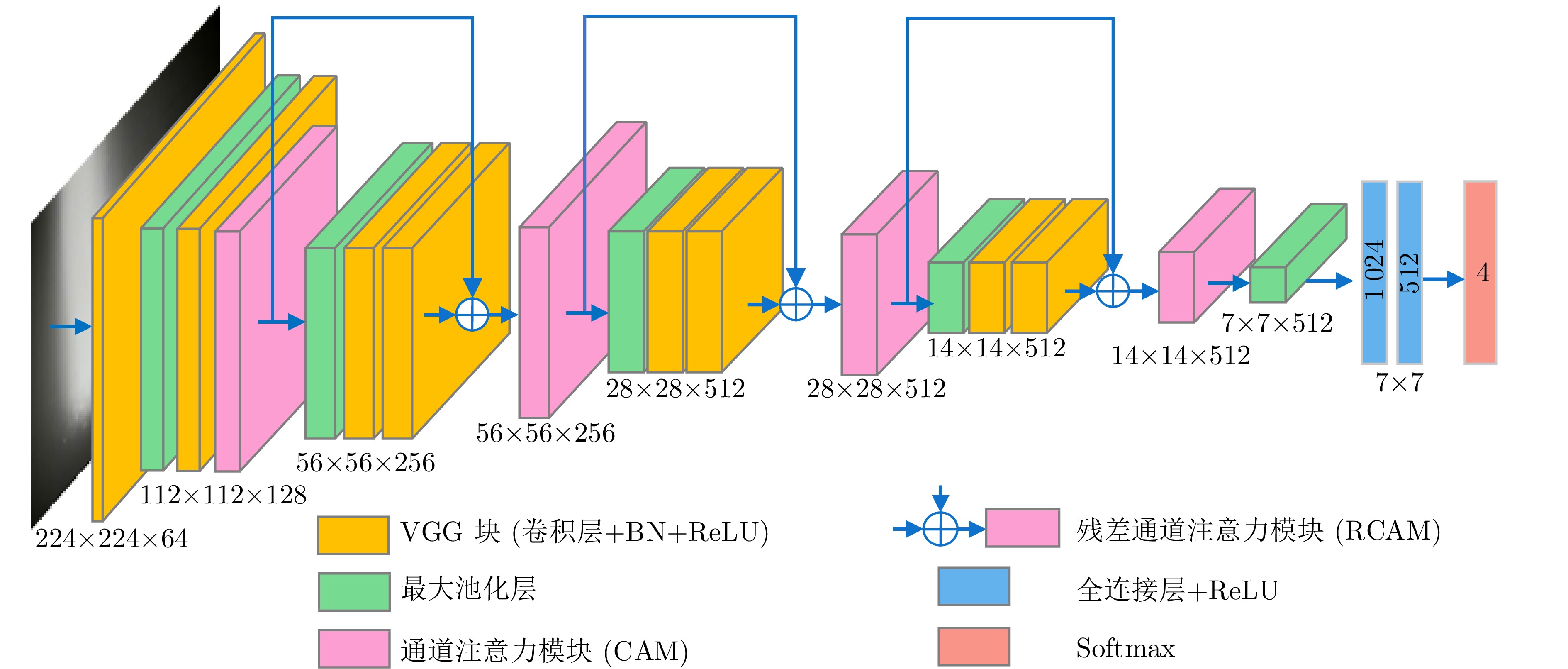
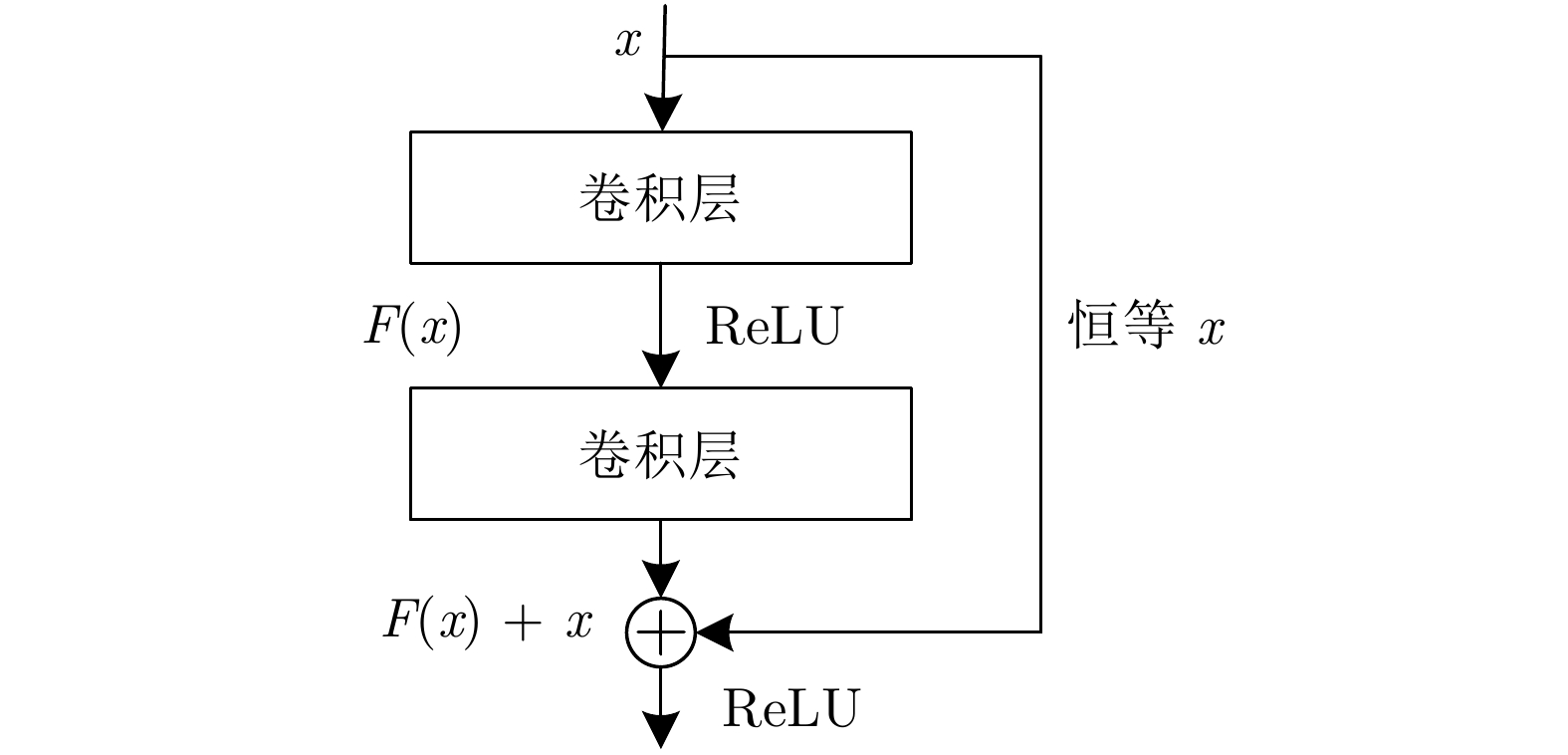
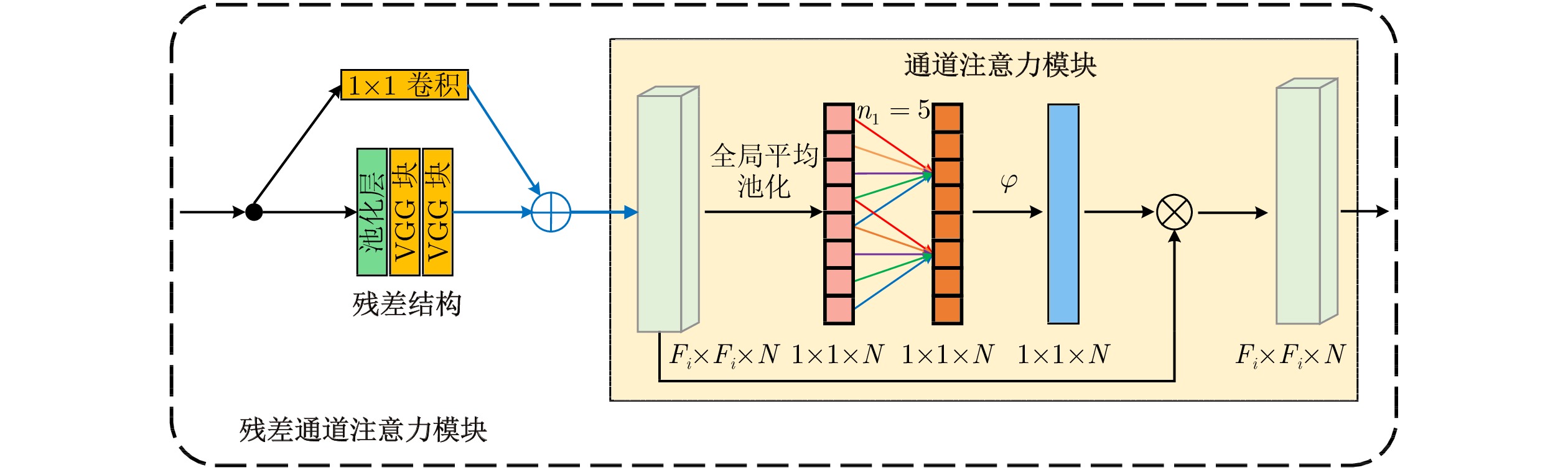
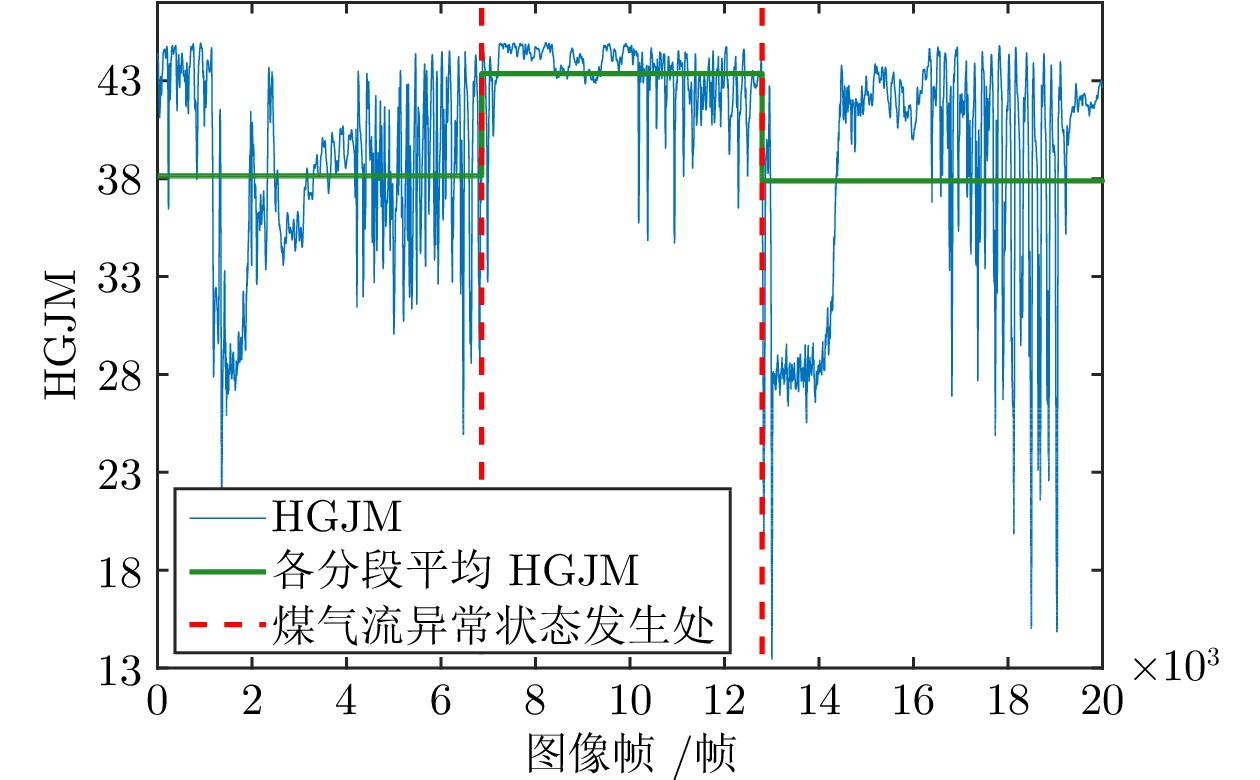
摘要: 智能感知、精准识别高炉(Blast furnace, BF)异常状态对高炉调控优化和稳定运行至关重要, 但高炉内部的黑箱状态致使传统检测方法难以直接感知并准确识别多种高炉异常状态. 新型工业内窥镜可获取大量料面视频图像, 为直接观测炉内运行状态提供了全新的手段. 基于此, 提出一种基于料面视频图像分析的高炉异常状态智能感知与识别方法. 首先, 提出基于多尺度纹理模糊C均值(Multi-scale texture fuzzy C-means, MST-FCM)聚类的高温煤气流区域提取方法, 准确获取煤气流图像, 并提取煤气流图像多元特征; 其次, 提出基于特征编码的高维特征降维方法, 结合自适应K-means++ 算法, 实现煤气流异常状态的粗粒度感知; 在此基础上, 通过改进雅可比−傅立叶矩(Jacobi-Fourier moments, JFM) 提取煤气流图像深层特征变化趋势, 进而提出细粒度煤气流异常状态感知方法; 最后, 基于煤气流异常状态感知结果, 结合料面视频图像, 提出多级残差通道注意力模块(Multi-level residual channel attention module, MRCAM), 建立高炉异常状态识别模型ResVGGNet, 实现高炉煤气流异常、塌料和悬料的精准在线识别. 实验结果表明, 所提方法能准确识别不同的高炉异常状态且识别速度快, 可为高炉平稳运行提供重要保障.
-
关键词:
- 高炉 /
- 料面图像 /
- 高炉异常状态感知 /
- 高炉异常状态识别 /
- 多级残差通道注意力模块
Abstract: The intelligent perception and precise recognition of blast furnace (BF) anomalies are important for BF regulation, optimization and stable operation. However, the opaque nature of the internal workings of the BF makes it difficult for traditional detection methods to directly perceive and accurately recognize various BF anomalies. The novel industrial endoscope can capture a large number of BF burden surface video images, providing a new way for direct observation of the furnace's operational status. Based on this, an intelligent perception and precise recognition method for BF anomalies is proposed via burden surface video image analysis. Firstly, a method for extracting high-temperature gas flow regions based on multi-scale texture fuzzy C-means (MST-FCM) clustering is proposed to accurately obtain gas flow images and extract multi-features of gas flow images. Secondly, a high-dimensional feature dimensionality reduction method based on feature encoding is proposed, which is combined with the adaptive K-means++ algorithm to achieve coarse-grained perception of gas flow anomalies. On this basis, a fine-grained perception method for gas flow anomalies is proposed by refining Jacobi-Fourier moments (JFM) to extract the deep feature change trend of gas flow images. Finally, based on the perception results of gas flow anomalies, and combined with BF video images, a multi-level residual channel attention module (MRCAM) is put forward and the BF anomalies recognition model ResVGGNet is established. This model achieves precise and online recognition of gas flow anomalies, collapsing and hanging burden surface in the BF. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can accurately recognize different BF anomalies with a fast recognition speed, providing crucial assurance for the smooth operation of the BF. -
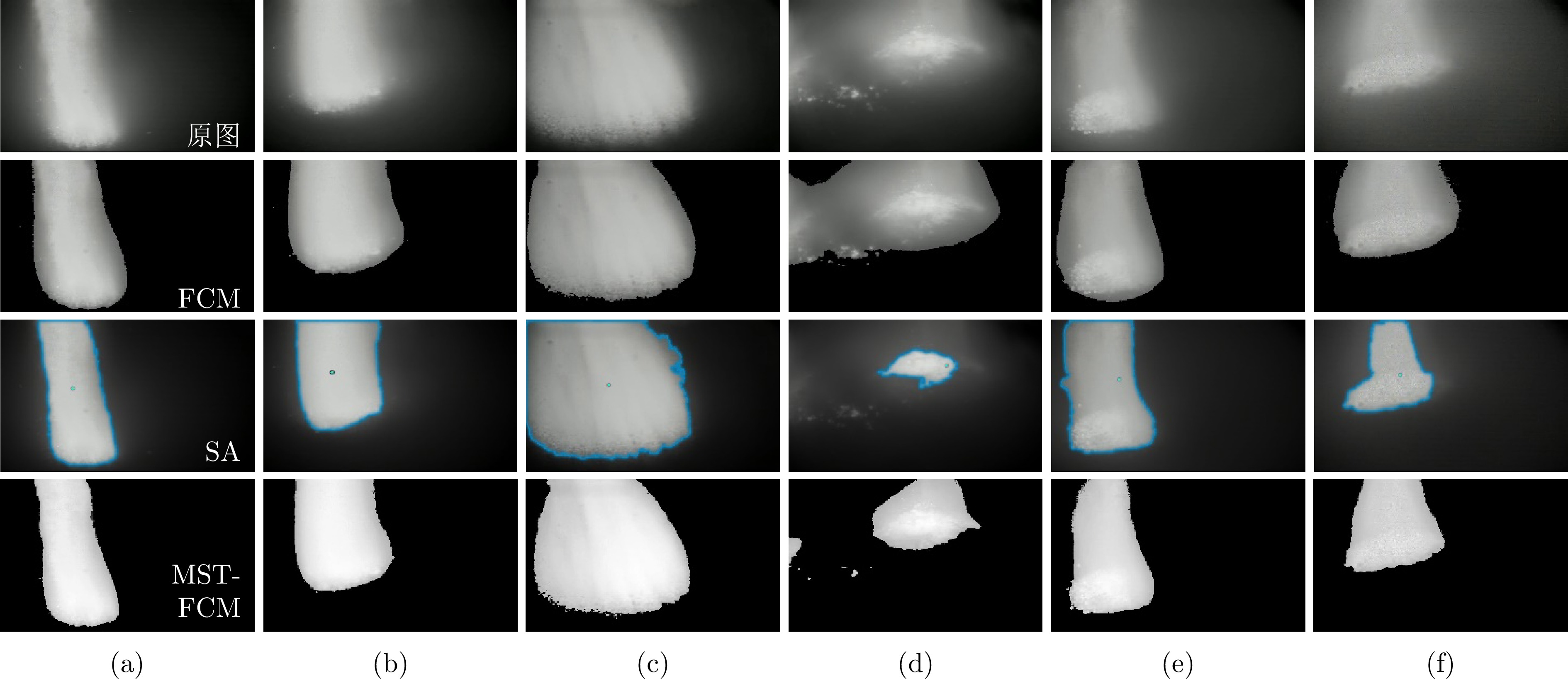
图 3 不同炉况下不同方法获取高温煤气流图像对比结果 ((a) 稳定1; (b) 稳定2; (c) 煤气流状态异常; (d) 悬料1; (e) 悬料2; (f) 高料位)
Fig. 3 Comparison results of high temperature gas flow images acquired by different methods under different BF conditions ((a) Stable 1; (b) Stable 2; (c) Abnormal gas flow status; (d) Hanging 1; (e) Hanging 2; (f) High stockline)
表 1 高炉料面图像数据集
Table 1 Dataset of BF burden surface images
高炉状态 塌料 煤气流异常 悬料 正常 训练集 640 1920 960 1920 测试集 160 480 240 480 表 2 不同分类网络在高炉料面图像数据集下的识别结果
Table 2 Recognition results of different classification networks under BF burden surface image dataset
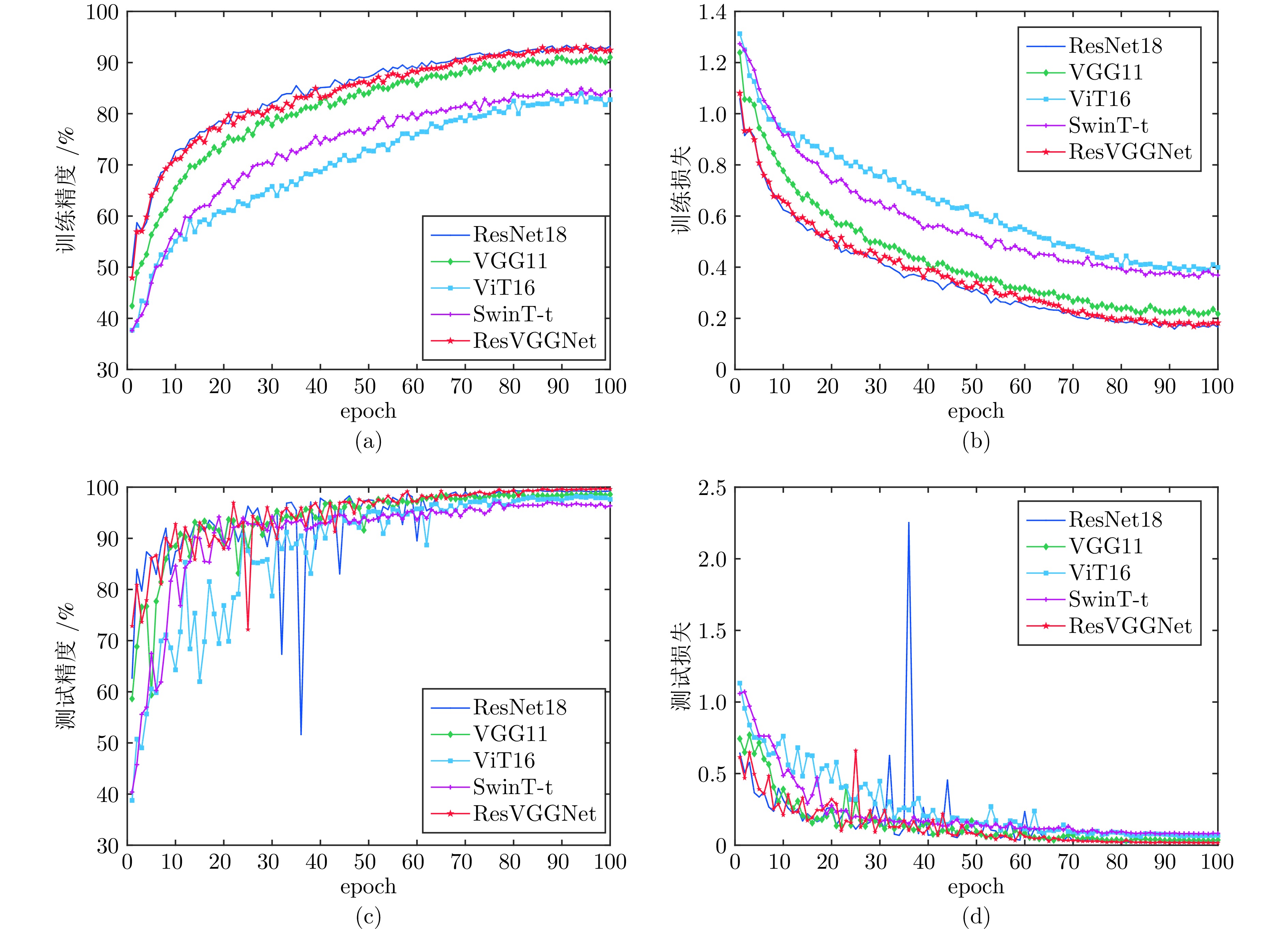
网络名称 异常状态检测率↑ 误报率↓ 速度(帧/s)↑ 塌料 煤气流异常 悬料 正常状态 ResNet18 100.00% 98.54% 99.58% 0.42% 42.94 VGG11 100.00% 98.33% 99.58% 2.29% 35.29 ViT16 100.00% 99.38% $\underline{98.75\%}$ 1.67% 23.32 SwinT-t 100.00% $\underline{93.96\%}$ 99.58% $\underline{3.96\%}$ $\underline{8.98}$ ResVGGNet 100.00% 99.30% 99.58% 0.21% 60.26 注: ↑ 表示指标越大越好, ↓ 表示指标越小越好, 粗体表示指标最优, 下划线表示指标最差. 表 3 不同高炉异常状态识别方法对比
Table 3 Comparison among different BF anomaly recognition methods
类型 方法名称 悬料状态 正常状态 检测率↑ 误报率↓ 多元统计分析 CA $\underline{71.20\%}$ 4.60% MWPCA 96.45% 3.76% SFICVA 89.50% 3.00% L-DBKSSA 100.00% 1.24% A-DiASSA 92.80% 1.40% 深度学习 DSKL-SVM 100.00% $\underline{17.00\%}$ SD-DAE 93.77% 10.40% 料面图像法 所提方法 99.58% 0.21% 注: ↑ 表示指标越大越好, ↓ 表示指标越小越好, 粗体表示指标最优, 斜体表示指标第二优, 下划线表示指标最差. -
[1] Liu J S, Jiang Z H, Gui W H, Chen Z W. A novel particle size detection system based on RGB-laser fusion segmentation with feature dual-recalibration for blast furnace materials. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(10): 10690−10699 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3219054 [2] Zhu J L, Gui W H, Chen Z P, Jiang Z H. A novel non-contact and real-time blast furnace stockline detection method based on burden surface video streams. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: Article No. 4502213 [3] 周平, 刘记平, 梁梦圆, 张瑞垚. 基于KPLS 鲁棒重构误差的高炉燃料比监测与异常识别. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(7): 1661−1671Zhou Ping, Liu Ji-Ping, Liang Meng-Yuan, Zhang Rui-Yao. KPLS robust reconstruction error-based monitoring and anomaly identification of fuel ratio in blast furnace ironmaking. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(7): 1661−1671 [4] Jiang K, Jiang Z H, Xie Y F, Pan D, Gui W H. Abnormality monitoring in the blast furnace ironmaking process based on stacked dynamic target-driven denoising autoencoders. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(3): 1854−1863 doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3084911 [5] Takatani K, Iwanaga Y. Fundamental study on thermal degradation of coke during rapid heating. Tetsu-to-Hagane, 1986, 72(2): 189−194 doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane1955.72.2_189 [6] 李骏峰. 高炉炉体热流强度与炉况顺行的研究 [硕士学位论文], 昆明理工大学, 中国, 2014.Li Jun-Feng. Study on Heat Flux Intensity of Blast Furnace Body and Smooth Operation of Blast Furnace Condition [Master thesis], Kunming University of Science and Technology, China, 2014. [7] Zhou P, Li H L, Shi P Y, Zhou C Q. Simulation of the transfer process in the blast furnace shaft with layered burden. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 95: 296−302 doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.11.004 [8] 陈建华, 徐红阳. “高炉专家系统”应用现状和发展趋势. 现代冶金, 2012, 40(3): 6−10Chen Jian-Hua, Xu Hong-Yang. Application status and development trend of “blast furnace expert system”. Modern Metallurgy, 2012, 40(3): 6−10 [9] Dong Y N, Qin S J. A novel dynamic PCA algorithm for dynamic data modeling and process monitoring. Journal of Process Control, 2018, 67: 1−11 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2017.05.002 [10] Zhou P, Zhang R Y, Xie J, Liu J P, Wang H, Chai T Y. Data-driven monitoring and diagnosing of abnormal furnace conditions in blast furnace ironmaking: An integrated PCA-ICA method. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(1): 622−631 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2967708 [11] Chen Q, Kruger U, Leung A Y T. Cointegration testing method for monitoring nonstationary processes. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(7): 3533−3543 [12] Lou S W, Wu P, Yang C J, Xu Y H. Structured fault information-aided canonical variate analysis model for dynamic process monitoring. Journal of Process Control, 2023, 124: 54−69 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2023.01.011 [13] 赵明. 基于神经网络的高炉炉况诊断与预报研究 [硕士学位论文], 东北大学, 中国, 2010.Zhao Ming. Study on Diagnose and Forecast of Blast Furnace Condition Based on Neural Network [Master thesis], Northeastern University, China, 2010. [14] Gao C H, Jian L, Luo S H. Modeling of the thermal state change of blast furnace hearth with support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(2): 1134−1145 [15] Luo S H, Dai Z A, Chen T X, Chen H Y, Jian L. A weighted SVM ensemble predictor based on AdaBoost for blast furnace ironmaking process. Applied Intelligence, 2020, 50: 1997−2008 doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-01662-y [16] Li J P, Hua C C, Yang Y N, Guan X P. Bayesian block structure sparse based T-S fuzzy modeling for dynamic prediction of hot metal silicon content in the blast furnace. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(6): 4933−4942 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2772141 [17] 赵辉, 赵德涛, 岳有军, 王红君. 基于深度置信网络的高炉炉况故障分类方法的研究. 铸造技术, 2018, 39(5): 1028−1032Zhao Hui, Zhao De-Tao, Yue You-Jun, Wang Hong-Jun. Research on fault classification of blast furnace condition based on deep belief network. Foundry Technology, 2018, 39(5): 1028−1032 [18] Lou S W, Yang C J, Wu P, Kong L Y, Xu Y H. Fault diagnosis of blast furnace iron-making process with a novel deep stationary kernel learning support vector machine approach. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: Article No. 3521913 [19] Han Y H, Li Q, Wang C, Zhao Q. A novel knowledge enhanced graph neural networks for fault diagnosis with application to blast furnace process safety. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 166: 143−157 doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.08.014 [20] Lou S W, Yang C J, Wu P. A local dynamic broad kernel stationary subspace analysis for monitoring blast furnace ironmaking process. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(4): 5945−5955 [21] Lou S W, Yang C J, Zhu X Z, Zhang H W, Wu P. Adaptive dynamic inferential analytic stationary subspace analysis: A novel method for fault detection in blast furnace ironmaking process. Information Sciences, 2023, 642: Article No. 119176 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.119176 [22] Shi L, Wen Y B, Zhao G S, Yu T. Recognition of blast furnace gas flow center distribution based on infrared image processing. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2016, 23(3): 203−209 doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30035-8 [23] Pan D, Jiang Z H, Chen Z P, Jiang K, Gui W H. Compensation method for molten iron temperature measurement based on heterogeneous features of infrared thermal images. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(11): 7056−7066 doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2972332 [24] He L, Jiang Z H, Xie Y F, Chen Z P, Gui W H. Velocity measurement of blast furnace molten iron based on mixed morphological features of boundary pixel sets. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: Article No. 5018312 [25] He L, Jiang Z H, Xie Y F, Gui W H, Chen Z P. Mass flow measurement of molten iron from blast furnace, based on trusted region stacking using single high-speed camera. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: Article No. 5013011 [26] Li Q, Wang Z J, Wang S, Li M M, Lei H, Zou Z S. A deep learning-based diagnosis model driven by tuyere images big data for iron-making blast furnaces. Steel Research International, 2022, 93(8): Article No. 2100826 doi: 10.1002/srin.202100826 [27] Yi Z H, Jiang Z H, Huang J C, Chen X F, Gui W H. Optimization method of the installation direction of industrial endoscopes for increasing the imaged burden surface area in blast furnaces. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(11): 7729−7740 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3151747 [28] Xu T X, Chen Z P, Jiang Z H, Huang J C, Gui W H. A real-time 3D measurement system for the blast furnace burden surface using high-temperature industrial endoscope. Sensors, 2020, 20(3): Article No. 869 doi: 10.3390/s20030869 [29] 赵志坚, 佘雪峰, 赵奕喆, 刘燕军, 王艾军, 李丽红, 等. 高炉料面结构对煤气流分布影响的模拟. 材料与冶金学报, 2023, 22(1): 38−44Zhao Zhi-Jian, She Xue-Feng, Zhao Yi-Zhe, Liu Yan-Jun, Wang Ai-Jun, Li Li-Long, et al. Numerical simulation study on the influence of burden profile on gas distribution in blast furnace. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2023, 22(1): 38−44 [30] 郭恒光, 朱默, 赵亮. 基于多尺度方向分解的纹理特征提取方法研究. 计算技术与自动化, 2021, 40(4): 102−107Guo Heng-Guang, Zhu Mo, Zhao Liang. Texture feature extraction method based on multiscale orientation decomposition. Computing Technology and Automation, 2021, 40(4): 102−107 [31] Guo W H, Xu G X, Liu B D, Wang Y J. Hyperspectral image classification using CNN-enhanced multi-level Haar wavelet features fusion network. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: Article No. 6008805 [32] Shi Z H, Wu D R, Guo C F, Zhao C M, Cui Y Q, Wang F Y. FCM-RDpA: TSK fuzzy regression model construction using fuzzy C-means clustering, regularization, DropRule, and Powerball AdaBelief. Information Sciences, 2021, 574: 490−504 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.05.084 [33] Kirillov A, Mintun E, Ravi N, Mao H Z, Rolland C, Gustafson L, et al. Segment anything. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2304.02643, 2023. [34] 朱叶, 申铉京, 陈海鹏. 基于彩色LBP的隐蔽性复制−粘贴篡改盲鉴别算法. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(3): 390−397Zhu Ye, Shen Xuan-Jing, Chen Hai-Peng. Covert copy-move forgery detection based on color LBP. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 390−397 [35] Hosny K M, Darwish M M, Aboelenen T. Novel fractional-order generic Jacobi-Fourier moments for image analysis. Signal Processing, 2020, 172: Article No. 107545 [36] 廖陆峰, 李思坤, 王向朝. 基于预训练VGG11模型的光刻坏点检测方法. 光学学报, 2023, 43(3): 140−149Liao Lu-Feng, Li Si-Kun, Wang Xiang-Chao. Bad spot detection method of lithography based on pre-trained VGG11 model. Journal of Optics, 2023, 43(3): 140−149 [37] Kakarwal S, Paithane P. Automatic pancreas segmentation using ResNet-18 deep learning approach. System Research and Information Technologies, DOI: https://doi.org/10.20535/SRIT.2308-8893.2022.2.08 [38] Zhang T, Qi G J, Xiao B, Wang J D. Interleaved group convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4383−4392 [39] Mao X F, Qi G G, Chen Y F, Li X D, Duan R J, Ye S K, et al. Towards robust vision Transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 12032−12041 [40] Liu Z, Lin Y T, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y X, Zhang Z, et al. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical vision Transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 9992−10002 [41] Wang X, Kruger U, Irwin G W. Process monitoring approach using fast moving window PCA. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2005, 44(15): 5691−5702 doi: 10.1021/ie048873f -




 下载:
下载: