Synergistic Potential Functions for Constrained Attitude Control of Rigid Spacecraft
-
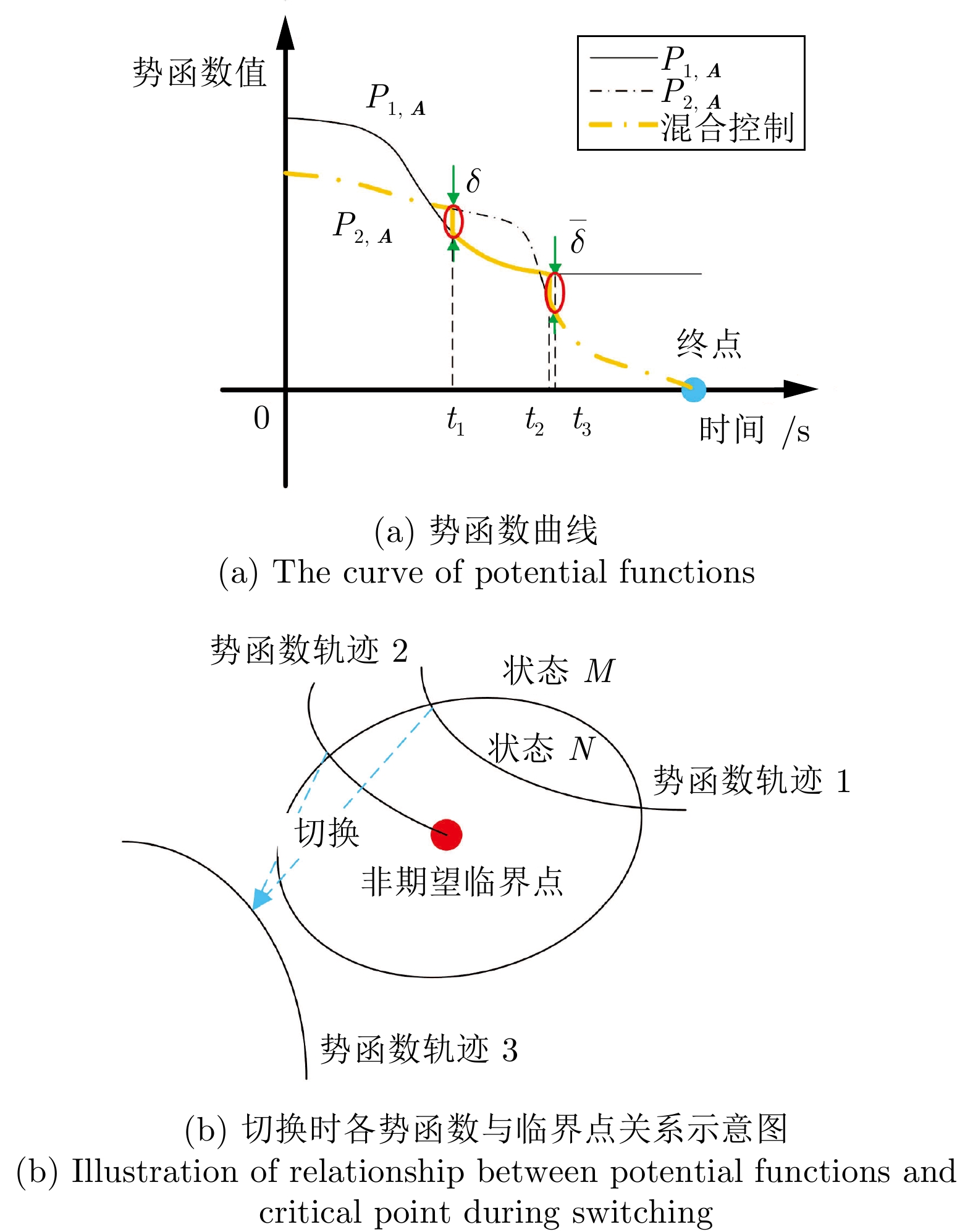
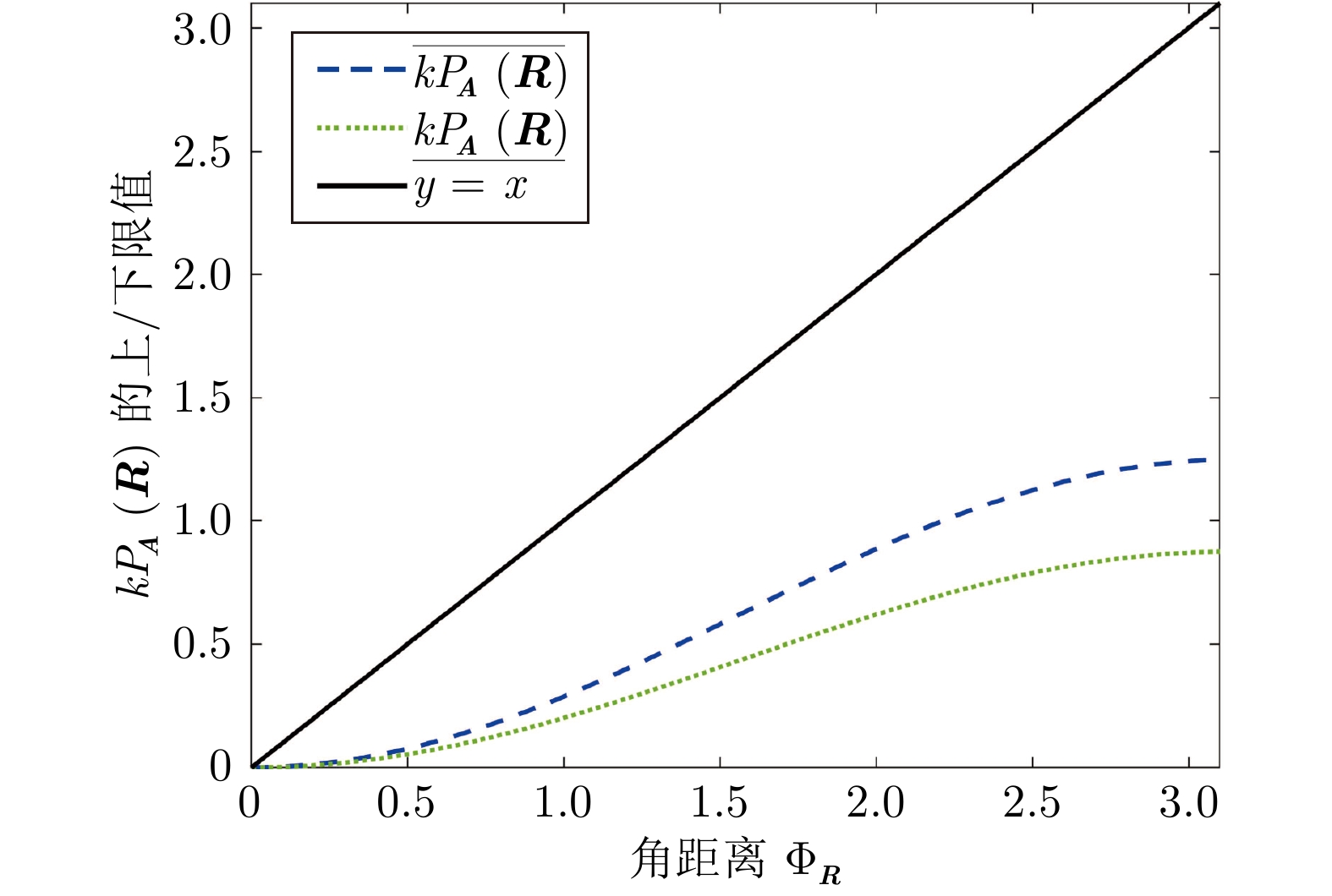
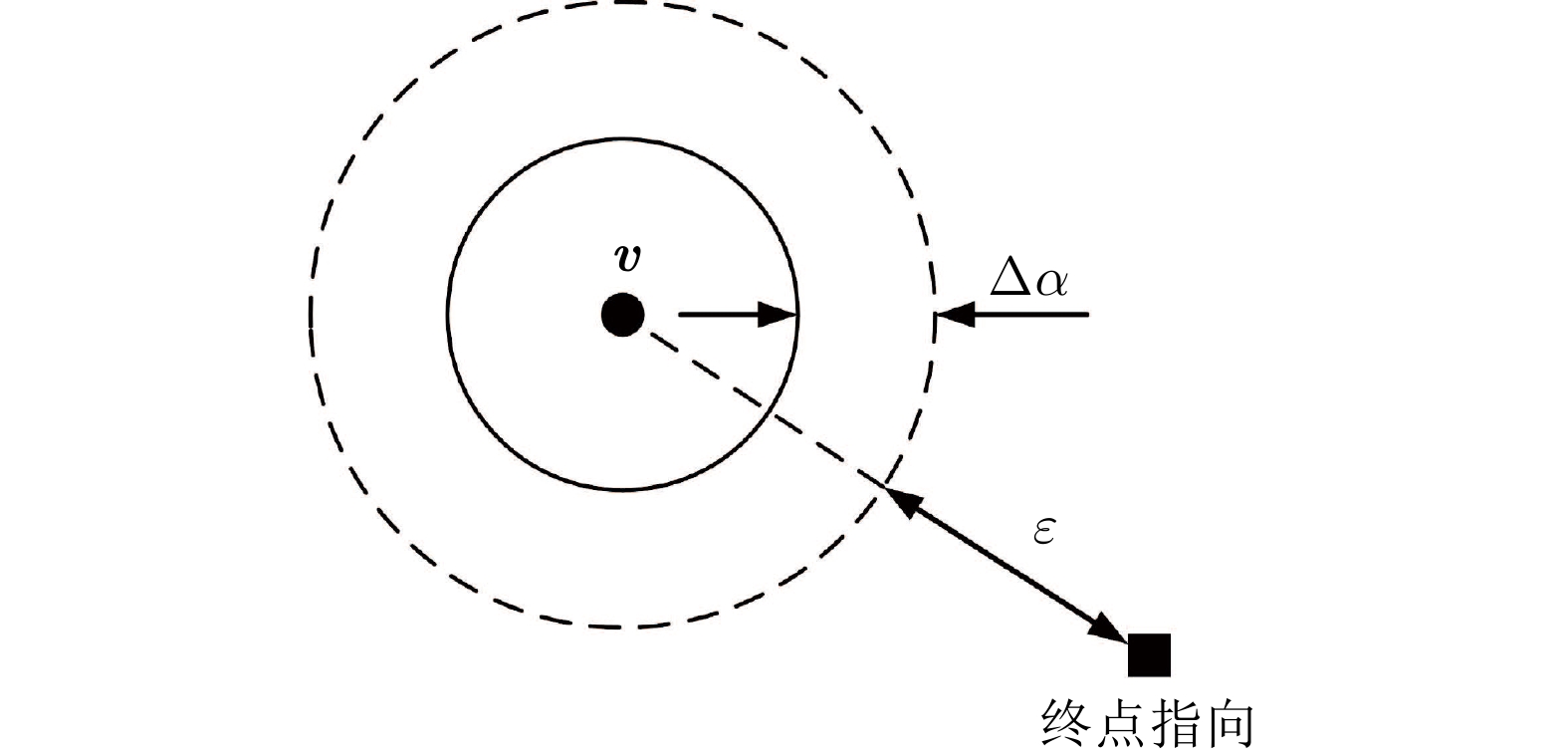
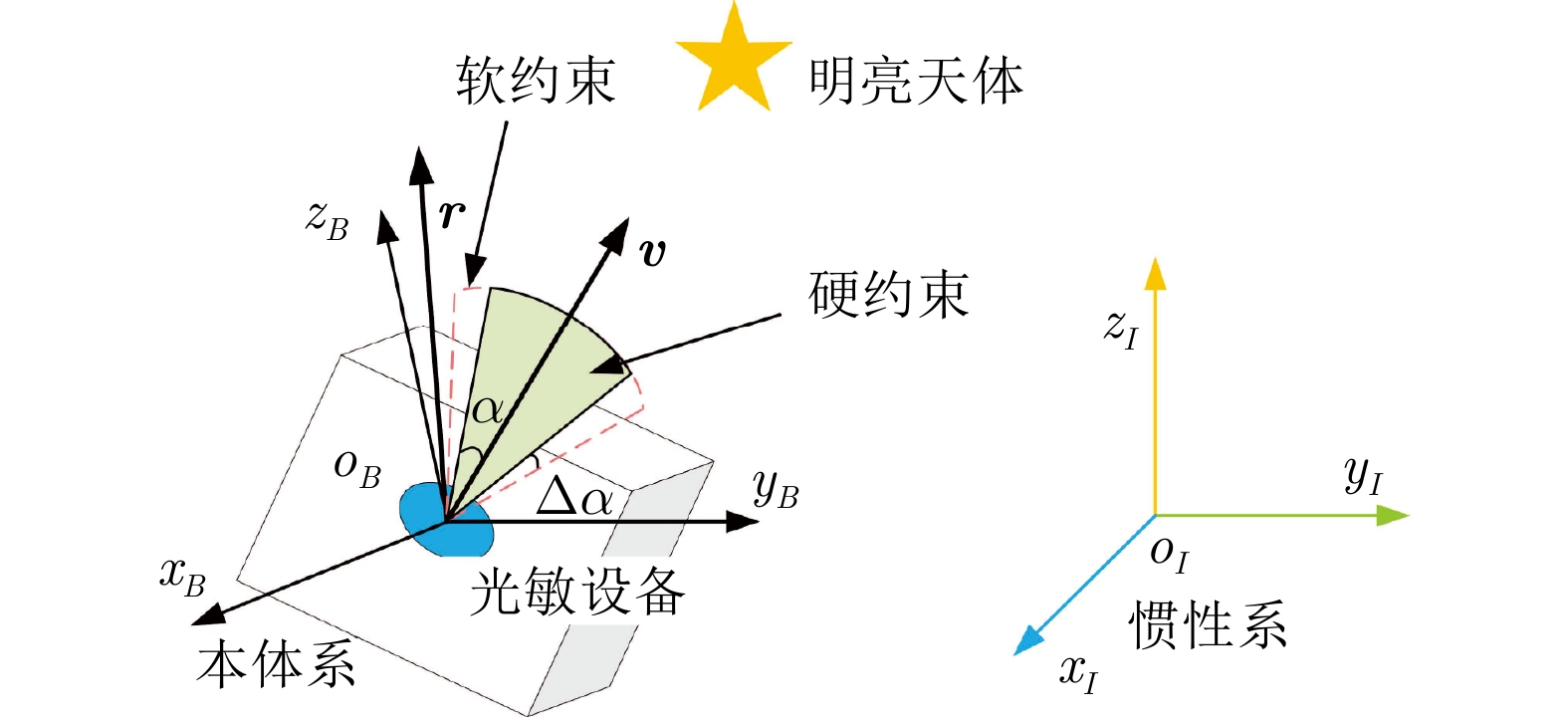
摘要: 提出一种考虑航天器姿态约束的协同势函数设计方法, 在姿态全局收敛的同时, 保证姿态在机动过程中始终满足姿态约束. 首先, 建立航天器姿态指向约束模型, 并针对每一个指向约束设计软约束区域; 然后, 基于“角度扰动”方法设计协同势函数族; 接着, 通过设计协同势函数族内函数切换规律, 在软约束区域内构建满足姿态约束的势函数, 并给出区域内势函数临界点分布的调整方法; 最后, 将所得的势函数用于航天器的避障控制, 以比例−微分控制为例, 通过数值仿真, 验证该方法的有效性.Abstract: A synergistic potential functions design method considering attitude constraints is proposed to ensure the global convergence of attitude while always satisfying attitude constraints during the attitude maneuver. First, an attitude pointing constraint model is developed, and a soft constraint region is designed for each pointing constraint. Then, a family of synergistic potential functions is designed based on the “angular warping”. Next, using the common fractional and logarithmic forms of repulsive potential functions, a potential function considering the attitude constraint is designed in the soft constraint region by using the synergistic potential functions and a method to adjust the distribution of critical points in the soft constraint region by controlling the parameters of this potential function is given. Finally, the designed potential function is used in the controller design. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by numerical simulations using proportional-derivative control as an example.
-
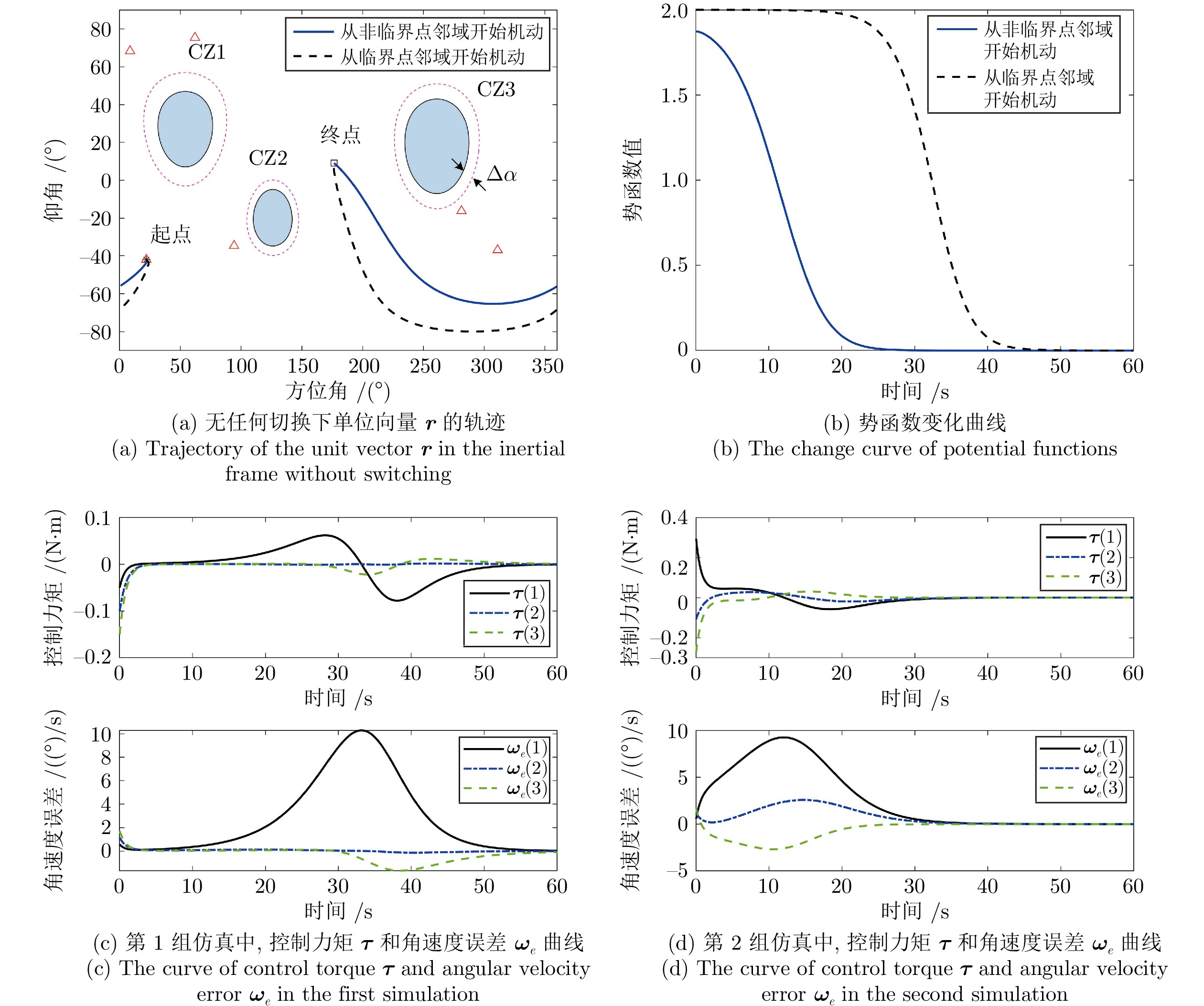
表 1 惯性系下姿态限制
Table 1 Attitude constraints in the inertial frame
序号 指向${\boldsymbol{v}}$ 角度$\alpha \ (^ \circ) $ CZ1 $\left[ {0.5237,0.7208,0.4540} \right]^{\rm{T}}$ 20 CZ2 $\left[ {-0.5530,0.7612,-0.3387} \right]^{\rm{T}}$ 15 CZ3 $\left[ {-0.1488,-0.9393,0.3090} \right]^{\rm{T}}$ 25 -
[1] 马亚杰, 姜斌, 任好. 航天器位姿运动一体化直接自适应容错控制研究. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 678-686Ma Ya-Jie, Jiang Bin, Ren Hao. Adaptive direct fault-tolerant control design for spacecraft integrated attitude and orbit system. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 678-686 [2] 钱辰, 方勇纯, 李友朋. 面向扑翼飞行控制的建模与奇异摄动分析. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(2): 434-443Qian Chen, Fang Yong-Chun, Li You-Peng. Control oriented modeling and singular perturbation analysis in flapping-wing flight. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(2): 434-443 [3] Bhat S P, Bernstein D S. A topological obstruction to continuous global stabilization of rotational motion and the unwinding phenomenon. Systems & Control Letters, 2000, 39(1): 63-70 [4] Sanyal A, Fosbury A, Chaturvedi N, Bernstein D S. Inertia-free spacecraft attitude tracking with disturbance rejection and almost global stabilization. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2009, 32(4): 1167-1178 doi: 10.2514/1.41565 [5] 郑重, 李鹏, 钱默抒. 具有角速度和输入约束的航天器姿态协同控制. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(6): 1444-1452Zheng Zhong, Li Peng, Qian Mo-Shu. Spacecraft attitude coordination control with angular velocity and input constraints. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(6): 1444-1452 [6] Wang W, Tayebi A. Hybrid feedback for global tracking on matrix Lie groups SO(3) and SE(3). IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(6): 2930-2945 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3097704 [7] Hashemi S H, Pariz N, Sani S K H. Observer-based adaptive hybrid feedback for robust global attitude stabilization of a rigid body. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(3): 1919-1929 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3050665 [8] Mayhew C G, Teel A R. Synergistic potential functions for hybrid control of rigid-body attitude. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2011. 875− 880 [9] Casau P, Sanfelice R G, Cunha R, Silvestre C. A globally asymptotically stabilizing trajectory tracking controller for fully actuated rigid bodies using landmark-based information. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2015, 25(18): 3617-3640 doi: 10.1002/rnc.3283 [10] Berkane S, Tayebi A. Construction of synergistic potential functions on SO(3) with application to velocity-free hybrid attitude stabilization. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(1): 495-501 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2560537 [11] Lee T. Global exponential attitude tracking controls on SO(3). IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(10): 2837-2842 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2407452 [12] 胡庆雷, 邵小东, 杨昊旸, 段超. 航天器多约束姿态规划与控制:进展与展望. 航空学报, 2022, 43(10): 22.527351Hu Qing-Lei, Shao Xiao-Dong, Yang Hao-Yang, Duan Chao. Spacecraft attitude planning and control under multiple constraints: Review and prospects. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(10): 22.527351 [13] Shen Q, Yue C, Goh C H, Wu B, Wang D. Rigid-body attitude stabilization with attitude and angular rate constraints. Automatica, 2018, 90: 157-163 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.12.029 [14] Tan X, Berkane S, Dimarogonas D V. Constrained attitude maneuvers on SO(3): rotation space sampling, planning and low-level control. Automatica, DOI: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108659 [15] Yue C, Huo T, Lu M, Shen Q, Li C, Chen X, Cao X. A systematic method for constrained attitude control under input saturation. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023: 1-12, Doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3268607, to be published [16] Tian Y, Hu Q, Shao X. Adaptive fault-tolerant control for attitude reorientation under complex attitude constraints. Aerospace Science and Technology, Doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120240 [17] Du Q H. Metrics for 3d rotations: comparison and analysis. Journal of Mathematical Imaging & Vision, 2009, 35(2): 155-164 [18] Murray R M, Li Z, Shankar S S. A Mathematical Introduction to Robotic Manipulation. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1994. 29−30 [19] Berkane S, Abdessameud A, Tayebi A. On the design of globally exponentially stable hybrid attitude and gyro-bias observers [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.05640, May 9, 2023 [20] Iwase N, Mimura M, Nishimoto T. Lusternik-schnirelmann category of non-simply connected compact simple lie groups. Topology and its Applications, 2005, 150(1): 111-123 [21] Chen T and Shan J. Continuous constrained attitude regulation of multiple spacecraft on SO(3). Aerospace Science and Technology, Doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105769 [22] Hu Q, Chi B, Akella M R. Anti-unwinding attitude control of spacecraft with forbidden pointing constraints. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2019, 42(4): 822-835 doi: 10.2514/1.G003606 [23] Mayhew C G, Teel A R. Hybrid control of rigid-body attitude with synergistic potential functions. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2011. 287−292 [24] Kulumani S, Lee T. Constrained geometric attitude control on SO(3). International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2017, 15(6): 2796-2809 doi: 10.1007/s12555-016-0607-4 -




 下载:
下载: