-
摘要: 基于视觉的人体动作质量评价利用计算机视觉相关技术自动分析个体运动完成情况, 并为其提供相应的动作质量评价结果. 这已成为运动科学和人工智能交叉领域的一个热点研究问题, 在竞技体育、运动员选材、健身锻炼、运动康复等领域具有深远的理论研究意义和很强的实用价值. 本文将从数据获取及标注、动作特征表示、动作质量评价3个方面对涉及到的技术进行回顾分析, 对相关方法进行分类, 并比较分析不同方法在AQA-7、JIGSAWS、EPIC-Skills 2018三个数据集上的性能. 最后讨论未来可能的研究方向.Abstract: Vision-based motion quality assessment utilizes computer vision techniques to analyze the quality of individual movement behavior automatically and provide the corresponding assessments of movement quality. It has gradually become the hot issue at the intersection of the sport science and artificial intelligence, and has widely used in the fields of sporting events, athlete selection, fitness and rehabilitation. This article conducts a retrospective analysis of the involved technologies from three aspects: Data acquisition and annotation, motion feature representation, and motion quality assessment. It categorizes and compares various mainstream methods on three datasets: AQA-7, JIGSAWS, and EPIC-Skills 2018. Finally, potential future research directions are discussed.
-
Key words:
- Motion quality /
- assessment /
- computer vision /
- data acquisition /
- feature representation /
- loss function
-
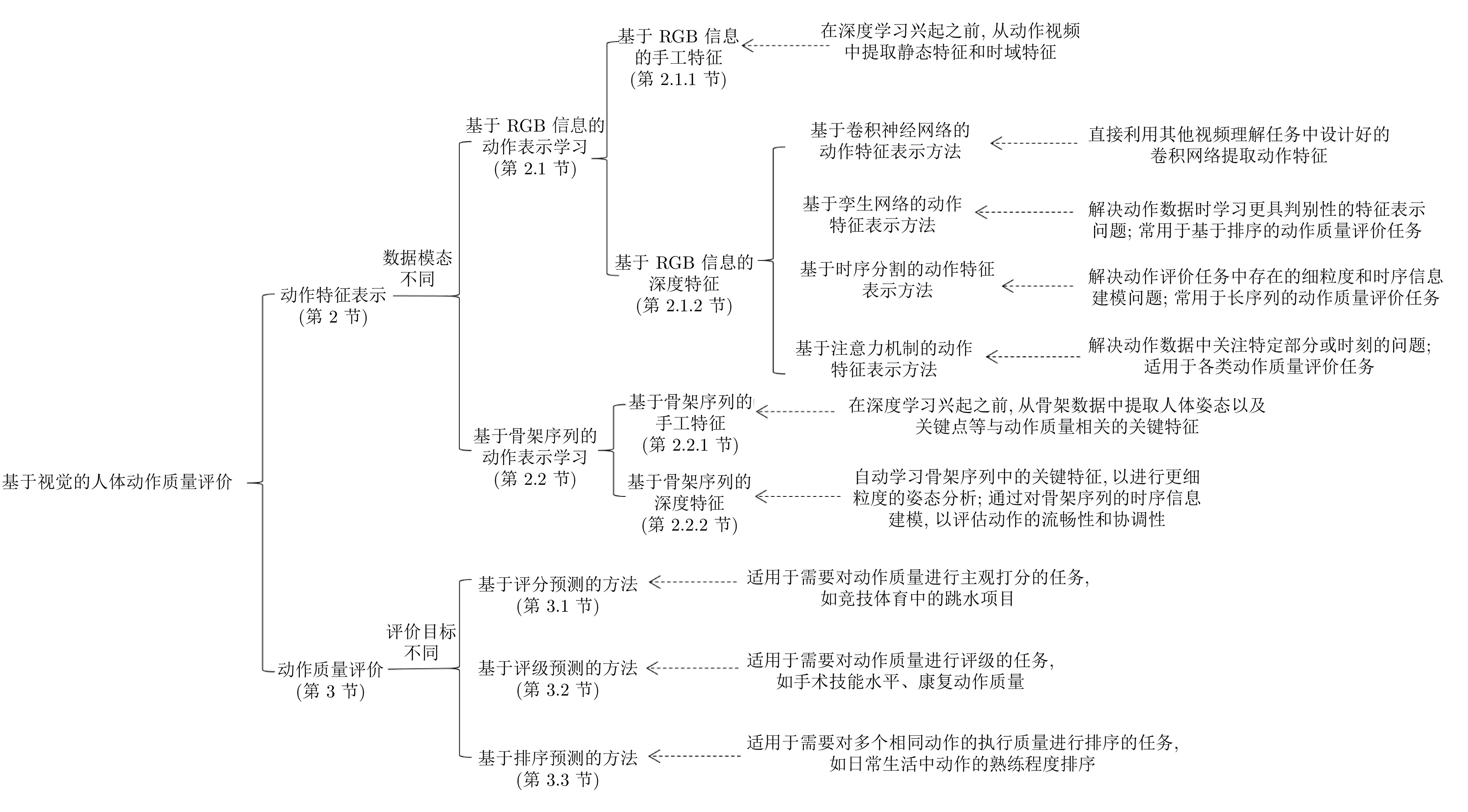
表 1 基于视觉的动作质量评价方法不同阶段的主要任务及存在的问题
Table 1 Main tasks and existing challenges in different stages of vision-based motion quality assessment
阶段 主要任务 存在的问题 动作数据获取 通过视觉传感器来收集和记录与动作相关的数据(RGB、深度图、骨架序列) 如何根据不同的应用场景选择适用的数据模态? 如何确保专家的评分质量? 动作特征表示 综合利用静态图像和人体动作等多方面信息, 设计具有区分性的特征向量以描述人体的运动过程 如何根据动作质量评价任务本身的特性学习具有强鉴别性的动作特征, 以有效地抽取和表示不同运动者在执行相同动作时的细微差异? 动作质量评价 设计特征映射方式, 将提取的特征与相应的评分、评级或排序评价目标关联起来 如何在设计损失函数时考虑标注不确定性(如不同专家的评分差异)、同一动作之间的评分差异等问题? 表 2 主流的动作质量评价数据集总览
Table 2 Brief overview of mainstream motion quality assessment dataset
数据集 动作类别 样本数(受试者人数) 标注类别 应用场景 数据模态 发表年份 Heian Shodan[25] 1 14 评级标注 健身锻炼 3D骨架 2003 FINA09 Dive[26] 1 68 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2010 MIT-Dive[8] 1 159 评分标注、反馈标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2014 MIT-Skate[8] 1 150 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2014 SPHERE-Staircase2014[10] 1 48 评级标注 运动康复 3D骨架 2014 JIGSAWS[9] 3 103 评级标注 技能训练 RGB视频、运动学数据 2014 SPHERE-Walking2015[16] 1 40 评级标注 运动康复 3D骨架 2016 SPHERE-SitStand2015[16] 1 109 评级标注 运动康复 3D骨架 2016 LAM Exercise Dataset[23] 5 125 评级标注 运动康复 3D骨架 2016 First-Person Basketball[27] 1 48 排序标注 健身锻炼 RGB视频 2017 UNLV-Dive[28] 1 370 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2017 UNLV-Vault[28] 1 176 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2017 UI-PRMD[20] 10 100 评级标注 运动康复 3D骨架 2018 EPIC-Skills 2018[24] 4 216 排序标注 技能训练 RGB视频 2018 Infant Grasp[29] 1 94 排序标注 技能训练 RGB视频 2019 AQA-7[30] 7 1189 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2019 MTL-AQA[31] 1 1412 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2019 FSD-10[32] 10 1484 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2019 BEST 2019[32] 5 500 排序标注 技能训练 RGB视频 2019 KIMORE[22] 5 78 评分标注 运动康复 RGB、深度视频、3D骨架 2019 Fis-V[33] 1 500 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2020 TASD-2(SyncDiving-3m)[34] 1 238 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2020 TASD-2(SyncDiving-10m)[34] 1 368 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2020 RG[35] 4 1000 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2020 QMAR[36] 6 38 评级标注 运动康复 RGB视频 2020 PISA[37] 1 992 评级标注 技能训练 RGB视频、音频 2021 FR-FS[38] 1 417 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2021 SMART[39] 8 640 评分标注 体育赛事、健身锻炼 RGB视频 2021 Fitness-AQA[40] 3 1000 反馈标注 健身锻炼 RGB视频 2022 Finediving[41] 1 3000 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2022 LOGO[42] 1 200 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2023 RFSJ[43] 23 1304 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频 2023 FineFS[44] 2 1167 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频、骨架数据 2023 AGF-Olympics[45] 1 500 评分标注 体育赛事 RGB视频、骨架数据 2024 表 3 两类动作特征表示方法优缺点对比
Table 3 Advantage and disadvantage comparison for two types of motion feature methods
表 4 基于RGB信息的深度动作特征方法优缺点对比
Table 4 Advantage and disadvantage comparison for RGB-based deep motion feature methods
方法分类 优点 缺点 基于卷积神经网络的动作特征
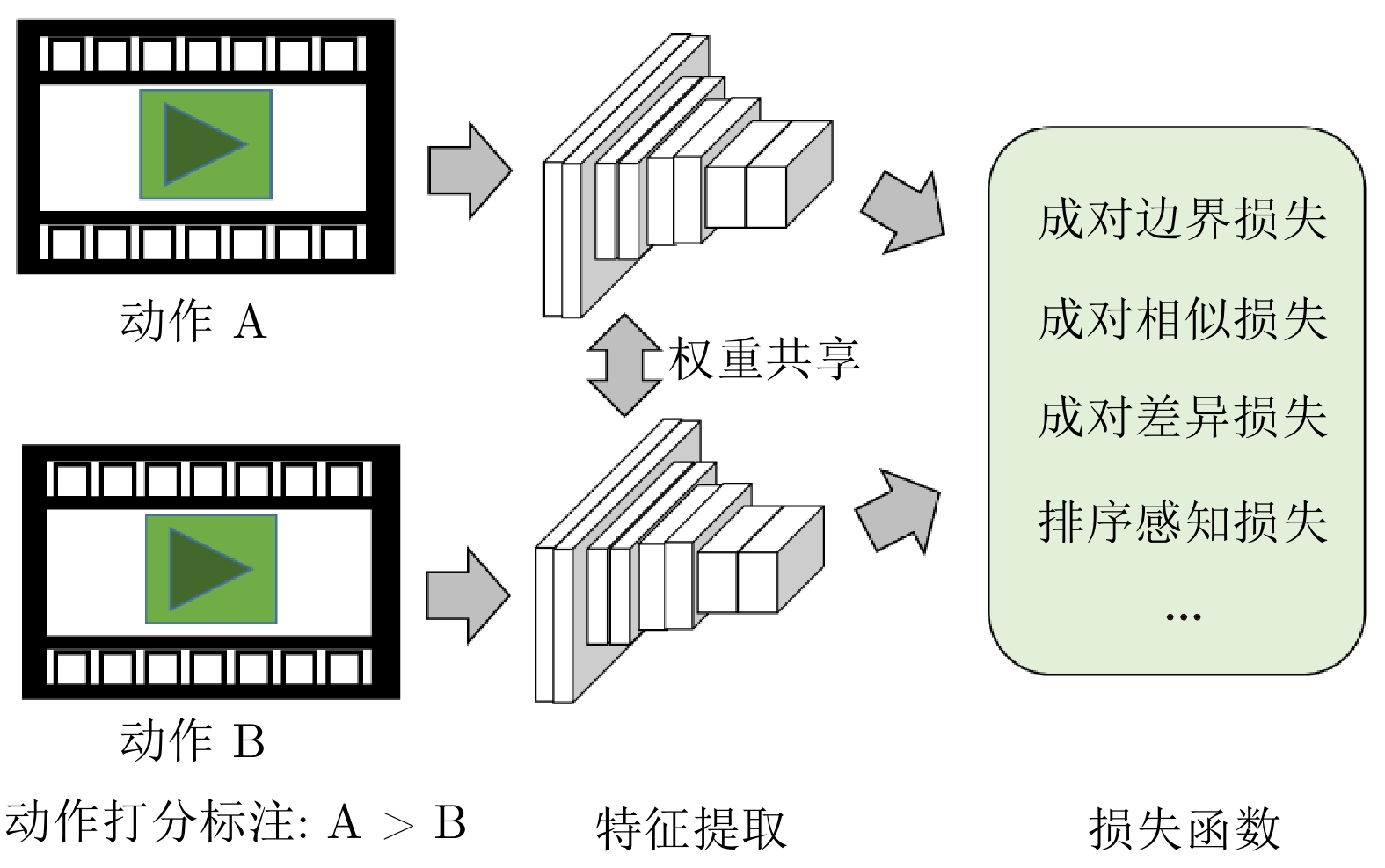
表示方法[12, 24, 28, 30−33, 48, 54, 59]简单易实现 无法充分捕捉动作特征的复杂性 基于孪生网络的动作特征
表示方法[24, 62−64]便于建模动作之间的细微差异 计算复杂度较高, 需要构建有效的样本对 基于时序分割的动作特征
表示方法[44, 48, 59, 65−68]降低噪声干扰, 更好地捕获动作的细节和变化 额外的分割标注信息, 片段划分不准确对性能影响较大 基于注意力机制的动作特征表示
方法[29, 32−35, 38, 41, 43−44, 68−72]自适应性好, 对重要特征的捕获能力强, 可解释性较好 计算复杂度高、内存消耗大 表 5 基于骨架序列的深度动作特征方法优缺点对比
Table 5 Advantage and disadvantage comparison for skeleton-based deep motion feature methods
表 6 在体育评分数据集AQA-7上的不同方法性能对比
Table 6 Performance comparison of different methods on sports scoring dataset AQA-7
方法 Diving Gym Vault Skiing Snowboard Sync. 3m Sync. 10m AQA-7 传统/深度 发表年份 Pose+DCT+SVR[8] 0.5300 0.1000 — — — — — 传统 2014 C3D+SVR[28] 0.7902 0.6824 0.5209 0.4006 0.5937 0.9120 0.6937 深度 2017 C3D+LSTM[28] 0.6047 0.5636 0.4593 0.5029 0.7912 0.6927 0.6165 深度 2017 Li 等[11] 0.8009 0.7028 — — — — — 深度 2018 S3D[59] — 0.8600 — — — — — 深度 2018 All-action C3D+LSTM[30] 0.6177 0.6746 0.4955 0.3648 0.8410 0.7343 0.6478 深度 2019 C3D-AVG-MTL[30] 0.8808 — — — — — — 深度 2019 JRG[49] 0.7630 0.7358 0.6006 0.5405 0.9013 0.9254 0.7849 深度 2019 USDL[12] 0.8099 0.7570 0.6538 0.7109 0.9166 0.8878 0.8102 深度 2020 AIM[36] 0.7419 0.7296 0.5890 0.4960 0.9298 0.9043 0.7789 深度 2020 DML[62] 0.6900 0.4400 — — — — — 深度 2021 CoRe[63] 0.8824 0.7746 0.7115 0.6624 0.9442 0.9078 0.8401 深度 2021 Lei 等[69] 0.8649 0.7858 — — — — — 深度 2021 EAGLE-EYE[98] 0.8331 0.7411 0.6635 0.6447 0.9143 0.9158 0.8140 深度 2021 TSA-Net[38] 0.8379 0.8004 0.6657 0.6962 0.9493 0.9334 0.8476 深度 2021 Adaptive[97] 0.8306 0.7593 0.7208 0.6940 0.9588 0.9298 0.8500 深度 2022 PCLN[64] 0.8697 0.8759 0.7754 0.5778 0.9629 0.9541 0.8795 深度 2022 TPT[70] 0.8969 0.8043 0.7336 0.6965 0.9456 0.9545 0.8715 深度 2022 表 7 JIGSAWS数据集上的不同方法性能对比
Table 7 Performance comparison of different methods on JIGSAWS
方法 数据模态 评价方法 技能水平
划分交叉验证方法 评测指标 SU KT NP 发表年份 k-NN[110] 动作特征 GRS 两类 LOSO Accuracy 0.897 — 0.821 2018 LOUO Accuracy 0.719 — 0.729 2018 LR[110] 动作特征 GRS 两类 LOSO Accuracy 0.899 — 0.823 2018 LOUO Accuracy 0.744 — 0.702 2018 SVM[110] 动作特征 GRS 两类 LOSO Accuracy 0.754 — 0.754 2018 LOUO Accuracy 0.798 — 0.779 2018 SMT[111] 动作特征 Self-proclaimed 三类 LOSO Accuracy 0.990 0.996 0.999 2018 LOUO Accuracy 0.353 0.323 0.571 2018 DCT[111] 动作特征 Self-proclaimed 三类 LOSO Accuracy 1.000 0.997 0.999 2018 LOUO Accuracy 0.647 0.548 0.357 2018 DFT[111] 动作特征 Self-proclaimed 三类 LOSO Accuracy 1.000 0.999 0.999 2018 LOUO Accuracy 0.647 0.516 0.464 2018 ApEn[111] 动作特征 Self-proclaimed 三类 LOSO Accuracy 1.000 0.999 1.000 2018 LOUO Accuracy 0.882 0.774 0.857 2018 CNN[102] 动作特征 Self-proclaimed 三类 LOSO Accuracy 0.934 0.898 0.849 2018 CNN[102] 动作特征 GRS 三类 LOSO Accuracy 0.925 0.954 0.913 2018 CNN[105] 动作特征 Self-proclaimed 三类 LOSO Micro F1 1.000 0.921 1.000 2018 Macro F1 1.000 0.932 1.000 2018 Forestier 等[112] 动作特征 GRS 三类 LOSO Micro F1 0.897 0.611 0.963 2018 Macro F1 0.867 0.533 0.958 2018 S3D[59] 视频数据 GRS 三类 LOSO SRC 0.680 0.640 0.570 2018 LOUO SRC 0.030 0.140 0.350 2018 FCN[99] 动作特征 Self-proclaimed 三类 LOSO Micro F1 1.000 0.921 1.000 2019 Macro F1 1.000 0.932 1.000 2019 3D ConvNet (RGB)[103] 视频数据 Self-proclaimed 三类 LOSO Accuracy 1.000 0.958 0.964 2019 3D ConvNet (OF)[103] 视频数据 Self-proclaimed 三类 LOSO Accuracy 1.000 0.951 1.000 2019 JRG[49] 视频数据 GRS 三类 LOUO SRC 0.350 0.190 0.670 2019 USDL[12] 视频数据 GRS 三类 4-fold cross validation SRC 0.710 0.710 0.690 2020 AIM[34] 视频数据
动作特征GRS 三类 LOUO SRC 0.450 0.610 0.340 2020 MTL-VF (ResNet)[113] 视频数据 GRS 三类 LOSO SRC 0.790 0.630 0.730 2020 LOUO SRC 0.680 0.720 0.480 2020 MTL-VF (C3D)[113] 视频数据 GRS 三类 LOSO SRC 0.770 0.890 0.750 2020 LOUO SRC 0.690 0.830 0.860 2020 CoRe[63] 视频数据 GRS 三类 4-fold cross validation SRC 0.840 0.860 0.860 2021 VTPE[106] 视频数据
动作特征GRS 三类 LOUO SRC 0.450 0.590 0.650 2021 4-fold cross validation SRC 0.830 0.820 0.760 2021 ViSA[107] 视频数据 GRS 三类 LOSO SRC 0.840 0.920 0.930 2022 LOUO SRC 0.720 0.760 0.900 2022 4-fold cross validation SRC 0.790 0.840 0.860 2022 Gao 等[108] 视频数据
动作特征GRS 三类 LOUO SRC 0.600 0.690 0.660 2023 4-fold cross validation SRC 0.830 0.950 0.830 2023 Contra-Sformer[109] 视频数据 GRS 三类 LOSO SRC 0.860 0.890 0.710 2023 LOUO SRC 0.650 0.690 0.710 2023 表 8 在EPIC-Skills 2018上的不同方法性能对比
Table 8 Performance comparison of different methods on EPIC-Skills 2018
-
[1] 朱煜, 赵江坤, 王逸宁, 郑兵兵. 基于深度学习的人体行为识别算法综述. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(6): 848−857Zhu Yu, Zhao Jiang-Kun, Wang Yi-Ning, Zheng Bing-Bing. A review of human action recognition based on deep learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6): 848−857 [2] Lei Q, Du J X, Zhang H B, Ye S, Chen D S. A survey of vision-based human action evaluation methods. Sensors, 2019, 19(19): Article No. 4129 doi: 10.3390/s19194129 [3] Ahad M A R, Antar A D, Shahid O. Vision-based action understanding for assistive healthcare: A short review. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1−11 [4] Voulodimos A, Doulamis N, Doulamis A, Protopapadakis E. Deep learning for computer vision: A brief review. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2018, 2018(1): Article No. 7068349 [5] 郑太雄, 黄帅, 李永福, 冯明驰. 基于视觉的三维重建关键技术研究综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(4): 631−652Zheng Tai-Xiong, Huang Shuai, Li Yong-Fu, Feng Ming-Chi. Key techniques for vision based 3D reconstruction: A review. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(4): 631−652 [6] 林景栋, 吴欣怡, 柴毅, 尹宏鹏. 卷积神经网络结构优化综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(1): 24−37Lin Jing-Dong, Wu Xin-Yi, Chai Yi, Yin Hong-Peng. Structure optimization of convolutional neural networks: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 24−37 [7] 张重生, 陈杰, 李岐龙, 邓斌权, 王杰, 陈承功. 深度对比学习综述. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(1): 15−39Zhang Chong-Sheng, Chen Jie, Li Qi-Long, Deng Bin-Quan, Wang Jie, Chen Cheng-Gong. Deep contrastive learning: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 15−39 [8] Pirsiavash H, Vondrick C, Torralba A. Assessing the quality of actions. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2014). Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 556−571 [9] Gao Y, Vedula S S, Reiley C E, Ahmidi N, Varadarajan B, Lin H C, et al. JHU-ISI gesture and skill assessment working set (JIGSAWS): A surgical activity dataset for human motion modeling. In: Proceedings of the Modeling and Monitoring of Computer Assisted Interventions (M2CAI)-MICCAI Workshop. 2014. [10] Paiement A, Tao L L, Hannuna S, Camplani M, Damen D, Mirmehdi M. Online quality assessment of human movement from skeleton data. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. Nottingham, UK: 2014. 153−166 [11] Li Y J, Chai X J, Chen X L. End-to-end learning for action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the 19th Pacific-Rim Conference on Multimedia, Advances in Multimedia Information Processing (PCM 2018). Hefei, China: Springer, 2018. 125−134 [12] Tang Y S, Ni Z L, Zhou J H, Zhang D Y, Lu J W, Wu Y, et al. Uncertainty-aware score distribution learning for action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 9839−9848 [13] Xu J L, Yin S B, Zhao G H, Wang Z S, Peng Y X. FineParser: A fine-grained spatio-temporal action parser for human-centric action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 14628−14637 [14] Morgulev E, Azar O H, Lidor R. Sports analytics and the big-data era. International Journal of Data Science and Analytics, 2018, 5(4): 213−222 doi: 10.1007/s41060-017-0093-7 [15] Butepage J, Black M J, Kragic D, Kjellström H. Deep representation learning for human motion prediction and classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1591−1599 [16] Tao L L, Paiement A, Damen D, Mirmehdi M, Hannuna S, Camplani M, et al. A comparative study of pose representation and dynamics modelling for online motion quality assessment. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2016, 148: 136−152 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2015.11.016 [17] Khalid S, Goldenberg M, Grantcharov T, Taati B, Rudzicz F. Evaluation of deep learning models for identifying surgical actions and measuring performance. JAMA Network Open, 2020, 3(3): Article No. e201664 doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.1664 [18] Qiu Y H, Wang J P, Jin Z, Chen H H, Zhang M L, Guo L Q. Pose-guided matching based on deep learning for assessing quality of action on rehabilitation training. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 72: Article No. 103323 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103323 [19] Niewiadomski R, Kolykhalova K, Piana S, Alborno P, Volpe G, Camurri A. Analysis of movement quality in full-body physical activities. ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems (TiiS), 2019, 9(1): Article No. 1 [20] Vakanski A, Jun H P, Paul D, Baker R. A data set of human body movements for physical rehabilitation exercises. Data, 2018, 3(1): Article No. 2 doi: 10.3390/data3010002 [21] Alexiadis D S, Kelly P, Daras P, O'Connor N E, Boubekeur T, Moussa M B. Evaluating a dancer's performance using Kinect-based skeleton tracking. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Scottsdale, USA: ACM, 2011. 659−662 [22] Capecci M, Ceravolo M G, Ferracuti F, Iarlori S, MonteriùA, Romeo L, et al. The KIMORE dataset: Kinematic assessment of movement and clinical scores for remote monitoring of physical rehabilitation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2019, 27(7): 1436−1448 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2923060 [23] Parmar P, Morris B T. Measuring the quality of exercises. In: Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). Orlando, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2241−2244 [24] Doughty H, Damen D, Mayol-Cuevas W. Who's better? Who's best? Pairwise deep ranking for skill determination. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 6057−6066 [25] Ilg W, Mezger J, Giese M. Estimation of skill levels in sports based on hierarchical spatio-temporal correspondences. In: Proceedings of the 25th DAGM Symposium on Pattern Recognition. Springer, 2003. 523−531 [26] Wnuk K, Soatto S. Analyzing diving: A dataset for judging action quality. In: Proceedings of the Asian 2010 International Workshops on Computer Vision (ACCV 2010 Workshops). Queenstown, New Zealand: Springer, 2010. 266−276 [27] Bertasius G, Park H S, Yu S X, Shi J B. Am I a baller? Basketball performance assessment from first-person videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2196−2204 [28] Parmar P, Morris B T. Learning to score Olympic events. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 76−84 [29] Li Z Q, Huang Y F, Cai M J, Sato Y. Manipulation-skill assessment from videos with spatial attention network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW). Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 4385−4395 [30] Parmar P, Morris B. Action quality assessment across multiple actions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa Village, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1468−1476 [31] Parmar P, Morris B T. What and how well you performed? A multitask learning approach to action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 304−313 [32] Doughty H, Mayol-Cuevas W, Damen D. The pros and cons: Rank-aware temporal attention for skill determination in long videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 7854−7863 [33] Xu C M, Fu Y W, Zhang B, Chen Z T, Jiang Y G, Xue X Y. Learning to score figure skating sport videos. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(12): 4578−4590 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2927118 [34] Gao J B, Zheng W S, Pan J H, Gao C Y, Wang Y W, Zeng W, et al. An asymmetric modeling for action assessment. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2020). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 222−238 [35] Zeng L A, Hong F T, Zheng W S, Yu Q Z, Zeng W, Wang Y W, et al. Hybrid dynamic-static context-aware attention network for action assessment in long videos. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Seattle, USA: ACM, 2020. 2526−2534 [36] Sardari F, Paiement A, Hannuna S, Mirmehdi M. VI-Net——View-invariant quality of human movement assessment. Sensors, 2020, 20(18): Article No. 5258 doi: 10.3390/s20185258 [37] Parmar P, Reddy J, Morris B. Piano skills assessment. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP). Tampere, Finland: IEEE, 2021. 1−5 [38] Wang S L, Yang D K, Zhai P, Chen C X, Zhang L H. TSA-Net: Tube self-attention network for action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Virtual Event: ACM, 2021. 4902−4910 [39] Chen X, Pang A Q, Yang W, Ma Y X, Xu L, Yu J Y. SportsCap: Monocular 3D human motion capture and fine-grained understanding in challenging sports videos. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(10): 2846−2864 doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01486-4 [40] Parmar P, Gharat A, Rhodin H. Domain knowledge-informed self-supervised representations for workout form assessment. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2022). Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 105−123 [41] Xu J L, Rao Y M, Yu X M, Chen G Y, Zhou J, Lu J W. FineDiving: A fine-grained dataset for procedure-aware action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 2939−2948 [42] Zhang S Y, Dai W X, Wang S J, Shen X W, Lu J W, Zhou J, et al. LOGO: A long-form video dataset for group action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 2405−2414 [43] Liu Y C, Cheng X N, Ikenaga T. A figure skating jumping dataset for replay-guided action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Ottawa, Canada: ACM, 2023. 2437−2445 [44] Ji Y L, Ye L F, Huang H L, Mao L J, Zhou Y, Gao L L. Localization-assisted uncertainty score disentanglement network for action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Ottawa, Canada: ACM, 2023. 8590−8597 [45] Zahan S, Hassan G M, Mian A. Learning sparse temporal video mapping for action quality assessment in floor gymnastics. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: Article No. 5020311 [46] Ahmidi N, Tao L L, Sefati S, Gao Y X, Lea C, Haro B, et al. A dataset and benchmarks for segmentation and recognition of gestures in robotic surgery. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 64(9): 2025−2041 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2016.2647680 [47] Liao Y L, Vakanski A, Xian M. A deep learning framework for assessing physical rehabilitation exercises. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2020, 28(2): 468−477 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.2966249 [48] Li Y J, Chai X J, Chen X L. ScoringNet: Learning key fragment for action quality assessment with ranking loss in skilled sports. In: Proceedings of the 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV 2018). Perth, Australia: Springer, 2018. 149−164 [49] Pan J H, Gao J B, Zheng W S. Action assessment by joint relation graphs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 6330−6339 [50] Lei Q, Zhang H B, Du J X, Hsiao T, Chen C C. Learning effective skeletal representations on RGB video for fine-grained human action quality assessment. Electronics, 2020, 9(4): Article No. 568 doi: 10.3390/electronics9040568 [51] Gordon A S. Automated video assessment of human performance. In: Proceedings of the AI-ED-World Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. Washington, USA: AACE Press, 1995. 541−546 [52] Venkataraman V, Vlachos I, Turaga P. Dynamical regularity for action analysis. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. Swansea, UK: BMVA Press, 2015. 67−78 [53] Zia A, Sharma Y, Bettadapura V, Sarin E L, Ploetz T, Clements M A, et al. Automated video-based assessment of surgical skills for training and evaluation in medical schools. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2016, 11(9): 1623−1636 doi: 10.1007/s11548-016-1468-2 [54] Parmar P. On Action Quality Assessment [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Nevada, USA, 2019. [55] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, US: ACM, 2014. 568−576 [56] Tran D, Bourdev L, Fergus R, Torresani L, Paluri M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 4489−4497 [57] Carreira J, Zisserman A. Quo Vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4724−4733 [58] Qiu Z F, Yao T, Mei T. Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3D residual networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 5534−5542 [59] Xiang X, Tian Y, Reiter A, Hager G D, Tran T D. S3D: Stacking segmental P3D for action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Athens, Greece: IEEE, 2018. 928−932 [60] Yu F, Koltun V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations. San Juan, Puerto Rico: ICLR, 2016. 928−932 [61] Bromley J, Bentz J W, Bottou L, Guyon I, Lecun Y, Moor C, et al. Signature verification using a "siamese" time delay neural network. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 1993, 7(4): 669−688 doi: 10.1142/S0218001493000339 [62] Jain H, Harit G, Sharma A. Action quality assessment using siamese network-based deep metric learning. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(6): 2260−2273 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.3017727 [63] Yu X M, Rao Y M, Zhao W L, Lu J W, Zhou J. Group-aware contrastive regression for action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 7899−7908 [64] Li M Z, Zhang H B, Lei Q, Fan Z W, Liu J H, Du J X. Pairwise contrastive learning network for action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2022). Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 457−473 [65] Dong L J, Zhang H B, Shi Q H Y, Lei Q, Du J X, Gao S C. Learning and fusing multiple hidden substages for action quality assessment. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 229: Article No. 107388 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107388 [66] Lea C, Flynn M D, Vidal R, Reiter A, Hager G D. Temporal convolutional networks for action segmentation and detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1003−1012 [67] Liu L X, Zhai P J, Zheng D L, Fang Y. Multi-stage action quality assessment method. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Control, Robotics and Intelligent System. Guangzhou, China: ACM, 2023. 116−122 [68] Gedamu K, Ji Y L, Yang Y, Shao J, Shen H T. Fine-grained spatio-temporal parsing network for action quality assessment. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 6386−6400 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3331212 [69] Lei Q, Zhang H B, Du J X. Temporal attention learning for action quality assessment in sports video. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2021, 15(7): 1575−1583 doi: 10.1007/s11760-021-01890-w [70] Bai Y, Zhou D S, Zhang S Y, Wang J, Ding E R, Guan Y, et al. Action quality assessment with temporal parsing transformer. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2022). Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 422−438 [71] Xu A, Zeng L A, Zheng W S. Likert scoring with grade decoupling for long-term action assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 3222−3231 [72] Du Z X, He D, Wang X, Wang Q. Learning semantics-guided representations for scoring figure skating. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 4987−4997 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2023.3328180 [73] Yan S J, Xiong Y J, Lin D H. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New Orleans, USA: AAAI, 2018. 7444−7452 [74] Gao X, Hu W, Tang J X, Liu J Y, Guo Z M. Optimized skeleton-based action recognition via sparsified graph regression. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Nice, France: ACM, 2019. 601−610 [75] Patrona F, Chatzitofis A, Zarpalas D, Daras P. Motion analysis: Action detection, recognition and evaluation based on motion capture data. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 76: 612−622 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.12.007 [76] Microsoft Development Team. Azure Kinect body tracking joints [Online], available: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/azure/kinect-dk/body-joints, December 12, 2024 [77] Yang Y, Ramanan D. Articulated pose estimation with flexible mixtures-of-parts. In: Proceedings of the CVPR 2011. Colorado Springs, USA: IEEE, 2011. 1385−1392 [78] Felzenszwalb P F, Girshick R B, McAllester D, Ramanan D. Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(9): 1627−1645 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.167 [79] Tian Y, Sukthankar R, Shah M. Spatiotemporal deformable part models for action detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 2642−2649 [80] Cao Z, Simon T, Wei S E, Sheikh Y. Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 7291−7299 [81] Fang H S, Xie S Q, Tai Y W, Lu C W. RMPE: Regional multi-person pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2353−2362 [82] He K, Gkioxari G, DollÁR P, Girshick R. Mask R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2980−2988 [83] Shotton J, Fitzgibbon A, Cook M, Sharp T, Finocchio M, Moore R, et al. Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images. In: Proceedings of the CVPR 2011. Colorado Springs, USA: IEEE, 2011. 1297−1304 [84] Rhodin H, Meyer F, Spörri J, Müller E, Constantin V, Fua P, et al. Learning monocular 3D human pose estimation from multi-view images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018. 8437−8446 [85] Dong J T, Jiang W, Huang Q X, Bao H J, Zhou X W. Fast and robust multi-person 3D pose estimation from multiple views. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 7784−7793 [86] Celiktutan O, Akgul C B, Wolf C, Sankur B. Graph-based analysis of physical exercise actions. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Workshop on Multimedia Indexing and Information Retrieval for Healthcare. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2013. 23−32 [87] Liu J, Wang G, Hu P, Duan L Y, Kot A C. Global context-aware attention LSTM networks for 3D action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3671−3680 [88] Lee I, Kim D, Kang S, Lee S. Ensemble deep learning for skeleton-based action recognition using temporal sliding LSTM networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1012−1020 [89] Li C, Zhong Q Y, Xie D, Pu S L. Co-occurrence feature learning from skeleton data for action recognition and detection with hierarchical aggregation. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Stockholm, Sweden: AAAI Press, 2018. 786−792 [90] Li Y S, Xia R J, Liu X, Huang Q H. Learning shape-motion representations from geometric algebra spatio-temporal model for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2019. 1066−1071 [91] Li M S, Chen S H, Chen X, Zhang Y, Wang Y F, Tian Q. Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3590−3598 [92] Shi L, Zhang Y F, Cheng J, Lu H Q. Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 12018−12027 [93] Yu B X B, Liu Y, Chan K C C. Skeleton-based detection of abnormalities in human actions using graph convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Transdisciplinary AI (TransAI). Irvine, USA: IEEE, 2020. 131−137 [94] Chowdhury S H, Al Amin M, Rahman A K M M, Amin M A, Ali A A. Assessment of rehabilitation exercises from depth sensor data. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology. Dhaka, Bangladesh: IEEE, 2021. 1−7 [95] Deb S, Islam M F, Rahman S, Rahman S. Graph convolutional networks for assessment of physical rehabilitation exercises. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2022, 30: 410−419 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2022.3150392 [96] Li H Y, Lei Q, Zhang H B, Du J X, Gao S C. Skeleton-based deep pose feature learning for action quality assessment on figure skating videos. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2022, 89: Article No. 103625 doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2022.103625 [97] Pan J H, Gao J B, Zheng W S. Adaptive action assessment. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(12): 8779−8795 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3126534 [98] Nekoui M, Cruz F O T, Cheng L. Eagle-eye: Extreme-pose action grader using detail bird's-eye view. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2021. 394−402 [99] Fawaz H I, Forestier G, Weber J, Idoumghar L, Muller P A. Accurate and interpretable evaluation of surgical skills from kinematic data using fully convolutional neural networks. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2019, 14(9): 1611−1617 doi: 10.1007/s11548-019-02039-4 [100] Roditakis K, Makris A, Argyros A. Towards improved and interpretable action quality assessment with self-supervised alignment. In: Proceedings of the 14th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference. Corfu, Greece: IEEE, 2021. 507−513 [101] Li M Z, Zhang H B, Dong L J, Lei Q, Du J X. Gaussian guided frame sequence encoder network for action quality assessment. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 2023, 9(2): 1963−1974 [102] Wang Z, Fey A M. Deep learning with convolutional neural network for objective skill evaluation in robot-assisted surgery. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2018, 13(12): 1959−1970 doi: 10.1007/s11548-018-1860-1 [103] Funke I, Mees S T, Weitz J, Speidel S. Video-based surgical skill assessment using 3D convolutional neural networks. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2019, 14(7): 1217−1225 doi: 10.1007/s11548-019-01995-1 [104] Wang Z, Fey A M. SATR-DL: Improving surgical skill assessment and task recognition in robot-assisted surgery with deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1793−1796 [105] Fawaz H I, Forestier G, Weber J, Idoumghar L, Muller P A. Evaluating surgical skills from kinematic data using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2018). Granada, Spain: Springer, 2018. 214−221 [106] Liu D C, Li Q Y, Jiang T T, Wang Y Z, Miao R L, Shan F, et al. Towards unified surgical skill assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 9517−9526 [107] Li Z Q, Gu L, Wang W M, Nakamura R, Sato Y. Surgical skill assessment via video semantic aggregation. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2022). Singapore: Springer, 2022. 410−420 [108] Gao J B, Pan J H, Zhang S J, Zheng W S. Automatic modelling for interactive action assessment. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2023, 131(3): 659−679 doi: 10.1007/s11263-022-01695-5 [109] Anastasiou D, Jin Y M, Stoyanov D, Mazomenos E. Keep your eye on the best: Contrastive regression transformer for skill assessment in robotic surgery. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023, 8(3): 1755−1762 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3242466 [110] Fard M J, Ameri S, Ellis R D, Chinnam R B, Pandya A K, Klein M D. Automated robot-assisted surgical skill evaluation: Predictive analytics approach. The International Journal of Medical Robotics and Computer Assisted Surgery, 2018, 14(1): Article No. e1850 [111] Zia A, Essa I. Automated surgical skill assessment in RMIS training. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2018, 13(5): 731−739 doi: 10.1007/s11548-018-1735-5 [112] Forestier G, Petitjean F, Senin P, Despinoy F, Huaulmé A, Fawaz H I, et al. Surgical motion analysis using discriminative interpretable patterns. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2018, 91: 3−11 doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2018.08.002 [113] Wang T Y, Wang Y J, Li M. Towards accurate and interpretable surgical skill assessment: A video-based method incorporating recognized surgical gestures and skill levels. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2020). Lima, Peru: Springer, 2020. 668−678 [114] Okamoto L, Parmar P. Hierarchical NeuroSymbolic approach for comprehensive and explainable action quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 3204−3213 -




 下载:
下载: