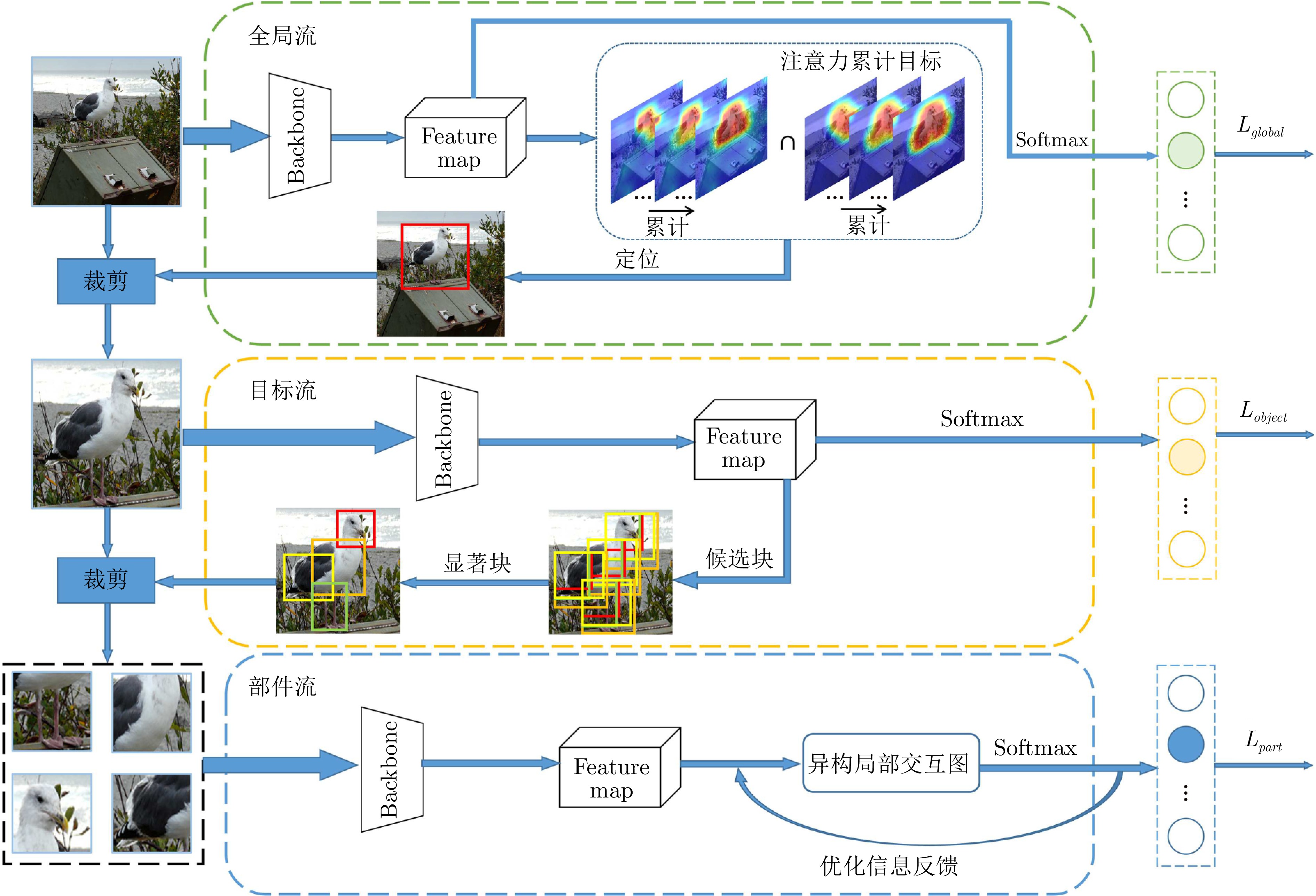
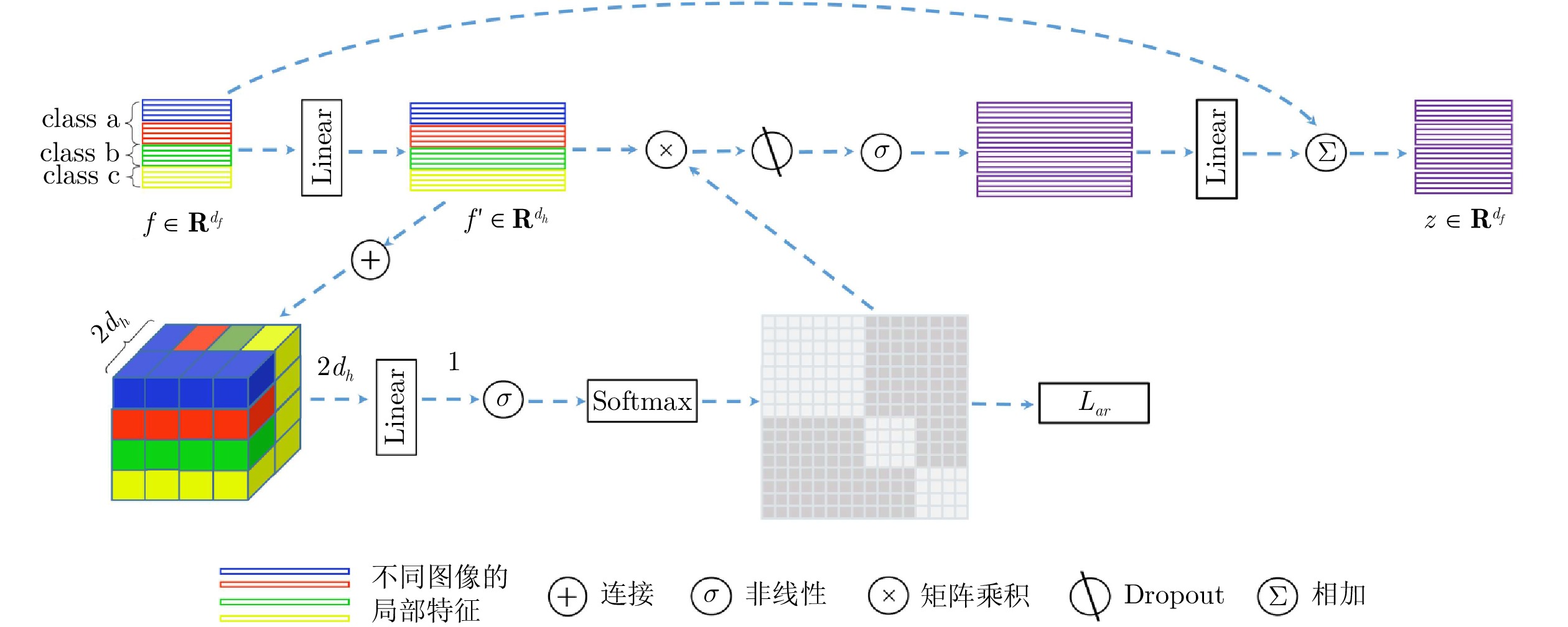
Fine-grained Image Classification by Integrating Object Localization and Heterogeneous Local Interactive Learning
-
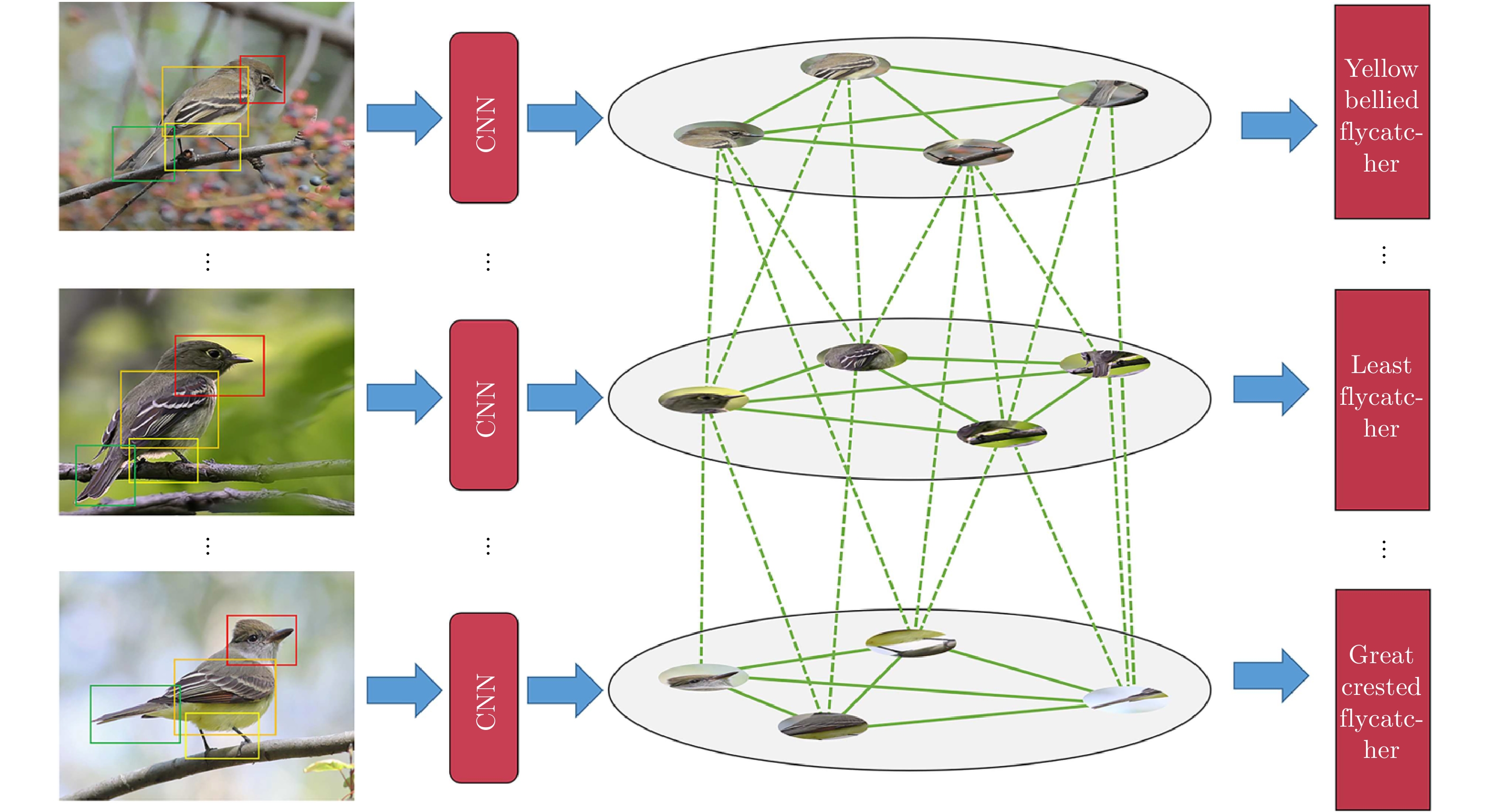
摘要: 由于细粒度图像之间存在小的类间方差和大的类内差异, 现有分类算法仅仅聚焦于单张图像的显著局部特征的提取与表示学习, 忽视了多张图像之间局部的异构语义判别信息, 较难关注到区分不同类别的微小细节, 导致学习到的特征缺乏足够区分度. 本文提出了一种渐进式网络以弱监督的方式学习图像不同粒度层级的信息. 首先, 构建一个注意力累计目标定位模块(Attention accumulation object localization module, AAOLM), 在单张图像上从不同的训练轮次和特征提取阶段对注意力信息进行语义目标集成定位. 其次, 设计一个多张图像异构局部交互图模块(Heterogeneous local interactive graph module, HLIGM), 提取每张图像的显著性局部区域特征, 在类别标签引导下构建多张图像的局部区域特征之间的图网络, 聚合局部特征增强表示的判别力. 最后, 利用知识蒸馏将异构局部交互图模块产生的优化信息反馈给主干网络, 从而能够直接提取具有较强区分度的特征, 避免了在测试阶段建图的计算开销. 通过在多个数据集上进行的实验, 证明了提出方法的有效性, 能够提高细粒度分类的精度.Abstract: Due to the existence of small inter-class differences and large intra-class variance among fine-grained images, the existing classification algorithms only focus on the extraction and representation learning of salient local features of a single image, ignoring the local heterogeneous semantic discrimination information between multiple images, difficult to pay attention to the subtle details that distinguish different categories, resulting in the lack of sufficient discrimination of the learned features. This paper proposes a progressive network to learn the information of different granularity levels of the image in a weakly supervised manner. First, attention accumulation object localization module (AAOLM) is constructed to perform semantic target integration localization on attention information from different training epochs and feature extraction stages on a single image. Second, a multi-image heterogeneous local interactive graph module (HLIGM) is designed to construct a graph network and aggregate information between the local region features of multiple images under the guidance of the category label after extracting the salient local region features of each image to enhance the discriminative power of the representation. Finally, the optimization information generated by HLIGM is fed back to the backbone by using knowledge distillation so that it can directly extract features with strong discrimination, avoiding the computational overhead of building the graph in the test phase. Through experiments on multiple data sets, it proves the effectiveness of the proposed method, which can improve the fine-grained classification accuracy.
-
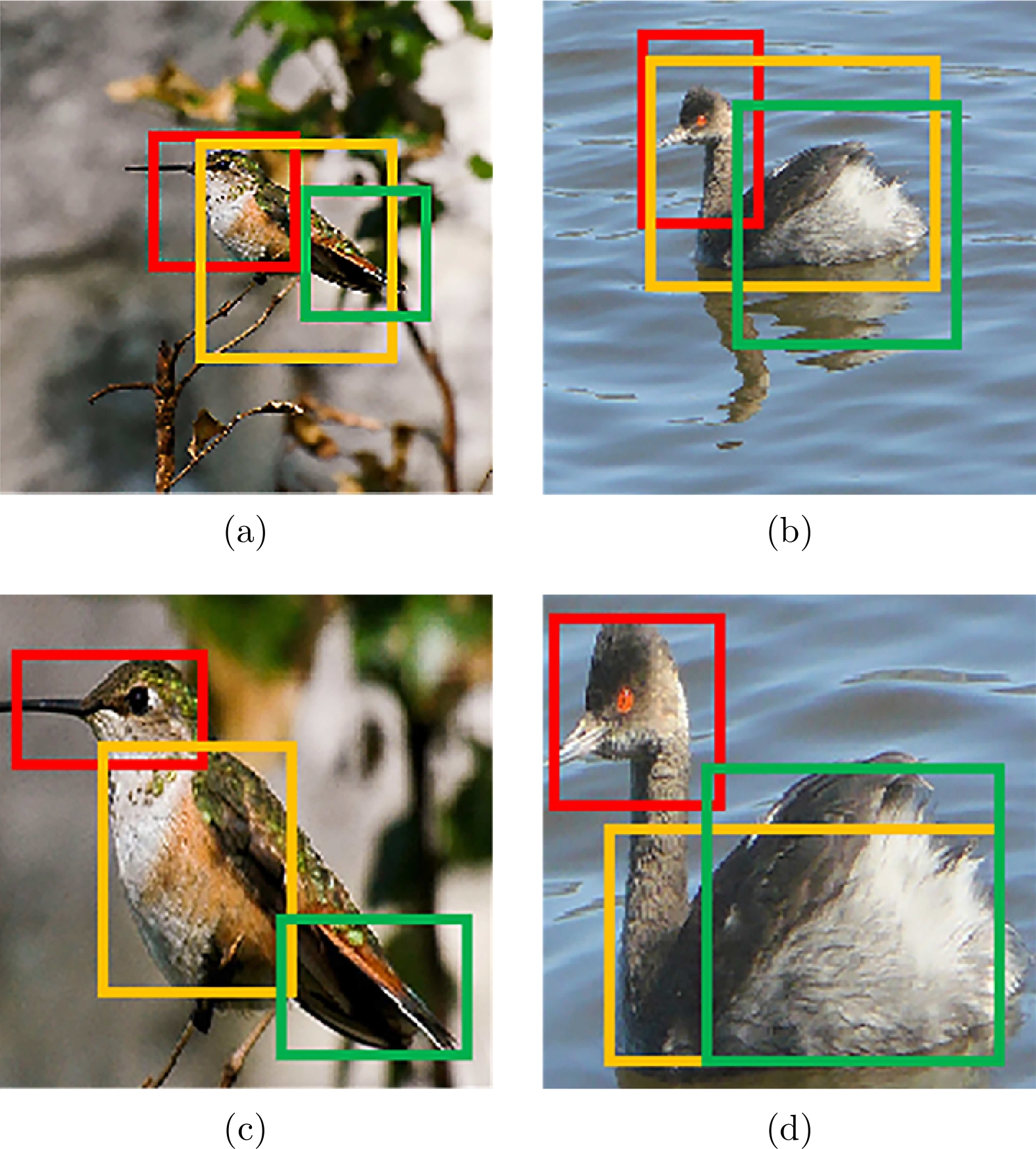
图 2 原始图像和目标图像上的部件采样对比 ((a)、(b)使用固定大小的锚框直接在原图中采样有用的目标局部部件, 没有很好地区分开不同的部件并且包含了更多无关的背景信息; (c)、(d) 展示了定位到目标后放大到一定的尺度再进行部件采样的效果)
Fig. 2 Comparison of patch sampling between original images and object images ((a)、(b) show that using the fixed-size anchor directly samples useful local patches of the object in the original image, which does not distinguish different patches well and contains more irrelevant background information; (c)、(d) show the effect of patch sampling that it is zoomed in to a certain scale after the object is located)
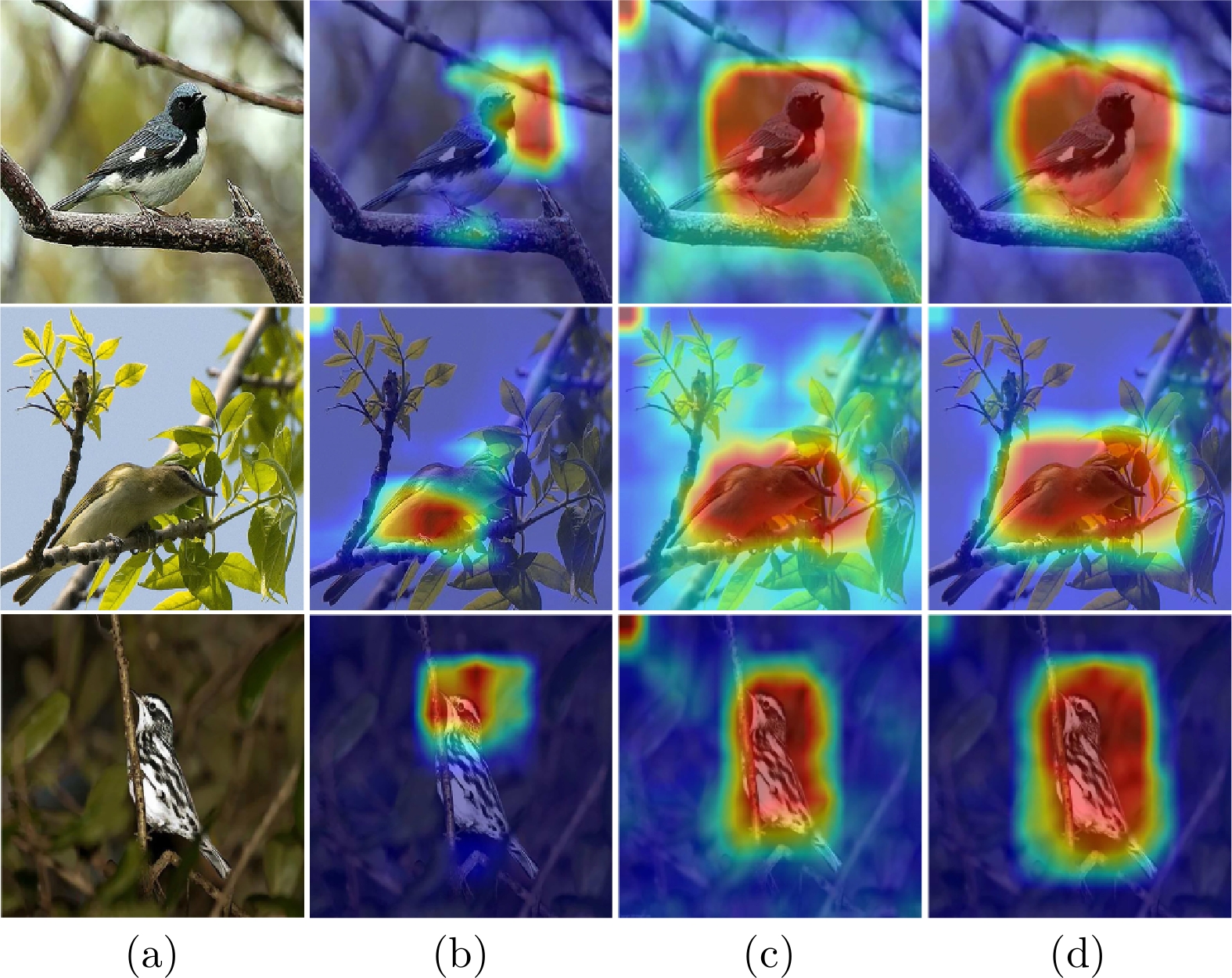
图 5 使用CAM和本文AAOLM的峰值响应图的可视化结果 ((a) 原始图像; (b) CAM生成的热力图; (c) AAOLM在ResNet-50的$ Conv_{5b} $卷积块输出特征上的注意力图; (d) AAOLM在ResNet-50的$ Conv_{5c} $卷积块输出特征上的注意力图)
Fig. 5 Visualization results of peak response maps using CAM and AAOLM in this paper ((a) Original image; (b) Heat map generated by CAM; (c) Attention map of $ Conv_{5b} $ convolution block of ResNet-50 by AAOLM; (d) The attention map of the $ Conv_{5c} $ convolution block of ResNet-50 by AAOLM)
表 1 在CUB-200-2011数据集上的对比实验结果, Anno./DATA表示是否使用了额外的标注信息或者辅助数据
Table 1 The comparative experimental results on CUB-200-2011 dataset, and Anno./DATA indicates whether additional labeling information or auxiliary data is used
方法 主干网络 Anno./DATA Accuracy (%) RA-CNN[6] VGG-19 — 85.3 HSnet[29] Inception Anno. 87.5 PART[27] ResNet-50 — 89.6 Mask-CNN[30] VGG-16 Anno. 87.3 S3N[28] ResNet-50 — 88.5 NTSN[46] ResNet-50 — 87.5 ACNet[47] ResNet-50 — 88.1 GDSMP-Net[48] ResNet-101 — 88.1 MetaFGNet[31] ResNet-50 DATA 87.6 DCL[37] ResNet-50 — 88.6 DBT[32] ResNet-101 — 88.1 GCL[12] ResNet-50 — 88.3 AENet[19] ResNet-101 — 88.6 MGE-CNN[17] ResNet-101 — 89.4 GHRD[20] ResNet-50 — 89.6 PMG[33] ResNet-50 — 89.9 Ours textNet-50 — 90.2 Ours ResNet-101 — 90.5 表 2 在NA Birds数据集上的对比实验结果
Table 2 The comparative experimental results on NA Birds dataset
方法 主干网络 Anno./DATA Accuracy (%) DSTL[49] Inception-v3 — 87.9 MaxEnt[50] DenseNet-161 — 83.0 PMG[33] ResNet-50 — 87.9 MGE-CNN[17] ResNet-101 — 88.6 CS-Part[51] ResNet-50 — 88.5 API-NET[52] ResNet-101 — 88.1 FixSENet-154[35] SENet-154 — 89.2 GHRD[20] ResNet-50 — 88.0 Ours ResNet-50 — 89.5 Ours ResNet-101 — 89.9 表 3 在StanfordCars数据集上的对比实验结果
Table 3 The comparative experimental results on StanfordCars dataset
方法 主干网络 Anno./DATA Accuracy (%) RA-CNN[6] VGG-19 — 92.5 PSA-CNN[53] VGG-19 Anno. 92.6 HSnet[29] Inception Anno. 93.9 ACNet[47] ResNet-50 — 94.6 S3N[28] ResNet-50 — 94.7 NTSN[46] ResNet-50 — 93.9 DCL[37] ResNet-50 — 94.5 GCL[12] ResNet-50 — 94.0 AENet[19] ResNet-101 — 93.7 MGE-CNN[17] ResNet-101 — 93.9 API-NET[52] ResNet-101 — 94.9 SDNs[54] ResNet-101 — 94.6 M2B[55] ResNet-50 — 94.7 TransFG[36] ViT-B 16 — 94.8 Ours ResNet-50 — 95.1 Ours ResNet-101 — 95.5 表 4 在FGVC-Aircraft数据集上的对比实验结果
Table 4 The comparative experimental results on FGVC-Aircraft dataset
方法 主干网络 Anno./DATA Accuracy (%) DTRG[56] ResNet-50 — 94.1 MG-CNN[40] VGG-19 Anno. 83.0 ACNet[47] ResNet-50 — 92.4 S3N[28] ResNet-50 — 92.8 NTSN[46] ResNet-50 — 91.4 DCL[37] ResNet-50 — 93.0 DBT[32] ResNet-101 — 91.6 GCL[12] ResNet-50 — 93.2 AENet[19] ResNet-101 — 93.8 API-NET[52] ResNet-101 — 93.4 GHRD[20] ResNet-50 — 94.3 M2B[55] ResNet-50 — 93.3 PMG[33] ResNet-50 — 94.1 Ours ResNet-50 — 94.6 Ours ResNet-101 — 94.8 表 5 在CUB-200-2011数据集上的消融实验结果
Table 5 Ablation experimental results on CUB-200-2011 dataset
方法 Accuracy (%) BL 84.5 BL+DP 85.0 BL+DP+ HLIGM 88.4 BL+DP+AAOLM 89.3 BL+DP+AAOLM+HLIGM 90.2 -
[1] 罗建豪, 吴建鑫. 基于深度卷积特征的细粒度图像分类研究综述. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1306−1318Luo Jian-Hao, Wu Jian-Xin. A survey on fine-grained image categorization using deep convolutional features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1306−1318 [2] 陈珺莹, 陈莹. 基于显著增强分层双线性池化网络的细粒度图像分类. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2021, 33(2): 241−249Chen Jun-Ying, Chen Ying. Saliency enhanced hierarchical bilinear pooling for fine-grained classification. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2021, 33(2): 241−249 [3] Liu D C, Zhao L J, Wang Y, Kato J. Learn from each other to classify better: Cross-layer mutual attention learning for fine-grained visual classification. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 140: Article No. 109550 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109550 [4] Song Y, Sebe N, Wang W. On the eigenvalues of global covariance pooling for fine-grained visual recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(3): 3554−3566 [5] Chou P Y, Kao Y Y, Lin C H. Fine-grained visual classification with high-temperature refinement and background suppression. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2303.06442, 2023. [6] Fu J L, Zheng H L, Mei T. Look closer to see better: Recurrent attention convolutional neural network for fine-grained image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4476−4484 [7] Nie X, Chai B S, Wang L Y, Liao Q Y, Xu M. Learning enhanced features and inferring twice for fine-grained image classification. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 82(10): 14799−14813 doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-13619-z [8] Zheng S J, Wang G C, Yuan Y J, Huang S Q. Fine-grained image classification based on TinyVit object location and graph convolution network. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2024, 100: Article No. 104120 doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2024.104120 [9] Hu X B, Zhu S N, Peng T L. Hierarchical attention vision transformer for fine-grained visual classification. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2023, 91: Article No. 103755 doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2023.103755 [10] Zheng H L, Fu J L, Mei T, Luo J B. Learning multi-attention convolutional neural network for fine-grained image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 5219−5227 [11] He X T, Peng Y X, Zhao J J. Fine-grained discriminative localization via saliency-guided faster R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Mountain View, USA: ACM, 2017. 627−635 [12] Wang Z H, Wang S J, Li H J, Dou Z, Li J J. Graph-propagation based correlation learning for weakly supervised fine-grained image classification. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 12289−12296 [13] Wang S J, Wang Z H, Li H J, Ouyang W L. Category-specific semantic coherency learning for fine-grained image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Seattle, USA: ACM, 2020. 174−183 [14] Li K P, Wu Z Y, Peng K C, Ernst J, Fu Y. Tell me where to look: Guided attention inference network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 9215−9223 [15] Jiang P T, Han L H, Hou Q B, Cheng M M, Wei Y C. Online attention accumulation for weakly supervised semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(10): 7062−7077 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3092573 [16] Liu Y, Zhou L, Zhang P C, Bai X, Gu L, Yu X H, et al. Where to focus: Investigating hierarchical attention relationship for fine-grained visual classification. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision. Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 57−73 [17] Zhang L B, Huang S L, Liu W, Tao D C. Learning a mixture of granularity-specific experts for fine-grained categorization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019. 8330−8339 [18] Chen W J, Ran S, Wang T, Cao L H. Learning how to zoom in: Weakly supervised ROI-based-DAM for fine-grained visual classification. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Bratislava, Slovakia: Springer, 2021. 118−130 [19] Hu Y T, Liu X H, Zhang B C, Han J G, Cao X B. Alignment enhancement network for fine-grained visual categorization. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2021, 17(1s): Article No. 12 [20] Zhao Y F, Yan K, Huang F Y, Li J. Graph-based high-order relation discovery for fine-grained recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 15074−15083 [21] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [22] Zhou B L, Khosla A, Lapedriza A, Oliva A, Torralba A. Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2921−2929 [23] Wei X S, Luo J H, Wu J X, Zhou Z H. Selective convolutional descriptor aggregation for fine-grained image retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(6): 2868−2881 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2688133 [24] Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640−651 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [25] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137−1149 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [26] Wah C, Branson S, Welinder P, Perona P, Belongie S. The Caltech-UCSD Birds-200-2011 Dataset, Technical Report CNS-TR-2011-001, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 2011. [27] Zhao Y F, Li J, Chen X W, Tian Y H. Part-guided relational transformers for fine-grained visual recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 9470−9481 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3126490 [28] Ding Y, Zhou Y Z, Zhu Y, Ye Q X, Jiao J B. Selective sparse sampling for fine-grained image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019. 6598−6607 [29] Lam M, Mahasseni B, Todorovic S. Fine-grained recognition as HSnet search for informative image parts. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6497−6506 [30] Wei X S, Xie C W, Wu J X, Shen C H. Mask-CNN: Localizing parts and selecting descriptors for fine-grained bird species categorization. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 76: 704−714 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.10.002 [31] Zhang Y B, Tang H, Jia K. Fine-grained visual categorization using meta-learning optimization with sample selection of auxiliary data. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 241−256 [32] Zheng H L, Fu J L, Zha Z J, Luo J B. Learning deep bilinear transformation for fine-grained image representation. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: ACM, 2019. Article No. 385 [33] Du R Y, Xie J Y, Ma Z Y, Chang D L, Song Y Z, Guo J. Progressive learning of category-consistent multi-granularity features for fine-grained visual classification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(12): 9521−9535 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3126668 [34] Van Horn G, Branson S, Farrell R, Haber S, Barry J, Ipeirotis P, et al. Building a bird recognition app and large scale dataset with citizen scientists: The fine print in fine-grained dataset collection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 595−604 [35] Touvron H, Vedaldi A, Douze M, Jegou H. Fixing the train-test resolution discrepancy. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: ACM, 2019. Article No. 741 [36] Krause J, Stark M, Deng J, Li F F. 3D object representations for fine-grained categorization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 554−561 [37] Chen Y, Bai Y L, Zhang W, Mei T. Destruction and construction learning for fine-grained image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 5152−5161 [38] He J, Chen J N, Liu S, Kortylewski A, Yang C, Bai Y T, et al. TransFG: A transformer architecture for fine-grained recognition. In: Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI, 2022. 852−860 [39] Maji S, Rahtu E, Kannala J, Blaschko M, Vedaldi A. Fine-grained visual classification of aircraft. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1306.5151, 2013. [40] Wang D Q, Shen Z Q, Shao J, Zhang W, Xue X Y, Zhang Z. Multiple granularity descriptors for fine-grained categorization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 2399−2406 [41] Van Der Maaten L. Accelerating t-SNE using tree-based algorithms. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 3221−3245 [42] Xiao J X, Hays J, Ehinger K A, Oliva A, Torralba A. Sun database: Large-scale scene recognition from abbey to zoo. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 3485−3492 [43] Chen T, Kornblith S, Norouzi M, Hinton G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. Vienna, Austria: ACM, 2020. 1597−1607 [44] Grill J B, Strub F, Altché F, Tallec C, Richemond P H, Buchatskaya E, et al. Bootstrap your own latent a new approach to self-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: ACM, 2020. Article No. 1786 [45] Mahajan D, Girshick R, Ramanathan V, He K M, Paluri M, Li Y X, et al. Exploring the limits of weakly supervised pretraining. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 185−201 [46] Yang Z, Luo T G, Wang D, Hu Z Q, Gao J, Wang L W. Learning to navigate for fine-grained classification. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 420−435 [47] Ji R Y, Wen L Y, Zhang L B, Du D W, Wu Y J, Zhao C, et al. Attention convolutional binary neural tree for fine-grained visual categorization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 10465−10474 [48] Ke X, Cai Y H, Chen B T, Liu H, Guo W Z. Granularity-aware distillation and structure modeling region proposal network for fine-grained image classification. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 137: Article No. 109305 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109305 [49] Cui Y, Song Y, Sun C, Howard A, Belongie S. Large scale fine-grained categorization and domain-specific transfer learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4109−4118 [50] Dubey A, Gupta O, Raskar R, Naik N. Maximum entropy fine-grained classification. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal, Canada: ACM, 2018. 635−645 [51] Korsch D, Bodesheim P, Denzler J. Classification-specific parts for improving fine-grained visual categorization. In: Proceedings of the 41st DAGM German Conference on Pattern Recognition. Dortmund, Germany: Springer, 2019. 62−75 [52] Zhuang P Q, Wang Y L, Qiao Y. Learning attentive pairwise interaction for fine-grained classification. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 13130−13137 [53] Krause J, Jin H L, Yang J C, Li F F. Fine-grained recognition without part annotations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 5546−5555 [54] Zhang L B, Huang S L, Liu W. Learning sequentially diversified representations for fine-grained categorization. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 121: Article No. 108219 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108219 [55] Liang Y Z, Zhu L C, Wang X H, Yang Y. Penalizing the hard example but not too much: A strong baseline for fine-grained visual classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(5): 7048−7059 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3213563 [56] Liu K J, Chen K, Jia K. Convolutional fine-grained classification with self-supervised target relation regularization. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 5570−5584 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3197931 -




 下载:
下载: