Observer-based Prescribed Performance Bipartite Consensus for Human-in-the-loop Multi-manipulator Systems
-
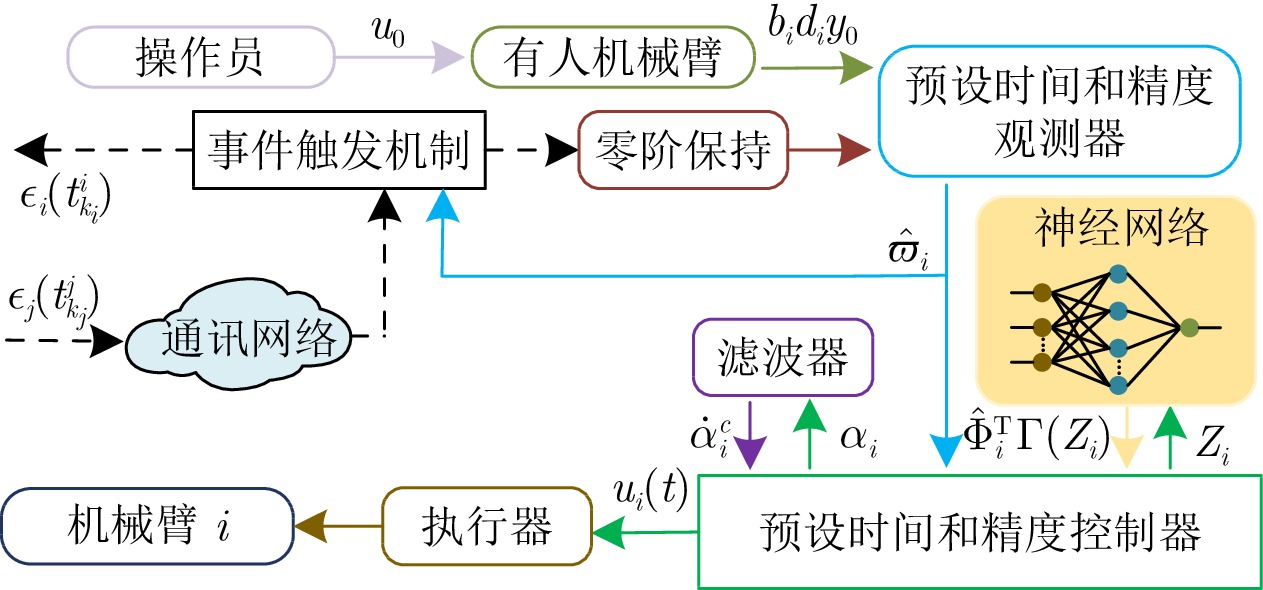
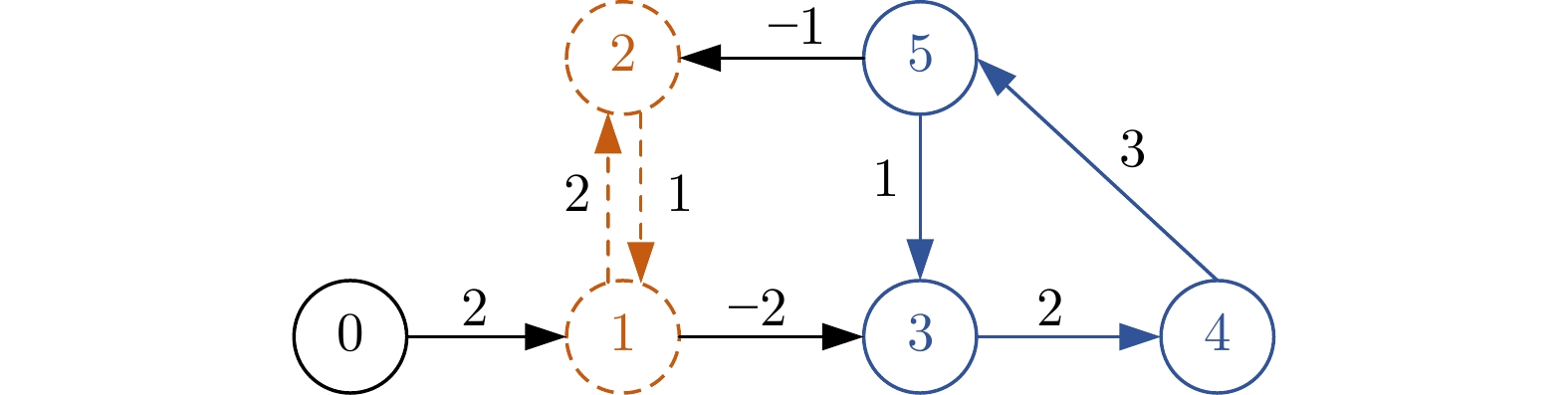
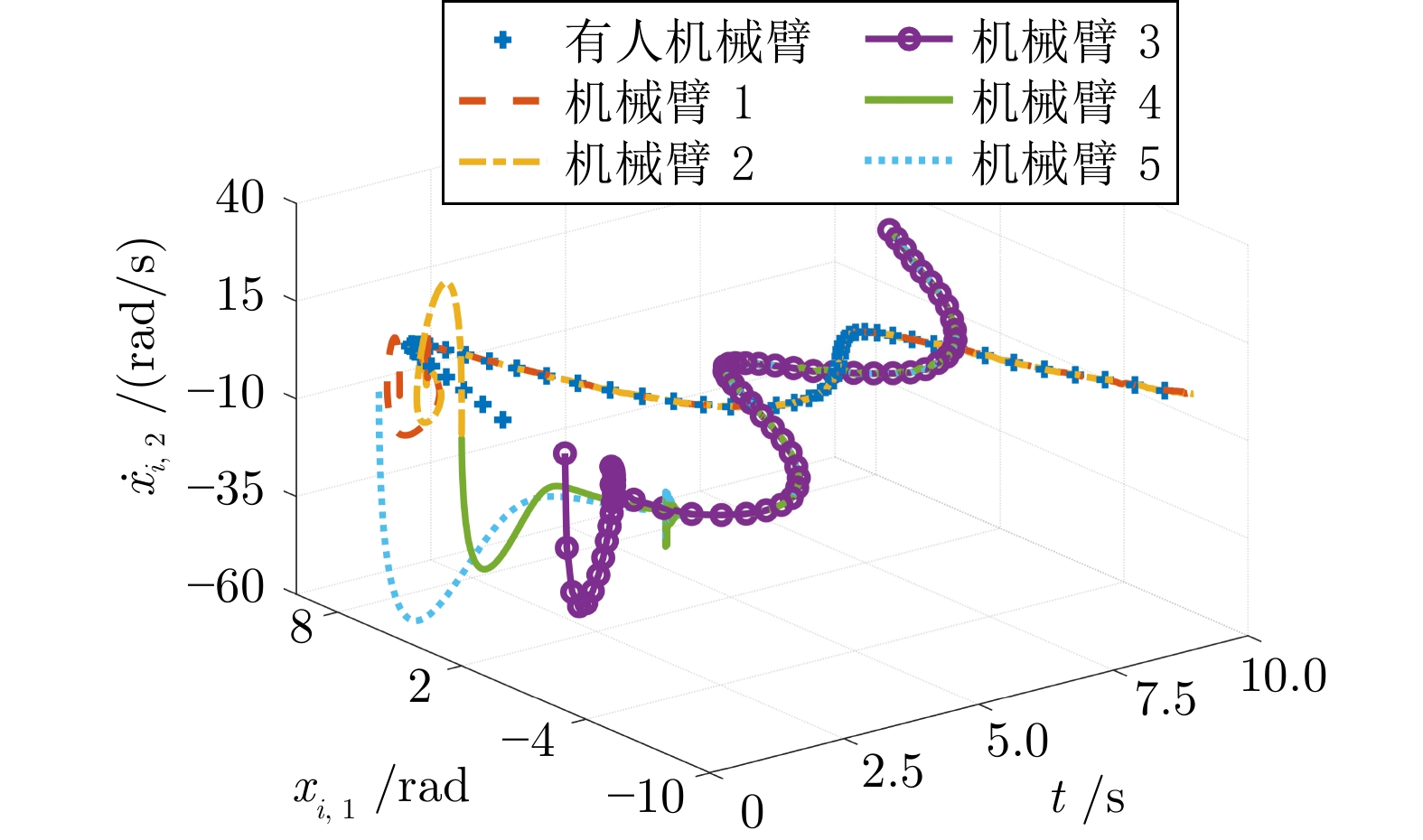
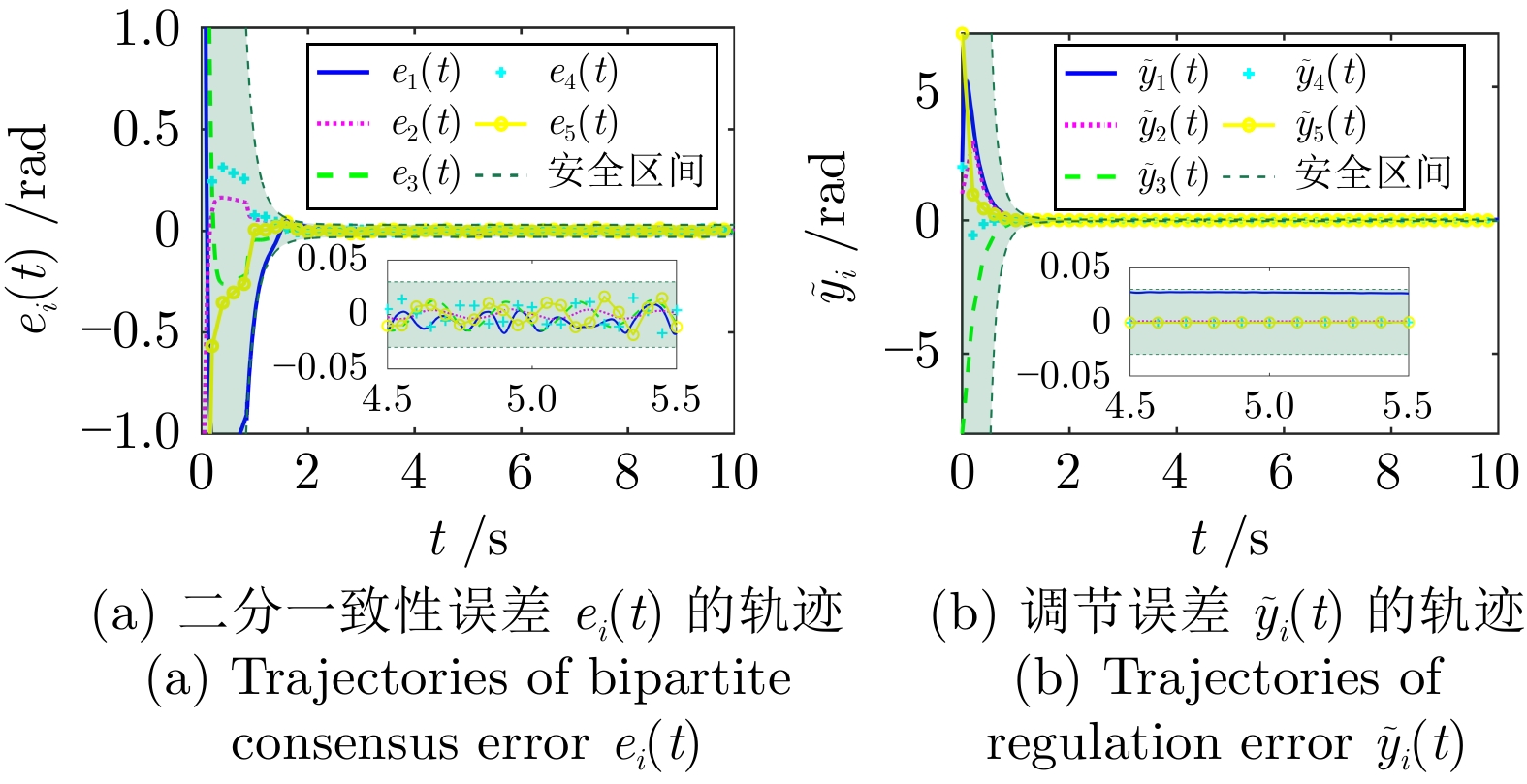
摘要: 研究通讯拓扑为符号有向图的人在环多机械臂系统的预设性能二分一致性跟踪控制问题. 为在预设时间内收敛到预设精度, 提出一种基于观测器的预设性能控制策略. 首先, 设计预设时间和精度的观测器以估计领导者的输出信息, 通过合作/竞争信息交互实现观测器输出的二分一致性. 该观测器不需要领导机械臂的输入信息及输出信息的高阶导数, 并通过无芝诺行为的事件触发机制降低不同机械臂间的通讯负担. 其次, 通过反步法及误差转化法将有约束的机械臂输出跟踪问题转化为无约束的误差系统稳定性问题, 进而基于观测器输出设计机械臂的输出调节控制器. 值得一提的是, 设计的控制策略不需要系统初始状态的先验知识且避免了预设时刻控制增益无穷大的现象, 增强了系统的可靠性. 最后, 仿真结果表明所提控制策略的可行性及优越性.Abstract: This paper investigates the problem of prescribed performance bipartite consensus tracking control of a class of human-in-the-loop multi-manipulator systems with communication topology represented by a signed directed graph. In order to converge to a prescribed accuracy within a prescribed time, an observer-based prescribed performance control strategy is proposed. First, a prescribed-time and prescribed-accuracy observer is designed to estimate the leader's output information. Meanwhile, the bipartite consensus of observer outputs is achieved through cooperation/competition information exchange. Notably, the designed observer does not require inputs and higher-order derivatives of outputs of the leader manipulator. In addition, an event-triggered mechanism without Zeno behavior is adopted to reduce the communication burden among different manipulators. Second, the constrained output tracking problem for manipulator systems is transformed into an unconstrained stability problem for error systems by using backstepping and error transformation techniques. Subsequently, an output regulation controller for manipulator systems is designed based on observer outputs. It is worth mentioning that the proposed control strategy does not necessitate prior knowledge of the system's initial states and avoids the issue of infinite control gains at prescribed time, thereby enhancing the system's reliability. Finally, simulation results demonstrate the feasibility and superiority of the proposed control strategy.
-
表 1 手势与领导机械臂动作的对应关系
Table 1 The corresponding relationship between the gesture and the action of the leader manipulator
手势 动作 $u_0$ 逆时针挥动 逆时针转动 $u_0=\Im_g\;{\rm{tanh}}(v_g)$ 顺时针挥动 顺时针转动 $u_0=-\Im_g\;{\rm{tanh}}(v_g)$ 注: $\Im_g>0$ 和$v_g>0$分别为放大系数及经过预处理的手势挥动速度. 表 2 预设性能反步控制器
Table 2 Prescribed performance backstepping controller
虚拟控制器 $\alpha_{i}=-\dfrac{\kappa_{i,\;2}+\varphi_{i,\;1}}{\kappa_{i,\;1}}+v_i$ (T2.1) $\kappa_{i,\;1}=\left\{\begin{aligned} &\dfrac{1}{h(\xi_i)}-\dfrac{4\delta_i q}{l_{2i}h^2(\xi_i)}(\dfrac{\xi_i}{l_{2i}}-1)^{2q-1}\tilde{y}_{i}^2>0,\; \\ &\qquad \qquad 0<\xi_i< l_{2i}\\ &1,\;\qquad \;\;\xi_i\ge l_{2i} \end{aligned}\right.$ $\kappa_{i,\;2}=\left\{\begin{aligned} &\dfrac{4\delta_{i}q}{l_{2i}h^2(\xi_i)}(\dfrac{\xi_i}{l_{2i}}-1)^{2q-1}\beta\dot{\beta}\tilde{y}_{i},&&0<\xi_{i}< l_{2i} \\&0,&& \xi_i\ge l_{2i} \end{aligned}\right.$ 控制器 $u_{i}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\varphi_{i,\;2}-\kappa_{i,\;1}\varphi_{i,\;1}-\hat{\Phi}_{i}^{\rm T}\Gamma(Z_{i})+\dot{\alpha}^c_{i}$ (T2.2) $\dot{\hat{\Phi}}_{i}=-r_{i,\;1}\hat{\Phi}_{i}+r_{i,\;2}\varphi_{i,\;2}\Gamma(Z_{i})$ (T2.3) 其中, $r_{i,\;1}$和$r_{i,\;2}$为正常数, $Z_{i}=[x_{i,\;1},\;x_{i,\;2}]^{\rm T}$. 表 3 控制器参数
Table 3 Parameters of the controllers
参数 值 参数 值 参数 值 $c_1$ 20 $c_2$ 15 $o_1$ $[0.8,\; 0.5]^{\rm T}$ $l_{1i}$ 2.100 $l_{2i}$ 1.500 $o_2$ $[2.8,\; 2.5]^{\rm T}$ $r_{i,\;1}$ 0.001 $r_{i,\;2}$ 0.500 $o_3$ $[1.1,\; 1.5]^{\rm T}$ $b_i$ 5 $c_3$ 0.001 $\pi_1$ $1.5$ $\psi_j$ 3 $\nu_i$ 0.001 $\pi_2$ $3.0$ $\delta_i$ 140 $M_1$ 3 $\pi_3$ $2.0$ -
[1] Mattila J, Koivumäki J, Caldwell D G, Semini C. A survey on control of hydraulic robotic manipulators with projection to future trends. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(2): 669−680 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2668604 [2] Zhai J Y, Xu G. A novel non-singular terminal sliding mode trajectory tracking control for robotic manipulators. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2021, 68(1): 391−395 [3] He W, Ouyang Y C, Hong J. Vibration control of a flexible robotic manipulator in the presence of input deadzone. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13(1): 48−59 doi: 10.1109/TII.2016.2608739 [4] Ning B D, Han Q L, Zuo Z Y. Bipartite consensus tracking for second-order multiagent systems: A time-varying function-based preset-time approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(6): 2739−2745 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3008125 [5] Guo H Z, Chen M, Jiang Y H, Lungu M. Distributed adaptive human-in-the-loop event-triggered formation control for QUAVs with quantized communication. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(6): 7572−7582 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3211508 [6] Cao Y C, Yu W W, Ren W, Chen G R. An overview of recent progress in the study of distributed multi-agent coordination. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(1): 427−438 doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2219061 [7] Liu P M, Guo X G, Wang J L, Xie X P, Yang F W. Fully distributed hierarchical ET intrusion-and fault-tolerant group control for MASs with application to robotic manipulators. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2024, 21 (3): 2868−2881 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2023.3270489 [8] 徐君, 张国良, 曾静, 孙巧, 羊帆. 具有时延和切换拓扑的高阶离散时间多智能体系统鲁棒保性能一致性. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(2): 360−373Xu Jun, Zhang Guo-Liang, Zeng Jing, Sun Qiao, Yang Fan. Robust guaranteed consensus for high-order discrete-time multi-agent systems with switching topologies and time delay. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(2): 360−373 [9] Guo X G, Zhang D Y, Wang J L, Ahn C K. Adaptive memory event-triggered observer-based control for nonlinear multi-agent systems under DoS attacks. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2021, 8(10): 1644−1656 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2021.1004132 [10] Chai J Y, Lu Q, Tao X D, Peng D L, Zhang B T. Dynamic event-triggered fixed-time consensus control and its applications to magnetic map construction. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(10): 2000−2013 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123444 [11] 郑维, 张志明, 刘和鑫, 张明泉, 孙富春. 基于线性变换的领导−跟随多智能体系统动态反馈均方一致性控制. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(10): 2474−2485Zheng Wei, Zhang Zhi-Ming, Liu He-Xin, Zhang Ming-Quan, Sun Fu-Chun. Dynamic feedback mean square consensus control based on linear transformation for leader-follower multi-agent systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(10): 2474−2485 [12] Lin G H, Li H Y, Ma H, Yao D Y, Lu R Q. Human-in-the-loop consensus control for nonlinear multi-agent systems with actuator faults. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2022, 9(1): 111−122 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003596 [13] Zhang Y F, Wu Z G, Shi P. Resilient event-/self-triggering leader-following consensus control of multiagent systems against DoS attacks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(4): 5925−5934 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3187747 [14] Zhao G L, Hua C C. Leaderless and leader-following bipartite consensus of multiagent systems with sampled and delayed information. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(5): 2220−2233 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3106015 [15] 马小陆, 谭毅波, 梅宏. 符号图下含扰动的多智能体系统预定时间二分一致性. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(5): 1517−1526Ma Xiao-Lu, Tan Yi-Bo, Mei Hong. Predefined-time bipartite consensus of multi-agent systems with disturbances under signed graph. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(5): 1517−1526 [16] Zhao G L, Cui H L, Hua C C. Hybrid event-triggered bipartite consensus control of multiagent systems and application to satellite formation. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(3): 1760−1771 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2022.3185643 [17] 陈世明, 姜根兰, 张正. 通信受限的MAS二分实用一致性. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(5): 1318−1326Chen Shi-Ming, Jiang Gen-Lan, Zhang Zheng. Bipartite practical consensus control of multi-agent systems with communication constraints. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(5): 1318−1326 [18] Cai Y L, Zhang H G, Duan J, Zhang J. Distributed bipartite consensus of linear multiagent systems based on event-triggered output feedback control scheme. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(11): 6743−6756 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.2964394 [19] Wang X J, Niu B, Zhai L, Kong J, Wang X M. A novel distributed bipartite consensus control of nonlinear multiagent systems via prioritized strategy approach. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(6): 2852−2856 [20] Tao M, Liu X Y, Shao S, Cao J D. Predefined-time bipartite consensus of networked Euler-Lagrange systems via sliding-mode control. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(12): 4989−4993 [21] Lin G H, Li H Y, Ma H, Zhou Q. Distributed containment control for human-in-the-loop MASs with unknown time-varying parameters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2022, 69(12): 5300−5311 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3205335 [22] Wu H N, Zhang X M, Li R G. Synthesis with guaranteed cost and less human intervention for human-in-the-loop control systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(8): 7541−7551 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3041033 [23] Lin G H, Li H Y, Ahn C K, Yao D Y. Event-based finite-time neural control for human-in-the-loop UAV attitude systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(12): 10387−10397 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3166531 [24] Cao Y, Cao J F, Song Y D. Practical prescribed time tracking control over infinite time interval involving mismatched uncertainties and non-vanishing disturbances. Automatica, 2022, 136: Article No. 110050 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.110050 [25] Li Y X, Wei M, Tong S C. Event-triggered adaptive neural control for fractional-order nonlinear systems based on finite-time scheme. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(9): 9481−9489 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3056990 [26] Li K W, Li Y M, Zong G D. Adaptive fuzzy fixed-time decentralized control for stochastic nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 29(11): 3428−3440 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3022570 [27] 孙梦薇, 任璐, 刘剑, 孙长银. 切换拓扑下动态事件触发多智能体系统固定时间一致性. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(6): 1295−1305Sun Meng-Wei, Ren Lu, Liu Jian, Sun Chang-Yin. Dynamic event-triggered fixed-time consensus control of multi-agent systems under switching topologies. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(6): 1295−1305 [28] Zhou B, Zhang K K, Jiang H Y. Prescribed-time control of perturbed nonholonomic systems by time-varying feedback. Automatica, 2023, 155: Article No. 111125 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.111125 [29] Li W Q, Krstic M. Prescribed-time output-feedback control of stochastic nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(3): 1431−1446 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3151587 [30] Lyu D, Sun M, Jia Q. Event-based prescribed-time synchronization of directed dynamical networks with Lipschitzian nodal dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(3): 1847−1851 [31] Liu Y J, Zeng Q, Tong S C, Chen C L P, Liu L. Actuator failure compensation-based adaptive control of active suspension systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(8): 7044−7053 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2937037 [32] Bechlioulis C P, Rovithakis G A. Prescribed performance adaptive control for multi-input multi-output affine in the control nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010, 55(5): 1220−1226 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2042508 [33] Chen P H, Luan X L, Liu F. MT-filters-based event-triggered adaptive prescribed performance tracking control of multi-agent systems with unknown direction actuator failure. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2023, 33(14): 8224−8253 doi: 10.1002/rnc.6817 [34] Liu D C, Liu Z, Chen C L P, Zhang Y. Prescribed-time containment control with prescribed performance for uncertain nonlinear multi-agent systems. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2021, 358(3): 1782−1811 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.12.021 [35] Wang H, Wen G H, Yu W W, Yu X H. Designing event-triggered observers for distributed tracking consensus of higher-order multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(5): 3302−3313 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3010947 [36] Liu P M, Guo X G, Wang J L, Coutinho D, Wu Z G. Preset-time and preset-accuracy human-in-the-loop cluster consensus control for MASs under stochastic actuation attacks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(3): 1675−1688 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3326059 [37] Ma Q, Wang Z, Miao G Y. Second-order group consensus for multi-agent systems via pinning leader-following approach. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2014, 351(3): 1288−1300 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2013.11.002 [38] Lu H Q, Hu Y, Guo C Q, Zhou W N. Cluster synchronization for a class of complex dynamical network system with randomly occurring coupling delays via an improved event-triggered pinning control approach. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2020, 357(4): 2167−2184 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.11.076 [39] Dong W J, Farrell J A, Polycarpou M M, Djapic V, Sharma M. Command filtered adaptive backstepping. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2012, 20(3): 566−580 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2011.2121907 -





 下载:
下载: